Author: Alan Weissberger
Iridium Introduces its NexGen Satellite IoT Data Service
Iridium Communications Inc. has announced the service introduction of Iridium Messaging TransportSM (IMTSM), a two-way cloud-native networked data service optimized for use over Iridium Certus® and designed to make it easier to add satellite connections to existing or new IoT solutions. IMT provides an IP data transport service unique to the Iridium® network, designed for small-to-moderate-sized messages supporting satellite IoT applications. Integrated with Iridium CloudConnect and Amazon Web Services (AWS), the new service can reduce development costs and speed time to market for new Iridium Connected® IoT devices. IMT has been highly anticipated by Iridium’s partner ecosystem and is currently available for the Iridium Certus 100 service with introduction on Iridium Certus 200, 350 and 700 planned for the first quarter of 2023.
As a connectionless messaging service for Iridium CertusTM modules, IMT aligns with current established server-device message constructs using hubs, Pub/Sub or queues, depending on application platforms. The IMT service can be used by a customer application that is ‘store and forward’ or has small amounts of data traffic that does not require a persistent connection between servers, utilizing an Iridium Certus terminal. Whether it’s machine-to-machine (M2M), e-mails, weather updates, transactions, or group communications, IMT enhances two-way messaging to and from anywhere in the world.

IMT is utilized with the Iridium CloudConnect model of server-side message processing, regardless of the underlying over-the-air and ground systems technologies and protocols. The Iridium CloudConnect service combines Iridium IoT capabilities with AWS cloud services extending customers’ IoT reach to the more than 85 percent of the earth that lacks terrestrial coverage. IMT utilizes industry-standard protocols and technology for managing and delivering messages in the cloud, including MQTT, HTTPS and WebSocket (WSS). This makes IMT an easier, faster, and less expensive protocol to develop with, supporting users with countless advantages to design applications that are scalable and easier to distribute to other platforms.
Among the first products built with IMT available are the RockREMOTE by Ground Control and STREAM+ by MetOcean Telematics. The RockREMOTE offers a reliable and flexible solution for industrial IoT applications including oil and gas, mining, utilities and renewables, and transport & cargo. It has a built-in MQTT application that allows developers to submit and receive data payloads across the MQTT protocol. Users can send and receive messages, pictures, to and from anywhere in the world utilizing this IMT implementation over the Iridium Certus 100 service.
Also powered by Iridium Certus 100, STREAM+ allows users to send and receive files and messages securely. Designed for field applications with size, weight, and power constraints, STREAM+ offers a range of industry standard protocols, features, and inputs simplifying integration and installation for end users and reducing development costs and overall time to market.
Also currently working on IMT service-based solutions are Iridium partners Beam Communications, Blue Sky Network, CLS Group, Globalsat Group, Lars Thrane A/S and Zunibal.
“The launch of Iridium Messaging Transport adds another powerful capability to the Iridium Certus portfolio and another value-added service for our partners and the growing IoT market,” said Bryan Hartin, executive vice president, sales and marketing, Iridium. “Our partners are excited about IMT as it will make it faster and easier for them to add Iridium satellite connectivity to new and existing solutions needed across a number of industries.”
Unique in the satellite industry, Iridium Certus is the only broadband service that provides reliable, weather-resilient connectivity for on-the-move internet, high-quality voice, email, live-action video and IoT data transfer. Through its constellation of crosslinked satellites in Low-Earth Orbit (LEO), Iridium is the only communications company that offers truly global coverage and is ideally suited for IoT applications.
In a 2021 blog post, Iridium wrote:
The Iridium® network is uniquely qualified to provide global satellite IoT services due to its network architecture of 66 Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites, blanketing the earth with reliable and ubiquitous coverage.
Examples of satellite IoT usage can be found across all industry verticals from the maritime market to machine-to-machine (M2M) applications in transportation, agriculture, oil and gas, utilities and construction, among many others. To help paint a clear picture of how satellite IoT is used today, let’s explore the heavy equipment market. Many of the world’s largest heavy equipment Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) rely on Iridium’s satellite IoT solutions to remotely monitor and manage deployed assets. For instance, Kobelco Construction Machinery (KCM) recently partnered with Iridium to integrate Iridium’s two-way satellite communications into its hydraulic excavator machinery, heavy equipment, and remote asset management platform. Through the addition of Iridium IoT services, KCM equipment is now fitted with truly global coverage for the first time. Additionally, KCM deployed assets can be programmed to automatically deliver recurring telematics information like engine performance, run time, fault diagnostics, and other maintenance related data to customers through critical, real-time, actionable reports and alerts.
About Iridium Communications:
Iridium® is the only mobile voice and data satellite communications network that spans the entire globe. Iridium enables connections between people, organizations and assets to and from anywhere, in real time. Together with its ecosystem of partner companies, Iridium delivers an innovative and rich portfolio of reliable solutions for markets that require truly global communications. In 2019, the company completed a generational upgrade of its satellite network and launched its new specialty broadband service, Iridium Certus®. Iridium Communications Inc. is headquartered in McLean, Va., U.S.A., and its common stock trades on the Nasdaq Global Select Market under the ticker symbol IRDM. For more information about Iridium products, services and partner solutions, visit www.iridium.com.
References:
RVA LLC: Fiber Deployment in U.S. Reaches Highest Level Ever; Google Fiber Returns
Fiber facility service providers passed 7.9 million additional homes in the U.S. in 2022—the highest annual deployment ever, even with challenges in materials supply chain and labor availability, according to a fiber deployment report from the Fiber Broadband Association.
The 2022 Fiber Provider Survey was based on research conducted by RVA LLC Market Research & Consulting (RVA). Their researchers found that there are now a total of 68 million fiber broadband passings in the U.S., with strong recent increases of 13% over the past 12 months and 27% over the past two years. The survey also found that 63 million unique homes have now been passed (this figure “excludes homes with two or more fiber passings”). To date, fiber has passed nearly half of primary homes and over 10% of second homes. The annual fiber deployment rate is likely to be even higher over the next five years as BEAD and other broadband funding programs kick in.
In its research, RVA notes that although deployment expectations from individual companies are in constant flux based on many factors, many service providers have announced network builds exceeding the fiber footprint they have built through private funding. Canada is seeing strong fiber deployment as well, with about 66% of homes passed.
“High-quality broadband has become more important to consumers every year. Fiber broadband exceeds all other types of delivery in every single measurement of broadband quality, including speeds, uptime, latency, jitter, and power consumption,” Gary Bolton, Fiber Broadband Association president and CEO, said in a prepared statement. “For the consumer this has real-world impacts, like more productivity, better access to health care and education, more entrepreneurism, and the option of more rural living. For society, this means more sustainability and, ultimately, digital equity.”
Mike Render, Founder and CEO of RVA, will present the findings of the 2022 Fiber Provider Survey on Fiber for Breakfast, Wednesday, December 28, 2022, at 10:00am ET. Click here to register for the episode.
About the Fiber Broadband Association (FBA):
The Fiber Broadband Association is the largest and only trade association that represents the complete fiber ecosystem of service providers, manufacturers, industry experts, and deployment specialists dedicated to the advancement of fiber broadband deployment and the pursuit of a world where communications are limitless, advancing quality of life and digital equity anywhere and everywhere. The Fiber Broadband Association helps providers, communities, and policy makers make informed decisions about how, where, and why to build better fiber broadband networks. Since 2001, these companies, organizations, and members have worked with communities and consumers in mind to build the critical infrastructure that provides the economic and societal benefits that only fiber can deliver. The Fiber Broadband Association is part of the Fibre Council Global Alliance, which is a platform of six global FTTH Councils in North America, LATAM, Europe, MEA, APAC, and South Africa. Learn more at fiberbroadband.org.
The Fiber Broadband Association is also helping with the expansion by helping to train installers through its Optical Telecom Installation Certification (OpTIC) Path program.
Press Contact:
Ashley Schulte
Connect2 Communications for the Fiber Broadband Association
[email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Light Reading says that Webpass to play role in Google Fiber’s new expansion efforts. “As we continue to grow our footprint across the country, we’re integrating this [wireless] method for delivering high-speed service in more areas where it makes sense in all our existing cities and in our new expansion areas as well,” Tom Brownlow, senior network operations manager at Google Fiber, and Blake Drager, the head of technology at Google Fiber’s Webpass business, wrote in a post to the company’s website.
Google Fiber recently announced talks were underway with city leaders in five states – Arizona, Colorado, Nebraska, Nevada and Idaho – about expanding fiber services to various communities. Cities to make Google Fiber’s new-build list recently include Omaha, Nebraska, Mesa, Arizona and Lakewood, Colorado. Brownlow and Drager didn’t specify which of those expansion markets might include wireless offerings.
References:
MoffettNathanson: ROI will be disappointing for new fiber deployments; FWA best for rural markets
From two recent research reports to clients, MoffettNathanson chief analyst Craig Moffett wrote:
There is no question that there will be a great deal of new fiber deployed in the U.S. But we expect it will be considerably less than current worst-case scenarios for two reasons.
- There simply isn’t sufficient labor availability for all operators to meet the projections they’ve set forth (this issue will be significantly exacerbated by the upcoming rural Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) program, which will introduce a dramatic new source of labor demand).
- The expected return from fiber overbuilds will be disappointing, in our view, both because deployment costs (including the cost of capital) have risen sharply, and because expected densities of available markets are falling sharply.
We are skeptical about the returns that will be generated by fiber builds, as costs are rising and densities are falling. The spiraling costs of fiber deployment also make it likely that there will be upward, not downward, pressure on broadband ARPU in competitive markets, as overbuilders scramble to cost-justify not only their existing projects, but, perhaps more importantly, the projects on which they have not yet broken ground (and which, without a more generous ARPU assumption, can no longer be return-justified). Craig had argued earlier this year that the fiber buildout bubble may pop.
Wireless operators have an enormous cost advantage in offering fixed wireless access (FWA) service on preexisting network facilities; the marginal cost of offering FWA is zero if it is simply using excess capacity. The capacity available for such a strategy is relatively limited, making the strategic leverage of FWA relatively limited as well. Cable operators have a smaller, but still significant, cost advantage in offering wireless services that can offload at least some of their traffic onto existing infrastructure. And unlike wireless operators offering FWA, their capacity to do so is unlimited.
Almost no telecom investor with whom we have spoken views FWA as an important part of the story for the companies that actually offer it. Investors seem to have already come to the view (for the wireless operators, at least) that FWA is at best a costly sideline in rural markets. Longer term, the bigger threat to cable broadband is likely fiber rather than fixed wireless, Moffett said. But even with that, the analyst seems to be less concerned that cable operators will overspend on fiber or that overbuilders will present more competition.
The convergence arguments for fiber to the home (FTTH) are arguably even weaker. As we’ve pointed out often, AT&T’s wireline footprint covers but 45% or so of the U.S. (by population), and of that, just a third is wired for fiber. In total, then, AT&T can deliver a bundled solution to just 15% or so of the population. In our view, a strategy (bundling) that “works” in 15% of the country isn’t a strategy.
We certainly aren’t convinced that the U.S. market will be fundamentally shaped by convergence. But if it is, the cable operators, not the telcos, are positioned to benefit.
References:
MoffettNathanson: Fiber Bubble May Pop; AT&T is by far the largest (fiber) overbuilder in U.S.
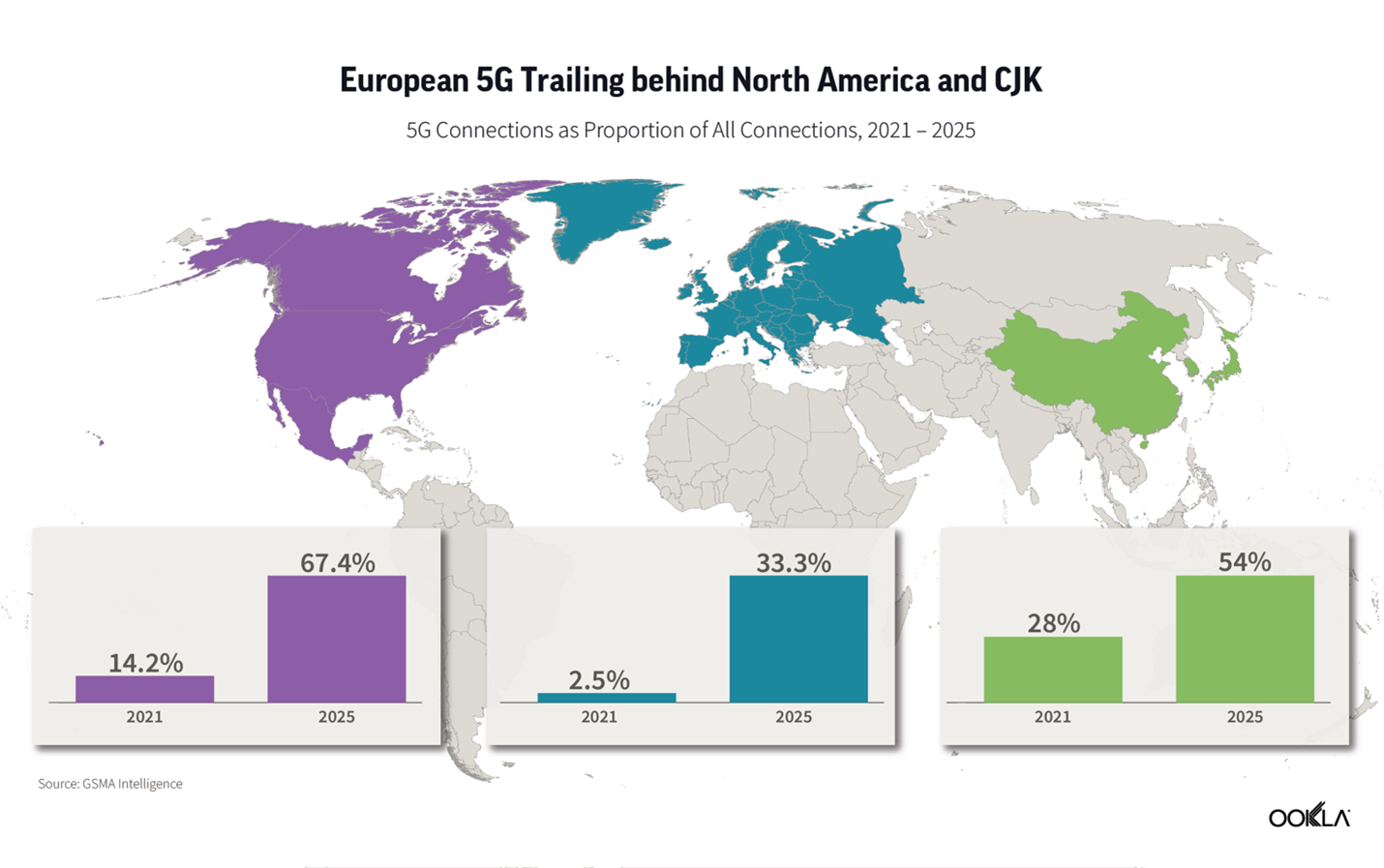
Ookla: State of 5G Worldwide in 2022 & Countries Where 5G is Not Available
Executive Summary:
In a new blog post, Ookla asseses The State of Worldwide 5G in 2022. The market research firm examined Speedtest Intelligence® data from Q3 2022 Speedtest® results to see how 5G performance has changed since last year, where download speeds are the fastest at the country level, and how satellite technologies are offering additional options to connect. Ookla also looked at countries that don’t yet have 5G to understand where consumers are seeing improvements in 4G LTE access.
Editor’s Note: for some unknown reason, China is not included in Ookla’s report
- 5G speeds were stable at the global level with:
a] Median global 5G download speed of 168.27 Mbps in Q3 2022 as compared to 166.13 Mbps in Q3 2021
b] Median upload speed over 5G slowed slightly to 18.71 Mbps (from 21.08 Mbps) during the same period
- Ookla® 5G Map™: 127,509 5G deployments in 128 countries as of November 30, 2022, compared to 85,602 in 112 countries the year prior
- South Korea and the United Arab Emirates led countries for 5G speeds
- 5G Availability points to on-going challenges


5G Availability measures the proportion of Speedtest users with 5G-capable handsets, who spend a majority of time connected to 5G networks. It’s therefore a function of 5G coverage and adoption. We see wide disparity in 5G Availability among markets worldwide, with for example the U.S. recording 54.3% in Q3 2022, well ahead of markets such as Sweden and the U.A.E., with 8.6% and 8.3% respectively.

Critical levers for mobile operators to increase 5G Availability include:
- Increasing 5G coverage by deploying additional base stations
- Obtaining access to, or refarming, sub-GHz spectrum, to help broaden 5G coverage, as sub-GHz spectrum has superior propagation properties than that of higher frequency spectrum bands.
- Encouraging 5G adoption among users with 5G-capable handsets.
Speedtest Intelligence points to 5G adoption challenges in some markets, with 5G Availability dropping in Bulgaria, South Korea, the Netherlands, and the U.A.E. As more users acquire 5G-capable devices, operators need to balance their pricing models to ensure users have sufficient incentives to purchase a 5G tariff.

Countries where 5G is not readily available:
Speedtest Intelligence showed 29 countries in the world where more than 20% of samples were from 2G and 3G connections (combined) during Q3 2022 and met our statistical threshold to be included (down from 70 in Q3 2021). These are mostly countries where 5G is still aspirational for a majority of the population, which is being left behind technologically, having to rely on decades-old technologies that are only sufficient for basic voice and texting, social media, and navigation apps. We’re glad to see so many countries fall off this list, but having so many consumers on 2G and 3G also prevents mobile operators from making 4G and 5G networks more efficient. If operators and regulators are able to work to upgrade their users to 4G and higher, everyone will benefit.
Countries That Still Rely Heavily on 2G and 3G Connections
Speedtest IntelligenceⓇ | Q3 2021
| Country | 2G & 3G Samples |
|---|---|
| Central African Republic | 76.2% |
| Turkmenistan | 58.5% |
| Kiribati | 51.6% |
| Micronesia | 47.4% |
| Rwanda | 41.1% |
| Belarus | 39.7% |
| Equatorial Guinea | 37.7% |
| Afghanistan | 36.7% |
| Palestine | 33.5% |
| Madagascar | 27.5% |
| Sudan | 27.4% |
| Lesotho | 26.5% |
| South Sudan | 26.3% |
| Benin | 26.0% |
| Guinea | 25.5% |
| Cape Verde | 24.3% |
| Tonga | 24.3% |
| Syria | 23.4% |
| The Gambia | 23.4% |
| Ghana | 23.3% |
| Palau | 22.9% |
| Niger | 22.8% |
| Tajikistan | 22.7% |
| Mozambique | 22.4% |
| Guyana | 21.8% |
| Togo | 21.8% |
| Congo | 21.1% |
| Moldova | 20.8% |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | 20.0% |
Conclusions:
Ookla was glad to see performance levels normalize as 5G expands to more and more countries and access improves and we are optimistic that 2023 will bring further improvements. Keep track of how well your country is performing on Ookla’s Speedtest Global Index™ or track performance in thousands of cities worldwide with the Speedtest Performance Directory™.
References:
Strand Consult: Market for 5G RAN in Europe: Share of Chinese and Non-Chinese Vendors in 31 European Countries
With its new report “The Market for 5G RAN in Europe: Share of Chinese and Non-Chinese Vendors in 31 European Countries,” Strand Consult brings valuable evidence of the location, amount, and share of Chinese and non-Chinese equipment in European telecom networks. This report, the second of its kind, describes the respective amounts of 5G equipment from Huawei, ZTE, and non-Chinese vendors in European mobile networks and the share of such in equipment in the 5G Radio Access Network (RAN). Here are the highlights from the new report.
- There is little transparency about the amount, type, location, and share of 4G and 5G Chinese equipment in European networks.
- In 8 of 31 countries, more than 50% of the 5G RAN equipment comes from Chinese vendors. In 2020, it was 16 of 31 countries in which the 4G RAN equipment came from Chinese vendors.
- In one country, 100% of the 5G RAN comes from Chinese vendors. In 2020 there were 3 European countries with 100% 4G RAN equipment from Chinese vendors.
- Only 11 of 31 European countries can offer their users access to clean, non-Chinese networks.
- 41% of the mobile subscribers in Europe have access to 5G RAN from Chinese vendors. In 2020, 51% of European mobile subscribers had access to 4G RAN from Chinese vendors.
- The large European countries–Germany, Italy, Poland, Portugal, Austria, and Spain–purchase significant amounts of 5G equipment from Chinese vendors.
- Operators like Telenor and Telia in Norway, TDC in Denmark, 3 in Denmark and Sweden, T-Mobile Nederland’s, and Proximus in Belgium have switched out Chinese suppliers. None of those operators report increased networks cost or delay in 5G rollout.
- The data suggests that Germany appears not to take the security threat of China seriously. Nord Stream 2 was Germany’s debacle oil energy supplies from Russia; it appears that Germany sets up a similar scenario in the communications domain with Huawei and ZTE.
- As Germany accounts for 25% of European mobile customers, the German government’s lax approach to communications infrastructure creates a risk for Germany and all people who interconnect with German networks.
- Germany together with Italy, Poland, and Austria, comprise 50% of European mobile customers. These countries are heavily dependent on Chinese equipment, creating risk for their own nations and others which use their networks.
- In 2020, 57% of Germany’s 4G RAN came from Chinese vendors. In 2022, 59% of the 5G RAN in Germany comes from Chinese vendors.
- Huawei enjoys a higher market share in Berlin than in Beijing where it shares the market with ZTE and other vendors.
- US General Darryl A. Williams serves as the commanding general of the United States Army Europe and Africa (based in Wiesbaden, German) and commander of the Allied Land Command. He oversees more than 20,000 staff. Unwittingly when he uses a commercial mobile phone, the traffic is sent through a network built with Chinese equipment. Similarly when American military use their personal devices, they engage on a Chinese network at risk for intrusion.
Strand Consult’s report delivers detailed information about Chinese and non-Chinese network equipment in Europe at country level. The report highlights of the importance of the EU’s 5G toolbox and provides recommendations to improve its implementation. The toolbox applies to most of Europe’s 102 mobile operators across 31 countries serving some 673 million mobile customers. The report also provides valuable economic context to understand the market for RAN equipment.
The focus on 5G and 4G RAN reflects the shift of the security debate. There is consensus across most countries outside China that equipment provided by vendors owned and affiliated with the Chinese government and military poses unacceptable risk for the security and integrity of the core of the network. The discussion has evolved to whether and to what degree should such vendors be allowed to supply the RAN.
The 4G RANs studied in the 2020 report were purchased in the 12-year period of 2008-2020. Most of RANs were delivered and installed during 2009-2016 when operators upgraded their 2G and 3G networks to 4G networks. The main part of the 5G RAN was purchased, delivered, and installed after 2020.
When performing a financial analysis of the cost of restricting Huawei, one must consider that network upgrades will happen regardless of selection of vendor. There is a sunk cost to network upgrades which must be subtracted from the total cost of using a Chinese vendor.
Despite the widespread knowledge of the threat associated with using Chinese equipment, some of Europe’s largest operators have purchased and deployed Chinese 5G equipment in their networks after 2020. That decision could have major consequences for their shareholders if Europe’s policymakers conclude that it is not smart to depend on Chinese telecommunications infrastructure in the same way as it did for Russian gas.
The report is valuable for mobile operators and their shareholders, communications policymakers, security and defense analysts, network engineers, and other professionals in the field. Contact Strand Consult today to get your free copy of the report “The Market for 5G RAN in Europe: Share of Chinese and Non-Chinese Vendors in 31 European Countries.”
References:
https://strandconsult.dk/field/reports/
Strand Consult: Open RAN hype vs reality leaves many questions unanswered
O-RAN Alliance tries to allay concerns; Strand Consult disagrees!
Strand Consult: What NTIA won’t tell the FCC about Open RAN
Strand Consult: MWC 2022 Preview and What to Expect
Strand Consult: 5G in 2019 and 2020 telecom predictions
Dell’Oro: SASE Market grew 33% in 2022; forecast to hit $8B in 2023
According to Dell’Oro Group, the ongoing need to modernize the network and security architecture for branch offices and hybrid users led to the vigorous 33% revenue growth in the SASE [1.] market. The market research firm anticipates that enterprises will continue to place a high priority on SASE and cause the overall SASE market to grow to $8B for the full year 2023. In contrast, Gartner forecasts that total worldwide end-user spending on SASE will reach $9.2 billion in 2023, a 39% increase from 2022.
Note 1. In 2019, Gartner coined the term secure access service edge, or SASE, that brings a more secure and flexible way to perform advanced security inspection directly in the cloud, instead of backhauling application traffic to a data center before forwarding it to the cloud. This cloud-first approach to security also aligns with the increasing adoption of hybrid work post-pandemic, where workers will balance their time in the office and working remote for the foreseeable future.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
“3Q 2022 was the seventh consecutive quarter of year-over-year SASE revenue growth topping 25%, which signals the importance enterprises are placing on SASE,” said Mauricio Sanchez, Research Director, Network Security, and SASE & SD-WAN at Dell’Oro Group. “Unlike some other network security markets we track, we expect the high investment priority will continue and lead to the SASE market eclipsing $8 B in 2023,” added Sanchez.

Image Source: https://trustgrid.io/sase/

Additional highlights from the 3Q 2022 SASE & SD-WAN Quarterly Report:
- SASE security, also referred to as SSE (the basket of products providing cloud-delivered SWG, CASB, ZTNA, and FWaaS), achieved its tenth consecutive quarter of sequential revenue expansion.
- SASE networking, synonymous with SD-WAN, had a challenging Y/Y comparison in 3Q 2022 against a very strong 3Q 2021 when enormous pent-up demand was a significant driver. Nonetheless, the ongoing trend of improved supply chains allowed vendors to better service demand and sustain a similar level of market growth compared to recent quarters.
Cisco, Fortinet, Palo Alto Networks, Symantec/Broadcom, Versa Networks, VMware and Zscaler are the leading SASE suppliers, according to Del’Oro (see different list below). However, Sanchez also mentioned another company not typically associated with SASE: Microsoft.
“The dark horse is Microsoft. Not a significant player today, but could easily become one virtually overnight,” he said. “Microsoft – Windows, Azure – has all the technology elements to not only do SASE but compete on a number of other fronts: identity management, firewalls, email/content security, WAF, DDoS, endpoint, cloud security, cloud networking. Moreover, Microsoft has been beating the drum louder about their security capabilities and desire to go after share of security wallet.”
Author’s Note: SASE is a single vendor turn key solution so vendor selection is ultra important.
The Dell’Oro Group SASE & SD-WAN report includes manufacturers’ revenue covering the SASE and Access Router markets. In addition, the report analyzes the SASE market from two perspectives, technology (SD-WAN networking and SSE security) and implementation (unified and disaggregated). The report also provides unit information for the Access Router market. To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, security, enterprise network, and data center infrastructure markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit www.delloro.com.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Definition: SASE (an acronym coined by Gartner) converges network (SD-WAN, ZTNA) and network security services (SWG, CASB, FWaaS, etc). All of these services are integrated and delivered based on user and device identities, context, policies with continuous assessment of risk/trust throughout a session. This combination creates small perimeters around users, devices, and applications, that are then additionally hardened by security services.
Netskope research says that by 2024, at least 40% of enterprises are expected to have explicit strategies for adopting SASE. SASE solutions will help small to large businesses with extracting the security incidents mentioned in the below image. According to MarketWatch, the global SASE market is expected to reach $3936.4 million by 2026.

Image Source: https://trustgrid.io/sase/
According to Software Testing Help, the leading SASE vendors are:
- #1) Cato SASE (Recommended)
- #2) Perimeter 81
- #3) Twingate
- #4) Netskope
- #5) Zscaler
- #6) Barracuda Networks
- #7) VMware
- #8) Fortinet
- #9) PaloAlto Network
- #10) Akamai Enterprise Application Access
- #11) Cisco
To leverage the SASE platform, it should have cloud-native & cloud-based architecture. It should support all edges and be distributed globally across many PoPs (Points of Presence). A SASE platform with significant geographical reach will let you compete effectively and meet the requirements of low latency. A platform with agent-based capabilities can facilitate policy-based access, and some on-premises-based capabilities can provide network functions like QoS.
References:
https://www.delloro.com/news/strong-enterprise-demand-drives-sase-growth-33-percent-in-3q-2022/
https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/top-sase-vendors/
Gartner: SASE tops Gartner list of 6 trends impacting Infrastructure & Operations over next 12 to 18 months
Dell’Oro: Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) market to hit $13B by 2026; Gartner forecasts $14.7B by 2025; Omdia bullish on security
Cheerleading from 5G Americas contradicts disappointing financial results from 5G telcos
Chris Pearson, President of 5G Americas said,”5G continues to make significant progress throughout the world. The foundation of this new era of innovation is spectrum, standards (lack thereof?) and a growing ecosystem of key technologies that are being adopted by operators, vendors and end users.”
With 75 countries reporting 5G connections, most recent data from Omdia suggests 433 million global 5G connections were added from Q3 2021 to Q3 2022, almost doubling connections from 489 million to 922 million. Overall, those figures represent 14.4 percent sequential quarterly growth from 806 million in Q2 2022 to 921 million in Q3 2022. Global 5G connections are forecast to again accelerate in 2023, approaching 2 billion and reaching 5.9 billion by the end of 2027.
North America is a leader in the uptake of wireless 5G connections with a total of 108 million 5G and 506 million LTE connections by the end of Q3 2022. 5G penetration of the population in the North American market is approaching 30 percent, as the region added 14 million 5G connections for the quarter – a gain of 15.47 percent over Q2 2022. Overall, a total of 137 million 5G connections is projected to come from North America by the end of 2022, bolstered by strong 5G smartphone shipments in the US. IDC predicts the US 5G smartphone market will reach 118.1 million units shipped in 2022, showing a 27% increase from 2021.
Kristin Paulin, Principal Analyst at Omdia said, “There is still much more to come from 5G that will drive growth. Expanding mid-band coverage will bring a better 5G experience, balancing coverage and speed. And the standalone 5G deployments in progress will enable new applications that take 5G to the next level.”
In comparison, 4G LTE is expected to remain strong in Latin America and the Caribbean through the end of 2022. In Q3 2022, there were 530 million 4G LTE connections, representing 2.14 percent quarterly growth with the addition of 11 million new LTE subscriptions. Latin America and the Caribbean is projected to have 22 million 5G connections by year end of 2022, and 399 million by 2027.
According to Jose Otero, Vice President of Caribbean and Latin America for 5G Americas, “With over half a billion connections, 4G LTE is the foundation of mobile wireless connectivity throughout the Latin America region. Yet, as we look forward to the future, 5G will begin to play a bigger and bigger role for citizens in the region as deployments and connections increase significantly.”
Overall, the number of 5G commercial networks globally has reached 250, according to data from TeleGeography and 5G Americas. That number is expected to reach 253 by the end of 2022 and 397 by the end of 2025 representing strong 5G network investment growth in many regions throughout the world.
The number of 5G and 4G LTE network deployments as of December 14, 2022, are summarized below:
5G:
- Global: 250
- North America: 14
- Caribbean and Latin America: 28
4G LTE:
- Global: 702
- North America: 17
- Caribbean and Latin America: 131
Visit www.5GAmericas.org for more information, statistical charts, infographic and a list of LTE and 5G deployments by operator and region. Subscriber and forecast data is provided by Omdia and deployment data by TeleGeography (GlobalComm).
About 5G Americas: The Voice of 5G and LTE for the Americas
5G Americas is an industry trade organization composed of leading telecommunications service providers and manufacturers. The organization’s mission is to facilitate and advocate for the advancement and transformation of LTE, 5G and beyond throughout the Americas. 5G Americas is invested in developing a connected wireless community while leading 5G development for all the Americas. 5G Americas is headquartered in Bellevue, Washington. More information is available at 5G Americas’ website and Twitter.
5G Americas’ Board of Governors Members include Airspan Networks Inc., Antel, AT&T, Ciena, Cisco, Crown Castle, Ericsson, Intel, Liberty Latin America, Mavenir, Nokia, Qualcomm Incorporated, Samsung, Shaw Communications Inc., T-Mobile US, Inc., Telefónica, VMware, and WOM.
Contacts
5G Americas
Viet Nguyen
+1 206 218 6393
[email protected]
Ericsson expects RAN market to be flat with 5G build-out still in its early days; U.S. cellular industry growth to slow in 2023
Ericsson is planning for a flat RAN market and is structuring its cost base and operations accordingly. Underlying the flat market is a technology shift to 5G from earlier generation. 5G build-out is still in its early days with only about 20% of all base station sites outside China installed with 5G mid-band. Because 5G is still in its early days, vendors like Ericsson and Nokia are seeing lower margins. Therefore, they are relying more heavily on patent royalties to boost profits. Because 5G is still in its early days, vendors like Ericsson and Nokia are seeing lower margins. Therefore, they are relying more heavily on patent royalties to boost profits.

Given the rapid increase in network traffic levels, operators’ investment in performance and capacity is expected to remain robust. The 5G RAN market is expected to grow by over 11% per annum over the next three years, with potential further upside from areas such as Fixed Wireless Access, Enterprise connectivity, XR and Mission Critical Services (which require URLLC which meets performance requirements in ITU M.2410).
In Networks, Ericsson expects to expand its global footprint and enhance gross income through continued investments in technology for performance and cost leadership and, in addition, improve productivity and capital efficiency across the supply chain. In particular the Segment will continue investing in enhanced portfolio energy performance, enabled by Ericsson Silicon and innovating next-generation open architecture, such as Cloud RAN – key areas of strategic importance for its operator customers. Cloud RAN also offers potential in the enterprise segment.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Separately, Morgan Stanley analysts forecast that the U.S. wireless industry growth will slow in 2023.
“Carriers could move to cut pricing in order to maintain their subscriber bases,” the Morgan Stanley analysts wrote in a report to investors issued Thursday. That could reduce the operators’ ability to make money, they noted. “A continued adoption of premium plans could also support wireless service revenue growth,” they added.
Morgan Stanley analysts expect the U.S. wireless industry – including Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, Dish Network and cable companies like Comcast and Charter Communications – to collectively add 8.7 million new postpaid phone customers during 2023. That’s down only slightly from 8.9 million during 2022 and just below the record 10 million that providers collectively added over the course of 2021.
“We see the biggest slowdown in 2023 adds at AT&T, while Verizon could grow adds modestly yoy [year over year] off a low base, and T-Mobile can do slightly better given this year saw the impact of the Sprint network shutdown,” the Morgan Stanley analysts wrote. “We will be watching the growing deployment of eSIM technology to see if it opens the door to higher switching activity, while it should also help carriers lower costs through an easier activation process.”
References:
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/ericsson-capital-markets-day-2022-301704231.html
https://telecoms.com/519003/ericsson-expects-ran-market-growth-to-be-flat-for-years/
T-Mobile and Cisco launch cloud native 5G core gateway
T-Mobile US announced today that it has collaborated with Cisco to launch a first-of-its kind cloud native 5G core gateway. T-Mobile has moved all of its 5G and 4G traffic to the new cloud native converged core which provides customers with more than a 10% improvement in speeds and lower latency. The new core gateway also allows T-Mobile to more quickly and easily test and deliver new 5G and IoT services, like network slicing and Voice over 5G (VoNR) thereby expediting time to market.
The T-Mobile US 5G SA core is based on Cisco’s cloud-native control plane that uses Kubernetes to orchestrate containers running on bare metal. The companies said this frees up more than 20% of the CPU cores.
It also uses Cisco’s 8000 Series routers, 5G and 4G LTE packet core gateways, its Unified Computing System (UCS) platform, and Cisco’s Nexus 9000 Series Switches that run the vendor’s Network Services Orchestrator for full-stack automation.
“T-Mobile customers already have access to the largest, most powerful 5G network in the country, and we’re innovating every day to supercharge their experience even further,” said Delan Beah, Senior Vice President of Core Network and Services Engineering at T-Mobile. “This cloud native core gateway takes our network to new heights, allowing us to push 5G forward by delivering next-level performance for consumers and businesses nationwide while setting the stage for new applications enabled by next-gen networks.”
With a fully automated converged core gateway, T-Mobile can simplify network functions across the cloud, edge and data centers to significantly reduce operational life cycle management. The increased efficiency is an immediate benefit for customers, providing them with even faster speeds. The new core is also more distributed than ever before, leading to lower latency and advancing capabilities like edge computing.
“Our strategic relationship with T-Mobile is rooted in co-innovation, with a shared vision to establish best practices for 5G and the Internet for the Future,” said Masum Mir, Senior Vice President and General Manager, Cisco Networking Provider Mobility. “This is the type of network every operator aspires to. It will support the most advanced 5G applications for consumers and businesses today and enables T-Mobile to test and deliver new and emerging 5G and IoT applications with simplicity at scale.”
The fully automated converged core architecture is based on Cisco’s cloud native control plane, optimized with Kubernetes orchestrated containers on bare metal, freeing up over 20% of the CPU (Central Processing Unit) cores. The converged core solution uses a broad mix of Cisco’s flagship networking solutions including the Cisco 8000 Series routers, 5G and 4G packet core gateways, Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS), and Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Switches with Cisco Network Services Orchestrator for full stack automation.
T-Mobile is the U.S. leader in 5G, delivering the country’s largest, fastest and most reliable 5G network. The Un-carrier’s Extended Range 5G covers 323 million people across 1.9 million square miles – more than AT&T and Verizon combined. 260 million people nationwide are covered by T-Mobile’s super-fast Ultra Capacity 5G, and T-Mobile plans to reach 300 million people with Ultra Capacity next year.
For more information on T-Mobile’s network, visit: https://www.t-mobile.com/coverage/4g-lte-5g-networks.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
Cisco was part of T-Mobile US’ initial 5G SA core launch in 2020. This included the user plane, session management, and policy control functions. Those network functions run on Cisco servers, switching, and its virtualization orchestration stack.
This 5G work built on Cisco providing its packet gateway for T-Mobile’s 4G LTE mobile core, later adding its evolved packet core (EPC), and eventually virtualized the operator’s entire packet core in 2017. T-Mobile was also the first major operator to introduce Cisco’s 4G control and user plane separation (CUPS) in the EPC at production scale in 2018.
Cisco has also been core to 5G SA work by operators like Dish Network and Rakuten Mobile
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/t-mobile-selects-cisco-for-cloud-native-5g-core/2022/12/
Comcast demos 10Gb/sec full duplex with DOCSIS 4.0; TDS deploys symmetrical 8Gb/sec service
Comcast announced in a press release it successfully tested a symmetrical multi-gigabit DOCSIS 4.0 connection on its live network, taking a major step toward “offering 10G-enabled services” in the second half of 2023. In Philadelphia, where Comcast is headquartered, it connected service at an undisclosed business location using multiple cable modems and a DOCSIS 4.0-enabled 10G node. If you’re wondering what 10G means, the answer is — more than 5G. As we noted in 2019, the cable industry rolled out its marketing term just in time to have something that’s twice as many Gb/sec as 5G wireless has.
DOCSIS 4.0 technology should enable download speeds of up to 10Gbps with 6Gbps uploads, and Comcast said a lab test in January achieved more than 4Gbps speed in both directions.

Earlier this year, Comcast announced it was working on rolling out multi-gig Internet speeds to more than 50 million residences and businesses in the U.S. by the end of 2025. The company planned on deploying 2Gbps speeds to 34 cities by the end of this month and has also given a slight bump to download speed on internet service in many areas.
The advantage of 10G tech is that it should make multi-gig speeds available for both downloads and uploads (currently, Comcast’s gigabit plans include upload speeds of just 200Mbps), just as it is with fiber optic internet connections. However, for anyone considering upgrading, we should note that you will probably need another new cable modem.
Ideally, this will increase speeds for those in places where fiber isn’t available, especially non-metropolitan areas. And in places that have competition, it measures closer against rivals that deliver fiber services, such as Verizon, AT&T, Google, and Frontier Communications, which are already offering some customers symmetrical multi-gigabit connections.
“We started this year with the announcement of our world-first test of 10G modem technology capable of delivering multi-gig speeds to homes and, as of today, 10G is a reality with the potential to transform and evolve the Internet as we know it,” said Elad Nafshi, EVP and Chief Network Officer at Comcast Cable. “It’s been an incredible year of progress, and we look forward to continuing to refine and harden our 10G technology as we work to make this service—and all its incredible benefits—available to all customers in the years ahead.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, TDS Telecom [1.] said its new symmetrical 8Gb/sec (gig) service is already available in more than 75 of its fiber markets and runs $295 per month. While most U.S. operators [2.] are sticking with 2-gig as their top tier product for now, a handful of others have already pushed further into multi-gig territory. AT&T and Ziply Fiber, for instance, both offer residential plans providing up to 5 Gbps. And fewer still have gone beyond that. Lumen Technologies introduced an 8-gig tier for its Quantum Fiber service in August and Google Fiber has announced plans to trot out 5-gig and 8-gig plans in early 2023. Lumen’s service costs $300 per month.
Note 1. TDS Telecom offers internet service across 31 states with the greatest coverage in Wisconsin, Tennessee, and Utah.
Note 2. TDS is competing directly against AT&T, Comcast, Consolidated Communications and Lumen in the territory it serves.
While TDS in a press release pitched the 8-gig product as suitable for power users such as gamers and content creators, an operator representative told Fierce Telecom it doesn’t initially expect significant uptake of the plan. Instead, such offerings are tools in a marketing war being waged across the broadband industry.
Wire 3 offers a 10-gig service to customers in Florida, and Tennessee’s EPB and also provides a 25-gig service. However, it is not likely that consumers need those kinds of speeds currently.
On TDS’s Q3 2022 earnings call, TDS CFO Michelle Brukwicki stated its 1-gig and 2-gig plans are “important tools that will allow us to defend and win new customers.” She added nearly a quarter of new customers are taking its 1-gig service where it is available and its faster, higher-APRU tiers helped it boost residential broadband revenue in the quarter. However, TDS expects to miss 2022 fiber build target.
References:
https://corporate.comcast.com/press/releases/comcast-live-10g-connection-4-gig-symmetrical-speeds
https://www.theverge.com/2022/12/12/23505779/comcast-multi-gigabit-10g-docsis-40-cable-fiber-isp
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/broadband/tds-cranks-fiber-speeds-8-gbps



