Vodafone and ITU establish new working group to close digital divide
Vodafone and the ITU have launched a major new initiative to address the global digital divide. The program aims to give an additional 3.4 billion worldwide the ability to access and use the internet through a smartphone by 2030, Vodafone announced.
The new working group, co-chaired by Vodafone Group CEO Nick Read and ITU Secretary-General Houlin Zhao, will identify policy, commercial and circular economy actions to increase smartphone access. Launch partners for the initiative include the GSMA, Vodacom Group, Safaricom, Smart Africa, the government of Ghana, the World Wide Web Foundation, and the Alliance for Affordable Internet.
In a statement announcing the initiative, Vodafone cited GSMA Connected Society research showing 82 per cent of the citizens of low- and middle-income countries are now covered by 4G mobile networks, but many lack a capable device.
Nick Read, CEO of Vodafone Group, said: “Vodafone is honored to be part of this monumental global initiative with the UN, to improve the lives of billions of people through smartphone access. As our societies become more digital, everyone should have the ability to find jobs, be able to get public services, financial services and critical information that are increasingly only available through the internet. This is such a complex challenge that no network operator, device manufacturer, financial services provider or national government can solve on their own – but working together we can break through the barriers.”
Houlin Zhao, Secretary General of the ITU, said: “Achieving the Broadband Commission Global Targets requires a multi-stakeholder approach. I am pleased to co-chair this newly established Working Group, which will also help address the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic and ensure that we put smart devices in the hands of those who are left behind.”
Ursula Owusu-Ekuful, Ghana’s Minister for Communications and Digitalization, stated 45 per cent of people in West Africa are covered by mobile broadband networks but do not use the internet.
Maria-Francesca Spatolisano, officer-in-charge of the office of the UN Secretary-General’s Envoy on Technology, explained the Vodafone and ITU working group will play a key role in helping the body achieve its goal of universal connectivity by 2030 by helping ensure the global shift to digital technology “is beneficial and makes our societies more equal and not less.”

The Broadband Commission Working Group will produce a report and set of recommendations including:
-
original analysis and data on the smartphone access gap;
-
quantification of the social and economic impact of providing everyone with smartphone access by 2030, including assessment of moving users from 2G feature phones to 4G smartphones; and
-
analysis of initiatives or pilots designed to increase smartphone access. Vodafone Group has committed to launch two pilot projects on device affordability as part of this process.
“This partnership is key to expand access to the internet,” said Doreen Bogdan-Martin, Director of the ITU Telecommunication Development Bureau. “I am confident that the outcome report will provide guidance to all our stakeholders as we prepare for the ITU World Telecommunication Development Conference in 2022 to build a world where no one is left off-line.”
To coincide with the creation of this new ITU working group, Vodafone, Safaricom and Vodacom have published the second Africa.Connected report in accelerating 4G roll-out in sub-Saharan Africa. The report, prepared by consultancy Caribou Digital, outlines four key steps to boosting digital access across African. This includes making 4G devices more accessible; investing in the demand for 4G services; providing targeted financing for underserved demographics; and re-farming 2G spectrum to enable more people to use 4G services.
References:
https://www.vodafone.com/sites/default/files/2021-09/Vodafone_Africa_Access_Paper.pdf
Cambium Networks Technology Enables Pentanet to Build a Multi-Gigabit Fixed Wireless Network in Perth, Australia
Cambium Networks, a global provider of wireless networking solutions, today announced that Pentanet is building neXus, a multi-gigabit fixed wireless network across the metro area in Perth, Australia, to provide internet access for business and residential subscribers. The exceptional speeds will be achieved by extending their existing infrastructure consisting of 300 km of “dark” fiber with Cambium Networks’ 60 GHz cnWave fixed wireless platform, using Terragraph, a mesh technology developed by Facebook Connectivity. The result will be network performance that even the most demanding video gamers will appreciate.
60 GHz cnWave V5000 V5000 is featured with two sectors covering up to 280 degrees with beamforming. A single V5000 can connect up to 30 devices, which includes up to four distribution nodes. V5000 can be used for PTP, PMP and mesh configurations.
Supports 57 to 66 GHz:
• Dual-sector with 280º coverage
• Up to 7.2 Gbps (1.8 Gbps DL and 1.8 Gbps UL per sector). Channel bonding typically doubles capacity
• TDMA/TDD channel access and Network Synchronization
• 802.11ay technology with Facebook Terragraph certification
“In 2019, Perth Australia was reported as having the second slowest internet speeds of all Australian capital cities, but we know that needs to change – and fast,” said Stephen Cornish, CEO of Pentanet. “Bandwidth-heavy and latency sensitive applications like cloud-gaming are already transforming connectivity demands, and reliable gigabit speeds are the future for Perth. With Cambium Networks’ 60 GHz cnWave technology, Pentanet’s neXus is driving a leap in internet connectivity throughout the city to gigabit speeds. Using our existing fixed wireless network infrastructure, Pentanet can rapidly deploy the next-generation of wireless technology to create the neXus.”
“Our development and support teams are collaborating closely with the Pentanet team to ensure our solution can scale rapidly to be able to provide connectivity across Perth,” said Atul Bhatnagar, president and CEO of Cambium Networks. “They are pioneering a new age of communications with their business model and network architecture. We are pleased to recognize Pentanet’s disruptive leadership in the industry with our Wireless Connectivity Hero award.”
Cambium Networks’ multi-gigabit fixed wireless broadband technology and centralized management are well suited for urban applications. The solution provides multi-gigabit wireless broadband performance and reliability at a fraction of the cost of fiber. With 60 GHz cnWave, Pentanet can rapidly deploy hybrid networks to extend the fiber plant to customer premises, accelerating time to revenue at lower operating and capital costs. This video details the value that Pentanet delivers.
Cambium Networks’ 60 GHz cnWave solution elements include:
- V5000 Distribution Node – Equipped with two sectors covering up to 280 degrees with beamforming. A single V5000 can connect up to 30 devices, which includes up to four distribution nodes. The V5000 can be used for point-to-point (PTP), point-to-multipoint (PtMP) and mesh configurations.
- V3000 Client Node – Featuring a 44.5 dBi high-gain antenna with beamforming, the client nodes can support up to 3.8 Gbps with the capability for even higher rates in the future with channel bonding for both PtMP and PTP configurations.
- V1000 Client Node – Includes wide-range, 80⁰ beamforming for easy installation. Powered by 802.3af PoE, V1000 supports gigabit throughputs in a compact easy to install form factor
The latest addition to Cambium Networks’ multi-gigabit wireless fabric portfolio of solutions, 60 GHz cnWave is fully integrated into LINKPlanner and cnMaestro™ end-to-end cloud management that provides a unified view of the entire network. The solution delivers reliable and secure connectivity for residential users, schools, enterprises, and industrial operations at a low total cost of ownership.
Find out more about mmWave products including 5G Fixed wireless, Wi-Fi 6 solutions and centralized management solutions at Cambium Connections’ of Cambium Networks’ online events in September. Stephen Cornish of Pentanet will be presenting live Tuesday, 21 September – Register Here.
Cambium Networks’ full wireless fabric portfolio of solutions are available through its global network of partners.
Cambium Networks is celebrating a Decade of Excellence in 2021 with more than 10 million radios shipped worldwide since commencing operations in 2011.
About Pentanet
Pentanet is a Perth-based, growth-focused telco delivering high-speed internet to a growing number of subscribers by providing them with next-generation internet speeds. This is achieved through Pentanet’s market-leading private fixed-wireless network, the largest in Perth, as well as reselling fixed-line services such as NBN, where its wireless is not yet available.
Pentanet’s flagship fixed wireless network has benefits for both customers and investors, offering an outstanding customer experience and a fixed-wireless product that is technically superior to most of the National Broadband Network (NBN) – with attractive margins for investors. This sets Pentanet apart from most broadband providers, which only resell the NBN.
Pentanet will also be part of the rollout of the next wave of subscription-based entertainment services – cloud gaming. The Company’s Alliance Partner Agreement with NASDAQ listed NVIDIA – one of the world’s largest producers of specialised graphic chips used in gaming – allows Pentanet to be the first to bring their GeForce NOW technology to Australia in 2021.
Media Contact (Pentanet)
Alison Balch – Pentanet
+61 (04) 14 545 118
[email protected]
About Cambium Networks
Cambium Networks delivers wireless communications that work for businesses, communities, and cities worldwide. Millions of our radios are deployed to connect people, places and things with a unified wireless fabric that spans multiple standards and frequencies of fixed wireless and Wi-Fi, all managed centrally via the cloud. Our multi-gigabit wireless fabric offers a compelling value proposition over traditional fiber and alternative wireless solutions. We work with our Cambium certified ConnectedPartners to deliver purpose-built networks for service provider, enterprise, industrial, and government connectivity solutions in urban, suburban, and rural environments, with wireless that just works.
Media Contact (Cambium)
Dave Reddy – Big Valley Marketing for Cambium
+1 (650) 868-4659
[email protected]
References:
https://www.cambiumnetworks.com/products/pmp-distribution/60-ghz-cnwave-v5000/
ZTE wins 50% of China Mobile’s high-end router centralized procurement in 2021-2022
ZTE has secured a 50% share in section 4 of China Mobile’s high-end router/switch centralized procurement for 2021-2022. It’s number one ranking was due to its high-end routers ZXR10 M6000-18 S and ZXR10 M6000-8S Plus. This contract is the largest one in the high-end router centralized procurement of China Mobile, which contains the largest number of switch/routers in China.
ZTE will provide the routers to take the role of SR (Service Router) and PE (Provider Edge) to be used in configurations such as cloud private network, network cloud, 5G UPF (User Plane Function), IP private network and MAN (Metropolitan Area Network).
In addition, ZTE will provide necessary equipment for the future IP network of China Mobile, especially cloud private networks and 5G transport networks.
Based on ROSng, the router operating system with its independent intellectual property rights, ZTE’s high-end router ZXR10 M6000-S supports SR/EVPN/SRv6/BIER and boosts the evolution of IP networks towards simplicity and intelligence. The router employs the in-house NP (Network Processor) to enable the single-slot 1T performance, and reaches the industry-leading standards in forwarding performance, energy saving and SDN (Software Defined Network).
In June 2021, ZTE’s high-end routers ZXR10 T8000 [1.] and ZXR10 M6000-3S ranked No. 2 in the comprehensive assessment, and were respectively selected for the bid section 3 and 5 of this procurement. In addition, in China Mobile’s high-end router centralized procurement 2019-2020, ZTE’s ZXR10 M6000-S ranked No. 1 in section 2 (for 2T high-end routers) and No. 2 in section 3 (for 400G high-end routers). So far, the ZXR10 M6000-S ranked top 2 in market share of the country.
Note 1. ZXR10 T8000 is ZTE’s flagship high-end router. It has been running stably for over 10 years in 23 provinces (including autonomous regions and municipalities) in China. With excellent performance, ZTE’s ZXR10 T8000 has been working on the core backbone layer and the important part of 5G network constructions of domestic operators.

ZXR10 T8000 Cluster Router
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In China Mobile’s largest centralized procurement of data communication product in 2019, ZTE’s ZXR10 M6000-S series high-end router grabbed the largest share in Section 2 (2T high-end routers) and the second largest share in Section 3 (400G high-end routers) respectively.
ZTE has been committed to delivering the leading digital infrastructure solutions as a driver of the digital economy. With its continuous innovation, the company has built up core competitiveness in standard patents, key technologies and product solutions to accelerate 5G network constructions.
Moving forward, ZTE, in partnership with China Mobile, will further innovate its 5G network technologies, and expedite commercial deployments of 5G networks to embrace a digital future.
Media Contacts:
Margaret Ma
ZTE Corporation
Tel: +86 755 26775189
Email: [email protected]
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
…………………………………………………………………………………
China Mobile didn’t even invite Ericsson and Nokia to its latest 5G tender
FTTH Council Europe: 197 million homes passed in 2026 in EU27+UK
On September 15 the FTTH Council Europe released its updated Market Forecasts for 2021-2026. Those market forecasts cover 39 European countries [1.] and provide an individual analysis for 15 countries. The forecasts are consistent with previous estimates and plan for around 197 million homes passed for FTTH/B in 2026 in EU27+UK compared to 118 million this year, with Germany, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands and Italy to experience the most remarkable growth.
Note 1. The 39 countries included in IDATE’s research are: the 27 EU member states; four CIS nations – Belarus, Kazakhstan, Russia and Ukraine; Iceland, Israel, North Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Switzerland, Turkey and the UK.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
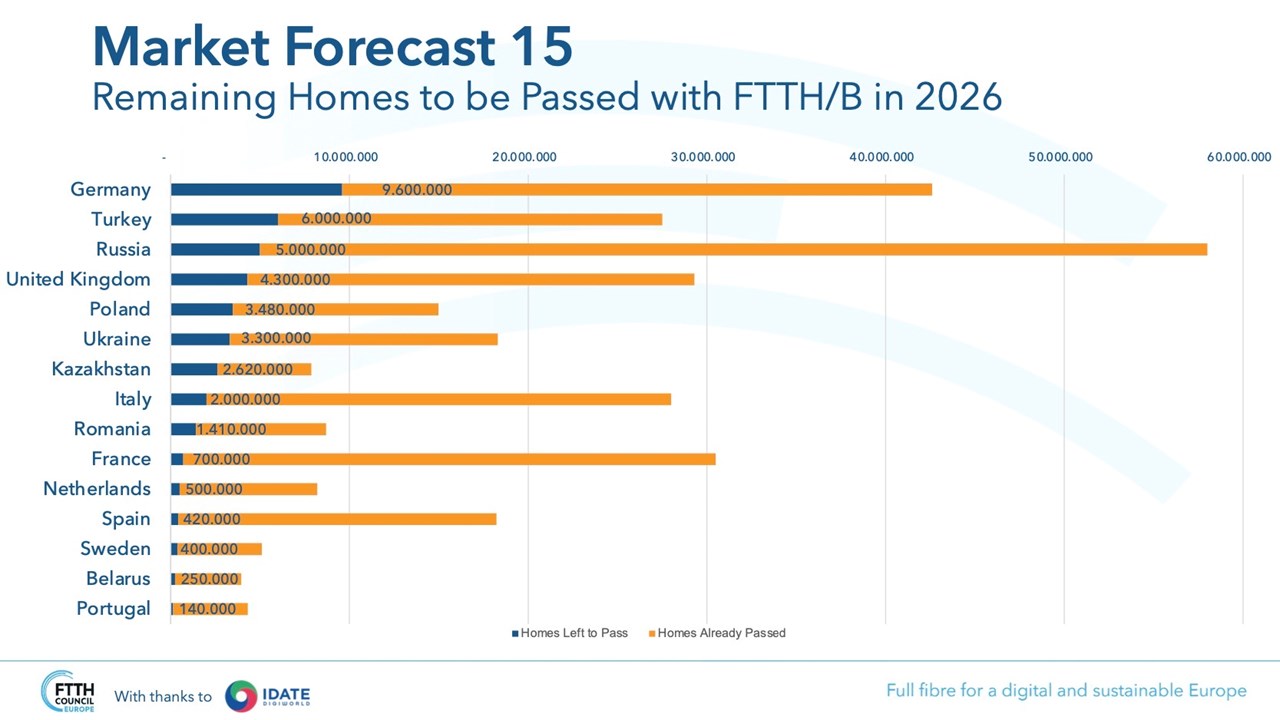
According to IDATE (which compiled the numbers) there will be 99 million households in the region (39 countries) with a fiber broadband connection at the end of this year, either directly via a fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) line or as part of a fiber-connected multi-dwelling building (FTTB), up from 81.9 million at the end of September 2020.
FTTH/B is progressively deployed, but at a very different pace amongst the countries under study. While Spain is championing the ranking with 60,5% rural FTTH/B coverage in 2020, Germany has still a long way to go with only 9,8% covered.
While more than two-third of rural households currently have an NGA2 access [2.]; FTTH/B coverage is still lagging behind in non-dense areas with only 22% households covered, compared to 45% for all territories in EU27+UK.
Note 2. NGA2 (Next Generation Access 2): NGA2 is a long-term solution with an entirely new optical network type. The objective of NGA2 is to provision an independent PON scheme, without being constrained by the GPON standards and the currently deployed outside plant.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Several factors have played a role in fostering the deployment of networks. The Covid-19 crisis led to more data traffic and more demand, which has resulted in private investors boosting considerably their deployment projects in favor of FTTH/B to support the ongoing traffic increase. Adding to this, the launch of national programs (infrastructures and digitalization) and new European digital targets for 2025 and 2030 will lead to the acceleration of full-fiber connectivity across all European countries.
Whereas the general market forecasts report is publicly available, members of the FTTH Council Europe are granted exclusive access to the extended version of the asset, featuring very detailed data. This unique data allows regional and international network operators, manufacturers, and investors, to efficiently navigate their business & direct their investments where it’s most needed or will be viable in years to come.
Members of the FTTH Council Europe can access the full asset and other content & exclusive services via member-restricted extranet (subject to certain conditions).
References:
https://www.ftthcouncil.eu/knowledge-centre/all-publications-and-assets/248/ftth-b-in-rural-areas
FTTH Council Europe: FTTH/B reaches nearly 183 million (>50% of all homes)
http://www.fiber-optic-components.com/tag/fiber-optic-network
Telstra’s T25 to extend 5G coverage and offer enhanced customer experiences
Australian network operator Telstra has unveiled a strategy it is calling T25, with the main aim of extending 5G coverage across Australia, as well as enhancing its customer service.
Telstra said that the T25 strategy is likely to come into effect by July 2022. The T25 strategy also aims to bring down the telco’s annual fixed costs by $366 million.
Telstra noted that the new plan will build on the operator’s previous T22 strategy. “T22 has been one of the largest, fastest and most ambitious transformations of a telco globally. Today we are a vastly different company, one poised for growth as our society and economy increasingly digitizes and we all work, study, transact and get our entertainment online,” Telstra’s CEO Andy Penn said.
“If T22 was a strategy of necessity, T25 is a strategy for growth. And in its implementation, we will be using exactly the same disciplines and governance that we used for T22 – the metrics and the milestones, the roadmaps and the scorecard which we will make transparent to you. And this is why I am confident it will be a success – why change a winning formula when you don’t need to,” Penn said.
T25 is Telstra’s strategy for growth, which is broken down into four pillars:
- Provide an exceptional customer experience you can count on
- Provide leading network and technology solutions that deliver your future
- Create sustained growth and value for our shareholders
- Be the place you want to work
Telstra said it aims to further invest in 5G with the goal of increasing the reach of its 5G network from the current 75% of the population to 95% population coverage.
“Our customers will keep enjoying our investment in 5G, which will deliver approximately 95% population coverage by fiscal year 2025 – including a 100,000 square kilometer increase in our 4G and 5G network footprint, substantially increasing regional coverage,” Penn explained.
“Over the next 3-5 years, this will be supported by our continued 5G network rollout and the doubling of metro cells to increase density for greater capacity and speed. As a result, we expect 80% of all mobile traffic to be on 5G by fiscal year 2025,” the executive added.
Penn also highlighted that Telstra will also extend its 4G coverage to 100% of its network by 2024, enabling the carrier to “continue to lead in composite coverage, speed and performance for 4G and 5G as we close 3G. This will set us up well for early planning on 6G, which will clearly be on the agenda by the end of T25,” Penn concluded.

Telstra, which had launched 5G in May 2020, is currently using its spectrum in the 3.6 GHz band to provide 5G technology across Australia. Some of the cities in which Telstra offers its 5G service are Canberra, Central Coast, Brisbane, Sidney, Cairns, Gold Coast, Adelaide, Hamilton, Melbourne and Perth.
In May last year, Telstra upgraded its 5G radio access network (RAN) coverage footprint across Australia, connecting a cloud-native 5G Core (5GC) network to handle new 5G standalone traffic.
Telstra used equipment from Swedish vendor Ericsson for the network upgrade.
References:
Introducing T25: our plan for growth and enhanced customer experiences
IQ Fiber to launch service in Jacksonville, FL after majority investment from SDC Capital Partners
Start-up network operator IQ Fiber has received a majority investment from SDC Capital Partners, which also owns a 48% stake in Midwest fiber provider Allo Communications. The transaction provides IQ Fiber with significant equity funding to complete the first phase of its all-fiber network build, passing more than 60,000 homes in the Jacksonville area.
“Consumers deserve a smarter internet choice,” said IQ Fiber CEO Ted Schremp. “High-speed internet has become a necessity and is truly the heartbeat of the modern home. With the launch of IQ Fiber, Jacksonville residents will soon have access to a state-of-the-art, 100% fiber-optic network with gigabit upload and download speeds, simple subscription plans and service experts who live and work in our community.”
“We are thrilled to partner with IQ Fiber in its initial launch in Jacksonville and are excited about the larger opportunity in Northeast Florida and beyond,” said Clinton Karcher, partner at SDC. “IQ Fiber’s commitment to providing exceptional customer service, coupled with state-of-the-art fiber network infrastructure in an underserved market, creates a formula for success.”
IQ Fiber plans to offer simple month-to-month rates with no hidden fees, surcharges or surprise price increases. IQ Fiber’s three service plans will deliver symmetrical internet speeds between 250 and 1,000 Mbps, with whole-home Wi-Fi service always included.
Fiber to the home represents the state-of-the-art for the delivery of broadband services, yet it is accessible to only 36% of the U.S. population. Compounding the consumer challenge, approximately 83 million Americans can only access broadband through a single provider. With today’s announcement, Jacksonville will soon have the freedom to choose a 100% fiber-optic network with simple, no-hassle plans, supported by local experts.
Though its initial plan will see it offer service in Jacksonville starting in early Q2 2022, CEO Ted Schremp said the company is eyeing an opportunity to expand across at least four counties, including Duval (where Jacksonville is located), Clay, Nassau and St. Johns.
“That four county area represents an opportunity for us that is five times bigger than our initial Phase I build,” he said. “So we know we’ve got not just opportunity to get this first 60,000 that we’ve announced, but plenty of additional opportunity as we go forward just inside this little corner of Florida that’s growing as quickly as it is.”
The company is deploying an XGS-PON fiber network and plans to offer three service tiers with symmetrical speeds of 250 Mbps for $65 per month, 500 Mbps for $75 per month and 1 gig for $85 per month. Those prices include taxes as well as whole-home Wi-Fi, Schremp said. While it’s not alone in providing the latter, he pitched it as a differentiator for consumers who just want simplicity and a good customer experience. The company states on its website:
Our 100% fiber-optic network is built for the modern home. With symmetrical speeds, your entire can stream, game, and work from home all at the same time and it won’t slow you down.
“A gig to the side of your house is useless if you went to Best Buy and bought a router five years ago and are just bumping along, and the average consumer just really doesn’t know how to contend with that,” he said. “The reality is they’re looking at the service provider to solve that for them and certainly that’s good for us in terms of the management of churn and the delivery of the full speeds.”
More than anything, Schremp said IQ Fiber is “trying to be what the incumbents are not. The incumbents here are Comcast with their traditional HFC [hybrid fiber coax] service, AT&T with some fiber build and a lot of legacy DSL and we know it can be done better,” the CEO said. “We certainly know that consumers react positively to choice. They certainly are irritated by the practices of many of the incumbent providers. And we’re trying to deliver the converse of that.”
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/operators/iq-fiber-prepares-to-take-at-t-comcast-florida
Hiber in deal with Shell for remote IoT monitoring of wells via HiberHilo
Dutch satellite asset tracking start-up Hiber has signed an agreement with Royal Dutch Shell to provide worldwide well monitoring systems. The global framework agreement will allow all Shell entities and subsidiaries to use the HiberHilo product worldwide for Industrial IoT applications.
HiberHilo, launched in October 2020, is an end-to-end IoT system that makes adds data and security to monitoring. Based on satellite technology, the system will enable oil and gas companies to measure real-time well temperature and pressure at disconnected wells in remote and offshore locations. HiberHilo is already installed in Shell operations in the North Sea. Shell is considering using HiberHilo for various operations in Africa, the Middle East and Southeast Asia.
“After testing HiberHilo, the opportunity was clear,” said Ian Taylor, Global Principal Technical Expert for well integrity at Shell. Operations in South-east Asia, the Middle East, and Africa are considering HiberHilo.
“HiberHilo is a simple solution to help oil and gas companies improve safety, optimize operations, and reduce their environmental footprint,” said Coen Jansen, Hiber’s Chief Strategy Officer. “We’re thrilled to be working with Shell toward a technologically cleaner future. Hiber’s mission is connecting everything everywhere to deliver productivity and sustainability in global industrial IoT,” he added.
Shell plans to use HiberHilo to reduce travel to and from wells in remote locations. The system will also let the company to gain more data on their well performance and better monitor well integrity issues, improving the safety of remote and offshore oil and gas wells.

Image Credit: Hiber Global
Hiber, founded in 2016 in the Netherlands, designs, builds and operates end to end solutions for the Internet of Things, focused on industrial uses such as well integrity or heavy equipment monitoring. The company is working on a network of 50 satellites aimed at making the ‘Internet of Things’ available all over the world. Its Hiberband network is described on their webpage as follows:
Hiberband is the world’s first LPGAN (Low Power Global Area Network) and it changes everything. It’s low cost thanks to using tiny nano satellites at a low orbit of just 600km above Earth. Unlike traditional satellite and cellular operators who launch gigantic, super expensive satellites at 60x higher with much higher costs.
Low orbit also means low power with modem batteries lasting 5-10 years. Just one of many factors that make experimenting with Hiberband-enabled devices a developer’s dream. We’ve even secured priority on our own dedicated frequency. Which is why everyone at Hiber believes Hiberband is the future of IoT connectivity.
Hiber acquired a new space permit in July 2020. On 29 February, the company launched a second-generation satellite into orbit through a SpaceX launch. A second Soyuz rocket launch followed in March. At the end of March, Hiber received an investment of 26 million EUROs to further expand its IoT satellite network. The funding came from the European Innovation Council Fund (EIC Fund), the EU’s innovation agency, which has a €278 million Innovation Fund. The EIC co-invested with an innovation credit provided by the Dutch government and existing shareholders. Other investors include Finch Capital, Netherlands Enterprise Agency and Hartenlust Group. Hiber’s satellite constellation tracks and monitors machines and devices in harder-to-reach places.
References:
https://hiber.global/press/hiberhilo-shell-deal/
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/hiber-signs-iiot-agreement-with-shell–1397276
Hiber signs deal with Shell for remote IoT well monitoring system
Shell hands major IoT contracts for oil well and refinery monitoring to Dutch startups
IoT satellite network startup Hiber secures €26M in funding round led by EU’s innovation agency
https://hiber.global/press/hiberhilo-wts-venture/
T-Mobile US CFO on the Big Hack, Verizon Tracfone, Supply Chain Shortages, and FWA
Peter Osvaldik (photo below), executive vice president & chief financial officer (CFO) of T-Mobile US provided a business update today at the BofA 2021 Media, Communications and Entertainment Conference.
Selected Quotes:
“With respect to the (well advertised) data breach, T-Mobile US is not immune to criminal acts, but we have a responsibility to our customers which we take very seriously. We acted quickly to shut down the attack, investigate and get in touch with the consumers that were impacted. We definitely saw some temporary customer cautiousness. But now, several weeks later, consumer flows have normalized. We’re taking significant steps to enhance our security.”
“$750M annual T-Mo revenues would go away if Verizon is successful in acquiring Tracfone, which is clearly a competitor. We feel good in that space, especially with Metro by T-Mobile as the leading pre-paid service provider.”
“The network experience will become more compelling with 5G, especially mid band (2.5GHz) 5G with 300M bit/sec targeted speeds and the massive capacity that brings. We’re exactly in the right spot as we take these assets and deploy them at breakneck speeds.”
“We are the 5G (U.S.) leader and that lead will continue to grow. We were first to bring a differentiated rate plan (Magenta MAX) that won’t slow you down.”
“Certainly, from a network perspective, we’re not experiencing any supply chain issues. From a home broadband (FWA) perspective, sometimes demand did exceed supply. We’re already seeing increasing supply there. We feel very good about our momentum on the home broadband side of the house.”
“Samsung has really fallen behind the eight ball relative to other OEMs [original equipment manufacturers] on the global supply chain issue.” Osvaldik noted that Samsung discontinued its Galaxy Note smartphone “which many of our customers just loved,” and that many of the company’s S-series smartphones “are in very short supply.”
“A lot of our customer base are very significant Samsung lovers, and so we probably saw a little bit more of the supply chain issue there. Others (wireless network operators) that have an Apple oriented customer base have been less impacted.”
“The demand we’re seeing for FWA, with download speeds of 100 M bit/sec and soon to increase, is very strong. We have a target of 7 to 8M FWA customers by the end of 2025. We’re confident we’ll receive our target (number of subscribers) this year.”
“Large enterprises and government are a tremendous opportunity for us. It’s opened up a lot of conversations with government organizations. We’re very pleased with the traction we’ve seen.”

Peter Osvaldik, Executive Vice President & CFO, T-Mobile
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Belgian trial of FWA using Pharrowtech’s mmWave technology
Vlaio has agreed to support a trial of fixed-wireless internet access (FWA) in the 60 GHz band using semiconductor start-up Pharrowtech’s mmWave technology. Belgian cable operator Telenet and wireless equipment supplier Unitron are also participating, with the trial services expected to start for homes and businesses in 2022.
The trial will focus on validating the performance of Pharrowtech’s mmWave technology, to help the company move towards commercialization of its products. Pharrowtech said its CMOS process technology makes mmWave services in the 60 GHz band a cost-effective, high-performance alternative to fibre roll-outs. The technology is reliable and robust enough to cope with the outdoors environment, while delivering superior performance compared to alternatives in the market, in urbran or rural areas, the company said.
The Vlaio grant will be used to support preparation and execution of the Telenet field trial of Pharrowtech’s mmWave RFIC technology using Unitron’s network elements. Beamforming and mesh control software developed by labs at the Flemish research institute Imec will also be used in the trial.
Telenet, which is controlled by the Liberty Global group, said it has multiple use cases in mind where FWA could bring benefits such as reducing installation and roll-out costs. The operator last year started exploring a cooperation on FTTH roll-out in Flanders, but has yet to commit to a technology for its next network upgrade after Docsis 3.1. In the US, operators such as Mediacom and Alaska Communications are already exploring FWA services.
Pharrowtech was founded in 2018 as a spin-off from Imec, where the founding team led CMOS IP generation and prototype development in mmWave wireless systems for more than fifteen years. In 2019, the company secured more than EUR 6 million in seed funding from imec-Xpand, Bloc Ventures and the KBC Focus Fund, and in June this year the company released its first evaluation board.
Pharrowtech CEO and Co-Founder, Wim van Thillo, said: “We are extremely pleased that VLAIO is supporting us to roll out our technology with these leading partners. This field trial perfectly represents the massive business opportunity that mmWave FWA offers. Even in areas as densely populated as Belgium, operators struggle to deploy gigabit internet services fast enough. This project will establish our technology as a key complement to fiber for fast and economical high-speed internet deployments everywhere.”
Unitron CTO, Stephen Deleu, said: “With this VLAIO project, UnitronGroup will expand its knowledge in the higher frequency ranges and discover new wireless applications for ultrafast broadband communication. UnitronGroup is the market leader in multiple high frequency technologies, and collaborating with knowledge partners helps us strengthen our position. As a key technology partner for multiple telecom operators, our role in this ambitious project is to provide the FWA customer and distribution node elements. We are excited to be part of this consortium and looking forward to the insights and outcomes of this VLAIO project.”
Telenet, Director Network & Infrastructure, Luk Bruynseels, said: “For Telenet it is paramount to keep on investing in innovative ways to deliver digital services to our customers. We have multiple use cases in scope where FWA technology brings opportunities and important benefits by reducing installation and roll-out costs. This VLAIO project is a great opportunity for Telenet to gather and share all required knowledge and expertise within the consortium to ensure we meet the expected outcome of the project.”
References:
Pharrowtech, Telenet, and Unitron secure public funding for Fixed Wireless Access field trial
O-RAN Alliance tries to allay concerns; Strand Consult disagrees!
The O-RAN Alliance reiterated its commitment towards Open and intelligent Radio Access Network (RAN) and said its board has approved changes to O-RAN “participation documents and procedures” to allay concerns of some participants who may be subjected to U.S. export regulations.
The O-RAN Alliance became aware of concerns regarding some participants that may be subject to U.S. export regulations, and has been working with O-RAN participants to address these concerns. The O-RAN Board has approved changes to O-RAN participation documents and procedures. While it is up to each O-RAN participant to make their own evaluation of these changes, O-RAN is optimistic that the changes will address the concerns and facilitate O-RAN’s mission.
“O-RAN is an open and collaborative global alliance operating in a way that promotes transparency and participation of our member companies in the development and adoption of global open specifications and standards,” said Andre Fuetsch, Chairman of the O-RAN ALLIANCE and Chief Technology Officer of AT&T.
“We remain fully committed to working together in the alliance to achieve the goals and objectives of O-RAN as quickly as possible,” said Alex Jinsung Choi, Chief Operating Officer of the O-RAN ALLIANCE and SVP of Strategy and Technology Innovation, Deutsche Telekom.
This comes after Nokia halted its work in the Open RAN industry alliance over concerns that it may face penalties from the U.S. government for working with blacklisted Chinese entities.
John Strand’s comments:
This statement is not solving the Chinese security problem. Even with the proposed changes, the five founding members, including China Mobile, still have a veto. The statement from O-RAN Alliance raises more questions than it answers. Who are the member companies, do the network operators agree with the O-RAN Alliance statement? How about contributors and the license adopters?
Strand Consult wants to create the transparency O-RAN Alliance are fighting against, and I share the concerns of the EU and the U.S. House Foreign Affairs Committee when it comes to transparency. At the same time, we believe it is a great idea for O-RAN Alliance to become WTO (World Trade Organization) compliant like other professional telecom standard bodies. What’s the problem for ORAN Alliance to be WTO compliant? It’s hard to see any downside.
Strand Consult doesn’t believe the changes will satisfy WTO requirements nor does it align with the practices of professional standards organizations nor with shareholder practices of U.S. and EU publicly traded companies.
Last year Strand Consult exposed the 44 Chinese companies involved in the O-RAN Alliance three of them on the entity list.
The O-RAN Alliance proposes changes to mitigate Chinese involvement. However these changes will probably not satisfy WTO compliance rules. Here are some relevant report from EU/WTO and European Commission (EC) on OpenRAN: https://www.wto.org/english/tratop_e/tbt_e/principles_standards_tbt_e.htm
https://ec.europa.eu/newsroom/dae/redirection/document/78778 (page 76).
The EC’s report is based on publicly available information and an interview with a legal expert on the WTO rules and EU Regulation No 1025/2012. It notes the following concerns with the O-RAN Alliance’s proposed changes:
- First, the required transparency, i.e. all essential information is easily accessible to all interested parties, is only partly fulfilled, e.g. the O-RAN specifications are not accessible at the homepage.
- Second, the procedure is not open in a non-discriminatory manner during all stages of the standard-setting process, because the founding members have access to more information than the contributors during the process.
- Third, although interested contributors have opportunities to contribute to the elaboration of the specifications, the founding members have a privilege, because they have the necessary minority of more than 25% to block proposals.
Overall, proof that the O-RAN Alliance complies with the various WTO criteria is still missing, although some of their members assure this compliance is in place. “Consequently, such an independent assessment is needed, which, however, cannot be realized within the context of this project.”
The O-RAN Alliance does not satisfy the openness criteria laid down in WTO Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations. The O-RAN Alliance is a closed industrial collaboration developing technical RAN specification over and above 3GPP specifications or ITU-R recommendations.
3GPP was formed after 2G (GSM) was developed this means that 3GPP did not develop 2G but 3GPP ensured backward compatibility for every G. Note that 3GPP specifications define the technical specifications for a complete mobile cellular network 2G/3G/4G/5G. ITU-R recommendations only cover the radio access interface technologies, e.g. ITU M.2150/IMT 2020 for “5G.”
It is possible that some U.S. firms could be satisfied with the O-RAN Alliances proposals, but the fact remains that Chinese companies still exert disproportionate authority on this industry group. It is not yet clear with U.S. President Biden or the NTIA will weigh in on the matter. If not, this could be interpreted as placating, or even going soft on China.
Strand Consult discloses on its website that it is a company providing knowledge to the mobile industry, specifically mobile operators and their managers, executives, and boards of directors. Strand Consult only sells knowledge to mobile operators, and Strand Consult has done this for 25 years (see About Strand Consult below).
About O-RAN ALLIANCE:
The O-RAN ALLIANCE is a world-wide community of over 300 mobile operators, vendors, and research & academic institutions operating in the Radio Access Network (RAN) industry. As the RAN is an essential part of any mobile network, the O-RAN ALLIANCE’s mission is to re-shape the industry towards more intelligent, open, virtualized and fully interoperable mobile networks. The new O-RAN standards will enable a more competitive and vibrant RAN supplier ecosystem with faster innovation to improve user experience. O-RAN based mobile networks will at the same time improve the efficiency of RAN deployments as well as operations by the mobile operators. To achieve this, the O-RAN ALLIANCE publishes new RAN specifications, releases open software for the RAN, and supports its members in integration and testing of their implementations.
About Strand Consult:
There are six focus areas:
– The mobile broadband market
– The MVNO market
– The market for Value Added Services
– Next Generation Prepaid Services
– The Smartphone market
– Digital strategy for the Telecom and Media industry.
We have spent many man years researching and publishing a series of comprehensive reports and workshops focused on these areas. Market players that have ambitions of being successful within these areas can either try to gain an overview themselves, find solutions and purchase external consultants to help them on their way, or alternatively use Strand Consult’s reports – with or without workshops -to acquire the knowledge they need to be successful in the future.
You can read more about some of our reports here:
Successful Strategies for the Mobile Broadband Market
References:




