NTT, VMware & Intel collaborate to launch Edge-as-a-Service and Private 5G Managed Services
Japan’s NTT Ltd. today announced the launch of Edge-as-a-Service, a managed edge compute platform that gives enterprises the ability to deploy quickly, manage and monitor applications closer to the edge.
NTT and VMware, in collaboration with Intel (whose role was not specified), are partnering to innovate on edge-focused solutions and services. NTT uses VMware’s Edge Compute Stack to power its new Edge-as-a-Service offering. Additionally, VMware is adopting NTT’s Private 5G technologies as part of its edge solution. The companies will jointly market the offering through coordinated co-innovation, sales, and business development.
NTT’s Edge-as-a-Service offering is a globally available integrated solution that accelerates business process automation. It delivers near-zero latency for enterprise applications at the network edge, optimizing costs and boosting end-user experiences in a secure environment.
NTT’s Edge-as-a-Service offering, powered by VMware’s Edge Compute Stack, includes Private 5G connectivity and will be delivered by NTT across its global footprint running on Intel network and edge technology. This work is an extension of NTT’s current membership in VMware’s Cloud Partner Program. VMware and NTT will each market their corresponding new services to their respective customer bases.
“Combining Edge and Private 5G is a game changer for our customers and the entire industry, and we are making it available today,” said Shahid Ahmed, Group EVP, New Ventures and Innovation CEO, NTT.
“The combination of NTT and VMware’s Edge Compute Stack and Private 5G delivers a unique solution that will drive powerful outcomes for enterprises eager to optimize the performance and cost efficiencies of critical applications at the network edge. Minimum latency, maximum processing power, and global coverage are exactly what enterprises need to accelerate their unique digital transformation journeys.”
“The whole premise behind it is that many of our customers are looking for an end-to-end solution when they’re buying either edge or private 5G architectures as opposed to buying edge compute from XYZ and then a private 5G from somebody else and an IoT solution from someone else. So we thought we would do a full one-stop solution for our customers, particularly those that are in manufacturing and industrial sectors.” Ahmed also said that NTT will also be able to break these services apart for customers that just want one of the services, but they will all be managed by NTT.
Ahmed added: “We have a very simple pricing structure, which is predictable and tier-based so the customer doesn’t have to put up upfront capex, it’s all opex based. Obviously, some verticals like to purchase or acquire technology as a capex, so we can do that as well.”
As factories increase their reliance on robotics, vehicles become autonomous, and manufacturers move to omnichannel models, there is a greater need for distributed compute processing power and data storage with near-instantaneous response times. VMware’s secure application development, resource management automation, and real-time processing capabilities combined with NTT’s multi-cloud and edge platforms, creates a fully integrated Edge+Private 5G managed service. VMware and NTT’s innovative offering resides closer to where the data is generated or collected, enabling enterprises to access and react to information instantaneously.
This solution, which leverages seamless multi-cloud and multi-tenant connectivity, combined with NTT’s capabilities in network segmentation, and expertise with movement from private to public 5G, provides critical benefits for multiple industries, including manufacturing, retail, logistics, and entertainment.
“Enterprises are increasingly distributed — from the digital architecture they rely on to the human workforce that powers their business daily. This has spurred a sea change across every industry, altering where data is produced, delivered, and consumed,” said Sanjay Uppal, senior vice president and general manager, service provider, and edge business unit, VMware. “Bringing VMware’s Edge Compute Stack to NTT’s Edge-as-a-Service will enable our mutual customers to build, run, manage, connect and better protect edge-native applications at the Near and Far Edge while leveraging consistent infrastructure and operations with the power of edge computing.”
NTT’s Edge-as-a-Service platform was developed to help secure, optimize and simplify organizations’ digital transformation journeys. Edge-as-a-Service is part of NTT’s Managed Service portfolio, which includes Network-as-a-Service and Multi-Cloud-as-a-Service, all designed for enterprises to focus on their core business.
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/ntt-vmware-intel-team-for-private-5g-edge-tasks/2022/08/
ITU-R urges Member States to take measures to prevent interference with radio navigation satellite service (RNSS) signals and receivers
Introduction:
Harmful frequency interference poses a significant and growing threat to critical infrastructure and safety services used every day, from commercial aviation to energy distribution to satellite navigation systems.
Protecting this ecosystem is essential for the safe and satisfactory operation of the growing number of devices, applications and autonomous vehicles that rely every day on positioning and navigation systems on air, sea, and land.
One of the principal objectives of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and its 193 Member States is to ensure interference-free operations of radiocommunication systems.
Article 45 of the ITU Constitution requires Member States “to take the steps required to prevent the transmission or circulation of false or deceptive distress, urgency, safety or identification signals, and to collaborate in locating and identifying stations under their jurisdiction transmitting such signals.”
Call for Action to mitigate interference with RNSS signals and receivers:
Following several incidences of harmful frequency interference brought to the attention of the ITU Radio Regulations Board, a recent Circular Letter urged ITU Member States to take measures to prevent interference with radio navigation satellite service (RNSS) signals and receivers.
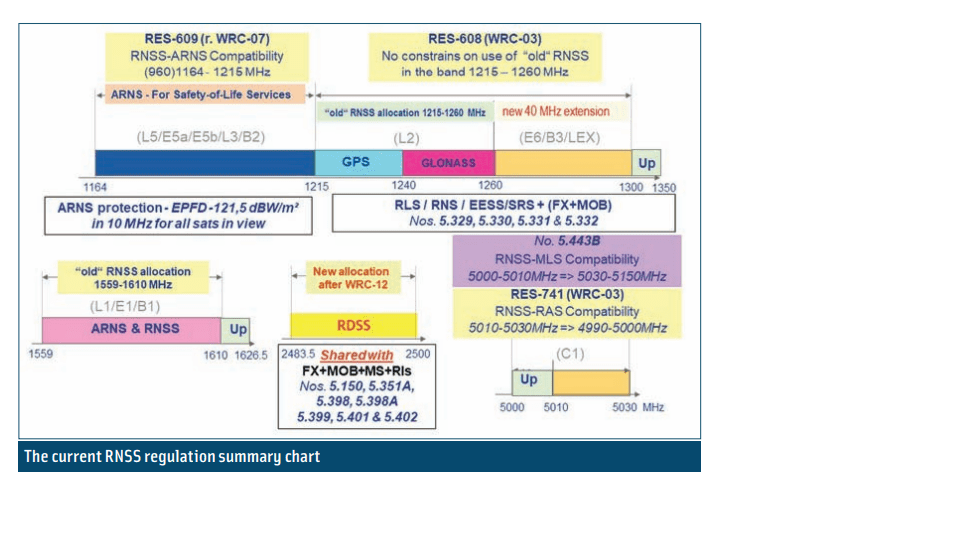
The RNSS is an essential component of global critical infrastructure, providing a “safety-of-life” service that must be protected from interference. It is used in GPS (the US-based Global Positioning System) and other global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) platforms, such as Europe’s GALILEO, Russia’s GLONASS and China’s BeiDou system.
Between 1 February 2021 and 31 January 2022, ITU received 329 reports of harmful interference or infringements of the Radio Regulations – the international treaty safeguarding the equitable and efficient use of the radio frequency spectrum.
Data collected by a major aircraft manufacturer shows that 10,843 radio-frequency interference events were detected globally over the same 12-month period, the circular notes. These figures were based on in-flight monitoring of GNSS receivers, which are standard onboard equipment for passenger or transport aircraft.
While most of the interference events occurred in the Middle East, several were also detected in the European, North American, African, and Asian regions.
The ITU Radiocommunication Bureau initially raised the issue of increasing interference to Member States at the 2019 World Radiocommunication Conference (WRC-19) in Sharm-El-Sheik, Egypt.
Since then, ITU has received reports about significant numbers of cases of harmful interference to the RNSS in the 1,559–1,610-megahertz (MHz) frequency band, also known as the “L1 band”.
What makes interference harmful:
Virtually all radio systems experience some interference. At very low levels, this can be considered acceptable or tolerable.
Harmful interference occurs when a radio system receives unwanted energy to an extent that inhibits the functioning of a radio-navigation service – such as those used onboard ships or aircraft – or seriously degrades, obstructs, or repeatedly interrupts any radiocommunication service that is operating in accordance with the Radio Regulations.
For example, harmful interference in the L1 band can disrupt the onboard receivers of aircraft, causing the degradation or total loss of communication for passenger, cargo, and humanitarian flights. In some cases, harmful interference in this frequency band can even cause RNSS receivers to provide misleading information to pilots, presenting a major safety risk.
Harmful interference with RNSS or GNSS signals – whether it is deliberate or inadvertent – constitutes a violation of the Radio Regulations, which state that “frequencies used for the safety and regularity of flight require absolute international protection from harmful interference and that administrations undertake to act immediately when their attention is drawn to any such harmful interference.”
One major source of such disruptions is unnecessary radio transmissions. But the interference prohibition also applies to the use of jamming devices, commonly referred to as “GNSS jammers,” “signal blockers” or “privacy jammers”.
Provision No. 15.1 of the Radio Regulations states that “all stations are forbidden to carry out unnecessary transmissions, or the transmission of superfluous signals, or the transmission of false or misleading signals.”
Handling harmful interference:
ITU’s Radiocommunication Bureau receives hundreds of interference reports each year. But ITU – the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies – is not alone in the battle to identify the sources of these potential cases and avert or eliminate resulting problems.
ITU collaborates with affected administrations and industry sectors, as well as with other UN agencies like the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the International Maritime Organisation (IMO).
While the Radiocommunication Bureau strives to deal with each report within 48 hours, the vital role of preventing harmful interference falls to governments around the world.
To mitigate this critical international issue, ITU asks its 193 Member States to take the following steps:
- Reinforce the resilience of navigation systems to interference by using technologies with multi-frequency/multi-system receivers and anti-jamming capabilities;
- Increase collaboration between radio regulatory, military, aviation, and law enforcement authorities;
- Reinforce civil-military coordination to address interference risks associated with RNSS testing and conflict zones;
- Retain essential conventional navigation infrastructure for contingency support in case of RNSS outages; and
- Develop mitigation techniques for loss of services.
References:
https://www.itu.int/hub/2022/08/warning-harmful-interference-rnss/
https://insidegnss.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/janfeb18-LAW.pdf
Spark New Zealand completes 5G SA core network trials with AWS and Mavenir software
Backgrounder:
Telecommunication companies in New Zealand are currently implementing ‘non-standalone’ 5G – while networks have been updated to 5G, data centres and network cores are still running on legacy, non-5G systems, which are dependent on 4G infrastructure.
To achieve standalone 5G, data centres and core mobile networks need to be upgraded and deployed on a cloud-native platform. Existing mobile networks run out of a centralised data centre have relatively static use-cases and are complex to customize.
A 5G standalone network is ‘cloud native’, meaning that it is fully virtualized, can run on any cloud service, is designed with a microservices approach and architected to address evolving customer needs in a scalable way, while also offering inherent resilience. This creates flexibility in an end-to-end 5G solution and allows users of the network to realise the full range of benefits of a standalone 5G network – including low latency, and advanced capabilities such as 5G network slicing, 5G security, 5G private networks, and multi access edge computing (MEC).
Spark’s 5G SA PoC Trials:
Spark New Zealand this week shared details of two 5G SA proof-of-concepts (PoCs) it carried out, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) was heavily involved in both of them. Spark deployed a 5G SA cloud-native core solution on AWS Snowball Edge, Amazon’s rugged, briefcase-sized edge cloud. It enabled the incumbent to create a portable storage and compute solution that can be deployed right at the edge of its 5G network, offering high throughput and low latency when and where it is needed.
The PoC also marked the first deployment of Mavenir’s 5G SA core network solution on Snowball Edge. Using this set-up, Spark tested a video analytics tool, recording a 70 percent reduction in latency compared to its 5G non-standalone network.
Spark’s other PoC used the same Mavenir 5G SA core software on AWS Outposts, a managed service that extends AWS infrastructure, APIs and tools to customer premises. It means a customer can work within the same development environment as the AWS public cloud, but use local storage a compute resources, resulting in lower latency. Spark said it wanted to see how this architecture might improve the performance of its 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) service. By deploying cloud-native core network software on AWS Outposts, the telco said it achieved faster download speeds and reduced latency compared to non-standalone FWA.
“These proof-of-concepts create line of sight for us to deliver the enhanced benefits of standalone 5G – both to New Zealand businesses looking to innovate using 5G connectivity and multi access edge compute (MEC), and to New Zealanders accessing a network that supports applications such as instant video streaming, cloud hosted gaming and the reaction times required for driverless vehicles,” said Josh Bahlman, Spark’s lead for telco cloud, in a statement.
“The 5G standalone network opens the door on capacity and low latency to help accelerate IoT trends, such as connected cars, smart cities and IoT in the home and office,” he added.

Amazon’s heavy involvement with these PoCs suggests Spark might be seriously considering a public cloud deployment for its 5G SA network. AT&T is doing exactly that with Microsoft Azure while Dish Network is using AWS public cloud. However, that 5G SA core network has yet to be deployed.
However, the overwhelming majority of telcos that have either deployed or committed to deploying 5G SA have also committed to rolling it out on their own telco cloud. Dell’Oro research director Dave Bolan recently wrote, “We found that 27 5G SA networks have been commercially deployed and only one MNO is running its 5G workloads in the public cloud. The balance chose to run their own telco clouds.”
Spark didn’t categorically state that its commercial 5G SA network will use AWS architecture, it might still go for an in-house option. At this stage, it doesn’t appear to have ruled anything in or out.
“The solutions offered by AWS and Mavenir provide an opportunity to test and learn by leveraging cloud-native solutions and multi access edge compute services optimised for 5G. Testing the technology in this way allows us to identify the optimal combination of vendors and solutions to deliver the benefits we want to achieve,” Bahlman said. “We have further proof-of-concepts underway as we work to bring relevant use cases specific to New Zealand’s local requirements.”
This is Mavenir’s first global edge deployment on Snowball Edge, and using such a device “allowed Spark to create a highly portable edge solution that could literally fit into a suitcase – to process and store data close to where it’s generated, enabling low latency and real time responsiveness”, said Spark.
The company said: “This is the first New Zealand mobile network deployment on AWS Outposts. Testing a wireless broadband service on this proof of concept showed faster download speeds and reduced latency when compared to pre-deployment results, providing a better experience for Spark’s wireless broadband customers.”
Mavenir’s president of core networks, Ashok Khuntia, said: “Our cloud-based network solution offers flexibility and advanced capabilities such as network slicing to enable efficiencies in overall service design and deployment times to accelerate trials and service rollouts.”
References:
https://www.sparknz.co.nz/news/spark-trials-5G-standalone-1/
https://www.capacitymedia.com/article/2ajorogc3p282dw7ozcw/news/aws-cloud-to-support-standalone-5g-in-new-zealand
https://www.spark.co.nz/5g/home.html
https://www.spark.co.nz/5g/home/5g-safety
https://about.att.com/story/2021/att_microsoft_azure.html
RailTel and CloudExtel partner to deploy India’s 1st shared RAN solution
RailTel, a Miniratna Central Public Center Enterprises (CPSU) [1.] of India’s Ministry of Railways and CloudExtel, a known Full Stack Network as a Service (NaaS) Provider have partnered together to launch India’s first shared Radio Access Network (RAN) solution for congested locations with the objective of enhancing telecom users’ experience.
Highlights are as follows:
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
RailTel and CloudExtel carried out the successful pilot of this project in partnership with Bharti Airtel, Vodafone Idea, Nokia, and the Telecom Infra Project (TIP)’s NaaS Solutions Group, with vital support from the Railways, in one of the most network stressed locations namely Mumbai Central railway station. The outcomes of the pilot project have been impressive with 5 times increase in average user speed of mobile data (from 3 Mbps to 15 Mbps) for the mobile phone networks of both Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea, while the data consumption jumped up by 20%.
Locations specifically like traffic junctions, airports, and railway stations are high-density areas for network congestion. Challenges multiply especially in cities like Mumbai which are densely populated. The success of the shared RAN solution holds promises for the customers of such highly populated and highly crowded areas to have better mobile data usage experience. In the initial phase, the focus will be on extending this technology at more railway stations in Mumbai. Later, more stations may be considered for coverage.

RailTel has so far set up public Wi-Fi hotspots at 5,848 railway stations and has resumed work on network expansion.
Photo credit: Livemint
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Aruna Singh, Chairman & Managing Director, RailTel said, “Facilitating seamless connectivity and an enhanced commute experience to passengers at railway stations has been our commitment. The impressive speed and data consumption enabled by Shared RAN has validated our belief in this technology, and we look forward to scaling this in all congested areas serving passengers and telecom operators while reducing the clutter of infrastructure and energy consumption in railway stations”.
Kunal Bajaj, Co-Founder and CEO, CloudExtel said, “The extensive consumption of multimedia-rich content and cloud applications are the new normal and will multiply with 5G offerings. In absence of shared RAN solutions, even 5G performance will get hampered in such congested locations, thus substantially compromising the user experience. Shared RAN solutions will become an architectural foundation for upcoming 5G deployments in the country.”
TIP enables Neutral Host NaaS business model deployments by promoting best practices and supporting market trials to achieve scale. Acknowledging the success of the pilot carried out at Mumbai Central railway station, Mr. David Nowicki, TIP NaaS Solution Group Co-Chair said, “TIP applauds CloudExtel’s remarkable achievement of unlocking transformative capacity in one of the world’s most challenging urban environments utilizing a neutral-host NaaS business model. The 5x Quality of Experience improvement demonstrates why this emerging business model should become the standard at urban train stations and similar venues across the globe.”
Mr. Vinish Bawa, Head of Emerging Business and Enterprise India at Nokia said, “We are delighted to partner with RailTel and CloudExtel in delivering higher data speeds and a better customer experience to commuters on Mumbai Central railways with our Multi-Operator RAN solution. Nokia also has a long heritage of working closely with major railway operators to bring the benefits of private LTE connectivity and pave the way for the adoption and deployment of Future Railway Mobile Communication Systems (FRMCS). For operators, these solutions bring cost savings and increased flexibility in their infrastructure deployments.”
The entire telecom landscape of India has undergone a transformation largely due to cheaper data connectivity and penetration. Network operators are now seeking shared solutions to bring in cost efficiency without compromising on deliverables to end consumers.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About CloudExtel:
CloudExtel is India’s first full-stack Network as a Service (NaaS) provider, reinventing digital infrastructure connectivity with enhanced coverage, capacity & speed. It caters to telecom operators, internet service providers, data centers, enterprises, and large content providers to address the challenges emerging from the hypergrowth of data consumption in India.
CloudExtel is rapidly building scale to enable the densification of 4G networks and to facilitate the transition to 5G, while driving emerging telecom architecture through ‘cloudification’ of networks.
Through its advanced network solutions, the company has enhanced connectivity in network-stressed, high-footfall iconic locations such as the Golden Temple, Varanasi Ghats, Gateway of India, Jalianwala Bagh, National Stock Exchange, Mantralaya Mumbai. CloudExtel caters to 20% of partner-deployed small cell requirements of large Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) through 4000 sites across 300+ towns and districts.
The imminent global shift to Open RAN (O-RAN) and Network Virtualization is expected to redefine the telecom and internet space. CloudExtel is set to leverage this transition. It is the first neutral host to deploy shared RAN in India, one of less than 10 players globally. The success of the shared RAN solution holds promises for the customers of such highly populated and highly crowded areas to have better mobile data usage experience.
About RailTel:
RailTel, a ‘Mini Ratna (Category-I)’ Central Public Sector Enterprise under Ministry of Railways, is one of the largest neutral telecom infrastructure & ICT Solutions & Services providers in the country, owning a Pan-India optic fiber network covering several towns and cities and rural areas of the country.
Along with a strong a reliable network of 61000+ RKM of Optic fibre, RailTel has two MeitY empanelled tier III data centers as well. With its Pan-India high-capacity network, RailTel is working towards creating a knowledge society at various fronts and has been selected for implementation of various mission-mode projects for the Government of India in the telecom field. RailTel offers a bundle of services like, MPLS VPN, Telepresence, leased line, Tower Co-location, Data center services, etc.
RailTel is also working with the Indian Railways to transform railway stations into digital hubs by providing public Wi-Fi at railway stations across the country and 6100+ stations are live with RailTel’s RailWire Wi-Fi.
References:
Musk’s SpaceX and T-Mobile plan to connect mobile phones to LEO satellites in 2023
During a live media event Thursday afternoon, T-Mobile’s Mike Sievert and SpaceX’s Elon Musk announced a new partnership that’s intended to connect T-Mobile sold phones to a new constellation of SpaceX’s Starlink satellites. The result, according to the companies, will be the elimination of all cellular dead zones around the U.S.
“It’s a lot like putting a cellular tower in the sky,” Sievert said, adding that the “vast majority” of T-Mobile’s existing phones would be supported by the service. Meaning, customers will not need to purchase new phones in order to connect them to Starlink’s second-generation satellites.
Sievert said that T-Mobile expects to offer the service for no additional charge on its more expensive plans. For customers on its cheaper plans, he said they may need to pay an additional monthly charge in order to be able to access satellite coverage.
Starlink’s satellites will use T-Mobile’s mid-band spectrum to create a new network. Most phones used by the company’s customers will be compatible with the new service, which will start with texting services in a beta phase beginning by the end of next year. The companies did not say when it might launch commercially.
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/WSL6VTEO3FONZGAOYYYFER22AU.jpg)
T-Mobile CEO Mike Sievert at a joint news conference at Space X facility in Brownsville, TX
REUTERS/Adrees Latif
SpaceX has launched nearly 3,000 low-Earth-orbiting (LEO) Starlink satellites since 2019, handily outpacing rivals OneWeb and Amazon.com Inc’s Project Kuiper. Starlink recently suffered a major setback when the FCC rejected the company’s application for almost $900 million in government subsidies. The agency ruled that Starlink’s service likely wouldn’t be able to meet the agency’s speed and service requirements.
SpaceX’s next-generation Starlink satellites, the first of which are planned to launch on SpaceX’s next-generation Starship rocket whenever it is fully developed, will have larger antennae that will allow connectivity directly to mobile phones on the T-mobile network, Musk said.
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/D53NNDMLVVKBDL27U25YAODCXA.jpg)
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/VX32JK5RMZMCHJKYGKRH3TNOMU.jpg)
SpaceX Starbase, in Brownsville, Texas, U.S., August 25, 2022. REUTERS/Adrees Latif
Meanwhile, U.S telecom firms are in a race to build up the mid-band portion of their 5G networks to catch up with T-Mobile, which bagged a chunky 2.5 GHz of mid-band spectrum thanks to a buyout of rival Sprint.
Mid-band or C-Band has proven to be perfect for 5G, as it provides a good balance of capacity and coverage. T-Mobile said it aims to pursue voice and data coverage after the texting services beta phase.
Others in the Mix:
Satellite communications firm AST SpaceMobile Inc is also building a global cellular broadband network in space that will operate with mobile devices without the need for additional hardware. AST SpaceMobile is relying on SpaceX’s rockets to get its satellites into orbit, having pivoted away from a plan to use Russian rockets after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
“Elon [Musk] and Mike [Sievert, of T-Mobile] helped the world focus attention on the huge market opportunity for SpaceMobile, the only planned space-based cellular broadband network,” AST SpaceMobile CEO Abel Avellan wrote on LinkedIn yesterday. “BlueWalker 3 … is scheduled for launch within weeks!”
Meanwhile, Verizon and AT&T each have their own satellite plans: Verizon plans to use Amazon’s planned Project Kuiper satellites to connect its rural cell towers to the Internet, and AT&T is planning a similar setup with OneWeb’s own growing constellation of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
In 2020, AT&T agreed to let startup AST SpaceMobile use its Band 5 spectrum to test transmissions from its BlueWalker 1 satellite to devices on the ground. AST SpaceMobile is now hoping to launch its new BlueWalker 3 prototype later next month. However, as reported by SpaceNews, supply chain issues delayed the launch of AST SpaceMobile’s first operational satellite by about six months, to late 2023.
AST SpaceMobile’s main rival, Lynk, already has one operational satellite in orbit for phone connections. As noted by Ars Technica, the company is hoping to receive FCC approval to offer satellite-to-phone services across 35 countries by the end of this year.
“Elon said it’s hard, and it’s only been done in the lab, but Lynk has done it in space already,” Lynk’s Charles Miller told the publication yesterday. “We’re the only company in the world that has done that.”
Lynk hasn’t yet announced an agreement with a major U.S. network operator, though it has agreements with a number of international operators. Lynk tested its services in the U.S. with Smith Bagley, a tiny wireless network operator offering services under the Cellular One brand in East Arizona.
“There are significant regulatory hurdles to clear, as the FCC is reviewing SpaceX’s request to launch a constellation of 30,000 Gen2 satellites, while other LEO proposals including Amazon’s Project Kuiper (with whom Verizon is collaborating) and AST SpaceMobile (financial backing from Vodafone and a commercial agreement with AT&T) are also working DC as well as international agencies to put some rules in place for this latest chapter of the Space Race,” Raymond James analysts wrote in a note to investors.
References:
UPDATE: Apple iPhone 14 text messages via Globalstar LEO satellites starting Nov 2022:
Ericsson and Nokia demonstrate 5G Network Slicing on Google Pixel 6 Pro phones running Android 13 mobile OS
In separate announcements today, Ericsson and Nokia stated they had completed 5G Network Slicing trials with Google on Pixel 6 Pro smart phones running the Android 13 mobile OS [1.].
Network Slicing is perhaps the most highly touted benefits of 5G, but its commercial realization is taking much longer than most of the 5G cheerleaders expected. That is because Network Slicing, like all 5G features, can only be realized on a 5G standalone (SA) network, very few of which have been deployed by wireless network operators. Network slicing software must be resident in the 5G SA Core network and the 5G endpoint device, in this case the Google Pixel 6 Pro smartphone.
Note 1. On August 15, 2022, Google released Android 13 -the latest version of its mobile OS. It comes with a number of new features and improvements, as well as offers better security and performance fixes. However, it’s implementation on smartphones will be fragmented and slow according to this blog post.
For devices running Android 12 or higher, Android provides support for 5G Network Slicing, the use of network virtualization to divide single network connections into multiple distinct virtual connections that provide different amounts of resources to different types of traffic. 5G network slicing allows network operators to dedicate a portion of the network to providing specific features for a particular segment of customers. Android 12 introduces the following 5G enterprise network slicing capabilities, which network operators can provide to their enterprise clients.
Android 12 introduces support for 5G network slicing through additions to the telephony codebase in the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) and the Tethering module to incorporate existing connectivity APIs that are required for network slicing.
Here’s a functional block diagram depicting 5G network slicing architecture in AOSP:
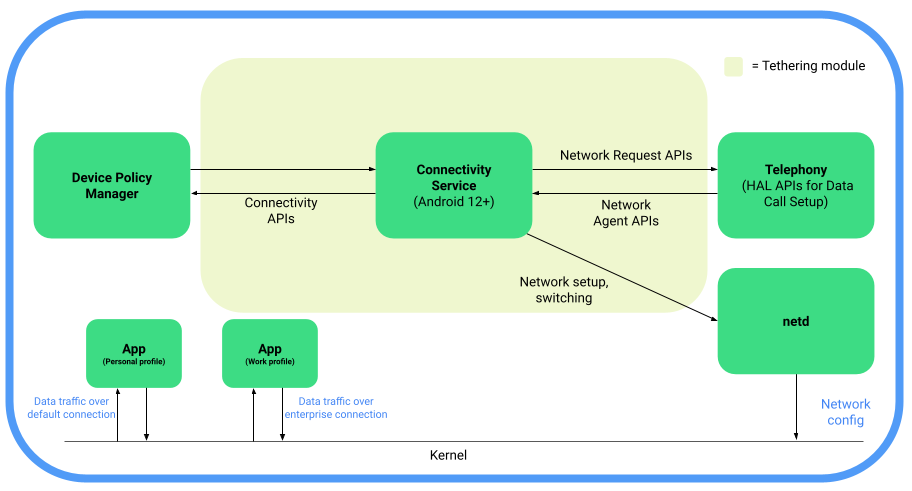
Image Credit: Android Open Source Project
1. Ericsson and Google demonstrated support on Ericsson network infrastructure for multiple slices on a single device running Android 13, supporting both enterprise (work profile) and consumer applications. In addition, for the first time, a slice for carrier branded services will allow communications service providers (CSP) to provide extra flexibility for customized offerings and capabilities. A single device can make use of multiple slices, which are used according to the on-device user profiles and network policies defined at the CSP level.
The results were achieved in an Interoperability Device Testing (IODT) environment on Google Pixel 6 (Pro) devices using Android 13. The new release sees an expansion of the capabilities for enterprises assigning network slicing to applications through User Equipment Route Selection Policy (URSP ) rules, which is the feature that enables one device using Android to connect to multiple network slices simultaneously.
Two different types of slices were made available on a device’s consumer profile, apart from the default mobile broadband (MBB) slice. App developers can now request what connectivity category (latency or bandwidth) their app will need and then an appropriate slice, whose characteristics are defined by the mobile network, will be selected. In this way either latency or bandwidth can be prioritized, according to the app’s requirements. For example, the app could use a low-latency slice that has been pre-defined by the mobile network for online gaming, or a pre-defined high-bandwidth slice to stream or take part in high-definition video calling.
In an expansion of the network slicing support offered by Android 12, Android 13 will also allow for up to five enterprise-defined slices to be used by the device’s work profile. In situations where no USRP rules are available, carriers can configure their network so traffic from work profile apps can revert to a pre-configured enterprise APN (Access Point Name) connection – meaning the device will always keep a separate mobile data connection for enterprise- related traffic even if the network does not support URSP delivery.
Monica Zethzon, Head of Solution Area Packet Core at Ericsson said: “As carriers and enterprises seek a return on their investment in 5G networks, the ability to provide for a wide and varied selection of use cases is of crucial importance. Communications Service Providers and enterprises who can offer customers the flexibility to take advantage of tailored network slices for both work and personal profiles on a single Android device are opening up a vast reserve of different uses of those devices. By confirming that the new network slicing capabilities offered by Android 13 will work fully with Ericsson network technology, we are marking a significant step forward in helping the full mobile ecosystem realize the true value of 5G.”
Ericsson and partners have delivered multiple pioneering network slicing projects using the Android 12 device ecosystem. In July, Telefonica and Ericsson announced a breakthrough in end-to-end, automated network slicing in 5G Standalone mode.
2. Nokia and Google announced that they have successfully trialed innovative network slice selection functionality on 4G/5G networks using UE Route Selection Policy (URSP) [2.] technology and Google Pixel 6 (Pro) phones running Android 13. Once deployed, the solution will enable operators to provide new 5G network slicing services and enhance the customer application experience of devices with Android 13. Specifically, URSP capabilities enable a smartphone to connect to multiple network slices simultaneously via different enterprise and consumer applications depending on a subscriber’s specific requirements. The trial, which took place at Nokia’s network slicing development center in Tampere, Finland, also included LTE-5G New Radio slice interworking functionality. This will enable operators to maximally utilize existing network assets such as spectrum and coverage.
Note 2. User Equipment Route Selection (URSP) is the feature that enables one device using Android to connect to multiple network slices simultaneously. It’s a feature that both Nokia and Google are supporting.
URSP capabilities extend network slicing to new types of applications and use cases, allowing network slices to be tailored based on network performance, traffic routing, latency, and security. For example, an enterprise customer could send business-sensitive information using a secure and high-performing network slice while participating in a video call using another slice at the same time. Additionally, consumers could receive personalized network slicing services for example for cloud gaming or high-quality video streaming. The URSP-based network slicing solution is also compatible with Nokia’s new 5G radio resource allocation mechanisms as well as slice continuity capabilities over 4G and 5G networks.
The trial was conducted using Nokia’s end-to-end 4G/5G network slicing product portfolio across RAN-transport-core as well as related control and management systems. The trial included 5G network slice selection and connectivity based on enterprise and consumer application categories as well as 5G NR-LTE slice interworking functionalities.
Nokia is the industry leader in 4G/5G network slicing and was the first to demonstrate 4G/5G network slicing across RAN-Transport-Core with management and assurance. Nokia’s network slicing solution supports all LTE, 5G NSA, and 5G SA devices, enabling mobile operators to utilize a huge device ecosystem and provide slice continuity over 4G and 5G.
Nokia has carried out several live network deployments and trials with Nokia’s global customer base including deployments of new slicing capabilities such as Edge Slicing in Virtual Private Networks, LTE-NSA-SA end-to-end network slicing, Fixed Wireless Access slicing, Sliced Private Wireless as well as Slice Management Automation and Orchestration.
Ari Kynäslahti, Head of Strategy and Technology at Nokia Mobile Networks, said: “New application-based URSP slicing solutions widen operator’s 5G network business opportunities. We are excited to develop and test new standards-based URSP technologies with Android that will ensure that our customers can provide leading-edge enterprise and consumer services using Android devices and Nokia’s 4G/5G networks.”
Resources:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Addendum:
- Google’s Pixel 6 and Pixel 6 Pro, which run on Android 12, are the first two devices certified on Rogers 5G SA network in Canada, which was deployed in October 2021. However, 5G network slicing hasn’t been announced yet.
- Telia deployed a commercial 5G standalone network in Finland using gear from Nokia and the operator highlighted its ability to introduce network slicing now that it has a 5G SA core.
- OPPO, a Chinese consumer electronics and mobile communications company headquartered in Dongguan, Guangdong, recently demonstrated the pre-commercial 5G enterprise network slicing product at its 5G Communications Lab in collaboration with Ericsson and Qualcomm. OPPO has been conducting research and development in 5G network slicing together with network operators and other partners for a number of years now.
- Earlier this month, Nokia and Safaricom completed Africa’s first Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) 5G network slicing trial.
References:
https://source.android.com/docs/core/connect/5g-slicing
Nokia and Safaricom complete Africa’s first Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) 5G network slicing trial
Vertical Systems Group: Mid-2022 U.S. Carrier Ethernet Leaders; Change is Coming
Vertical Systems Group (VSG) today revealed that seven companies achieved a rank on their Mid-2022 U.S. Provider Ethernet LEADERBOARD as follows (in order based on retail port share as of June 30, 2022): Lumen, AT&T, Spectrum Enterprise, Verizon, Comcast Business and Cox Business. To qualify for a rank on this LEADERBOARD, network providers must have four percent (4%) or more of the U.S. retail Ethernet services market.)
Research Highlights:
- Lumen continues to hold the top rank on the Mid-2022 U.S. Ethernet LEADERBOARD based on port share.
- Our latest Ethernet research shows that port shares are tightening between several of the market leading providers.
- Dedicated Internet/Cloud Access (DIA) was the fastest growing Ethernet service for the first half of 2022 and is on pace to be the largest Ethernet service overall by year-end based on billable U.S. customer installations. Primary Ethernet DIA applications are connectivity for Cloud services and Managed SD-WANs.
- Market demand is rising for Ethernet services ranging up to 100+ Gbps.
- Customers requiring higher bandwidth connectivity are also evaluating alternatives to Ethernet, including Wavelength and Dark Fiber services.
- Ethernet service providers continue to grapple with supply chain challenges, including lengthy lead times and shortages of the supplies necessary for customer deployments and backbone network operations.
- Lumen and Verizon are the only LEADERBOARD companies with MEF 3.0 Carrier Ethernet (CE) certification.

Challenge Tier citations were attained by the following six companies (in alphabetical order): Altice USA, Cogent, Frontier, GTT, Windstream and Zayo. The Challenge Tier includes providers with between 1% and 4% share of the U.S. retail Ethernet market.
The Market Player tier includes all providers with port share below 1%. Companies in the Market Player tier include the following providers (in alphabetical order): ACD, AireSpring, Alaska Communications, Alta Fiber, American Telesis, Arelion, Armstrong Business Solutions, Astound Business, Breezeline, BT Global Services, Centracom, Consolidated Communications, Conterra, Crown Castle, Douglas Fast Net, DQE Communications, ExteNet Systems, Fatbeam, FiberLight, First Digital, FirstLight, Flo Networks, Fusion Connect, Global Cloud Xchange, Great Plains Communications, Hunter Communications, Intelsat, Logix Fiber Networks, LS Networks, MetTel, Midco, Momentum Telecom, NTT, Orange Business, Pilot Fiber, PS Lightwave, Ritter Communications, Segra, Shentel Business, Silver Star Telecom, Sparklight Business, Syringa, T-Mobile, Tata, TDS Telecom, TPx, Unite Private Networks, Uniti, US Signal, WOW!Business, Ziply Fiber and other companies selling retail Ethernet services in the U.S. market.
“Share rankings on the U.S. Ethernet LEADERBOARD remain unchanged for the first half of 2022, however a shakeup is possible by the end of the year,” said Rick Malone, principal of Vertical Systems Group. “Escalating requirements for Gigabit Ethernet services – and particularly 100+Gbps – are spurring capacity upgrades and intensifying competition among fiber-based providers.”
In contrast, the 2021 Global Carrier Ethernet leaders are: Orange Business Services (France), Colt (U.K.), Verizon (U.S.), AT&T (U.S.), Lumen (U.S.), BT Global Services (U.K.) and NTT (Japan). This industry benchmark for multinational Ethernet network market presence ranks companies that hold a 4% or higher share of billable retail ports at sites outside of their respective home countries.
VSG Principal Rick Malone told Fierce Telecom that he expects a reshuffling in the order of the top six U.S. Carrier Ethernet operators by the end of this year. According to Malone, the U.S. Carrier Ethernet arena is a relatively mature market (this author says it is VERY MATURE as it’s >20 years old). Malone noted “there are multiple companies, not just the top two, but multiple companies that are fairly close together in share of those six” at the top of its leaderboard. Cox Business is the sixth company on the mid-2022 Leaderboard, ranking just behind Comcast.
Malone said VSG will be keeping a close eye on Lumen in light of the recent divestiture of its Latin America assets. While that move likely won’t have a direct impact on its number of Ethernet ports in the U.S., it could impact some of Lumen’s global customers, he said. Malone added that the market overall achieved a year-on-year port growth rate “in the low single digits,” so below 5%. But he noted only about half the companies VSG surveyed grew and that is to be expected in a mature market!
“There are quite a few of them (Carrier Ethernet service providers) that actually have lower port counts than they had previously. Some of that is that they’re consolidating lower speed circuits into higher speed circuits,” he explained. “But there are some that don’t view their Ethernet service as their lead strategic service when they go and talk to an enterprise. They are leading with SD-WAN and SASE and the security products that you’d expect.”
Some of the companies that have been successful in the Ethernet arena are those which have been migrating their customer base away from MPLS to SD-WAN and using Ethernet as a transport mechanism for the latter. “That managed migration is helping them sell additional Ethernet services as an underlay,” Malone concluded.
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/shakeup-brewing-lumen-led-us-carrier-ethernet-market
Dell’Oro: Demand for Optical Transport equipment strong and headed for double-digit growth in NA
In a new report, the Dell’Oro Group states that the demand for Optical Transport equipment remained strong in North America during 2Q 2022. In the quarter, the North American market for Optical Transport grew 10 percent year-over-year.
“At this pace, we could be headed for another year of double-digit growth in North America,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “While we expected another year of North American optical market expansion in 2022, we thought the growth rate could slow a bit after such a strong 2021. However, considering the first-half results and higher than usual backlog held by equipment manufacturers, we think a double-digit rate of growth could occur in 2022. Our biggest concern, however, remains to be the component shortage and supply chain issues that have limited revenue growth for the past couple years,” added Yu.
Additional highlights from the 2Q 2022 Quarterly Report:
- The worldwide Optical Transport market excluding China grew 2 percent in 2Q 2022 and is projected to grow a little over 4 percent in 2022.
- The region with the lowest year-over-year growth rate in the quarter was Asia Pacific due to lower demand in China.
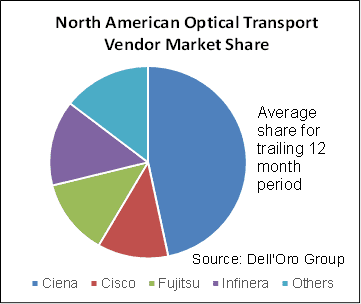
- The system manufacturers with the highest share of North America Optical Transport revenue in the quarter were Ciena, Infinera, Cisco, and Fujitsu. These four vendors held a combined market share of approximately 85 percent. Please see chart below:
The Dell’Oro Group Optical Transport Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, and unit shipments (by speed including 100 Gbps, 200 Gbps, 400 Gbps, and 800 Gbps). The report tracks DWDM long haul, WDM metro, multiservice multiplexers (SONET/SDH), optical switch, optical packet platforms, data center interconnect (metro and long haul), and disaggregated WDM.
To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
Cable Labs: Interoperable 200-Gig coherent optics via Point-to-Point Coherent Optics (P2PCO) 2.0 specs
Cablecos use of 200-Gig coherent optical signals in their broadband access network progressed following a recent interop event at CableLabs that involved a five suppliers of coherent optical modules.
CableLabs confirmed that equipment and silicon from those players – Acacia (now part of Cisco), Ciena, Fujitsu Optical Components, Lumentum and Marvell – were found to interoperate with the organization’s Point-to-Point Coherent Optics (P2PCO) 2.0 specs [1.]. The number of participants might not be high, but what’s important is that the participants include DSP silicon from multiple manufacturers that represent the majority of the coherent optics industry.
Note 1. The P2PCO 2.0 specs doubled the operating capacity – from 100 Gbit/s per wavelength in the 1.0 specs, to 200 Gbit/s.
Demonstrating interoperability among so many different coherent DSP suppliers bodes incredibly well for network operators as it provides multi-vendor interoperability, which promotes scale and competition.
Image Courtesy of Cable Labs
Cable Labs conducted 100-Gig interops in 2018 and 2019. Those efforts tie into a broader initiative to use coherent optics technologies, typically used for long-haul, metro and submarine networks, to expand the capacity of fiber that’s already deployed on the hybrid fiber/coax (HFC) access network.
The CableLabs specs also describe a new technology called the Coherent Termination Device (CTD), which can be deployed in an outdoor aggregation node.
Matt Schmitt, a principal architect at CableLabs, said the scope of CableLabs’ interoperability efforts focus on the modules on the optical end – basically describing how a transceiver works at the physical layer.
And to help fit the cable network environment, the end of the network using the CTD is made to reside outdoors, rather than inside a facility.
“Almost every other application of coherent that you see, both ends of the link are in facilities,” such as a data center interconnect where many links are densely packed with racks and modules, Schmitt explained. The cable access application of coherent optics might involve one end that does sit at a facility, such as a hub site, with the other end involving the aforementioned field-deployed CTD.
“Those field boxes didn’t really exist when we started this,” he said.
The broader concept is to help cable operators improve the performance of their access network fibers situated between headends and hubs and fiber nodes for a range of use cases, and to do so without getting locked into one supplier.
CableLabs and its partners originally thought this 200-Gig interop would be completed sooner, but it was delayed a bit during the pandemic when travelling and in-person gatherings were limited or non-existent.
But Schmitt said the plus side of that intervening period meant that the interop ended up with wider supplier participation, particularly at the DSP (digital signal processor) level, than it might have otherwise.
Beyond raw capacity, the 200-Gig capability should help to support the new distributed access architecture (DAA), supported by multiple remote PHY or remote MAC/PHY devices, and the cable’s industry’s broader pursuit of delivering symmetrical 10Gbit/s performance to customers on the access network.
Schmitt said 200-Gig technology gets particularly interesting when operators look to support large, high-density areas that are being split into smaller service groups. It might also factor in as operators explore services beyond high-speed data over cable, such as mobile XHaul.
The use of CTDs with pluggable optics is also designed to support a relatively easy upgrade path. If an operator starts with 100-Gig, those modules can be swapped out for 200-Gig modules later.
This point-to-point P2P use case is just one aspect of coherent optics being explored by CableLabs. A separate-but-related coherent PON initiative still uses coherent signaling, but is focused on point-to-multipoint links.
For now, Schmitt said CableLabs doesn’t plan to hold another interop for P2PCO v2.0 products. “It really just worked so well. I’m not sure what more there will be to do in a follow-up interop,” he said.
CableLabs would be open to doing qualification testing for these new P2P coherent products if the market demands it. “Thus far, I haven’t been hearing of a big push for that,” Schmitt said. “I think people have been comfortable with what we’re getting from the interops and doing their own testing to see how it works.” As for next steps, this latest batch of handiwork will be showcased at the 10G Lab at CableLabs, Schmitt said.
Meanwhile, future commercial deployments will be determined by the availability of CPDs and interest form cable operators.
Among suppliers involved in the recent interop, Ciena confirmed that it currently has interoperable, CableLabs-compliant 200G coherent pluggables available as part of the supplier’s WaveLogic 5 Nano coherent pluggable portfolio.
Another factor for adoption will be costs compared to the 10-Gig DWDM tech that’s in use today. Schmitt acknowledges that the first endpoint is going to be greater with coherent technology, since it involves putting a switch or router in the field.
“Where it gets interesting is every time you need to add another device that’s sharing that same fiber run,” Schmitt said.
“With coherent, you have a higher upfront cost, but you’re going to have a much lower slope, because as you add more devices, all you have to do is add a pair of gray (standard) optics modules – very low cost … Where’s that crossover point in terms of number of endpoints? To me, is going to be one of the big deciders on when and how widespread the deployment of this technology gets.”
References:
A Jolt of Light: CableLabs Holds First 200G P2P Coherent Optics Interop
First Light for CableLabs® Point-to-Point Coherent Optics Specifications
MediaTek to expand chipset portfolio to include WiFi7, smart homes, STBs, telematics and IoT
Taiwanese fabless chipmaker MediaTek is gearing up to expand its customer base beyond the increasingly saturated smartphone segment to include connected devices for smart homes, electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers and the smart retail field.
Chunyan See, Thailand country manager for MediaTek, said the company is offering chipsets beyond the smartphone segment to WiFi 7-linked products, set-top boxes (with video streaming so popular aren’t STBs a thing of the past?), telematics, and Internet of Things. Some market leaders and mobile operators plan to launch WiFi 7 products in the first quarter of 2023. Mediatek previously announced chipsets for WiFi 6 and 6E.
“We see the gaps to change from WiFi 6 to WiFi 6E and WiFi 7 becoming shorter and shorter,” said Mr See. “Service operators typically take one to 1.5 years for internal testing to get the requirements finalized.”
Demand for higher wireless connection speed in Thailand is pushing local mobile operators to aggressively invest in 5G and fixed broadband services, he said. With rising inflation and a weaker baht, the overall smartphone market in Thailand will be tough this year, with the market size expected to drop to 19.2 million units, from 20-21 million last year, he said. In the second half of this year, 5G-enabled smartphones are expected to account for 40% of the total market, versus 32% in the first half and 24% in 2021, said Mr See.

MediaTek is also working with local partners beyond the smartphone segment in three fields — smart homes, smart retail, and smart logistics. For smart homes, the company will power the next generation of smart home accessories, including smart lighting and sensors. In smart retail, the firm supports smart point-of-sale devices that can cater for face payments, which is already the norm in China. Regarding smart logistics, 5G equipment powered by the firm’s chipsets can play a key role in telematics, which is a method of monitoring vehicles and other assets by using GPS technology, and can serve EVs. Chinlin Low, technical account manager for Asia-Pacific at MediaTek, said.
ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) is expected see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 83% for 5G subscriptions from 2021 to 2027, when they are forecast to reach 570 million.
Mobile data traffic per smartphone is expected to reach 45 gigabytes per month in 2027, up from 9.4GB in 2021, with a CAGR of 30%, driven by the rise of virtual and augmented reality services.
MediaTek has a broad range of chipsets to offer, including Dimensity 9000, 8100 and 8000 to cater for premium smartphones, he added.
Daniel Lin, MediaTek’s deputy director of corporate sales and emerging markets, said the company sees an opportunity to increase its share of the global premium smartphone segment. “MediaTek has a strong market share in smartphones costing between US$99 to $299, but the firm aims to increase its share in premium smartphones with the launch of new chipsets,” he said.
In 2021, the firm’s overall market share in the smartphone segment rose to 42%, from 32% in 2020. Its share in Android-powered handsets surpassed 50% in 2021, up from 38% in 2020.
MediaTek posted revenue of $17.6 billion in 2021, up from $10.9 billion a year earlier.
References:
https://www.bangkokpost.com/business/2373841/mediatek-explores-a-host-of-opportunities
Nokia, China Mobile, MediaTek speed record of ~3 Gbps in 3CC carrier aggregation trial
MediaTek Announces Filogic Connectivity Family for WiFi 6/6E
Nokia and MediaTek use Carrier Aggregation to deliver 3.2 Gbps to end users