Month: February 2024
Highlights of GSMA study: Mobile Net Zero 2024, State of the Industry on Climate Action
Reducing carbon emissions has been a top priority for global network operators and equipment vendors for the past few years. Many have published net zero targets and use every opportunity to include their sustainability agenda into their public announcements. In 2019, the mobile industry set a goal to reach net zero by 2050, becoming one of the first sectors in the world to set such an ambitious target.
A new GSMA study titled Mobile Net Zero 2024, State of the Industry on Climate Action, the fourth of its kind, provides a glimpse of how they are progressing.

Over the past year, eight network operators submitted new near-term targets to the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi), bringing the total to 70 operators and
representing nearly half of global mobile connections. Fifty-three operators have also
committed to net zero targets.
GSMA found that European telcos are leading the way forward. Operational emissions in Europe fell by half in the 2019-2022 period, with some telcos getting a special mention for exceeding that 50% level; Tele2, Telefónica, Telenor, Telia and Vodafone all achieved deeper reductions.
North America also performed well, with operational emissions falling by around 30% over the period, as did Latin America, where TIM Brasil and Telefonica got a shout-out for driving a 22% reduction. And Turkcell was credited as the main orchestrator of a decline of around a fifth in emissions in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA).
However, emissions from operators in Greater China rose by 3% and those from the Asia-Pacific by 10%. While those numbers are not huge, the relative sizes of those markets mean there is a significant impact on the overall figures.
“While this appears challenging, recent progress shows this is within reach,” the report reads. Yet the target reduction rate for operational emissions was exceeded for the past three years in Europe (21% per year), North America (11%), Latin America (8%) and MENA (8%).
Three-quarters of the mobile industry’s carbon emission come from its value chain (Scope 3), highlighting the importance of engaging supply chains and customers. More than 90% of Scope 3 emissions came from just five Scope 3 categories: 1) Purchased goods and services; 2) Capital goods; 3) Fuel- and energy-related activities; 11) Use of sold products; and 15) Investments.
GSA says there is an urgent need for improved data and further analysis to better understand Scope 3 trends.
“The evidence shows that the mobile industry’s commitment to net zero by 2050 is paying off. Despite surging demand for connectivity and data, the global carbon emissions of operators continued to fall,” said John Giusti, Chief Regulatory Officer at the GSMA.
The number of mobile connections globally rose by 7% between 2019 and 2022, and Internet traffic more than doubled, the GSMA said. As such, the industry’s carbon reductions were mainly driven by energy efficiency and the use of renewable energy.
“Although we see the strongest early lead from Europe in the race to net zero, and encouraging progress in the Americas and MENA, this is a race that everybody needs to win – or else we all lose,” Giusti said, assiduously avoiding naming those trailing markets.
References:
Mobile Net Zero 2024: State of the Industry on Climate Action
NTT DOCOMO & SK Telecom Release White Papers on Energy Efficient 5G Mobile Networks and 6G Requirements
NGMN Alliance: Green benchmark for mobile networks
Huawei Execs: ICT Industry Initiatives for 5G and Green 5G Networks for a Low-Carbon Future
Huawei pushes 5.5G (aka 5G Advanced) but there are no completed 3GPP specs or ITU-R standards!
During MWC 2024, Huawei held a new product solution launch event, where George Gao, President of Huawei Cloud Core Network Product Line, released the 5.5G (aka 5G Advanced) intelligent core network solution.
Huawei claims 2024 is the first year for commercialization of 5.5G (this author strongly disagrees- 3GPP 5G Advanced specs are not nearly complete and ITU-R standards work hasn’t even started yet).
“The first year of commercial use of 5.5G has officially arrived, and the commercial rollout of 5.5G is accelerating worldwide,” the China based vendor said. “While Middle Eastern operators have achieved scaled 5.5G commercialization, operators across Europe, Asia Pacific, and Latin America are verifying 10 Gbps [1.], preparing for 5.5G commercialization in 2024,” Huawei added.
Note 1. CCS Insight wrote last month, “operators are deploying greenfield networks in new cities, such as STC in Bahrain and Zain in Saudi Arabia, both of which have achieved 10 Gbps downlink speeds on their 5G-Advanced test networks.”
The company says announced their 5.5G intelligent core network as an important part of 5.5G, incorporating service intelligence, network intelligence, and O&M intelligence.
The claim is that 5.5G technology will improve both business value and development potential. We seriously doubt that!
Service Intelligence Expands the Profitability of Calling Services:
In 2023, New Calling [2.] was put into commercial use for serving up to 50 million subscribers across 31 provinces in China. It has also been verified in Europe, Latin America, the Middle East, and Asia Pacific, and is set to be commercialized in these regions in 2024.
Note 2. New Calling essentially combines voice calls with other elements – fun calling with avatars, for example, or calling with real-time translation or speech-to-text. It is backed by the GSMA (which is NOT a standards body), but to date has been deployed only in China.
As stated by George, the industry’s first New Calling-Advanced solution launched by Huawei embraces enhanced intelligence and data channel-based interaction capabilities. Huawei says that will take us to a multi-modal communication era and helping operators reconstruct their service layout. In addition, Huawei also introduced the Multi-modal Communication Function (MCF) to allow users to control digital avatars through voice during calls, delivering a more personalized calling experience. An enterprise can also customize their own avatar as an enterprise ambassador to promote their branding.
Network Intelligence Enables Experience Monetization and Differentiated Operations:
For a long period of time, operators have strived to realize traffic monetization on MBB networks. However, there are three technical gaps: not assessable user experience, no dynamic optimization, and no-closed-loop operations. To bridge these gaps, Huawei has launched the industry’s first Intelligent Personalized Experience (IPE) solution, aiming to help operators add experience privileges to service packages and better monetize differentiated experiences.
In the industry, the user plane on the core network usually processes and forwards one service flow using one vCPU. As heavy-traffic services increase, such as 2K or 4K HD video and live streaming, microbursts and elephant flows frequently occur. It is, therefore, more likely that a vCPU will become overloaded, causing packet loss. To address this issue, Huawei releases the Intelligent UDG. According to George, this is the industry’s first Intelligent UDG product that can deliver ubiquitous 10 Gbps superior experiences.
O&M Intelligence Achieves High Network Stability and Efficiency:
Empowered by the multi-modal large model, the Digital Assistant & Digital Expert (DAE) reduces O&M workload and improves O&M efficiency. It reshapes cloud-based O&M from “experts+tools” to intelligence-centric “DAE+manual assistance”. With DAE, 80% of trouble tickets can be automatically processed, which is much more efficient than 100% manual processing as it used to be. DAE also enables intent-driven O&M, avoiding manual decision-making. Before, it usually took over five years to cultivate experts in a single domain, however, the multi-modal large model is now able to be trained and updated within just weeks.
Huawei published eight innovation practices which cover key 5.5G technology areas, including antenna evolutions, mmWave bandwidth, network intelligence in the RAN, and energy efficiency. The full list is here, along with details of Huawei’s proposed 5.5G offerings.
With the 2024 commercial launch of 5.5G, Huawei is collaborating with wireless network operators and partners around the world to pursue exciting new innovation in networks, cloud, and intelligence. Huawei plans to drive its 5G business and foster a thriving industry ecosystem, creating a new era for intelligent digital transformation.
For more information, please visit: https://carrier.huawei.com/en/events/mwc2024.
Closing Comments:
This author feels it’s extremely dangerous to announce any IMT products in advance of 3GPP specifications and ITU-R standards. It unrealistically raises expectations and of course there’s no interoperability without specs/standards.
References:
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2024/2/5ga-practices-multipath
What is 5G Advanced and is it ready for deployment any time soon?
Nokia plans to investment €360 million in microelectronics & 5G Advanced/6G technology in Germany
Nokia exec talks up “5G Advanced” (3GPP release 18) before 5G standards/specs have been completed
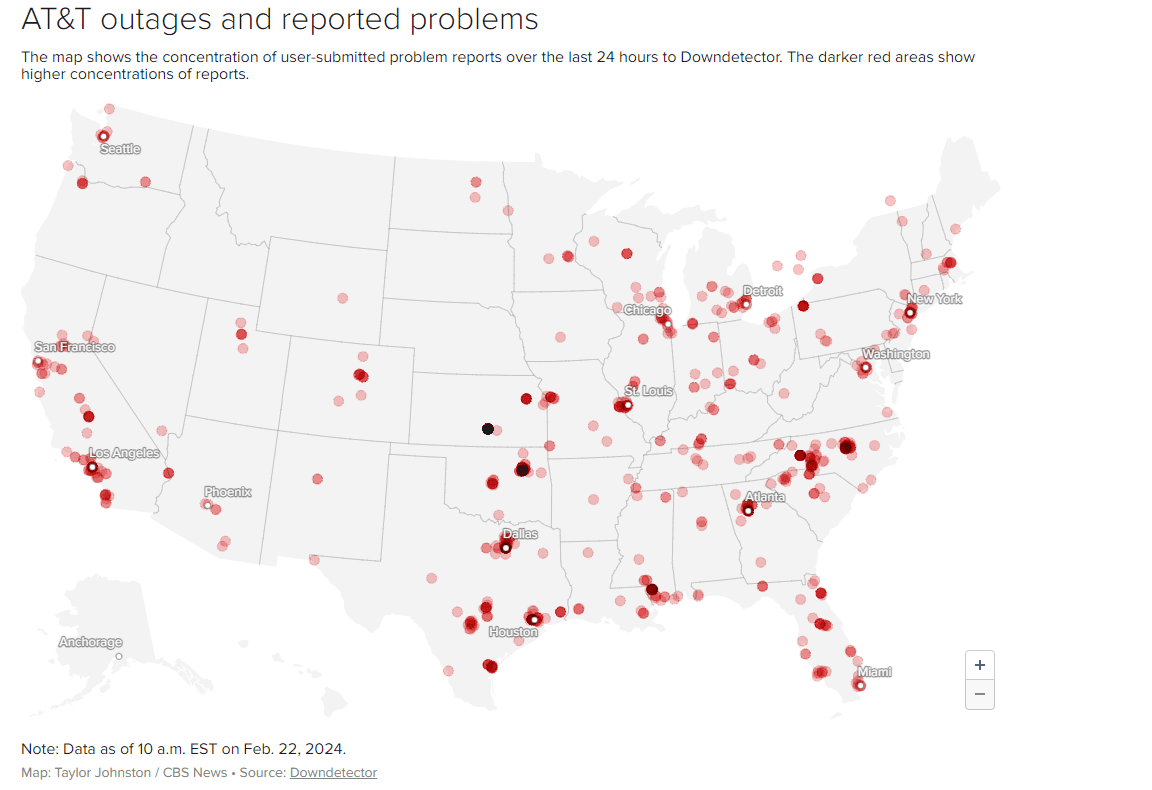
AT&T wireless outage effected more than 74,000 U.S. customers with service disruptions lasting up to 11 hours for some
AT&T’s cellular network went down for many of its customers across the United States Thursday morning, leaving its wireless customers unable to place calls, text or access the internet. Thursday morning, more than 74,000 AT&T customers reported outages on digital-service tracking site DownDetector, with service disruptions beginning around 4 a.m. ET. Most of the complaints were focused on problems with mobile phones or wireless service.
At 3:10 p.m. EST, roughly 11 hours after reports of the outage first emerged, the company said that it had restored service to all impacted customers. “We have restored wireless service to all our affected customers. We sincerely apologize to them,” AT&T said in a statement. The company added that it is “taking steps to ensure our customers do not experience this again in the future.” AT&T hasn’t disclosed the cause of the outages, but the problem snarled 911 centers, with some law enforcement officials noting that some people were calling the emergency number to test whether their phones worked.
The Federal Communications Commission confirmed Thursday afternoon that it is investigating the outage. The White House says federal agencies are in touch with AT&T about network outages but that it doesn’t have all the answers yet on what exactly led to the interruptions.
Earlier Thursday, AT&T acknowledged that it had a widespread outage and suggested a ridiculous alternative. “Some of our customers are experiencing wireless service interruptions this morning. We are working urgently to restore service to them,” AT&T said in a statement at 11:15 a.m. ET. “We encourage the use of Wi-Fi calling until service is restored.” AT&T says on its website that there is no extra cost for WiFi calling. Once set up, Wi-Fi calling works automatically when you’re connected to a Wi-Fi network that you choose. The catch here is that if your away from home, there probably won’t be WiFi hot spot you can connect with or you end up paying for that WiFi Internet service. You are in luck if you’re an Xfinity home internet customer, in which case you can use Xfinity WiFi hotspots for free once you sign in using your Xfinity account log-in credentials.
Initially, AT&T provided no official reason for the outage, but provided an update at 7.46pm EST: “Based on our initial review, we believe that today’s outage was caused by the application and execution of an incorrect process used as we were expanding our network, not a cyber attack. We are continuing our assessment of today’s outage to ensure we keep delivering the service that our customers deserve.” That sounds like a flimsy excuse to this author. The software update went wrong, according to preliminary information from two anonymous sources familiar with the situation.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency is “working closely with AT&T to understand the cause of the outage and its impacts, and stand[s] ready to offer any assistance needed,” Eric Goldstein, the agency’s executive assistant director for cybersecurity, said in a statement to CNN.
White House National Security spokesman John Kirby said Thursday afternoon that the Department of Homeland Security and the FBI were looking into the matter and working with partners in the tech industry to “see what we can do from a federal perspective to lend a hand to their investigative efforts to figure out what happened here. The bottom line is we don’t have all the answers,” he said. “We’re working very hard to see if we can get to the ground truth of exactly what happened.”
Several police departments and municipalities warned local residents of what they described as a nationwide outage. In turn, officials urged callers to contact emergency services by alternative means but did not specify what those means were?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://about.att.com/pages/network-update
https://www.wbaltv.com/article/report-nationwide-outage-atandt-users/46900396
https://www.cbsnews.com/news/outage-map-att-where-cell-phone-service-down/
https://abcnews.go.com/US/att-outage-impacting-us-customers-company/story?id=107440297
Rogers Telecommunications restores service after 19 hour outage disrupting life in Canada
Telecom layoffs continue unabated as AT&T leads the pack – a growth engine with only 1% YoY growth?
SK Telecom, DOCOMO, NTT and Nokia develop 6G AI-native air interface
SK Telecom, DOCOMO, NTT and Nokia today announced they have partnered to develop the 6G AI-native air interface (AI-AI), a critical next-generation technology that could greatly boost network performance while increasing energy efficiency. The four companies will show video demonstration of an AI-AI proof of concept at SKT’s booth at Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, Feb. 26-29.
This new 6G collaboration builds on an existing relationship between DOCOMO, NTT and Nokia targeted at 6G innovation. With the addition of SKT, the four companies will be able to expand the scope and scale of 6G AI-AI testing and validation as well as explore a broader range of business use cases for the technology.
The collaboration is developing future proof-of-concept 6G AI-AI systems, which will then be put to the test using selected use cases and real environmental scenarios. These over-the-air validation tests will be conducted both in the lab and outdoors to best simulate real network results. SKT, NTT, DOCOMO and Nokia will cooperate on improving AI model performance by utilizing data generated from real networks or through simulation. This will be instrumental in developing AI training models for a best-in-industry AI-AI solution.
By working together, SKT, DOCOMO, NTT and Nokia will be able to combine their research efforts and bring their core areas of expertise to the table. SKT, DOCOMO and NTT are recognized worldwide for their successful adoption of every generation of networking and their ability to create new business value from advanced technologies, while Nokia’s industrial research arm, Nokia Bell Labs, is a leader in 6G innovation.
Yu Takki, Vice President and Head of Infra Tech at SKT, said: “ This milestone represents a significant step forward in collaborative efforts towards the development of 6G core technology involving technology leaders from Korea, Japan, Europe and the United States. SKT will maintain its momentum in its R&D efforts of applying AI technology to network infrastructure as we move forward to become a global AI company.”
Takaaki Sato, Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer at DOCOMO said: “DOCOMO and NTT are delighted to advance this project with Nokia, a global vendor leading the world, and SKT, a mobile operator co-leading Asia. Through this collaboration, we will take the lead in innovative technology development and standardization of 6G, and focus on building a global ecosystem that includes future industries and technologies.”
Peter Vetter, President of Bell Labs Core Research at Nokia, said: “For Nokia to create a world-class 6G system, it’s critical we get input from the service providers that will one day deploy 6G. SKT, NTT and DOCOMO are among the most innovative service providers in the world, which gives us the perfect partners to design the networks of the future.”
Editor’s Note: This 6G AI initiative has NOT yet been submitted to ITU-R WP 5D for inclusion in any IMT 2030 related draft document.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
About SK Telecom:
SK Telecom has been leading the growth of the mobile industry since 1984. Now, it is taking customer experience to new heights by extending beyond connectivity. By placing AI at the core of its business, SK Telecom is rapidly transforming into an AI company with a strong global presence. It is focusing on driving innovations in areas of AI Infrastructure, AI Transformation (AIX) and AI Service to deliver greater value for industry, society, and life.
References:
https://www.sktelecom.com/en/press/press_detail.do?idx=1602¤tPage=1&type=&keyword=
https://www.kedglobal.com/tech,-media-telecom/newsView/ked202402220013
https://www.sktelecom.com/en/press/press_detail.do?idx=1601¤tPage=1&type=&keyword=
SK Telecom, Intel develop low-latency technology for 6G core network
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom to Jointly Develop Telco-specific Large Language Models (LLMs)
NTT DOCOMO successful outdoor trial of AI-driven wireless interface with 3 partners
Nokia utilizes Intel technology to drive greater 5G SA core network energy savings
Nokia and Intel today announced that they are targeting greater energy efficiency improvements in 5G networks by using Xeon processors and power management software from Intel that will power Nokia’s cloud-native 5G Core solutions [1.] The two companies’ advances, building on years of innovation, will give communication service providers (CSPs) more leverage in reducing electricity usage and costs in their networks.
Note 1. The Nokia packet core provides key components needed for a webscale-class evolved packet core (EPC) and 5G core system (5GC). With its virtualized, cloud-native disaggregated and state-efficient design, it is well suited for multi-cloud environments. It is also infrastructure agnostic and independent of the underlying cloud infrastructure used for orchestration, lifecycle management (LCM) and infrastructure resource management.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In testing demonstrations, Nokia achieved approximately 40% runtime power savings using Nokia’s cloud-native 5G Core, integrated with Intel Infrastructure Power Manager (IPM) software and 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors*, while maintaining key network performance metrics.
Such energy savings are achieved through the careful integration of Nokia’s Core with Intel’s power modulation capabilities, which result in the energy consumption of the chips being proportional to the amount of traffic on the network – which varies considerably during any 24-hour period. Nokia intends to deliver these energy savings capabilities to the market as early as the second half of 2024, starting with Nokia’s Cloud Packet Core. Nokia and Intel will demonstrate these capabilities at MWC Barcelona at Intel’s booth 3E31.
The announcement underscores Nokia’s ongoing broader efforts to help CSPs and other network-dependent industries reduce their environmental footprint, become more resource efficient, and drive increased value from their networks. Nokia has set its key greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction target through the Science Based Targets (SBT) initiative, which is aligned with the goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C. Nokia was the first telecoms equipment vendor to have a science-based target accepted by the SBT initiative in 2017.
Marcelo Madruga, Head of Technology and Platforms, Products & Engineering, Cloud and Network Services at Nokia, said: “I am very pleased with the brilliant work that Nokia and Intel are doing to deliver very meaningful reductions in the energy footprint of 5G networks. Network data and computation usage only continues to grow, with the clear implication that has for continued energy demand growth. What we are doing today demonstrates not only superior software and technology but delivering on our broader commitments to cut carbon emissions across value chains.”
Alex Quach, Vice President & GM, Wireline and Core Network Division at Intel, said: “This is another solid proof point in the long-standing Intel-Nokia collaboration that highlights the strength of our teams in empowering CSPs with innovative solutions. Integrating the Intel Infrastructure Power Manager into Nokia’s widely deployed packet core software will help deliver the power savings CSPs require and strengthens network operations through intelligent resource allocation.”
Stéphane Demartis, VP Telco Cloud Infrastructure at Orange, said: “We are delighted to start a collaboration with Nokia and Intel to optimize our power consumption. This will provide a major step forward in delivering energy efficient solutions in the core network infrastructure. Orange is looking forward to working with Nokia and Intel to explore implementation of these innovations for a sustainable 5G Core network through the #Sylva project.”
References:
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core-networks/cloud-packet-core/
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/newsroom/resources/2024-mwc-barcelona.html#gs.5dbwdb
https://www.nokia.com/events/mobile-world-congress/
China backed Volt Typhoon has “pre-positioned” malware to disrupt U.S. critical infrastructure networks “on a scale greater than ever before”
On Sunday, FBI Director Christopher Wray said Beijing’s efforts to covertly plant offensive malware inside U.S. critical infrastructure networks [1.] is now at “a scale greater than we’d seen before,” an issue he has deemed a defining national security threat. He said that China backed Volt Typhoon was pre-positioning malware that could be triggered at any moment to disrupt U.S. critical infrastructure. “It’s the tip of the iceberg…it’s one of many such efforts by the Chinese,” he said on the sidelines of the security conference.
Wray had earlier told conference delegates, that China was increasingly inserting “offensive weapons within our critical infrastructure poised to attack whenever Beijing decides the time is right.” The FBI chief said the U.S. is particularly focused on the threat of pre-positioning, which some European officials have described as the cyber equivalent of pointing a ballistic missile at critical infrastructure. “Those attacks are now being amplified by artificial intelligence tools. The word ‘force multiplier’ is not really enough,” Wray added.
Note 1. The FBI Director declined to elaborate on what other critical infrastructure had been targeted, stressing that the Bureau had “a lot of work under way.”

Image Credits: imaginima / Getty Images
Machine learning translation has helped Chinese security operatives to more plausibly recruit assets, steal secrets and rapidly process more of the information they are collecting, the Wray said. “They already have built economic espionage and theft of personal and corporate data as a kind of a bedrock of their economic strategy and are eagerly pursuing AI advancements to try to accelerate that process,” Wray added.
FBI Director Christopher Wray PHOTO: KEVIN DIETSCH/GETTY IMAGES
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Western intelligence officials say China’s scale and sophistication of cyberattacks has accelerated over the past decade. Officials have grown particularly alarmed at Beijing’s interest in infiltrating U.S. critical infrastructure networks, planting malware inside U.S. computer systems responsible for everything from safe drinking water to aviation traffic so it could detonate, at a moment’s notice, damaging cyberattacks during a conflict.
In California, Wray met with counterparts from the Five Eyes intelligence community—which encompasses the U.S., Australia, New Zealand, Canada and the U.K.—to share respective strategies for cyber defense. He has also traveled to Malaysia and India to discuss China’s hacking campaign with authorities in both countries.
“I am seeing more from Europe,” he said. “We’re laser focused on this as a real threat and we’re working with a lot of partners to try to identify it, anticipate it and disrupt it.”
The Netherlands’ spy agencies said earlier this month that Chinese hackers had used malware to gain access to a Dutch military network last year. The agency, considered to have one of Europe’s top cyber capabilities, said it made the rare disclosure to show the scale of the threat and reduce the stigma of being targeted so allied governments can better pool knowledge.
A report released this month by agencies including the FBI, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency and the National Security Agency said Volt Typhoon hackers had maintained access in some U.S. networks for five or more years, and while it targeted only U.S. infrastructure directly, the infiltration was likely to have affected “Five Eyes” allies.
Author’s Note:
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Volt Typhoon, the China-sponsored hacking group, has been targeting U.S. critical infrastructure, including satellite and emergency management services and electric utilities, according to a new report from the industrial cybersecurity firm Dragos. That report outlines how the notorious hacking group is positioning themselves to have disruptive or destructive impacts on critical infrastructure in the U.S.
Robert M. Lee, founder and CEO of Dragos, warned during a media briefing that Volt Typhoon is not an opportunistic group, but is instead targeting specific sites that assist U.S. adversaries “trying to hurt or cripple U.S. infrastructure. It’s hitting the specific electric and satellite communication providers that would be important for disrupting major portions of the U.S. electric infrastructure,” Lee added.
The report comes shortly after the National Security Agency, FBI, and Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, revealed that Volt Typhoon has been in some critical infrastructure networks for at least five years. That alert warned of Volt Typhoon operations that targeted the aviation, railways, mass transit, highway, maritime, pipeline, and water and sewage sectors.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The NSA, CISA and FBI said in a joint advisory report that Volt Typhoon has been burrowing into the networks of aviation, rail, mass transit, highway, maritime, pipeline, water and sewage organizations — none of which were named — in a bid to pre-position themselves for destructive cyberattacks, published on February 7th. The release of the advisory, which was co-signed by cybersecurity agencies in the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada and New Zealand, comes a week after a similar warning from FBI Director Christopher Wray. Speaking during a U.S. House of Representatives committee hearing on cyber threats posed by China, Wray described Volt Typhoon as “the defining threat of our generation” and said the group’s aim is to “disrupt our military’s ability to mobilize” in the early stages of an anticipated conflict over Taiwan, which China claims as its territory.
According to Wednesday’s technical advisory, Volt Typhoon has been exploiting vulnerabilities in routers, firewalls and VPNs to gain initial access to critical infrastructure across the country. The China-backed hackers typically leveraged stolen administrator credentials to maintain access to these systems, according to the advisory, and in some cases, they have maintained access for “at least five years.”
This access enabled the state-backed hackers to carry out potential disruptions such as “manipulating heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems in server rooms or disrupting critical energy and water controls, leading to significant infrastructure failures,” the advisory warned. In some cases, Volt Typhoon hackers had the capability to access camera surveillance systems at critical infrastructure facilities — though it’s not clear if they did.
Volt Typhoon also used living-off-the-land techniques, whereby attackers use legitimate tools and features already present in the target system, to maintain long-term, undiscovered persistence. The hackers also conducted “extensive pre-compromise reconnaissance” in a bid to avoid detection. “For example, in some instances, Volt Typhoon actors may have abstained from using compromised credentials outside of normal working hours to avoid triggering security alerts on abnormal account activities,” the advisory said.
Earlier this year, the FBI and U.S. Department of Justice announced that they had disrupted the “KV Botnet” run by Volt Typhoon that had compromised hundreds of U.S.-based routers for small businesses and home offices. The FBI said it was able to remove the malware from the hijacked routers and sever their connection to the Chinese state-sponsored hackers.
According to a May 2023 report published by Microsoft, Volt Typhoon has been targeting and breaching U.S. critical infrastructure since at least mid-2021.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Volt Typhoon targeted emergency management services, per report
US disrupts China-backed hacking operation amid warning of threat to American infrastructure
https://www.controlglobal.com/home/blog/11293192/information-technology
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
A new report from the Dell’Oro Group reveals that the global Radio Access Network (RAN) market concluded the year with another difficult quarter, resulting in a global decrease of nearly $4 billion in RAN revenues for the full year of 2023. However, despite these challenges, the results for the quarter exceeded expectations, partly due to robust 5G deployments in China.
“Following the intense rise between 2017 and 2021, it’s clear that the broader RAN market is now experiencing a setback, as two out of the six tracked regions are facing notable declines,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President for RAN market research at the Dell’Oro Group. “In addition to challenging conditions in North America and Europe, the narrowing gap between advanced and less advanced operators (e.g. India) in this first 5G wave, compared to previous technology cycles, initially had a positive impact but is now constraining global 5G and broader RAN growth prospects,” Pongratz added.
Additional highlights from the 4Q 2023 RAN report:
- Overall concentration in the RAN market showed signs of improvement in 2021 and 2022, but this progress slowed down in 2023.
- While full-year RAN rankings remained mostly unchanged for major suppliers, revenue shares within the RAN market showed more variability, with Huawei and ZTE enhancing their global revenue shares. Similarly, Huawei and Nokia saw improvements in their revenue shares outside of China.
- The top 5 RAN suppliers based on worldwide revenues are Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, and Samsung.
- Regional projections are mostly unchanged, with market conditions expected to remain tough in 2024 due to difficult comparisons in India. Nevertheless, the base-case scenario anticipates a more moderate pace of decline this year.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Source: Dell’Oro Group
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Rémy Pascal of Omdia says that global RAN revenues (including both hardware and software) declined by 11% last year to just over $40 billion. The worst performing region by far was North America, which almost halved, but this should be viewed in the context of a relatively strong 2022.
India and China were been the best performing countries for new RAN deployments. This partly explains why Huawei continues to be the top RAN vendor despite attempts by the U.S. and its allies to prevent that, but as the Omdia table below shows, the Chinese vendor is still doing well in many other regions too. We’re told this table looked pretty much the same last year.
Top RAN vendors by region, full year 2023:
|
North America |
Asia & Oceania |
Europe, Middle East and Africa |
Latin America & the Caribbean |
|
Ericsson |
Huawei |
Ericsson |
Huawei |
|
Nokia |
ZTE |
Nokia |
Ericsson |
|
Samsung |
Ericsson |
Huawei |
Nokia |
Source: Omdia
Omdia expects the RAN market size to decrease by around 5% compared to 2023. That’s an improvement on the 11% 2022-23 decline but still not good news for the RAN industry.
For all the talk of Open RAN, it clearly has yet to inspire significant capex from operators. The same goes for private 5G or programmable networks. Less than halfway through the presumed 5G cycle, spending has stalled and it’s not at all clear what will restart it.
Dell’Oro Group’s RAN Quarterly Report offers a complete overview of the RAN industry, with tables covering manufacturers’ and market revenue for multiple RAN segments including 5G NR Sub-7 GHz, 5G NR mmWave, LTE, macro base stations and radios, small cells, Massive MIMO, Open RAN, and vRAN. The report also tracks the RAN market by region and includes a four-quarter outlook. To purchase this report, please contact us by email at [email protected].
References:
RAN Market Shows Faint Signals of Life in 4Q 2023, According to Dell’Oro Group
https://www.telecoms.com/wireless-networking/global-ran-market-declined-by-11-in-2023
Dell’Oro: RAN market declines at very fast pace while Mobile Core Network returns to growth in Q2-2023
Dell’Oro: RAN Market to Decline 1% CAGR; Mobile Core Network growth reduced to 1% CAGR
https://www.silverliningsinfo.com/5g/ericsson-nokia-and-state-global-ran-2024
LightCounting: Open RAN/vRAN market is pausing and regrouping
What is 5G Advanced and is it ready for deployment any time soon?
The 3GPP roadmap (see figure below) is continuously evolving to fulfill the larger 5G vision. In this initial 5G wave that began in 2018, 3GPP has completed three major releases (new releases every 1.5 to 2 years): 15, 16, and 17.
Release 17 is included in the ITU-R M.2150-1 recommendation which is the only standard for IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT (i.e. 5G RAN interface). 3GPP contributes its completed radio interface specifications to ITU-R WP5D via ATIS where they are discussed and approved for inclusion into the next version of the ITU-R M.2150 recommendation. The same procedure is likely for IMT 2030 RIT/SRIT (i.e. 6G RAN).
3GPP Release 18 and beyond (often referred to as 5G-Advanced or 5.5G) involve gradual technology improvements aimed at elevating 5G to the next level, creating a foundation for more demanding applications and a broader set of use cases. In addition to performance improvements and support for new applications, sustainability and intelligent network automation are also important building blocks in the broader 5G-Advanced vision (source: Ericsson).
The scope of 5G Advanced in Release 19 was approved at the December 2023 3GPP Plenary Meeting in Edinburgh, Scotland. Release 19 builds on Release 18 and focuses on enhancing 5G performance while expanding the capability of 5G across devices and deployments. In addition, it will establish the technical foundations for 6G and will include preliminary work on new 6G capabilities. Release 19 will be followed by Release 20, the first 3GPP release for 6G studies.
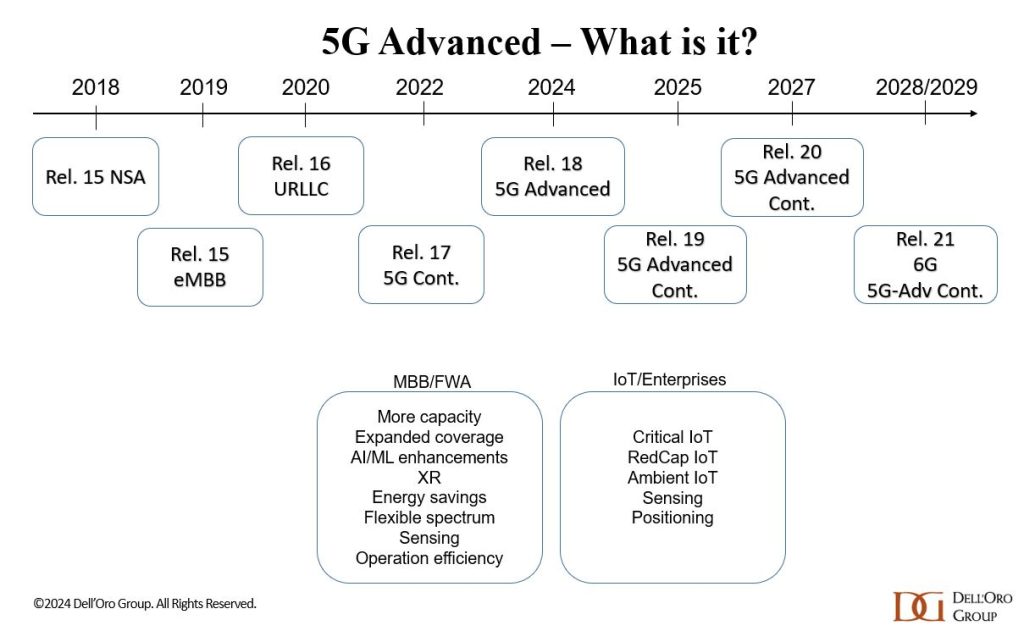
5G Advanced continues to push the spectral efficiency limits and coverage in both sub-7GHz and millimeter wave spectrum. In addition to continued enhancements to massive MIMO radios and mobility, 3GPP Release 19 provides advancements for new use cases such as XR and Non-Terrestrial Networks.
- Massive MIMO Radio – Release 18 introduced improvements to massive MIMO uplink and downlink throughput. Release 19 will boost capacity further by improving multi-user MIMO, which enables more UEs to share the same time and frequency resources.
Release 19 will also enable the cost-efficient realization of distributed transmitters and receivers, thus improving signal quality. This is an important step towards enabling fully distributed MIMO (D-MIMO) systems. Other enhancements include 5G beam management with UE-initiated measurement reporting, thus resulting in faster beam selection. - Mobility – 5G Advanced introduces a new handover procedure known as low-layer (i.e. L2) triggered mobility (LTM). In Release 18, LTM is supported between cells served by the same gNB. In Release 19, the LTM framework will be extended to support handover between cells served by different gNBs.
- XR and the Metaverse – Release 19 builds on the low latency and power saving features of Release 18 by enabling higher XR capacity by adding improved uplink and downlink scheduling using packet delay information.
- Non-Terrestrial Networks – 5G Advanced combines terrestrial and satellite communications under one standard for the first time. Release 19 will build on the enhancements introduced in Release 18 with a focus on increasing satellite downlink coverage, introducing UEs with higher output power and providing Redcap device support. It will also investigate whether additional support is required for regenerative payloads.
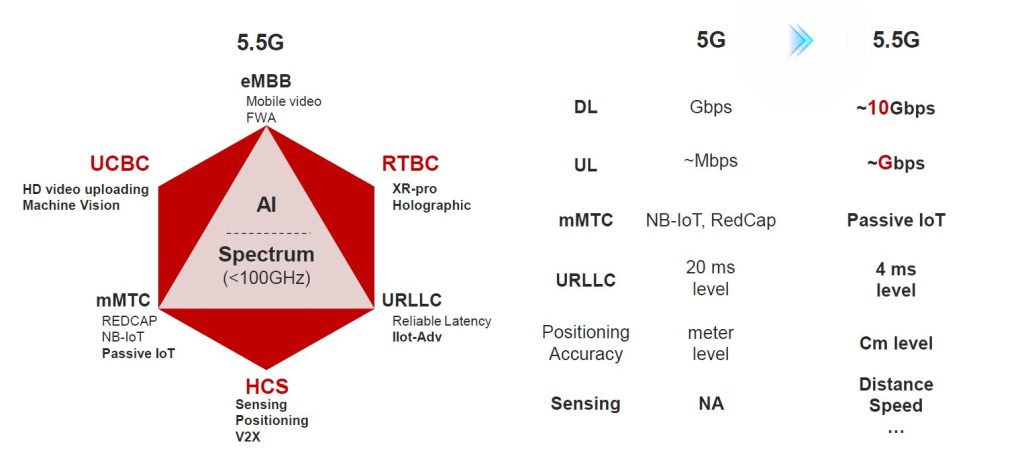
Current priorities for 5G-Advanced include:
- More capacity and better performance. Some estimates suggest that MIMO enhancements, better beam management, and full duplex technologies taken together with other advancements, including multi-band serving cell (MB-SC) and Extremely Large Antenna Array (ELAA) will deliver another 20% of efficiency improvements relative to today’s 5G. Enhanced uplink (UL) and multi-cell UL improvements could pave the way for greater data rate and latency improvements in the UL. For reference, Huawei defines 5G-Advanced as a site that can support at least 10 Gbps of cell capacity. ZTE is also targeting 10 Gbps+ with 5G-Advanced.
- Expanded coverage. In addition to MIMO and IAB coverage enhancements, 5G-Advanced includes Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) connectivity improvements, building on the NR/LTE-based NTN support that was introduced with Release 17.
- More intelligence. Releases 15-17 already include some AI/ML features. 5G-Advanced will offer AI/ML enhancements in the RAN (including the air interface) and the management layers. In addition, Intelligent RAN and AI-powered analytics will help operators to improve the performance and proactively address network issues before they become a problem.
- Energy savings. Release 18 includes a confluence of static and dynamic power-saving enhancements for the radios and the overall RAN. Also, the specification is targeting to define a base station energy consumption model with various KPIs to better evaluate transmission and reception consumption/savings.
- Flexible spectrum (FD, DSS, CA). NR is currently based on TDD or FDD spectrum. Full duplex (FD), a 5G-Advanced contender, improves spectrum utilization by allowing UL and DL to share the same spectrum (FD should improve capacity and latency, especially in the UL). Release 18 also includes DSS capacity enhancements (increasing PDCCH capacity by allowing NR PDCCH to be transmitted in symbols overlapping with LTE CRS). Other spectrum-related upgrades with 5G-Advanced include multi-carrier enhancements and NR support for dedicated spectrum bandwidths below 5 MHz.
- Critical IoT. 5G-Advanced includes multiple industrial and IoT related advancements. Release 17 included support for Time Sensitive Networking (TSN), which will be expanded in 5G-Advanced to support Deterministic Networking (DetNet).
- RedCap IoT. 5G NR-Light or Reduced Capability (RedCap) was introduced with 3GPP NR Release 17. 5G-Advanced will introduce lower-tier RedCap devices, seeking to find a better set of tradeoffs between cost, performance, and power consumption.
- Ambient IoT. Passive IoT, sometimes referred to as Ambient IoT, will allow devices/objects to connect without a power source.
- Sensing. Harmonized communication and sensing (HCS) is a Release 19 study item.
- Positioning. Positioning is already supported in Release 16/17, though 5G-Advanced is expected to improve positioning accuracy and power consumption (Nokia has said sub-10 cm positioning is doable). In addition, Release 18 will include support for RedCap devices.
Role of AI/ML in 5G Advanced:
AI/ML will become a key feature of 5G networks with numerous applications ranging from network planning and network operations optimization to full network automation. Another important application is the use of AI/ML to improve the performance and functionality of the 5G air interface.
3GPP studied the use of AI/ML in the air interface in Release 18 and defined three use cases: channel state feedback (CSF) information, beam management and positioning. Based on the conclusions of Release 18 studies, Release 19 will specify a general AI/ML framework, i.e. actual specifications to support the above three use cases as well as specific support for each individual use case. Release 19 will also explore new areas in the AI/ML air interface such as mobility improvement and AI/ML-related model training, model management and global 5G data collection.
AI/ML is another major focus for Qualcomm. The company has dedicated significant technical resources to develop full-scale demonstrations of the three Release 18 defined use cases. For example, it recently demonstrated CSF-based cross-node machine learning involving E2E optimization between devices and the network. This reduces device communication overheads resulting in improved capacity and throughput. Qualcomm has also demonstrated the use of AI/ML to improve beam prediction on its 28GHz massive MIMO test network and is heavily involved in positioning technologies. For example, it has showcased its outdoor precise positioning technology, which uses multi-cell roundtrip (RTT) and angle-of-arrival (AoA) based technologies, as well as its RF finger printing technology operating in an indoor industrial private network.
Over the next few months, 3GPP will continue exploring the applicability of AI/ML based solutions for other use cases such as load balancing between cells, mobility optimization and network energy savings. For example, there will be support for conditional Layer 2 mobility in Release 19 and a new study item targeting new use cases designed to improve coverage and capacity optimization, such as AI-assisted dynamic cell shaping.
Enhancing Device and Network Sustainability:
5G Advanced focuses on sustainability and introduces energy-saving features for devices and networks as well as exploring end-to-end energy saving opportunities that benefit devices. There are also improved features for RedCap and the study of ambient IoT as a new device type.
- Power-optimized devices – Releases 18 and 19 build on existing energy saving features, for example, a new low-power wakeup signal (LP-WUS). A low-complexity, power-optimized receiver is specified to monitor low-power wake-up signals from the network which only wakes-up the main radio when data is available at the device. This avoids the significant power consumption required to keep the main radio monitoring control signals from the network.
- Ambient IoT – enables new use cases enabled by very-low power devices that harvest energy from the ambient environment, for example, RF waves. Release 19 will investigate new architectures for ambient IoT devices and will include the development of a harmonized specification. Numerous use cases will be studied, including smart agriculture, industrial wireless sensor networks, smart logistics, warehousing, etc.
- Network energy savings – 5G Advanced reduces network energy consumption by dynamically adjusting the network’s operation based on feedback from the device, i.e. shutting down parts of the network when idle and transmitting less power depending on the overall traffic load or using more efficient antennas.

Dell’Oro’s Stefan Pongratz says “one fundamental aspect of 5G-Advanced will be to support more demanding consumer MBB applications. The days of exponential data traffic growth are clearly in the past; however, global mobile data traffic is still projected to increase threefold over the next five years, reaching 0.5 ZB/month by 2028 (mobile plus FWA). While operators are currently in a fairly good position from a capacity perspective, especially those not aggressively pursuing FWA, some of the technology improvements with 5G-Advanced can help to address capacity limitations in hotspot areas.”
Omdia (owned by Omdia) expects leading network service providers in Asia and Oceania are expected to launch 5G-Advanced between 2024 and 2025. They aim to leverage the new capabilities and features offered by 5G-Advanced to enhance their network infrastructure and offer innovative services to their customers. These advancements include enhanced performance metrics such as higher data rates, lower latency, improved reliability, and greater network efficiency.
During the next few years, 5G Advanced will continue to evolve within 3GPP while the specification of 6G officially starts to ramp up in parallel, leading to the ITU-R IMT 2030 standard.
Setting The Stage For 6G:
Although Release 19 will be the last release focused on 5G, it will also include some longer-term technologies that will become the foundation of 6G, thus setting the direction for Release 20. For example, Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC), which combines wireless communications with RF sensing, will enable a raft of new position-based use cases. Release 19 will study channel characteristics suitable for the sensing of various objects, including vehicles, UAVs and humans. Full duplex, another 6G technology, allows transmitters and receivers to operate simultaneously on the same frequency, potentially resulting in a doubling of network capacity. Release 19 will study sub-band full duplex, a type of full duplex, which will improve capacity and latency, particularly for the uplink. Release 19 will also include channel model studies for the upper mid-band spectrum (7-16GHz), which will be supported by “Giga-MIMO” in the 6G timeframe, in order to enable wide-area coverage in this higher band.
Whereas AI/ML is a key pillar of 5G Advanced, it will be a core foundational technology of 6G and will underpin the key features that will make 6G revolutionary. For example, 6G will start to move away from the traditional, model-driven approach of designing communication systems and transition towards a more data-driven design. Indeed, it is likely that the 6G air-interface will be designed to be AI-native from the outset, thus signalling a paradigm change in the way communication systems are designed. An AI-native air interface could offer many benefits. For example, it could refine existing communication protocols by continuously learning and improving them, thereby enabling the air interface to be customized dynamically to suit local radio environments.
References:
NGMN issues ITU-R framework for IMT-2030 vs ITU-R WP5D Timeline for RIT/SRIT Standardization
Nokia plans to investment €360 million in microelectronics & 5G Advanced/6G technology in Germany
ZTE and China Telecom unveil 5G-Advanced solution for B2B and B2C services
ABI Research: 5G-Advanced (not yet defined by ITU-R) will include AI/ML and network energy savings
Draft new ITU-R recommendation (not yet approved): M.[IMT.FRAMEWORK FOR 2030 AND BEYOND]
Deutsche Telekom migrates IP-based voice telephony platform to the cloud
Deutsche Telekom has successfully transitioned its IP-based voice telephony platform to the cloud. Landline connections are now centrally controlled from cloud data centers in Germany. Over seventeen million customer connections have been migrated. Billions of voice minutes are now handled entirely through the NIMS platform (NIMS: Next Generation IP Multimedia Subsystem) with around 100 interconnect partners.
Thanks to disaggregation, services can be provided through an optimized solution portfolio of software modules from a wide ecosystem of industry partners. The near-complete automation of the Telco Cloud provides a more efficient process, leading to significantly more flexibility and speed in the introduction of new service features and capacity expansion.

Image credit: Deutsche Telekom
“This project is a game changer in the industry,” says Abdu Mudesir, Chief Technology Officer of Deutsche Telekom Deutschland. “It is the result of excellent cooperation with partners such as Juniper Networks, Mavenir, Microsoft, HPE, Red Hat, and Lenovo. Our common goal in this innovation project has always been to set a benchmark for excellence in the industry, for our customers. The success has spread, many network operators are now asking us specifically how we managed to achieve this.”
“The cloud isn’t just a technology, but rather an entirely new operating model that can yield tremendous agility, cost efficiencies and better user experiences. I am so proud that Juniper was able to play a role in bringing Deutsche Telekom’s visionary strategy for NIMS to life and even more thrilled to see this project, which I consider a blueprint for the rest of the telecom industry, now complete,” says Rami Rahim, CEO – Juniper Networks.
“With NIMS, Deutsche Telekom has leveraged the benefits of cloud native network functions, hyper scaler technology and extreme automation to deliver mission critical carrier grade performance; it’s a huge step forward in the Telecommunications industry,” says Yousef Khalidi CVP, Azure for Operators – Microsoft.
“Telekom´s vision was unique because it was not just a pure technology play. Its goal to change the old development paradigms, driving automation and interoperability into the very fabric of the Telco Cloud architecture. The NIMS platform offers a transformative lifecycle automation for all telco cloud and payload components and Mavenir is proud to be part of the multi-vendor ecosystem delivering this innovation,” says Bejoy Pankajakshan, EVP & Chief Technology and Strategy Officer of Mavenir.
“The platform is a key building block for ´Zero Touch operations´ where manual intervention and operations to handle network management and configuration are reduced in favor of a more advanced, software-based solution,” says David Stark, VP & GM, Telco Solutions – HPE.
Telekom has already established follow-up projects to consistently implement the successful model of cloudification, disaggregation, and complete automation in other voice applications, 5G Core and the access networks.
References:
Deutsche Telekom Network Day: Fiber, Mobile Network, Open RAN and 5G SA Launch in 2024
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom to Jointly Develop Telco-specific Large Language Models (LLMs)
Deutsche Telekom with AWS and VMware demonstrate a global enterprise network for seamless connectivity across geographically distributed data centers
Deutsche Telekom exec: AI poses massive challenges for telecom industry
Deutsche Telekom’s fiber optic expansion in 140 of the 179 municipalities within the Gigabit region of Stuttgart
Deutsche Telekom Global Carrier Launches New Point-of-Presence (PoP) in Miami, Florida
NEC’s new AI technology for robotics & RAN optimization designed to improve performance
NEC Corporation has developed AI technology for robotics that enables precise handling operations on unorganized and disorderly placed items. By predicting both the areas hidden by obstacles and the results of a robot’s actions, this technology makes it possible for robots to perform tasks that were previously performed manually, thereby contributing to the improvement of productivity and work-styles.
NEC has developed AI technology for robotics that consists of two technologies based on “World Models“:
“Spatiotemporal Prediction,” in which a robot precisely predicts the work environment and the results of its own actions from camera data, and
“Robot Motion Generation,” which automatically generates optimal and precise actions based on these predictions. According to NEC research, this is the world’s first technology of its kind to be applied to robot operations.

1. Autonomously executes precise actions in optimal sequences for items of various shapes and sizes:
The handling of objects performed manually at a work site are executed by a combination of various actions. For example, in packing items, people can instantly execute a combination of precise actions such as “placing and then pushing items” without hitting other objects or obstacles. In robot control that uses conventional technologies, however, actions such as “push” and “pull” are more difficult to execute with high precision than actions such as “pick up” and “place.” This is because slight differences in actions or shapes significantly influence how objects move in response to actions. In addition, as the number and types of actions to be considered increases, the combination and sequence of actions becomes more complex, which makes real-time planning a challenge.
This technology uses World Models to accurately predict the results of robot actions on objects of various shapes from video camera data, enabling robots to execute precise actions such as “push” and “pull.” Moreover, robots can autonomously and instantly execute combinations of multiple actions such as “place and push” and “pull and pick up” by generating the appropriate action sequence at real-time speed depending on the work environment.
2. Operates while predicting hidden and invisible items:
In a work environment where multiple items are closely arranged or disorderly piled up, people naturally predict the hidden areas and act accordingly, such as picking up items while avoiding interference with hidden objects. However, conventional recognition technology for robots has been difficult for practical use because it requires the preparation and learning of a large amount of teaching data showing the state of hidden objects in order to predict the hidden areas.
This new technology enables unsupervised learning that does not require labeling through the application of World Models and is able to efficiently learn prediction models of hidden object shapes. This enables robots to accurately predict a work environment from camera data and automatically generate optimal actions that do not collide with other objects or obstacles.

NEC will test this technology in logistics warehouses and other sites where much of the work is done manually by the end of 2024. By promoting social implementation of this technology in various industries with significant need for automation, NEC will contribute to improved productivity and work style reform.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, NEC has developed a RAN autonomous optimization technology that dynamically controls 5G Radio Access Networks (RAN) according to the status of each user terminal, dramatically improving the productivity of applications, such as the remote control of robots and vehicles. NEC will incorporate the technology into RAN Intelligent Controllers (RIC) and conduct demonstration tests using this technology by March 2025.
There is growing momentum to promote digital transformation (DX) by utilizing the latest technologies such as 5G, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) with the aim of resolving labor shortages and improving productivity.
When using these technologies for remote control of robots and vehicles, two-way communication consisting of status monitoring and control instructions for each robot/vehicle must be completed within a certain period of time.
However, if the communication latency exceeds the requirement, the operation is repeatedly suspended for safety reasons, resulting in a decrease in the operation rate and productivity. The communication delays, such as retransmission delays due to poor radio quality and queuing delays (*) due to congestion on the radio links, have been a barrier to the introduction of remote control systems.
Currently, stable communications environments have been achieved by installing high performance network equipment, providing sufficient frequency resources, increasing redundancy in coding and communication paths, and pre-configuration of RAN parameters according to the application. However, with these methods, it is difficult to widely support applications that are diversifying with the advancement of DX, and the time and cost required for implementation is also an issue.
About the RAN autonomous optimization technology:
The RAN autonomous optimization technology developed by NEC consists of AI that analyzes communication requirements and radio quality fluctuations on a per-user terminal basis, such as robots and vehicles, and AI that dynamically controls RAN parameters on a per-user terminal basis based on the results of that analysis. This AI learns from past operational records of robots and vehicles, and optimally controls RAN parameters such as modulation and coding scheme (target block error rate), radio resource allocation (resource block ratio), and maximum allowable delay (delay budget) while predicting the probability of exceeding communication latency requirements. Whereas in a typical 5G network, RAN parameters are fixed and set for the entire network, this technology dynamically controls them on a per-user terminal basis to improve application productivity.
Technology features are as follows.
1. Flexible support for a variety of applications
RAN parameters can be dynamically controlled according to the communication requirements of applications, enabling overall optimization even in environments where diverse applications are mixed.
2. O-RAN Alliance-compliant and easy to deploy
Since it can be mounted on RIC that are compliant with O-RAN Alliance standard specifications, it is easy to install or add to existing facilities.
3. Dramatic productivity gains are possible at industrial sites
Simulation results of applying this technology to a system that remotely controls multiple autonomous robots operating in factories or warehouses confirmed that the number of robot stoppages can be reduced by 98% or more compared to cases where this technology is not used.
NEC plans to incorporate the technology into RIC platforms compliant with the O-RAN Alliance standard specifications and conduct demonstration tests using this technology by March 2025.
NEC will exhibit this technology at MWC Barcelona 2024, the world’s largest mobile exhibition, which will be held from February 26 to February 29, 2024 at Fira Gran Via, Barcelona, Spain.
When using these technologies for remote control of robots and vehicles, two-way communication consisting of status monitoring and control instructions for each robot/vehicle must be completed within a certain period of time. However, if the communication latency exceeds the requirement, the operation is repeatedly suspended for safety reasons, resulting in a decrease in the operation rate and productivity. The communication delays, such as retransmission delays due to poor radio quality and queuing delays due to congestion on the radio links, have been a barrier to the introduction of remote control systems.