Netherlands again delays 5G spectrum auction
The 5G spectrum auction in the Netherlands has been delayed again, much to the local telecom companies’ frustration. “An auction this year is no longer a possibility,” a spokesperson for the National Digital Infrastructure Service (RDI) confirmed to NU.nl. “A new date for the auction has yet to be announced.”
KPN, Vodaphone, and Odido, formerly T-Mobile, are eagerly awaiting the chance to bid on frequencies so they can offer 5G mobile services. Mobile internet traffic in the Netherlands is growing by 30 to 50 percent per year, and consumers expect faster internet on their phones.
The RDI intended to release the 5G spectrum on the 3.5GHz band before the end of the year. But an adjustment to the National Frequency Plan (NFP) has thrown a spanner in the works. According to the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate, several parties have appealed against the adjustment. “The court will hear the appeal on October 11 and 12,” a spokesperson for the ministry told NU.nl. “Only then can we provide more clarity about when the auction can take place.”
The Dutch telecom companies were disappointed by this new delay. “This auction should have taken place a long time ago,” a KPN spokesperson told the newspaper. “We are several years out of step with other countries in Europe, and there is still a lot of uncertainty.”
“The 3.5GHz band is particularly important to us and an essential part of the development of our network,” a spokesperson for Vodafone said. “We hope that this will be available for national mobile communications in the short term.”
The Netherlands is at risk of losing its position as the country with the best mobile networks in the world, Odibo said. The new frequencies are desperately needed to handle the ever-increasing mobile internet traffic and enable faster mobile internet traffic. The latter is especially vital for Dutch industry, the Odido spokesperson told the newspaper. Mobile internet traffic is expected to grow by 30% to 50% per year in the country.

Telecom towers – Credit: mrfotos / DepositPhotos – License: DepositPhotos
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://nltimes.nl/2023/09/22/dutch-delay-5g-spectrum-auction
Potential delays in Netherlands’ 5G 3.5GHz frequency auction
Ericsson and Google Cloud expand partnership with Cloud RAN solution
Ericsson has announced an expansion of its successful and long-standing partnership with Google Cloud to develop an Ericsson Cloud RAN solution on Google Distributed Cloud (GDC) [1.] that offers integrated automation and orchestration and leverages AI/ML for additional communications service providers (CSP) benefits. The companies have successfully demonstrated the full implementation of the Ericsson vDU and vCU on GDC Edge and the solution is running live in the Ericsson Open Lab in Ottawa, Canada, with joint ambition for market development.
Note 1. GDC is a portfolio of fully managed hardware and software solutions which extends Google Cloud’s infrastructure and services to the edge and into your data centers.
Deploying Ericsson Cloud RAN on GDC Edge enables the delivery of a fully automated and very large-scale distributed cloud, resulting in an efficient, reliable, highly performant and secured software centric radio access network infrastructure. In this setup, the on-premises GDC Edge is managed using functions such as fleet management from the public cloud through a dedicated secure connection between on-prem hardware and the cloud, while also addressing sovereignty and privacy requirements of the CSP customers. This architecture ensures the clear path for CSPs toward the implementation of a fully hybrid cloud solution for RAN.
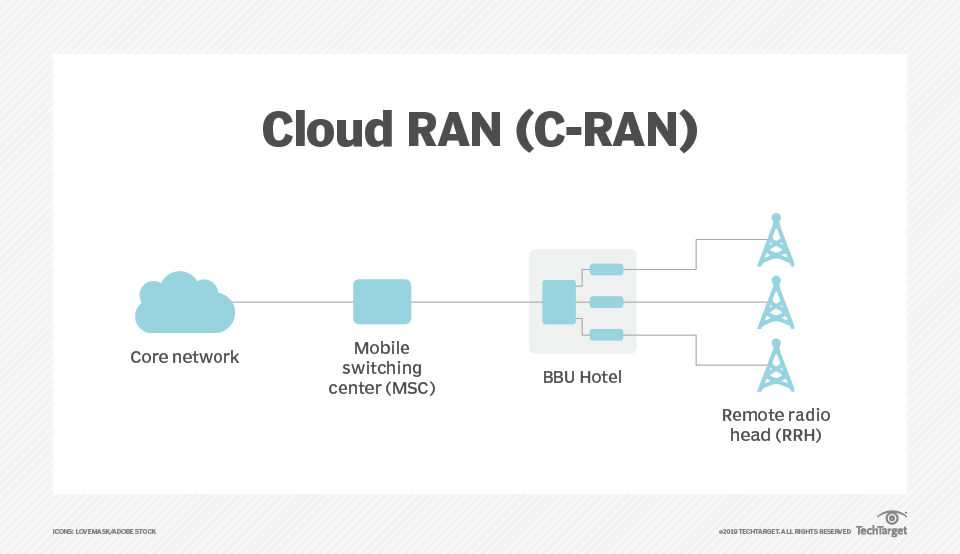
Cloud RAN comprises a mobile switching center, a BBU hotel and a remote radio head
C-RAN networks comprise three primary components:
- A BBU hotel. This is a centralized site that functions as a data or processing center. Individual units can stack together without direct linkage or interconnect to dynamically allocate resources based on network needs. Communication between units has high bandwidth and low latency.
- A remote radio unit (RRU) network. Also known as a remote radio head, an RRU is a traditional network that connects wireless devices to access points.
- A fronthaul or transport network. Also known as a mobile switching center, a fronthaul or transport network is the connection layer between a BBU and a set of RRUs that use optical fiber, cellular or mmWave communication.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Running Ericsson Cloud RAN on GDC Edge will enable CSPs to utilize Google Cloud Vertex AI, BigQuery and other cloud services, to improve the usability of the massive data sets being provided by Cloud RAN applications. This in turn, will open a number of opportunities for CSPs to control, inspect, configure, and optimize their RAN infrastructure.
Ericsson Cloud RAN provides CSPs additional choice for creating networks based on open standards and interfaces using multiple vendors. The Ericsson Cloud RAN solution is infrastructure agnostic, allowing RAN applications to be deployed on any infrastructure chosen by the CSP. Ericsson is continuously collaborating with ecosystem partners and adapting its Cloud RAN applications to work on different infrastructures and configurations.
To further a cloud-native automation approach to network workloads, Ericsson and Google Cloud are jointly enhancing the solution through the Linux Foundation open-source project Nephio (a Kubernetes-based automation platform for deploying and managing highly distributed, interconnected workloads such as 5G network functions), where we jointly drive standardization of critical functionality.
Mårten Lerner, Head of Product Line Cloud RAN, Ericsson, says: “This partnership enables us to deepen and expand our valuable collaboration with Google Cloud, and it opens new opportunities for operators to utilize the benefits of cloud-native solutions and automation. Ericsson remains committed to ensuring the adaptability of its Cloud RAN applications on diverse cloud infrastructures, offering operators enhanced flexibility and choice in deploying Cloud RAN as well as supporting the evolving hybrid cloud architectures together with Google Cloud.”
Gabriele Di Piazza, Senior Director, Telecom Products, Google Cloud, says:
“We’re proud to enable Ericsson Cloud RAN to run on Google Distributed Cloud Edge infrastructure, which includes access to our AI/ML capabilities as well as cloud-native automations. We’re delighted to recognize Ericsson as a distinguished Google Cloud Partner and look forward to a continued strong partnership in support of our mutual customers.”
https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/cloud-radio-access-network-C-RAN
Ericsson and O2 Telefónica demo Europe’s 1st Cloud RAN 5G mmWave FWA use case
Cloud RAN with Google Distributed Cloud Edge; Strategy: host network functions of other vendors on Google Cloud
Vodafone Trials Nokia’s Cloud RAN; Other 5G Research Partnerships
Nokia launches anyRAN to drive CloudRAN partnerships for mobile network operators and enterprises
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
AST SpaceMobile: “5G” Connectivity from Space to Everyday Smartphones
AST SpaceMobil announced its latest satellite-based connectivity milestone, making “5G” voice and data connections between a standard smartphone and a satellite. We say “5G” because there are no 5G satellite standards – only ITU-R M.2150 for terrestrial 5G. 3GPP Rel 17-20 will specify 5G SatCom.
Using the BlueWalker 3 test satellite and its 693-square-foot array — the largest such commercial telecommunications array in low Earth orbit — engineers at AST SpaceMobile made history on September 8, 2023, by demonstrating the first-ever 5G cellular connectivity from space directly to everyday smartphones. The company proved the feat using AT&T cellular spectrum in Maui, Hawaii, to make a voice call to Vodafone in Madrid, Spain. The call was facilitated by Nokia’s network core. The company also recently achieved other firsts in space-based cellular broadband, an industry it pioneered: voice calls, 4G data downloads of more than 14 Mbps, and 4G video calls.

AST SpaceMobile has included a YouTube link of its own in its latest announcement.
The two new milestones come in the wake of AST SpaceMobile’s announcement in April that it had completed the first ever space-based voice calls using normal smartphones.
It has, of course, come under scrutiny for that claim. In July Lynk, which is building an LEO constellation to create what it terms ‘cell towers in space,’ also claimed to have completed the world’s first voice calls over its network. Lynk seemed to hang much of its claim on the fact that it had a video as proof, although opinions vary on how conclusive such a video could be.
“Once again, we have achieved a significant technological advancement that represents a paradigm shift in access to information. Since the launch of BlueWalker 3, we have achieved full compatibility with phones made by all major manufacturers and support for 2G, 4G LTE, and now 5G,” said AST SpaceMobile CEO Abel Avellan. It’s worth noting that BlueWalker 3 is a test satellite; AST Space Mobile plans to launch its first five commercial satellites in the first quarter of next year.
“Making the first successful 5G cellular broadband connections from space directly to mobile phones is yet another significant advancement in telecommunications AST SpaceMobile has pioneered,” Avellan declared. Vodafone, AT&T and Nokia also contributed – slightly less self-congratulatory – statements about their own roles in proceedings and the potential of the technology to connect the unconnected.
It’s hard to argue with that last point, which is part of the reason why satellite-based connectivity is having something of an extended moment in the spotlight, with AST SpaceMobile, Lynk, Sateliot and others talking up their various achievements.
AST SpaceMobile describes itself as “the company building the first and only space-based cellular broadband network accessible directly by standard mobile phones.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
First-Ever 5G Connectivity from Space to Everyday Smartphones Achieved by AST SpaceMobile
Juniper Research: 5G Satellite Networks are a $17B Operator Opportunity
AST SpaceMobile achieves 4G LTE download speeds >10 Mbps during test in Hawaii
AST SpaceMobile completes 1st ever LEO satellite voice call using AT&T spectrum and unmodified Samsung and Apple smartphones
FCC proposes regulatory framework for space-mobile network operator collaboration
AST SpaceMobile Deploys Largest-Ever LEO Satellite Communications Array
KDDI Partners With SpaceX to Bring Satellite-to-Cellular Service to Japan
China’s answer to Starlink: GalaxySpace planning to launch 1,000 LEO satellites & deliver 5G from space?
Betacom and UScellular Introduce 1st Private/Public Hybrid 5G Network
Private wireless network provider Betacom today announced a partnership with UScellular to deliver the industry’s first private/public hybrid 5G networks, advancing Industry 4.0 initiatives across the United States. The service provides security and control over business data, both on-premises and while roaming among company facilities. This seems to be similar to the “hybrid cloud” concept where a public cloud is used for general computing while a private cloud is used for mission critical applications and secure storage.
The private/public hybrid 5G network service allows organizations with multiple sites across numerous locations to maintain connectivity between locations. Enterprises working to modernize their operations across dispersed locations now have a cohesive mobility strategy with trusted partners for Industry 4.0. Uptime and performance are assured for improved operational efficiency and productivity with Betacom-backed Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
“This relationship with Betacom helps to establish a new bar for how the entire wireless industry thinks about, builds, delivers and utilizes wireless networks,” said Kim Kerr, senior vice president, enterprise sales and operations for UScellular. “These new capabilities significantly accelerate the return on investment for digital transformation and modernization initiatives for organizations of all types, from enterprise to retail to government, and move the industry as a whole forward, faster.”
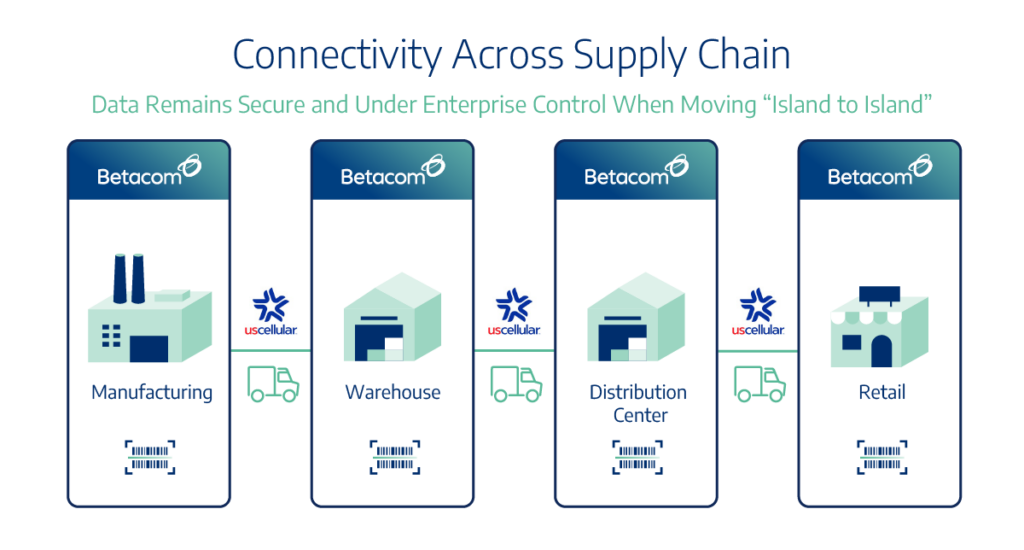
Nationwide Mobility:
UScellular’s network and extensive access agreements give customers connectivity across the United States. UScellular also provides data backhaul between sites. Enabling devices to use a single SIM with profiles for both Betacom private CBRS networks and the UScellular network ensures mobility, while integrated communication and coordination between the two companies’ 5G network cores enables seamless roaming across the country.
“Betacom and UScellular are breaking new ground for their customers and setting new precedents for the industry,” said Joe Madden, Founder and President, Mobile Experts Inc. “Enabling device mobility from facility to facility with a transition from CBRS to cellular in both directions has never been solved. This makes private/public hybrid 5G networks extremely valuable for a wide range of industries.”
Michael Davies, VP of business partner strategy and 5G-as-a-service at Betacom, explained in an interview that Betacom’s authentication system is the “secret sauce” to securing this seamlessness within an “island” environment. “We have joined together to provide a single SIM that is authenticated within the static network and then is accepted, secured and maintained throughout the mobile network into the next static environment of the island,” Davies said.
David Allen, director of emerging technologies at UScellular, added that this approach also is key to how the operator segments the private network service. “We treat that private cellular network as a peer of ours, and so when we see that SIM in the public cellular domain, whether it’s on our native network or it’s on one of our roaming partners network, we will authenticate against that private [home subscriber server], that private cellular network, get the corresponding authentication, accept or deny and then that device can proceed with the policy controls that that private network has put in place for it,” Allen said.
“You may see other people claim hybridization. We’ve been early in that messaging of hybridization of networks, the public-private hybrid networks. Others have started saying that as well, but it’s really when you peel back the layers it’s typically a two-SIM solution. That’s for the most part, historically, the way that solution’s gone. We’re working together to drive toward that single-SIM solution so that we’re authenticating a private SIM and a private device that happens to be in the public network against that private network.”
Improved Security and Control:
The solution establishes and maintains end-to-end security, utilizing virtual private networks (VPNs) to ensure that all data effectively remains on the customer premises while devices and sensors are in transit between locations. It also provides unmatched resiliency by using the cellular network for failover in cases where the CBRS network or local internet service providers (ISPs) suffer an outage. The new network architecture utilized for this service facilitates mission-critical Command, Control, Communication, Computers, and Intelligence (C4I) services and solutions which require the highest degrees of data and device security. Reducing dependency on public clouds for data transfer by creating a private network through the carrier network results in fewer vulnerabilities and fewer attacks.
“The service we are announcing today recognizes that the wireless world is changing, and that connectivity, in all of its forms, must change with it,” said Betacom CEO Johan Bjorklund. “Organizations today need seamless mobility with incredibly high densities of sensors and devices to accelerate their Industry 4.0 initiatives. This new service acknowledges and uniquely meets that need.”
About Betacom:
Betacom offers the first fully-managed private 5G network, building on its long history as a wireless infrastructure provider to AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon. Founded in 1991 and headquartered in Bellevue, Washington, the company has regional offices throughout the country. Having completed more than 800 large-scale design and deployment projects, Betacom inspires confidence among their customers who have worked closely with them to meet their pressing high-performance connectivity needs. Its secure private 5G wireless service is the first managed service of its kind in the United States.
Betacom earlier this year expanded the ecosystem around its platform with more than a dozen partners. This included mobile edge compute work with Google Cloud, Ingram Micro and Intel; application work with ADB SAFEGATE Americas, Evolon, Ingram Micro and Solis Energy; industrial IoT devices from Axis Communications, Ingram Micro, Qualcomm Technologies, SVT Robotics and Vecna Robotics; 5G work with Airspan, Druid Software, FibroLAN and Qualcomm; and system integration work with CDW, Ingram Micro and QuayChain.
The vendor at that time said the expanded ecosystem alleviates ongoing concerns by enterprise IT departments that they will need to manage a disparate combination of equipment, services and connectivity to deploy a private network. This should be beneficial to those enterprise IT staffs that have so far eschewed potential network complexity by going with a private network platform.
For more information, visit https://www.betacom.com.
References:
UScellular’s Home Internet/FWA now has >100K customers
UScellular Launches 5G Mid-Band Network in parts of 10 states
US Cellular touts 5G millimeter wave and cell tower agreement with Dish Network
Ooredoo Qatar is first operator in the world to deploy 50G PON
Ooredoo Qatar announced that it has become the first operator in the world to deploy 50G PON (Passive Optical Network) connectivity, the 50 Gbps-capable fiber-based access connection for consumers. According to Ooredoo, the 50G PON technology, which has been adopted as an ITU standard, delivers fiber-based access connections with speeds of up to 50 Gbps on a single connection.
The 50G-PON system capitalizes on fundamental advances in the optical transceiver components working in conjunction with enhanced error correction and coding. It also introduces key innovations in activation procedures, contention-based operation, and expanded cryptographic features. With these improved capabilities, the 50G-PON system is ready to meet the new, and demanding, requirements of emerging services.
This new technology enables consumers to use high-bandwidth latency-sensitive applications such as 8k-interactive video applications, online collaboration and coordination solutions, 3D cloud design, high-graphic/high-quality AI applications, etc.
Dell’Oro Group believes total 50G-PON equipment revenue will increase from less than $3M in 2023 to $1.5B in 2027. Much more significant growth is expected after 2027, as operators begin to evolve their 10Gbps PON networks to next-generation technologies.

Sheikh Ali Bin Jabor Al Thani, Chief Executive Officer, Ooredoo Qatar, said: “We’re proud to be the first operator globally capable of deploying such powerful technology, which aligns perfectly with our overarching aim of upgrading our customers’ worlds. We have long had a strategic commitment to partnering with global leaders in technology and innovation, enabling us to leverage both our expertise and experience and our partners’ capabilities. This latest launch is an excellent example of the benefits we, and our customers, enjoy as a result of such partnerships. We look forward to further enhancing our offering as technology develops ever further in the years to come.”
Ooredoo’s 50G PON technology can meet the bandwidth requirements of both consumers and enterprises. Initial deployment will be for B2B customers and areas that require high-speed connectivity, with roll-out to consumers – for 8k content and AR/VR gaming, as an example – to follow.
ITU-T standards for 50G PON:
In April 2021, the ITU-T reached a major mile-stone, consenting the first three Recommendations defining a 50G PON system:
- General Requirements (G.9804.1): The legacy features linked to deployed fiber infra-structure are complemented by support for new services requiring high capacity, efficiency, low latency, and security. Coexistence with, and migration from, the installed PON systems are essential.
- Common Transmission Convergence Layer (ComTC) specification (G.9804.2): This is defined in a line rate agnostic way and thus applicable to future single-wavelength time-division multiplexing (TDM) and multi-wavelength time-and-wavelength-divi-sion multiplexing (TWDM) PON systems.
- The single-wavelength 50G-PON PMD (G.9804.3) specification is the first in the HS-PON PMD family.
References:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9743347
Juniper Research: 5G Satellite Networks are a $17B Operator Opportunity
New research from Juniper Research forecasts that network operators will generate $17 billion of additional revenue from 3GPP‑compliant 5G satellite networks between 2024 and 2030.
Editor’s Note: There is no serious work in ITU-R on 5G satellite networks as we’ve previously detailed. The real SatCom air interface specifications work is being done by 3GPP, under the umbrella term of NTN (Non-terrestrial Networks), in Release 17 and the forthcoming Release 18.
ITU-R WP5D is responsible for terrestrial IMT radio interfaces (IMT-2000, IMT-Advanced and IMT-2020/M.2150 as well as IMT for 2030 and Beyond), so it won’t be involved in standardizing radio interfaces satellite networks.
ITU-R Working Party 4B (WP 4B) is responsible for recommendations related to: Systems, air interfaces, performance and availability objectives for FSS, BSS and MSS, including IP-based applications and satellite news gathering.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The market research firm urges network operators to sign partnerships with SNOs (Satellite Network Operators) which will enable operators to launch monetizable satellite-based 5G services to their subscribers. SNOs possess capabilities to launch next-generation satellite hardware into space, as well as being responsible for the operation and management of the resulting networks.
The new report, Global 5G Satellite Networks Market 2023-2030 offers the most reliable source of data for the market.
Operators Hold the Key Billing Relationship:
Juniper Research predicts the first commercial launch of a 5G satellite network will occur in 2024, with over 110 million 3GPP‑compliant 5G satellite connections in operation by 2030. To capitalise on this growth, the research urges operators to prioritise immediate partnerships with SNOs that can launch GSO (Geostationary Orbit) satellites. These satellites follow the rotation of the earth to always be located above the country that the operator serves; providing consistent connectivity.
Additionally, operators must leverage their pre-existing billing relationship with mobile subscribers and enterprises as a platform to grow 5G satellite connectivity revenue over the next seven years. The report anticipates this existing billing relationship will enable operators to rapidly drive the adoption of satellite connectivity by integrating satellite services into existing terrestrial networks.
Key Forecasts:
- Total Operator-billed 5G Satellite Revenue 2024-2030: $17bn
- Total 3GPP-compliant 5G Satellite Connections in 2030; $110mn
- Average Revenue per 5G Satellite Connection in 2030: $7.98
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
3GPP Releases related to SatCom:
3GPP Rel-17 is enabling the launch of satellite-based communications. Unlike traditional telecommunications ecosystems, the development of this market will be defined by the entrance of a new category of players – satellite vendors. These vendors will work with network operators to deploy NTNs (Non-terrestrial Networks) that side alongside terrestrial networks.
NTNs are a joint development between network operators and satellite vendors to drive growth of telecommunications services. In the future, NTNs will integrate directly with satellite-based networks to provide connectivity with comprehensive services.
However, the development of NTN specifications is far from complete, the 3GPP roadmap includes provisions in 3GPP Releases 18 and 19 for enhancements to satellite services. 3GPP Release 20 includes the provision of satellite-based standards for future 6G networks. It is only with these standards that satellite networks can progress past traditional use cases, such as weather monitoring, global positioning services and broadcasting, which require low-to-medium throughput rates and do not need low latency.
Additionally, satellites have not been required, as the low data rates provided by previous iterations of satellite technologies, combined with the high costs of satellite connectivity, have not been able to compete with the service provided by terrestrial networks.
These will be the most immediate benefits of satellite-based services for 5G networks:
• Increased network coverage: Satellites will provide increased coverage to areas where terrestrial networks are financially unviable. This is most notable in rural areas where there is little demand for cellular connectivity; leaving operators with no return on investment into the needed backhaul infrastructure and base stations.
• Increased support of backhaul infrastructure: Given the data-intensive nature of 5G services, satellite infrastructure will be used to carry data in a similar fashion to fibre services in terrestrial networks.
• Increase network capacity and throughput: Satellites can offload data from terrestrial networks. As the number of 5G connections increases, so will the data generated. In turn, satellites can not only provide coverage in areas where there is little support for 5G services, but they can also alleviate geographical areas that require high throughput and support for a large number of connections.
• More network resilience: Satellites will provide an additional layer of network redundancy for communication services during natural disasters or network outages. When terrestrial networks are inoperable, satellites will be used for connectivity in the absence of terrestrial network.
Preparation for 6G Networks:
However, the research predicts operators will increasingly rely on SNOs for service provision as 6G development accelerates. Research author Sam Barker commented:
“Operators must not only think of 5G satellite services when choosing an SNO partner, but also the forward plan for 6G networks, including coverage and throughput capabilities.”
About the Research Suite:
This new Juniper market research suite offers the most comprehensive assessment of the 3GPP‑compliant 5G satellite network to date; providing analysis and forecasts of over 24,000 data points across 60 markets over five years.
View the 5G Satellite Networks market research: https://www.juniperresearch.com/researchstore/operators-providers/5g-satellite-networks-research-report
Download a free sample: https://www.juniperresearch.com/whitepapers/5g-satellite-networks-the-17bn-operator
References:
SatCom market services, ITU-R WP 4G, 3GPP Release 18 and ABI Research Market Forecasts
GSMA- ESA to collaborate on on new satellite and terrestrial network technologies
Samsung and VMware Collaborate to Advance 5G SA Core & Telco Cloud
Samsung and VMware are continuing their collaboration to offer a powerful and comprehensive 5G solution—combining Samsung 5G Core and VMware Telco Cloud Platform 5G [1.]. This partnership makes it easier for telecom operators using the VMware platform to deploy Samsung’s 5G components. The validation supports Samsung’s ongoing attempts to boost its 5G core market share and further enhances VMware’s telecom efforts.
Note 1. VMware’sTelco cloud is a next-generation network architecture that combines software-defined networking, network functions virtualization, and cloud native technology into a distributed computing network. Since the network and the computing resources are distributed across sites and clouds, automation and orchestration are required.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Joining Samsung’s expertise in 5G Core with the power of the VMware Telco Cloud, the combined 5G solution improves the performance and reliability of core networks. In addition, the collaboration offers increased agility and scalability for network infrastructure, enabling operators to rapidly adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands.
The companies have been involved in continuous testing, certification and validation efforts to ensure that Samsung’s 5G Core network functions are fully compatible with VMware Telco Cloud Platform 5G. After validation, Samsung received certification for its 5G Core network functions by the VMware Ready for Telco Cloud program, ensuring compatibility and reliability with VMware technology.
VMware Ready for Telco Cloud certification has been granted to Samsung’s Core network functions, including UPF, NSSF, SMF, AMF, and NRF. The Ready for Telco Cloud certification ensures that network functions are ready for deployment and lifecycle operations with VMware technology. These certified network functions will deliver improved performance, enhanced security features and increased agility and scalability for core networks.
VMware initially rolled out its overarching Telco Cloud Platform in early 2021, which itself was an expansion of its reorganized and repacked stack of technologies for network operators. It has since updated that specific platform as well as expanded its reach into other 5G markets like private 5G and mobile edge compute.
Specific to its work with Samsung, VMware began those efforts in late 2020. That move called for Samsung to integrate its network core, edge, and radio access network (RAN) offerings with VMware and for Samsung to extend its support for cloud-native architecture by adapting its suite of products for containerized network functions (CNFs) and virtual network functions (VNFs) on VMware’s software stack and network automation services.
earlier this year announced the first commercial collaboration with Samsung, which involved integrating Samsung’s virtualized RAN (vRAN) with VMware’s Telco Cloud Platform as part of Dish Network’s ongoing 5G network deployment.
That work built on Dish Network’s plan to deploy 24,000 Samsung open RAN-compliant radios and 5G vRAN software systems running on VMware’s platform that underlines Dish Network’s nascent 5G network.
The companies’ continued collaboration will accelerate the advancement of 5G Core networks and help operators to introduce innovative services that will lead to revenue growth and enhanced customer experiences.
References:
https://www.vmware.com/in/topics/glossary/content/telco-cloud.html
Another 5G Open Innovation Lab: AT&T, Comcast, Nokia, Intel, Microsoft, Dell assist 118 startups in search of 5G Killer Apps
AT&T and Comcast have become “founding partners” of the 5G Open Innovation Lab, which invests in 5G use case development. The companies essentially replaced T-Mobile, which is no longer participating in the lab it helped to launch in 2020. The Lab now also includes Dell, Nokia, Intel, Microsoft, and Deloitte. It is currently assisting 118 startups in search of “5G Killer Apps.”
“As evidenced by the 118 startups in our ecosystem, the combination of 5G and edge is unlocking a massive wave of collaborative innovation in Cloud, Edge and AI across every industry from agriculture and power generation to manufacturing, logistics and medicine,” said Jim Brisimitzis, Founder and General Partner of the 5G Open Innovation Lab in in a statement. “We are thrilled to welcome AT&T and Comcast as founding partners to help drive our vision to bring industry experts together and, collectively, drive innovation into overlapping ecosystems. 5G and edge are new foundations that can be used to drive new business models and technology across segments and companies,” he added.
Those startups could stand to benefit from the two companies. AT&T was one of the first carriers to launch a 5G network (based on 3GPP Release 15 in December 2018) and has been working on this technology for a long time.
“Collaboration is the key to innovation,” Jay Cary, VP, Strategic Alliances, Corporate Strategy at AT&T said in a statement. “As we continue forging ahead to realize 5G’s full potential, it is important to work with the nimble startup and innovation community so we can move faster and solve real-world technology challenges more holistically and effectively for our customers.”
While Comcast doesn’t have a 5G network, the company has increasingly gotten into the wireless business through a reseller agreement with Verizon. It’s also talked about small network build outs that would increase the coverage for customers in its territories.
“The cycle of innovation often begins in small companies where a new idea can challenge existing ones, and Comcast has had success taking risks and embracing these new ideas,” Tom Nagel, senior vice president of wireless strategy at Comcast, said. “Engaging with the startup community through our own Lift Labs or with organizations like the 5G Open Innovation Lab is an important factor not only in our own efforts but to push the industry forward in exciting new ways.”
On Monday, AT&T said it’s adding thousands of new customers every day to its standalone 5G network along with subscribers to Internet Air. So far, the home broadband system has launched in 16 markets and boasts 40-140 Mbps down and 5-25 Mbps up, costs about $55 a month with no data caps. Internet Air will provide DSL customers with faster internet without having to replace copper lines, which more companies are starting to shut down.
Yesterday, Comcast said in a Securities Exchange Commission filing agreed to sell some, if not all, of its 600MHz spectrum holdings to T-Mobile. The deal is valued between $1.2 and $3.3 billion, depending on how much spectrum T-Mobile acquires. Comcast has also flirted with the idea of building its own mobile network for markets inside its cable footprint.
Batch #8 welcomes 17 new startups to 5G OI Lab’s open ecosystem bringing the total number of participating companies to 118. The multi-stage startups selected for the Lab’s Fall Batch #8 hail from around the Globe and represent cutting-edge enterprise solutions in fields such as real-time logistics and tracking, robotics, private mobile network security and IoT enablement.
Since the 5G Open Innovation Lab’s program inception in 2020, participating startups and alumni have raised a lifetime total of $2.088B with several exits valued at $200+M.
The startups selected to join the 5G Open Innovation Lab’s Fall Batch #8 include:
- Airspace – At Airspace, we believe in the potential drones have to positively impact the ways in which we do business, deliver services, and respond to emergencies. In order for that to happen, drones need to be flown safely.
- ASOCS – ASOCS provides a fully virtualized Private 5G Network solution, along with 5G Positioning Services for enterprises that require mission-critical, data-driven applications. ASOCS products are delivered on a scalable Software as a Service (SaaS) model.
- Clevon – Clevon develops and manufactures autonomous robot carriers, making last-mile delivery more innovative, environmentally friendly and efficient.
- Cumucore – Cumucore is a light mobile core with Industry 4.0 specific feature set to enable affordable next-generation mobile private networks.
- Eridan – Eridan is building the world’s first digital sampling radio for 4G, 5G, and beyond.
- Expanso – Expanso, building upon their open-source project Bacalhau, offers a platform for distributed compute. They orchestrate jobs to run where the data is generated and stored, providing a fast and secure solution for large-scale data processing.
- Golioth – Golioth is uniquely positioned to enable custom IoT hardware to scale easily from one device to millions.
- HeadSpin – HeadSpin enables testing and monitoring of mobile, web, audio/video applications in real-time with AI-based insights.
- Intuitive Robotics – Intuitive Robotics leverages cutting-edge technologies, including 5G, edge computing, computer vision AI, generative AI, IoT, data analytics, and cloud computing, to deliver innovative SaaS solutions capable of addressing complex challenges across diverse industries such as agriculture, renewable energies, oil and gas, mining, and public safety.
- Kallipr – Kallipr are experts in remote monitoring IoT solutions that automate data generation at the extreme edge, allowing industries to increase operational efficiency, reduce operating costs and improve sustainability.
- Namla – Namla Cloud provides a platform that allows companies of any size to automatically deploy & manage thousands of edges in the best-optimized way.
- Nubix – Nubix is an edge native application platform that makes it easy to build, deploy and manage IoT and edge applications.
- OneLayer – OneLayer provides zero trust security and full asset management capabilities to IoT and other devices connected to a private cellular network.
- Orion Labs – Orion provides edge-optimized voice collaboration for frontline workers with encrypted, secure Push-to-Talk (PTT), location and media, and Voice AI Commands, Queries and Workflows for process automation.
- Pratexo – Pratexo brings the benefits of hybrid and distributed cloud computing to the edge of power systems that drive the energy transition.
- Real Life Robotics – Real Life Robotics is changing the way companies manage their labor. With our customizable cargo robotics platform, BUBs, we help clients fill the labor gap and focus their people on more value-added tasks.
- Reelables – Reelables smart labels automate data collection with real-time visibility into supply chain operations and performance.
About 5G Open Innovation Lab
The 5G Open Innovation Lab is a global innovation ecosystem that brings together multi-stage startups, enterprise and global technology platforms and investors to connect and collaborate on developing disruptive new enterprise technologies and solutions that capitalize on the power of edge computing connected to public and private 5G networks.
In just 4 years, the Lab has attracted a roster of world-class corporate and industry partners as well as 118 multi-stage enterprise startups who have collectively raised $2.088B of venture capital. Through 5G OI Lab’s unique model of open collaborative innovation, corporate partners work directly with ecosystem startups to accelerate commercialization through proof of concept, go-to-market, and other engagements and opportunities.
References:
T-Mobile and Charter propose 5G spectrum sharing in 42GHz band
This June, we noted that the FCC was exploring shared use of the 42 GHz band using in 500 megahertz of spectrum. Recently, T-Mobile and Charter voiced support for some kind of spectrum sharing scenario.
“While wireless carriers continue to require additional spectrum that is licensed on an exclusive-use basis, T-Mobile agrees that the technical characteristics of the 42GHz band, along with its separation from other millimeter wave spectrum that has already been licensed, means that the commission may wish to consider a different approach here,” T-Mobile wrote in an August 30th FCC filing.
“The commission, however, should avoid applying untested, novel sharing approaches to the 42GHz band. Instead, it should implement the nationwide non-exclusive licensing framework currently used in the 70/80/90GHz bands, with a few modifications to ensure that the spectrum will be used efficiently and may be deployed for [a] variety of advanced communications services.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Charter has long eyed the 37GHz band as a way to bolster mobile operations in its planned 3.5GHz CBRS network. The MSO/cableco has said it could offer speeds up to 1 Gbit/s via concurrent operations in the CBRS and 37GHz bands.
Charter’s FCC filing is similar to T-Mobile’s, as it supports a “unified nationwide, non-exclusive simple shared licensing regime.” The company urged the FCC to implement the same spectrum sharing design across both the lower 37GHz band and the 42GHz band.
“Allocating the lower 37GHz band for non-exclusive use would offer 600 megahertz for innovative new wireless connectivity in the United States,” Charter noted. “The allocation of the 42GHz band alongside the lower 37GHz band would of course increase the total spectrum available for innovative new deployments by 500 megahertz.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Backgrounder:
The 42GHz band resides in what is known as millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum. 5G transmissions in those bands are at very high speeds, but they typically travel just a few thousand feet, and generally cannot pass through obstructions like walls, trees, glass or concrete, i.e. they require line of sight communications.
WRC 19 identified mmWave frequencies for 5G, but ITU-R WP 5D did not complete and agree on the frequency arrangements for same (revision 6 of ITU-R M.1036) until very recently. WRC 19 identified the frequency bands: 24.25-27.5 GHz, 37-43.5 GHz, 45.5-47 GHz, 47.2-48.2 and 66-71 GHz for the deployment of 5G networks and the frequency arrangements for them is in draft recommendation ITU-R M.1036 which is expected to be approved this November. Note that 42GHz is not included!
Some analysts are quite positive on mmWave communications. For example, “mmWave 5G offers a way to improve on the current situation because the bands have extremely high capacity that are able to support very large amounts of data traffic and users, although in a small area,” wrote OpenSignal analyst Ian Fogg in a post on the network-monitoring firm’s website.
Qualcomm is also an advocate of spectrum sharing in mmWave bands since at least July 2022.
Image Credit: Qualcomm
Qualcomm’s filings to open the Lower 37 GHz band to shared licensed access ask the FCC to adopt a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) to allocate six 100-MHz-wide priority licenses in the Lower 37 GHz band and allow each priority operator—which may be a federal government or a commercial operator—to use the rest of the band on a secondary basis. To enable these secondary operations on an interference-free basis, each priority operator would implement a technology-neutral, equipment-based rule to provide coordinated, periodic listening of the channel, referred to as long term sensing (LTS), to determine whether its secondary operations on spectrum outside its priority licensed spectrum may cause harmful interference to the priority license holder of that swath of spectrum.
Secondary operations are only allowed for communications links that sensing determines will not cause interference to the priority licensee. The coordinated sensing procedure allows each priority license holder to access all other channels (i.e., the other 500 MHz) on a secondary – and interference-free – basis, increasing overall spectrum utilization while not degrading the QoS for the priority licensee.
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/ecfs/document/10830309419380/1
https://www.fcc.gov/ecfs/document/10830021467677/1
WRC 19 Wrap-up: Additional spectrum allocations agreed for IMT-2020 (5G mobile)
MediaTek will use TSMC to make its Dimensity SoC’s in 2024
Taiwan’s MediaTek, one of the few 5G merchant semiconductor vendors, has successfully developed its first chip using TSMC’s leading-edge 3nm technology, taping out MediaTek’s flagship Dimensity system-on-chip (SoC) with volume production expected in 2024. MediaTek joins Apple as an early adopter of TSMC’s 3-nanometer tech, a rare joint statement by a chip developer and chip manufacturer.
This marks a significant milestone in the long-standing strategic partnership between MediaTek and TSMC, with both companies taking full advantage of their strengths in chip design and manufacturing to jointly create flagship SoCs with high performance and low power features, empowering global end devices.
“We are committed to our vision of using the world’s most advanced technology to create cutting edge products that improve our lives in meaningful ways,” said Joe Chen, President of MediaTek. “TSMC’s consistent and high-quality manufacturing capabilities enable MediaTek to fully demonstrate its superior design in flagship chipsets, offering the highest performance and quality solutions to our global customers and enhancing the user experience in the flagship market.”
“This collaboration between MediaTek and TSMC on MediaTek’s Dimensity SoC means the power of industry’s most advanced semiconductor process technology can be as accessible as the smartphone in your pocket,” said Dr. Cliff Hou, Senior Vice President of Europe and Asia Sales at TSMC. “Throughout the years, we have worked closely with MediaTek to bring numerous significant innovations to the market and are honored to continue our partnership into the 3nm generation and beyond.”

Image Credit: AP
TSMC’s 3nm process technology provides enhanced performance, power, and yield, in addition to complete platform support for both high performance computing and mobile applications. Compared with TSMC’s N5 process, TSMC’s 3nm technology currently offers as much as 18% speed improvement at same power, or 32% power reduction at same speed, and approximately 60% increase in logic density.
MediaTek’s Dimensity SoCs, built with industry-leading process technology, are designed to meet the ever-increasing user experience requirements for mobile computing, high-speed connectivity, artificial intelligence, and multimedia. MediaTek’s first flagship chipset using TSMC’s 3nm process is expected to empower smartphones, tablets, intelligent cars and various other devices starting in the second half of 2024.
References: