Month: March 2021
Starlink now covers all of UK; Plans to connect vehicles with satellite Internet service
Starlink has expanded to all regions of the United Kingdom. The SpaceX owned company’s satellite Internet service is still in beta and was previously available in only the southern England part of the UK. Today, the company announced an expansion to cover parts of Wales, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and northern England. Starlink says users should currently expect data speeds to vary between 50Mb/s to 150Mb/s over the next several months, with brief periods of no connectivity whatsoever.
Starlink’s Email:
Starlink is now available in parts of Wales, Scotland, Northern Ireland and northern England, in addition to existing service areas in southern England.
During beta, users can expect to see data speeds vary from 50Mb/s to 150Mb/s over the next several months as we enhance the Starlink system. There will also be brief periods of no connectivity at all.
As we launch more satellites, install more ground stations and improve our networking software, data speed, latency and uptime will improve dramatically.
To check availability for your location, visit starlink.com and re-enter your service address. If Starlink is not yet available in your area, you can place a deposit to hold your space in line for future service.
The UK’s average download speed across all broadband providers is around 67.23Mb/s, but climbing as the rollout of full-fiber starts picking up pace again following a pandemic-induced slowdown.
Starlink wants to quickly deliver decent broadband connectivity to rural locations which have been left underserved due to the difficulties and cost of laying traditional fiber.
“This will transform rural WiFi,” says Compare Fibre’s co-founder Nathan Hill-Haimes. “We are really keen to stress the impact this can have on connecting rural locations with high-speed internet.”
A Starlink user from Devon told the Press Association: “If you need connectivity to run a business and if you need connectivity for communication, particularly in Covid times, £90 a month is quite justifiable.”

Starlink was issued a UK “Earth station network license” in November, an Ofcom spokesperson told CNBC. The £200 ($272) a year license allows Starlink to sell satellite dishes and other communications equipment in the U.K. so that people can pick up signals emitted by Starlink’s network of satellites.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, SpaceX wants to begin connecting large vehicles – from trucks to jets to ships – to its Starlink satellite Internet network, according to a request the company filed with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
“This application would serve the public interest by authorizing a new class of ground-based components for SpaceX’s satellite system that will expand the range of broadband capabilities available to moving vehicles throughout the United States and to moving vessels and aircraft worldwide,” SpaceX director of satellite policy David Goldman wrote in a letter to the FCC filed on Friday.
Starlink is the company’s capital-intensive project to build an interconnected internet network with thousands of satellites, known in the space industry as a constellation, designed to deliver high-speed internet to consumers anywhere on the planet.
To date SpaceX has launched more than 1,100 satellites for Starlink. In October, SpaceX began rolling out early service in a public beta to customers in the U.S., Canada and the U.K., with service priced at $99 a month. Additionally, in a late January update, SpaceX told the FCC that its Starlink beta now has more than 10,000 users.
The Starlink service also includes a $499 upfront cost for the hardware needed to connect to the network. Known as the Starlink Kit, it includes a user terminal (the small, dish-like antenna) and a Wi-Fi router.
SpaceX did not indicate in its filing Friday whether the Starlink user terminals for moving vehicles will have a different design than the dishes currently being shipped to early customers. But SpaceX said each “ESIM,” or Earth Station In Motion, is “electrically identical to its previously authorized consumer user terminals,” with added “mountings that allow them to be installed on vehicles, vessels and aircraft.”
The company also noted that it “will ensure installation” of the vehicle terminals through “qualified installers.” While SpaceX did not say whether those installers would be company employees, it continues to expand Starlink manufacturing and operations – including plans for a new equipment factory in Austin, Texas.
Over 1,000 Starlink satellites are currently in orbit of the total 12,000 satellites which have been authorized. Filings have been submitted to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) requesting permission to launch 30,000 additional Starlink satellites.
Increasing competition:
Starlink is, by far, the biggest satellite broadband deployment. However, rivals such as Amazon’s “Project Kuiper” will be looking to challenge the titleholder in the coming years.
Project Kuiper was given the green light by the FCC last year to launch 3,236 of its own satellites.
“We are doing an incredible amount of invention to deliver fast, reliable broadband at a price that makes sense for customers,” Rajeev Badyal, Vice President of Technology for Project Kuiper, said at the time.
SpaceX is currently launching around 60 satellites at a time and aims to have deployed 1,440 by late 2021 to provide near-global service.
“As we launch more satellites, install more ground stations and improve our networking software, data speed, latency and uptime will improve dramatically,” the company wrote in a release announcing Starlink’s expansion in the UK.
Starlink and Kuiper will also be competing against promising satellite broadband firm OneWeb.
OneWeb nearly collapsed after crucial funding was pulled last-minute during the first peak of the COVID-19 pandemic and filed Chapter 11 bankruptcy. However, the company was rescued following a $1bn (£800m) investment from the UK government and Bharti Global Ltd of India.
Kwasi Kwarteng, Secretary of State for Business, Energy, and Industrial Strategy, said: “Our investment in OneWeb is part of our continued commitment to the UK’s space sector, putting Britain at the forefront of the latest technological advances.”
Since the UK and Bharti’s investment, OneWeb has continued to receive large investments. In January, the company announced that it has raised $1.4 billion in total funding after securing investments from SoftBank Group and Hughes Network Systems.
Masayoshi Son, Chairman and CEO of SoftBank, commented: “We are excited to support OneWeb as it increases capacity and accelerates towards commercialization. We are thrilled to continue our partnership with Bharti, the UK government, and Hughes to help OneWeb deliver on its mission to transform internet access around the world.”
OneWeb is the smallest of the three satellite broadband firms but has launched 74 of its innovative ultrafast broadband satellites to date and plans to launch a total of 648 by the end of 2021.
Neil Masterson, CEO of OneWeb, said: “OneWeb’s mission is to connect everyone, everywhere. We have made rapid progress to re-start the business since emerging from Chapter 11 in November.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
AT&T Adds 5G to Nationwide Business-Focused Broadband Network
AT&T is adding fixed 5G wireless solutions to what it claims is the first nationwide business-focused broadband network, which combines AT&T Wireless Broadband and its business fiber optics network.
AT&T’s business fiber network already connects more than 2.5M business customer locations with fixed and wireless solutions nationwide, delivering speeds 20 times faster than cable. AT&T is now adding more 5G power to AT&T Wireless Broadband.
Beginning in April, the telcoand media giant will be offering new fixed wireless router options from Sierra Wireless and Cradlepoint to give businesses better access to all the benefits of 5G – and the flexibility to choose the right speeds and quality of service options for their business.
AT&T Wireless Broadband with 5G is helping businesses boost their performance with a variety of router choices. Businesses can use it as a primary connection, a secondary connection to enhance reliability, to set up a temporary work site, or even to deliver highly secure connectivity needs for work-from-home employees independent of their home broadband connection.
AT&T Wireless Broadband has no overage charges. This fixed wireless solution is an essential ingredient we laid out more than two years ago in our pathway to 5G for businesses. New 5G routers, combined with the AT&T Wireless Broadband plans, will together provide options that make sense for how businesses use the service.
“It is now almost a full year since the global pandemic accelerated remote work adoption by almost a decade – and throughout the rapid evolution of related business needs, AT&T has been there to enable continued success,” said Mo Katibeh, Chief Product and Platform Officer, AT&T Business. “And today, we’re excited to build on the first, true nationwide business-focused broadband network with fixed wireless 5G connectivity. It’s the ideal solution for businesses to continue to innovate, serve their customers and enable employees to efficiently and effectively work – even when they can’t walk down the hall to someone else’s office.”
Other Voices:
“We work in construction sites across the country, designing and building the electrical systems for new buildings, and we need to be agile for fast-moving construction projects,” says Joe Meadors, Vice President of Information Services for Gaylor Electric. “While working in our trailers at these construction sites across the country, quick service turn up, reliability and flexibility, without overage costs, are hugely important. The lower latency and higher bandwidth that will come with AT&T Wireless Broadband using 5G will be perfect for keeping us connected on the job sites.”
Louis Malooley, Owner and General Manager of AlphaGraphics in Atlanta uses AT&T Business Fiber to keep his printing and marketing business connected. With equivalent Fiber speeds for downloads and uploads, he can reliably process huge documents and presentations that need immediate attention. With AT&T Office@Hand, he can keep employees connected and productive while on the go with voice, fax, text messaging, and audio and video conferencing cloud -based services. “You guys are reliable. The service just works,” he said.
“At The Washington Post, we value being forward-looking especially when it comes to new ways to think about news gathering, production and immersive storytelling. As our staff works outside of the office, even in remote areas, it’s critical that we have fast and reliable technology tools, such as wireless connectivity and 5G capabilities, to keep our teams connected and to ensure our readers can be quickly informed,” said Shailesh Prakash, Chief Information Officer at The Washington Post.
“AT&T is very strong in the global enterprise mobility services market, offering professional services, mobile platforms, devices, and managed applications, with single billing and point of care, to provide business transformation,” says Kathryn Weldon, Research Director at GlobalData. “AT&T continues its investment in the breadth, densification and technical capabilities in mobile security, device management, and end-to-end gigabit connectivity options for businesses looking to transform to match today’s environment. In 2020, AT&T announced a collaboration with Cradlepoint, to bring end-to-end gigabit LTE and 5G wireless WAN solutions to enterprise and public safety customers; and alliances with Nokia and Ericsson to build private cellular networks solutions over CBRS. AT&T’s enterprise mobility management portfolio leverages the best platforms available, alongside professional services to manage and secure devices.”
Why choose “enterprise-grade” solutions?
AT&T says they have always been focused on delivering enterprise-grade solutions. Businesses of all sizes turn to us because we’re mission-tested and compete on a global scale.
Dating back to March 2020, AT&T quickly saw large-scale work-from-home policies become commonplace. Enterprise-grade solutions were quickly needed for everyone working from home, and broadband connectivity was essential. And the right data plans were critical for AT&T’s customers. (Shared, pooled rate plans are desired for thousands of businesses across every vertical industry.)
AT&T says they have continued delivering enterprise-grade solutions to solve real business CIO and CTO challenges – collaboration tools for employees, managing networks that balance performance and privacy, and protecting its users, devices, data, and applications.
- Enterprise-grade work-from-everywhere collaboration: All of us are accessing different video and voice platforms throughout the day. Businesses everywhere must ensure they have the right software-based collaboration tools to meet their needs. This is why we deliver recognized industry leading enterprise-grade options – for well over a decade blending the wired and wireless worlds to ensure businesses never miss a call. And we don’t limit you to only mobile solutions. AT&T creates the seamless ability for your business to be on, across all devices – mobile, desk phones, tablets, personal computers – in the office, or on the go.
- Enterprise-grade security: From small businesses to global enterprises, everyone needs unified protection against security threats for office, home office and roaming users. Businesses must protect their employees against these threats, while also restricting access to unauthorized content. We provide remote workforce security solutions, including AT&T’s Global Security Gateway, to protect work-from-home capabilities.
- Enterprise-grade customer experience: To help ensure seamless employee remote capabilities, businesses of all sizes have turned to us to help navigate the shift to work from home. In fact, from mid-March through May 2020 when the pandemic quickly dispersed the workforce to work from home, we quickly delivered over 16,000 business-critical requests for our customers. Businesses turn to us because we’re mission-tested, compete on a global scale and provide trusted advice to develop the right path aligning to their needs. And, of course, because most businesses don’t close on the weekends, we don’t either in our 24×7 customer support. Surprisingly, some of our competitors don’t do this … that’s an odd “customer-first approach.”
Businesses can learn more about AT&T’s remote and home workforce connectivity solutions and sign up for AT&T Wireless Broadband. You can check out AT&T’s connectivity solutions here, and check out all our AT&T Wireless Broadband Plans and find out how your business can sign up here.
SOURCE AT&T Communications

Key Findings from Flexera’s 2021 State of the Cloud report
Cloud computing adoption was expanding rapidly even before the COVID-19. The urgent changes to business operations and procedure caused organization plans and adoption to increase at an even greater rate.
According to Flexera’s 2021 State of the Cloud report, organizations are rapidly progressing their journey to cloud. The report found that public cloud spending is now a significant line item in IT budgets, especially among enterprise organizations (31%) that said they spent more than $12 million a year on public cloud services.
The survey polled 750 “cloud decision-makers and users” from organizations ranging from 100 employees to more than 10,000 employees around the world and across a cross-section of organizations. It specifically asked about services run on AWS, Microsoft Azure, GCP, VMware Cloud on AWS, IBM Public Cloud, Oracle Infrastructure Cloud, and Alibaba Cloud.
AWS continues to be the leading cloud service provider with 79% of enterprise respondents saying they use the platform and 9% saying they are “experimenting” with AWS. Microsoft’s Azure was used by 76% of respondents. 11% of respondents said they are experimenting with Azure.
Azure adoption increased among all respondents in 2020. It increased from 63% last year to 73% this year. By comparison, AWS’ year-over-year growth was just 1 percentage point to 77%.
While AWS and Azure are compete for the #1 cloud service provider, GCP saw the strongest growth among the top three, growing from 34% usage last year to 49% usage this year. Additionally, GCP and VMware Cloud on AWS reported the highest number of respondents experimenting on their platforms, which the Flexera report says could drive future cloud adoption.
The following are some of the responses of interest:
Enterprises embrace multi-cloud:
• 92 percent of enterprises have a multi-cloud strategy; 80 percent have a hybrid cloud strategy
• 49 percent silo workloads by cloud, with 45 percent integrating data between clouds
• Only 42 percent of all participating organizations use multi-cloud management tools
• Respondents use an average of 2.6 public and 2.7 private clouds
Public cloud adoption continues to accelerate:
• 36 percent of enterprises spend more than $12 million per year on public clouds
• 55 percent of enterprise workloads are expected to be in a public cloud within twelve months
• 90 percent of respondents who answered a question about COVID-19 expect cloud use to exceed plans due to the pandemic
• The top challenge in cloud migration is understanding application dependencies
Understanding cloud initiatives and metrics:
• 61 percent of organizations plan to optimize cloud costs in 2021, making it the top initiative for the fifth year in a row
• 59 percent of organizations plan to focus on cloud migration
• 76 percent of organizations use cost efficiency and savings to measure cloud progress
Organizations are taking a centralized approach to cloud:
• 77 percent of enterprises have a central cloud team or cloud center of excellence (CoE)
• 54 percent of cloud teams are responsible for governing infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS)/ platform-as-a-service (PaaS) usage and costs
• 63 percent of enterprises reported using cloud managed service providers (MSPs) to manage public cloud use
The Flexera survey found that it remains difficult to map all of the relationships across applications, hardware, and networking devices for each service, especially in a rapidly evolving environment. Just over half of respondents reported understanding application dependencies as the top cloud migration challenge.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Selected Charts from the Flexera 2021 Cloud Report:




References:
https://info.flexera.com/CM-REPORT-State-of-the-Cloud
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2021/02/10/oracele-expands-cloud-portfolio-key-themes-for-cloud-in-2021/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2021/03/01/ibms-cloud-satellite-service-in-generally-available-orbit/
ITU-R and 3GPP: Use of IMT for Cellular-Vehicle-to-Everything Applications
ITU-R WP5D is working on a preliminary draft report titled, “The use of the Terrestrial Component of IMT for [Cellular-Vehicle-to-Everything] Application.”
When completed (TBD), the report will address the perceived mutual relationship between IMT (International Mobile Telecommunications) technologies and Cellular-Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2X) as a specific application and elements of functions in IMT technologies that are used to realize C-V2X applications.
Author’s Note:
Vehicle to everything (V2X) is a term that refers to high-bandwidth, low latency and highly reliable communication between a broad range of transport and traffic-related sensors. Many pundits and cheerleaders say that 5G mobile networks will be key to providing connectivity for vehicle to vehicle (V2V) and vehicle to infrastructure (V2I) communications. Others say that the 4G-LTE V2X sidelink will do just fine.

Also, there are two different types of V2X systems – one based on IEEE 802.11 standards and another (cellular) based on 3GPP specifications. That’s illustrated in this chart:

The focus of this article is on the Cellular-V2X system, previously developed by 3GPP and now via the aforementioned new draft ITU-R report.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The future ITU-R report will provide details and an overview on: Usage of IMT technology, Relationship between IMT and C-V2X, Characteristics and Capabilities supported by IMT, and Case Studies associated with C-V2X for the various scenarios including eMBB, mMTC, and URLLC of terrestrial component of IMT.
IMT usages relevant to vehicle communication are also indicated in the ITU-R M.2445 “ITS usage” report.
The C-V2X applications [described in the 3GPP Release 16 specifications], referred to as Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X), contain the following four different types:
– Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V)
– Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I)
– Vehicle-to-Network (V2N)
– Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P)
…………………………………………………………………………………….
Utilizing 5G to enhance automotive safety was a focus area for 3GPP Release 16. Release 14 C-V2X introduced a 4G-LTE sidelink (V2V, V2I, V2P) to support basic safety use cases. Release 16 builds on Release 14/15 by introducing a NR-based sidelink that will enable new advanced safety use cases while also paving the path for autonomous driving. Release 16 supports reliable and efficient multicast communication based on HARQ feedback and uses distance as a new dimension at the physical layer, which enables “on-the-fly” multicast groups based on distance and applications.

Relevant ITU-R Recommendations and Reports:
Recommendation ITU-R M.1890 Operational radiocommunication objectives and requirements for advanced Intelligent Transport Systems
Recommendation ITU-R M.2083 IMT Vision – Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2020 and beyond
Recommendation ITU-R M.2084 Radio interface standards of vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure two-way communications for Intelligent Transport System applications
Recommendation ITU-R M.2121 Harmonization of frequency bands for Intelligent Transport Systems in the mobile service
Report ITU-R M.2228 Advanced intelligent transport systems (ITS) radiocommunications
Report ITU-R M.2441 Emerging usage of the terrestrial component of International Mobile Telecommunication (IMT)
Report ITU-R M.2444 Examples of arrangements for Intelligent Transport Systems deployments under the mobile service
Report ITU-R M.2445 Intelligent transport systems (ITS) usage
Handbook on Land Mobile (including Wireless Access) – Volume 4: Intelligent Transport Systems
[Editor’s note: More references to be added]
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://blog.3g4g.co.uk/2020/07/an-introduction-to-vehicle-to.html
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9212349
https://www.gsma.com/iot/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/02_5GAA_Maxime-Flament.pdf
https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-r/opb/rep/R-REP-M.2441-2018-PDF-E.pdf
http://www.eng.auburn.edu/~szm0001/papers/3gpp_v2x.pdf
PON’s Vulnerability to Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
by Shrihari Pandit
Introduction:
The dominant architecture used in fiber optic deployment -Passive Optical Networks (PONs) may be vulnerable to attack. It is important to bring attention to this under-appreciated weakness and discuss what steps are possible to protect fiber infrastructure.
As various PON technologies are long standing and widely deployed, this is a matter of no small concern. PONs are widely deployed by Verizon FiOS, AT&T U-verse and many others.
The PON architecture is a hodgepodge of old and new technologies, hardware and strategy, limited budget and often is not overseen by a single team.
In this article we describe how fiber optic infrastructure based on PONs may be open to potential denial of service (DoS) attacks via optical signal injections. Security experts warn that this is a growing issue, which could take down entire sectors of PON segments.
Considering the ever increasing state-sponsored and non-state-actor cyber attacks, these types of vulnerabilities that allow for massive disruption for large groups of people are very attractive targets.
PON Overview:
The cost advantages of PON architecture make it the overwhelming choice for FTTH deployments. PON allows wireline network providers to deliver service to businesses and homes without having to install costly active electronics on roads, curb-side or even within buildings themselves.
Active electronics, on the other hand, add cost and create operational complexity as deployments scale. The conveniences and differentiators of PONs are precisely what opens up the floodgates to serious vulnerabilities.
PONs are fundamentally susceptible due to the architecture from the passive optical splitter (POS) to the optical network unit (ONU) within the overall network infrastructure. The POS component of the network functions like a bridge, allowing any and all communications to transverse without the ability to filter, limit or restrict flow.
The fiber optic market currently boasts 585.9 million subscribers worldwide, with that number set to grow to 897.8 million subscribers by 2021.
The industry has moved to upgrade 1st generation GPONs and EPONs to next-generation PONs, like NG-PON2 (the favorite), XG-PON1 and XGS-PON. For example, Verizon uses the Calix AXOS E9-2 Intelligent Edge System for large-scale NG-PON2 deployments that began in the first quarter of 2018.
However, with subscriber density significantly increasing per PON segment, the risks increase as more subscribers are affected by a cyber attack on a single fiber.
Sidebar: NG-PON2
NG-PON2 combines multiple signals onto a single optical fiber by using the different wavelengths of laser light (wave division multiplexing), and then splits transmission into time slots (time division multiplexing), in order to further increase capacity. NG-PON2 is illustrated in the figure below.

Legend:
OLT =Optical Line Termination ONT =Optical Network Termination
NGPON2 has three key advantages for operators:
1. Cost
Firstly, it can co-exist with existing GPON and NGPON1 systems and is able to use existing PON-capable outside plant. Since the cost of PON FTTH roll out is 70 per cent accounted for by the optical distribution network (ODN), this is significant. Operators have a clear upgrade path from where they are now, until well into the future.
2. Speed
Initially NGPON2 will provide a minimum of 40 Gb/s downstream capacity, produced by four 10 Gb/s signals on different wavelengths in the O-band multiplexed together in the central office with a 10 Gb/s total upstream capacity. This capability can be doubled to provide 80 Gb/s downstream and 20 Gb/s upstream in the “extended” NGPON2.
3. Symmetrical upstream/downstream capacity
Both the basic and extended implementations are designed to appeal to domestic consumers where gigabit downstream speeds may be needed but more modest upstream needs prevail. For business users with data mirroring and similar requirements, a symmetric implementation will be provided giving 40/40 and 80/80 Gb/s capacity respectively.
………………………………………………………………………………………
The Essence of a PON Cyber Attack:
Given the flashpoints around the globe, it doesn’t take much imagination to envision how state and non-state actors might want to cause such a chaotic and widespread disruption.
If a “cyber criminal” gains access to the underlying fiber, they could inject a wideband optical signal to disrupt communications for all subscribers attached to the PON segment.
Alternatively, at your home the adversary could manipulate the ONU’s optical subsystem to transmit abnormal PON signals and impact service to all subs on that segment. Communications including internet, voice and even analog TV signals that operate on nearby wavelengths would be susceptible to these serious DoS attacks.
Possible Solutions, Preventive Methods and Procedures:
So, what can be done with current equipment without a massive and costly fiber optic network overhaul? The unfortunate answer is that an overarching vulnerability will always exist as long as the passive components are in place. A reactionary process is the best and only option.
The current primary solution for operators is to reduce the number of subscribers per PON segment as a way to manage risks. If an attack was detected, the network operator would be able to localize the source and identify and disconnect the bad actor from the network. But it’s easier said than done.
This sort of manual process is not ideal. Extensive PON outages means spending the time and money to send personnel to optical line terminals to check each individual port until the attacker is found. The installation of active electronics on each PON segment or near PON subscribers is unrealistic and impractical. That undertaking would actually be more costly in terms of time, money and location.
The best ongoing solution is that operators should consider installing passive tap points per PON segment. Each can be independently routed back and managed at a provider’s operations center and allow operators to effectively analyze segments and detect unusual optical light levels that may signal an attack.
At that point the operator could physically dispatch techs on-site to continue the localization and resolution process while ensuring other non-threatening users remain unaffected. This solution is to effectively take a reactionary restriction and make it as automatic and proactive as currently possible.
Conclusions:
P2MP (point to multi-point) architecture has become the most popular solution for FTTH and FTTP. Yet there needs to be a severe increase in awareness to potential PON vulnerability into the next generation.
If we can catalyze the telecom industry to develop methods and measures to protect infrastructure, such crippling network security issues will be stopped before widespread exploits occur.
The industry needs to address these concerns sooner rather than later or else be left without effective countermeasures against these very real threats.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/cyberpedia/what-is-a-denial-of-service-attack-dos
https://s2.ist.psu.edu/paper/ddos-chap-gu-june-07.pdf
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G93I_v2pa24
……………………………………………………………………………….
About Shrihari Pandit:
Shrihari Pandit is the President and CEO of Stealth Communications, the NYC-based ISP he co-founded in 1995. Stealth, having built its own fiber-optic network throughout the city, provides high-bandwidth connectivity services to a broad roster of customers in business, education and government.
Prior to Stealth, Mr. Pandit was a network-security consultant to various software and telecom companies, including MCI, Sprint and Sun Microsystems. He also served as an independent consultant to several U.S. agencies, including NASA and the National Infrastructure Protection Center (NIPC), now part of the Department of Homeland Security.
Dell’ Oro: Huawei still top telecom equipment supplier; optical transport market +1% in 2020
Huawei has increased its lead as the#1 global telecoms network equipment vendor, boosting its revenue share by a three percentage points last year, according to Dell’Oro Group. Nokia lost one percentage point of revenue share year-on-year, as did Cisco, the latter falling to 6%. Ericsson gained one percentage point to match Nokia at 15% of the market and ZTE also saw a 1% uptick to 10% of the global telecom market. (Please refer to chart below).
Dell’Oro Group’s preliminary estimates suggest the overall telecom equipment market – Broadband Access, Microwave & Optical Transport, Mobile Core & Radio Access Network, SP Router & Carrier Ethernet Switch (CES) – advanced 7% year-over-year (Y/Y) for the full year 2020, growing at the fastest pace since 2011.
The telecom and networking market research firm suggests revenue rankings remained stable between 2019 and 2020, with Huawei, Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Cisco, Ciena, and Samsung ranked as the top seven suppliers, accounting for 80% to 85% of the total market. At the same time, revenue shares continued to be impacted by the state of the 5G rollouts in highly concentrated markets. While both Ericsson and Nokia improved their RAN positions outside of China, initial estimates suggest Huawei’s global telecom equipment market share, including China, improved by two to three percentage points for the full year 2020.
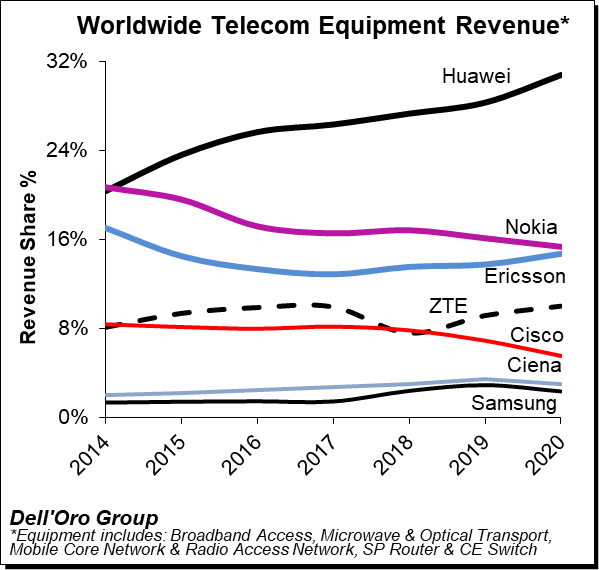
Dell’Oro now estimates the following revenue shares for the top seven suppliers:
| Top 7 Suppliers | Year 2019 | Year 2020 |
| Huawei | 28% | 31% |
| Nokia | 16% | 15% |
| Ericsson | 14% | 15% |
| ZTE | 9% | 10% |
| Cisco | 7% | 6% |
| Ciena | 3% | 3% |
| Samsung | 3% | 2% |
Additional key takeaways from the 4Q2020 reporting period:
- Preliminary estimates suggest that the positive momentum that has characterized the overall telecom market since 1Q-2020 extended into the fourth quarter, underpinned by strong growth in multiple wireless segments, including RAN and Mobile Core Networks, and modest growth in Broadband Access and CES.
- Helping to drive this output acceleration for the full year 2020 is faster growth in Mobile Core Networks and RAN, both of which increased above expectations.
- Covid-19 related supply chain disruptions that impacted some of the telco segments in the early part of the year had for the most part been alleviated towards the end of the year.
- Not surprisingly, network traffic surges resulting from shifting usage patterns impacted the telecom equipment market differently, resulting in strong demand for capacity upgrades with some technologies/regions while the pandemic did not lead to significant incremental capacity in other cases.
- With investments in China outpacing the overall market, we estimate Huawei and ZTE collectively gained around 3 to 4 percentage points of revenue share between 2019 and 2020, together comprising more than 40% of the global telecom equipment market.
- Even with the higher baseline, the Dell’Oro analyst team remains optimistic about 2021 and projects the overall telecom equipment market to advance 3% to 5%.
Dell’Oro Group telecommunication infrastructure research programs consist of the following: Broadband Access, Microwave Transmission & Mobile Backhaul, Mobile Core Networks, Mobile Radio Access Network, Optical Transport, and Service Provider (SP) Router & Carrier Ethernet Switch.
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
Last week, Dell’Oro Group reported that the optical transport equipment revenue increased 1% in 2020 reaching $16 billion. In this period, all regions grew with the exception of North America and Latin America.
“Between concerns on starting new optical builds during the start of the pandemic and aggressive plans on 5G deployments that required a larger share of a service provider’s capital budget, the spending on optical transport dramatically slowed by the end of 2020,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group.
“It was a really dramatic drop in optical equipment purchases in the fourth quarter. While we anticipated a slowdown near the end of the year due to concerns around COVID-19, we were surprised by a 29 percent year-over-year decline in WDM purchases in North America as well as a 12 percent decline in China. That said, there was good growth in the other parts of the world, especially Japan,” continued Yu.
| Optical Transport Equipment Market | |
| Regions | Growth Rate in 2020 |
| North America | -6% |
| Europe, Middle East and Africa | 2% |
| China | 1% |
| Asia Pacific excluding China | 13% |
| Caribbean and Latin America | -14% |
| Worldwide | 1% |
The Dell’Oro Group Optical Transport Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, unit shipments (by speed including 100 Gbps, 200 Gbps, 400 Gbps, and 800 Gbps). The report tracks DWDM long haul, WDM metro, multiservice multiplexers (SONET/SDH), optical switch, optical packet platforms, data center interconnect (metro and long haul), and disaggregated WDM. To purchase this report, please email [email protected].
References:
Deutsche Telekom tests 5G standalone video call
“Our goal is to continue to actively shape the future of mobile communications. 5G standalone is important to be able to use technologies such as network slicing or edge computing,” says Claudia Nemat, Board Member Technology and Innovation at Telekom. “We are very proud to have taken the next innovation step in 5G. With this test, we are once again demonstrating our innovation leadership.”
DT first announced tests of its 5G standalone network in February. At the time, Walter Goldenits said the Garching test represented the first step towards the 5G standalone live network, although he also noted that a rollout “will then also depend on the requirements of our customers. Technology and the market will play a joint role in further development.”
Goldenits said more than two thirds of people in Germany are now covered by the operator’s non-standalone 5G network (5G NSA), which is anchored to the existing 4G-LTE infrastructure.
5G NSA (EPC) vs 5G SA (5G Core):

Image Courtesy of GSMA
Important Question:
We wonder how DT is collaborating with T-Mobile US which has already deployed a 5G SA/5G Core network? DT owns 43% of T–Mobile, but the shareholder pact with Softbank assures it of strategic control and allows it to consolidate results of its largest subsidiary at group level. Cooperation is essential to ensure interoperability and 5G SA roaming, because there is no implementation standard or open specification for 5G SA/5G Core network (as we have written so many times).
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
Deutsche Telekom, Orange, Telefónica and Vodafone also recently pledged their support for Open RAN technology in the hope a joint commitment will attract investment, speed up the development of products that can be used in mainstream networks and produce new European wireless network equipment suppliers.
Leichtman Research Group: Top U.S. Broadband Providers Add; PayTV Providers Lose Subscribers in 2020
Leichtman Research Group reports that largest U.S. broadband network providers added almost twice as many fixed subscribers in 2020 as they did the previous year, largely due to the Covid-19 pandemic. However, some large broadband providers (like AT&T) lost customers.
The largest cable and wireline phone providers in the U.S. – representing about 96% of the market – acquired about 4,860,000 net additional broadband Internet subscribers in 2020, compared to a pro forma gain of about 2,550,000 subscribers in 2019.
These top broadband providers now account for 105.8 million subscribers, with top cable companies having 72.8 million broadband subscribers, and top wireline phone companies having 33 million subscribers.
Comcast and Charter accounted for 4.19 million, or 86%, of the total number of net additions, with the other six cablecos’ adds coming in significantly lower, ranging from 210,000 for Cox to just under 38,000 for Atlantic Broadband.
For wireline telcos, the best performance came from Verizon, which added a fairly respectable 173,000 fixed broadband customers, but three of the eight posted net customer losses. In particular, AT&T’s net broadband losses came in at 5,000 while CenturyLink and Frontier both lost well over 100,000 customers.
[As per the report below, AT&T’s DirecTV lost more than 3.26 million subscribers which was ~60% of all U.S. pay TV losses in 2020.]
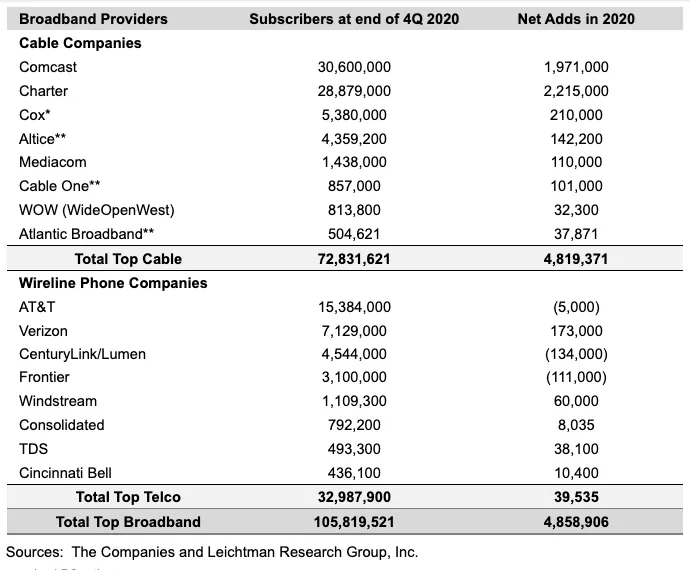
Notes:
* LRG estimate
** Includes recent small acquisitions/sales and LRG pro forma estimates
^ Frontier’s total for 4Q 2020 is an LRG estimate due to later year-end reporting
TDS includes 283,900 wireline broadband subscribers, and 209,400 cable broadband subscribers
…………………………………………………………………………………….
Key findings for the year 2020 include:
- Overall, broadband additions in 2020 were 190% of those in 2019, and more than in any year since 2008
- Top cable and wireline phone companies represent approximately 96% of all subscribers
- The top cable companies added about 4,820,000 subscribers in 2020 – compared to about 3,145,000 net adds in 2019, and the most in any year since 2006
- Charter’s 2,215,000 net broadband additions in 2020 were more than any company had in a year since 2006
- The top wireline telecom companies added about 40,000 subscribers in 2020 – compared to a loss of about 590,000 subscribers in 2019
- Telcos had positive net annual broadband adds for the first year since 2014
- At the end of 2020, cable had a 69% market share vs. 31% for Telcos
“With the impact of the coronavirus pandemic, there were more net broadband additions in 2020 than in any year since 2008,” said Bruce Leichtman, president and principal analyst for Leichtman Research Group, Inc (LRG). “The top cable and Telco broadband providers in the U.S. cumulatively added about 4,860,000 subscribers in 2020, compared to about 5,100,000 subscribers in 2018 and 2019 combined.”
Separately, LRG found that the largest pay-TV providers in the U.S. – representing about 95% of the market – lost about 5,120,000 net video subscribers in 2020, compared to a pro forma net loss of about 4,795,000 in 2019.
The top pay-TV providers now account for about 81.3 million subscribers – with the top seven cable companies having 43.9 million video subscribers, satellite TV services having about 21.8 million subscribers, the top telephone companies having 7.9 million subscribers, and the top publicly reporting Internet-delivered (vMVPD) pay-TV services having 7.7 million subscribers.
AT&T had a net loss of about 3,260,000 subscribers across its four pay-TV services (DIRECTV, AT&T U-verse, AT&T TV, and AT&T TV NOW) in 2020 – compared to a net loss of about 4,095,000 subscribers in 2019.
AT&T “Premium TV” services (not including the vMVPD service AT&T TV NOW) lost 15.3% of subscribers in 2020 – compared to a 4.6% loss among all other traditional pay-TV services.
Key findings for the year include:
- Satellite TV services lost about 3,440,000 subscribers in 2020 – compared to a loss of about 3.700,000 subscribers in 2019
- The top seven cable companies lost about 1,915,000 video subscribers in 2020 – compared to a loss of about 1,560,000 subscribers in 2019
- The top telco TV companies lost about 405,000 video subscribers in 2020 – compared to a loss of about 630,000 subscribers in 2019
- The top publicly reporting Internet-delivered (vMVPD) services (Hulu + Live TV, Sling TV, AT&T TV NOW, and fuboTV) added about 640,000 subscribers in 2020 – compared to about 1,095,000 net adds in 2019
- Traditional pay-TV services (not including vMVPDs) lost about 5,765,000 subscribers in 2020 – compared to a net loss of about 5,890,000 in 2019
“Net pay-TV losses of over 5 million subscribers in 2020 were slightly higher than in 2019, and more than in any previous year,” said Bruce Leichtman, president and principal analyst for Leichtman Research Group, Inc. “Overall, the top pay-TV providers lost 5.9% of subscribers in 2020, compared to 5.2% in 2019.”
About Leichtman Research Group, Inc.
Leichtman Research Group, Inc. (LRG) specializes in research and analysis on broadband, media and entertainment industries. LRG combines ongoing consumer surveys with industry tracking and analysis, to provide companies with a richer understanding of current market conditions, and the potential impact and adoption of new products and services. For more information about LRG, please call (603) 397-5400 or visit www.LeichtmanResearch.com.
References:
https://www.leichtmanresearch.com/about-4860000-added-broadband-from-top-providers-in-2020/
https://www.leichtmanresearch.com/major-pay-tv-providers-lost-about-5120000-subscribers-in-2020/
https://telecoms.com/508907/pandemic-provided-a-shot-in-the-arm-for-us-fixed-broadband/
Verizon is again top U.S. telco brand; AT&T falling behind T-Mobile
According to Brand Finance’s new rankings, Verizon recently widened its lead over AT&T as the world’s most valuable telecoms brand. The firm reported Verizon’s brand rose 8% in its rankings to a value of $68.9 billion.
For the second year in a row Verizon has claimed the title of the world’s most valuable telecoms brand following an 8% increase in brand value to US$68.9 billion. This brand value growth has not only propelled it back into the top 10 most valuable brands globally in the Brand Finance Global 500 2021 ranking, but has meant the brand has continued to widen the lead over second placed AT&T (brand value down 13% to US$51.4 billion). 15 further US brands feature in the Brand Finance Telecoms 150 2021 ranking, with a combined brand value of US$182.8 billion.
Two years since the beginning of Verizon’s business transformation program, Verizon 2.0 – focusing on the transformation of the network, the go-to-market, the brand, and the culture of the business – the brand continues to make leaps and bounds across the industry. The giant is widely recognized to have the best-in-class network and the widest coverage in the US, with the network’s usage surging during the pandemic, handling a staggering 800 million phone calls and 8 billion texts per day.
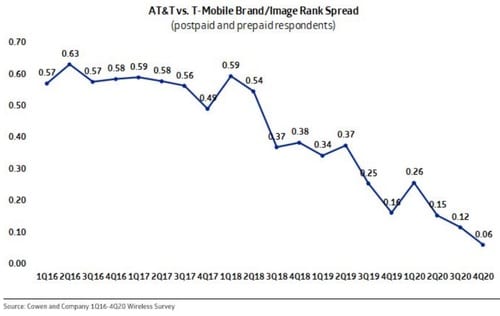
Meanwhile, Cowen and Company sees T-Mobile overtaking AT&T to be the second most popular telecom brand after Verizon. Cowen analysts conduct quarterly surveys of mobile customers, asking them to rank providers for “overall brand/image.”
In the 4th Quarter of 2020, the perceived difference between T-Mobile and AT&T was at its narrowest point since they started conducting their survey. As per the chart below, there was only a 0.06 difference between the two brands (we do not know how Cowen calculated the Rank Spread).
Cowen stated this brand perception issue will be an important to watch during 2021 because “network quality/coverage has historically been one of the main reasons for subscribers to leave their current wireless provider and likely a key driver of brand perception.”
The Cowen Telco Perceptions report (clients only) comes months after T-Mobile boasted that it surpassed AT&T in terms of total number of mobile phone customers.
Analyst Craig Moffett was shocked with AT&T’s $23.4 billion spent at the recently completed C-band auction. He wrote in a note to clients:
“At $23.4B, AT&T spent more than would have been expected a month ago, but expectations for their spend had been rising (notwithstanding the fact that they have only financed half of what they bought, and even that with only short-term debt), so the surprise may not be large there, either. But again, it’s a shock to see the number.”
“AT&T emerges from the auction with leverage of 4.1x EBITDA (assuming all debt financing). Can their dividend be sustained?”
AT&T bought 80 MHz of C-band spectrum in almost all of the top 50 U.S. markets.
How will they be able to finance the buildout of their 5G network to deploy that spectrum?
If you have an opinion on that, please post a comment in the box below this article. Thanks in advance!
References:
TIP OpenRAN project: New 5G Private Networks and ROMA subgroups
The Telecom Infra Project (TIP), one of several industry consortiums creating specifications for open radio access networks (Open RAN), recently announced a new 5G Private Networks subgroup.
Editor’s Note:
We don’t know whether the TIP OpenRAN project or the O-RAN Alliance has (and will have) more industry influence and impact. In addition, there are many splinter partnerships forming; many of them led by Rakuten Mobile. What’s mind boggling is that none of the groups have liaison agreements with either ITU-R WP5D (responsible for all IMT standards, including 4G and 5G) or 3GPP (the prime spec writing organization for mobile networks).
……………………………………………………………………………………
5G Private Networks contribute to improve the quality of experience for 5G connectivity, including better coverage and capacity through on-premise radio equipment, the ability to support low latency and high bandwidth service requirements through edge compute & routing of private traffic, and the potential to support the increasing demand for privacy and localized data analytics.
For network operators, 5G Private Networks also create the opportunity to implement new network management and operational models, enabling full automation of the operation of the enterprise network while improving end customer application experience.
However, to fully capture the benefits of 5G Private Networks, a different approach is required, because traditional network architectures, focused on large scale deployments and operations don’t have the right economics or the operational flexibility to efficiently deliver on the emerging needs of enterprise customers.
The 5G Private Networks Solution Group will develop a new approach to manage and operate 5G Private Networks, based on a cloud-native architecture, and making use of a new class of software management tools, based on the paradigms currently used for the cloud, but adapted to deliver the requirements of a telecom network environment. Telefónica will test the solution in their local TIP Community Lab in Madrid and then move to field trials in Málaga (Spain).
Juan Carlos Garcia, SVP Technology Innovation & Ecosystem, Telefónica, and TIP Board Director said: “This new solution group will enable operators to address the exciting opportunities that 5G is creating in the enterprise segment, both through valuable features for our customers and more efficient network operations. The TIP community is the perfect environment for this innovation, as it will allow us to leverage multiple current project groups (Open Core Networks, OpenRAN) to deliver an end-to-end Minimum Viable Product that we will then test in Telefonica’s TIP Community Lab.”
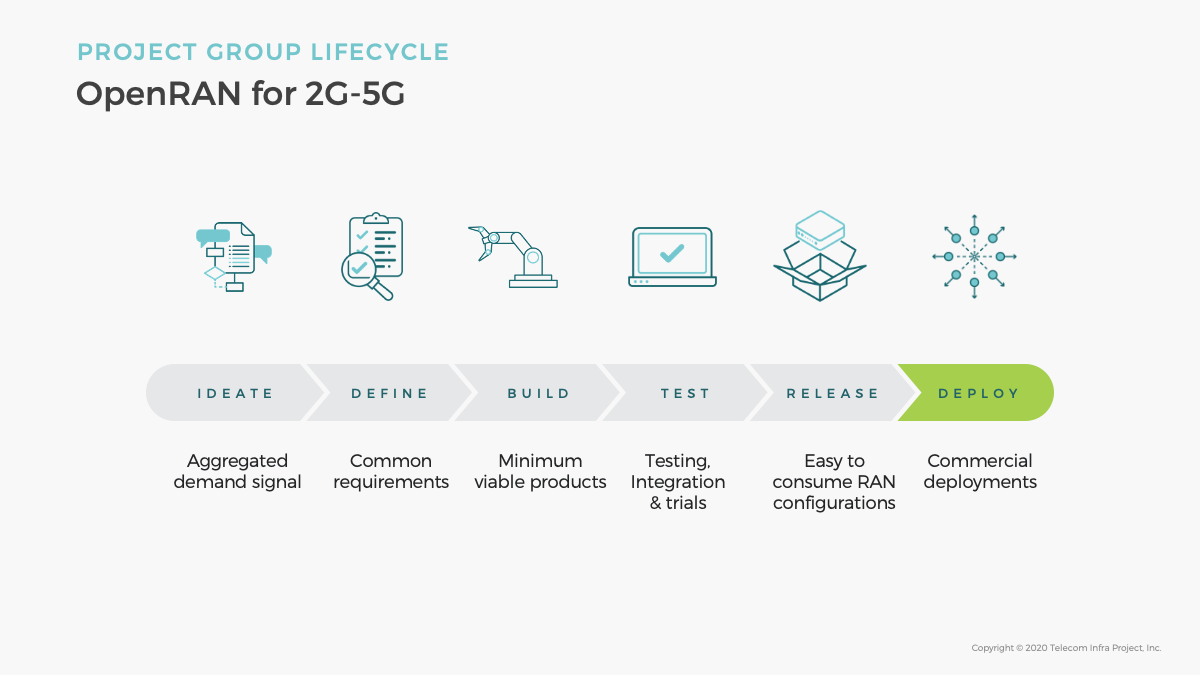
In particular, the new Solutions Group will leverage previous work contributed to TIP’s OpenRAN Project Group, on a first version of a CI/CD platform that applies traditional IT methodologies to automate integration, testing and deployment of OpenRAN software.
Ihab Tarazi, CTO and SVP, Networking and Solutions, Dell Technologies and TIP Board Director, said: “For open networks to deliver their benefits, the telecom industry needs an abstraction layer that helps integrate different components into end-to-end solutions. New software management tools based on the ones currently used for the cloud can address this need, and this Solution Group is a timely initiative for the industry to collaborate on making this happen.”
Caroline Chan, VP and GM Network Business Incubation Division, Intel and TIP Board Director, said: “Through the recently launched solution groups, TIP is expanding its scope to include the validation of interoperability between different elements across the whole network, and insights and recommendations about how to operate them. The new 5G Private Networks Solution Group is a strong example of this approach. With dedicated local private high-performance network connectivity as a key emerging deployment model for 5G and edge buildout, this group can help foster important ecosystem collaboration.”
As a result, this new solution group will help drive:
- Improved network economics, through the use of commoditized hardware and open source software, and more efficient and flexible network operations and automation, enabled by the adoption of cloud-native technologies.
- Dedicated local high-performance 5G connectivity and edge computing infrastructure, appealing to multiple B2B & B2B2C verticals.
- Better network security and performance.
Telefónica is one of the five European telcos that announced that they will work together on open RANs for mobile networks. The others are Deutsche Telekom, Orange, TIM and Vodafone. A memorandum of understanding (MOU) for that grouping commits the five to the O-RAN Alliance, which has 27 network operator members from AT&T to Vodafone, and to “other industry initiatives, such as the Telecom Infra Project, that contribute to the development of open RAN and that aim to create a healthy and competitive open RAN ecosystem and advance R&D efforts.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, the charter of the new OpenRAN Orchestration and Management Automation (ROMA) subgroup was approved by the OpenRAN PG. ROMA focuses on aggregating and harmonizing mobile network operators requirements on Open RAN orchestration and lifecycle management automation, fostering ecosystem partners to develop products and solutions that meet ROMA requirements.
The goal of ROMA is to:
· Develop a common set of use cases for OpenRAN lifecycle management automation and orchestration that are agreed across multiple MNO and OpenRAN ecosystem members
· Develop Technical Requirements on products and solutions that support the identified use cases, including interfaces and data models
· Facilitate product and solution development through lab testing, field trials, participating TIP Plugfest and badging on TIP exchange etc.
· Support large scale OpenRAN deployment with lifecycle management automation, including Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) frameworks and tool sets.
It will bring better coverage and capacity through on-premise radio equipment, says TIP, and the ability to support low latency and high bandwidth service requirements through edge compute and routing of private traffic, and the potential to support the increasing demand for privacy and localized data analytics.
……………………………………………………………………
About the Telecom Infra Project:
The Telecom Infra Project (TIP) is a global community of companies and organizations that are driving infrastructure solutions to advance global connectivity. Half of the world’s population is still not connected to the internet, and for those who are, connectivity is often insufficient. This limits access to the multitude of consumer and commercial benefits provided by the internet, thereby impacting GDP growth globally. However, a lack of flexibility in the current solutions – exacerbated by a limited choice in technology providers – makes it challenging for operators to efficiently build and upgrade networks.
Founded in 2016, TIP is a community of diverse participants that includes hundreds of companies – from service providers and technology partners, to systems integrators and other connectivity stakeholders. We are working together to develop, test and deploy open, disaggregated, and standards-based solutions that deliver the high-quality connectivity that the world needs – now and in the decades to come.
Find out more: www.telecominfraproject.com
References:
Learn more and join the new 5G Private Networks Solution Group here.
https://telecominfraproject.com/tip-launches-5g-private-networks-solution-group/