Nokia
Nokia will manufacture broadband network electronics in U.S. for BEAD program
Nokia has become the first telecom company to announce the manufacturing of fiber-optic broadband network electronics products and optical modules in the U.S. for use in the Broadband Equity, Access and Deployment (BEAD) program.
Using thin strands of glass to transmit data with light, fiber-optic networks have become the backbone of today’s digital economy and are used to connect everything to fast, reliable gigabit data services. Seventy percent of fiber broadband lines in North America are powered by Nokia. Now, partnering with Sanmina Corporation, Nokia will manufacture in the U.S. several fiber-optic broadband products at Sanmina’s state-of-the-art manufacturing facility located in Pleasant Prairie, Kenosha County, Wisconsin, bringing up to 200 new jobs to the state.
By manufacturing fiber-optic technology in the U.S., Nokia will be able to supply its products and services to critical projects like BEAD that are focused on narrowing the digital divide, helping to further contribute to the nation’s economic growth and job creation. Having access to technology that is built in the U.S. is an important requirement for states and infrastructure players seeking to participate in BEAD and the $42.45bn of available funding allocated for broadband rollouts to unserved and underserved communities.
Pekka Lundmark, President and CEO of Nokia, said: “At Nokia, we create technology that helps the world act together. We are committed to connecting people and communities. However, many Americans still lack adequate connectivity, leaving them at a disadvantage when it comes to accessing work, education and healthcare. Programs like BEAD can change this. By bringing the manufacturing of our fiber-optic broadband access products to the U.S., BEAD participants will be able to work with us to bridge the digital divide. We look forward to bringing more Americans online.”
Vice President of the United States, Kamala Harris, said: “President Biden and I are delivering on our promise to strengthen our economy by investing in working people, expanding domestic manufacturing, empowering small business owners, and rebuilding our nation’s infrastructure—today’s announcement is a direct result of this work. Our investments in broadband infrastructure are creating jobs in Wisconsin and across the nation, and increasing access to reliable, high-speed internet so everyone in America has the tools they need to thrive in the 21st century.”
U.S. Secretary of Commerce, Gina Raimondo, said: “President Biden promised to bring high-speed internet to every corner of America, and to do it with American workers and American-made equipment. This announcement is proof that he’s delivering on that promise. When we invest in American manufacturing and American jobs, there’s no limit to what we can achieve. Thanks to the President’s leadership, we’re going to connect everyone in America and create a strong and equitable economy that’s built for the future.”
Jure Sola, Chairman and CEO of Sanmina, said: “Sanmina has been manufacturing in the U.S. for more than forty years and we are excited to partner with Nokia to support their efforts to build robust and resilient high-tech fiber broadband networks that will connect people and societies. By continuing to invest in domestic manufacturing, Nokia and Sanmina will be able to help create a sustainable future for the industry, one that drives job growth and ensures the fiber products produced embody the quality and excellence associated with American manufacturing.”
Nokia fiber-optic broadband products manufactured in the U.S. will include:
- Optical Line Termination card for a modular Access Node
- A small form factor OLT
- OLT optical modules
- An “outdoor-hardened” Optical Network Terminal (ONT)

Resources and additional information
- Seven out of ten fiber broadband connections in North America are made through Nokia equipment.
- Nokia is the top supplier of fiber-optic broadband technology for service providers in the U.S.
- Nokia is the number one vendor for XGS-PON technology globally and in the U.S. market. XGS-PON can deliver up to 10 Gbps (Gigabits-per-second) broadband speeds to end-users. With 10 Gbps, you can download a 4K movie in less than 30 seconds or stream around 1,700 movies simultaneously.
- Nokia was the first to deploy 1, 10 and 25 Gigabit fiber-optic broadband networks in the U.S. with the Electric Power Board (EPB) in Chattanooga, Tennessee.
- Website: More about funding opportunities and Nokia broadband solutions
- Infograph: Why Fiber Broadband is Essential
- Article: U.S. Broadband Infrastructure Funding explained
- Video: Explaining the limitless speeds for fiber broadband
- https://www.nokia.com/about-us/news/releases/2023/08/03/nokia-first-to-announce-manufacturing-of-broadband-network-electronics-products-for-bead-program-in-us/
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
August 16, 2023 Addendum:
Nokia announced today its partnership with Fabrinet to become the first telecom vendor to manufacture fiber broadband optical modules in the U.S. for use in the Broadband Equity, Access and Deployment (BEAD) program.
Starting in 2024, Nokia’s next generation, multi-rate optical modules for Optical Line Terminals (OLTs) will be produced at Fabrinet’s state-of-the- art manufacturing facility located in Santa Clara, California, bringing high-tech innovation and additional jobs to the country.
This news builds on Nokia’s recent announcement that they will produce fiber-optic broadband network electronic products in Kenosha, Wisconsin – expanding Nokia’s list of products and solutions for networks rollouts using BEAD or other funding to help bridge the digital divide.
U.S. Network Operators and Equipment Companies Agree: 5G CAPEX slowing more than expected
We noted in a recent IEEE Techblog post that the 5G spending slowdown in the U.S. is broader than many analysts and executives expected. Well, it’s worse than that! The previously referenced negative comments from the CEO of Crown Castle, were corroborated by American Tower last week:
“The recent pullback was more abrupt than our initial expectations,” said Rod Smith, the CFO for cell tower firm American Tower, during his company’s quarterly conference call last week, according to Seeking Alpha. Smith was discussing the reduction in US operator spending on 5G, a situation that is now cutting $40 million out of American Tower’s margin expectations. “The initial burst of 5G activity has slowed down,” agreed the financial analysts at Raymond James in a note to investors following the release of American Tower’s earnings.
Cell tower giant SBA Communications said it too is seeing the broad pullback in spending that has affected its cell tower competitors (i.e. American Tower and Crown Castle). But the company’s management sought to reassure investors with promises of continued growth over the long term. During their earnings call, SBA executives said they expect activity to increase next year as T-Mobile looks to add 3.45GHz and C-band spectrum to its network, and as Dish Network restarts its network buildout.
The two largest 5G network equipment vendors that sell gear in the U.S. are seeing similar CAPEX cutbacks. “We see some recovery in the second half of the year but it will be slower than previously expected,” Nokia CEO Pekka Lundmark said earlier this month during his company’s quarterly conference call, in response to a question about the company’s sales in North America. His comments were transcribed by Seeking Alpha. Ericsson’s CEO, Borje Ekholm, is experiencing similar trends: “We see the buildout pace being moderated,” he said of the North American market, according to a Seeking Alpha transcript
AT&T’s CFO Pascal Desroches confirmed the #1 U.S. network operator is slowing its network spending. “We expect to move past peak capital investment levels as we exit the year,” he said during AT&T’s quarterly conference call, as per a Seeking Alpha transcript. AT&T’s overall CAPEX would be $1 billion lower in the second half of 2023 when compared with the first half of this year due to greatly reduced 5G network build-outs.
“This implies full year capex of ~$23.7 billion, which management believes is consistent with their prior full year 2023 capex guidance of ‘~$24 billion, near consistent with 2022 levels’ and includes vendor financing payments,” wrote the financial analysts at Raymond James in their assessment of AT&T’s second quarter results, citing prior AT&T guidance.
“Although management declined to guide its 2024 outlook, it has suggested that it expects capital investments to come down as it progresses past the peak of its 5G investment and deployments. We believe the trends present largely known CY23 [calendar year 2023] headwinds for direct 5G plays CommScope, Ericsson and Nokia. Opportunities from FWA [fixed wireless access] might provide modest offsets and validate Cambium’s business. AT&T’s focus on meeting its FCF [free cash flow] targets challenge all of its exposed suppliers, which also include Ciena, Infinera and Juniper,” the financial services firm added.
Verizon CEO Hans Vestberg told a Citi investor conference in January that CAPEX would drop to about $17bn in 2024, down from $22bn in 2022″ “We continue to expect 2023 capital spending to be within our guidance of $18.25 billion to $19.25 billion. Our peak capital spend is behind us, and we are now at a business-as-usual run rate for capex, which we expect will continue into 2024,” explained Verizon CFO Tony Skiadas during his company’s quarterly conference call last week, according to Seeking Alpha.
“After years of underperformance, perhaps the best argument for Verizon equity is that expectations are very low. They are coming into a phase where capex will fall now that they’ve largely completed their 5G network augmentation. Higher free cash flow will flatter valuations, but it will also, more importantly, lead to de-levering first, and potentially even to share repurchases down the road,” speculated the analysts at MoffettNathanson in a research note to investors following the release of Verizon’s earnings.

T-Mobile USA had previously said its expansive 5G build-out had achieved a high degree of scale and it would reduce its capex sharply starting in 2023.”We expect capex to taper in Q3 and then further in Q4,” said T-Mobile USA’s CFO Peter Osvaldik during his company’s quarterly conference call last week, according to Seeking Alpha. He said T-Mobile’s capex for 2023 would total just under $10 billion. T-Mobile hopes to cover around 300 million people with its 2.5GHz midband network by the end of this year. Afterward, it plans to invest in its network only in locations where such investments are necessary.
Similarly, Verizon and AT&T are completing deployments of their midband C-band 5G networks, and will slow spending after doing so. That’s even though neither telco has deployed a 5G SA core network which involves major expenses to build, operate and maintain.
Dish Network managed to meet a federal deadline to cover 70% of the U.S. population with it’s 5G OpenRAN in June. As a result, the company said it would pause its spending until next year at the earliest.
American Tower was a bit more hopeful that CAPEX would pick up in the future:
- “Moderation in carrier spend following the recent historic levels of activity we’ve seen in the industry isn’t unexpected and is consistent with past network generation investment cycles,” explained CFO Rod Smith.
- “The cycles typically progress as there’s a coverage cycle. It’s what we’ve seen in past cycles, including 3G and 4G. It’s an initial multiyear period of elevated coverage capex, and it’s tied to new G spectrum aimed at upgrading the existing infrastructure,” said American Tower’s CEO Tom Bartlett. “And then later in the cycle, it will fill back into a capacity stage where we’ll start to see more densification going on. So I’m hopeful that our investor base doesn’t get spooked by the fact that this is a pullback. It’s very consistent. The cadence is really spot on with what we’ve seen with other technologies.”
In April, Dell’Oro Group analyst Stefan Pongratz forecast global telecom capex is projected to decline at a 2% to 3% CAGR over the next 3 years, as positive growth in India will not be enough to offset sharp capex cuts in North America. He also predicted that wireless CAPEX in the North America (NA) region would decline 10% to 20% in 2023 as per this chart:
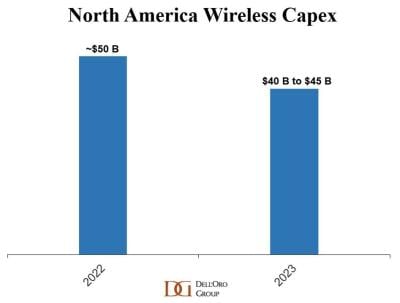
Now, that NA CAPEX decline seems more like 30% this year!
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
U.S. 5G spending slowdown continues; RAN revenues set to decline for years!
USA’s 5G capex bubble will burst this year as three main operators cut back
GSM 5G-Market Snapshot Highlights – July 2023 (includes 5G SA status)
Worldwide Telecom Capex to Decline in 2023, According to Dell’Oro Group
https://www.fiercewireless.com/wireless/wireless-capex-north-america-expected-decline-10-20-2023
Dell’Oro: Telecom Capex Growth to Slow in calendar years 2022-2024
Reliance Jio to sign $1.5 billion 5G network equipment deal with Nokia (“Home grown 5G” never happened)
Whatever happened to Jio’s claim of “home grown 5G“? Answer: It was a big bold faced lie! Almost 3 years ago, Jio Chairman Mukesh Ambani said his company had developed its own 5G solution “from scratch.” He said at the time, “Jio plans to launch “a world-class 5G service in India…using 100% home grown technologies and solutions,” he said in a statement at the Reliance Industries annual shareholders meeting. “Once Jio’s 5G solution is proven at India-scale, Jio Platforms would be well-positioned to be an exporter of 5G solutions to other telecom operators globally, as a complete managed service,” he added.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Fast forward to today. Jio, India’s largest telecoms operator, is set to sign a contract at Nokia’s Headquarters in Helsinki, Finland, according to sources speaking to the Economic Times.

The purchase will be financed by several global banks, including HSBC, Citigroup, and JP Morgan, whose combined loans will total around $4 billion. Finnish state-owned export credit agency Finnvera is set to issue guarantees to the lenders. Representatives from the banks are likely to be present at the signing, as well as Senior Executives from Reliance Group.
At the time, financial details of the deals were not disclosed; however, media reports have since suggested that the deal with Ericsson was worth $2.1 billion. Now, this deal with Nokia will see the total 5G investment reach roughly $3.6 billion.
Earlier this year, Jio’s president Mathew Oommen said the company aimed to become “the largest 5G SA (standalone) only network operator in the world in the second half of 2023”, with the company targeting nationwide coverage by the end of the year.
In October 2022, Jio signed 5G equipment contracts with both Nokia and Ericsson.
In related news, earlier this week, Reliance Industries announced the launch of a budget 4G phone, (costing $12), aiming to convert the 250 million 2G users in India to 4G. The company says its goal is to pass the benefits of the internet-capable mobile technology to every Indian.

References:
https://totaltele.com/indias-jio-to-sign-1-5-billion-5g-equipment-deal-with-nokia/
Reliance Jio’s “Home Grown” 5G? Ericsson and Nokia in multi-year deals with Jio to build a mega 5G network
Reliance Jio claim: Complete 5G solution from scratch with 100% home grown technologies
Charter Communications selects Nokia AirScale to support 5G connectivity for Spectrum Mobile™ customers
Nokia will deliver its AirScale portfolio, including 5G Radio Access Network (RAN), to support Charter Communications’ 5G rollout in trial markets. It marks Nokia’s first win in the cablecos/MSO space for large-scale wireless 5G deployments. Charter will use Nokia’s 5G RAN solutions to deliver wireless 5G connectivity, faster speeds, and increased network capacity to Spectrum Mobile customers in its trial markets in the United States.
Up until now, cablecos have been MVNO rather than actually deploying their own wireless networks. All of the cable companies in the U.S. with mobile aspirations have had to partner with an existing mobile network operator – Verizon, AT&T or T-Mobile – to sell mobile services. And those MVNO partnerships are not cheap. For example, the financial analysts at Wells Fargo estimate that Charter and Comcast pay Verizon $12-$13 per month for each of their mobile customers.
Cable operators have spent more than $1 billion on Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) spectrum with the intention to build 5G networks to offload traffic from their leased mobile networks and to deliver the fastest wireless service. Using compact and lightweight small cell products, cable operators can more easily and cost-effectively provide 5G wireless connectivity by leveraging their existing DOCSIS infrastructure without having to build additional cell sites.
With 6 million customer lines as of Q1-2023, Charter’s Spectrum Mobile is the nation’s fastest growing mobile network provider. Charter offers its Spectrum Mobile service through an MVNO deal with Verizon but touts its ability to combine that with its Wi-Fi network. It’s also using Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) spectrum to offload mobile traffic from the leased network. Charter spent more than $464 million in the CBRS auction in 2020.
As Charter continues to grow its mobile customers, the company needed a 5G wireless connectivity solution to offload traffic from its leased mobile network. Charter will deploy Nokia’s 5G RAN products, including strand mounted radios for CBRS, baseband units, and a newly developed 5G CBRS Strand Mount Small Cells All-in-One portfolio on the company’s assets, which will help Charter continue to deliver mobile traffic in strategic locations across its 41-state footprint while providing customers with the best possible 5G service experience.
Justin Colwell, EVP, Connectivity Technology at Charter Communications, said: “Charter is committed to providing our customers a fully converged connectivity experience that combines high value plans with the fastest wired and wireless speeds throughout our footprint. Incorporating Nokia’s innovative 5G technology into our advanced wireless converged network will help us ensure that Spectrum customers in areas with a high concentration of mobile traffic continue to receive superior mobile connectivity, including the nation’s fastest wireless speeds.”
Shaun McCarthy, President of North America Sales at Nokia, said: “This news builds on our more than 20-year relationship working with Charter to enhance its network. We are excited to expand its current trial to additional select metropolitan markets in the US, enabling an enhanced user experience for Spectrum Mobile subscribers. This win strengthens Nokia’s leadership position in the MSO space for 5G wireless deployments.”

Nokia in the U.S.
Nokia is supplying 5G technologies across its portfolio to the major service providers and leading operators, as well as hyperscalers, enterprises, and government organizations in the US. The company has an unrivaled track record of innovation in the U.S. including Nokia Bell Labs, which pioneered many of the fundamental technologies that are being used to develop 5G and broadband standards. Today, more than 90 percent of the U.S. population is connected by Nokia network solutions.
*Based on year end 2022 subscriber data among top 3 cellular carriers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Nokia may have competition in the CBRS/MSO space. Samsung will be introducing a new solution within its already existing CBRS portfolio: a new 5G CBRS Strand Small Cell. Designed to be easily deployed on the MSOs aerial strand assets, it enables use of their existing infrastructure, helping them save on deployment costs.
References:
Nokia in multi-year deal with Zain to provide 5G RAN equipment throughout Jordan
Nokia has announced a multi-year deal with Zain Jordan to provide 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) equipment throughout Jordan. The contract is aimed at supporting the digital transformation of the country by offering advanced 5G services with improved connectivity and capacity to customers.
As part of the agreement, Nokia will deploy the latest generation of its AirScale Baseband, Massive MIMO radios, and Remote Radio Head products to over 3,000 sites nationwide. These latest generation products are all powered by Nokia’s energy-efficient ReefShark System on Chip (SoC) technology and are designed to provide superior coverage and capacity.
In addition to deploying 5G, Nokia will also upgrade Zain’s existing 4G infrastructure. The deployment of 5G is expected to accelerate the growth of new technologies and industries in Jordan, contributing to the country’s economic growth and development.
Nokia has a longstanding partnership with Zain across several territories, including the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The deal is expected to be completed during 2023, with the majority of the deployment scheduled to take place during the year.
Tommi Uitto, President of Mobile Networks at Nokia, said: “We are delighted to be partnering with Zain Jordan on this project to modernize their complete Radio Access Network and introduce 5G technology, and by doing so, support the Jordanian Government’s digital transformation objectives. The deployment of 5G is expected to stimulate the incubation and growth of new technologies and industries.”
Resources and additional information:
5G Radio Access Networks (RAN)
AirScale Radio Access
Nokia 5G
References:
Comcast selects Nokia’s 5G SA Core software to support its mobile connectivity efforts
Nokia introduces new Wavence microwave solutions to extend 5G reach in both urban and rural environments
Nokia and Kyndryl extend partnership to deliver 4G/5G private networks and MEC to manufacturing companies
Nokia to open 5G and 6G research lab in Amadora, Portugal
Ericsson and Nokia demonstrate 5G Network Slicing on Google Pixel 6 Pro phones running Android 13 mobile OS
Nokia and Safaricom complete Africa’s first Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) 5G network slicing trial
Comcast selects Nokia’s 5G SA Core software to support its mobile connectivity efforts
Today, Comcast announced it will roll out Nokia’s 5G Stand Alone Core networking software to support its deployment of CBRS and 600MHz spectrum to Xfinity Mobile and Comcast Business Mobile customers in its service areas across the United States.
Comcast will deploy that spectrum in select, high-traffic areas in support of both residential and business customers that take mobile services from the operator. Deploying fresh spectrum in those areas will give Comcast a greater degree of ownership economics with wireless and help to offset a portion of the MVNO costs associated with its pact with Verizon. Those deployments will also build on Comcast’s current Wi-Fi offload strategy that involves millions of access points deployed in customer homes and in certain metro areas.
Nokia will supply Comcast with its 5G Stand Alone Core networking software, including Packet Core, delivering near zero touch automation and ultra low latency capabilities, as well as operations software and consulting services. These offerings will support Comcast’s efforts to deliver enhanced 5G access to consumer and business customers in the U.S. using Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) and 600 MHz spectrum.
By combining Nokia’s software with Comcast’s targeted, capital-light network design, Comcast can cost-effectively deliver enhanced 5G and WiFi mobile connectivity to its more than five million Xfinity Mobile and Comcast Business Mobile customers. Comcast and Nokia are currently conducting field trials, which includes Comcast employee testing.
As the demand for reliable Internet access inside and outside of the home and office rapidly increases, Comcast’s mid-band (CBRS) and low-band (600MHz) spectrum enable the company to supplement its existing Xfinity WiFi network and cellular network partnership with additional targeted 5G coverage in certain high-traffic areas within its service territory.
Xfinity Mobile and Comcast Business Mobile services are built for the way people use mobile today, with the Internet at the core of the experience. Calls and texts are free, and customers can experience the freedom of paying by the gig or unlimited, and switch between payment options at any time for any line on their account. For complete pricing and availability details, please visit Xfinity Mobile or Comcast Business Mobile.
Nokia claims to be leading the 5G Standalone Core market, with over 80 communication service provider (CSP) customers around the world. In addition, 25 of the top 40 CSPs by revenue rely on Nokia Core network products.

Comcast and Nokia are currently conducting field trials, including tests with Comcast employees. Comcast didn’t reveal the location of its test markets, but the announcement indicates the operator is finally starting to gear up this important piece of its wireless strategy.
This deal comes more than two years after the company bid for and won licensed CBRS spectrum. Comcast also spent $1.7 billion on 600MHz spectrum licenses in 2017.
Though Comcast has no plans to deploy a national wireless network, it estimates that its current spectrum holdings cover roughly 80% of its homes passed and about 50% of the US population.
Tom Nagel, SVP, Wireless Strategy at Comcast, said: ”We are pleased to be working with Nokia to enable Comcast’s advanced 5G mobile products and services for our customers. Combining Nokia’s industry-leading solutions with Comcast’s targeted network design and new dual SIM technology allows us to create exciting next-generation wireless offerings.”
Fran Heeran, SVP & General Manager of Core Networks, Cloud and Network Services, at Nokia, said: “We are delighted to partner with Comcast and provide Nokia’s advanced 5G Core portfolio to deliver innovative 5G customer offerings securely, at scale, and with advanced operational efficiencies.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Last fall, Comcast announced it would use Samsung radios, including strand-mounted small cells, for its targeted 5G network. Comcast will deploy separate Samsung radios for the CBRS and 600MHz bands and use its wireline network to help backhaul traffic.
At the time, Comcast confirmed to Light Reading that its wireless network deployment is “using a multi-vendor solution but not within an open RAN framework.”
Comcast’s wireless network evolution is underway as the operator continues to grow a mobile business that launched almost six years ago. Comcast added a record 365,000 mobile lines in Q4 2022, raising its total to 5.31 million.
Meanwhile, Comcast recently introduced a limited-time service convergence bundle for new customers that offers one unlimited mobile line and a 200Mbit/s home broadband service (with the Wi-Fi gateway included) for $50 per month – for a period of 24 months.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g-and-beyond/comcast-shares-wireless-wealth-with-nokia/d/d-id/783415
Counterpoint Research: Ericsson and Nokia lead in 5G SA Core Network Deployments
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core/5g-core/
Nokia and Kyndryl extend partnership to deliver 4G/5G private networks and MEC to manufacturing companies
Following their first partnership one year ago, Nokia and Kyndryl have extended it for three years after acquiring more than 100 customers for automating factories using 4G/5G private wireless networks as well as multi-access edge computing (MEC) technologies. Nokia is one of the few companies that have been able to get any traction in the private 4G/5G business which is expected to grow by billions of dollars every year. The size of the global private 5G network market is expected to reach $41.02 billion by 2030 from 1.38 billion in 2021, according to a study by Grand View Research.
The companies said some customers were now coming back to put private networks into more of their factories after the initial one. “We grew the business significantly last year with the number of customers and number of networks,” Chris Johnson, head of Nokia’s enterprise business, told Reuters.
According to the companies, 90% of those engagements—which span “from advisory or testing, to piloting, to full implementation”—are with manufacturing firms. In Dow Chemical’s Freeport, Texas, manufacturing facility which is leveraging a private LTE network using CBRS frequencies to cover 40 production plants over 50-square-kilometers. The private wireless network increased worker safety, enabled remote audio and video collaboration, personnel tracking, and vehicle telematics, the companies said. Dow Chemical is now planning to expand the same coverage to dozens of its factories, said Paul Savill, Kyndryl’s [1.] global practice leader. “Our pipeline has been growing fundamentally faster than it has been in the last 12 months,” he said. “We now have over 100 customers that we’re working with in the private wireless space … in around 24 different countries.”
Note 1. After getting spun off from IBM in 2021, Kyndryl has focused on building its wireless network business and has signed several agreements with cloud providers.
The current active engagements are across more than 24 countries, including markets like the U.S. where regulators have set aside spectrum assets for direct use by enterprises; this means it’s increasingly possible for buyers to access spectrum without the involvement of mobile network operators.
“As enterprises seek to accelerate and deliver on their journeys towards Industry 4.0 and digitalization, the effective integration and deployment of advanced LTE and 5G private wireless networking technologies becomes instrumental to integrate all enterprise operations in a seamless, reliable, efficient and built in a secure manner,” said Alejandro Cadenas, Associate Vice President of Telco and Mobility Research at IDC. “This expanding, powerful, relationship between Nokia and Kyndryl is a unique combination of vertical and horizontal capabilities, and offers IT, OT and business leaders access to the innovation, tools, and expert resources they need to digitally transform their operations. The partnership offers a compelling shared vision and execution that will enable customers across all industries and geographies to access the ingredients they need to deliver against the promise of digital acceleration, powered by network and edge computing.”
The expanded effort will be enhanced with Kyndryl’s achievement of Nokia Digital Automation Cloud (DAC) Advanced accreditation status, which helps ensure that enterprise customers benefit from an expanded lineup of expert resources and skilled practitioners who have extensive training and deep understanding of Nokia products and solutions. In addition, customers will gain access to Kyndryl’s accelerated network deployment capabilities and support of Nokia cellular radio expertise in selected markets.
In response to a question about how direct enterprise access to spectrum has informed market-by-market activity, Kyndryl Global Practice Leader of Network and Edge Paul Savill told RCR Wireless News in a statement, “Spectrum availability is rapidly becoming less of a barrier, with governments allocating licensed spectrum for industrial use and the emergence of unlicensed wireless networking options (such as CBRS in the US, and MulteFire).”
The companies have also developed automated industrial drones that can monitor a site with different kinds of sensors such as identifying chemicals and video recognition as part of surveillance. While drones have not yet been deployed commercially yet, customers are showing interest in rugged, industrialized non-stop automated drone surveillance, Johnson said.
References:
Ericsson and Nokia demonstrate 5G Network Slicing on Google Pixel 6 Pro phones running Android 13 mobile OS
In separate announcements today, Ericsson and Nokia stated they had completed 5G Network Slicing trials with Google on Pixel 6 Pro smart phones running the Android 13 mobile OS [1.].
Network Slicing is perhaps the most highly touted benefits of 5G, but its commercial realization is taking much longer than most of the 5G cheerleaders expected. That is because Network Slicing, like all 5G features, can only be realized on a 5G standalone (SA) network, very few of which have been deployed by wireless network operators. Network slicing software must be resident in the 5G SA Core network and the 5G endpoint device, in this case the Google Pixel 6 Pro smartphone.
Note 1. On August 15, 2022, Google released Android 13 -the latest version of its mobile OS. It comes with a number of new features and improvements, as well as offers better security and performance fixes. However, it’s implementation on smartphones will be fragmented and slow according to this blog post.
For devices running Android 12 or higher, Android provides support for 5G Network Slicing, the use of network virtualization to divide single network connections into multiple distinct virtual connections that provide different amounts of resources to different types of traffic. 5G network slicing allows network operators to dedicate a portion of the network to providing specific features for a particular segment of customers. Android 12 introduces the following 5G enterprise network slicing capabilities, which network operators can provide to their enterprise clients.
Android 12 introduces support for 5G network slicing through additions to the telephony codebase in the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) and the Tethering module to incorporate existing connectivity APIs that are required for network slicing.
Here’s a functional block diagram depicting 5G network slicing architecture in AOSP:
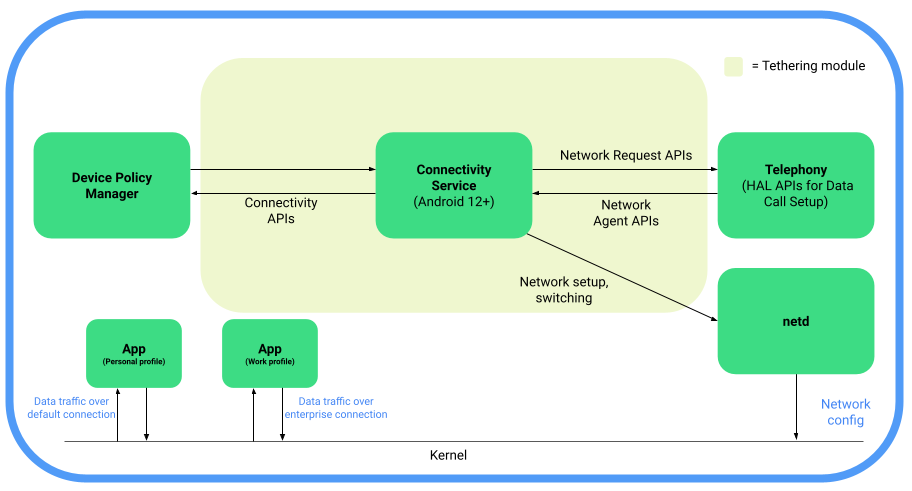
Image Credit: Android Open Source Project
1. Ericsson and Google demonstrated support on Ericsson network infrastructure for multiple slices on a single device running Android 13, supporting both enterprise (work profile) and consumer applications. In addition, for the first time, a slice for carrier branded services will allow communications service providers (CSP) to provide extra flexibility for customized offerings and capabilities. A single device can make use of multiple slices, which are used according to the on-device user profiles and network policies defined at the CSP level.
The results were achieved in an Interoperability Device Testing (IODT) environment on Google Pixel 6 (Pro) devices using Android 13. The new release sees an expansion of the capabilities for enterprises assigning network slicing to applications through User Equipment Route Selection Policy (URSP ) rules, which is the feature that enables one device using Android to connect to multiple network slices simultaneously.
Two different types of slices were made available on a device’s consumer profile, apart from the default mobile broadband (MBB) slice. App developers can now request what connectivity category (latency or bandwidth) their app will need and then an appropriate slice, whose characteristics are defined by the mobile network, will be selected. In this way either latency or bandwidth can be prioritized, according to the app’s requirements. For example, the app could use a low-latency slice that has been pre-defined by the mobile network for online gaming, or a pre-defined high-bandwidth slice to stream or take part in high-definition video calling.
In an expansion of the network slicing support offered by Android 12, Android 13 will also allow for up to five enterprise-defined slices to be used by the device’s work profile. In situations where no USRP rules are available, carriers can configure their network so traffic from work profile apps can revert to a pre-configured enterprise APN (Access Point Name) connection – meaning the device will always keep a separate mobile data connection for enterprise- related traffic even if the network does not support URSP delivery.
Monica Zethzon, Head of Solution Area Packet Core at Ericsson said: “As carriers and enterprises seek a return on their investment in 5G networks, the ability to provide for a wide and varied selection of use cases is of crucial importance. Communications Service Providers and enterprises who can offer customers the flexibility to take advantage of tailored network slices for both work and personal profiles on a single Android device are opening up a vast reserve of different uses of those devices. By confirming that the new network slicing capabilities offered by Android 13 will work fully with Ericsson network technology, we are marking a significant step forward in helping the full mobile ecosystem realize the true value of 5G.”
Ericsson and partners have delivered multiple pioneering network slicing projects using the Android 12 device ecosystem. In July, Telefonica and Ericsson announced a breakthrough in end-to-end, automated network slicing in 5G Standalone mode.
2. Nokia and Google announced that they have successfully trialed innovative network slice selection functionality on 4G/5G networks using UE Route Selection Policy (URSP) [2.] technology and Google Pixel 6 (Pro) phones running Android 13. Once deployed, the solution will enable operators to provide new 5G network slicing services and enhance the customer application experience of devices with Android 13. Specifically, URSP capabilities enable a smartphone to connect to multiple network slices simultaneously via different enterprise and consumer applications depending on a subscriber’s specific requirements. The trial, which took place at Nokia’s network slicing development center in Tampere, Finland, also included LTE-5G New Radio slice interworking functionality. This will enable operators to maximally utilize existing network assets such as spectrum and coverage.
Note 2. User Equipment Route Selection (URSP) is the feature that enables one device using Android to connect to multiple network slices simultaneously. It’s a feature that both Nokia and Google are supporting.
URSP capabilities extend network slicing to new types of applications and use cases, allowing network slices to be tailored based on network performance, traffic routing, latency, and security. For example, an enterprise customer could send business-sensitive information using a secure and high-performing network slice while participating in a video call using another slice at the same time. Additionally, consumers could receive personalized network slicing services for example for cloud gaming or high-quality video streaming. The URSP-based network slicing solution is also compatible with Nokia’s new 5G radio resource allocation mechanisms as well as slice continuity capabilities over 4G and 5G networks.
The trial was conducted using Nokia’s end-to-end 4G/5G network slicing product portfolio across RAN-transport-core as well as related control and management systems. The trial included 5G network slice selection and connectivity based on enterprise and consumer application categories as well as 5G NR-LTE slice interworking functionalities.
Nokia is the industry leader in 4G/5G network slicing and was the first to demonstrate 4G/5G network slicing across RAN-Transport-Core with management and assurance. Nokia’s network slicing solution supports all LTE, 5G NSA, and 5G SA devices, enabling mobile operators to utilize a huge device ecosystem and provide slice continuity over 4G and 5G.
Nokia has carried out several live network deployments and trials with Nokia’s global customer base including deployments of new slicing capabilities such as Edge Slicing in Virtual Private Networks, LTE-NSA-SA end-to-end network slicing, Fixed Wireless Access slicing, Sliced Private Wireless as well as Slice Management Automation and Orchestration.
Ari Kynäslahti, Head of Strategy and Technology at Nokia Mobile Networks, said: “New application-based URSP slicing solutions widen operator’s 5G network business opportunities. We are excited to develop and test new standards-based URSP technologies with Android that will ensure that our customers can provide leading-edge enterprise and consumer services using Android devices and Nokia’s 4G/5G networks.”
Resources:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Addendum:
- Google’s Pixel 6 and Pixel 6 Pro, which run on Android 12, are the first two devices certified on Rogers 5G SA network in Canada, which was deployed in October 2021. However, 5G network slicing hasn’t been announced yet.
- Telia deployed a commercial 5G standalone network in Finland using gear from Nokia and the operator highlighted its ability to introduce network slicing now that it has a 5G SA core.
- OPPO, a Chinese consumer electronics and mobile communications company headquartered in Dongguan, Guangdong, recently demonstrated the pre-commercial 5G enterprise network slicing product at its 5G Communications Lab in collaboration with Ericsson and Qualcomm. OPPO has been conducting research and development in 5G network slicing together with network operators and other partners for a number of years now.
- Earlier this month, Nokia and Safaricom completed Africa’s first Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) 5G network slicing trial.
References:
https://source.android.com/docs/core/connect/5g-slicing
Nokia and Safaricom complete Africa’s first Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) 5G network slicing trial
Nokia and Safaricom complete Africa’s first Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) 5G network slicing trial
Nokia today announced that it has successfully piloted its 4G and 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) network slicing with mobile operator, Safaricom on its live commercial network. This is the first-time 4G/5G network slicing has been successfully achieved in Africa. The trial utilized a multi-vendor network environment and included RAN, transport and core as well as software upgrades to a range of Nokia’s products and services.
The successful trial demonstrates that Safaricom is now poised to support new types of enterprise network services, including fast lane internet access and application slicing. In addition, Nokia is enabling secured FWA slice connectivity to enterprise locations, as well as to private or public application clouds.
The multi-vendor pilot which took place in Kenya’s Western Region, strengthens the strategic partnership between the two companies, with Nokia already providing a wide variety of services and solutions. The pilot demonstrated a number of solutions including Nokia’s AirScale 4G/5G base stations, the NetAct network management and assurance system and Nokia’s FastMile 4G/5G CPE.
Network slicing (which requires a 5G SA Core Network) enables operators the ability to divide a network into multiple virtual slices, which can be optimized for a specific target application or service. The end user of each network slice can then be serviced with different priorities, routing, levels of network performance and security capabilities. Slices can be managed and deployed in minutes, and each one has key performance indicators used for service assurance.
Nokia’s 4G/5G network slicing solution (SORRY, no such thing as 4G network slicing), which received a prestigious award from GTI 2021 in the ‘Innovative Breakthrough in Mobile Technology’ category, supports LTE, 5G NSA and 5G SA technologies with slice service continuity between the networks. This enables slicing services for all LTE and 5G devices.
James Maitai, Network Director, Safaricom, said: “We are proud to have hosted Africa’s first successful pilot of 4G/5G FWA slicing on our network, and looking forward to tailoring our service offerings to individual customers and industries, to meet their needs for high-speed connectivity precisely and without unnecessary cost. Nokia’s expertise has been key to this success, and we anticipate many more strategic wins in this area as our business expands.”
Ramy Hashem, Head of Safaricom Customer Team at Nokia, said: “It is great to have successfully completed this pilot with Safaricom, which is a huge step forward in providing Safaricom with state-of-the-art connectivity. Early experience of new slicing technology is invaluable in understanding the new business opportunities it enables. Nokia was the first vendor to offer a slicing solution and we are looking forward to continuing our partnership with Safaricom in providing world-class 4G and 5G network slicing services to its customers.”
Resources:
Webpage: Automated network slicing
Webpage: 5G Edge Slicing
Webpage: Nokia AirScale
Webpage: Nokia FastMile
Webpage: Nokia 5G RAN
Webpage: Nokia NetAct
BT tests 4CC Carrier Aggregation over a standalone 5G network using Nokia equipment
BT announced Monday that it has successfully tested four component-carrier (4CC) carrier aggregation on a 5G Standalone (SA) network in commercial frequencies. Using EE’s live network, BT said it and Nokia were able to combine four low-band and mid-band radio channels in and 2 GHz and 3 GHz range. BT claims to be the first operator in Europe to achieve this feat, calling this particular demonstration of advanced carrier aggregation “a major leap forward” for the evolution of 5G. Carrier aggregation is seen as the key to achieving optimal data transmission speeds for 5G.
“As we migrate to a 5G standalone core network, this technology milestone is vital to giving our customers the best experience” commented Greg McCall, Managing Director of Service Platforms at BT.
Working in collaboration with Nokia, BT’s Networks team have successfully combined four low-band and mid-band radio channels, (2.1, 2.6, 3.4, 3.6 GHz), using Nokia’s 5G Radio Access Network technology in EE’s live network spectrum.
The trial was conducted in two stages; it was first performed in BT’s Radio Lab in Bristol, and then moved outdoors, onto a radio mast at BT’s Adastral Park in Suffolk, where the team successfully achieved 4CC on 5G SA radiating in EE’s regular radio spectrum. Not only is it the first time in Europe that a network operator has achieved 4CC on 5G SA using commercial spectrum, but it is also the first time it has been achieved outside of a lab in Europe.
Most 5G networks today are Non-Standalone (“NSA”), meaning 5G is supported by existing 4G infrastructure. 5G Carrier Aggregation (“CA”) over a standalone 5G network represents a major leap forward in the evolution of 5G infrastructure, effectively combining several transmission bands into one connection. Every new carrier added allows for higher capacity and speed directly to customer devices.

Greg McCall, Managing Director Service Platforms BT, commented: “Our trial with Nokia is another demonstration of building the most advanced network for our customers. 5G Standalone, coupled with edge compute, will unlock new opportunities for customers looking to develop new services. Furthermore, this technology showcases what’s possible for devices in the future in terms of supporting carrier aggregation, which is an important part of customer experience.”
“Carrier Aggregation (CA) means combining or aggregating several carriers within or across available frequency bands – referred to as component carriers – for achieving higher data rates. Each additional component carrier increases the available bandwidth and, therefore, improves throughput. In the case of carrier aggregating Frequency-Division Duplex (FDD) and Time-Division Duplex (TDD) spectrum together, this also enables a value-adding solution that “stretches” the site coverage area that can offer those higher data rates,” said Nokia.
Mark Atkinson, SVP, Radio Access Networks PLM, Nokia, commented: “We are once again delighted to be deepening our partnership with BT, supporting them with our industry-leading Carrier Aggregation technology for this trial. Nokia and BT have a long history in investing in cutting-edge technologies and this trial is another example of what our companies can achieve together.”
Greg McCall, managing director of service platforms at BT, said the test showcases demonstrates his company’s commitment to building out the most advanced mobile network.
“5G Standalone, coupled with edge compute, will unlock new opportunities for customers looking to develop new services,” said McCall.
In May, Australian mobile operator Optus, Nokia, and Samsung Electronics Australia announced a successful test of three-component-carrier (3CC) CA technology over a 5G SA network. At the time, Nokia noted its commitment to prioritize the development of 5G carrier aggregation across the sub-6 GHz 5G spectrum. At the time, Nokia used its latest commercial AirScale Baseband and radio portfolio over Optus’ commercial network. The trial combined the FDD band (2.1 GHz) with the TDD band (2.2 GHz + 3.5 GHz) using CA technology.
References:


