Ookla: Fixed Broadband Speeds Increasing Faster than Mobile: 28.4% vs 16.8%
A new report from Ookla shows that fixed broadband speeds are gaining faster than mobile speeds globally. Speedtest Global Index™, tracks countries’ internet speeds and the overall global median internet speeds which are increasing across the world as countries continue to invest in fiber and 5G. Fixed broadband download speeds increased by 28% over the past year. That’s compared to a nearly 17% increase for mobile speeds, according to Speedtest Global Index™ data from November 2021 to November 2022.
Here are selected charts from their report:





Ookla is excited to see how global speeds and rankings change over the next year as individual countries and their providers choose to invest and expand different technologies, particularly in 5G and fiber. Be sure to track your country’s and check in on our monthly updates on the Speedtest Global Index. If you want more in-depth analyses and updates, subscribe to Ookla Insights™.
References:
https://www.ookla.com/articles/global-index-internet-speed-growth-2022
Ookla: State of 5G Worldwide in 2022 & Countries Where 5G is Not Available
Performance analysis of big 3 U.S. mobile operators; 5G is disappointing customers
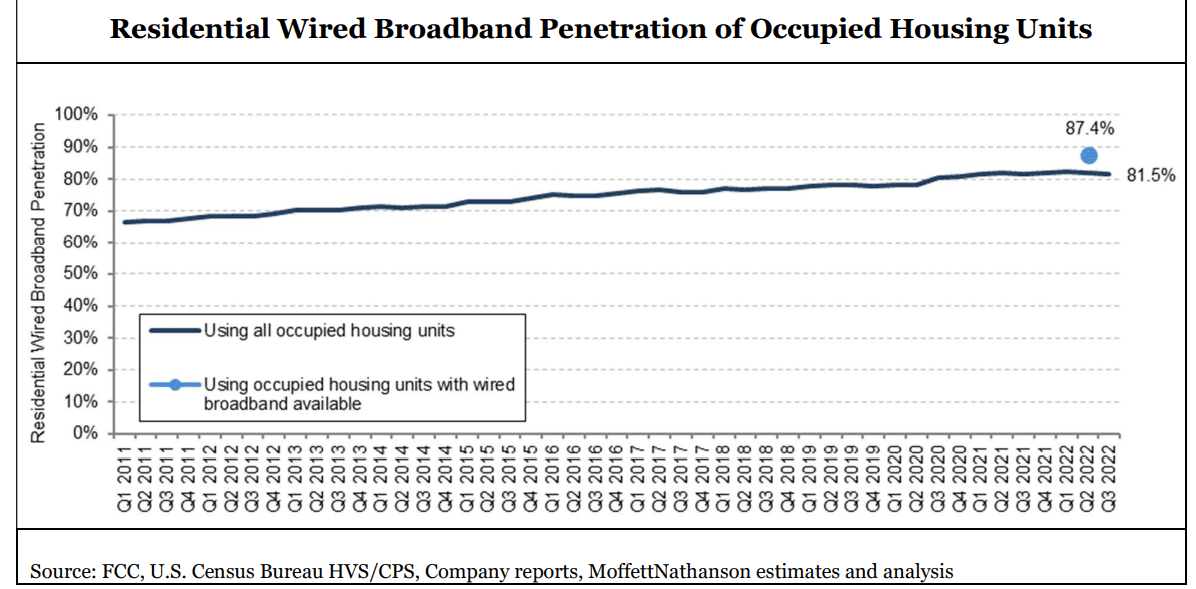
MoffettNathanson: 87.4% of available U.S. homes have broadband; Leichtman Research: 90% of U.S. homes have internet
When the FCC announced the November 18th release date for their long-awaited broadband mapping update, reflecting location-specific broadband availability as of June 2022, analysts at MoffettNathanson thought it would contain information on how many of U.S. homes have access to broadband and how many are too rural and are therefore unserved. However, that FCC release didn’t offer the numbers they needed, and the market research fim didn’t
have the necessary information to calculate it themselves.
In the underlying FCC datasets, which are provided for public download, each location served by a given technology or provider is a separate entry. One location is equivalent to one street address. But many street addresses in the U.S. correspond to multiple living units, and the number of units per location is not publicly available (the location fabric used by the FCC was contracted to a third party, CostQuest Associates, and that fabric is provided only to the FCC, broadband providers, state/local government entities, and select other interested parties). With approximately 31% of residences in multifamily homes, according to a 2019 survey by the Census Bureau, the number of units per location was, as of the November 18th release, a crucial missing piece for any meaningful coverage analysis we could do on our own.
Principal Analyst Craig Moffett wrote:
The FCC’s new maps of broadband availability can tell us coverage for residential locations or business locations, but not the combined total. The companies we cover sometimes break out residential and commercial, but not always. [As an aside, about half of small businesses in the U.S. are actually operated out of peoples’ homes, but hopefully this, at least, doesn’t introduce further distortion, since we are presumably still seeing just one subscription for one location]. So we’ll do our best to make sure we’re matching numerator and denominator by specifying whether we’re looking at all locations or residential locations only.
The FCC’s coverage data also doesn’t distinguish between occupied and vacant units. For our calculation of penetration, we’d want to exclude most vacant units, since vacant units don’t need broadband. Excluding all vacant units likely understates the denominator, though; for example, some second homes (which are treated as vacant) may have year-round broadband subscriptions. The best we can do is assume the coverage of total units is the same as the coverage of occupied units, and that vacant units with broadband subscriptions are negligible.
The FCC does report service coverage for satellite and fixed wireless. But some of those FWA subscribers are in areas where there’s no access to wired broadband, while others are in areas where wired broadband is available. Naturally, the companies won’t tell us how many of each there are. So we’ll just have to leave them all out. We’ll focus just on the availability of wired broadband.
Editor’s Note: The FCC broadband map for my address show a Licensed Fixed Wireless operator serves my condo. It’s California Internet with symmetrical 1G upstream/1G downstream. Also, there are two Satellite providers – Hughes Network Systems, LLC 25M/3M and Space X 350M/40M. Wired internet is available from AT&T and Comcast.
We’d really want to know how many DSL subscribers are in each of those different cohorts. But the
companies we cover don’t report how many of their DSL subscribers are in areas where there is
also a cable or fiber operator, and how many are in areas where DSL is the only option. The first
group is at risk. The second group is not. So, we’ll just have to include all DSL.
According to the FCC’s current estimates, wired broadband (defined as anything over 200 kbps downstream and 200 kbps upstream) was available to 93.7% of residential units in America as of June 30, 2022. Again, we don’t know the percentage of occupied housing units with wired broadband available, but let’s assume it’s the same. And we don’t know the number of residential units in the location fabric, so we’ll use the Census Bureau’s estimate of 128.1M occupied housing units in the U.S. Given these assumptions, we estimate wired broadband was available to around 120.0M occupied housing units as of June 30, 2022. With, by our count, an estimated 104.9M residential wired broadband subscriptions in America in Q2 2022 – again, including DSL, and sometimes including commercial as well as residential subscribers – that translates into penetration of 87.4% of broadband-available homes. We estimate that 81.5% of all households subscribe to wired broadband.
Craig’s Conclusions:
The goal for the FCC is to create maps that are not frozen in time but instead become living and breathing reflections of a dynamic marketplace. The new maps are subject to a public challenge process, enabling interested parties, including operators, local governments, and even individual would-be subscribers, to dispute reported availability. Challenges will eventually be part of a routine updating process. Indeed, the maps released in November were the product of what had already been a months-long initial challenge process. The maps are, again, a critical input to distribution of $42.5 billion of funds earmarked for rural broadband by the JOBS/Infrastructure Act. The National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) is required by law to use the FCC’s new map to distribute those funds in what is referred to as the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) Program, something they have committed to do by June 2023. They are likely to begin that process almost immediately, based on the number of unserved locations in each state, although NTIA chief Alan Davidson has said they will wait for the FCC to release the second version of its coverage map, later this year, before they actually begin to disburse those funds.
The network operators themselves, including the cable operators in particular, will in our view be major participants in the BEAD process, bidding aggressively to bring broadband to unserved census blocks on the periphery of their current franchise areas.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Meanwhile, Leichtman Research Group indicates that 90 per cent of U.S. households get an Internet service at home, compared to 84 per cent in 2017, and 74 per cent in 2007. Broadband accounts for 99 per cent of households with an Internet service at home, and 89 per cent of all households get a broadband Internet service – an increase from 82 per cent in 2017, and 53 per cent in 2007.
These findings are based on a survey of 1,910 households from throughout the United States and are part of a new LRG study, Broadband Internet in the U.S. 2022. This is LRG’s twentieth annual study on this topic.
Other related findings include:
- Individuals ages 65+ account for 34% of those that do not get an Internet service at home
- 56% of broadband subscribers are very satisfied (8-10 on a 1-10 scale) with their Internet service at home, while 6% are not satisfied (1-3).
- 44% of broadband subscribers do not know the download speed of their service – compared to 60% in 2017
- 61% reporting Internet speeds of >100 Mbps are very satisfied with their service, compared to 41% with speeds <50 Mbps, and 57% that do not know their speed
- 40% of broadband households get a bundle of services from a single provider – compared to 64% in 2017, and 78% in 2012
- 59% of adults with an Internet service at home watch video online daily – compared to 59% in 2020, 43% in 2017, and 17% in 2012
“The percentage of households getting an Internet service at home, including high-speed broadband, is higher than in any previous year,” said Bruce Leichtman, president and principal analyst for Leichtman Research Group, Inc. “Computer usage and knowledge remain the foundation for Internet services in the home. Among those that do not get an Internet service at home, 58% also do not use a computer at home..”
References:
https://broadbandmap.fcc.gov/home
https://www.leichtmanresearch.com/90-of-u-s-households-get-an-internet-service-at-home/
NaaS emerges as challenger to legacy network models; likely to grow rapidly along with SD WAN market
Enterprises are starting to think “much more strategically” about how to support remote and hybrid workers, with as-a-service network models beginning to take over the market, IDC Analyst Brandon Butler told SDxCentral. Organizations are increasingly looking to extend enterprise-class networks to remote and hybrid workers, a concept IDC calls “the branch of one.” IDC reported that 69% of global respondents to a recent survey are planning to invest in network transformation over the next 12 months, highlighting network-as-a-service (NaaS) as a challenger to legacy network models that necessitate substantial upfront capital.
“I would say in the early days there were a lot of what I would call band-aid solutions in terms of, well, maybe I’m just going to spin up some more VPN capacity to be able to support my remote and hybrid workers,” Butler told SDxCentral. IDC conducted a web survey of technology-buying decision makers in 402 medium to large organizations (with 500+ employees), across 13 countries in North America, Europe, and Asia/Pacific, and in nine industries to understand the role of Network as a Service in their network strategy. Here is what they found:
As organizations leverage the value of their networks to jumpstart digital transformation, the Network as a Service market is expected to grow rapidly, at a similar rate as the SD WAN market, which is forecast at a 41% compound annual growth rate from 2019 to 2024.
- The most important Network as a Service capabilities are a hybrid network and SD WAN [1.].
- Real-time, high-bandwidth capabilities are needed for the future network.
- Many enterprises outsource network services, mainly ongoing managed network services, preventative management, and network design.
- Virtualizing, automating, and modernizing the network as well as dealing with security threats are top priorities in a pandemic and post-pandemic world. Specifically – adding virtualized network and security services as well as cloud security are top of the list of things to upgrade.The majority of enterprises plan a network transformation in the next two years. Skills shortages, stakeholder buy-in, and legacy infrastructure hold back progress. The cost of doing nothing can be significant.
Note 1. According to Reasarch@Markets, the global SD-WAN market is projected to grow from USD 3.4 billion in 2022 to USD 13.7 billion by 2027, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 31.9% during the forecast period.
In 2022, companies like Verizon and Aruba worked to bolster their NaaS offerings. The global NaaS market generated $11.2 billion in revenues in 2021, and is estimated to reach $72.2 billion in revenue by 2031, according to a report from Allied Market Research.
NaaS replaces legacy network architecture like hardware-based VPNs and MPLS connections or on-premises networking appliances like firewalls and load balancers. Enterprises use NaaS to operate and control a network without needing to purchase, own, or maintain network infrastructure.

Butler said these as-a-service models are “really helping organizations sort of transform how they’re thinking about their relationships with their vendors. Things like as-a-service models, they certainly take into account a sort of consumption model and having more subscriptions, and operating expenses versus capital expenses.”
NaaS models also bring in other benefits, like “being able to be faster or to be able to spin up services or spin down services, that sort of elasticity of them.”
The ability to add and remove features more dynamically, and manage networks from the cloud is another “tenant” that Butler said is key to as-a-service models.
“I always like to say that it’s it’s important to think about what the business needs from the IT department,” he added.
“That’s, I think, the best place to start in terms of what sort of business problems is your broader organization looking to solve and what goals does your organization have,” Butler said. “And then I think that can help determine what sort of technology solutions are the right fit to help meet those business goals.”
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/interview/will-2023-be-the-year-of-naas/2023/01/
https://www.naasenterprisesurvey.com/#executive-summary
https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/network-as-a-service-market
https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/network-as-a-service-naas/
ABI Research: Network-as-a-Service market to be over $150 billion by 2030
MediaTek Introduces Global Ecosystem of Wi-Fi 7 Products at CES 2023
Taiwan based MediaTek, one of the first adopters of Wi-Fi 7 [1.] technology, will be demonstrating a full ecosystem of production-ready devices featuring the next generation of wireless connectivity for the first time at CES 2023. These products are the culmination of MediaTek’s investment in Wi-Fi 7 technology, focusing on reliable and always-on connected experiences on a wide variety of devices in several product categories, including residential gateways, mesh routers, televisions, streaming devices, smartphones, tablets, laptops, and more.
Note 1. Wi-Fi 7 refers to the IEEE 802.11be standard, whereas Wi-Fi 6 was IEEE 802.11ax, and Wi-Fi 5 was IEEE 802.11ac.
As the most current and powerful Wi-Fi standard, Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be) utilizes record-breaking 320MHz channel bandwidth and 4096-QAM modulation to greatly improve overall user experience. Multi-Link Operation (MLO) also enables the Wi-Fi connection to aggregate channel speeds and alleviate link interruption in congested environment for time-demanding applications.
“Last year, we gave the world’s first Wi-Fi 7 technology demonstration, and we are honored to now show the significant progress we have made in building a more complete ecosystem of products,” said Alan Hsu, corporate vice president and general manager of the Intelligent Connectivity Business unit at MediaTek. “This lineup of devices, many of which are powered by the CES 2023 Innovation Award-winning Filogic 880 flagship chipset, illustrates our commitment to providing the best wireless connectivity.”
Using a 6nm process, MediaTek’s Wi-Fi 7 solution offers a reduction in main power consumption by 50% and 100x lower MLO switch latency when compared to competing options. 4T5R and penta-band mesh are also included to address a larger area of coverage and higher number of linked devices.
The devices on demonstration this week utilize MediaTek’s latest Filogic chips, which combines a Wi-Fi 7 access point technology to broadband operators, retail router channels and enterprise markets; and the Filogic 380 chipset, designed to bring Wi-Fi 7 connectivity to all client devices, including smartphone, tablet, laptops, TVs, and streaming devices.
“We are excited to collaborate with MediaTek on the latest Wi-Fi 7 technology. Fast and reliable wireless connectivity is crucial for consumers, and we believe that combining powerful AMD Ryzen processors with MediaTek’s advanced connectivity technologies will deliver an excellent user experience,” said Jason Banta, corporate vice president and general manager, client OEM at AMD.

“A strong, fast, and reliable Wi-Fi connection is one of the most critical components of competitive gaming, and can mean the difference between winning and losing a match,” said Ouyang Jun, Vice President and General Manager of Consumer Business Segment, Lenovo’s Intelligent Device Group. “MediaTek’s vision for excellence in Wi-Fi connectivity mirrors our own commitment to empowering gamers with immersive, high-performance PC gaming experiences, and we look forward to collaborating together to bring MediaTek’s Wi-Fi 7 technology to upcoming Lenovo Legion devices.”
“We greatly enjoy MediaTek Filogic’s, fast, reliable and always-on connected Wi-Fi solution,” said Rangoon Chang, head of Gaming Business Unit, ASUS. “With MediaTek’s world leading Wi-Fi technology and innovative ecosystem, we strive for leadership in providing the extreme experience for gamers around the globe.”
“With the introduction of 320 MHz channels in the 6 GHz band and Multi-Link Operation (MLO), Wi-Fi 7 will deliver ultra-high speed and lower latency,” said Pingji Li, VP & GM, TP-Link Corporation Limited. “MediaTek Filogic 880’s innovative design delivers outstanding performance on top of Wi-Fi 7 standards, such as 4×5 6 GHz and single-chip MLO. We are excited to collaborate with our longtime partner, MediaTek, on Wi-Fi 7 to create new ways for customers to experience applications.”
“As a leader in networking products and services for more than 23 years, BUFFALO has always been among the first to implement new Wi-Fi technology, and Wi-Fi 7 is no exception,” said Nobuhiro Tamura, General Manager, Network Product Development Division, BUFFALO INC. “We are glad to see MediaTek put a lot of investment in leading technology, and would like to congratulate them on showcasing the latest Wi-Fi 7 solutions at CES 2023.”
“Today’s consumers want fast, reliable and always-on connected Wi-Fi for many applications such as video calls, 4K/8K TV entertainment, real-time gaming, streaming and more,” said Byung-Kyun Kim, Senior Vice President, Korea Telecom. “MediaTek Wi-Fi 7 technology is equipped with extremely high throughput and single MAC MLO (Multi-Link Operation), which can fulfill every demanding application consumers enjoy today.”
“With MediaTek’s single chip MLO technology, we can bring high throughput and low latency performance to enhance user experience on streaming, gaming, and various immersive contents,” said Mr. Yu, SVP in Hisense Group. “Hisense is excited to continue the partnership with MediaTek to bring Wi-Fi 7 on Hisense TV products.”
“MediaTek recognizes the demand and expectation for the fastest speeds and lowest latency from wireless devices,” said John O’Neill, Vice President, Marketing, Skyworks. “Together, our joint reference design provides customers a platform to develop new and unimagined applications. We are excited to deliver cutting-edge technology together that allows consumers to realize the full potential of Wi-Fi 7 that supports 320 MHz channels, 4K QAM and Multi-Link Operation (MLO).”
“As a strong driver of Wi-Fi 7, MediaTek helps its customers harness the massive improvements in throughput, latency, client connections and reliability,” said Tony Testa, General Manager Connectivity Components, Qorvo. “We are excited to utilize MediaTek’s Wi-Fi 7 solution in order to tackle its impressive 4K QAM, 320 MHz, 6 GHz channels and Multi-Link Operation.”
“As companies move to Wi-Fi 7 it is critical that they be able to test the fastest available data rate modes, and we have worked with MediaTek to create an industry leading test solution that meets this vital need,” said John Lukez, Vice President LitePoint Applications, Litepoint. “As we head into this new era of wireless connectivity, working with a leading Wi-Fi innovator like MediaTek will enable our mutual customers to quickly and seamlessly ramp their products into high volume production.”
“We are truly impressed with MediaTek’s speed to market with almost every cutting-edge technology, such as single MAC MLO, 320MHz BW and 4096 QAM,” said Jesse Lyles, Vice President of Semiconductor Validation and Electronics Solutions, NI. “The increased amount of complexity needed to achieve top performance and backward compatibility with Wi-Fi 7 drastically increases the need for a full-scale automated test and validation solution. NI works together with MediaTek with its software-connected RF instrumentation to achieve the time-to-market goals of mutual customers and to ensure their superior performance capabilities.”
To learn more about MediaTek’s Filogic portfolio, please visit: https://www.mediatek.com/products/networking-and-connectivity/.
About MediaTek Inc.
MediaTek Incorporated is a global fabless semiconductor company that enables nearly 2 billion connected devices a year. We are a market leader in developing innovative systems-on-chip (SoC) for mobile, home entertainment, connectivity and IoT products. Our dedication to innovation has positioned us as a driving market force in several key technology areas, including highly power-efficient mobile technologies, automotive solutions and a broad range of advanced multimedia products such as smartphones, tablets, digital televisions, 5G, Voice Assistant Devices (VAD) and wearables. MediaTek empowers and inspires people to expand their horizons and achieve their goals through smart technology, more easily and efficiently than ever before. We work with the brands you love to make great technology accessible to everyone, and it drives everything we do. Visit www.mediatek.com for more information.
References:
MediaTek to expand chipset portfolio to include WiFi7, smart homes, STBs, telematics and IoT
Qualcomm FastConnect 7800 combining WiFi 7 and Bluetooth in single chip
Intel and Broadcom complete first Wi-Fi 7 cross-vendor demonstration with speeds over 5 Gbps
Cybersecurity to be a top priority for telcos in 2023
Telecom has always been susceptible to cyberattacks and data breaches. With increasing deployment of IoT devices, attackers will have more opportunities to obtain our data as more gadgets are connected to our network. OpenRAN, with many more exposed interfaces, widens the attack surface for bad actors.
Different security risks brought on by 5G will leave the sector open to cyberattacks. To strengthen security surrounding connected devices, cloud systems, and the networks that connect them, telecom operators must invest in implementing stringent cybersecurity measures because there is a significant amount of sensitive data dispersed across intricate, private, and private networks.
According to Gartner, there will be 43 billion IoT-connected devices by the end of 2023. For those in charge of cybersecurity, it’s necessary to keep in mind IoT devices, such as smartwatches or human-wearable biometrics, monitoring systems, robotics, alarm systems, sensors, IT devices, and industrial equipment. IoT security is essential as more telecoms embrace the industry and implement these devices in their networks because they can remotely access base stations and data centers.
Finally, enterprises deploying SD-WANs and other private or virtual private networks. In particular:
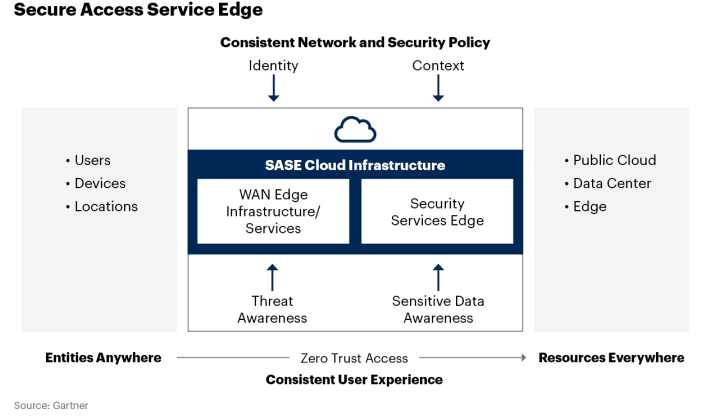
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) combines network security functions (such as SWG, CASB, FWaaS and ZTNA), with WAN capabilities (e.g. SD-WAN) to support businesses’ secure access needs. Previously, security for SD-WAN was an open, unresolved issue.
- Secure Service Edge (SSE) is the security components of SASE focusing largely on the cloud access security broker, secure web gateway, and zero-trust network access products to enable secure use of the internet and cloud services for a hybrid workforce working from anywhere,” said Gartner analyst Charlie Winckless.
A Dell’Oro group July 2022 report found that the SSE market grew 40% year-over-year to more than $800 million in the first quarter. A December report noted that SSE achieved its tenth consecutive quarter of sequential revenue expansion in 3Q-2022. Dell’Oro’s Director of Network Security, SASE, and SD-WAN Mauricio Sanchez said the strong growth is a testament to more enterprises preferring cloud-delivered security over traditional on-premises solutions. Sanchez told SDX Central: “The growth factors that have existed largely since the pandemic started are still with us. That’s the shift to hybrid work, the shift of workloads to the cloud, and the importance of the digital experience.”
References:
https://insidetelecom.com/a-look-at-the-telecommunication-industry-trends/
Summary of EU report: cybersecurity of Open RAN
IEEE/SCU SoE Virtual Event: May 26, 2022- Critical Cybersecurity Issues for Cellular Networks (3G/4G, 5G), IoT, and Cloud Resident Data Centers
U.S. cybersecurity firms seek tech standards to secure critical infrastructure
Enterprises Deploy SD-WAN but Integrated Security Needed
Have we come full circle – from SD-WAN to SASE to SSE? MEF’s SD-WAN and SASE standards
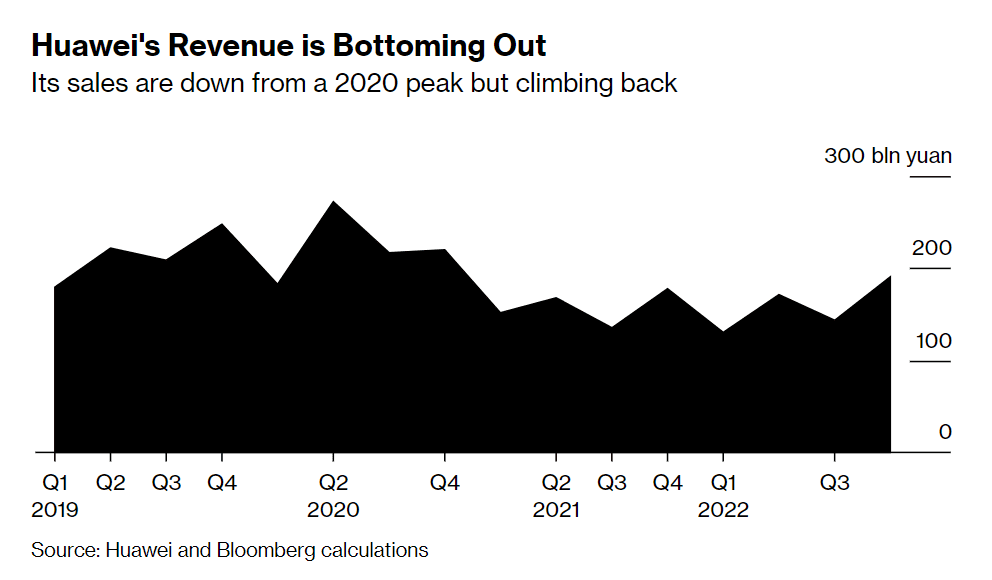
Huawei reports 3rd straight quarter of revenue growth despite U.S. sanctions
Industry Analysts: Important Optical Networking Trends for 2023
Optical Transceivers:
Optical transceivers save space and reduce the need for additional transmitting and receiving devices because they transmit and receive information all in one device! Additionally, they are an economical, compact tool to enable networks to send information over larger distances, come in a variety of Ethernet speeds from Fast Ethernet to 100 Gigabit Ethernet, and offer great flexibility to grow your network while leveraging existing network devices and infrastructure.
Many newer, high quality Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) modules have Diagnostic Monitoring Interface (DMI), which automatically monitors SFP operations such as output and input power, temperature, and supply voltage in addition to providing multimode, single mode, and multi-rate SFP options for more flexibility.
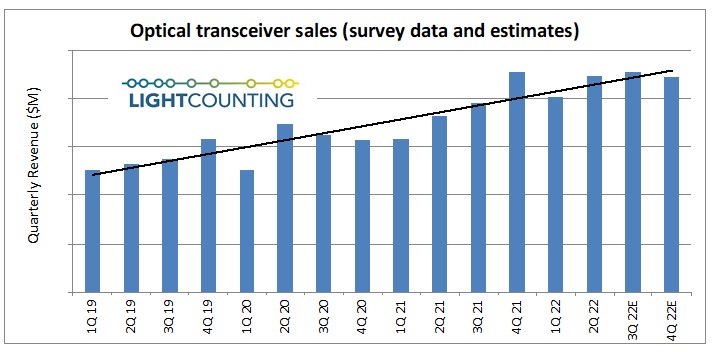
Market Research Future® (MRFR) predicts that the global optical transceiver market will rise to 8 billion in the U.S. by 2023.
Pluggable optics:
400ZR coherent pluggable optics emerged as a connectivity tool for metro-distributed data center connectivity. In 2023, look for three additional innovations to enable even more opportunities for coherent pluggables.
High-performance pluggables with 0 dBm transmit power and low out-of-band noise will enable coherent pluggable transceivers to cover a richer set of use cases, including deployment in metro networks with multiple cascaded ROADMs. This increased transceiver performance will also push some pluggables beyond the 600-km metro threshold and into a portion of the long-haul network.
Advances in intelligent pluggables management, as being defined in the 28-member Open XR Forum and with inputs to other organizations like the OIF, will ease deployment complexity and enable operational support for advanced functionality like remote diagnostics, auto-discovery, spectrum analysis, and streaming telemetry in all types of non-optical hosts, including switches and routers.
A new class of coherent pluggables, such as Infinera’s ICE-XR with digital subcarrier technology, will enable commercial deployment of point-to-multipoint architectures, where a single high-speed (e.g., 400G) hub optic can communicate with multiple lower-speed (e.g., 25G to 100G in 25G increments) optics without requiring intermediate electrical aggregation – thus reducing the amount of equipment, space, and power utilized and the total cost of network ownership by up to 70% over multiple years.
Heavy Reading’s optical networking analyst Sterling Perrin sees “pluggable optics everywhere” being a dominant theme. “This includes the continuing trends in 400ZR and ZR+ but also a big focus on migrating down to small coherent 100G pluggables, pluggables across 5G XHaul networks, and pluggables in PON,” he writes in a note to Light Reading.
Data center transmission:
In 2023, look for modular, distributed data center deployments to accelerate, along with 400 Gb/s, 600 Gb/s, and 800 Gb/s per wavelength coherent optical connectivity to support their interconnection
Modular data centers, where construction and integration tasks are moved offsite and then shipped and assembled onsite, are becoming mainstream and enabling compute and storage to be quickly and reliably deployed in all types of settings – from just a few racks in a small hut to megawatts of equipment in a multi-story configuration. In 2023, look for modular, distributed data center deployments to accelerate, along with 400 Gb/s, 600 Gb/s, and 800 Gb/s per wavelength coherent optical connectivity to support their interconnection.
Lisa Huff, Omdia’s senior principal analyst covering optical components will keep an eye out for whether 800G and 1.6T transmission will show up next in data centers. “We are in the middle of 400G deployment inside the data center and, as always, there is much hype around what the next data rate will be,” she writes.
“Omdia expects to see 2x400G and 8x100G solutions start to be deployed inside the data center in 2023, but we will not see high-volume deployment until about 2025 when DR4 and FR4 variants mature and 400G starts to slow down,” she writes. Deployments of 1.6T may start in 2026, but Huff said it might be 2027 or later before we see significant volume.
Coherent routing:
Omdia Senior Principal Analyst Timothy Munks said that with data traffic growing at the network’s edge, network operators are looking for better solutions to collect and move that data into metro and core networks.
“The convergence of IP and optical, or coherent routing, provides cost effective aggregation and transport of diverse traffic streams and offers network operators a pure pay-as-you-grow business model for adding capacity,” he writes.
In this video, Cisco’s Bill Gartner, SVP/GM Optical Systems & Optics, chats with Phil Harvey to discuss their Leading Lights Award and how Routed Optical Networking is transforming infrastructure and the economics of the network.
References:
Have we come full circle – from SD-WAN to SASE to SSE? MEF’s SD-WAN and SASE standards
Backgrounder – SD-WAN and SASE:
A software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) uses software-defined network technology, mostly to communicate over the Internet using overlay tunnels which are encrypted when destined for internal organization locations. If standard tunnel setup and configuration messages are supported by all of the network hardware vendors, SD-WAN simplifies the management and operation of a WAN by decoupling the networking hardware from its control mechanism. This concept is similar to how software-defined networking implements virtualization technology to improve data center management and operation.[1] In practice, proprietary protocols are used to set up and manage an SD-WAN, meaning there is no decoupling of the hardware and its control mechanism.
A key application of SD-WAN is to allow companies to build higher-performance WANs using lower-cost and commercially available Internet access. That enables businesses to partially or wholly replace more expensive private WAN connection technologies such as MPLS. When SD-WAN traffic is carried over the Internet, there are no end-to-end performance guarantees. In sharp contrast, Carrier MPLS VPN WAN services are not carried as Internet traffic, but rather over carefully-controlled carrier capacity, and do come with an end-to-end performance guarantee.
Gartner’s 2022 SD-WAN Magic Quadrant report identified Cisco, Fortinet, VMware, Palo Alto Networks, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) Aruba, and Versa Networks as market leaders. The analyst firm estimates the top 10 vendors make up more than 80% of the market. To determine SD-WAN leaders, Gartner reviewed vendors’ product capabilities such as the ability to operate as a branch office router, and having a centralized management for devices, zero-touch configuration, and VPN with a basic firewall. The analyst firm also reviewed vendors’ business and financial performance based on their volume of customers, sites, and contracts.
