AI spending is surging; companies accelerate AI adoption, but job cuts loom large
Global AI market is experiencing significant growth. Companies are adopting AI at an accelerated rate, with 72% reporting adoption in at least one business function in 2024, a significant increase from 55% in 2023, according to S&P Global. This growth is being driven by various factors, including the potential for enhanced productivity, improved efficiency, and increased innovation across industries.
Global spending on AI is projected to reach $632 billion by 2028, according to the IDC Worldwide AI and Generative AI Spending Guide. 16 technologies will be impacted: hardware (IaaS, server, and storage), software (AI applications [content workflow and management applications, CRM applications, ERM applications], AI application development and deployment, AI platforms [AI life-cycle software, computer vision AI tools, conversational AI tools, intelligent knowledge discovery software], AI system infrastructure software), and services (business services and IT services)
Grand View Research estimates that the global AI market, encompassing hardware, software, and services, will grow to over $1.8 trillion by 2030, compounding annually at 37%.
Barron’s says AI spending is surging, but certain job types are at risk according to CIOs. On Wednesday, two major U.S. investment banks released reports based on surveys of chief information officers, or CIOs, at corporations that suggest rising spending plans for AI infrastructure.
- Morgan Stanley’s technology team said AI tops the priority list for projects that will see the largest spending increase, adding that 60% of CIOs expect to have AI projects in production by year end. Military spending for AI applications by NATO members is projected to exceed $112 billion by 2030, assuming a 4% AI investment allocation rate.
- Piper Sandler analyst James Fish noted 93% of CIOs plan to increase spending on AI infrastructure this year with 48% saying they will increase spending significantly by more than 25% versus last year. Piper Sandler said that is good news for the major cloud computing vendors—including Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud, Amazon.com’s Amazon Web Services, and Google Cloud by Alphabet.
- More than half the CIOs in Piper Sandler’s survey admitted the rise of AI made certain jobs more vulnerable for headcount reduction. The job categories most at risk for cuts are (in order): IT administration, sales, customer support, and IT help desks.
–>Much more on AI related job losses discussion below.
Executives’ confidence in AI execution has jumped from 53% to 71% in the past year, driven by $246 billion in infrastructure investment and demonstrable business results. Another article from the same date notes the introduction of “AI for Citizens” by Mistral, aimed at empowering public institutions with AI capabilities for their citizens, according to an artticle.
This strong growth in the AI market is driven by several factors:
- Technological advancements: Improvements in machine learning algorithms, computational power, and the development of new frameworks like deep learning and neural networks are enabling more sophisticated AI applications.
- Data availability: The abundance of digital data from various sources (social media, IoT devices, sensors) provides vast training datasets for AI models, according to LinkedIn.
- Increasing investments: Significant investments from major technology companies, governments, and research institutions are fueling AI research and development.
- Cloud computing: The growth of cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud provides scalable infrastructure and tools for developing and deploying AI applications, making AI accessible to a wider range of businesses.
- Competitive advantages: Businesses are leveraging AI/ML to gain a competitive edge by enhancing product development, optimizing operations, and making data-driven decisions.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Some sources predict that AI could replace the equivalent of 300 million full-time jobs globally, with a significant impact on tasks performed by white-collar workers in areas like finance, law, and consulting.
- Entry-level positions are particularly vulnerable, with some experts suggesting that AI could cannibalize half of all entry-level white-collar roles within five years.
- Sectors like manufacturing and customer service are also facing potential job losses due to the automation capabilities of AI and robotics.
- A recent survey found that 41% of companies plan to reduce their workforce by 2030 due to AI, according to the World Economic Forum.
- BT CEO Allison Kirkby hinted at mass job losses due to AI. She told the Financial Times last month that her predecessor’s plan to eliminate up to 45,000 jobs by 2030 “did not reflect the full potential of AI.” In fact, she thinks AI may be able to help her shed a further 10,000 or so jobs by the end of the decade.
- Microsoft announced last week that it will lay off about 9,000 employees across different teams in its global workforce.
- “Artificial intelligence is going to replace literally half of all white-collar workers in the U.S.,” Ford Motor CEO Jim Farley said in an interview last week with author Walter Isaacson at the Aspen Ideas Festival. “AI will leave a lot of white-collar people behind.”
- Amazon CEO Andy Jassy wrote in a note to employees in June that he expected the company’s overall corporate workforce to be smaller in the coming years because of the “once-in-a-lifetime” AI technology. “We will need fewer people doing some of the jobs that are being done today, and more people doing other types of jobs,” Jassy said.
- Technology-related factors such as automation drove 20,000 job cuts among U.S.-based employers in the first half of the year, outplacement firm Challenger, Gray & Christmas said in a recent report. “We do see companies using the term ‘technological update’ more often than we have over the past decade, so our suspicion is that some of the AI job cuts that are likely happening are falling into that category,” Andy Challenger, a senior vice president at the Chicago, Illinois-based outplacement firm, told CFO Dive. In some cases, companies may avoid directly tying their layoffs to AI because they “don’t want press on it,” he said.
- In private, CEOs have spent months whispering about how their businesses could likely be run with a fraction of the current staff. Technologies including automation software, AI and robots are being rolled out to make operations as lean and efficient as possible.
- Four in 10 employers anticipate reducing their workforce where AI can automate tasks, according to World Economic Forum survey findings unveiled in January.
The long-term impact of AI on employment is still being debated, with some experts predicting that AI will also create new jobs and boost productivity, offsetting some of the losses. However, reports and analysis indicate that workers need to prepare for significant changes in the job market and develop new skills to adapt to the evolving demands of an AI-driven economy.
References:
https://my.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=IDC_P33198
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/press-release/global-artificial-intelligence-ai-market
https://www.barrons.com/articles/ai-jobs-survey-cios-619d2a5e?mod=hp_FEEDS_1_TECHNOLOGY_3
https://www.hrdive.com/news/ai-driven-job-cuts-underreported-challenger/752526/
https://www.lightreading.com/ai-machine-learning/telcos-are-cutting-jobs-but-not-because-of-ai
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/ai-white-collar-job-loss-b9856259
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/ai-white-collar-job-loss-b9856259
HPE cost reduction campaign with more layoffs; 250 AI PoC trials or deployments
AT&T and Verizon cut jobs another 6% last year; AI investments continue to increase
Verizon and AT&T cut 5,100 more jobs with a combined 214,350 fewer employees than 2015
AI adoption to accelerate growth in the $215 billion Data Center market
Big Tech post strong earnings and revenue growth, but cuts jobs along with Telecom Vendors
Nokia (like Ericsson) announces fresh wave of job cuts; Ericsson lays off 240 more in China
AI wave stimulates big tech spending and strong profits, but for how long?
Liquid Dreams: The Rise of Immersion Cooling and Underwater Data Centers
By Omkar Ashok Bhalekar with Ajay Lotan Thakur
As demand for data keeps rising, driven by generative AI, real-time analytics, 8K streaming, and edge computing, data centers are facing an escalating dilemma: how to maintain performance without getting too hot. Traditional air-cooled server rooms that were once large enough for straightforward web hosting and storage are being stretched to their thermal extremes by modern compute-intensive workloads. While the world’s digital backbone burns hot, innovators are diving deep, deep to the ocean floor. Say hello to immersion cooling and undersea data farms, two technologies poised to revolutionize how the world stores and processes data.
Heat Is the Silent Killer of the Internet – In each data center, heat is the unobtrusive enemy. If racks of performance GPUs, CPUs, and ASICs are all operating at the same time, they generate massive amounts of heat. The old approach with gigantic HVAC systems and chilled air manifolds is reaching its technological and environmental limits.
In the majority of installations, over 35-40% of total energy consumption is spent on simply cooling the hardware, rather than running it. As model sizes and inference loads explode (think ChatGPT, DALL·E, or Tesla FSD), traditional cooling infrastructures simply aren’t up to the task without costly upgrades or environmental degradation. This is why there is a paradigm shift.
Liquid cooling is not an option everywhere due to lack of infrastructure, expense, and geography, so we still must rely on every player in the ecosystem to step up the ante when it comes to energy efficiency. The burden crosses multiple domains, chip manufacturers need to deliver far greater performance per watt with advanced semiconductor design, and software developers need to write that’s fundamentally low power by optimizing algorithms and reducing computational overhead.
Along with these basic improvements, memory manufacturers are designing low-power solutions, system manufacturers are making more power-efficient delivery networks, and cloud operators are making their data center operations more efficient while increasing the use of renewable energy sources. As Microsoft Chief Environmental Officer Lucas Joppa said, “We need to think about sustainability not as a constraint, but as an innovative driver that pushes us to build more efficient systems across every layer of the stack of technology.”
However, despite these multifaceted efficiency gains, thermal management remains a significant bottleneck that can have a deep and profound impact on overall system performance and energy consumption. Ineffective cooling can force processors to slow down their performance, which is counterintuitive to better chips and optimized software. This becomes a self-perpetuating loop where wasteful thermal management will counteract efficiency gains elsewhere in the system.
In this blogpost, we will address the cooling aspect of energy consumption, considering how future thermal management technology can be a multiplier of efficiency across the entire computing infrastructure. We will explore how proper cooling strategies not only reduce direct energy consumption from cooling components themselves but also enable other components of the system to operate at their maximum efficiency levels.
What Is Immersion Cooling?
Immersion cooling cools servers by submerging them in carefully designed, non-conductive fluids (typically dielectric liquids) that transfer heat much more efficiently than air. Immersion liquids are harmless to electronics; in fact, they allow direct liquid contact cooling with no risk of short-circuiting or corrosion.
Two general types exist:
- Single-phase immersion, with the fluid remaining liquid and transferring heat by convection.
- Two-phase immersion, wherein fluid boils at low temperature, gets heated and condenses in a closed loop.
According to Vertiv’s research, in high-density data centers, liquid cooling improves the energy efficiency of IT and facility systems compared to air cooling. In their fully optimized study, the introduction of liquid cooling created a 10.2% reduction in total data center power and a more than 15% improvement in Total Usage Effectiveness (TUE).
Total Usage Effectiveness is calculated by using the formula below:
TUE = ITUE x PUE (ITUE = Total Energy Into the IT Equipment/Total Energy into the Compute Components, PUE = Power Usage Effectiveness)
Reimagining Data Centers Underwater
Imagine shipping an entire data center in a steel capsule and sinking it to the ocean floor. That’s no longer sci-fi.
Microsoft’s Project Natick demonstrated the concept by deploying a sealed underwater data center off the Orkney Islands, powered entirely by renewable energy and cooled by the surrounding seawater. Over its two-year lifespan, the submerged facility showed:
- A server failure rate 1/8th that of land-based centers.
- No need for on-site human intervention.
- Efficient, passive cooling by natural sea currents.
Why underwater? Seawater is an open, large-scale heat sink, and underwater environments are naturally less prone to temperature fluctuations, dust, vibration, and power surges. Most coastal metropolises are the biggest consumers of cloud services and are within 100 miles of a viable deployment site, which would dramatically reduce latency.
Why This Tech Matters Now Data centers already account for about 2–3% of the world’s electricity, and with the rapid growth in AI and metaverse workloads, that figure will grow. Generative inference workloads and AI training models consume up to 10x the power per rack that regular server workloads do, subjecting cooling gear and sustainability goals to tremendous pressure. Legacy air cooling technologies are reaching thermal and density thresholds, and immersion cooling is a critical solution to future scalability. According to Submer, a Barcelona based immersion cooling company, immersion cooling has the ability to reduce energy consumed by cooling systems by up to 95% and enable higher rack density, thus providing a path to sustainable growth in data centers under AI-driven demands
Advantages & Challenges
Immersion and submerged data centers possess several key advantages:
- Sustainability – Lower energy consumption and lower carbon footprints are paramount as ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) goals become business necessities.
- Scalability & Efficiency – Immersion allows more density per square foot, reducing real estate and overhead facility expenses.
- Reliability – Liquid-cooled and underwater systems have fewer mechanical failures including less thermal stress, fewer moving parts, and less oxidation.
- Security & Autonomy – Underwater encased pods or autonomous liquid systems are difficult to hack and can be remotely monitored and updated, ideal for zero-trust environments.
While there are advantages of Immersion Cooling / Submerges Datacenters, there are some challenges/limitations as well –
- Maintenance and Accessibility Challenges – Both options make hardware maintenance complex. Immersion cooling requires careful removal and washing of components to and from dielectric liquids, whereas underwater data centers provide extremely poor physical access, with entire modules having to be removed to fix them, which translates to longer downtimes.
- High Initial Costs and Deployment Complexity – Construction of immersion tanks or underwater enclosures involves significant capital investment in specially designed equipment, infrastructure, and deployment techniques. Underwater data centers are also accompanied by marine engineering, watertight modules, and intricate site preparation.
- Environmental and Regulatory Concerns – Both approaches involve environmental issues and regulatory adherence. Immersion systems struggle with fluid waste disposal regulations, while underwater data centers have marine environmental impact assessments, permits, and ongoing ecosystem protection mechanisms.
- Technology Maturity and Operational Risks – These are immature technologies with minimal historical data on long-term performance and reliability. Potential problems include leakage of liquids in immersion cooling or damage and biofouling in underwater installation, leading to uncertain large-scale adoption.
Industry Momentum
Various companies are leading the charge:
- GRC (Green Revolution Cooling) and submersion cooling offer immersion solutions to hyperscalers and enterprises.
- HPC is offered with precision liquid cooling by Iceotope. Immersion cooling at scale is being tested by Alibaba, Google, and Meta to support AI and ML clusters.
- Microsoft is researching commercial viability of underwater data centers as off-grid, modular ones in Project Natick.
Hyperscalers are starting to design entire zones of their new data centers specifically for liquid-cooled GPU pods, while smaller edge data centers are adopting immersion tech to run quietly and efficiently in urban environments.
- The Future of Data Centers: Autonomous, Sealed, and Everywhere
Looking ahead, the trend is clear: data centers are becoming more intelligent, compact, and environmentally integrated. We’re entering an era where: - AI-based DCIM software predicts and prevents failure in real-time.
- Edge nodes with immersive cooling can be located anywhere, smart factories, offshore oil rigs.
- Entire data centers might be built as prefabricated modules, inserted into oceans, deserts, or even space.
- The general principle? Compute must not be limited by land, heat, or humans.
Final Thoughts
In the fight to enable the digital future, air is a luxury. Immersed in liquid or bolted to the seafloor, data centers are shifting to cool smarter, not harder.
Underwater installations and liquid cooling are no longer out-there ideas, they’re lifelines to a scalable, sustainable web.
So, tomorrow’s “Cloud” won’t be in the sky, it will hum quietly under the sea.
References
- https://news.microsoft.com/source/features/sustainability/project-natick-underwater-datacenter/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/381537233_Advancement_of_Liquid_Immersion_Cooling_for_Data_Centers
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_Natick
- https://theliquidgrid.com/underwater-data-centers/
- https://www.sunbirddcim.com/glossary/submerged-server-cooling
- https://www.vertiv.com/en-us/solutions/learn-about/liquid-cooling-options-for-data-centers/
- https://submer.com/immersion-cooling/
About Author:
Omkar Bhalekar is a senior network engineer and technology enthusiast specializing in Data center architecture, Manufacturing infrastructure, and Sustainable solutions. With extensive experience in designing resilient industrial networks and building smart factories and AI data centers with scalable networks, Omkar writes to simplify complex technical topics for engineers, researchers, and industry leaders.
Google Fiber and Nokia demo network slicing for home broadband in GFiber Labs
Network slicing has previously been restricted to 5G Stand Alone (SA) networks, which the IEEE Techblog regularly covers (see References below). However, network slicing software may also have a place in the home broadband network, as per a demo from Google Fiber and Nokia. Google Fiber says that this use of “network slicing gives us the ability to carve up a customer’s home network into different “lanes,” each optimized for a specific use.” In a GFiber Labs demo, gaming was used as the test scenario.
Google Fiber placed two gaming consoles next to each other and simulated network congestion, which drove the game’s latency up to 90 milliseconds. Unsurprisingly, “it was stalling, pixelating…a really ill experience for the end user,” said Nick Saporito, Google Fiber’s head of product. “This was a foundational test and it worked,” he added.

In the long-term, this could truly change how home internet works, especially when it’s driven by the customer. Today’s one-size-fits-all connections treat all traffic the same. But we know not everyone uses the internet the same way: gamers care about latency, remote workers need video stability, home businesses rely on solid uptime and security, and, we can see a future where applications (AI, VR, etc.) may require next-level performance. Network slicing could be how we level up network performance.
Network slicing opens the door to something new: the ability for customers to tailor their connection to the categories of Internet use that matter most in their home. It’s not about prioritizing traffic behind the scenes, it’s about giving you more control, more flexibility, and more ways to get the performance you need, when you need it. And with GFiber, it will always be in service of giving customers more control, without compromising our commitment to an open, unrestricted internet.
There’s also potential for something called “transactional slices.” These would spin up automatically, just for a few seconds, to keep things like financial logins secure. For example, connecting you directly to a service like your bank without routing traffic across the broader internet. You wouldn’t even notice it happening, but it could add meaningful peace of mind.
Network slicing is the next logical step in how we think about GFiber service — especially our lifestyle products like Core, Home, and Edge, built to meet the needs of customers’ unique internet lifestyles. Those products are designed to better match the way people live and work. Network slicing takes that a step further: adding real-time customization and control at the network level.
While we’re very excited about the possibilities here, there are few things that have to happen before we roll out network slicing across our network. Automation is a key piece of the puzzle. We’ll be diving deeper with Nokia later this year to explore how we can bring some of these ideas to life. This kind of innovation is exactly what GFiber Labs was built for and we’re excited about potentially leveling up the GFiber customer experience — again.
When considering how to implement network slicing on a wider scale, Saporito noted two key challenges. First, “a lot” of network automation is required to ensure a seamless experience. Google Fiber currently has a “mini-app” that lives on the router to help on the automation front, so that a technician doesn’t have to log onto the router and manually configure the settings.
Another challenge is determining how to effectively sell network slicing capabilities to customers. Given how prevalent multi-gig internet has become, Google Fiber is thinking about whether it makes sense to give customers more “ISP-like controls over their pipe,” Saporito said, rather than just providing a one-size-fits-all product.
“Much like you can put your car in sport or comfort mode, maybe our customers could go to the GFiber app and put their internet in gaming mode, for example, and then all their gaming traffic is special handled by network slicing,” he explained. “Those are ways that we’re kind of thinking about how we would productize it.”
But widespread adoption of broadband network slicing is still a ways away, according to Dell’Oro Group VP Jeff Heynen, as most ISPs and equipment providers are still in the proof-of-concept phase. “That being said, if you look down the road and you don’t expect downstream bandwidth consumption to grow as quickly as it historically has, then network slicing could be a way to help ISPs charge more for their service or, less likely, charge for specific slices,” Heynen said.
Aside from improving gaming or AI applications, one interesting use case for slicing is to provide additional security around financial transactions, Heynen noted. An operator could create a slice on a “per-transaction basis,” complementing a more standard encryption method like SSL.
“You could imagine an ISP differentiating themselves from their competition by highlighting that they have the most secure broadband network, for example,” he added. Saporito similarly noted the value of a so-called “transactional slice.” Though Google Fiber has yet to demo the concept, the idea is to create a temporary slice that would work when a customer logs onto their bank account. “We could create an automatic slice in the background to where that banking traffic is going directly to the financial institution’s back-end, versus traversing the transport network,” he said. “The customer wouldn’t even really notice it.”
https://fiber.google.com/blog/2025/06/network-slicing-demo.html
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/google-fiber-puts-nokia-network-slicing-technology-test
Téral Research: 5G SA core network deployments accelerate after a very slow start
5G network slicing progress report with a look ahead to 2025
ABI Research: 5G Network Slicing Market Slows; T-Mobile says “it’s time to unleash Network Slicing”
Is 5G network slicing dead before arrival? Replaced by private 5G?
5G Network Slicing Tutorial + Ericsson releases 5G RAN slicing software
Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison and Nokia use AI to reduce energy demand and emissions
Indonesian network operator Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison has deployed Nokia Energy Efficiency (part of the company’s Autonomous Networks portfolio – described below) to reduce energy demand and carbon dioxide emissions across its RAN network using AI. Nokia’s energy control system uses AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze real-time traffic patterns, and will enable the operator to adjust or shut idle and unused radio equipment automatically during low network demand periods.
The multi-vendor, AI-driven energy management solution can reduce energy costs and carbon footprint with no negative impact on network performance or customer experience. It can be rolled out in a matter of weeks.
Indosat is aiming to transform itself from a conventional telecom operator into an AI TechCo—powered by intelligent technologies, cloud-based platforms, and a commitment to sustainability. By embedding automation and intelligence into network operations, Indosat is unlocking new levels of efficiency, agility, and environmental responsibility across its infrastructure.
Earlier this year Indosat claimed to be the first operator to deploy AI-RAN in Indonesia, in a deal involving the integration of Nokia’s 5G cloud RAN solution with Nvidia’s Aerial platform. The Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the three firms included the development, testing, and deployment of AI-RAN, with an initial focus on transferring AI inferencing workloads on the AI Aerial, then the integration of RAN workloads on the same platform.
“As data consumption continues to grow, so does our responsibility to manage resources wisely. This collaboration reflects Indosat’s unwavering commitment to environmental stewardship and sustainable innovation, using AI to not only optimize performance, but also reduce emissions and energy use across our network.” said Desmond Cheung, Director and Chief Technology Officer at Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison.
Indosat was the first operator in Southeast Asia to achieve ISO 50001 certification for energy management—underscoring its pledge to minimize environmental impact through operational excellence. The collaboration with Nokia builds upon a successful pilot project, in which the AI-powered solution demonstrated its ability to reduce energy consumption in live network conditions.
Following the pilot project, Nokia deployed its Energy Efficiency solution to the entire Nokia RAN footprint within Indonesia, e.g. Sumatra, Kalimantan, Central and East Java.
“We are very pleased to be helping Indosat deliver on its commitments to sustainability and environmental responsibility, establishing its position both locally and internationally. Nokia Energy Efficiency reflects the important R&D investments that Nokia continues to make to help our customers optimize energy savings and network performance simultaneously,” said Henrique Vale, VP for Cloud and Network Services APAC at Nokia.
Nokia’s Autonomous Networks portfolio, including its Autonomous Networks Fabric solution, utilizes Agentic AI to deliver advanced security, analytics, and operations capabilities that provide operators with a holistic, real-time view of the network so they can reduce costs, accelerate time-to-value, and deliver the best customer experience.
Autonomous Networks Fabric is a unifying intelligence layer that weaves together observability, analytics, security, and automation across every network domain; allowing a network to behave as one adaptive system, regardless of vendor, architecture, or deployment model.
References:
Upcoming IEEE Region 6 Events and IEEE Funding Opportunities
Backgrounder:
IEEE Region 6 is one of the ten geographical regions of the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) and covers the Western United States, including Alaska, Hawaii, and all states in between. It spans a vast area, from the Pacific coast to the Rocky Mountains and includes states like California, Oregon, Washington, Nevada, Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, Montana, and more. Within Region 6, there are 35 Sections and 2 sub-sections, organized into 5 Areas: Central, Northeast, Northwest, Southern, and Southwest. The region also has a strong volunteer base and offers various activities, including conferences, workshops, and awards programs, to its members.
IEEE Region 6 Director Joseph Wei (photo below) a very good friend of this author, has requested bi-monthly posting of Region 6 events that might be of interest to IEEE Techblog readers.
Please contact Joseph Wei at [email protected] for volunteer opportunities in IEEE Region 6.
Upcoming Region 6 Events:
Forecasting and Planning for Grid Evolution with LoadSEER: A Spatial Approach to Electric Expansion and Risk | Seattle Section Chapter, Date: 15 July 2025 Event Format: Virtual. Register at https://events.vtools.ieee.org/m/489844
Abstract: As distribution systems grow more complex due to electrification, distributed energy resources (DERs), and climate-driven volatility, utilities need advanced tools to plan effectively at the local level. LoadSEER — Spatial Electric Expansion and Risk — is a powerful spatial analytics platform developed by Integral Analytics to support long-term electric system planning under uncertainty. This presentation will explore how LoadSEER enables utilities to model localized growth, assess risk, and test investment strategies under a wide range of future scenarios. With capabilities including circuit-level forecasting, geospatial scenario analysis, and integrated risk scoring, LoadSEER helps planners prioritize infrastructure upgrades, integrate DERs, and align with regulatory and decarbonization goals. The session will include use cases and lessons learned from utilities deploying LoadSEER to improve capital efficiency, system resilience, and planning transparency in rapidly changing environments.
Agentic AI themed 4th International Conference on Applied Data Science (ICADS) 2025 | Santa Clara Valley (SCV) Section, Date: 17 July 2025 Event Format: Virtual. Register at https://events.vtools.ieee.org/m/487442
Abstract – In this talk, Kamer Ali Yuksel (Head of Agentic AI @ aiXplain) describes how LLM-driven agents are transforming autonomy across research, enterprise, and design. He shows that today’s agents aren’t just “smart autocomplete” but self-directed ideators, experimenters, analysts, and creators. Drawing on his recent publications, he argues that AI agents already deliver end-to-end autonomy: how aiXplain autonomously refine Agentic AI workflows via continuous LLM-driven feedback loops, ideate and implement enterprise Agentic AI use-cases, and derive actionable business insights from enterprise data—producing executive-ready reports without human intervention.
Brew with the Crew: Representation & Impact of Hydrological Conditions of Power System Planning and Operations | Eastern Idaho Section Date: 17 July 2025 Event Format: Virtual. Register at https://events.vtools.ieee.org/m/489811
Abstract: As inverter-based resources grow and synchronous generators retire, the grid loses not only inertia but also essential ancillary services. Hydropower can help fill this gap, but accurate planning requires utilities to understand and model its capabilities. Currently, gaps exist in how hydropower plants are represented—many units lack modeled frequency response or omit governor data, and hydrological constraints are often excluded. This talk highlights efforts to address two key gaps: (a) incorporating hydrological data, and (b) accurately modeling response capabilities in steady-state and dynamic simulations. The impact of these improvements on system planning and reliability will be discussed, with contributions from PNNL and V&R Energy.
Technologies for a Circular Economy Webinar Series | IEEE SusTech and IEEE Future Directions. This webinar series follows the successful workshop on the same topic at the IEEE SusTech 2025 conference in Santa Ana, CA. Date: 17 July 2025 Event Format: Virtual. Register at https://sustech.ieee.org/circular-economy/webinar-series

IEEE Milestone dedication at the Intel Jones Farm Conference Center |IEEE Region 6 Milestones -Dedication and Unveiling of the IEEE Milestones for the Universal Serial Bus (USB), 1996 on July 30th. Date: 30 July 2025 (12:30pm check-in in the JFCC lobby, main program from 1:30pm – 3pm). Event Format: in-person at 2111 NE 25th Avenue, Hillsboro, Oregon, Building: Jones Farm Conference Center. Register at https://events.vtools.ieee.org/event/register/491146
IEEE at SeattleCon: Digital Preservation and Biomedical Technologies | Seattle Section Date: 13 – 17 August 2025. Event Format: In-person. Register at https://seattlein2025.org/
More IEEE Region 6 events can be found at https://events.vtools.ieee.org/events/search/advanced
IEEE SCV events are listed at https://egrid.ieeesfbac.org/
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
IEEE FUNDING OPPORTUNITIES
IEEE New Initiatives Program:

The New Initiatives Program is designed to support potential new IEEE programs, products, or services that will provide significant benefit to IEEE members, the public, the technical community, and customers, or which could have lasting impact on the IEEE or its business processes. Initiatives must be of strategic importance to IEEE.
Details on specific procedures for the submission are at https://www.ieee.org/about/corporate/initiatives
IEEE Future Directions:

The IEEE Future Directions Committee (FDC) seeks to identify, develop, and promote projects that are value-added for IEEE and its members, bringing together multiple Societies and Councils to provide broad and deep perspectives on a particular topic, application, or technology. These projects range from short term activities to reach a specific goal to Future Directions Initiatives seeking longer-term cross-collaborative engagement among industry, academia, and government striving to develop and deploy
various future technologies.
Details information can be found at https://cmte.ieee.org/futuredirections/projects/
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Again, please contact Joseph Wei at [email protected] for volunteer opportunities in IEEE Region 6.
References:
IEEE SCV March 28th Event: A Conversation with IEEE President and IEEE Region 6 Director Elect
IEEE President’s Priorities and Strategic Direction for 2024
IEEE President Elect: IEEE Overview, 2024 Priorities and Strategic Plan
Nokia’s Bell Labs to use adapted 4G and 5G access technologies for Indian space missions
Nokia’s Bell Labs is receptive to collaborating with the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), government agencies, and private players in India’s space sector to support future lunar missions with 4G, 5G and other advanced wireless networking technologies. Thierry Klein, President of Bell Labs Solutions Research, visited India in late June to explore potential partnerships and deepen engagement with the country’s growing space ecosystem. In an interview with Moneycontrol, Klein said India’s space ambitions present a compelling opportunity for collaboration.
“We are in a lot of conversations globally, working with government agencies and private companies to see how we can support their missions from a communications perspective. This is really the reason why I came to India—because it is a great opportunity for me to learn more about the space ecosystem and build relations and explore collaboration opportunities with the Indian space sector,” Klein said. He emphasized that while these space networks make use of existing 3GPP 4G and 5G cellular specifications, they must be drastically reengineered to withstand extreme temperatures, mechanical stress, radiation, and power constraints.
With India opening its space sector to private participation and international collaboration, Nokia’s proposed engagement could bring advanced telecom capabilities to future Indian lunar missions. Klein affirmed the company’s openness to working with both public and private entities in India to advance lunar and deep space communications.
India plans to launch the Chandrayaan-4 mission in 2027, aiming to bring back samples of moon rocks to Earth. Chandrayaan-4 will involve at least two separate launches of the heavy-lift LVM-3 rocket, which will carry five different components of the mission that will be assembled in orbit.

Asked if Nokia Bell Labs is engaging with ISRO, which is the primary agency in India for space exploration and research, Klein said, “Yeah, we definitely want to engage with them [ISRO]. I met people from both the government and private companies. They are very interested in continuing the conversations on both sides, the private sector as well as the public sector. I have had lots of conversations and lots of interest in exploring working together.”
Nokia Bell Labs has been developing cutting-edge communication systems for future lunar missions, with the aim of supporting the growing global interest from governments, such as India, and private space enterprises in establishing a permanent presence on the Moon and, eventually, Mars.
“Unlike the Apollo era, which relied on basic voice and low-resolution imagery, future lunar missions will demand high-definition video, data-rich applications, and low-latency networks to support scientific research, mining, transportation, and habitation on the Moon,” said Klein.
To meet those demands, Bell Labs is adapting commercial-grade 4G and 5G cellular technologies, currently used globally on Earth, for use in space. The first real-world test of this technology was conducted during the Intuitive Machines IM-2 mission, which landed on the moon on March 6, 2024, and successfully demonstrated a functioning 4G LTE network on the lunar surface.
“So that’s been our vision for seven or eight years, and that’s what we’ve really done with the Intuitive Machines 2 mission…We built the first cellular network and wanted to prove that we could do this. It was a technology demonstration to show that we can take something based on the networks we use on Earth, make all the necessary adaptations I mentioned, deploy the network, operate it successfully, and prove that cellular technology is a viable solution for space operations,” Klein said.
Klein said Bell Labs envisions the Moon’s communication infrastructure developing similarly to Earth’s surface networks, supporting permanent lunar bases, while satellites in lunar orbit provide 5G-based backhaul or coverage for remote regions. “We think of 5G as both providing surface capabilities as well as orbit-to-surface capabilities,” he said, likening it to non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) on Earth.
The company initially opted for 4G due to its maturity at the time the project began in 2020. Looking ahead, the migration to 5G is on the horizon, likely coinciding with the shift to 6G on Earth in 2030. “We would expect that we have 5G on the lunar surface by 2030,” Klein said, explaining that staying one generation behind Earth networks allows lunar missions to benefit from economies of scale, mature ecosystems, and deployment experience.
Nokia and Intuitive Machines successfully delivered a 4G LTE network to the Moon. However, a planned wireless call couldn’t be made because the Athena lander tipped over, limiting its ability to recharge. Still, Nokia’s Lunar Surface Communications System (LSCS), including its base station, radio, and core, ran flawlessly during the 25-minute power window.
Klein also revealed that Nokia is working with Axiom Space to integrate 4G LTE into next-generation space suits, which are slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission in 2027. Nokia continues to engage with governments and commercial partners globally. “Everybody realizes there is a need for communication. We are really open to working with anybody that we could support,” Klein said.
References:
5G connectivity from space: Exolaunch contract with Sateliot for launch and deployment of LEO satellites
AST SpaceMobile: “5G” Connectivity from Space to Everyday Smartphones
U.S. military sees great potential in space based 5G (which has yet to be standardized)
China’s answer to Starlink: GalaxySpace planning to launch 1,000 LEO satellites & deliver 5G from space?
Samsung announces 5G NTN modem technology for Exynos chip set; Omnispace and Ligado Networks MoU
Telecoms.com’s survey: 5G NTNs to highlight service reliability and network redundancy
Telecoms.com survey results, presented in the report Private networks and NTNs: Transcending the boundaries of 5G, highlight the reinforcement of service reliability and additional layer of network redundancy as the most frequently selected impact of the convergence of 5G and Non Terrestrial Networks (NTN)s, according to nearly half of respondents. Engineers and developers are the biggest proponents of this impact with more than three in five respondents highlighting its value from a technical perspective. The extra network redundancy is backup connectivity from NTNs to existing 5G networks (e,g, dye to a cell tower failure or massive power outage) and the ability to ensure continued service whether in times of crisis or otherwise.
Meanwhile, two in five C-Suite executives think it’s either too early to determine the benefits or that NTNs will only achieve a minimal impact on 5G performance, hinting that they may need more convincing to achieve full buy-in.

‘Deployment costs’ are identified as the top concern when converging NTNs with 5G for many organisations in telecoms and particularly so for CSPs, while ‘cost of infrastructure’ is the most frequently selected key challenge slowing down the large-scale adoption of private 5G.
The cost barrier is neither new nor surprising for these topics, or for many other telecom topics being surveyed, but what this is compounded with now is a global economy that hasn’t been stable for some time, whether due to the global pandemic, or the ever-growing number of wars around the world.
On private 5G, the report also highlights several 5G standalone features that are considered most important to enterprises. Here, network responsiveness (low latency, handover time, and ultra-low data rates) is flagged as the top feature closely followed by network slicing in radio (that is, reserving capacity for specific applications).
The report argues that “while these results shed light on key technical capabilities that telecom professionals consider to be critical for the use of enterprises in a private 5G environment, it is also important to note that focusing on business outcomes and use cases versus technical capabilities is likely more meaningful in discussions with enterprises.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3GPP introduced NTN into its Release 17, which provided an initial framework and Release 18 which included enhancements. 3GPP continues to work on NTN in Release 19 and beyond, focusing on aspects like onboard satellite processing, Ku-band frequencies, and integration with terrestrial networks.
-
Release 17: This release introduced the initial framework for 5G NTN, including support for NB-IoT and 5G NR NTN.
-
Release 18: This release focused on performance enhancements and additional frequency bands for 5G NTN.
-
Release 19 and beyond: Future releases, including 19, will continue to build on the NTN standard, with plans to enhance onboard satellite processing, expand to Ku-band frequencies for 5G NTN, and improve the integration between terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks.
3GPP looks forward to the continuous collaboration with ITU-R WP 4B for the finalization of Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT-2020-SAT.SPECS], which will be the official standard for 5G satellite to ground communications.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://tc-resources.telecoms.com/free/w_defa8859/
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/ntn-overview
ITU-R recommendation IMT-2020-SAT.SPECS from ITU-R WP 5B to be based on 3GPP 5G NR-NTN and IoT-NTN (from Release 17 & 18)
Standards are the key requirement for telco/satellite integration: D2D and satellite-based mobile backhaul
5G connectivity from space: Exolaunch contract with Sateliot for launch and deployment of LEO satellites
Momentum builds for wireless telco- satellite operator engagements
Samsung announces 5G NTN modem technology for Exynos chip set; Omnispace and Ligado Networks MoU
Téral Research: 5G SA core network deployments accelerate after a very slow start
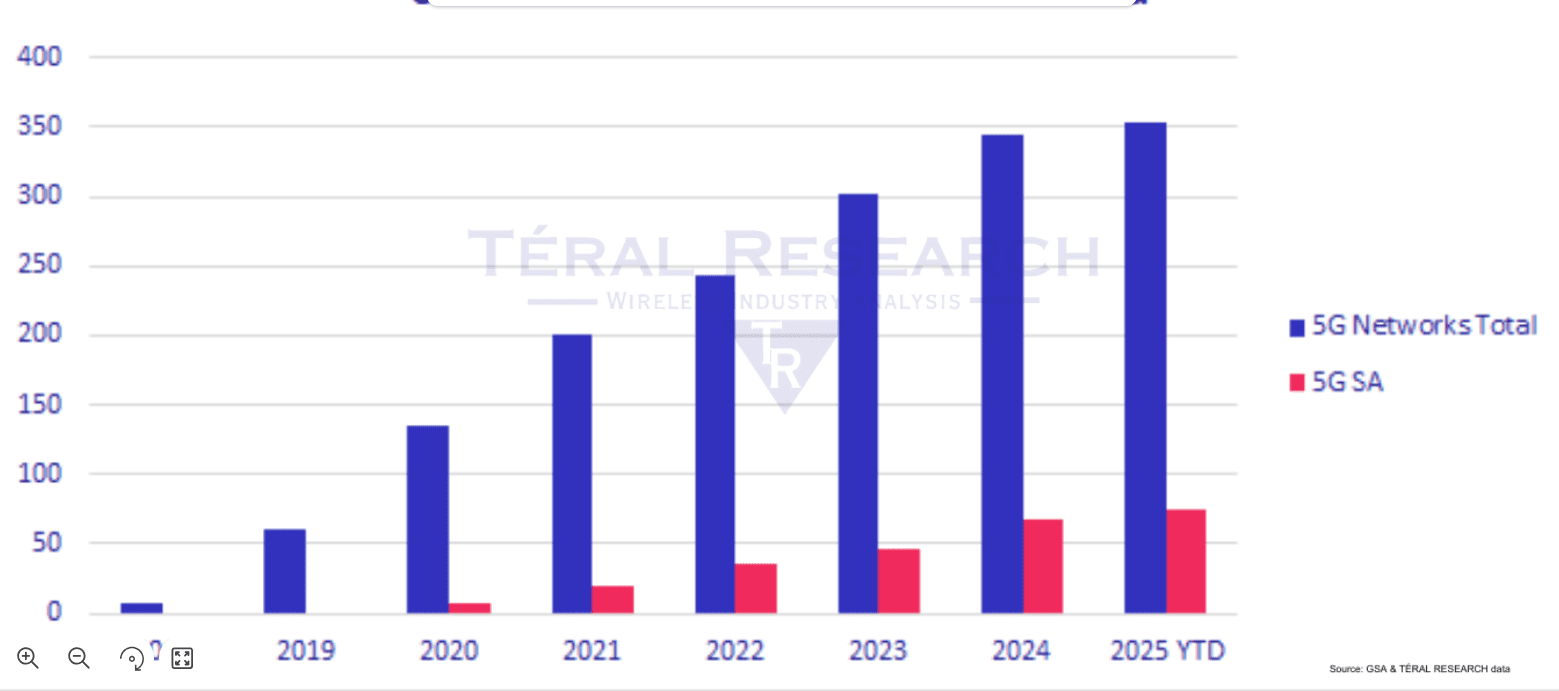
5G deployments started with the non-standalone (NSA) mode (using a 4G core network) and are now gradually migrating to Stand Alone (SA) core network to unleash a plethora of use cases. 5G SA offers improved latency and bandwidth, enabling advanced services and applications. 5G SA goes far beyond mobile and will eventually become the network that bridges all networks together, with the new sophisticated service-based architecture (5G SBA) designed by the 3GPP. Although many of the network functions (NFs) featured in the 5G SBA come from existing ones currently active in 2G/3G and 4G networks, novel functions such as the network slice selection function (NSSF) are being introduced.
After a very slow start during the past five years, Téral Research [1.] says the migration to 5G SA has increased. Of the total 354 commercially available 5G public networks reported at the end of 1Q25, 74 are 5G SA – up from 49 one year ago.
Note 1. Based on a communications service provider (CSP) survey and discussions with many vendors, Téral Research’s 5G SA report analyzes several of the 5G Core SBA functions and provides global and regional market sizes and forecasts by focusing on the NFs implemented by CSPs (e.g., UDM, UDR, AUSF, NRF, NEF and NSSF, PCF, BSF, CHF) to enable use cases beyond enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), fixed wireless access (FWA), and private 5G.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2024 had the highest number of 5G SA commercial launches: 21 networks went live to offer commercial 5G SA services last year. The success of FWA services, the introduction of smartphone plans enabled by the increasing number of available 5G SA devices, and the rise of VoNR drove this SA migration.
Key findings include:
-
Network slicing is taking off for various services, including for military use cases.
-
The single vendor approach remains predominant for each domain.
-
67% of 5G SA core deployment are cloud-based but due to data sovereignty concerns,
CSPs favor private cloud infrastructures.
-
The global 2024 market for 5G SA Core + SDM + Policy & Charging grew 12% YoY and hit $3.8B, slightly below our forecast.
-
Sustained by its domestic market, Huawei leads global 2024 sales for 5G SA Core + SDM + Policy & Charging, followed by Ericsson and Nokia, respectively. However, Nokia leads the global commercial 5G SA footprint. ZTE comes in fourth place for global total sales and second for 5G SA core sales behind Huawei.
In the meantime, technical challenges related to 5G network architecture complexity, 3GPP methods for exchanging information across 4G vs. 5G, policy orchestration and enforcement, real-time analytics and insights and data analytics are still lingering but being solved.
Built on a solid CSP pipeline of 559 cellular networks in the world that have yet to be migrated to 5G SA, Téral’s model produced a forecast that shows the global 5G SA Core/5G Data Management/5G Policy market to cross the $4B bar by year-end, which is 20% YoY growth. Last year’s downward revision put our forecast on track and therefore we have not made any significant change in this forecast update.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Editor’s Note: In 2025, about a dozen more mobile network operators (MNOs) are expected to deploy 5G Standalone (SA) networks, according to Fierce Network and Moniem-Tech. This will include some major CSPs like AT&T and Verizon, who have previously deployed 5G SA on a limited basis. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In the long run, Teral foresees a significant ramp up in CSPs’ migration to 5G SA that adds to the ongoing activity continuously fueled by the emergence of new use cases going beyond eMBB, FWA, and private 5G. Therefore, Téral expects the market to grow at a 2025-2030 CAGR of 11%. Asia Pacific will remain the largest market throughout the forecast period and 5G SA core the most important domain to start with, followed by 5G Data Management.
Finally, the disaggregated multi-domain nature of 5G core SBA brings a broad range of contenders that include the traditional telecom network equipment vendors, a few mobile core specialists, a handful of subscriber data management (SDM) specialists, a truck load of policy and charging rules function (PCRF) players, the OSS/BSS providers and the system integrators and providers of IT services.
References:
Téral Research :: June 2025 5G SA Core, SDM and Policy
Ookla: Europe severely lagging in 5G SA deployments and performance
Vision of 5G SA core on public cloud fails; replaced by private or hybrid cloud?
GSA: More 5G SA devices, but commercial 5G SA deployments lag
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
Latest Ericsson Mobility Report talks up 5G SA networks and FWA
Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market has lowest growth rate since 4Q 2017
5G SA networks (real 5G) remain conspicuous by their absence
Big Tech and VCs invest hundreds of billions in AI while salaries of AI experts reach the stratosphere
Introduction:
Two and a half years after OpenAI set off the generative artificial intelligence (AI) race with the release of the ChatGPT, big tech companies are accelerating their A.I. spending, pumping hundreds of billions of dollars into their frantic effort to create systems that can mimic or even exceed the abilities of the human brain. The areas of super huge AI spending are data centers, salaries for experts, and VC investments. Meanwhile, the UAE is building one of the world’s largest AI data centers while Softbank CEO Masayoshi Son believes that Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) will surpass human-level cognitive abilities (Artificial General Intelligence or AGI) within a few years. And that Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) will surpass human intelligence by a factor of 10,000 within the next 10 years.
AI Data Center Build-out Boom:
Tech industry’s giants are building AI data centers that can cost more than $100 billion and will consume more electricity than a million American homes. Meta, Microsoft, Amazon and Google have told investors that they expect to spend a combined $320 billion on infrastructure costs this year. Much of that will go toward building new data centers — more than twice what they spent two years ago.
As OpenAI and its partners build a roughly $60 billion data center complex for A.I. in Texas and another in the Middle East, Meta is erecting a facility in Louisiana that will be twice as large. Amazon is going even bigger with a new campus in Indiana. Amazon’s partner, the A.I. start-up Anthropic, says it could eventually use all 30 of the data centers on this 1,200-acre campus to train a single A.I system. Even if Anthropic’s progress stops, Amazon says that it will use those 30 data centers to deliver A.I. services to customers.

Amazon is building a data center complex in New Carlisle, Ind., for its work with the A.I. company Anthropic. Photo Credit…AJ Mast for The New York Times
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Stargate UAE:
OpenAI is partnering with United Arab Emirates firm G42 and others to build a huge artificial-intelligence data center in Abu Dhabi, UAE. The project, called Stargate UAE, is part of a broader push by the U.A.E. to become one of the world’s biggest funders of AI companies and infrastructure—and a hub for AI jobs. The Stargate project is led by G42, an AI firm controlled by Sheikh Tahnoon bin Zayed al Nahyan, the U.A.E. national-security adviser and brother of the president. As part of the deal, an enhanced version of ChatGPT would be available for free nationwide, OpenAI said.
The first 200-megawatt chunk of the data center is due to be completed by the end of 2026, while the remainder of the project hasn’t been finalized. The buildings’ construction will be funded by G42, and the data center will be operated by OpenAI and tech company Oracle, G42 said. Other partners include global tech investor, AI/GPU chip maker Nvidia and network-equipment company Cisco.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Softbank and ASI:
Not wanting to be left behind, SoftBank, led by CEO Masayoshi Son, has made massive investments in AI and has a bold vision for the future of AI development. Son has expressed a strong belief that Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI), surpassing human intelligence by a factor of 10,000, will emerge within the next 10 years. For example, Softbank has:
- Significant investments in OpenAI, with planned investments reaching approximately $33.2 billion. Son considers OpenAI a key partner in realizing their ASI vision.
- Acquired Ampere Computing (chip designer) for $6.5 billion to strengthen their AI computing capabilities.
- Invested in the Stargate Project alongside OpenAI, Oracle, and MGX. Stargate aims to build large AI-focused data centers in the U.S., with a planned investment of up to $500 billion.
Son predicts that AI will surpass human-level cognitive abilities (Artificial General Intelligence or AGI) within a few years. He then anticipates a much more advanced form of AI, ASI, to be 10,000 times smarter than humans within a decade. He believes this progress is driven by advancements in models like OpenAI’s o1, which can “think” for longer before responding.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Super High Salaries for AI Researchers:
Salaries for A.I. experts are going through the roof and reaching the stratosphere. OpenAI, Google DeepMind, Anthropic, Meta, and NVIDIA are paying over $300,000 in base salary, plus bonuses and stock options. Other companies like Netflix, Amazon, and Tesla are also heavily invested in AI and offer competitive compensation packages.
