Author: Alan Weissberger
Broadcom: 5nm 100G/lane Optical PAM-4 DSP PHY; 200G Optical Link with Semtech
Broadcom Inc. today announced the availability of its 5nm 100G/lane optical PAM-4 DSP PHY with integrated transimpedance amplifier (TIA) and laser driver, the BCM85812, optimized for 800G DR8, 2x400G FR4 and 800G Active Optical Cable (AOC) [1.] module applications. Built on Broadcom’s proven 5nm 112G PAM-4 DSP platform, this fully integrated DSP PHY delivers superior performance and efficiency and drives the overall system power down to unprecedented levels for hyperscale data center and cloud providers.
Note 1. Active Optical Cable (AOC) is a cabling technology that accepts same electrical inputs as a traditional copper cable, but uses optical fiber “between the connectors.” AOC uses electrical-to-optical conversion on the cable ends to improve speed and distance performance of the cable without sacrificing compatibility with standard electrical interfaces.
BCM85812 Product Highlights:
- Monolithic 5nm 800G PAM-4 PHY with integrated TIA and high-swing laser driver
- Delivers best-in-class module performance in BER and power consumption.
- Drives down 800G module power for SMF solutions to sub 11W and MMF solutions to sub 10W.
- Compliant to all applicable IEEE and OIF standards, capable of supporting MR links on the chip to module interface.
- Fully compliant with OIF 3.2T Co-Packaged Optical Module Specs
- Capable of supporting optical modules from 800G to 3.2T
Demo Showcases at OFC 2023:
Broadcom will demonstrate the BCM85812 in an end-to-end link connecting two Tomahawk 5 (TH5) switches using Eoptolink’s 800G DR8 optical modules. Attendees will see live traffic stream of 800GbE data running between two TH5 switches. Broadcom will showcase various 800G DR8, 2x400G FR4, 2x400G DR4, 800G SR8, and 800G AOC solutions from third party transceiver vendors that interoperate with each other, all using Broadcom’s DSP solutions. Following are module vendors that will be participating in a multi-vendor interop plug-fest on the latest Tomahawk 5 switch platform: Eoptolink, Intel, Molex, Innolight, Source Photonics, Cloud Light Technology Limited and Hisense Broadband.
Additionally, Broadcom in collaboration with Semtech and Keysight will demonstrate a 200G per lane (200G/lane) optical transmission link leveraging Broadcom’s latest SerDes, DSP and laser technology. These demonstrations will be in Broadcom Booth 6425 at the Optical Fiber Communication (OFC) 2023 exhibition in San Diego, California from March 7th to 9th.
“This first-to-market highly integrated 5nm 100G/lane DSP PHY extends Broadcom’s optical PHY leadership and demonstrates our commitment to addressing the stringent low power requirements from hyperscale data center and cloud providers,” said Vijay Janapaty, vice president and general manager of the Physical Layer Products Division at Broadcom. “With our advancement in 200G/lane, Broadcom continues to lead the industry in developing next generation solutions for 51.2T and 102.T switch platforms.”
“By 2028, optical transceivers are projected to account for up to 8% of total power consumption in cloud data centers,” said Bob Wheeler, principal analyst at Wheeler’s Network. “The integration of TIA and driver functions in DSP PHYs is an important step in reducing this energy consumption, and Broadcom is leading the innovation charge in next-generation 51.2T cloud switching platforms while also demonstrating a strong commitment to Capex savings.”
Availability:
Broadcom has begun shipping samples of the BCM85812 to its early access customers and partners. Please contact your local Broadcom sales representative for samples and pricing.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Semtech Corp. with Broadcom will demonstrate a 200G per lane optical transmission link that leverages Semtech’s latest FiberEdge 200G PAM4 PMDs and Broadcom’s latest DSP PHY. The two companies plan to recreate the demonstration this week at OFC 2023 in San Diego in their respective booths. Such a capability will be useful to enable 3.2-Tbps optical modules to support 51.2- and 102.4-Tbps switch platforms, Semtech points out.
The two demonstrations will leverage Semtech’s FiberEdge 200G PAM4 EML driver and TIA and Broadcom’s 5-nm 112-Gbaud PAM4 DSP platform. Instrumentation from Keysight Technologies Inc. will verify the performance of the links.
“We are very excited to collaborate with Broadcom and Keysight in this joint demonstration that showcases Semtech’s 200G PMDs and their interoperability with Broadcom’s cutting-edge 200G/lane DSP and Keysight’s latest 200G equipment,” said Nicola Bramante, senior product line manager for Semtech’s Signal Integrity Products Group. “The demonstration proves the performance of a 200G/lane ecosystem, paving the way for the deployment of next-generation terabit optical transceivers in data centers.”
“This collaboration with Semtech and Keysight, two of the primary ecosystem enablers, is key to the next generation of optical modules that will deliver increased bandwidth in hyperscale cloud networks. This achievement demonstrates our commitment to pushing the boundaries of high-speed connectivity, and we are excited to continue working with industry leaders to drive innovation and deliver cutting-edge solutions to our customers,” added Khushrow Machhi, senior director of marketing of the Physical Layer Products Division at Broadcom.
“Semtech’s and Broadcom’s successful demonstration of the 200-Gbps optical link is another important milestone for the industry towards ubiquitous future 800G and 1.6T networks. Keysight’s early engagement with leading customers and continuous investments in technology and tools deliver the needed insights that enable these milestones,” said Dr. Joachim Peerlings, vice president and general manager of Keysight’s Network and Data Center Solutions Group.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About Broadcom:
Broadcom Inc. is a global technology leader that designs, develops and supplies a broad range of semiconductor and infrastructure software solutions. Broadcom’s category-leading product portfolio serves critical markets including data center, networking, enterprise software, broadband, wireless, storage and industrial. Our solutions include data center networking and storage, enterprise, mainframe and cyber security software focused on automation, monitoring and security, smartphone components, telecoms and factory automation. For more information, go to https://www.broadcom.com.
Broadcom, the pulse logo, and Connecting everything are among the trademarks of Broadcom. The term “Broadcom” refers to Broadcom Inc., and/or its subsidiaries. Other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About Semtech:
Semtech Corporation is a high-performance semiconductor, IoT systems and Cloud connectivity service provider dedicated to delivering high quality technology solutions that enable a smarter, more connected and sustainable planet. Our global teams are dedicated to empowering solution architects and application developers to develop breakthrough products for the infrastructure, industrial and consumer markets.
References:
https://www.broadcom.com/company/news/product-releases/60996
https://www.fiberoptics4sale.com/blogs/archive-posts/95047430-active-optical-cable-aoc-explained-in-details
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
ZTE, in partnership with China Telecom, has released a 5G-Advanced solution, named Cluster DFS at Mobile World Congress 2023 in Barcelona, Spain. According to ZTE, the new offering will facilitate the development of specific B2B and B2C services using a single 5G network.
China Telecom claims to have deployed the world’s largest 5G SA network with more than 1 million 5G base stations based on a RAN-sharing strategy. The Chinese carrier noted it continues to focus in the B2B segment, with the number of private 5G networks hitting over 3,000, and commercial projects in this segment totaling 9,000 by the end of 2022.

Image Credit: ZTE
ZTE explained that that the new solution will be key as the service-level agreements (SLAs) requirements for the provision of 5G for industrial verticals such as smart manufacturing or smart grid are different from the requirements for the provision of 5G services for consumers. ZTE further explained that it launched the new solution given to the increasing complexity of 5G networks and to enable a coordinated development of B2B and B2C services on a single network and deliver differentiated service experiences.
To adapt to vertical application traffic dynamics on uplink and downlink, China Telecom and ZTE have introduced the innovative Cluster DFS, by which, base stations with same heavy uplink characteristics are intelligently formed as “cluster” to implement accurate adaptation between frame structure and services requirements. Consequently, a 5G network can synergize B2B and B2C services with optimal user experiences.
Li Peng, Director of Network Development and Sharing Department of China Telecom, said, “5G has become an important driving force of digital economy development. China Telecom is continuously exploring and promoting innovative technologies and solutions that combine the development of 5G high-quality networks and industrial applications.”
“Based on previous successful experience of Cluster DSS, China Telecom further extends ‘cluster-level’ radio resource management mechanism from ‘frequency domain’ to ‘time domain’, which provides more flexible radio resource strategy and promotes the development of fully-connected factories. The commercial trial of Lierda shows that Cluster DFS has increased the uplink throughput of B2B applications by 60~80% while ensuring stable B2C experiences, significantly improving network performance and efficiency, ” added Huang Lilian.
Tang Xue, VP of RAN Products, said, “B2B and B2C coordinated development on one network requires more flexible and more intelligent resource management strategy, therefore, RAN intelligence is of great importance. ZTE uses RAN native-AI to enable adaptive radio resource adjustment, including spectrum, frame structure, power and beams. With four key features, specifically, intelligent traffic prediction, cluster self-generating, intra-cluster traffic shaping and inter-cluster coordination, the potential of commercial 5G networks can be fully unlocked to offer optimal experiences for both industrial applications and consumer users.”
Cluster DFS provides precise and on-demand user experiences for both consumers and enterprises based on AI capability, enabling network policy shift from “one-size-fit-all” to “context-aware” and coordinating the development of B2B and B2C on 5G commercial networks.
Moving forward, ZTE and China Telecom will continue working together to carry out innovative practices and facilitate the development of 5G-Advanced applications for a digital, intelligent and green future.
ZTE said Cluster DFS provides precise on-demand user experiences for consumers and enterprises based on its AI capability to coordinate the development of B2B and B2C on 5G commercial networks.
China Telecom and rival network operator China Unicom had previously signed an agreement to co-build and co-share their 5G networks. According to the latest available statistics, China Telecom added a total of 5 million 5G subscribers during the first months of the year to take its total 5G subscribers base to 273 million. During 2022, the telco added a total of 80.16 million 5G subscribers.
References:
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/news/china-telecom-and-zte-release-cluster-dfs-at-mwc-2023.html
https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/news/20220526e2.html
NTT to offer optical technology-based next-generation network services under IOWN initiative; 6G to follow
Japan’s Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corp. (NTT) said it will start providing its first services under an optical technology-based next-generation network initiative to its corporate clients. The major Japanese telecommunications company plans to start offering the services from March 16 for a monthly fee of 1.98 million yen through its regional arms Nippon Telegraph and Telephone East Corp. and Nippon Telegraph and Telephone West Corp.
NTT rival telco KDDI Corp. will also take part in the Innovative Optical and Wireless Network (IOWN) initiative which was first announced by NTT in 2019. It’s goal is to reduce electricity consumption (power) and achieve high-capacity communication by converting electric signals into optical ones to cope with surging network traffic. It will join the IOWN Global Forum, comprising over 100 members including NTT and many information technology companies in and outside Japan. Founding IOWN members are NTT, Sony and Intel. The forum will be discussing technical specifications for optical and wireless networks with a view to developing an international standard for 6G communications.

Source: IOWN Global Forum
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The two Japanese rival firms will work together to make IOWN a 6G platform, pundits said. That’s amazing as all previous IMT standards (3G, 4G, 5G) were developed by 3GPP and then ITU-R WP 5D.
At a news conference, NTT Senior Executive Vice President Katsuhiko Kawazoe said: “We hope [IOWN] will help resolve social issues and create new value.”
NTT plans to announce the second round of IOWN services as early as 2025.
References:
https://www.nippon.com/en/news/yjj2023030200965/
https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2023/03/03/business/ntt-6g-network/
ASPI’s Critical Technology Tracker finds China ahead in 37 of 44 technologies evaluated
The Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI finds that China is further ahead in more technologies than has been realized. It’s the leading country in 37 of the 44 technologies evaluated, often producing more than five times as much high-impact research as its closest competitor. This means that only seven of the 44 analysed technologies are currently led by a democratic country, and that country in all instances is the U.S. Of the ten AI and ICT-related technologies examined, China dominates in seven, the study concluded.
The ASPI study is based on an analysis of the top 10% most-cited papers in each area of research published between 2018 and 2022 – a total of 2.2 million papers. It acknowledges that a widely cited piece of research does not automatically translate into successfully deployed technology. The study also does not reflect the current state of commercialization or of technology diffusion. Here’s a table showing China leading technologies:
![]()
Source: Australian Strategic Policy Institute
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
China leads globally in photonic sensors (43% of world’s top 10% high-impact research, 3.41 times the US), quantum communications (31%, 1.89 times the US), advanced optical communications (38%, 2.95 times the US) and post-quantum cryptography (31%, 2.3 times the US). Taken together, these observations increase the risk of Chinese communications going dark83 to the efforts of western intelligence services. This reduces the capacity to plan for contingencies in the event of hostilities85 and tensions.
China has reportedly built the physical infrastructure to claim the world’s largest quantum communication network,86 and has even established quantum communication with moving drones87 and satellites.88 As with many things, the risk is cumulative—the risk increases as China leads in both cryptography resistant to decryption by quantum computers and the ability to share encryption keys via quantum communication. One mitigating factor is the current US lead in quantum computing (34% of world’s top 10% high-impact research output, 2.26 times China).
Here are three key tech areas where China dominates in high-impact research papers:
- In advanced radiofrequency communications, including 5G and 6G, (there is no such thing as 6G radio) China ranks 1st with 29.65% vs 9.50% for the U.S. and 5.2% for the UK.
- In advanced optical communications, China ranks 1st with 37.69% vs. 12.76% for the U.S.
- In artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms and hardware accelerators, China ranks 1st with 36.62% vs. 13.26% for the U.S.
The ASPI report designates China’s lead in these technologies as “high-risk,” meaning it is a long way ahead of its closest competitor and that it is home to most of the world’s leading research bodies in that field.
Quantum communications is another area of strength for China. USTC is the top institution irrespective of the quality metrics, and a total of eight out of 20 top institutions are based in China (see Figure 9). Tsinghua University and Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands occupy the second and third places depending on the quality metrics. China’s lead in quantum communications is especially prominent in the proportion of publications in the top 10% of highly cited papers. China’s quantum research was spearheaded by the Xiangshan Science Forum for quantum information in Beijing in 1998, which resulted in experimental research in quantum information within several Chinese universities and research institutes, including USTC, Shanxi University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Physics.
USTC scientist Jian-Wei Pan to demonstrate the potential of quantum communications to Xi Jinping and other Politburo members, and he became known as the founder of Chinese quantum science. In China’s Thirteenth Five-Year National Science and Technology Innovation Plan announced in August 2016,163 the CCP strengthened its quantum strategy further by listing quantum communications and computing as major science and technology projects for advances by 2030. USTC demonstrated China’s dominance in quantum communication by building the first fibre-based ‘Beijing–Shanghai Quantum Secure Communication Backbone’ in 2013, connecting Beijing, Shanghai, Jinan Hefei and 32 reliable nodes over a total transmission distance of more than 2,000 kilometres.164 The strength of quantum communications is that it ensures secure communication due to quantum entanglement, which effectively ensures that any quantum information is modified when observed. This effectively makes it difficult to amplify quantum signals in the conventional way used for current optical communications. Pan’s research team made another significant breakthrough in 2017 by using the first quantum satellite (Micius, launched in 2016), and the free space reduced attenuation to transmit image and sound information using quantum keys over 7,600 kilometres between Austria and China.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
ASPI warns that China’s advanced research “at the intersection of” photonic sensors, quantum communications, optical communications and post-quantum cryptography could undermine the U.S. led “Five Eyes” global intelligence network.
“Taken together, these observations increase the risk of Chinese communications going dark to the efforts of western intelligence services,” the report said. ASPI said its research will be updated with the aim of assessing the future tech capabilities of nations and to highlight long-term strategic trends.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.aspi.org.au/report/critical-technology-tracker
https://techtracker.aspi.org.au/
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/china-dominates-research-in-6g-and-optical-report/d/d-id/783630?
China’s MIIT to prioritize 6G project, accelerate 5G and gigabit optical network deployments in 2023
China Mobile unveils 6G architecture with a digital twin network (DTN) concept
With no 5G standard (IMT 2020) China is working on 6G!
Swisscom, Ericsson and AWS collaborate on 5G SA Core for hybrid clouds
Swiss network operator Swisscom have announced a proof-of-concept (PoC) collaboration with Ericsson 5G SA Core running on AWS. The objective is to explore hybrid cloud use cases with AWS, beginning with 5G core applications. The plan is for more applications to then gradually be added as the trial continues. With each cloud strategy (private, public, hybrid, multi) bringing its own drivers and challenges the idea here seems to be enabling the operator to take advantage of the specific characteristics of both hybrid and public cloud.
The PoC reconfirms Swisscom and Ericsson’s view of the potential hybrid cloud has as a complement to existing private cloud infrastructure. Both Swisscom and Ericsson are on a common journey with AWS to explore how use cases can benefit telecom operators.
The PoC will examine use cases that take advantage of the particular characteristics of hybrid and public cloud. In particular, the flexibility and elasticity it can offer to customers which can mean deployment efficiencies for use cases where capacity is not constantly needed. An example of this could be when maintenance activities are undertaken in Swisscom’s private cloud, or when there are traffic peaks, AWS can be used to offload and complement the private cloud.