Gartner coined the acronym SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) in an August 2019 report The Future of Network Security in the Cloud and expanded its functionality in their 2021 Strategic Roadmap for SASE Convergence. SASE combines network security functions (such as SWG, CASB, FWaaS and ZTNA), with WAN capabilities (e.g. SD-WAN) to support businesses’ secure access needs. Previously, security for SD-WAN was an open, unresolved issue.
SASE is a holistic framework that brings security and networking connectivity together through a cloud-centric base. Businesses can save equipment, human and financial resources thanks to SASE’s underlying cloud design, and they can scale performance with minimal hardware needs.
Omdia Analyst Fernando Montenegro describes SASE as a “framework architecture, not a solution.”
MEF SD-WAN and SASE Standards:
In August 2019, the MEF published the industry’s first global standard defining an SD-WAN service and its service attributes. SD-WAN Service Attributes and Services (MEF 70). The MEF SD-WAN standard describes requirements for an application-aware, over-the-top WAN connectivity service that uses policies to determine how application flows are directed over multiple underlay networks irrespective of the underlay technologies or service providers who deliver them. However, it does not address interoperability because it does not specify either a UNI or NNI protocol stack.
MEF 70 defines:
- Service attributes that describe the externally visible behavior of an SD-WAN service as experienced by the subscriber.
- Rules associated with how traffic is handled.
- Key technical concepts and definitions like an SD-WAN UNI, the SD-WAN Edge, SD-WAN Tunnel Virtual Connections, SD-WAN Virtual Connection End Points, and Underlay Connectivity Services.
SD-WAN standardization offers numerous benefits that will help accelerate SD-WAN market growth while improving overall customer experience with hybrid networking solutions. Key benefits include:
- Enabling a wide range of ecosystem stakeholders to use the same terminology when buying, selling, assessing, deploying, and delivering SD-WAN services.
- Making it easier to interface policy with intelligent underlay connectivity services to provide a better end-to-end application experience with guaranteed service resiliency.
- Facilitating inclusion of SD-WAN services in standardized LSO architectures, thereby advancing efforts to orchestrate MEF 3.0 SD-WAN services across automated networks.
- Paving the way for creation and implementation of certified MEF 3.0 SD-WAN services, which will give users confidence that a service meets a fundamental set of requirements.
Last year MEF introduced an updated version of its SD-WAN standard, MEF 70.1, which added critical enhancements. MEF is also currently at work on version MEF W70.2 and MEF W119 Universal SD-WAN Edge, which will address the need for interoperability, among other things.
In December 2022, MEF published two Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) standards defining 1.] SASE service attributes, common definitions & a framework and 2.] a Zero Trust framework that together allow organizations to implement dynamic policy-based actions to secure network resources for faster decision making and implementation for enterprises. MEF’s SASE standard defines common terminology and service attributes which is critically important when buying, selling, and delivering SASE services. It also makes it easier to interface policy with security functions for cloud-based cybersecurity from anywhere. MEF’s Zero Trust framework defines service attributes to enable service providers to implement and deliver a broad range of services that comply with Zero Trust principles.
- SASE Service Attributes and Service Framework Standard: specifies service attributes to be agreed upon between a service provider and a subscriber for SASE services, including security functions, policies, and connectivity services. The standard defines the behaviors of the SASE service that are externally visible to the subscriber irrespective of the implementation of the service. A SASE service based upon the framework defined in the standard enables secure access and secure connectivity of users, devices, or applications to resources for the subscriber. MEF’s SASE standard (MEF 117) includes SASE service attributes and a SASE service framework.
- Zero Trust Framework for MEF Services: The new Zero Trust Framework for MEF Services (MEF 118) defines a framework and requirements of identity, authentication, policy management, and access control processes that are continuously and properly constituted, protected, and free from vulnerabilities when implemented and deployed. This framework also defines service attributes, which are agreed between a subscriber and service provider, to enable service providers to implement and deliver a broad range of services that comply with Zero Trust principles.
–>PLEASE SEE Pascal Menezes CTO of MEF COMMENTS BELOW THIS ARTICLE.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Enter SSE (Secure Service Edge):
In it’s above referenced 2021 report, Gartner defined SSE (Secure Service Edge) which is a separate entity that doesn’t include SD-WAN. “SSE is the security components of SASE focusing largely on the cloud access security broker, secure web gateway, and zero-trust network access products to enable secure use of the internet and cloud services for a hybrid workforce working from anywhere,” Gartner analyst Charlie Winckless told SDxCentral.
Telefónica tapped cloud security vendor Zscaler to develop a new managed SSE platform in a bid to address changing workforce dynamics and cloud consumption. The announcement illustrated a growing trend around the Gartner-coined product category, in which cloud security and SASE vendors alike announce “new” products and services around the buzzword.
But for the most part, these SSE products aren’t so much new as they’re rebranded and repackaged SASE services that’ve been stripped of their SD-WAN capabilities, if they ever had them in the first place. Zscaler’s SSE is built around the same Zscaler Internet Access and Zscaler Private Access products that, just a few months ago, it was calling SASE.
“The contrast is that SASE focuses on a user’s secure access needs as a part of the solution. SSE, on the other hand, mainly focuses on cloud-centric security services for the protection of users,” according to Juta Gurinaviciute, Forbes Councils Member and CTO for NordLayer, a remote access security provider. Gurinaviciute explained that SSE is SASE minus SD-WAN. SSE is essentially a way for enterprises to focus more on cloud-based security as a stepping stone to a full SASE service. She wrote:
As per Gartner’s suggestion, some companies may select a single-provider SASE offering, while others prefer partnered SD-WAN and SSE offerings from separate providers based on companies’ needs. Your business may have already invested in SD-WAN in advance. SSE would be a more meaningful choice in the short-term in such a case. If your company’s current setup doesn’t need SD-WAN, security may be a much more urgent requirement, in which case SSE would make more sense. Even if your organization only has a single regional branch or a simple branch, SSE may still be helpful.
Considering all of these reasons, SASE, the implementation of which may seem challenging and daunting for security professionals, can be done much faster with SSE adaptation first. The journey can be completed much more smoothly using this option, and SSE may benefit a wide range of companies that need robust protection.
“I think everybody’s really excited about SASE because enterprises keep asking about it,” Omdia Analyst Adeline Phua told Light Reading in a recent podcast. “It’s got so much buzz in the market.” However, Phua found that excitement about SASE/SSE hasn’t necessarily equated to mass adoption of the service. “We’re thinking that maybe adoption is really hitting that tipping point, only to find out when we talk to service providers and to enterprises that the adoption is really not there yet,” she added.
A Dell’Oro group July 2022 report found that the SSE market grew 40% year-over-year to more than $800 million in the first quarter. A December report noted that SSE achieved its tenth consecutive quarter of sequential revenue expansion in 3Q-2022. Dell’Oro’s Director of Network Security, SASE, and SD-WAN Mauricio Sanchez said the strong growth is a testament to more enterprises preferring cloud-delivered security over traditional on-premises solutions. Sanchez told SDX Central: “The growth factors that have existed largely since the pandemic started are still with us. That’s the shift to hybrid work, the shift of workloads to the cloud, and the importance of the digital experience.”
While Dell’Oro forecasts the overall SASE market to grow to $8 B for the full year 2023, an Omdia survey found that SD-WAN is only expected to achieve 87% market penetration at the end of 2023. Omdia’ Phua says that enterprises which are using SD-WAN aren’t deploying it at all their sites. Part of the problem stems from supply chain challenges triggered by COVID-19 which have resulted in a shortage of products and SD-WAN deployment delays.
Where service providers can make progress in assisting their enterprise customers’ adoption of SASE is by providing it as a managed service with significant value add “on top of just the staff, the platform itself,” explained Omdia’s Fernando Montenegro. That might look like providing more visibility into network health and potential security threats.
Phua echoed Montenegro’s assessment: “Service providers will still need to keep looking out for new innovations and what else can we onboard to make sure that is a more complete solution for the enterprise customers. So there’s still a lot of way to go in terms of this journey.”
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SD-WAN#
https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/3957375
https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/3999828
https://www.lightreading.com/sd-wan/looking-ahead-sase-is-too-messy/a/d-id/782090?
Dell’Oro: SASE Market grew 33% in 2022; forecast to hit $8B in 2023
Gartner: SASE tops Gartner list of 6 trends impacting Infrastructure & Operations over next 12 to 18 months
Dell’Oro: Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) market to hit $13B by 2026; Gartner forecasts $14.7B by 2025; Omdia bullish on security
Enterprises Deploy SD-WAN but Integrated Security Needed
MEF survey reveals top SD-WAN and SASE challenges
MEF New Standards for SD-WAN Services; SASE Work Program
Shift from SDN to SD-WANs to SASE Explained; Network Virtualization’s important role
ITU-T: 25 years of increasing fixed-broadband speeds over copper and fiber optic networks
by ITU News
The ITU Telecommunications standardization (ITU-T) working groups on broadband access over metallic conductors (Q4/15) and optical systems for fiber access networks (Q2/15), established in 1997 (25 years ago), laid the foundations for fixed broadband and have since then facilitated the meteoric rise in access speeds. Both groups are part of ITU-T Study Group 15, which looks at networks, technologies and infrastructures for transport, access and home.
DSL: ITU-T Q4/15 was formed to make DSL globally scalable:
“What followed was a 25-year journey of dedicated engineers fighting physics for ever-higher broadband speeds, through several generations of ITU-standardized DSL technology,” says Q4/15 Rapporteur Frank Van der Putten (a strong colleague of this author from 1996-2002 when both of us worked on ADSL and VDSL standards in T1E1.4 and the ADSL Forum).
Building on prior work by Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions (ATIS) committee T1E1.4 and European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) working group TM6, the DSL technologies standardized by ITU now connect over 600 million homes and businesses to the Internet.
“DSL changed the world by enabling mass-market broadband,” Van der Putten says.
DSL enabled rapid broadband deployment at low cost because it used the existing telephone wires to the home.
“Championed at first by an impassioned few, continually provoking debates among Q4/15 experts, it has been an intellectual catalyst for the advancement of communications technology,” he adds. “We are proud to have played a part in that.”
While ADSL (asymmetric DSL), as defined by ITU in 1999, could deliver 8 megabits per second (Mbit/s), it was followed by ADSL2plus in 2003 at 24 Mbit/s and the very high speed VDSL2 at 70 Mbit/s. With the introduction of vectoring, VDSL2 reached 100 Mbit/s by 2010 and 300 Mbit/s by 2014.
In 2014, G.fast raised the bar to 1 Gbit/s, doubling this to 2 Gbit/s in 2016. Its successor standard, MGfast, achieves an aggregate bit rate up to 8 gigabits per second (Gbit/s) in Full Duplex mode and 4 Gbit/s in Time Division Duplexing mode.
The architecture standards for DSL, G.fast and MGfast were defined by the Broadband Forum (once known as the ASDL forum), which also plays a key part in promoting interoperability.
Van der Putten explains: “Both technologies intend to meet service providers’ need for a complement to the fibre-to-the-home technologies in scenarios where G.fast or MGfast prove the more cost-efficient strategy.”
The continual upgrading of ITU’s standards has also sparked huge upward revisions in forecasts for the life left in traditional telephone wiring.
Future directions for Q4/15 work include G.fast-based backhaul, MGfast at aggregate data rates of 10 Gbit/s, and ultra-low latency transmission optimized for 5G wireless back/mid-haul, he says.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Cost-efficient fiber access – PON and FTTH:
ITU-T Q2/15 paved the way for passive optical network (PON) technologies as a highly cost-efficient means of enabling FTTH. Optical access networks now serve over a billion users worldwide, mostly based on PON. Q2/15 works closely with Full Service Access Network (FSAN), which collects system requirements from operators to determine common requirements for ITU standards.
“The result has been systems ideally suited for a large group of networks and applications,” says Q2/15 Rapporteur Frank Effenberger.
“The first widely deployed system, G-PON [Gigabit PON], is found almost everywhere now,” he adds.
Q2/15 has developed seven generations of PON systems. The first, pi-PON, operated at 50 Mbit/s. This was followed by A-PON (155 Mbit/s), B-PON (622 Mbit/s), G-PON (2.5 Gbit/s), XG(S)-PON (10 Gbit/s), and NG-PON2 (4 x 10 Gbit/s).
To provide the basis for interoperability, ITU standards specify the control system for PON systems. Q2/15 has also developed a range of implementer’s guides and works closely with FSAN, ATIS, and the Broadband Forum to foster common designs and interoperability.
From 10 to 50 Gbit/s PONs:
Demand for higher capacity keeps growing fast. Optical access solutions also support 5G wireless communications and innovation for smart cities and factories.
“What we are seeing is a gradual evolution from G-PON to XG-PON [a 10G, or 10 Gbit/s, network] and XGS-PON [a 10G symmetric network], which is now being deployed at scale in many countries,” says Effenberger.
The latest generation of ITU-standardized PON, known as “Higher Speed PON”, provides for speeds of 50 Gbit/s per wavelength, up from the 10 Gbit/s of its predecessors. Market demand for Higher Speed PON is expected to begin in 2024.
“Given the large size and cost of the fixed access network, upgrades generally come once per decade,” says Effenberger.
