Intel to spin off its Networking & Edge Group into a stand-alone business
As originally reported by CRN, Intel revealed its plan to spin off its Network and Edge Group in a memo addressed to customers and said it will seek outside investment for the business unit. Intel will be an anchor investor in the stand-alone business. The memo, seen by CRN, was authored by Sachin Katti, who has led the Network and Edge Group, abbreviated as NEX, since early 2023. He was given the extra role of chief technology and AI officer by Intel CEO Lip-Bu Tan in April to lead the chipmaker’s AI strategy. An Intel spokesperson confirmed the contents of the memo to CRN.
“We plan to establish key elements of our Networking and Communications business as a stand-alone company and we have begun the process of identifying strategic investors,” the representative said in a statement. “Like Altera, we will remain an anchor investor enabling us to benefit from future upside as we position the business for future growth,” the spokesperson added.
The NEX spin-off plan was announced to Intel customers and employees the same day the semiconductor giant revealed more changes under Tan’s leadership, including a 15% workforce reduction and a more conservative approach to its foundry business. “We are laser-focused on strengthening our core product portfolio and our AI roadmap to better serve customers,” Tan said in a statement.

In Katti’s memo, he said Intel “internally announced” on Thursday its plan to “establish its NEX business as a stand-alone company.” This will result in a “new, independent entity focused exclusively on delivering leading silicon solutions for critical communications, enterprise networking and ethernet connectivity infrastructure,” he added.
Katti did not give a timeline for when Intel could spin off NEX, which has been mainly focused on networking and communications products after the company moved its edge computing business to the Client Computing Group last September. Intel also shifted its integrated photonics solutions to the Data Center Group that same month. Similar to other businesses Intel has spun off, the company plans to maintain a stake in the stand-alone NEX company as it seeks out other investors, according to Katti. “While Intel will remain an anchor investor in the new company, we have begun the process of identifying additional strategic and capital partners to support the growth and development of the new company,” he wrote.
Katti said the move is “rooted in our commitment to serving” Intel’s customers better and promised that there will be “no change in service or the support” they rely on. He added that it will also help NEX “expand into new segments more effectively. Backed by Intel, this new, independent company will be positioned to accelerate its customer-facing strategy and product road map by innovating faster and investing in new offerings.”
Katti said he expects the transition to be “seamless” for Intel’s customers. “What we expect to change is our ability to operate with greater focus, speed and flexibility—all to better meet your needs,” he wrote.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Intel was rumored to be looking for a buyer for its Network and Edge group in May. This business produced $5.8 billion in revenue in 2024.
This strategy seems similar to the company’s decision to spin off RealSense, its former stereoscopic imaging technology business, earlier this month. Intel decided to spin RealSense out during former CEO Pat Gelsinger’s tenure and the company struck out on its own with $50 million in venture funding.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Shortly after Tan became Intel’s CEO in March, the leader made clear that he would seek to spin off businesses he considers not core to its strategy. Then in May, Reuters reported that the company was exploring a sale of the NEX business unit as part of that plan.
While Tan didn’t reference Intel’s decision to spin off NEX in the company’s Thursday earnings call, he discussed other actions it has taken to monetize “non-core assets,” including the sale of a portion of Intel’s stake in Mobileye earlier this month.
The company is also expected to complete its majority stake sale of the Altera programmable chip business to private equity firm Silver Lake by late September, according to Tan. Silver Lake will gain a 51 percent stake in the business while Intel will own the remaining 49%. “I will evaluate other opportunities as we continue to sharpen our focus around our core business and strategy,” Tan said on the earnings call.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
In 2019, Apple acquired the majority of Intel’s smartphone modem business for $1 billion. This deal included approximately 2,200 Intel employees, intellectual property, equipment, leases, and over 17,000 wireless technology patents. The acquisition allowed Apple to accelerate its development of 5G modem technology for its iPhones, reducing reliance on third-party suppliers like Qualcomm. Intel, in turn, refocused its 5G efforts on areas like network infrastructure, PCs, and IoT devices
References:
https://www.crn.com/news/networking/2025/intel-reveals-plan-to-spin-off-networking-business-in-memo
https://techcrunch.com/2025/07/25/intel-is-spinning-off-its-network-and-edge-group/
https://www.lightreading.com/semiconductors/intel-sale-of-networks-sounds-like-an-ericsson-problem
CES 2025: Intel announces edge compute processors with AI inferencing capabilities
Massive layoffs and cost cutting will decimate Intel’s already tiny 5G network business
Nokia utilizes Intel technology to drive greater 5G SA core network energy savings
Nokia selects Intel’s Justin Hotard as new CEO to increase growth in IP networking and data center connections
T-Mobile’s growth trajectory increases: 5G FWA, Metronet acquisition and MVNO deals with Charter & Comcast
T-Mobile US is having a banner year. The “uncarrier” has again increased its annual earnings outlook, supported by the acquisition of fiber network operator Metronet and strong mobile customer growth in Q2. After gaining another 1.73 million postpaid customers in the quarter, T-Mobile now expects total postpaid net additions this year of 6.1-6.4 million, up from its previous guidance of 5.5-6.0 million. Postpaid customer growth strengthened compared to the first quarter and included 830,000 new phone customers and 902,000 other devices, while churn was little changed at 0.90 percent. Prepaid growth was more muted, with just 39,000 net additions. T-Mobile counted 132.778 million mobile customers at the end of June, up by around 1.9 million from a year ago. 5G broadband customers rose by 454,000 in the three months to 7.308 million.
In the three months to June, the company posted service revenues up 6% year-on-year to $17.4 billion, and core adjusted EBITDA (after leases) also was up 6% to $8.5 billion. The net profit rose 10 percent to a record $3.2 billion, and adjusted free cash flow increased 4% to $4.6 billion. Cash CAPEX rose 17.5 percent to $2.4 billion in Q2 and is still expected to reach $9.5 billion over the full year. The company also spent $2.5 billion buying back its own shares in Q2.
“T-Mobile crushed our own growth records with the best-ever total postpaid and postpaid phone nets in a Q2 in our history,” said Mike Sievert, CEO of T-Mobile. “T-Mobile is now America’s Best Network. When you combine that with the incredible value that we have always been famous for, it should surprise no one that customers are switching to the Un-carrier at a record pace. These durable advantages enabled us to once again translate customer growth into financial growth, with the industry’s best service revenue growth by a wide mile and record Q2 Adjusted Free Cash Flow.”

The new forecast includes the expected close of the Metronet acquisition on July 24th (today). The Metronet deal – crafted as a joint venture with KKR – will expand T-Mobile’s fiber reach by about 2 million homes across 17 states. It follows the completion of the deal with EQT to buy fiber operator Lumos.
T-Mobile plans to close the UScellular buyout and “become one team” on August 1st. “The combination gives us an expected 50% or more increase in capacity, in the combined footprint, and our site coverage will expand by a third from 9,000 to 12,000 sites,” CEO Mike Sievert said, noting that this will be in addition to 4,000 greenfield sites planned for this year, of which 1,000 have already been “lit up” to date.
T-Mobile stands at a critical juncture in its history, as it prepares to absorb more wireless and fiber assets, build a fiber network access business and enter a new market with the launch of T-Satellite in collaboration with Elon Musk’s Starlink. T-Mobile has already launched T-Mobile Fiber Home Internet and has forecast 100,000 fiber net customer adds in the second half of 2025 following the Lumos and Metronet deals. Sievert also reiterated that T-Mobile would continue to “keep an open mind” about any further fiber M&A.
T-Mobile is now the market’s fifth-largest ISP. Currently, the operator’s goals are to reach 12 million fixed wireless access subscribers by 2028 and to pass 12 million to 15 million households with fiber by the end of 2030, through both the fiber joint ventures and wholesale partnerships.
COO Srini Gopalan said on the earnings call, “We’re positioned to be a scale player in broadband,” claiming that the combined FWA and fiber targets would be equivalent to 40 million to 45 million homes passed as a broadband player, “and that’s before we go make other investments. As we’ve said before, we’re very open to looking at investments in fiber,” he added.
Separately, Charter Communications and Comcast announced Tuesday that they’ve cut a multi-year MVNO agreement with T-Mobile focused on their respective business customers. As the telecom industry growth rate is very low (real growth rate is barely positive), this additional source of revenue will be most welcome by the uncarrier. T-Mobile is expected to generate $850 million in incremental after tax income from its MVNO deals with Charter and Comcast. This revenue is included in the company’s updated guidance, but that guidance excludes the planned acquisition of UScellular assets.
T-Mobile Recognized as Network Leader by Third Parties:
- Ookla awarded T-Mobile as the only carrier in the country to win back-to-back Best Mobile Network awards in the largest, most-comprehensive tests of their kind, each leveraging half a billion real world data points on millions of devices measuring speed and experience
- Recognized by Opensignal for best Overall Experience for the fourth consecutive year and blew away the competition in best download speeds, nearly 200% faster than the nearest competitor, and upload speeds, approximately 65% faster than the nearest competitor
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/fttx/t-mobile-readies-for-the-next-stage-after-a-record-breaking-q2
Evercore: T-Mobile’s fiber business to boost revenue and achieve 40% penetration rate after 2 years
T-Mobile posts impressive wireless growth stats in 2Q-2024; fiber optic network acquisition binge to complement its FWA business
T-Mobile to acquire UScellular’s wireless operations in $4.4 billion deal
T-Mobile & EQT Joint Venture (JV) to acquire Lumos and build out T-Mobile Fiber footprint
T-Mobile US, Ericsson, and Qualcomm test 5G carrier aggregation with 6 component carriers
ITU-R WP5D IMT 2030 Submission & Evaluation Guidelines vs 6G specs in 3GPP Release 20 & 21
Like previous generations of international mobile telecommunications (IMT) recommendations, ITU-R defines the 6G terrestrial radio access network requirements while 3GPP develops the standardized technology specifications that will be the project’s candidate to the ITU-R process. The target date for “Technology proposals for IMT-2030 RIT/SRITs” has been defined by ITU-R to be early 2029, and resulting specifications (i.e. full system definition) are to be submitted by mid-2030 at the latest. 3GPP contributions to ITU-R WP 5D are made via ATIS – its North American partner standards organization. That is effectively how IMT 2020 RIT/SRIT became standardized in ITU-R M.2150 (5G RIT/SRITs).
At it’s July 2025 meeting in Japan, ITU-R WP 5D generated an outline of a working document that, when completed, will specify the requirements, evaluation criteria and submission templates for the development of IMT-2030 recommendation(s) sometime in 2030. The structure of this working document is based on Report ITU-R M.2411, and the sections and contents of each section are to be further discussed. This meeting also discussed 16 contributions on evaluation guidelines for IMT-2030 and that working document was updated
Meanwhile, 3GPP has concluded that two 3GPP Releases are needed to specify 6G: Release 20 for Studies and Release 21 for the normative work that will produce 6G specs. Technical studies on the 6G radio interface and 6G core network architecture within the RAN and SA Working Group to start in June 2025. Release 21 will be the official start of normative 6G work.

Juan Montojo, Qualcomm’s vice president of technical standards, told Light Reading that all of today’s 3GPP 6G contributors are committed. “I can say I’m very confident that every player that comes to the 3GPP is a full believer in the value of having a single, global standard,” he told Light Reading. “I’ve not seen any exception, or any [other] indication.” 3GPP Release 20 lays an important foundation for 6G, said Montojo in a blog post.
Huawei had way more delegates attending 3GPP 5G sessions than any other company which raised concerns that the company might exert undue influence on the development of 3GPP 5G specs to its advantage. However, it has now become much harder for companies from a particular region to dominate proceedings, according to Montojo. “There are very recent decisions where working group officials cannot all come from the same region,” he explained. The system has also been changed so that companies with operations in multiple geographies, such as Huawei and Qualcomm, cannot claim to be from any region except that of their headquarters, Montojo said.
Future 6G Patents:
While the standardization process remains open to new entrants, the likelihood is that 6G’s ultimate patent owners will be drawn heavily from the ranks of today’s 5G network equipment vendors, chipmakers and smartphone companies that actively participate at 3GPP and ITU-R meetings. Several independent assessments forecast that Qualcomm and Huawei will likely remain at or near the top for the forthcoming 6G related patents,. In January, a LexisNexis study ranked Huawei first in 5G based on patent ownership and standards contributions. A separate LexisNexis ranking called the Patent Asset Index, which attempted to score organizations based on the value of their patents, gave the top spot to Qualcomm. In 2024, patent licensing accounted for only 14% of Qualcomm’s revenues but ~39% of its pre-tax earnings.
- Huawei (China): Huawei holds a significant share of 5G patents and is actively developing 6G technology, according to Williams IP Law. They are also a strong contributor to 5G technical standards.
- Qualcomm (US): Qualcomm is evolving its research from 4G and 5G towards 6G, holding a notable percentage of global 5G patents. They are also a major player in software-defined network solutions for 6G.
- Samsung (South Korea): Samsung is a prominent player in 5G patent ownership and is leading efforts in 6G standardization, including chairing the ITU-R 6G Vision Group. They are also investing heavily in terahertz communication technologies for 6G.
- Ericsson (Sweden): Ericsson is recognized for its strong 5G patent portfolio and contributions to technical standards. They are actively engaged in 6G research and development, including collaborations and investments in areas like network compute fabric and trustworthy systems.
- Nokia (Finland): Nokia is another key player in 5G patent ownership and a significant contributor to 5G technical standards. They identified key technologies for 6G early on and are actively testing and setting 6G standards through collaborations and research labs.
Higher Spectrum Bands for 6G:
Much of the industry’s recent attention has been captured by the upper 6GHz band and the 7GHz to 15GHz range. Unfortunately, signals do not travel as far or penetrate walls and other obstacles as effectively in these higher bands. To compensate, 6G’s active antenna systems are set to include four times as many elements as today’s most advanced 5G technologies, according to Montojo.
“It is part of the requirement in 3GPP to reduce the site grid of the existing C-band,” he said. “You would not want to require a densification beyond the levels that we currently have but can actually guarantee reuse of the site grid of the C-band into these higher bands.” Some analysts, however, remain dubious. A so-called massive MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) radio loaded with an even bigger number of antennas is likely to be expensive, meaning the deployment of 6G for mass-market mobile services in higher spectrum bands might not be economically viable.
6G Core Network (3GPP only- no ITU involvement):
“The best-case scenario, and I would say default scenario, is that 6G radio will be connected to 6G core as basically the standards-based approach,” said Montojo. “What 6G core will be is TBD, but there is a lot of desire from the operator community to have a 6G core that is an evolved 5G core with some level, to be defined, of backwards compatibility.”
Here’s an AI generated speculation on the 6G core network to be specified by 3GPP in Release 21:
- AI and Machine Learning (ML) will be fundamental to the 6G core, moving beyond supplementary roles to become an inherent part of the network’s design and operation.
- Every network function may be AI-powered, enabling advanced decision-making, predictive maintenance, and real-time optimization.
- 6G core will be designed to support the full lifecycle of AI components, including data collection, model training, validation, deployment, and performance monitoring.
- Network slicing will evolve further in 6G, enabling even more flexible, customized, and isolated network slices tailored to the diverse requirements of emerging applications.
- The 6G core will likely leverage a streamlined, unified, and future-proof exposure framework, potentially building on the 3GPP Common API Framework (CAPIF), to enable new value creation and monetization opportunities through network service exposure to third parties.
- The 6G core will be designed with a strong focus on energy efficiency and sustainability, considering the growing demands and environmental impact of network operations.
- It will need to be resilient to handle high mobility conditions of devices across various networks and administrative domains, including terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) like satellites & drones.
- Security and trustworthiness will be paramount, requiring a strong emphasis on authentication, data privacy, integrity, and operational resilience.
- The 6G core will likely incorporate quantum-safe cryptography to address the threat of quantum computing.
- While many in the industry favor an evolutionary path building upon the 5G core, some in the Chinese telecom ecosystem have advocated for a completely new 6G core network architecture.
- This suggests a potential for divergence in the early stages of 6G development, with discussions and debates within 3GPP shaping the ultimate architectural choices.
In summary, the 6G core network to be specified by 3GPP is anticipated to be a highly intelligent, flexible, and efficient platform, deeply integrated with AI/ML, supporting diverse services through enhanced network slicing and exposure, while addressing critical challenges in security, sustainability, and global connectivity.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.3gpp.org/specifications-technologies/releases/release-20
The SA1 road to 6G: https://www.3gpp.org/news-events/3gpp-news/sa1-6g-road
Introduction to 3GPP Release 19 and 6G Planning – Contains an introduction to the preparation for 6G in 3GPP: https://atis.org/webinars/introduction-to-3gpp-release-19-and-6g-planning/
Advancing 5G towards 6G, TSDSI Workshops (Jan 2023): https://www.3gpp.org/news-events/partner-news/tsdsi-workshops
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/qualcomm-is-optimistic-geopolitics-won-t-tear-6g-apart
ITU-R WP 5D reports on: IMT-2030 (“6G”) Minimum Technology Performance Requirements; Evaluation Criteria & Methodology
Highlights of 3GPP Stage 1 Workshop on IMT 2030 (6G) Use Cases
ITU-R: IMT-2030 (6G) Backgrounder and Envisioned Capabilities
ITU-R WP5D invites IMT-2030 RIT/SRIT contributions
NGMN issues ITU-R framework for IMT-2030 vs ITU-R WP5D Timeline for RIT/SRIT Standardization
IMT-2030 Technical Performance Requirements (TPR) from ITU-R WP5D
Draft new ITU-R recommendation (not yet approved): M.[IMT.FRAMEWORK FOR 2030 AND BEYOND]
IMT Vision – Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and beyond
Gen AI eroding critical thinking skills; AI threatens more telecom job losses
Two alarming research studies this year have drawn attention to the damage that Gen AI agents like ChatGPT are doing to our brains:
The first study, published in February, by Microsoft and Carnegie Mellon University, surveyed 319 knowledge workers and concluded that “while GenAI can improve worker efficiency, it can inhibit critical engagement with work and can potentially lead to long-term overreliance on the tool and diminished skills for independent problem-solving.”
An MIT study divided participants into three essay-writing groups. One group had access to Gen AI and another to Internet search engines while the third group had access to neither. This “brain” group, as MIT’s researchers called it, outperformed the others on measures of cognitive ability. By contrast, participants in the group using a Gen AI large language model (LLM) did the worst. “Brain connectivity systematically scaled down with the amount of external support,” said the report’s authors.
Across the 20 companies regularly tracked by Light Reading, headcount fell by 51,700 last year. Since 2015, it has dropped by more than 476,600, more than a quarter of the previous total.
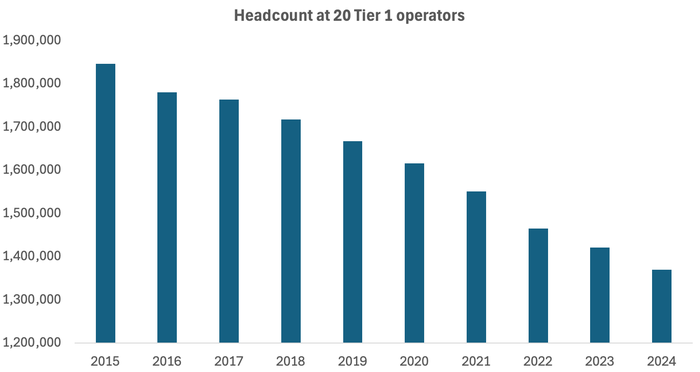
Source: Light Reading
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Doing More with Less:
- In 2015, Verizon generated sales of $131.6 billion with a workforce of 177,700 employees. Last year, it made $134.8 billion with fewer than 100,000. Revenues per employee, accordingly, have risen from about $741,000 to more than $1.35 million over this period.
- AT&T made nearly $868,000 per employee last year, compared with less than $522,000 in 2015.
- Deutsche Telekom, buoyed by its T-Mobile US business, has grown its revenue per employee from about $356,000 to more than $677,000 over the same time period.
- Orange’s revenue per employee has risen from $298,000 to $368,000.
Significant workforce reductions have happened at all those companies, especially AT&T which finished last year with 141,000 employees – about half the number it had in 2015!
Not to be outdone, headcount at network equipment companies are also shrinking. Ericsson, Europe’s biggest 5G vendor, cut 6,000 jobs or 6% of its workforce last year and has slashed 13,000 jobs since 2023. Nokia’s headcount fell from 86,700 in 2023 to 75,600 at the end of last year. The latest message from Börje Ekholm, Ericsson’s CEO, is that AI will help the company operate with an even smaller workforce in future. “We also see and expect big benefits from the use of AI, and that is one reason why we expect restructuring costs to remain elevated during the year,” he said on this week’s earnings call with analysts.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Other Voices:
Light Reading’s Iain Morris wrote, “An erosion of brainpower and ceding of tasks to AI would entail a loss of control as people are taken out of the mix. If AI can substitute for a junior coder, as experts say it can, the entry-level job for programming will vanish with inevitable consequences for the entire profession. And as AI assumes responsibility for the jobs once done by humans, a shrinking pool of individuals will understand how networks function.
“If you can’t understand how the AI is making that decision, and why it is making that decision, we could end up with scenarios where when something goes wrong, we simply just can’t understand it,” said Nik Willetts, the CEO of a standards group called the TM Forum, during a recent conversation with Light Reading. “It is a bit of an extreme to just assume no one understands how it works,” he added. “It is a risk, though.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
AI spending is surging; companies accelerate AI adoption, but job cuts loom large
Verizon and AT&T cut 5,100 more jobs with a combined 214,350 fewer employees than 2015
Big Tech post strong earnings and revenue growth, but cuts jobs along with Telecom Vendors
Nokia (like Ericsson) announces fresh wave of job cuts; Ericsson lays off 240 more in China
Deutsche Telekom exec: AI poses massive challenges for telecom industry
Lack of wireless network operator consolidation & EU over-regulation weakened mobile network infrastructure investments
by John Strand of Strand Consult
Over-regulation in the European Union (EU) has had a negative impact on mobile network operator’s investment in both fixed and mobile infrastructure. Years ago, the EU identified a €100 billion investment gap in telecommunications. By 2025, this gap has reportedly doubled to €200 billion. Why did that happen?
The EU telecom market has a large number of operators, many of whom lack the subscriber base to generate sufficient returns on capital to justify large infrastructure investments. In contrast, countries like the US and China have a smaller number of larger operators, allowing for greater economies of scale and more investment per operator.
Regulatory Complexity and Costly Landscape: Overregulation and fragmented national rules create a complex and costly environment that stifles innovation and adds uncertainty for telecom companies, says the ECIPE. This impacts the ability to attract investment, according to the European Investment Bank.

Mobile operators around the world would like to merge four mobile networks in their respective nations into three. This would improve the business case for investment by eliminating duplicative administrations, improving spectrum synergies, and upgrading customers to better networks. Strand Consult has studied mobile industry consolidation since 2000 with the groundbreaking case of South Korea merging five operators into three and being first in the world to launch 3G. South Korea has remained at the forefront of mobile industry innovation, investment, and rollout ever since.
Unfortunately, during the period 2014 to 2024 European Union Vice President for Competition Margrethe Vestager had a crude view on in market consolidation. She did not understand that market consolidation could have a positive impact on the wireless infrastructure that citizens have access to.
The result is that this proceeding appears to overlook that critical lever—making it unlikely to achieve its core goal of boosting private-sector investment in broadband, fiber, and next-generation networks like 5G and 6G. While reducing compliance and reporting burdens is welcome, if the overarching regulatory model remains flawed, the fundamental barriers to investment will persist.
If you look at countries such as the United States, India and Brazil, the in-market consolidation has had a positive impact on the infrastructure to which citizens have access. Today, in a country like India, there is better 5G infrastructure than there is in large parts of Europe.
There is no requirement that EU Competition authorities justify their merger decisions empirically. Only occasionally are official post-mortems issued examining whether their decision was right. Generally, such reports conclude that prices remain low. However, in a world in which mobile prices are flat or falling anyway, a merger rejection is not needed to ensure competitive prices. Competing voice technologies like WhatsApp and Telegram drive down mobile prices, as do the competitive wireless offerings by fixed line providers.
Notably few, if any, competition authorities have studied how the length of merger review impacts network investment. When companies request permission to merge, it’s as if time stops. Operators must hold back on critical capital decisions while authorities assess the merger request.
In the United Kingdom, some analysts have blamed poor mobile coverage on new restrictions placed on Huawei and ZTE. This is nonsense. Operators across the EU have switched and upgraded to trusted equipment vendors without impacting coverage. See TDC Denmark, Telenor and Telia in Norway, T-Mobile in the Netherlands (Odido), and Proximus in Belgium.
The UK has had two recent mobile merger attempts: O2/Hutchison (2015-2016), which Vestager blocked in May 2016. The parties sued the Commission and won in 2020. However, the EC appealed and won in 2023. By that point, the issue was moot as the UK had left the Union. Most competition authorities don’t care that their review of transactions can take years, but markets do. Few companies can afford to tie up so much capital for so long, and fewer still can afford to challenge such decisions when they are unfavorable. Hence the Draghi report is on to something.
Vodafone and Hutchison have tried to merge since June 2023. Upon leaving the EU, UK merger decisions were restored to local authorities. The UK Competition and Markets Authority issued a favorable decision last year.
Slow merger review process is almost as bad as a merger rejection. Before firms announce a merger, they have done their internal due diligence, perhaps over 12-18 months. Once submitted, a merger review can take 12 to 24 months. If approved, the merger can take another 18 to 24 months to implement. This process can take from 36-66 months from start to finish. This period of planning, submission, review, merger, and implementation puts network investment on hold. The numbers speak for themselves just look at Ookla´s numbers for the UK.
T-Mobile – Sprint Merger:
In US, it’s a wonder that the merger of #3 T-Mobile and operator #4 Sprint happened at all. Depending on the asset and transfer, telecom merger review can include the Department of Justice, the Federal Communications Commission, the Attorneys General of the 50 states and other gatekeepers, all of whom want to extract concessions from the transaction. While there are fewer authorities in the case of Vodafone and Hutchison, it still takes time.
With the Sprint acquisition, T-Mobile wanted to create an operator to compete at scale with AT&T and Verizon. Today the merger is an unqualified success; customers have gained access to a better network, while T-Mobile today has grown the muscle to compete head on with AT&T and Verizon.
The military needs to get access to 5G SA:
In the telecommunications industry, there has been talk for many years about how mobile companies can gain access to new sources of revenue. 5G and not least 5G SA and 5G private networks have received a lot of attention. Conversely, there has not been much talk about what communication solutions the defense system needs in the future.
The war in Ukraine and shifting geopolitical realities have dramatically changed perspectives in recent years. There is now a fundamentally different understanding of why and how defense investments must be made. We live in a world in which Russia has invaded Ukraine; China counts Russia, North Korea, and Iran as allies; and these countries support Russia’s invasion of Ukraine
All countries across NATO are in the process of modernizing the defense systems, gigantic sums will be invested in new and advanced equipment. The shopping list is very long, on the other hand, all these new defense solutions have in common that they need access to modern communication solutions.
Modern militaries cannot function without secure, advanced, and integrated communications. 5G SA is the go-to solution for its speed, security, and adaptability. When it comes to the limited rollout of 5G SA in Europe, it has major implications for NATO´s access to access to a single national network free from untrusted vendors like Huawei and ZTE.
At the same time NATO does not use equipment from countries like China, Russia, North Korea, or Iran. Indeed, NATO’s procurement rules prohibit its contracting with communist countries. NATO would not purchase Chinese fighter jets from Chengdu Aircraft Corporation and Shenyang Aircraft Corporation, nor Huawei network equipment. The rationale is that ill-advised to acquire critical supplies from one’s adversary.