Meta has been offering compensation packages worth as much as $100 million per person. The owner of Facebook made more than 45 offers to researchers at OpenAI alone, according to a person familiar with these approaches. Meta’s CTO Andrew Bosworth implied that only a few people for very senior leadership roles may have been offered that kind of money, but clarified “the actual terms of the offer” wasn’t a “sign-on bonus. It’s all these different things.” Tech companies typically offer the biggest chunks of their pay to senior leaders in restricted stock unit (RSU) grants, dependent on either tenure or performance metrics. A four-year total pay package worth about $100 million for a very senior leader is not inconceivable for Meta. Most of Meta’s named officers, including Bosworth, have earned total compensation of between $20 million and nearly $24 million per year for years.
Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg on Monday announced its new artificial intelligence organization, Meta Superintelligence Labs, to its employees, according to an internal post reviewed by The Information. The organization includes Meta’s existing AI teams, including its Fundamental AI Research lab, as well as “a new lab focused on developing the next generation of our models,” Zuckerberg said in the post. Scale AI CEO Alexandr Wang has joined Meta as its Chief AI Officer and will partner with former GitHub CEO Nat Friedman to lead the organization. Friedman will lead Meta’s work on AI products and applied research.
“I’m excited about the progress we have planned for Llama 4.1 and 4.2,” Zuckerberg said in the post. “In parallel, we’re going to start research on our next generation models to get to the frontier in the next year or so,” he added.
On Thursday, researcher Lucas Beyer confirmed he was leaving OpenAI to join Meta along with the two others who led OpenAI’s Zurich office. He tweeted: “1) yes, we will be joining Meta. 2) no, we did not get 100M sign-on, that’s fake news.” (Beyer politely declined to comment further on his new role to TechCrunch.) Beyer’s expertise is in computer vision AI. That aligns with what Meta is pursuing: entertainment AI, rather than productivity AI, Bosworth reportedly said in that meeting. Meta already has a stake in the ground in that area with its Quest VR headsets and its Ray-Ban and Oakley AI glasses.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
VC investments in AI are off the charts:
Venture capitalists are strongly increasing their AI spending. U.S. investment in A.I. companies rose to $65 billion in the first quarter, up 33% from the previous quarter and up 550% from the quarter before ChatGPT came out in 2022, according to data from PitchBook, which tracks the industry.
This astounding VC spending, critics argue, comes with a huge risk. A.I. is arguably more expensive than anything the tech industry has tried to build, and there is no guarantee it will live up to its potential. But the bigger risk, many executives believe, is not spending enough to keep pace with rivals.
“The thinking from the big C.E.O.s is that they can’t afford to be wrong by doing too little, but they can afford to be wrong by doing too much,” said Jordan Jacobs, a partner with the venture capital firm Radical Ventures. “Everyone is deeply afraid of being left behind,” said Chris V. Nicholson, an investor with the venture capital firm Page One Ventures who focuses on A.I. technologies.
Indeed, a significant driver of investment has been a fear of missing out on the next big thing, leading to VCs pouring billions into AI startups at “nosebleed valuations” without clear business models or immediate paths to profitability.
Conclusions:
Big tech companies and VCs acknowledge that they may be overestimating A.I.’s potential. Developing and implementing AI systems, especially large language models (LLMs), is incredibly expensive due to hardware (GPUs), software, and expertise requirements. One of the chief concerns is that revenue for many AI companies isn’t matching the pace of investment. Even major players like OpenAI reportedly face significant cash burn problems. But even if the technology falls short, many executives and investors believe, the investments they’re making now will be worth it.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.nytimes.com/2025/06/27/technology/ai-spending-openai-amazon-meta.html
Meta is offering multimillion-dollar pay for AI researchers, but not $100M ‘signing bonuses’
https://www.theinformation.com/briefings/meta-announces-new-superintelligence-lab
OpenAI partners with G42 to build giant data center for Stargate UAE project
AI adoption to accelerate growth in the $215 billion Data Center market
Will billions of dollars big tech is spending on Gen AI data centers produce a decent ROI?
Networking chips and modules for AI data centers: Infiniband, Ultra Ethernet, Optical Connections
Superclusters of Nvidia GPU/AI chips combined with end-to-end network platforms to create next generation data centers
Proposed solutions to high energy consumption of Generative AI LLMs: optimized hardware, new algorithms, green data centers
Verizon partners with Nokia to deploy large private 5G network in the UK
Nokia and Verizon Business are collaborating to deploy a private 5G network across the Thames Freeport, a major UK industrial cluster including the Port of Tilbury and Ford Dagenham. This project is one of the UK’s largest private 5G deployments. It aims to modernize operations, boost efficiency, and drive economic growth in the region. The Thames Freeport, a 34 km-wide economic corridor, is the site of the deployment. This includes major industrial sites like the Port of Tilbury, Ford Dagenham, and DP World London Gateway. The deployment will cover 1,700 acres across multiple industrial sites within the Freeport.
Nokia will be the sole hardware and software provider, utilizing its Digital Automation Cloud (DAC) and MX Industrial Edge (MXIE) solutions.
This private 5G network will enable advanced use cases like AI-driven data analytics, predictive maintenance, process automation, autonomous vehicle control, and real-time logistics orchestration, according to Telecoms Tech News. The network is expected to modernize port operations, improve cargo handling, and enhance overall efficiency in the Freeport. The project also aims to boost the local economy, support job creation and training, and foster innovation and R&D collaborations.

Verizon and Nokia win a Thames Freeport private 5G deal. (Art by midJourney for Fierce Network)
“Band 77 in the U.K. is available at low cost on a local-area licensed basis — enterprises can readily get access to exclusive use mid-band spectrum in the 3.8-4.2 GHz range. The U.K. regulator, Ofcom, has pioneered this model globally,” said Heavy Reading Senior Principal Analyst for Mobile Networks Gabriel Brown in an email to Fierce Network. Brown noted that though it is based in the U.S., Verizon has an established smart ports business in the U.K., with the Port of Southhampton one of its private 5G network clients. He added the operator also has an ongoing relationship with Nokia around private 5G. “This new win shows advanced wireless technologies can scale to support nationally critical infrastructure with diverse stakeholders and use cases,” Brown said.
“To date, over 530 licenses have been issued to more than 90 licensees in this frequency range,” said SNS Telecom & IT 5G research director Asad Khan.
Verizon Business has been working on building its ports business for a while now, having already scored the aforementioned Southampton deal in April 2021. And its efforts appear to be paying off.
“I know there’s been chatter about how Verizon Business was able to outbid domestic carriers,” AvidThink Principal Roy Chua stated. “It’s likely some combination of demonstrated expertise in rolling out similar deployments and favorable financial terms. Definitely a win for Verizon Business (and Nokia) for sure.”
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/wireless/verizon-and-nokia-win-one-largest-private-5g-projects-uk