Swisscom had already been collaborating with AWS on migrating its 5G infrastructure towards standalone 5G. In addition, it has also used the hyperscaler’s public cloud platform for its IT environments. Telco concerns linger [1.] around the use of public cloud in telecoms infrastructure (especially the core networks) for some operators, hybrid cloud is seemingly gaining momentum as a transitional approach.
Note 1. Telco concerns over public cloud:
- In a recent survey by Telecoms.com more than four in five industry respondents feared security concerns over running telco applications in the public cloud, including 37% who find it hard to make the business case for public cloud as private cloud remains vital in addressing security issues. This also means that any efficiency gains are offset by the IT environment and the network running over two cloud types.
- Many in the industry also fear vendor lock-in and lack of orchestration from public cloud providers. Around a third of industry experts from the same survey find it a compelling reason not to embrace and move workloads to the public cloud unless applications can run on all versions of public cloud and are portable among cloud vendors.
- There’s also a lack of interoperability and interconnectedness with public clouds. The services of different public cloud vendors are indeed not interconnected nor interoperable for the same types of workloads. This concern is one of the drivers to avoid public cloud, according to some network operators.
–>PLEASE SEE THE COMMENT ON THIS TOPIC IN THE BOX BELOW THE ARTICLE.
Quotes:
Mark Düsener, Executive Vice President Mobile Network & Services at Swisscom, says: “By bringing the Ericsson 5G Core onto AWS we will substantially change the way our networks will be built and operated. The elasticity of the cloud in combination with a new magnitude in automatization will support us in delivering even better quality more efficiently over time. In order to shape this new concept, we as Swisscom believe strategic and deep partnerships like the ones we have with Ericsson and AWS are the key for success.”
Monica Zethzon, Head of Solution Area Core Networks, Ericsson says: “5G innovation requires deep collaboration to create the foundations necessary for new and evolving use cases. This Proof-of-Concept project with Swisscom and AWS is about opening up the routes to innovation by using hybrid cloud’s flexible combination of private and public cloud resources. It demonstrates that through partnership, we can deliver a hybrid cloud solution which meets strict telecoms industry requirements and security while making best use of HCP agility and cloud economy of scale.”
Fabio Cerone, General Manager AWS Telco EMEA at AWS, says: “With this move, Swisscom is opening the door to cloud native networks, delivering full automation and elasticity at scale, with the ability to innovate faster and make 5G impactful to their customers. We are committed to working closely with partners, such as Ericsson, to explore new use cases and strategies that best support the needs of customers like Swisscom.”
“How to deploy software in different cloud environments – at a high level, it is hard making that work in practice,” said Per Narvinger, the head of Ericsson’s cloud software and services unit. “You have hyperscalers with their offering and groups trying to standardize and people trying to do it their own way. There needs to be harmonization of what is wanted.”
https://telecoms.com/520337/swisscom-ericson-and-aws-collaborate-on-hybrid-cloud-poc-on-5g-core/
https://telecoms.com/520055/telcos-and-the-public-cloud-drivers-and-challenges/
AWS Telco Network Builder: managed network automation service to deploy, run, and scale telco networks on AWS
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
SKT with Global Telcos to Expand Metaverse Platform in US, Europe and Southeast Asia
On February 27 at MWC Barcelona 2023, South Korean network operator SK Telecom (SKT) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Deutsche Telekom and T-Mobile US to jointly explore opportunities for expanding its metaverse platform ifland into Germany and the U.S.

Image Credit: SKT
The three companies will begin to conduct market tests in the U.S. and Germany in the second quarter of this year, with the main goal of the trials being to try “more diverse metaverse services in Europe and the U.S.”
SKT, Deutsche Telekom and T-Mobile US will also produce content tailored to local preferences, and will jointly promote the metaverse offering.
The ifland platform is also set to be made available to more countries in South East Asia, and the telco has agreed a partnership with its Malaysian partner CelcomDigi to boost its ifland user numbers in the country and develop new business models. It will also be made available to all 11 subsidiaries of Axiata operating in the ASEAN (Association of South-east Asian Nations) and South Asian regions, including Malaysia, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Cambodia, Bangladesh and Nepal.
SKT and Axiata also plan to develop “metaverse platform-related business models” and create business opportunities based on artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the competitiveness of these models.
By expanding its metaverse service into the Southeast Asian market, where Korean culture such as K-content is gaining popularity, SKT expects to expand ifland’s services and develop new business opportunities.
“As we advance into the global market with our metaverse platform ifland, major telecommunications companies in each country and region play an important role as our partners,” said Ryu Young-sang, CEO of SKT. “Going forward, we will continue to work closely with diverse global companies to expand the scope of our metaverse service.”
“The collaboration between the leading Malaysian telecoms operator serving more than 20 million customers and global ICT leader SKT will set the stage for the nation’s metaverse development, and drive growth and digitalisation within the digital economy,” said Datuk Idham Nawawi, CEO of CelcomDigi. “We look forward to working together on leveraging innovative technologies and practices particularly in virtual spaces to develop and deliver a wider range of innovative solutions for our customers and Malaysian businesses.”
“Axiata is deeply committed to leveraging emerging technologies towards the inclusive advancement of Societies and Economies across Asia,” said Dr Hans Wijayasuriya, CEO of Axiata. “We are proud to partner with SKT and the ifland platform and consider the partnership a significant component of our participation in the metaverse going forward.”
SKT pointed out that each of the three operator partners has more than 100 million customers, giving it a solid foundation on which to expand the international impact of ifland. The company’s CEO, Ryu Young-sang, pointed out that partnering with major telcos “in each country and region” plays a key role in advancing ifland’s influence, so it plans to continue working closely with global companies to broaden the scope of the service.
SKT’s metaverse platform launched in June 2021 and after an initial collaboration with Deutsche Telekom, it aggressively moved to global expansion across North America, Europe, the Middle East and Asia in November 2022.
References:
https://www.sktelecom.com/en/press/press_detail.do?idx=1560
SK Telecom launches its metaverse platform ‘ifland’ in 49 countries and regions
NTT Docomo will use its wireless technology to enter the metaverse
Cloud RAN with Google Distributed Cloud Edge; Strategy: host network functions of other vendors on Google Cloud
At MWC 2023 Barcelona, Google Cloud announced that they can now run the radio access network (RAN) functions as software on Google Distributed Cloud Edge, providing communications service providers (CSPs- AKA telcos) with a common and agile operating model that extends from the core of the network to the edge, for a high degree of programmability, flexibility, and low operating expenses. CSPs have already embraced open architecture, open-source software, disaggregation, automation, cloud, AI and machine learning, and new operational models, to name a few. The journey started in the last decade with Network Functions Virtualization, primarily with value added services and then deeper with core network applications, and in the past few years, that evolved into a push towards cloud-native. With significant progress in the core, the time for Cloud RAN is now, according to Google. However, whether for industry or region-specific compliance reasons, data sovereignty needs, or latency or local data-processing requirements, most of the network functions deployed in a mobile or wireline network may have to follow a hybrid deployment model where network functions are placed flexibly in a combination of both on-premises and cloud regions. RAN, which is traditionally implemented with proprietary hardware, falls into that camp as well.
In 2021,the company launched Google Distributed Cloud Edge (GDC Edge), an on-premises offering that extends a consistent operating model from our public Google Cloud regions to the customer’s premises. For CSPs, this hybrid approach makes it possible to modernize the network, while enabling easy development, fast innovation, efficient scale and operational efficiency; all while simultaneously helping to reduce technology risk and operational costs. GDC Edge became generally available in 2022.

Google Cloud does not plan to develop its own private wireless networking services to sell to enterprise customers, nor does the company plan to develop its own networking software functions, according to Gabriele Di Piazza, an executive with Google Cloud who spoke at MWC 2023 in Barcelona. Instead, Google Cloud would like to host the networking software functions of other vendors like Ericsson and Mavenir in its cloud. It would also like to resell private networking services from operators and others.
Rather than develop its own cloud native 5G SA core network or other cloud networking software (like Microsoft and AWS are doing), Google Cloud wants to “avoid partner conflict,” Di Piazza said. Google has been building its telecom cloud story around its Anthos platform. That platform is directly competing against the likes of AWS and Microsoft for telecom customers. According to a number of analysts, AWS appears to enjoy an early lead in the telecom industry – but its rivals, like Google, are looking for ways to gain a competitive advantage. One of Google’s competitive arguments is that it doesn’t have aspirations to sell network functions. Therefore, according to Di Piazza, the company can remain a trusted, unbiased partner.

Image Credit: Google Cloud
Last year, the executive said that moving to a cloud-native architecture is mandatory, not optional for telcos, adding that telecom operators are facing lots of challenges right now due to declining revenue growth, exploding data consumption and increasing capital requirements for 5G. Cloud-native networks have significant challenges. For example, there is a lack of standardization among the various open-source groups and there’s fragmentation among parts of the cloud-native ecosystem, particularly among OSS vendors, cloud providers and startups.
In recent years, Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Oracle and other cloud computing service providers have been working to develop products and services that are specifically designed to allow telecom network operator’s to run their network functions inside a third-party cloud environment. For example, AT&T and Dish Network are running their 5G SA core networks on Microsoft Azure and AWS, respectively.
Matt Beal, a senior VP of software development for Oracle Communications, said his company offers both a substantial cloud computing service as well as a lengthy list of network functions. He maintains that Oracle is a better partner for telecom network operators because of it. Beal said Oracle has long offered a wide range of networking functions, from policy control to network slice management, that can be run inside its cloud or inside the cloud of other companies. He said that, because Oracle developed those functions itself, the company has more experience in running them in a cloud environment compared with a company that hasn’t done that kind of work. Beal’s inference is that network operators ought to partner with the best and most experienced companies in the market. That position runs directly counter to Google’s competitive stance on the topic. “When you know how these things work in real life … you can optimize your cloud to run these workloads,” he said.
While a number of other telecom network operators have put things like customer support or IT into the cloud, they have been reluctant to release critical network functions like policy control to a cloud service provider.
References:
https://cloud.google.com/solutions/telecommunications
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/telecommunications
GSMA Intelligence: 5G connections to double over the next two years; 30 countries to launch 5G in 2023
GSMA Intelligence forecasts 5G connections are expected to double over the next two years, expedited by technological innovations and new 5G network deployments in more than 30 countries in 2023. Of the new networks to be deployed in 2023, it is expected that 15 will be 5G Standalone (SA) networks. As of January 2023, there were 229 commercial 5G networks globally and over 700 5G smartphone models available to users.
GSMA Intelligence, announced its latest 5G forecast during MWC Barcelona 2023, point to a significant period of growth in terms of mobile subscribers and enterprise adoption. Consumer connections surpassed one billion at the end of 2022 and will increase to around 1.5 billion this year – before reaching two billion by the end 2025.
India will lead the 5G expansion globally in 2023, with the expansion of services from Airtel and Jio in 2023 expected to be pivotal to the region’s ongoing adoption. GSMA Intelligence predicts there will be four 5G networks in India by the end of 2025, accounting for 145 million additional users. With operators such as Jio announcing ambitions to connect as many as 100 million homes across India to its 5G FWA network, the number of FWA users looks likely to grow substantially over the next few years, the report added.

Growth will also come from key markets within APAC and LATAM, such as Brazil and India, which have recently launched 5G networks. India will be especially significant, with the expansion of services from Airtel and Jio in 2023 expected to be pivotal to the region’s ongoing adoption. GSMA Intelligence predicts there will be four 5G networks in India by the end of 2025, accounting for 145 million additional users.
Many of the new 5G markets scheduled to launch networks in 2023 are in developing regions across Africa – including Ethiopia and Ghana – and Asia. Today, 5G adoption in the sub-Saharan region sits below 1% but will reach over 4% by 2025 and 16% in 2030, largely thanks to a concerted effort from industry and government organizations to provide connectivity to citizens.
“Until now, 5G adoption has been driven by relatively mature markets and consumer use cases like enhanced mobile broadband, but that’s changing. We’re now entering a second wave for 5G that will see the technology engage a diverse set of new markets and audiences,” said Peter Jarich, Head of GSMA Intelligence. “The extension to new use cases and markets will challenge the mobile ecosystem to prove that 5G truly is flexible enough to meet these diverse demands in a way that’s both inclusive and innovative.”
The Rise of 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA):
As of January 2023, more than 90 FWA broadband service providers (the vast majority of which are mobile operators) had launched commercial 5G-based fixed wireless services across over 48 countries. This means around 40% of 5G commercial mobile launches worldwide currently include an FWA offering.
In the U.S., T-Mobile added over half a million 5G FWA customers in Q4 2021 and Q1 2022 combined. By 2025, it expects to have eight million FWA subscribers, while Verizon is targeting five million FWA subscribers for the same period. The conventional wisdom holds that FWA is primarily useful as a rural service, targeted mostly at the previously unserved or underserved. Verizon says their FWA service is primarily urban and suburban service with target customers that are dissatisfied with terrestrial broadband services. Verizon has increasingly come to view FWA as an integral part of their broadband access offering everywhere that FiOS isn’t available.
Reliance Jio (India) announced ambitions to connect as many as 100 million homes across India to its 5G FWA network, the number of FWA users looks likely to grow substantially over the next few years.
While the majority of current 5G FWA deployments focus on the 3.5–3.8 GHz bands, several operators around the world are already using 5G mmWave spectrum as a capacity and performance booster to complement coverage provided by lower bands.
Only 7% of 5G launches have been in 5G mmWave spectrum so far but this looks set to change given 27% of spectrum allocations and 35% of trials are already using 5G mmWave bands. Furthermore, in 2023 alone, the industry will see ten more countries assigned 5G mmWave spectrum for use – a significant increase from the 22 countries who have been assigned it to date. Spain received the first European 5G mmWave spectrum allocation this year, resulting in Telefónica, Ericsson and Qualcomm launching its first commercial 5G mmWave network at MWC Barcelona 2023.
Enterprise IoT Driving Growth:
The figures from GSMA Intelligence also suggest that, for operators, the enterprise market will be the main driver of 5G revenue growth over the next decade. Revenues from business customers already represent around 30% of total revenues on average for major operators, with further potential as enterprise digitization scales. Edge computing and IoT technology presents further opportunities for 5G, with 12% of operators having already launched private wireless solutions – a figure that will grow with a wider range of expected IoT deployments in 2023.
Another major development for the enterprise will be the commercial availability of 5G Advanced (3GPP Release 18) in 2025. Focusing on uplink technology, 5G Advanced will improve speed, coverage, mobility and power efficiency – and support a new wave of business opportunities. GSMA’s Network Transformation survey showed half of operators expect to support 5G Advanced commercial networks within two years of its launch. While this is likely optimistic, it presents the ecosystem with a clear opportunity to execute on.
Editor’s Note:
GSMA’s 5G forecast is a direct contradiction to Omdia’s which expects weaker 5G growth in the near term. Which forecast do you believe?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Omdia forecasts weaker 5G market growth in near term, 4G to remain dominant
Huawei’s blueprint to lay the foundation for 5.5G and the “intelligent world”
According to Huawei, the intelligent world will be deeply integrated with the physical world. Everything, including personal entertainment, work, and industrial production, will be intelligently connected. This means that networks will have to evolve from ubiquitous Gbps to ubiquitous 10Gbps, connectivity and sensing will need to be integrated, and the ICT industry will have to shift its focus from energy consumption to energy efficiency. The evolution from 5G to 5.5G will be key to meeting these growing requirements.
At MWC 2023, Huawei unveiled its “GUIDE to the Intelligent World“ as a business blueprint to lay the foundation for 5.5G. Whatever happened to 5G Advanced and 3GPP Release 18? and ITU-R WP5D M.2150 recommendation?.
Following on from Huawei’s concept of “Striding Towards the 5.5G Era” that was proposed in July 2022, Huawei is highlighting the five major characteristics of the 5.5G era:
- 10 Gbps experiences
- Full-scenario interconnection
- Integrated sensing and communication
- L4 autonomous driving networks
- Green ICT
For Huawei, 5.5G represents a 10-fold improvement in performance over 5G in every metric. That means 10 Gbps headline connection speeds, 10 times the number of IoT connections – which translates to 100 billion in total – and reducing latency by a factor of 10. Networks also need to consume a tenth of the energy that they consume today on a per Terabyte basis, and they need to be 10x more intelligent, which means supporting level 4 autonomous driving, and making operations and maintenance (O&M) more efficient by a factor of 10.
With these capabilities in place, 5.5G networks will enable a boom in immersive interactive experiences, like VR gaming in 24K resolution, and glasses-free 3D video, predicts Huawei. It expects the installed user base of these services will grow 100-fold to 1 billion. On the enterprise side, the vendor expects the number of private cellular networks to increase from 10,000 today to 1 million by 2030.
Huawei says that leading global operators, standards organizations, and industry ecosystem partners are coming together to promote innovation and exploration for this 5.5G era, as it will create more new applications and business opportunities. This author disagrees- they are not coming together at all!
According to Ookla’s latest 5G City Benchmark Report, Huawei has played an important part in 5G network construction in all of the top 10 cities among the world’s 40 representative 5G-enabled cities. It’s important to note that 5G performance results in these 10 cities show that the 5G networks constructed by Huawei offer the best experience.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
David Wang, Huawei’s Executive Director of the Board, Chairman of the ICT Infrastructure Managing Board, and President of the Enterprise BG, said, “Huawei will deepen our roots in the enterprise market and continue our pursuit of innovation. We are ready to use leading technologies and dive deep into scenarios. Together with our partners, we will enable industry digitalization, help SMEs access intelligence, and promote sustainable development, creating new value together.”
Bob Chen, Vice President of Huawei Enterprise BG, delivered a keynote speech entitled “Digital Technology Leads the Way to the Intelligent World,” which outlined how digital technologies have impacted the development of the world’s economy, cultures, societies, and environment. He stated, “Archimedes, a great Greek physicist, said, ‘Give me a place to stand and I shall move the earth.’ Digital technology is the right place for us to help industries go digital. Huawei will focus on connectivity, computing, cloud, and other digital technologies. We will continue inspiring innovation to drive industry digital transformation. Together, let’s build a fully connected, intelligent world!”
Huawei said they would continue to work with customers to build next-generation network infrastructure to better serve all industries. Here are a few of their focus areas:
- Smart campus: Huawei redefines campus networks and launches the Next-Generation enterprise flagship core switch CloudEngine S16700, first enterprise-level Wi-Fi 7 AP AirEngine 8771-X1T, along with first 50G PON OLT and optical terminal product.
- Easy branch: Huawei launches the industry’s first simplified hyper-converged branch solution.
- Single OptiX: Huawei launches the industry’s first end-to-end optical service unit (OSU) product portfolio.
- Cloud WAN: Huawei defines a brand-new cloud WAN and launches the NetEngine 8000 series routers oriented to the all-service intelligent router platform in the cloud era.
- Data Center solution: Four industry-first products and product portfolios, unleashing the power of digital innovation
Storage and computing power have become one of the core strategic resources of enterprises. Huawei focuses on data center infrastructure innovation, leads the development of new data centers, helps enterprises cope with uncertain threats, ensures ultimate service experience, processes massive and diversified computing power, and brings data centers more green, more reliability, and more efficiency.
For large enterprises,Huawei launches the industry’s first multi-layer DC ransomware protection solution powered by network-storage collaboration, the industry’s first unified DC DR product portfolio featuring storage and optical connection coordination (SOCC),and CloudEngine 16800-X, which is the industry’s first DC switch designed for diversified computing power.
For SMEs, Huawei also launches OceanStor Dorado 2000 and OceanProtect X3000, which are the industry’s first entry-level storage combination based on the active-active architecture.
Juan De Dios Navarro Caballero, councillor of Alicante province, Spain, stated, “Huawei’s SDN-based CloudFabric Solution and All-Wireless Campus Network Solution enable network automation, intelligent O&M, and ubiquitous connectivity. Through these solutions, the government offices of Alicante province are now more efficient, and offer a better user experience for public services. The province has seen faster digital transformation along with digital economy development.”
Faith Burn, CIO of Eskom, a South African electric power company, shared the company’s digital transformation methodology and practical experience. She stressed that Eskom seeks to work with partners that can help realize the company’s digital vision, saying that, “It is very important to find capable partners to realize our digital vision. Eskom would like to collaborate with OEMs like Huawei to build advanced electricity ICT infrastructure to achieve comprehensive digitalization.”
Steven Zhu, President of Partner Development and Management of Huawei Enterprise BG, mentioned that “Huawei is committed to working with partners to complement each other, motivate partners to support customers proactively, and serve customers well together.”
In the future, Huawei says they will continue to invest and innovate, working alongside global customers and partners to deeply integrate ICT, accelerate digital transformation, promote digital economy development and speed up the realization of the intelligent world within industries, in order to create new value.
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2023/2/mwc2023-5g-huawei%20-connectivity
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2023/2/mwc2023-industry-digital-transformation
https://telecoms.com/520240/huaweis-5-5g-vision-is-what-5g-should-have-been-all-along/
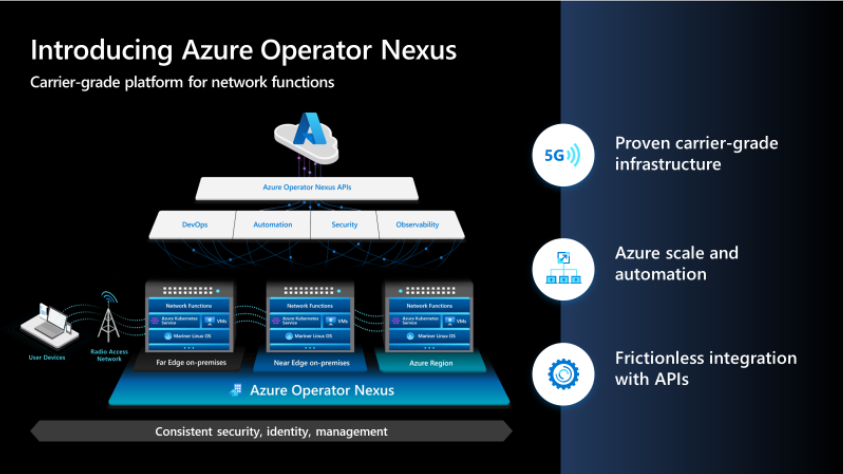
Microsoft announces Azure Operator Nexus; Enea to deliver subscriber data management and traffic management in 4G & 5G
Microsoft launched its brand new next-gen hybrid cloud platform – Azure Operator Nexus – for network operators today. Azure Operator Nexus is an expansion of the Azure Operator Distributed Services private preview. Azure Operator Nexus is a hybrid, carrier-grade cloud platform designed for the specific needs of the operator in running network functions such as packet core, virtualized radio access networks (vRAN), subscriber data management, and billing policy. Azure Operator Nexus is a first-party Microsoft product that builds on the functionality of its predecessor, adding essential features of key Microsoft technologies such as Mariner Linux, Hybrid AKS, and Arc while continuing to leverage Microsoft Services for security, lifecycle management, Observability, DevOps and automation.
Azure Operator Nexus has already been released to our flagship customer, AT&T, and the results have been incredibly positive. Now, we’re selectively working with operators for potential deployments around the world. In this blog post, we provide an overview of the service from design and development to deployment and also discuss benefits the customers can expect, including research and analysis into the total cost of ownership (TCO).
Overview:
Microsoft Azure Operator Nexus leverages cloud technology to modernize and monetize operator network investments to deliver benefits such as:
- Lower overall TCO
- Greater operations efficiency and resiliency through AI and automation
- Improved security for highly-distributed, software-based networks
Azure Operator Nexus is a purpose-built service for hosting carrier-grade network functions. The service is specifically designed to bring carrier-grade performance and resiliency to traditional cloud infrastructures. Azure Operator Nexus delivers operator mobile core and vRAN network functions securely in on-premises (far-edge, near-edge, core datacenters) and on-Azure regions. This delivers a rich Azure experience, including visibility into logging, monitoring, and alerting for infrastructure components and workloads. Operators will have a consistent environment across both on-premises and Azure regions, allowing network function workloads to move seamlessly from one location to another based on application needs and economics.
Whether deployed on-premises or in Azure infrastructure, network functions may access an identical set of platform capabilities. On-premises, the service uses a curated hardware BOM of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS)-based servers, network switches, dedicated storage arrays, and terminal servers. Both deployment models are Linux-based, in alignment with network function needs, telecommunications industry trends, and relevant open-source communities. Additionally, the service supports both virtualized network functions (VNFs) and containerized network functions (CNFs).
The Azure Operator Nexus is based on the experience of a large telecommunications operator that has spent the past seven years virtualizing more than 75 percent of its network and overcoming the scale challenges of network-function virtualization. From this deep networking and virtualization experience, Operator Nexus was designed to:
- Provide the network function runtime that allows the fast-packet processing required to meet the carrier-grade-network demands of network functions supporting tens of millions of subscribers. Examples of requirements the platform delivers include optimized container support, flexible, fine-grained VM sizing, NUMA alignment to avoid UPI performance penalties, Huge Pages, CPU pinning, CPU isolation, Multiple Network Attachments, SR-IOV & OVS/DPDK host coexistence, SR-IOV trusted mode capabilities and complex scheduling support across failure domains.
- Ensure the quality, resiliency, and security required by network-function workloads through robust test automation.
- Deliver lifecycle automation to manage cloud instances and workloads from their creation through minor updates and configuration changes, and even major uplifts such as VMs and Kubernetes upgrades. This is accomplished via a unified and declarative framework driving low operational cost, high-quality performance, and minimal impact on mission-critical running network workloads.
In addition to the performance-enhancing features, Azure Operator Nexus also includes a fully integrated solution of software-defined networking (SDN), low latency storage, and an integrated packet broker. The connectivity between the Operator premises and Azure leverages Express Route Local capabilities to address the transfer of large volumes of operational data in a cost-effective manner.
One of the key benefits of a hybrid cloud infrastructure is its ability to provide harmonized observability for both infrastructure and applications. This means one can easily monitor and troubleshoot any issues that may arise, ensuring systems are running smoothly and efficiently. The platform collects logs, metrics, and traces from network function virtualization infrastructure (NFVI) and network functions (NFs). It also offers a rich analytical, AI/ML-based toolset to develop descriptive and prescriptive analytics. Our goal with this observability architecture is to securely bring all operator data into a single data lake where it can be processed to provide a global-network view and harvested for operational and business insights.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Stockholm Sweden based Enea is amongst the first to join the program. They will deliver subscriber data management and traffic management in 4G and 5G for the new platform.
The introduction of Enea’s Telecom product portfolio will further enhance mobile operators’ ability to unlock the potential of 5G and provide more choice in pre-validated solutions to ensure a faster time to deployment for solutions. Enea’s telecom products include the Stratum Network Data layer, 5G Service Engine, Subscription Manager and Policy Manager, providing a range of subscriber data management, authorization and traffic management capabilities for both 4G & 5G mobile environments.
Azure Operator Nexus program provides an API layer to automate and manage network functions. The Enea network functions will integrate and validate at both the API interoperability level and the automated deployment level to provide telecom operators the option to build, host and operate these containerized functions as part of a network in a cloud or hybrid cloud environment. As pre-validated services, the Enea network functions will be available in the Azure Marketplace.
“The integration with Microsoft Azure Operator Nexus demonstrates Enea’s commitment to multi-vendor telecom architecture, software-based solution and open interoperability.”, said Osvaldo Aldao, Vice President of Product Management at Enea. Further adding, “The addition of our Stratum network data layer as an open 5G UDR & UDSF will provide the data management foundation to drive a fully cloud native architecture with Azure Operator Nexus”.
“Enea joining the Microsoft Azure Operator Nexus Ready Program enables both network function expertise and deployment experience from their extensive portfolio”, said Ross Ortega, Vice President – Azure for Operators, “Enea’s pre-validated functions in the Azure Marketplace will be an essential building block for operator networks.”
References:
Microsoft Azure for Operators:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/solutions/industries/telecommunications/#overview
Enea software portfolio:
Network Data Layer: https://www.enea.com/solutions/4g-5g-network-data-layer/
5G Applications https://www.enea.com/solutions/data-management-applications/
Traffic Management – https://www.enea.com/solutions/traffic-management/4g-5g-user-plane-dual-mode-services/
About Enea:
Enea is a world-leading specialist in software for telecom and cybersecurity. The company’s cloud-native solutions connect, optimize, and secure services for mobile subscribers, enterprises, and the Internet of Things. More than 100 communication service providers and 4.5 billion people rely on Enea technologies every day.
Enea has strengthened its product portfolio and global market position by integrating a number of acquisitions, including Qosmos, Openwave Mobility, Aptilo Networks, and AdaptiveMobile Security.
Contact: Stephanie Huf, Chief Marketing Officer [email protected]