One of NATO´s key problems in Europe is a large number of operators have chosen to use equipment from suppliers like Huawei and ZTE there are unlikely to meet the security requirements from NATO. The qualification review and exercise which will be undertaken among the 32 NATO countries and many other nations around the world aligned with NATO, countries like Japan, the Philippines, and others. Countries which consider China a military partner (Pakistan, Belarus, and Cambodia) use Huawei and ZTE equipment.
The European Commission wants to transform telecom regulation in Europe:
The EU will have a public consultation regarding The Digital Networks Act (DNA). It is EU’s initiative to modernize telecom regulation by harmonizing rules, spurring infrastructure investment, and cutting red tape. It seeks to streamline spectrum licensing, network authorizations, and reporting across member states, while promoting sustainability and consumer protection. These are worthy aims—but past experience suggests the European Commission lacks the resolve, or the “DNA,” to turn vision into action. While Strand Consult supports the effort to bring telecom policy into the 21st century, the proposals arrive too little, too late to inspire investors, entrepreneurs, or citizens. Outside of standout digital performers like Denmark, Europe’s digital sector has long trailed the U.S., South Korea, Norway, and Switzerland by most competitive benchmarks.
At Strand Consult, we are concerned that the EU’s ongoing regulatory reforms will once again fail to address the fundamental challenges. Years ago, the EU identified a €100 billion investment gap in telecommunications. By 2025, this gap has reportedly doubled to €200 billion.
The EU’s record on AI is similarly illustrative. In 2018, the EU announced its ambition to lead in AI. However, by 2023, it had passed legislation that imposed significant constraints on AI development. In 2025, despite limited presence in the global AI landscape, the EU reiterated its ambition to lead, this time with an “AI Continent Action Plan.”
These historical examples suggest that the European Commission excels at producing regulations that slow technological development and deter investment. There are few—if any—notable technology firms that owe their success to EU regulatory frameworks. In contrast, we see a steady decline in key sectors like telecommunications and hardware, driven by regulatory missteps.
The European Commission has now pledged to transform telecom regulation in Europe. It may be too little, too late to address the deep-rooted challenges the EU itself has acknowledged and in part, created.
The bottom line is that The European figures from Ookla speak for themselves. The problem that they have uncovered is a problem that many of us have talked about a lot for many years.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Consolidation would renew European telecoms, says digital industry chief
https://www.eib.org/files/publications/thematic/accelerating_the_5g_transition_in_europe_en.pdf
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
John Strand is the CEO of Strand Consult. He founded Strand Consult in 1995. Strand Consult is an independent telecom consultancy known for its expert knowledge and many reports which help mobile operators and their shareholders navigate an increasing complex world. It has 170 mobile operators from around the world on its client list.
GEO satellite internet from HughesNet and Viasat can’t compete with LEO Starlink in speed or latency
GEO satellite internet providers provide reliable connectivity across large land masses, but their distance from Earth presents challenges to delivering low-latency and high-speed satellite Internet services. HughesNet and Viasat operate stationary satellites 22,000 miles above Earth, whereas LEO satellite operators such as Starlink have satellites orbiting a mere 340 miles above Earth. GEO satellites are also less ubiquitous than LEO satellites – GEO operators have fewer satellites in their constellations.
According to Ookla, GEO satellite providers HughesNet and Viasat can’t compete with Starlink when it comes to latency and download speeds. HughesNet and Viasat are best-known for providing consistent coverage across large land masses. But because they operate in geostationary orbit rather than low-Earth orbit (LEO) and because they have fewer satellites in their constellations, they struggle with speed limitations and latency, making it difficult for them to compete with LEO providers such as SpaceX’s Starlink.
HughesNet and Viasat have three satellites each in their fleet delivering fixed broadband service. Viasat plans to launch its Viasat-3 F2 satellite later this year and the Viasat-3 F3 in 2026. In addition, it owns a fleet of satellites from the company’s Inmarsat acquisition in May 2023 which are primarily used in maritime and mission-critical applications.
The challenges facing these GEO satellite providers have become more pronounced over the past few years, particularly as Starlink has moved aggressively into the U.S. market with promotions such as its recent offer to provide free equipment to new customers in states where it has excess capacity.
“HughesNet and Viasat are losing subscribers at a rapid rate thanks to competition from LEO satellite provider Starlink with its lower latency and faster download speeds,” according to Sue Marek, editorial director and analyst with Ookla.
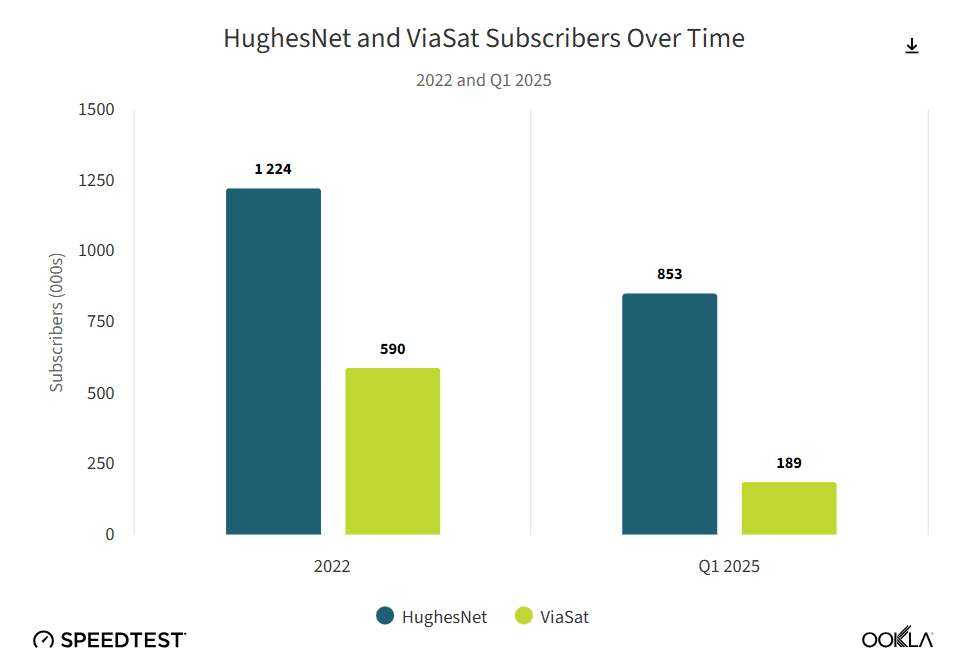
Ookla’s Key Takeaways:
- HughesNet saw its median multi-server latency improve from 1019 milliseconds (ms) in Q1 2022 to 683 ms in Q1 2025. Viasat’s median latency increased slightly over that time period from 676 ms in Q1 2022 to 684 ms in Q1 2025. But neither are remotely close to matching Starlink with its median latency of just 45 ms in Q1 2025.
- HughesNet more than doubled its median download speeds from 20.87 Mbps in Q1 2022 to 47.79 Mbps in Q1 2025 while Viasat increased its median download speeds from 25.18 Mbps to 49.12 Mbps during that same time period.
- Upload speeds are another area where GEO satellite constellations struggle to compete with Starlink and other low-Earth orbit systems. HughesNet has increased its median upload speeds from 2.87 Mbps in Q1 2022 to 4.44 Mbps in Q1 2025 but that is still far lower than Starlink, which has a median upload speed of 14.84 Mbps in Q1 2025. Viasat saw its median upload speeds decline over that same time period from 3.06 Mbps in Q1 2022 to 1.08 Mbps in Q1 2025.
- HughesNet and Viasat are losing subscribers at a rapid rate thanks to competition from LEO satellite provider Starlink with its lower latency and faster download speeds.
Meanwhile, Starlink has nearly 8,000 satellites in low earth orbit (LEO) as part of its mega-constellation, according to Space.com. Starlink’s median download speeds, according to data from Ookla’s Speedtest users, almost doubled from 53.95 Mbit/s in Q3 2022 to 104.71 Mbit/s in Q1 2025. These latest average download speeds are also nearly twice that of HughesNet and Viasat.
In addition to network performance, Starlink has made strides in the U.S. market with promotions and distribution of free equipment to “new customers in states where it has excess capacity,” said Marek. In May, Starlink offered its Standard Kit, priced at $349, for free to consumers in select areas who agree to a one-year service commitment. But, “high demand” areas would still need to pay a one-time, upfront “demand surcharge” of $100, the company said.
Starlink is making headway teaming up with terrestrial service providers on direct-to-device (D2D) services, which connect smartphones and mobile devices directly to satellite networks in areas of spotty wireless service. Canada’s Rogers Communications launched a beta D2D service this week that initially supports text messaging via Starlink LEO satellites. The Canadian operator is also working with Lynk Global in a multi-vendor approach to D2D. Starlink announced this week that it has over 500,000 customers across Canada.
T-Mobile’s D2D service, T-Satellite with Starlink, will be commercially available later this month and will include SMS texting, MMS, picture messaging and short audio clips. In October, T-Satellite will add a data service to its Starlink-based satellite offering.
However, T-Mobile announced it would bump up the launch of T-Satellite to areas impacted by the recent flooding in central Texas. During a number of recent natural disasters, Starlink has offered free services and/or satellite equipment kits to affected communities.
Starlink is providing Mini Kits, which support 50 gigabyte and unlimited roaming data subscriptions, for search and rescue efforts in central Texas, in addition to one month of free service to customers in the areas impacted by recent flooding. In January, the satellite operator offered about a month of free service to new customers and a one-month service credit to existing customers in areas affected by the Los Angeles wildfires.
Starlink could be facing increasing competition from Project Kuiper, Amazon’s LEO satellite broadband service, as it ramps up deployment of a planned LEO constellation of over 3,000 satellites. However, Project Kuiper has fallen far behind schedule in meeting the FCC’s deadline of having more than 1,600 LEO satellites in orbit by the summer of 2026. Since its initial launch in April, Amazon only has a total of 78 satellites in orbit, according to CNBC. Meanwhile, Starlink has launched over 2,300 satellites in the past year alone.
References:
https://www.ookla.com/articles/hughesnet-viasat-performance-2025
https://www.space.com/space-exploration/launches-spacecraft/spacex-starlink-15-2-b1093-vsfs-ocisly
KDDI unveils AU Starlink direct-to-cell satellite service
Telstra selects SpaceX’s Starlink to bring Satellite-to-Mobile text messaging to its customers in Australia
One NZ launches commercial Satellite TXT service using Starlink LEO satellites
SpaceX launches first set of Starlink satellites with direct-to-cell capabilities
FCC: More competition for Starlink; freeing up spectrum for satellite broadband service
U.S. BEAD overhaul to benefit Starlink/SpaceX at the expense of fiber broadband providers
Starlink’s Direct to Cell service for existing LTE phones “wherever you can see the sky”
ABI Research and CCS Insight: Strong growth for satellite to mobile device connectivity (messaging and broadband internet access)
AST SpaceMobile completes 1st ever LEO satellite voice call using AT&T spectrum and unmodified Samsung and Apple smartphones
PCMag Study: Starlink speed and latency top satellite Internet from Hughes and Viasat’s Exede
Ookla: Uneven 5G deployment in Europe, 5G SA remains sluggish; Ofcom: 28% of UK connections on 5G with only 2% 5G SA
According to Ookla, Europe is a “two-speed” 5G competitiveness landscape,” with some countries surging ahead and others falling well behind, In Q2-2025, Nordic and southern Europe countries maintained a substantial lead in 5G availability, helped by recent 700MHz band deployments in countries such as Sweden and Italy. By contrast, 5G availability in central and western European laggard countries such as Belgium, the UK and Hungary remains less than half that of the 5G pacemakers, says the study. On average, mobile subscribers in the EU spent 44.5% of their time connected to 5G networks in Q2 2025, up from 32.8% a year earlier.
The deployment and adoption of 5G SA in Europe remain sluggish, increasing slowly from a very low base and further widening the region’s gap with North America and Asia. Spain stands out as a clear leader in 5G SA deployment, reaching an 8% Speedtest® sample share compared with the EU average of just 1.3% as of Q2 2025. This progress has been driven by Spain’s proactive use of EU recovery funds to subsidize 5G SA rollouts in underserved areas, with a particular focus on bridging the rural-urban digital divide. However, the U.S. and China are still far ahead, with 5G SA sample shares above 20% and 80% respectively, reflecting a much greater pace of coverage and adoption in those markets.
Northern Europe Maintains 5G Availability Lead – Speed Test Intelligence Q2-2025: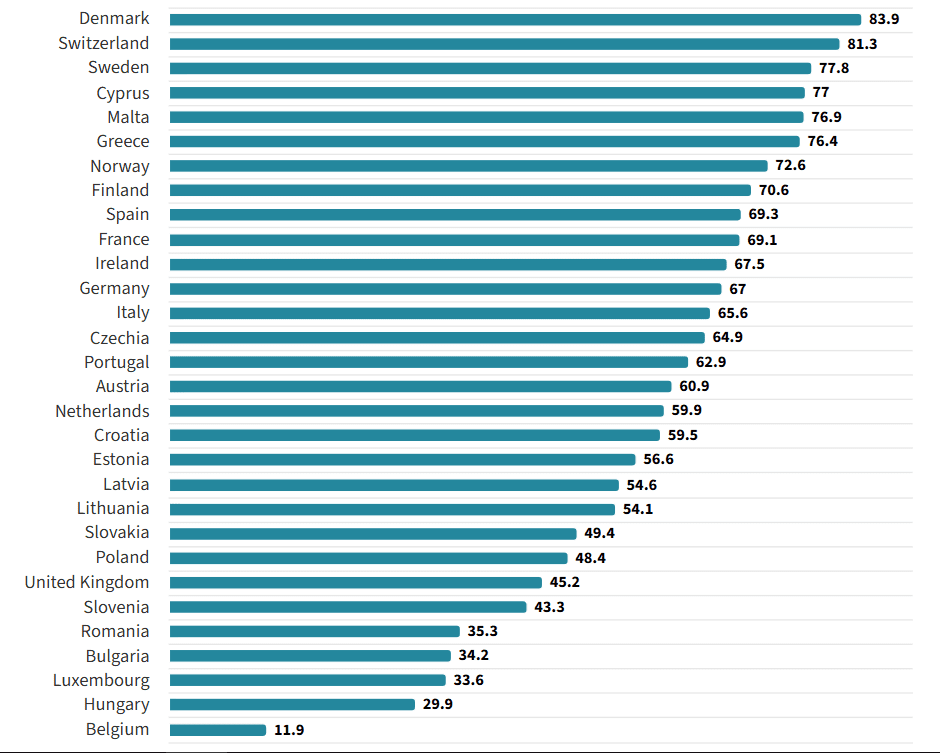
Fragmented 5G Availability across Europe is driven by a complex mix of national policies on spectrum assignment and broader economic factors, rather than by simple geographic or demographic differences. 5G Availability is more strongly correlated with policy-driven factors such as spectrum allocation timelines and costs, coverage obligations, subsidy mechanisms, and regulations for infrastructure sharing and permitting, than with structural factors like urbanization rates or the number of operators. This indicates that 5G competitiveness is shaped less by technology gaps or inherent market imbalances and more by effective policy execution.
Northern Europe Maintains 5G Availability Lead; Other Countries Lag:
Fragmentation remains a persistent theme, shaping stark 5G deployment asymmetries that cannot be explained by geography or demographics alone. Northern and Southern European countries such as Denmark (83.9%), Sweden (77.8%), and Greece (76.4%) are disproportionately represented among the countries with the highest 5G Availability in Q2 2025, with coverage rates up to twice as high as those in Western and Eastern countries like the United Kingdom (45.2%), Hungary (29.9%), and Belgium (11.9%).
Low-band deployment and DSS use continue to lift 5G availability in lagging countries:
Recent advances in 5G Availability have been driven by low-band deployments and the use of DSS, raising the average proportion of time spent on 5G networks in the EU from 32.8% in Q2 2024 to 44.5% in Q2 2025. The pace of coverage growth, and the corresponding increase in 5G usage, has primarily reflected each country’s starting point. Lagging countries like Latvia, Poland, and Slovenia have seen double-digit gains in 5G Availability from a low base. By contrast, leading countries such as Switzerland and Denmark, where 5G coverage is now nearly ubiquitous, have shifted their focus to targeted capacity upgrades through site densification and mid-band expansion.
About Ookla:
Ookla, a global leader in connectivity intelligence, brings together the trusted expertise of Speedtest®, Downdetector®, Ekahau®, and RootMetrics® to deliver unmatched network and connectivity insights. By combining multi-source data with industry-leading expertise, we transform network performance metrics into strategic, actionable insights. Solutions empower service providers, enterprises, and governments with the critical data and insights needed to optimize networks, enhance digital experiences, and help close the digital divide. At the same time, we amplify the real-world experiences of individuals and businesses that rely on connectivity to work, learn, and communicate. From measuring and analyzing connectivity to driving industry innovation, Ookla helps the world stay connected.
Ookla is a division of Ziff Davis, a vertically focused digital media and internet company whose portfolio includes leading brands in technology, entertainment, shopping, health, cybersecurity, and martech.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Mobile Matters report from communications regulator Ofcom discusses 5G’s share of network connections in UK. Ofcom’s analysis – based on crowdsourced data collected by Opensignal and covering the period October 2024 to March 2025 – showed that 28% of connections were on 5G, with 71% still on 4G, 0.7% on 3G and a holdout 0.2% on 2G. In terms of mobile network operators, BT-owned EE had the highest proportion of network connections on 5G, at 32%, while Vodafone had the lowest, at 24%. O2, which is now the mobile arm of Virgin Media, had the lowest share of 4G connections (68%) and the highest proportion on 3G (3%).
5G standalone vs 5G non-standalone performance:
• 5G standalone (SA) accounted for 2% of all 5G connection attempts in the six months to March 2025. UK MNOs have started to offer 5G SA but its use is currently low.
• Standalone 5G’s average response time (latency) was about 15% lower (better) than for 5G NSA. However, our analysis also indicated that 5G SA had a lower average connection success rate (95.9%) than 5G NSA (97.6%), although this was slightly higher than 4G’s.
• 5G SA provided significantly higher download speeds than 5G NSA. Seventy per cent of 5G SA download speeds measurements were at 100 Mbit/s or higher, compared to 46% for 5G NSA, and 2MB, 5MB and 10MB file download times, on average, were about 45% faster on 5G SA than over 5G NSA.
• The picture was more mixed for uploads. While 5G NSA had a higher proportion of low-speed connections (18% of 5G NSA upload speeds provided less than 2 Mbit/s compared to 10% on 5G SA) it also had a slightly higher share of higher-speed connections (30% of 5G NSA uploads were 20 Mbit/s or higher vs 28% on 5G SA).
References:
https://www.ookla.com/articles/europe-5g-q2-2025
Ookla: Europe severely lagging in 5G SA deployments and performance
Téral Research: 5G SA core network deployments accelerate after a very slow start
Softbank developing autonomous AI agents; an AI model that can predict and capture human cognition
Speaking at a customer event Wednesday in Tokyo, Softbank Chairman and CEO Masayoshi Son said his company is developing “the world’s first” artificial intelligence (AI) agent system that can autonomously perform complex tasks. Human programmers will no longer needed. “The AI agents will think for themselves and improve on their own…so the era of humans doing the programming is coming to an end,”
Softbank estimated it needed to create around 1000 agents per person – a large number because “employees have complex thought processes. The agents will be active 24 hours a day, 365 days a year and will interact with each other.” Son estimates the agents will be at least four times as productive and four times as efficient as humans, and would cost around 40 Japanese yen (US$0.27) per agent per month. At that rate, the billion-agent plan would cost SoftBank $3.2 billion annually.
“For 40 yen per agent per month, the agent will independently memorize, negotiate and conduct learning. So with these actions being taken, it’s incredibly cheap,” Son said. “I’m excited to see how the AI agents will interact with one another and advance given tasks,” Son added that the AI agents, to achieve the goals, will “self-evolve and self-replicate” to execute subtasks.
Unlike generative AI, which needs human commands to carry out tasks, an AI agent performs tasks on its own by designing workflows with data available to it. It is expected to enhance productivity at companies by helping their decision-making and problem-solving.
While the CEO’s intent is clear, details of just how and when SoftBank will build this giant AI workforce are scarce. Son admitted the 1 billion target would be “challenging” and that the company had not yet developed the necessary software to support the huge numbers of agents. He said his team needed to build a toolkit for creating more agents and an operating system to orchestrate and coordinate them. Son, one of the world’s most ardent AI evangelists, is betting the company’s future on the technology.
According to Son, the capabilities of AI agents had already surpassed PhD-holders in advanced fields including physics, mathematics and chemistry. “There are no questions it can’t comprehend. We’re almost at a stage where there are hardly any limitations,” he enthused. Son acknowledged the problem of AI hallucinations, but dismissed it as “a temporary and minor issue.” Son said the development of huge AI data centers, such as the $500 billion Stargate project, would enable exponential growth in computing power and AI capabilities.

Softbank Group Corp. Chairman and CEO Masayoshi Son (L) and OpenAI CEO Sam Altman at an event on July 16, 2025. (Kyodo)
The project comes as SoftBank Group and OpenAI, the developer of chatbot ChatGPT, said in February they had agreed to establish a joint venture to promote AI services for corporations. Wednesday’s event included a cameo appearance from Sam Altman, CEO of SoftBank partner OpenAI, who said he was confident about the future of AI because the scaling law would exist “for a long time” and that cost was continually going down. “I think the first era of AI, the…ChatGPT initial era was about an AI that you could ask anything and it could tell you all these things,” Altman said.
“Now as these (AI) agents roll out, AI can do things for you…You can ask the computer to do something in natural language, a sort of vaguely defined complex task, and it can understand you and execute it for you,” Altman said. “The productivity and potential that it unlocks for the world is quite huge.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
According to the NY Times, an international team of scientists believe that A.I. systems can help them understand how the human mind works. They have created a ChatGPT-like system that can play the part of a human in a psychological experiment and behave as if it has a human mind. Details about the system, known as Centaur, were published on Wednesday in the journal Nature. Dr. Marcel Binz, a cognitive scientist at Helmholtz Munich, a German research center, is the author of the new AI study.
References:
https://english.kyodonews.net/articles/-/57396#google_vignette
https://www.lightreading.com/ai-machine-learning/softbank-aims-for-1-billion-ai-agents-this-year
https://www.nytimes.com/2025/07/02/science/ai-psychology-mind.html
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09215-4
AI spending is surging; companies accelerate AI adoption, but job cuts loom large
Big Tech and VCs invest hundreds of billions in AI while salaries of AI experts reach the stratosphere
Ericsson reports ~flat 2Q-2025 results; sees potential for 5G SA and AI to drive growth
Agentic AI and the Future of Communications for Autonomous Vehicle (V2X)
Dell’Oro: AI RAN to account for 1/3 of RAN market by 2029; AI RAN Alliance membership increases but few telcos have joined
Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison and Nokia use AI to reduce energy demand and emissions
Deloitte and TM Forum : How AI could revitalize the ailing telecom industry?
McKinsey: AI infrastructure opportunity for telcos? AI developments in the telecom sector
ZTE’s AI infrastructure and AI-powered terminals revealed at MWC Shanghai
Ericsson revamps its OSS/BSS with AI using Amazon Bedrock as a foundation
Big tech firms target data infrastructure software companies to increase AI competitiveness
SK Group and AWS to build Korea’s largest AI data center in Ulsan
OpenAI partners with G42 to build giant data center for Stargate UAE project
Nile launches a Generative AI engine (NXI) to proactively detect and resolve enterprise network issues
AI infrastructure investments drive demand for Ciena’s products including 800G coherent optics
Ericsson reports ~flat 2Q-2025 results; sees potential for 5G SA and AI to drive growth
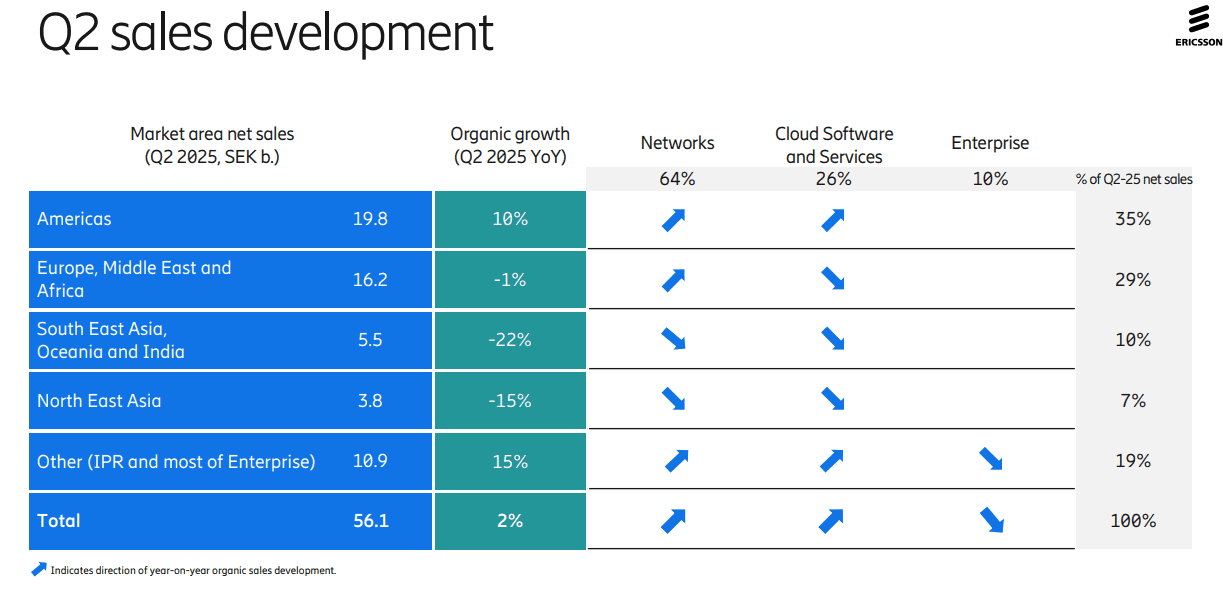
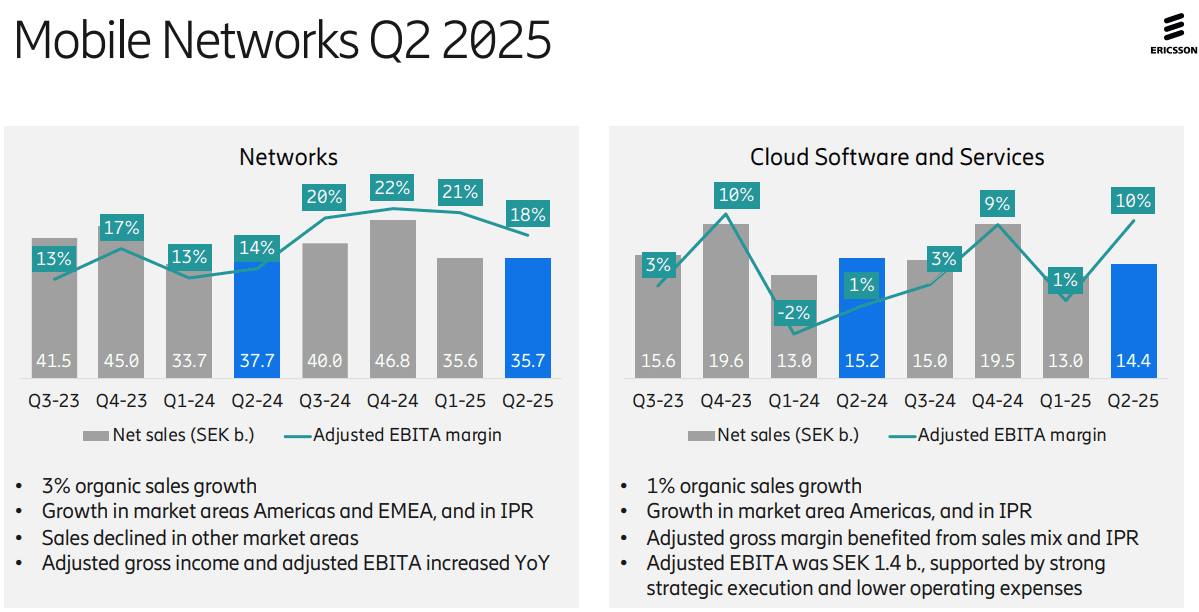
Ericsson’s second-quarter results were not impressive, with YoY organic sales growth of +2% for the company and +3% for its network division (its largest). Its $14 billion AT&T OpenRAN deal, announced in December of 2023, helped lift Swedish vendor’s share of the global RAN market by +1.4 percentage points in 2024 to 25.7%, according to new research from analyst company Omdia (owned by Informa). As a result of its AT&T contract, the U.S. accounted for a stunning 44% of Ericsson’s second-quarter sales while the North American market resulted in a 10% YoY increase in organic revenues to SEK19.8bn ($2.05bn). Sales dropped in all other regions of the world! The charts below depict that very well:
Ericsson’s attention is now shifting to a few core markets that Ekholm has identified as strategic priorities, among them the U.S., India, Japan and the UK. All, unsurprisingly, already make up Ericsson’s top five countries by sales, although their contribution minus the US came to just 15% of turnover for the recent second quarter. “We are already very strong in North America, but we can do more in India and Japan,” said Ekholm. “We see those as critically important for the long-term success.”
Opportunities: As telco investment in RAN equipment has declined by 12.5% (or $5 billion) last year, the Swedish equipment vendor has had few other obvious growth opportunities. Ericsson’s Enterprise division, which is supposed to be the long-term provider of sales growth for Ericsson, is still very small – its second-quarter revenues stood at just SEK5.5bn ($570m) and even once currency exchange changes are taken into account, its sales shrank by 6% YoY.
On Tuesday’s earnings call, Ericsson CEO Börje Ekholm said that the RAN equipment sector, while stable currently, isn’t offering any prospects of exciting near-term growth. For longer-term growth the industry needs “new monetization opportunities” and those could come from the ongoing modest growth in 5G-enabled fixed wireless access (FWA) deployments, from 5G standalone (SA) deployments that enable mobile network operators to offer “differentiated solutions” and from network APIs (that ultra hyped market is not generating meaningful revenues for anyone yet).
Cost Cutting Continues: Ericsson also has continued to be aggressive about cost reduction, eliminating thousands of jobs since it completed its Vonage takeover. “Over the last year, we have reduced our total number of employees by about 6% or 6,000,” said Ekholm on his routine call with analysts about financial results. “We also see and expect big benefits from the use of AI and that is one reason why we expect restructuring costs to remain elevated during the year.”
Use of AI: Ericsson sees AI as an opportunity to enable network automation and new industry revenue opportunities. The company is now using AI as an aid in network design – a move that could have negative ramifications for staff involved in research and development. Ericsson is already using AI for coding and “other parts of internal operations to drive efficiency… We see some benefits now. And it’s going to impact how the network is operated – think of fully autonomous, intent-based networks that will require AI as a fundamental component. That’s one of the reasons why we invested in an AI factory,” noted the CEO, referencing the consortium-based investment in a Swedish AI Factory that was announced in late May. At the time, Ericsson noted that it planned to “leverage its data science expertise to develop and deploy state-of-the-art AI models – improving performance and efficiency and enhancing customer experience.
Ericsson is also building AI capability into the products sold to customers. “I usually use the example of link adaptation,” said Per Narvinger, the head of Ericsson’s mobile networks business group, on a call with Light Reading, referring to what he says is probably one of the most optimized algorithms in telecom. “That’s how much you get out of the spectrum, and when we have rewritten link adaptation, and used AI functionality on an AI model, we see we can get a gain of 10%.”
Ericsson hopes that AI will boost consumer and business demand for 5G connectivity. New form factors such as smart glasses and AR headsets will need lower-latency connections with improved support for the uplink, it has repeatedly argued. But analysts are skeptical, while Ericsson thinks Europe is ill equipped for more advanced 5G services.
“We’re still very early in AI, in [understanding] how applications are going to start running, but I think it’s going to be a key driver of our business going forward, both on traffic, on the way we operate networks, and the way we run Ericsson,” Ekholm said.
Europe Disappoints: In much of Europe, Ericsson and Nokia have been frustrated by some government and telco unwillingness to adopt the European Union’s “5G toolbox” recommendations and evict Chinese vendors. “I think what we have seen in terms of implementation is quite varied, to be honest,” said Narvinger. Rather than banning Huawei outright, Germany’s government has introduced legislation that allows operators to use most of its RAN products if they find a substitute for part of Huawei’s management system by 2029. Opponents have criticized that move, arguing it does not address the security threat posed by Huawei’s RAN software. Nevertheless, Ericsson clearly eyes an opportunity to serve European demand for military communications, an area where the use of Chinese vendors would be unthinkable.
“It is realistic to say that a large part of the increased defense spending in Europe will most likely be allocated to connectivity because that is a critical part of a modern defense force,” said Ekholm. “I think this is a very good opportunity for western vendors because it would be far-fetched to think they will go with high-risk vendors.” Ericsson is also targeting related demand for mission-critical services needed by first responders.
5G SA and Mobile Core Networks: Ekholm noted that 5G SA deployments are still few and far between – only a quarter of mobile operators have any kind of 5G SA deployment in place right now, with the most notable being in the US, India and China. “Two things need to happen,” for greater 5G SA uptake, stated the CEO.
- “One is mid-band [spectrum] coverage… there’s still very low build out coverage in, for example, Europe, where it’s probably less than half the population covered… Europe is clearly behind on that“ compared with the U.S., China and India.
- “The second is that [network operators] need to upgrade their mobile core [platforms]... Those two things will have to happen to take full advantage of the capabilities of the [5G] network,” noted Ekholm, who said the arrival of new devices, such as AI glasses, that require ultra low latency connections and “very high uplink performance” is starting to drive interest. “We’re also seeing a lot of network slicing opportunities,” he added, to deliver dedicated network resources to, for example, police forces, sports and entertainment stadiums “to guarantee uplink streams… consumers are willing to pay for these things. So I’m rather encouraged by the service innovation that’s starting to happen on 5G SA and… that’s going to drive the need for more radio coverage [for] mid-band and for core [systems].”
Ericsson’s Summary -Looking Ahead:
- Continue to strengthen competitive position
- Strong customer engagement for differentiated connectivity
- New use cases to monetize network investments taking shape
- Expect RAN market to remain broadly stable
- Structurally improving the business through rigorous cost management
- Continue to invest in technology leadership
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.telecomtv.com/content/5g/ericsson-ceo-waxes-lyrical-on-potential-of-5g-sa-ai-53441/
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/ericsson-targets-big-huawei-free-places-ai-and-nato-as-profits-soar
Ericsson revamps its OSS/BSS with AI using Amazon Bedrock as a foundation
Agentic AI and the Future of Communications for Autonomous Vehicles (V2X)
by Prashant Vajpayee (bio below), edited by Alan J Weissberger
Abstract:
Autonomous vehicles increasingly depend on Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communications, but 5G networks face challenges such as latency, coverage gaps, high infrastructure costs, and security risks. To overcome these limitations, this article explores alternative protocols like DSRC, VANETs, ISAC, PLC, and Federated Learning, which offer decentralized, low-latency communication solutions.
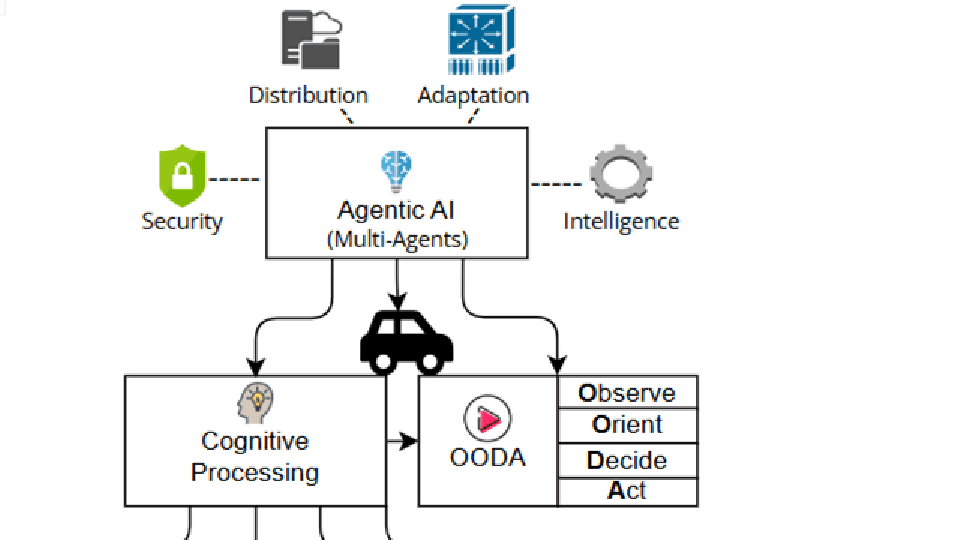
Of critical importance for this approach is Agentic AI—a distributed intelligence model based on the Object, Orient, Decide, and Act (OODA) loop—that enhances adaptability, collaboration, and security across the V2X stack. Together, these technologies lay the groundwork for a resilient, scalable, and secure next-generation Intelligent Transportation System (ITS).
Problems with 5G for V2X Communications:
There are several problems with using 5G for V2X communications, which is why the 5G NR (New Radio) V2X specification, developed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) in Release 16, hasn’t been widely implemented. Here are a few of them:
- Variable latency: Even though 5G promises sub-milliseconds latency, realistic deployment often reflects 10 to 50 milliseconds delay, specifically V2X server is hosted in cloud environment. Furthermore, multi-hop routing, network slicing, and delay in handovers cause increment in latency. Due to this fact, 5G becomes unsuitable for ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) in critical scenarios [1, 2].
- Coverage Gaps & Handover Issues: Availability of 5G network is a problem in rural and remote areas. Furthermore, in fast moving vehicle, switching between 5G networks can cause delays in communication and connectivity failure [3, 4].
- Infrastructure and Cost Constraint: The deployment of full 5G infrastructure requires dense small-cell infrastructure, which cost burden and logistically complex solution especially in developing regions and along highways.
- Spectrum Congestion and Interference: During the scenarios of share spectrum, other services can cause interference in realm of 5G network, which cause degradation on V2X reliability.
- Security and Trust Issues: Centralized nature of 5G architectures remain vulnerable to single point of failure, which is risky for autonomous systems in realm of cybersecurity.
Alternative Communications Protocols as a Solution for V2X (when integrated with Agentic AI):
The following list of alternative protocols offers a potential remedy for the above 5G shortcomings when integrated with Agentic AI.
|
While these alternatives reduce dependency on centralized infrastructure and provide greater fault tolerance, they also introduce complexity. As autonomous vehicles (AVs) become increasingly prevalent, Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication is emerging as the digital nervous system of intelligent transportation systems. Given the deployment and reliability challenges associated with 5G, the industry is shifting toward alternative networking solutions—where Agentic AI is being introduced as a cognitive layer that renders these ecosystems adaptive, secure, and resilient.
The following use cases show how Agentic AI can bring efficiency:
- Cognitive Autonomy: Each vehicle or roadside unit (RSU) operates an AI agent capable of observing, orienting, deciding, and acting (OOAD) without continuous reliance on cloud supervision. This autonomy enables real-time decision-making for scenarios such as rerouting, merging, or hazard avoidance—even in disconnected environments [12].
- Multi-Agent Collaboration: AI agents negotiate and coordinate with one another using standardized protocols (e.g., MCP, A2A), enabling guidance on optimal vehicle spacing, intersection management, and dynamic traffic control—without the need for centralized orchestration [13].
- Embedded Security Intelligence: While multiple agents collaborate, dedicated security agents monitor system activities for anomalies, enforce access control policies, and quarantine threats at the edge. As Forbes notes, “Agentic AI demands agentic security,” emphasizing the importance of embedding trust and resilience into every decision node [14].
- Protocol-Agnostic Adaptability: Agentic AI can dynamically switch among various communication protocols—including DSRC, VANETs, ISAC, or PLC—based on real-time evaluations of signal quality, latency, and network congestion. Agents equipped with cognitive capabilities enhance system robustness against 5G performance limitations or outages.
- Federated Learning and Self-Improvement: Vehicles independently train machine learning models locally and transmit only model updates—preserving data privacy, minimizing bandwidth usage, and improving processing efficiency.
The figure below illustrates the proposed architectural framework for secure Agentic AI enablement within V2X communications, leveraging alternative communication protocols and the OODA (Observe–Orient–Decide–Act) cognitive model.
Conclusions:
With the integration of an intelligent Agentic AI layer into V2X systems, autonomous, adaptive, and efficient decision-making emerges from seamless collaboration of the distributed intelligent components.
Numerous examples highlight the potential of Agentic AI to deliver significant business value.
- TechCrunch reports that Amazon’s R&D division is actively developing an Agentic AI framework to automate warehouse operations through robotics [15]. A similar architecture can be extended to autonomous vehicles (AVs) to enhance both communication and cybersecurity capabilities.
- Forbes emphasizes that “Agentic AI demands agentic security,” underscoring the need for every action—whether executed by human or machine—to undergo rigorous review and validation from a security perspective [16]. Forbes notes, “Agentic AI represents the next evolution in AI—a major transition from traditional models that simply respond to human prompts.” By combining Agentic AI with alternative networking protocols, robust V2X ecosystems can be developed—capable of maintaining resilience despite connectivity losses or infrastructure gaps, enforcing strong cyber defense, and exhibiting intelligence that learns, adapts, and acts autonomously [19].
- Business Insider highlights the scalability of Agentic AI, referencing how Qualtrics has implemented continuous feedback loops to retrain its AI agents dynamically [17]. This feedback-driven approach is equally applicable in the mobility domain, where it can support real-time coordination, dynamic rerouting, and adaptive decision-making.
- Multi-agent systems are also advancing rapidly. As Amazon outlines its vision for deploying “multi-talented assistants” capable of operating independently in complex environments, the trajectory of Agentic AI becomes even more evident [18].
References:
-
- Coll-Perales, B., Lucas-Estañ, M. C., Shimizu, T., Gozalvez, J., Higuchi, T., Avedisov, S., … & Sepulcre, M. (2022). End-to-end V2X latency modeling and analysis in 5G networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 72(4), 5094-5109.
- Horta, J., Siller, M., & Villarreal-Reyes, S. (2025). Cross-layer latency analysis for 5G NR in V2X communications. PloS one, 20(1), e0313772.
- Cellular V2X Communications Towards 5G- Available at “pdf”
- Al Harthi, F. R. A., Touzene, A., Alzidi, N., & Al Salti, F. (2025, July). Intelligent Handover Decision-Making for Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) 5G Networks. In Telecom (Vol. 6, No. 3, p. 47). MDPI.
- DSRC Safety Modem, Available at- “https://www.nxp.com/products/wireless-connectivity/dsrc-safety-modem:DSRC-MODEM”
- VANETs and V2X Communication, Available at- “https://www.sanfoundry.com/vanets-and-v2x-communication/#“
- Yu, K., Feng, Z., Li, D., & Yu, J. (2023). Secure-ISAC: Secure V2X communication: An integrated sensing and communication perspective. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.01720.
- Study on integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) for C-V2X application, Available at- “https://5gaa.org/content/uploads/2025/05/wi-isac-i-tr-v.1.0-may-2025.pdf“
- Ramasamy, D. (2023). Possible hardware architectures for power line communication in automotive v2g applications. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B, 104(3), 813-819.
- Xu, K., Zhou, S., & Li, G. Y. (2024). Federated reinforcement learning for resource allocation in V2X networks. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing.
- Asad, M., Shaukat, S., Nakazato, J., Javanmardi, E., & Tsukada, M. (2025). Federated learning for secure and efficient vehicular communications in open RAN. Cluster Computing, 28(3), 1-12.
- Bryant, D. J. (2006). Rethinking OODA: Toward a modern cognitive framework of command decision making. Military Psychology, 18(3), 183-206.
- Agentic AI Communication Protocols: The Backbone of Autonomous Multi-Agent Systems, Available at- “https://datasciencedojo.com/blog/agentic-ai-communication-protocols/”
- Agentic AI And The Future Of Communications Networks, Available at- “https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2025/05/27/agentic-ai-and-the-future-of-communications-networks/”
- Amazon launches new R&D group focused on agentic AI and robotics, Available at- “Amazon launches new R&D group focused on agentic AI and robotics”
- Securing Identities For The Agentic AI Landscape, Available at “https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2025/07/03/securing-identities-for-the-agentic-ai-landscape/”
- Qualtrics’ president of product has a vision for agentic AI in the workplace: ‘We’re going to operate in a multiagent world’, Available at- “https://www.businessinsider.com/agentic-ai-improve-qualtrics-company-customer-communication-data-collection-2025-5”
- Amazon’s R&D lab forms new agentic AI group, Available at- “https://www.cnbc.com/2025/06/04/amazons-rd-lab-forms-new-agentic-ai-group.html”
- Agentic AI: The Next Frontier In Autonomous Work, Available at- “https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2025/06/27/agentic-ai-the-next-frontier-in-autonomous-work/”
About the Author:
Prashant Vajpayee is a Senior Product Manager and researcher in AI and cybersecurity, with expertise in enterprise data integration, cyber risk modeling, and intelligent transportation systems. With a foundation in strategic leadership and innovation, he has led transformative initiatives at Salesforce and advanced research focused on cyber risk quantification and resilience across critical infrastructure, including Transportation 5.0 and global supply chain. His work empowers organizations to implement secure, scalable, and ethically grounded digital ecosystems. Through his writing, Prashant seeks to demystify complex cybersecurity as well as AI challenges and share actionable insights with technologists, researchers, and industry leaders.