Higher Speed PON includes both single-channel 50 Gbit/s systems to succeed XG(S)-PON and multi-channel 50 Gbit/s systems to succeed today’s NG-PON2 – a 40G PON that operates at 10Gbit/s per wavelength.
Although Higher Speed PON offers a five-fold capacity increase over its predecessors, it has been designed to work with the same fibre plant as G-PON, XG(S)-PON and NG-PON2.
“A successful technology requires a coincidence of both technical feasibility and strong global market demand,” notes Effenberger. “We strongly believe that 50G PON will provide the right capacity, at the right price, and at the right time.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
All-fiber future at Gbit/s speeds:
Q2/15 aims to continue delivering higher-capacity PON solutions, such as a multi-wavelength version of Higher Speed PON, and speeds even higher than 50 Gbit/s on a single wavelength. But passive networks cannot handle all foreseen demand.
“Certain applications will require more dedicated and higher-capacity solutions than PON,” says Effenberger, highlighting the motivations behind Q2/15’s development of various point-to-point bidirectional optics with speeds of 1 Gbit/s, 10 Gbit/s, 25 Gbit/s, and 50 Gbit/s.
Q2/15 continues to study 100 Gbit/s transmission and point-to-point wavelength connections over a shared optical distribution network based on wavelength division multiplexing. “These are likely to find use in wireless fronthaul applications, given their exacting latency requirements,” says Effenberger.

References:
AT&T and BlackRock’s Gigapower fiber JV may alter the U.S. broadband landscape
AT&T and a unit of investment titan BlackRock will form a joint venture to operate a commercial fiber-optic platform, with AT&T as its first wholesale tenant. The objective is to further propel AT&T’s fiber ambitions outside of the carrier’s traditional 21-state wireline footprint and move on AT&T’s long-simmering fiber expansion plans. The newly formed joint venture (JV) — Gigapower, LLC — expects to provide a best-in-class fiber network to internet service providers (ISPs) and other businesses across the United States.
The Gigapower joint venture will operate the commercial fiber service. That service – not to be confused with AT&T’s previous “GigaPower” broadband offering – will be targeted at internet service providers (ISPs) and enterprises.
BlackRock’s work in the venture will be through its Alternatives division and through a fund managed by its Diversified Infrastructure business. That business recently raised $4.5 billion in initial investor commitments. AT&T executive veteran Bill Hogg was named CEO of Gigapower.
The JV’s initial plans are to deploy a multi-gigabit fiber network to 1.5 million customer locations using a commercial open access platform. This will be incremental to AT&T’s own fiber deployment plans targeted at reaching more than 30 million locations within its 21-state wireline footprint by the end of 2025. The JV will tap into AT&T’s nationwide 5G wireless service to support sales outside of its traditional wireline footprint. This will allow it to take advantage of AT&T’s already established enterprise arrangements and more quickly get a sales channel up and running.
“Now more than ever, people are recognizing that connecting changes everything,” said John Stankey, CEO of AT&T. “With this joint venture, more customers and communities outside of our traditional service areas will receive the social and economic benefits of the world’s most durable and capable technology to access all the internet has to offer.”
“We are excited to form the Gigapower joint venture in partnership with AT&T, which will be serving as not only a joint owner but also the first wholesale tenant. We believe Gigapower’s fiber infrastructure designed as a commercial open access platform will more efficiently connect communities across the United States with critical broadband services,” said Mark Florian, Global Head of Diversified Infrastructure, BlackRock. “We look forward to partnering with Gigapower’s highly experienced management team to support the company’s fiber deployment plans and shared infrastructure business model.”
Gigapower plans to deploy a reliable, multi-gig fiber network to an initial 1.5 million customer locations across the nation using a commercial open access platform. The Gigapower fiber deployment will be incremental to AT&T’s existing target of 30 million-plus fiber locations, including business locations, by the end of 2025. Combined with existing efforts within AT&T’s 21-state footprint, this capital efficient network deployment will advance efforts to bridge the digital divide, ultimately helping to provide the fast and highly secure internet people need. This network expansion will also help spur local economies in each of the communities in which Gigapower operates.
“Fiber is the lifeblood of digital commerce,” said Bill Hogg, CEO of Gigapower. “We have a proven team of professionals building this scalable, commercial open access wireline fiber network. Our goal is to help local service providers provide fiber connectivity, create the communications infrastructure needed to power the next generation of services and bring multi-gig capabilities to help close the gap for those who currently are without multi-gig service.”
Tammy Parker, Principal Analyst at GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company, wrote:
“AT&T is pursuing a shrewd path to extend its fiber footprint nationwide without assuming all the risk by itself. Although the new Gigapower platform will be operated as a joint venture with BlackRock, offering commercial open access to not only AT&T but also other internet service providers and businesses, the carrier’s influence features prominently: the moniker ‘GigaPower’ was formerly applied to AT&T’s fiber-based service, which was renamed ‘AT&T Fiber’ in October 2016.
“The Gigapower platform will serve customers outside of AT&T’s traditional 21-state wireline footprint, and as the platform’s first wholesale tenant AT&T will be able to sell fiber service in more wireline markets, complement its nationwide mobile service footprint, and enable the carrier to market fixed-mobile service bundles in those markets. Over time, AT&T should be able to leverage this dual-technology capability to not only attract new customers and revenue streams, but also increase customer retention as subscribers who take multiple services from a carrier tend to be ‘stickier’ and less likely to stray to a rival service provider.
“The AT&T and BlackRock JV poses a competitive challenge to cable providers and regional fiber providers, whose broadband reaches are geographically restricted, though those carriers could possibly become tenants on the open access Gigapower platform to extend their own footprints.
“Gigapower will also help AT&T extend its fiber offerings to compete against the highly successful fixed wireless access (FWA) services being marketed by rivals T-Mobile US and Verizon to residential and business broadband customers both inside and outside of AT&T’s existing wireline service area. However, unlike FWA services, which can ride on top of existing mobile network coverage and are often self-installable, fiber requires the deployment of new infrastructure and truck rolls to the premises to be served, impacting time to market for AT&T and BlackRock’s ambitious plan. Additionally, Gigapower’s initial footprint will cover only 1.5 million customer locations, and it is unclear what the deployment timeline will be.
“After largely extracting itself from its previous foray into entertainment, AT&T continues doubling down on its broadband focus, committing to both 5G and fiber nationwide. AT&T’s JV with BlackRock has the potential to alter the broadband landscape, not only by enabling AT&T to market fiber in more markets but also by providing a platform for public-private broadband partnerships between Gigapower and local municipalities. However, it will take time to see results from this long-term play.”
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/analysis/att-bags-blackrock-for-gigapower-fiber-jv/2022/12/