Hiber in deal with Shell for remote IoT monitoring of wells via HiberHilo
Dutch satellite asset tracking start-up Hiber has signed an agreement with Royal Dutch Shell to provide worldwide well monitoring systems. The global framework agreement will allow all Shell entities and subsidiaries to use the HiberHilo product worldwide for Industrial IoT applications.
HiberHilo, launched in October 2020, is an end-to-end IoT system that makes adds data and security to monitoring. Based on satellite technology, the system will enable oil and gas companies to measure real-time well temperature and pressure at disconnected wells in remote and offshore locations. HiberHilo is already installed in Shell operations in the North Sea. Shell is considering using HiberHilo for various operations in Africa, the Middle East and Southeast Asia.
“After testing HiberHilo, the opportunity was clear,” said Ian Taylor, Global Principal Technical Expert for well integrity at Shell. Operations in South-east Asia, the Middle East, and Africa are considering HiberHilo.
“HiberHilo is a simple solution to help oil and gas companies improve safety, optimize operations, and reduce their environmental footprint,” said Coen Jansen, Hiber’s Chief Strategy Officer. “We’re thrilled to be working with Shell toward a technologically cleaner future. Hiber’s mission is connecting everything everywhere to deliver productivity and sustainability in global industrial IoT,” he added.
Shell plans to use HiberHilo to reduce travel to and from wells in remote locations. The system will also let the company to gain more data on their well performance and better monitor well integrity issues, improving the safety of remote and offshore oil and gas wells.

Image Credit: Hiber Global
Hiber, founded in 2016 in the Netherlands, designs, builds and operates end to end solutions for the Internet of Things, focused on industrial uses such as well integrity or heavy equipment monitoring. The company is working on a network of 50 satellites aimed at making the ‘Internet of Things’ available all over the world. Its Hiberband network is described on their webpage as follows:
Hiberband is the world’s first LPGAN (Low Power Global Area Network) and it changes everything. It’s low cost thanks to using tiny nano satellites at a low orbit of just 600km above Earth. Unlike traditional satellite and cellular operators who launch gigantic, super expensive satellites at 60x higher with much higher costs.
Low orbit also means low power with modem batteries lasting 5-10 years. Just one of many factors that make experimenting with Hiberband-enabled devices a developer’s dream. We’ve even secured priority on our own dedicated frequency. Which is why everyone at Hiber believes Hiberband is the future of IoT connectivity.
Hiber acquired a new space permit in July 2020. On 29 February, the company launched a second-generation satellite into orbit through a SpaceX launch. A second Soyuz rocket launch followed in March. At the end of March, Hiber received an investment of 26 million EUROs to further expand its IoT satellite network. The funding came from the European Innovation Council Fund (EIC Fund), the EU’s innovation agency, which has a €278 million Innovation Fund. The EIC co-invested with an innovation credit provided by the Dutch government and existing shareholders. Other investors include Finch Capital, Netherlands Enterprise Agency and Hartenlust Group. Hiber’s satellite constellation tracks and monitors machines and devices in harder-to-reach places.
References:
https://hiber.global/press/hiberhilo-shell-deal/
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/hiber-signs-iiot-agreement-with-shell–1397276
Hiber signs deal with Shell for remote IoT well monitoring system
Shell hands major IoT contracts for oil well and refinery monitoring to Dutch startups
IoT satellite network startup Hiber secures €26M in funding round led by EU’s innovation agency
https://hiber.global/press/hiberhilo-wts-venture/
T-Mobile US CFO on the Big Hack, Verizon Tracfone, Supply Chain Shortages, and FWA
Peter Osvaldik (photo below), executive vice president & chief financial officer (CFO) of T-Mobile US provided a business update today at the BofA 2021 Media, Communications and Entertainment Conference.
Selected Quotes:
“With respect to the (well advertised) data breach, T-Mobile US is not immune to criminal acts, but we have a responsibility to our customers which we take very seriously. We acted quickly to shut down the attack, investigate and get in touch with the consumers that were impacted. We definitely saw some temporary customer cautiousness. But now, several weeks later, consumer flows have normalized. We’re taking significant steps to enhance our security.”
“$750M annual T-Mo revenues would go away if Verizon is successful in acquiring Tracfone, which is clearly a competitor. We feel good in that space, especially with Metro by T-Mobile as the leading pre-paid service provider.”
“The network experience will become more compelling with 5G, especially mid band (2.5GHz) 5G with 300M bit/sec targeted speeds and the massive capacity that brings. We’re exactly in the right spot as we take these assets and deploy them at breakneck speeds.”
“We are the 5G (U.S.) leader and that lead will continue to grow. We were first to bring a differentiated rate plan (Magenta MAX) that won’t slow you down.”
“Certainly, from a network perspective, we’re not experiencing any supply chain issues. From a home broadband (FWA) perspective, sometimes demand did exceed supply. We’re already seeing increasing supply there. We feel very good about our momentum on the home broadband side of the house.”
“Samsung has really fallen behind the eight ball relative to other OEMs [original equipment manufacturers] on the global supply chain issue.” Osvaldik noted that Samsung discontinued its Galaxy Note smartphone “which many of our customers just loved,” and that many of the company’s S-series smartphones “are in very short supply.”
“A lot of our customer base are very significant Samsung lovers, and so we probably saw a little bit more of the supply chain issue there. Others (wireless network operators) that have an Apple oriented customer base have been less impacted.”
“The demand we’re seeing for FWA, with download speeds of 100 M bit/sec and soon to increase, is very strong. We have a target of 7 to 8M FWA customers by the end of 2025. We’re confident we’ll receive our target (number of subscribers) this year.”
“Large enterprises and government are a tremendous opportunity for us. It’s opened up a lot of conversations with government organizations. We’re very pleased with the traction we’ve seen.”

Peter Osvaldik, Executive Vice President & CFO, T-Mobile
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Belgian trial of FWA using Pharrowtech’s mmWave technology
Vlaio has agreed to support a trial of fixed-wireless internet access (FWA) in the 60 GHz band using semiconductor start-up Pharrowtech’s mmWave technology. Belgian cable operator Telenet and wireless equipment supplier Unitron are also participating, with the trial services expected to start for homes and businesses in 2022.
The trial will focus on validating the performance of Pharrowtech’s mmWave technology, to help the company move towards commercialization of its products. Pharrowtech said its CMOS process technology makes mmWave services in the 60 GHz band a cost-effective, high-performance alternative to fibre roll-outs. The technology is reliable and robust enough to cope with the outdoors environment, while delivering superior performance compared to alternatives in the market, in urbran or rural areas, the company said.
The Vlaio grant will be used to support preparation and execution of the Telenet field trial of Pharrowtech’s mmWave RFIC technology using Unitron’s network elements. Beamforming and mesh control software developed by labs at the Flemish research institute Imec will also be used in the trial.
Telenet, which is controlled by the Liberty Global group, said it has multiple use cases in mind where FWA could bring benefits such as reducing installation and roll-out costs. The operator last year started exploring a cooperation on FTTH roll-out in Flanders, but has yet to commit to a technology for its next network upgrade after Docsis 3.1. In the US, operators such as Mediacom and Alaska Communications are already exploring FWA services.
Pharrowtech was founded in 2018 as a spin-off from Imec, where the founding team led CMOS IP generation and prototype development in mmWave wireless systems for more than fifteen years. In 2019, the company secured more than EUR 6 million in seed funding from imec-Xpand, Bloc Ventures and the KBC Focus Fund, and in June this year the company released its first evaluation board.
Pharrowtech CEO and Co-Founder, Wim van Thillo, said: “We are extremely pleased that VLAIO is supporting us to roll out our technology with these leading partners. This field trial perfectly represents the massive business opportunity that mmWave FWA offers. Even in areas as densely populated as Belgium, operators struggle to deploy gigabit internet services fast enough. This project will establish our technology as a key complement to fiber for fast and economical high-speed internet deployments everywhere.”
Unitron CTO, Stephen Deleu, said: “With this VLAIO project, UnitronGroup will expand its knowledge in the higher frequency ranges and discover new wireless applications for ultrafast broadband communication. UnitronGroup is the market leader in multiple high frequency technologies, and collaborating with knowledge partners helps us strengthen our position. As a key technology partner for multiple telecom operators, our role in this ambitious project is to provide the FWA customer and distribution node elements. We are excited to be part of this consortium and looking forward to the insights and outcomes of this VLAIO project.”
Telenet, Director Network & Infrastructure, Luk Bruynseels, said: “For Telenet it is paramount to keep on investing in innovative ways to deliver digital services to our customers. We have multiple use cases in scope where FWA technology brings opportunities and important benefits by reducing installation and roll-out costs. This VLAIO project is a great opportunity for Telenet to gather and share all required knowledge and expertise within the consortium to ensure we meet the expected outcome of the project.”
References:
Pharrowtech, Telenet, and Unitron secure public funding for Fixed Wireless Access field trial
O-RAN Alliance tries to allay concerns; Strand Consult disagrees!
The O-RAN Alliance reiterated its commitment towards Open and intelligent Radio Access Network (RAN) and said its board has approved changes to O-RAN “participation documents and procedures” to allay concerns of some participants who may be subjected to U.S. export regulations.
The O-RAN Alliance became aware of concerns regarding some participants that may be subject to U.S. export regulations, and has been working with O-RAN participants to address these concerns. The O-RAN Board has approved changes to O-RAN participation documents and procedures. While it is up to each O-RAN participant to make their own evaluation of these changes, O-RAN is optimistic that the changes will address the concerns and facilitate O-RAN’s mission.
“O-RAN is an open and collaborative global alliance operating in a way that promotes transparency and participation of our member companies in the development and adoption of global open specifications and standards,” said Andre Fuetsch, Chairman of the O-RAN ALLIANCE and Chief Technology Officer of AT&T.
“We remain fully committed to working together in the alliance to achieve the goals and objectives of O-RAN as quickly as possible,” said Alex Jinsung Choi, Chief Operating Officer of the O-RAN ALLIANCE and SVP of Strategy and Technology Innovation, Deutsche Telekom.
This comes after Nokia halted its work in the Open RAN industry alliance over concerns that it may face penalties from the U.S. government for working with blacklisted Chinese entities.
John Strand’s comments:
This statement is not solving the Chinese security problem. Even with the proposed changes, the five founding members, including China Mobile, still have a veto. The statement from O-RAN Alliance raises more questions than it answers. Who are the member companies, do the network operators agree with the O-RAN Alliance statement? How about contributors and the license adopters?
Strand Consult wants to create the transparency O-RAN Alliance are fighting against, and I share the concerns of the EU and the U.S. House Foreign Affairs Committee when it comes to transparency. At the same time, we believe it is a great idea for O-RAN Alliance to become WTO (World Trade Organization) compliant like other professional telecom standard bodies. What’s the problem for ORAN Alliance to be WTO compliant? It’s hard to see any downside.
Strand Consult doesn’t believe the changes will satisfy WTO requirements nor does it align with the practices of professional standards organizations nor with shareholder practices of U.S. and EU publicly traded companies.
Last year Strand Consult exposed the 44 Chinese companies involved in the O-RAN Alliance three of them on the entity list.
The O-RAN Alliance proposes changes to mitigate Chinese involvement. However these changes will probably not satisfy WTO compliance rules. Here are some relevant report from EU/WTO and European Commission (EC) on OpenRAN: https://www.wto.org/english/tratop_e/tbt_e/principles_standards_tbt_e.htm
https://ec.europa.eu/newsroom/dae/redirection/document/78778 (page 76).
The EC’s report is based on publicly available information and an interview with a legal expert on the WTO rules and EU Regulation No 1025/2012. It notes the following concerns with the O-RAN Alliance’s proposed changes:
- First, the required transparency, i.e. all essential information is easily accessible to all interested parties, is only partly fulfilled, e.g. the O-RAN specifications are not accessible at the homepage.
- Second, the procedure is not open in a non-discriminatory manner during all stages of the standard-setting process, because the founding members have access to more information than the contributors during the process.
- Third, although interested contributors have opportunities to contribute to the elaboration of the specifications, the founding members have a privilege, because they have the necessary minority of more than 25% to block proposals.
Overall, proof that the O-RAN Alliance complies with the various WTO criteria is still missing, although some of their members assure this compliance is in place. “Consequently, such an independent assessment is needed, which, however, cannot be realized within the context of this project.”
The O-RAN Alliance does not satisfy the openness criteria laid down in WTO Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations. The O-RAN Alliance is a closed industrial collaboration developing technical RAN specification over and above 3GPP specifications or ITU-R recommendations.
3GPP was formed after 2G (GSM) was developed this means that 3GPP did not develop 2G but 3GPP ensured backward compatibility for every G. Note that 3GPP specifications define the technical specifications for a complete mobile cellular network 2G/3G/4G/5G. ITU-R recommendations only cover the radio access interface technologies, e.g. ITU M.2150/IMT 2020 for “5G.”
It is possible that some U.S. firms could be satisfied with the O-RAN Alliances proposals, but the fact remains that Chinese companies still exert disproportionate authority on this industry group. It is not yet clear with U.S. President Biden or the NTIA will weigh in on the matter. If not, this could be interpreted as placating, or even going soft on China.
Strand Consult discloses on its website that it is a company providing knowledge to the mobile industry, specifically mobile operators and their managers, executives, and boards of directors. Strand Consult only sells knowledge to mobile operators, and Strand Consult has done this for 25 years (see About Strand Consult below).
About O-RAN ALLIANCE:
The O-RAN ALLIANCE is a world-wide community of over 300 mobile operators, vendors, and research & academic institutions operating in the Radio Access Network (RAN) industry. As the RAN is an essential part of any mobile network, the O-RAN ALLIANCE’s mission is to re-shape the industry towards more intelligent, open, virtualized and fully interoperable mobile networks. The new O-RAN standards will enable a more competitive and vibrant RAN supplier ecosystem with faster innovation to improve user experience. O-RAN based mobile networks will at the same time improve the efficiency of RAN deployments as well as operations by the mobile operators. To achieve this, the O-RAN ALLIANCE publishes new RAN specifications, releases open software for the RAN, and supports its members in integration and testing of their implementations.
About Strand Consult:
There are six focus areas:
– The mobile broadband market
– The MVNO market
– The market for Value Added Services
– Next Generation Prepaid Services
– The Smartphone market
– Digital strategy for the Telecom and Media industry.
We have spent many man years researching and publishing a series of comprehensive reports and workshops focused on these areas. Market players that have ambitions of being successful within these areas can either try to gain an overview themselves, find solutions and purchase external consultants to help them on their way, or alternatively use Strand Consult’s reports – with or without workshops -to acquire the knowledge they need to be successful in the future.
You can read more about some of our reports here:
Successful Strategies for the Mobile Broadband Market
References:
Dell’Oro: Worldwide Telecom Equipment Revenue +10% Year over Year
Dell’Oro Group has completed its 1H2021 reports on “Telecommunications Infrastructure programs” including Broadband Access, Microwave & Optical Transport, Mobile Core & Radio Access Network (RAN), Service Provider Router & Switch markets. The data contained in these reports suggest that the positive trends that characterized the broader telecom equipment market extended into the second quarter, even if the pace of the growth slowed somewhat between the first and the second quarter.
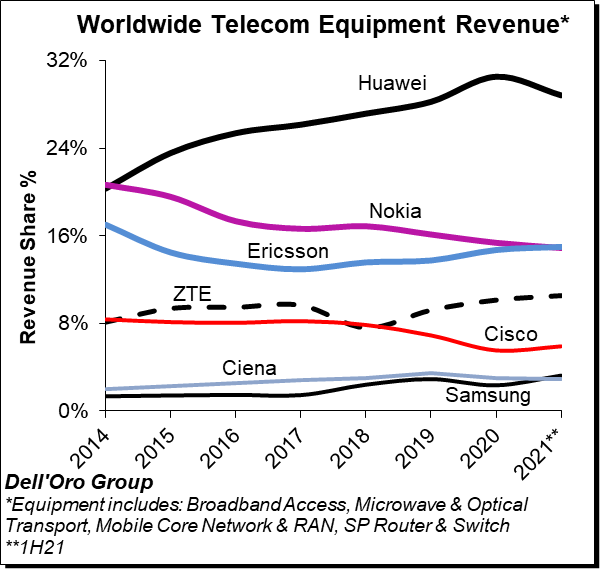
Preliminary estimates suggest the overall telecom equipment market advanced 10% year-over-year (Y/Y) during 1H21 and 5% Y/Y in the quarter, down from 16% Y/Y in the first quarter. The growth in the first half was primarily driven by strong demand for both wireless and wireline equipment, lighter comparisons, and the weaker US Dollar (USD). Helping to explain the Y/Y growth deceleration between 1Q and 2Q is slower growth in China.
The analysis contained in these reports suggests the collective global share of the leading suppliers remained relatively stable between 2020 and 1H21, with the top seven vendors comprising around ~81% of the total market.
Huawei is still the overall market leader by some margin, despite its sales and marketing challenges in many other parts of the world. Huawei’s market share slid below 30%, though that still almost double the share of its nearest rivals Ericsson and Nokia. Within the mix, Dell-Oro estimates Huawei and Nokia lost some ground between 2020 and 1H21 while Cisco, Ericson, Samsung, and ZTE recorded minor share gains over the same period.
Additional key takeaways from the 1H2021 reporting period include:
- Following the Y/Y decline in 1Q20, our analysis suggests the overall telecom equipment market recorded a fifth consecutive quarter of growth in the second quarter.
- The improved market sentiment in the first half was relatively broad-based, underpinned by single-digit growth in SP Routers and double-digit advancements in Broadband Access, Microwave Transport, Mobile Core Networks, and RAN.
- Aggregate 2Q21 revenues were in line with expectations, however, within the programs both Broadband Access and Microwave Transport were surprised on the upside while Optical Transport and SP Routers came in below expectations.
- From a regional perspective, China underperformed in the quarter, impacting the demand for both wireless and wireline-related infrastructure.
- Ongoing efforts by the US government to curb the rise of Huawei are starting to show in the numbers outside of China, not just for RAN but in other areas as well.
- Though Huawei is not able to procure custom ASICs for its telecom products, the supplier is assuring the analyst community its current inventory levels is not a concern over the near term for its infrastructure business.
- The majority of the vendors have through proactive measures been able to navigate the ongoing supply chain shortages and minimize the infrastructure impact. At the same time, the supply constraints appear more pronounced with higher volume residential and enterprise products including CPE and WLAN endpoints.
- Even with the unusual uncertainty surrounding the economy, the supply chains, and the pandemic, the Dell’Oro analyst team remains optimistic about the second half – the overall telecom equipment market is projected to advance 5% to 10% for the full-year 2021, unchanged from last quarter.
Two of the key telecom revenue drivers will be the RAN and Broadband Access markets, both of which have been growing at a strong pace this year so far: The RAN market is set to grow at between 10% and 15% this year, which means it could be worth as much as $40 billion, while the increasing number and size of investments in fibre broadband access networks around the world is driving growth in the Broadband Access market, which Dell’Oro reports was worth $3.6 billion during the second quarter alone.
Dell’Oro Group telecommunication infrastructure research programs consist of the following: Broadband Access, Microwave Transmission & Mobile Backhaul, Mobile Core Networks, Mobile Radio Access Network, Optical Transport, and Service Provider (SP) Router & Switch.
SpaceX and KDDI to test Satellite Internet in Japan
KDDI, Japan’s second-largest mobile provider, has emerged as one of SpaceX’s partners in rolling out high-speed wireless Internet coverage via satellites, according to Nikkei Asia. It’s all part of SpaceX CEO Elon Musk’s goal of connecting the entire world to the internet via satellites.
SpaceX has launched hundreds of Starlink telecommunications satellites with the goal of fully starting services in Japan by the end of the year. KDDI and SpaceX will begin a network proving test in Japan this month, and coverage is expected to be commercially available next year.
The two companies will start by offering internet service to customers living in mountainous regions and islands for no additional charge. The satellite network will also serve as backup in case terrestrial telecom lines are disrupted during natural disasters or blackouts.
Once Satellite Internet service coverage increases, Starlink could field a network for smart devices, which would be used for data collection in sparsely populated places or for drone operation in otherwise hard-to-access areas.
The transmission of visuals and other large pieces of data will allow officials to remotely monitor volcanic eruptions or floods or inspect bridges and electrical towers.
For farmers, Starlink will allow them to monitor weather and crop conditions so they are better informed of when to fertilize or harvest.
Terrestrial telecom infrastructure involves a web of base stations, switching stations, fiber optic cables and backbone networks. Starlink will connect data transmissions between phones and base stations to backbone networks via satellites.
The new service is expected to provide a low-cost communications infrastructure for low-population areas because it renders fiber optic cables unnecessary. KDDI will add satellite communication antennas to base stations and install a new SpaceX transmission station at the Yamaguchi Satellite Communication Center.
Japan still has a few areas with incomplete telecom networks. At the end of March, about 9,900 people lived in locations with no mobile coverage. Even in areas with wireless coverage, it is often hard to connect with devices on islands.
KDDI covers over 90% of the population with 4G communication, but so-called platinum frequency band only extends over 60% of the land area.
A Starlink satellite can exchange signals across more than 1,000 km with low latency. The satellites orbit at lower altitudes than conventional communication satellites, which hover about 36,000 km above ground. The lower altitudes are said to enable faster communication compared to normal satellite services.
Such satellite networks services need approval from Japan’s communications ministry before operations can begin. The ministry amended rules in August that opened the doors to SpaceX launching internet services in Japan. Both SpaceX and KDDI plan to obtain licenses by the end of the year.
Back when KDDI has been strong in satellite control signals ever since the company was known as Kokusai Denshin Denwa. The carrier has collaborated with SpaceX on the technological front since last year.
This current partnership entails SpaceX providing the satellites while KDDI takes care of terrestrial telecom connections.
Musk mentioned “two quite significant partnerships with major country telcos” in June during the Mobile World Congress in Barcelona. Although Musk did not disclose the companies’ names, it turns out that KDDI is one of them.
SpaceX will use the service rollout in Japan, where customers expect high-quality connections, as the model for a global network.
SpaceX has been launching Starlink satellites at a rapid pace. About 400 units alone were sent into space in 12-month period starting May 2019, according to NASA. More than 1,500 of the satellites are believed to be currently in orbit.
Musk’s company will continue launching satellites until it forms a constellation of over 10,000 units. There are over 3 billion people worldwide without internet access. The expansion of services would enable the global spread of digitalization.
A satellite network will be essential for making sixth generation communication a feasible reality. Driverless vehicles and similar applications will use 6G. To prevent latencies and disruptions in service, terrestrial base stations will need to work together with satellites and aerial communication drones.
Other players are jumping into the satellite telecom business. Amazon.com is spending $10 billion to create a network of over 3,000 satellites. Japanese counterpart Rakuten Group has partnered with a U.S. startup with the goal of launching satellite-powered mobile services in the next fiscal year.
NTT, Japan’s leading telecom group, has teamed with Sky Perfect JSAT Holdings on developing what are essentially data processing centers in space. Those services are expected to go live in 2026.
References:
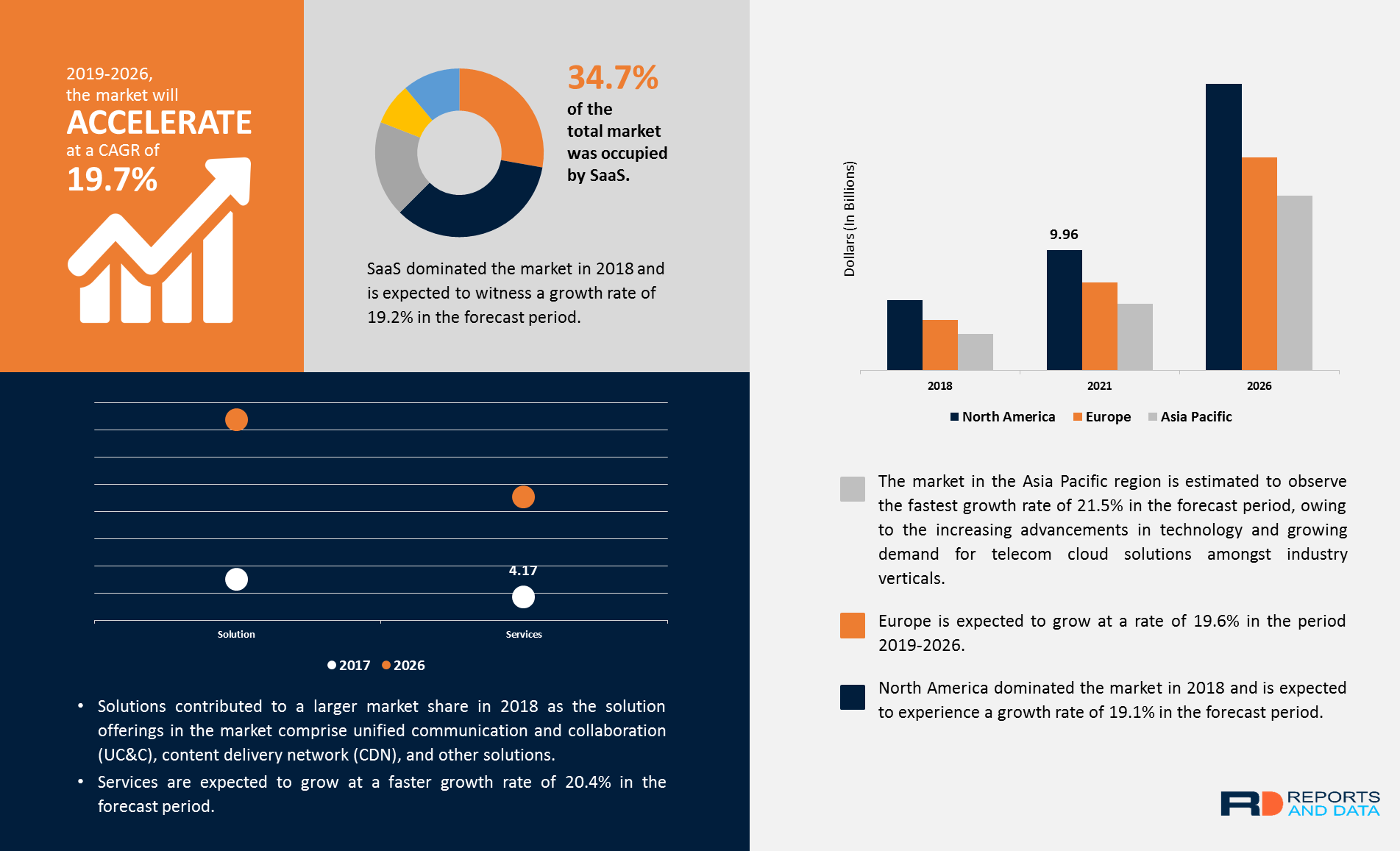
Reports and Data: Telecom Cloud Market to grow at CAGR of 19.7% through 2026
The global Telecom Cloud Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 19.7% in terms of value, from 2019 to reach USD 59.25 Billion by 2026, according to a new report by Reports and Data. OTT (Over-the-top) consumers demand more flexibility in scheduling, arranging videos, live events, and recording of favorite shows, thereby pushing the service providers to opt for more resources, infrastructure scalability, and computing resources to cater demands. By adopting a cloud-based workflow, video service providers can efficiently hand off duty for the infrastructure and networking supporting their OTT services. Telecom cloud can be instrumental in meeting the needs of OTT service providers, thus resulting in the growth of the market.
The telecom cloud market Modernization of IT platforms is estimated to fuel the growth of the market in the forecast period. As some of the largest communication service providers across the globe modernize their networks, they facilitate large enterprises to transform the way they involve with a progressively digital world. By leveraging IP-based technology, UCaaS (Unified Communications-as-a-Service), embedded communications (such as voice, chat, and video built into web and business applications) and other novelties on an IP network, communication service providers and the organizations they cater to can provide enhanced service to their customers and reap higher margins by reducing their expenses along with the lower total cost of ownership delivered by software-defined real-time communications (RTC).
Increasing demand for over-the-top cloud services is one of the significant factors influencing market growth. The telecom cloud leads to low operational costs, which is expected to drive the market growth in the forecast period. By deploying cloud computing, service providers can host services and software at a considerably lower cost. Provisioning and virtualization software allows organizations to efficiently assign computing resources, thus lowering the cost of hardware. Service providers can locate facilities at low-cost locations, provisioning, which cannot be replicated by most enterprises, resulting in low up-front costs.
Additionally, the proliferation of the internet, especially in developing nations, is expected to propel the growth of the telecom cloud market in the upcoming years.
Key participants include AT&T Inc., Verizon Communications Inc., Ericsson, Deutsche Telekom, BT Group PLC, CenturyLink Inc., Orange Business Services, NTT Communication Services, Singapore Telecommunications Limited, and Telstra Corporation Limited, among others.
Key findings from the report:
• By offering, solutions contributed to a larger market share in 2018 as the solution offerings in the market comprise unified communication and collaboration (UC&C), content delivery network (CDN), and other solutions.
• By service type, SaaS dominated the market in 2018 and is expected to witness a growth rate of 19.2% in the forecast period. The swift growth of on-demand services among consumers has resulted in a high demand for this service type in the telecom cloud market.
• By organization size, small & medium-sized enterprises are expected to witness a higher CAGR of 20.5% in the period 2019-2026 as services and solutions have the potential to produce enhanced efficiency, quality, and business productivity.
• By industry verticals, BFSI (Banking, financial services and insurance) held the largest market share in 2018 and is expected to grow at a rate of 19.6% in the forecast period.
• North America dominated the market in 2018 and is expected to experience a growth rate of 19.1% in the forecast period. The market dominance of North America is attributed to the presence of leading telecom companies mainly in the U.S. and Canada
The growing concerns pertaining to spectrum crunch in the developing nations are driving the market for telecom cloud as it helps telecom companies to increase their profitability in the telecom market. In countries with a high population, especially Countries in the Asia Pacific region, the telecom cloud plays an instrumental role in enabling telecom market players to gain a competitive edge in the market.
Incorporating cloud computing platforms into telecommunication allows Network functions virtualization (NFV) to virtualize servers, networks, and storage augments the utilization of available system resources and lowers infrastructure cost. Besides, network virtualization offers the implementation of numerous applications and features an open environment. Thus, telecom cloud virtualization is linked to many significant advantages, including enhanced scalability, flexibility of deployment, and a reduction in cost of the equipment, which permits reiteration of application software, better support for resolving faults, and enhanced security, among others.
References:
https://www.reportsanddata.com/report-detail/telecom-cloud-market
LightBox Internet Coverage Map finds 4X as many unserved in U.S. then FCC report
LightBox has released its nationwide internet connectivity map, a first of its kind, showing that nearly 60 million Americans remain unconnected to the Internet. This new map layers the location of approximately two billion Wi-Fi access points on top of LightBox’s national Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric, which details the precise geospatial extent, address(es), occupancy classification, and number of business or dwelling units for structures across the United States.
LightBox said the map was created by combining the company’s granular location data with information from 2 billion different Wi-Fi access points. The result is a highly-detailed picture of broadband connectivity across the country.

LightBox Internet Connectivity Map, Census tract-level aggregate view. Red indicates very poor connectivity, orange poor connectivity, yellow ok connectivity, and green good connectivity. White areas indicate locations with no connectivity detected.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Through its granular location fabric and geospatial expertise, LightBox says it has developed the necessary foundation for a true broadband availability map. Combined with ISP data on broadband serviceable locations, LightBox could produce a nationwide broadband connectivity map that would offer the most precise analysis of true accessibility.
“Accurate and granular maps based upon precise location data, serviceability, and analytics are required for government investment to be targeted and rapidly deployed to the communities in need,” says LightBox CEO Eric Frank. “LightBox has created this map based on our national Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric. Geospatially overlaying Wi-Fi location data has identified the gaps in connectivity. Whether the gaps are a function of lack of adoption or lack of service can now be tracked and appropriate remedies can be set in motion.”
LightBox has taken an approach which yields significantly greater precision. “We have combined two granular data assets to construct a precise view of connectivity in the US. This new map shows which structures have active internet and identifies connected structures with low adoption relative to the number of housing units. Where available, we can also layer in speed test data to understand where internet is operating below broadband speeds,” explained Zach Wade, VP of Data Science for LightBox. “What’s even more exciting is that we can update this view monthly to deliver an audit mechanism that tracks where and when new internet locations go online.”
The evolution of federal and state programs to map broadband with greater accuracy will allow government to apply rigor to complex broadband infrastructure design and investment—a process that Georgia, which produced the most granular broadband map to-date, has proven requires high-precision maps to execute accurately and equitably. “We simply couldn’t have built the master location fabric for broadband maps in Georgia without LightBox’s unparalleled data solutions,” said Bill Price, former Senior Strategist for Georgia, now VP of Government Solutions at LightBox. With LightBox support, Georgia was able to identify upwards of 400,000 additional unserved locations over traditional mapping approaches. LightBox can provide state-level mapping currently and encourages being informed of any updated locations not currently tracked.
The 60 million unconnected U.S. residents cited by LightBox is more than four times higher than the 14.5 million Americans the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) said were unserved in its most recent Broadband Deployment Report. That FCC report included data through the end of 2019. In May, BroadbandNow released its own report which found 42 million Americans lack access to terrestrial broadband.
The FCC’s broadband coverage data and maps have long been a source of anger and indignation for many in the telecom industry, given both are used by the FCC and state-level officials to determine eligibility for broadband funding. The agency’s reliance on providers’ self-reported coverage statistics (known as Form 477 data) has repeatedly been highlighted as a key flaw.
An FCC official recently told Fierce Telecom it is in the process of collecting more granular data for fresh coverage maps. However, the release of new maps is likely a year or more away.
The map available on the LightBox website displays a nationwide view of internet connectivity rates across the country, aggregated at the Census tract level. Interested parties may contact LightBox for access to the complete map, which shows data down to each location. For researchers seeking additional insights, LightBox has several hundred data layers that can be readily overlayed on this map. Some of the more popular data sets leveraged by LightBox clients include demographic data, boundary data, purchasing data, internet speed test data, climate data, fiber location data and measuring tools.
Currently covering about 97 percent of the United States, LightBox is hard at work filling in the gaps, including for tribal lands and US Territories.
About LightBox:
LightBox is the world’s leading real estate information and technology platform. Through operational excellence and a passion for innovation, LightBox facilitates transparency, efficiency, insight, and prediction for real estate investment and location analytics. LightBox customers include commercial and government agencies requiring definitive real estate data and powerful workflow solutions, including brokers, developers, investors, lenders, insurers, technology providers, environmental consultants, and valuation professionals. LightBox is backed by Silver Lake and Battery Ventures.
For more information about LightBox services, contact Caroline Stoll at [email protected]
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/lightbox-beats-fcc-to-punch-fresh-broadband-map
Huawei CTO Says No to Open RAN and Virtualized RAN
Paul Scanlan, CTO of Huawei Carrier Business Group made clear what everyone already knew- that the Chinese tech giant doesn’t support Open RAN or Virtualized RAN (vRAN). On a media call today, Scanlan noted that Open RAN has a lot of problems: It isn’t standardized, it can’t be easily integrated with existing network infrastructure, and it’s not ready for the most intense period of 5G deployments coming up with 5G SA core networks.
“It’s not that it’s not going to happen, and I believe it will in different guises but I’m not sure whether … from a commercial perspective, is it too late practically? The challenge is it’s not standardized. It’s an association. Because things are not standardized, no standards, you don’t get cooperation, you don’t get competition, you don’t get innovation to drive this,” Scanlan said, describing groups such as the O-RAN Alliance as “just a bunch of friends.”
Absent standardization, technologies like open RAN become fragmented and lack interoperability — two outcomes that most network operators are unwilling to accept, according to Scanlan.
The IEEE Techblog has noted from day one that neither the O-RAN Alliance or TIP Open RAN project are standards development organizations (SDOs). Worse, is they don’t even have liaisons with ITU-R, ETSI, or 3GPP which are (although 3GPP specs must be transposed by SDOs like ETSI or submitted to ITU-R WP 5D to become binding standards).
In June, Scanlan told Asia Times that Huawei has already built enterprise networks for 2,000 manufacturing companies and plans to build 16,000 next year. The Chinese tech giant has also built 5,300 private networks for mining companies, Scanlan stated. Today, he said that the real cost for network operators is opex, rather than capex.
“The telecom operator’s problem is not capex, it’s actually opex,” he said, adding that opex eats up about 65% of the average cost per site for site rental, backhaul, and energy. RAN comprises about 12% of opex costs per site on average, he said. The implication is that Open RAN opex will be higher than that of conventional RANs with purpose built network equipment from legacy base station vendors.
Another challenge for open RAN involves security and point of responsibility. That’s because of many more exposed interfaces between different vendor equipment. In a typical open RAN deployment “you’ve got three or four vendors all providing components (modules) that are going to be patched together. Scanlan asked, “Who’s responsible for making sure that it’s going to be secure or it’s going to deliver” on performance and fall in line with guaranteed operating costs?”
“Everybody says from a cybersecurity perspective it’ll be more secure. Well, I don’t agree with that. I mean, who’s going to be responsible?”
Critics of O-RAN argue that the much-touted alternative to Huawei will be costly, cumbersome and ineffective. Henry Kressel wrote in Asia Times on December 29, 2020:
O-RAN proposes to open up only part of the proprietary wireless network, namely the part that goes from the antenna to the delivery of transportable data packets to the extended interconnection network that routs the packets to their ultimate destination. These functions are currently performed using equipment and software proprietary to each equipment vendor.
This is a big ,multiyear project that requires the collaborative efforts of industry and governments. These technologies are complex and require extremely high levels of reliability – hence, extensive and costly testing.
The O-RAN Coalition has recommended that US federal sources put $1 billion into the project. But even if government money is forthcoming, it will be only the beginning of a costly development project. One estimate from a reliable industry expert states that at least five years might be needed before competitive products meeting the new standards could reach the market.
“So many people just throw out (?) virtualization or throw out (?) vRAN, or open RAN, and all the rest for different types of reasons,” he said. “If you’ve not been either developing the technology or you’re not at the operator’s point to understand the challenges and the pain points of each of them, then often a lot of the reasons why we want to do something is perhaps for political reasons [1.] and just haven’t been very well thought out.”
Note 1. Many believe the motivation and impetus for Open RAN is to permit new base station vendors, particularly skilled in virtualization software, to enter the 4G/5G market. Two particular politically inspired vendor targets are Huawei and ZTE who are not permitted to join either O-RAN or TIP projects.
Of course there are also performance issues with the commoditized chips that will be used for Open RAN. Several years ago, Huawei explored the use of commoditized silicon in its 5G network equipment, but “the problem was that the jitter at the substrate level was too high. It would not achieve the targets that we wanted in terms of latency, so we had to develop the chip ourselves,” Scanlan said.
“For virtualized RAN, what do you want to do with virtualization, what’s the target objective? When we put things in a cloud the first thing we’re really trying to do is create flexibility and resource scaling. And because it’s software driven, we’re able to change those things and downstream everything can operate from it,” Scanlon explained.
“Within the next two or three years, there are no commercial opportunities for open RAN because of technological maturity,” Victor Zhang, Huawei’s vice president, told Light Reading when asked what Huawei was doing to support the concept. “There is still a long way to go with open RAN.”
One problem is that the general-purpose processors used in open RAN baseband equipment are less power-efficient than customized gear. Huawei summed this up in 2019. “There is a specific R&D team doing research on using white boxes with Intel CPUs [central processing units] in 4G basestations and the power consumption is ten times more,” said Peter Zhou, the chief marketing officer of Huawei’s wireless products line, at a London event. “5G is [even] more complicated and an Intel CPU gives you a problem with jitter. In terms of existing CPU technology, we haven’t seen the possibility of using that with 5G basestations.”
John Strand, the CEO of Strand Consult, thinks it inconceivable that Huawei is not privy to the O-RAN Alliance’s activities. Smaller Chinese vendors could even be representing Huawei, he has suggested. It seems highly likely that links between China Mobile and Huawei are much stronger than connections between a European operator and its main supplier.
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/huawei-cto-disses-virtualized-open-ran/2021/09/
Dell’Oro Group increases Open RAN radio and baseband revenue forecast
Nokia & Vodafone Turkey new milestone in optical transmission speed; Nokia -UScellular 5G SA/Core Network agreement
Nokia claims a new speed record with Vodafone Turkey with a regional demonstration of a 1 Tbps per channel coherent transmission over a live optical network. The companies proved a capacity increase of 150 percent over a single channel coherent transmission, and the ability to scale network capacity up to 70 Tbps per fiber. This capacity milestone is part of an ongoing modernization effort with Nokia to future-proof Vodafone Turkey’s optical network architecture.
This optical transmission test builds upon an earlier trial conducted by Nokia and Vodafone Turkey that validated a 1Tbps clear channel IP router interface, further preparing the operator’s network for the future.
The optical network speed test showcased 1 Tbps capacity over 130 GHz bandwidth without any errors on Vodafone Turkey’s live optical network between its data centers. The trial was conducted over the operator’s in-service optical network, based on Nokia’s wavelength routing technology, which includes its non-blocking CDC-F ROADM optical switch architecture. Supporting operation over C+L bands, Nokia’s optical line system also enables a doubling of the total fibre capacity of Vodafone Turkey’s network.
Nokia’s photonic service engine (PSE) technology, providing maximum performance and spectral efficiency. The Nokia PSE coherent optics are deployed in Vodafone Turkey’s network using the 1830 PSI-M (Photonic Service Interconnect-Modular) compact modular optical networking platform, optimized for data center interconnect applications over metro, regional and long-haul distances.
Thibaud Rerolle, CTO at Vodafone Turkey, said: “At Vodafone Turkey, we are committed to using next generation technology to provide the most convenient services to our customers – uninterrupted and reliably. Our fiber optic backbone is an important step on the way to 5G and, with Nokia, we continue to equip our optical network with the latest technologies and innovations for our services today and in the future.”
James Watt, Head of Optical Networks Division, Nokia, said: “Our field-proven optical technologies and solutions are enabling service providers like Vodafone Turkey to meet growing capacity demand and provide the best end-user experience. We are pleased to complement our deployment of advanced optical transport solutions with the successful and timely completion of this crucial trial to modernize Vodafone Turkey’s optical network. Together, we are accelerating their digital transformation with solutions that can be easily scaled to meet 5G demands.”
References:
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, Nokia today announced that it has been selected to roll out UScellular’s standalone 5G core network with deployment expected to be completed by the end of 2022.
- UScellular will deploy Nokia’s portfolio of hardware, software and services to enable its 5G standalone (SA) core network
- UScellular’s 5G SA network will provide its 5 million customers with superior service, capacity, and reliability
By implementing Nokia’s 5G SA core, UScellular will be able to unlock the full potential of 5G for its customers, delivering the high speeds and low latencies that will power new applications such as virtual and augmented reality. UScellular will also be able to leverage Nokia’s cloud-native, open modular structure to rapidly introduce and scale future network functions for new revenue opportunities.
UScellular’s deployment of Nokia’s 5G core adds to its existing support for the Radio Access Network (RAN) where Nokia is supplying its AirScale radios for both low-band and mmWave 5G.
Mike Irizarry, Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer, UScellular:
“As we continue to expand and enhance our 5G network, we value the innovation and support that Nokia provides to help us deliver a superior wireless experience to our residential and business customers. As we deploy 5G SA core, Nokia brings expertise, technology excellence and the right mix of hardware, software and services to meet our requirements for high performance and low latency.”
Ed Cholerton, President of Nokia North America:
“We are thrilled to be selected by UScellular to deliver a full 5G experience to its customers. Our 5G SA core and 5G radios provide not only new capabilities, scale, operational efficiencies, and revenue opportunities, but drive a far better user experience that customers expect. Working with UScellular to provide the core network function software and cloud infrastructure continues our momentum in the North American standalone 5G core market.”
Nokia’s 5G SA core is a cloud-native architecture with network functions deployed as microservices that can be moved to the network edge to meet low latency requirements for software-driven services, like network slicing. Globally, Nokia has already deployed over 250+ cloud core networks and 70+ 5G standalone core networks.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Nokia said its 5G SA core is currently deployed in more than 70 networks globally, but very few of those are commercially available.
Nokia also sold its 5G SA core to T-Mobile US, the first operator to deploy a 5G SA core. It remains the only U.S. operator with a commercially available standalone 5G network.
5G SA cores remain incredibly scarce. Most of the 141 live 5G networks at the end of April 2021 were still operating in non-standalone mode (5G NSA), Stéphane Téral, chief analyst at LightCounting, noted during a panel discussion at MWC Barcelona 2021. As of the end of July, there were only nine standalone networks globally, he said. The latest was KT Corp.’s 5G SA core deployment using Samsung’s technology.
A 5G SA core introduces many unique 5G features, including higher data throughput and performance, lower latency, network slicing. It separates the data and control planes which is required for mobile edge computing and many industrial applications.
References:



