Japan to support telecom infrastructure in South Pacific using Open RAN technology
Japan’s government and private sector will offer support for telecommunications infrastructure in Pacific island countries, starting with a data center and telecom project in Palau, in an effort to improve the security of vital networks connecting Asia and North America. The initiative will be led by Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications and is expected to include telecom company NTT Group, internet service provider Internet Initiative Japan and other companies. It aims to increase Japan’s participation in the South Pacific, a region crisscrossed with undersea communications cables linking East Asia, the U.S., Australia and Southeast Asia. Funding will come from the ministry’s international cooperation budget. Several billion yen (1 billion yen equals $7.1 million) in public-private investment is expected to be mobilized over the first two years.
The infrastructure improvements will use Open Radio Access network (RAN) technology, which Japan has sought to promote as a low-cost way of building wireless networks from components made by different manufacturers.
Japan, the U.S., and Australia — which, along with India, make up the security dialogue known as the Quad — all support improving communications security in Pacific island countries. These island countries are reliant on equipment from Chinese telecom company Huawei Technologies for their land-based networks. The U.S. and others say Huawei has ties to the Chinese military and poses a security risk. Western officials have raised concerns about the potential for eavesdropping on communications and other activities. Huawei denies such accusations.
Quad members have agreed to support the modernization of Palau’s telecommunications infrastructure. Japan’s communications ministry will start putting this initiative to work as early as fiscal 2025, which begins in April. It will then seek to expand aid in fiscal 2026 to other countries in the region. Tuvalu and the Marshall Islands — two of the dwindling number of countries to maintain formal diplomatic relations with Taiwan — are likely to be candidates for such support. The effort will also seek to train cybersecurity personnel. Island countries with understaffed cybersecurity capabilities are seen as a potential vulnerability that can be exploited to launch attacks against Japan, experts say.
Tuvalu-an island country roughly halfway between Australia and Hawaii-is expected to be a candidate to receive Japanese support for telecommunications infrastructure. © Reuters
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
China has worked to extend its influence in the South Pacific. In recent years, the Solomon Islands, Kiribati and Nauru have all cut diplomatic ties with Taiwan in favor of relations with Beijing. The Solomon Islands also formed a security agreement with China. Including Palau, only three countries in the region still maintain diplomatic relations with Taiwan.
Telecommunications infrastructure is becoming increasingly important for island countries in their own right.
“A stable network connecting a country with the rest of the world is essential for receiving remittances from migrant workers. Better telecommunications infrastructure is of great significance in improving ties between countries,” said Motohiro Tsuchiya, a professor at the Keio University Graduate School of Media and Governance in Japan.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://market.us/report/open-ran-market/
https://www.o-ran.org/otics/japan-otic
https://www.lowyinstitute.org/the-interpreter/japan-s-5g-ambitions-quad
NTT advert in WSJ: Why O-RAN Will Change Everything; AT&T selects Ericsson for its O-RAN
NTT DOCOMO OREX brand offers a pre-integrated solution for Open RAN
Cloud Hosting- A Deep Dive into a Rapidly Growing Market
By Paribhasha Tiwari, Market Analyst and Content Curator
What is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting that uses a network of virtual servers to host websites, applications, or data. Unlike traditional hosting, which relies on a single server, cloud hosting spreads the load across multiple interconnected servers, ensuring better scalability, reliability, and performance.
As digital transformation continues to accelerate across the globe, the Cloud Hosting Market is emerging as a key enabler of business agility, scalability, and innovation. Whether its large enterprises seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure or startups aiming to minimize overhead, cloud hosting has become the go-to solution. With the market poised for substantial growth, driven by the demands of modern business environments, this post will explore the factors fueling the expansion of cloud hosting, the challenges that must be navigated, and the future trends shaping this dynamic industry.
The Growth of Cloud Hosting- A Market Overview:
The global cloud hosting market has experienced tremendous growth over the past decade, becoming one of the most critical components of the broader cloud services ecosystem. According to market research, the cloud hosting market was valued at $60 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach over $100 billion by 2026, reflecting a CAGR of 18% during the forecast period. This growth can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing adoption of digital services, the rise of e-commerce, and the surge in remote working practices following the COVID-19 pandemic.
The transition from on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based hosting solutions offers businesses greater flexibility in scaling their operations. Unlike traditional hosting services, where companies are locked into a fixed amount of server capacity, cloud hosting allows for on-demand resource allocation, ensuring businesses only pay for what they use. This model provides substantial cost savings, particularly for industries with fluctuating traffic and demand, such as retail, media, and financial services.
Why Businesses are Migrating to Cloud Hosting Solutions?
Cloud hosting’s advantages extend far beyond cost savings. Companies today are looking for more than just affordable IT infrastructure—they need reliability, performance, and scalability. These three elements have made cloud hosting the preferred choice for businesses of all sizes. Here’s why-
- Scalability and Flexibility– The most compelling reason businesses are moving to the cloud is the ability to scale IT resources dynamically. Whether it’s handling a sudden spike in website traffic or expanding business operations globally, cloud hosting allows enterprises to scale resources up or down based on real-time needs. This elasticity ensures businesses remain agile and responsive to market conditions without worrying about over-provisioning or underutilization of hardware.
- Cost Efficiency– Cloud hosting significantly reduces the capital expenditure (CapEx) associated with setting up and maintaining physical servers. Instead of investing in costly infrastructure, businesses can convert these expenses to operational expenditures (OpEx) by paying only for the computing power they need. This is especially beneficial for startups and small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) that need to manage their budgets tightly while still accessing world-class hosting services.
- Performance and Uptime– Leading cloud hosting providers guarantee uptime of 99.99% or higher, thanks to their globally distributed data centers and redundant systems. Downtime can be catastrophic, especially for e-commerce platforms, fintech companies, and digital service providers where revenue and customer satisfaction are directly tied to system availability. With cloud hosting, businesses can rely on seamless performance, even during peak demand periods.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity– Another critical advantage of cloud hosting is the ability to integrate disaster recovery (DR) strategies into the hosting plan. In traditional hosting, implementing a comprehensive DR plan is complex and costly. Cloud hosting, however, offers built-in DR features like data backups, redundancy, and geo-replication, ensuring businesses can recover swiftly from any unplanned outage or data loss event.

Survey of Cloud Network Access Alternatives- Wireless and Wireline Solutions:
The growing adoption of cloud hosting has raised an important question for businesses- How should they connect to the cloud? Network access plays a critical role in determining the performance, reliability, and cost-efficiency of cloud hosting services. As businesses weigh their options, they typically consider two main types of cloud access solutions- wireline (fixed-line) and wireless alternatives.
- Wireline Access– Traditionally, businesses have relied on fixed-line connections, such as fiber-optic, DSL, or Ethernet, for cloud access. These wireline solutions provide stable, high-bandwidth connections and are often favored by enterprises with high-performance computing needs or large volumes of data traffic. Fiber-optic connections, in particular, offer ultra-high speeds and low latency, making them ideal for industries like finance, healthcare, and media, where data-intensive operations are critical.
- Advantages of Wireline Access– Wireline access is known for its reliability and low-latency performance, making it an excellent choice for mission-critical applications that require real-time data processing. Additionally, wireline connections tend to offer better security and dedicated bandwidth, reducing the risk of network congestion.
- Challenges of Wireline Access– The main downside to wireline solutions is the lack of mobility and flexibility. Fixed-line connections are geographically limited, which can pose challenges for businesses with distributed workforces or operations in remote areas.
- Wireless Access– As cloud technology evolves, wireless access solutions, particularly through 4G LTE, 5G, and Wi-Fi 6, are becoming increasingly popular. Wireless cloud access is particularly appealing for businesses with remote or mobile operations, where flexibility and mobility are critical. The advent of 5G has been a game-changer, offering near fiber-optic speeds, reduced latency, and massive device connectivity—all of which are crucial for sectors like logistics, manufacturing, and retail.
- Advantages of Wireless Access– Wireless solutions enable businesses to connect to the cloud from virtually anywhere, without the need for fixed infrastructure. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with multiple locations or a high degree of mobility. Wireless connections, particularly with 5G and Wi-Fi 6, provide speeds and performance that rival many traditional wireline solutions, making wireless access a viable alternative for many use cases.
- Challenges of Wireless Access– Despite its flexibility, wireless cloud access can be more prone to latency and security concerns compared to wireline solutions. While advances in 5G and Wi-Fi technology are helping to mitigate these issues, businesses must carefully assess their wireless infrastructure to ensure performance and security standards are met.
Security and Compliance- Addressing Concerns in the Cloud:
For many businesses, security remains a primary concern when moving to the cloud. Despite the growing adoption of cloud services, there are lingering worries about data breaches, hacking attempts, and regulatory compliance. However, cloud hosting providers have significantly improved their security protocols, and many offer industry-leading security measures that far surpass traditional on-premises hosting.
- Advanced Encryption– Data is often stored in encrypted formats, both at rest and in transit, ensuring that unauthorized users cannot access sensitive information. Leading cloud providers offer 256-bit encryption standards, along with secure key management systems to further bolster security.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards– Cloud hosting platforms comply with major regulatory standards, including GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, and ISO 27001 certifications. This compliance ensures that businesses operating in regulated industries such as healthcare, finance, and retail can meet legal requirements without having to manage their own data compliance infrastructure.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) and Identity Management– Cloud providers also implement stringent access controls, using technologies like MFA, identity and access management (IAM) systems, and biometric authentication to safeguard user data.
Challenges Facing the Cloud Hosting Market:
Despite its numerous benefits, the cloud hosting sector still faces challenges that need to be addressed for continued growth-
- Latency and Regional Data Centers– One of the key challenges is latency, particularly for businesses with a global customer base. To ensure minimal latency, cloud hosting providers need to offer data centers in geographically diverse locations. However, regions with limited data center infrastructure, such as parts of Africa and Latin America, may still face connectivity and latency issues.
- Data Sovereignty and Privacy– Another challenge is navigating data sovereignty laws, which dictate that certain types of data must be stored within specific geographical regions. Businesses operating across borders must ensure compliance with local data regulations, which may complicate cloud hosting strategies.
- Vendor Lock-In– Vendor lock-in occurs when a business becomes too dependent on a single cloud hosting provider, limiting its flexibility to switch providers or adopt new technologies. While many cloud providers offer tools to mitigate lock-in, businesses must carefully plan their cloud strategy to avoid over-reliance on a single vendor.
What’s Next for Cloud Hosting- Key Emerging Trends:
As the market continues to grow, several trends are emerging that will shape its future trajectory-
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies– Businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, combining public and private cloud environments to optimize cost, performance, and security. Hybrid cloud allows companies to store sensitive data in a private cloud while taking advantage of the scalability of the public cloud for less sensitive workloads.
- Edge Computing– With the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the need for low-latency computing, edge computing is becoming a critical component of cloud hosting. By bringing computing resources closer to the data source, edge computing reduces latency, enhances real-time processing, and improves the overall performance of IoT applications.
- AI and Automation in Cloud Hosting– Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation are transforming cloud hosting services. AI-powered cloud infrastructure can optimize resource allocation, predict maintenance needs, and enhance cybersecurity. Automation tools are also helping businesses manage their cloud environments more efficiently, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Conclusion- Making the Most of Cloud Hosting:
The cloud hosting industry is not just growing, it is evolving to meet the complex demands of modern businesses. With its scalable, secure, and cost-effective infrastructure, cloud hosting offers unparalleled opportunities for companies to innovate and stay competitive in an increasingly digital world. By understanding the benefits, challenges, and future trends, businesses can make informed decisions to maximize the potential of their cloud hosting strategies and drive long-term growth.
Author: Paribhasha Tiwari, Market Analyst and Content Curator
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
What is Cloud Hosting? Benefits and Risks
https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/cloud-hosting/
IDC: Public Cloud services spending to hit $1.35 trillion in 2027
https://www.forbes.com/advisor/business/software/best-cloud-hosting/
AI adoption to accelerate growth in the $215 billion Data Center market
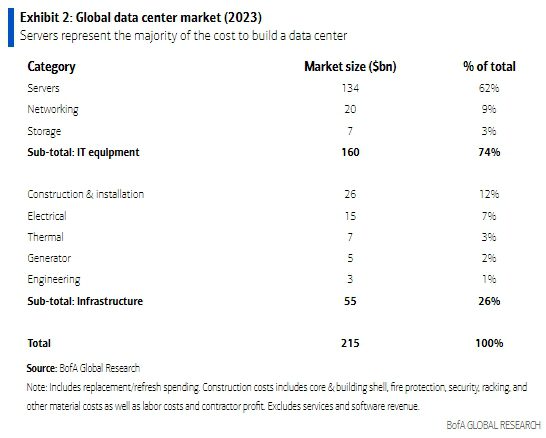
Market Overview:
Data Centers are a $215bn global market that grew 18% annually between 2018-2023. AI adoption is expected to accelerate data center growth as AI chips require 3-4x more electrical power versus traditional central processing units (CPUs).
AI adoption is poised to accelerate this growth meaningfully over coming years. BofA‘s US Semis analyst, Vivek Arya, forecasts the AI chip market to reach ~$200bn in 2027, up from $44bn in 2023. This has positive implications for the broader data center industry.
AI workloads are bandwidth-intensive, connecting hundreds of processors with gigabits of throughput. As these AI models grow, the number of GPUs required to process them grows, requiring larger networks to interconnect the GPUs. See Network Equipment market below.
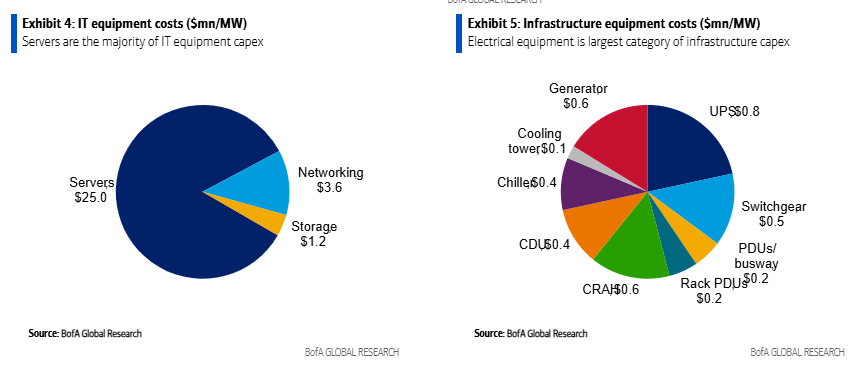
The electrical and thermal equipment within a data center is sized for maximum load to ensure reliability and uptime. For electrical and thermal equipment manufacturers, AI adoption drives faster growth in data center power loads. AI chips require 3-4x more electrical power versus traditional CPUs (Central Processing Units).
BofA estimates data center capex was $215bn globally in 2023. The majority of this spend is for compute servers, networking and storage ($160bn) with data center infrastructure being an important, but smaller, piece ($55bn). For perspective, data center capex represented ~1% of global fixed capital formation, which includes all private & public sector spending on equipment and structures.
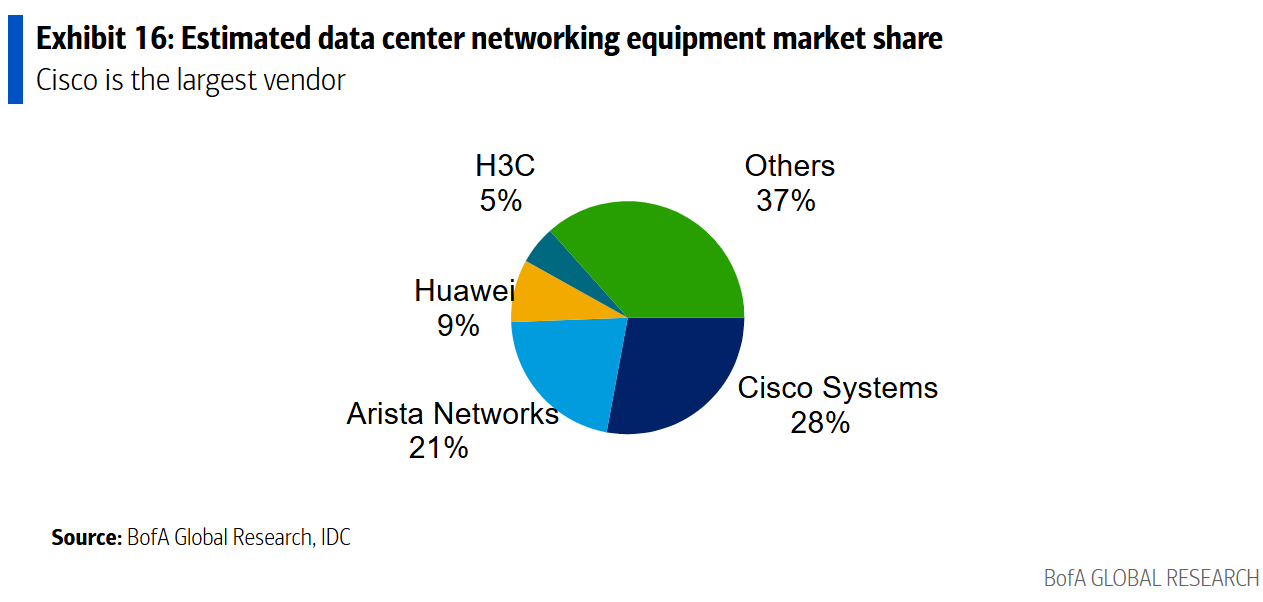
Networking Equipment Market:
BofA estimates a $20bn market size for Data Center networking equipment. Cisco is the market share leader, with an estimated 28% market share.
- Ethernet switches which communicate within the data center via local area networks. Typically, each rack would have a networking switch.
- Routers handle traffic between buildings, typically using internet protocol (IP). Some cloud service providers use “white box“ networking switches (e.g., manufactured by third parties, such as Taiwanese ODMs, to their specifications).
Data center speeds are in a state of constant growth. The industry has moved from 40G speeds to 100G speeds, and those are quickly giving way to 400G speeds. Yet even 400G speeds won’t be fast enough to support some emerging applications which may require 800G and 1.6TB data center speeds.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Data Centers are also a bright spot for the construction industry. BofA notes that construction spending for data centers is approaching $30bn (vs $2bn in 2014) and accounts for nearly 21% of data center capex. At 4% of private construction spending (vs 2% five years ago), the data center category has surpassed retail, and could be a partial offset in a construction downturn.
Source: BofA Global Research
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.belden.com/blogs/smart-building/faster-data-center-speeds-depend-on-fiber-innovation#
Proposed solutions to high energy consumption of Generative AI LLMs: optimized hardware, new algorithms, green data centers
Nvidia enters Data Center Ethernet market with its Spectrum-X networking platform
Co-Packaged Optics to play an important role in data center switches
EdgeCore Digital Infrastructure and Zayo bring fiber connectivity to Santa Clara data center
Deutsche Telekom with AWS and VMware demonstrate a global enterprise network for seamless connectivity across geographically distributed data centers
New venture to sell Network Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) on a global scale
Overview:
Some of the world’s largest telecom operators, including América Móvil, AT&T, Bharti Airtel, Deutsche Telekom, Orange, Reliance Jio, Singtel, Telefonica, Telstra, T-Mobile, Verizon and Vodafone, together with network gear maker Ericsson (the largest shareholder) are announcing a new venture to combine and sell network Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) on a global scale to spur innovation in digital services. Network APIs are the way to easily access, use and pay for network capabilities. The venture will drive implementation and access to common APIs from multiple telecom service providers to a broader ecosystem of developer platforms. All the APIs on offer will be based on CAMARA – the open source API project led by the GSMA and the Linux Foundation.
Modern mobile networks have advanced and intelligent capabilities, which have historically been inaccessible to developers. Additionally, it has been impractical for developers to integrate the different capabilities of hundreds of individual telecom operators. The newly formed company will combine network APIs globally, with a vision that new applications will work anywhere and on any network, making it easier and quicker for developers to innovate.
Easily accessible advanced network capabilities will open up the next frontier in app development and empower developers to create new use cases across many sectors. These could include anti-fraud verification for financial transactions and the ability to check device status so streaming providers can dynamically adjust video quality.
The newly formed company will provide network APIs to a broad ecosystem of developer platforms, including hyperscalers (HCPs), Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) providers, System Integrators (SIs) and Independent Software Vendors (ISVs), based on existing industry-wide CAMARA APIs (the open-source project driven by the GSMA and the Linux Foundation). Vonage and Google Cloud will partner with the new company, providing access to their ecosystems of millions of developers as well as their partners. The new venture shareholders will bring funding and important assets, including Ericsson’s platform and network expertise, global telecom operator relationships, knowledge of the developer community and each telecom operator’s network APIs, expertise and marketing.
Ericsson-owned Vonage and Google Cloud have already agreed to partner with the new venture, providing access to their respective ecosystems of millions of developers as well as their partners.
“We have a common concern that we’ve made it difficult for developers to program on wireless networks,” said Niklas Heuveldop, CEO of Vonage, stressing that this initiative is all about removing any friction and roadblocks that may be preventing developers taking full advantage of the programmable networks opportunity. He added that, for Vonage, this means a smaller piece of a bigger network API pie.
Closing of the transaction is expected early 2025, subject to regulatory approvals and other customary conditions. Upon closing, Ericsson will hold 50% of the equity in the venture while the telecom providers will hold 50% in total. Built on a deep understanding of developer and enterprise needs and in keeping with the industry-body GSMA Open Gateway principles, the new venture’s platform and partner ecosystem will remain open and non-discriminatory to maximize value creation across the industry.
Comment and Analysis:
Much has already been made of the industry’s decision to open up and (attempt) to monetize network APIs. Optimistic estimates, like the one proffered by McKinsey, claim that network APIs represent a $300 billion opportunity for telcos between now and the end of the decade. However, some like Kearney, have warned that all will be for naught without proper industry coordination and collaboration to drive software developer uptake.
“Today’s announcement is an important step in that direction by addressing one of the major challenges for developers seeking to engage with mobile operators – sector fragmentation,” said Kester Mann, director of consumer and connectivity at CCS Insight. “In the past, the telecom industry – with many competing players each deploying different strategies for their specific regions – has struggled to present a united and coherent front.” Despite their dubious track record, Mann reckons this particular venture stands a better chance of success than most, thanks to the urgent need for operators to earn a return on 5G, and due to the involvement of major technology partners in the form of Google and Ericsson. “There should be fresh optimism that the new company unveiled will enjoy more success than previous failed ventures,” he added.
While open network APIs will work on compatible hardware from any vendor – whether it’s Nokia or Ericsson or Huawei – this new venture represents an opportunity for Ericsson to play a central role in the emerging ecosystem.
Quotes from the partners:
América Móvil
Daniel Hajj, Chief Executive Officer, AMX: “We are very excited to join Ericsson and other key players in our industry in this innovative global platform initiative that will benefit the digital ecosystem as a whole. New API solutions will establish exciting value-added offerings to our customers on the top of our networks’ infrastructure.”
AT&T
Jeremy Legg, Chief Technology Officer, AT&T: “At AT&T, we’ve been creating API tools to empower developers for well over a decade. Now, with a broad-based, interoperable API platform, we’re giving innovators a new global toolbox where the world’s best app developers can create exciting user experiences at scale. This high-performance mobile ecosystem will usher in a new era of greater possibility for customers and mobile users around the world.”
Bharti Airtel
Gopal Vittal, Managing Director and CEO, Bharti Airtel: “Today marks a defining moment as the industry comes together to form a unified platform that will allow more developers and businesses to utilize our networks and explore API opportunities through open gateway principles. This move will enhance network monetization opportunities. Airtel is delighted to partner in this initiative that will help enable the telecom sector to drive growth and innovation across the ecosystem.”
Deutsche Telekom
Tim Höttges, CEO of Deutsche Telekom: “The new company accelerates our leading work with MagentaBusiness APIs to expose our network capabilities for customers and developers. We believe that this company will open up new monetization opportunities for the industry. We encourage and look forward to more telecom operators joining us to expand and develop this ecosystem.”
Ericsson
Börje Ekholm, President and CEO, Ericsson: “Today is a defining moment for the industry and milestone in our strategy to open up the network for increased monetization opportunities. A global platform built on Ericsson’s deep technical capabilities and with a comprehensive ecosystem, that provides millions of developers with a single connection, will enable the telecom industry to invest deeper into the network API opportunity, driving growth and innovation for everyone.”
Orange
Christel Heydemann, Chief Executive Officer, Orange: “This is a critical first step in our innovation journey to fully harness the power of our networks at scale, providing secure access to new on-demand network services and advanced network capabilities. By delivering a common and simple set of network APIs for developers globally, we can unleash this network value for businesses, large and small. This is a definitive gamechanger for businesses, opening up the possibility of a new wave of digital services.”
Reliance Jio
Mathew Oommen, President, Reliance Jio: “We spearheaded the transformation of both mobile and fixed home broadband by delivering affordable, high-quality broadband to everyone, across India. As we rapidly adopt an AI and API-driven technology ecosystem—by collaborating with global leaders, Jio is thrilled to offer a suite of innovative and transformative APIs to enterprises and developers worldwide. Together, we are not just building networks; we are laying the foundation for a smarter, more connected, and inclusive world in the AI era.”
Singtel
Mr Yuen Kuan Moon, Group Chief Executive Officer, Singtel: “This unified platform and global eco-system will enable even more developers and businesses to leverage 5G quality networks to exploit API opportunities using GSMA’s open gateway principles. We look forward to helping even more enterprises and organizations in Asia to use network API solutions to drive growth and innovation through this timely collaboration.”
Telefonica
José María Álvarez-Pallete, Chairman & CEO of Telefónica: “This collaboration will drive the GSMA Open Gateway initiative and provide customers with a consistent set of Camara APIs. Our belief is that this industry movement, which will be open to all networks, can set the stage for unprecedented innovation and value creation for the sector, by unlocking the potential of network capabilities.”
Telstra
Vicki Brady, CEO of Telstra: “This is a groundbreaking initiative for our industry. This new global venture will create an ecosystem that provides developers, partners and customers with access to programmable, advanced network capabilities that will unleash a new wave of innovation in digital services and further unlocks the benefits of our 5G network. We’ve been making good progress locally with Ericsson and other partners, and we look forward to further accelerating digital transformation for our Australian customers and bringing value and simplicity to application developers around the world.”
T-Mobile
Ulf Ewaldsson, President of Technology, T-Mobile: “At T-Mobile, we’ve always been laser focused on championing change across the industry to create the best customer experiences, while fueling growth and innovation across the entire wireless ecosystem. That level of transformation takes unprecedented collaboration and expertise. We are excited about the possibilities this venture will create for developers and wireless customers around the world.”
Verizon
Joe Russo, EVP & President, Global Network and Technology of Verizon: “The depth and value of the services and data insights accessible through Verizon’s renowned 5G network are practically boundless. Verizon has been at the forefront of developing various network APIs to assist developers in enhancing customer security, reducing pain points in customer interactions, and enabling the creation of novel experiences. This exciting collaboration with global partners will broaden the availability of these services and accelerate adoption of APIs worldwide.”
Vodafone
Margherita Della Valle, Vodafone Group Chief Executive, said: “Network APIs are reshaping our industry. This pioneering partnership will enable businesses and developers to use the collective strength of our global networks to develop applications that drive growth, create jobs, and improve public services. Just as 4G and smartphones made apps integral to our everyday life, the power of our 5G network will stimulate the next wave of digital services.”
Google Cloud
Thomas Kurian, CEO of Google Cloud: “We understand the power of an open platform and ecosystem in driving innovation. We are proud to participate in this important partnership in the telco industry to create value for our global customers via network APIs – and ultimately deliver on the promise of the public cloud.”
Vonage
Niklas Heuveldop, CEO Vonage: “This groundbreaking, open industry collaboration effectively removes the single largest barrier for developers to leverage mobile networks to their full potential. Developers across the world’s leading developer platforms will benefit from accessing advanced network capabilities in partner networks globally through common APIs, accelerating the digital transformation of businesses and the public sector. As one of the leading developer platforms, we look forward to engaging our developer community as we grow the network API business.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Telefónica and Nokia partner to boost use of 5G SA network APIs
Analysts: Telco CAPEX crash looks to continue: mobile core network, RAN, and optical all expected to decline
Analysys Mason Open Network Index: survey of 50 tier 1 network operators
Ericsson expects continuing network equipment sales challenges in 2024
Nvidia enters Data Center Ethernet market with its Spectrum-X networking platform
Nvidia is planning a big push into the Data Center Ethernet market. CFO Colette Kress said the Spectrum-X Ethernet-based networking solution it launched in May 2023 is “well on track to begin a multi-billion-dollar product line within a year.” The Spectrum-X platform includes: Ethernet switches, optics, cables and network interface cards (NICs). Nvidia already has a multi-billion-dollar play in this space in the form of its Ethernet NIC product. Kress said during Nvidia’s earnings call that “hundreds of customers have already adopted the platform.” And that Nvidia plans to “launch new Spectrum-X products every year to support demand for scaling compute clusters from tens of thousands of GPUs today to millions of DPUs in the near future.”
- With Spectrum-X, Nvidia will be competing with Arista, Cisco, and Juniper at the system level along with “bare metal switches” from Taiwanese ODMs running DriveNets network cloud software.
- With respect to high performance Ethernet switching silicon, Nvidia competitors include Broadcom, Marvell, Microchip, and Cisco (which uses Silicon One internally and also sells it on the merchant semiconductor market).

Image by Midjourney for Fierce Network
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
In November 2023, Nvidia said it would work with Dell Technologies, Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Lenovo to incorporate Spectrum-X capabilities into their compute servers. Nvidia is now targeting tier-2 cloud service providers and enterprise customers looking for bundled solutions.
Dell’Oro Group VP Sameh Boujelbene told Fierce Network that “Nvidia is positioning Spectrum-X for AI back-end network deployments as an alternative fabric to InfiniBand. While InfiniBand currently dominates AI back-end networks with over 80% market share, Ethernet switches optimized for AI deployments have been gaining ground very quickly.” Boujelbene added Nvidia’s success with Spectrum-X thus far has largely been driven “by one major 100,000-GPU cluster, along with several smaller deployments by Cloud Service Providers.” By 2028, Boujelbene said Dell’Oro expects Ethernet switches to surpass InfiniBand for AI in the back-end network market, with revenues exceeding $10 billion.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In a recent IEEE Techblog post we wrote:
While InfiniBand currently has the edge in the data center networking market, but several factors point to increased Ethernet adoption for AI clusters in the future. Recent innovations are addressing Ethernet’s shortcomings compared to InfiniBand:
- Lossless Ethernet technologies
- RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE)
- Ultra Ethernet Consortium’s AI-focused specifications
Some real-world tests have shown Ethernet offering up to 10% improvement in job completion performance across all packet sizes compared to InfiniBand in complex AI training tasks. By 2028, it’s estimated that: 1] 45% of generative AI workloads will run on Ethernet (up from <20% now) and 2] 30% will run on InfiniBand (up from <20% now).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/cloud/data-center-ethernet-nvidias-next-multi-billion-dollar-business
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/spectrumx/
Will AI clusters be interconnected via Infiniband or Ethernet: NVIDIA doesn’t care, but Broadcom sure does!
Data Center Networking Market to grow at a CAGR of 6.22% during 2022-2027 to reach $35.6 billion by 2027
LightCounting: Optical Ethernet Transceiver sales will increase by 40% in 2024
FCC: More competition for Starlink; freeing up spectrum for satellite broadband service
More Competition for Starlink Needed:
FCC chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel said Wednesday that she wants to see more competition for SpaceX‘s internet satellite constellation Starlink. Starlink (owned by SpaceX, which provides launch services) controls nearly two thirds of all active satellites and has launched about 7,000 satellites since 2018. Rosenworcel said at a conference Wednesday that Starlink has “almost two-thirds of the satellites that are in space right now and has a very high portion of (satellite)) internet traffic… Our economy doesn’t benefit from monopolies. So we’ve got to invite many more space actors in, many more companies that can develop constellations and innovations in space.”
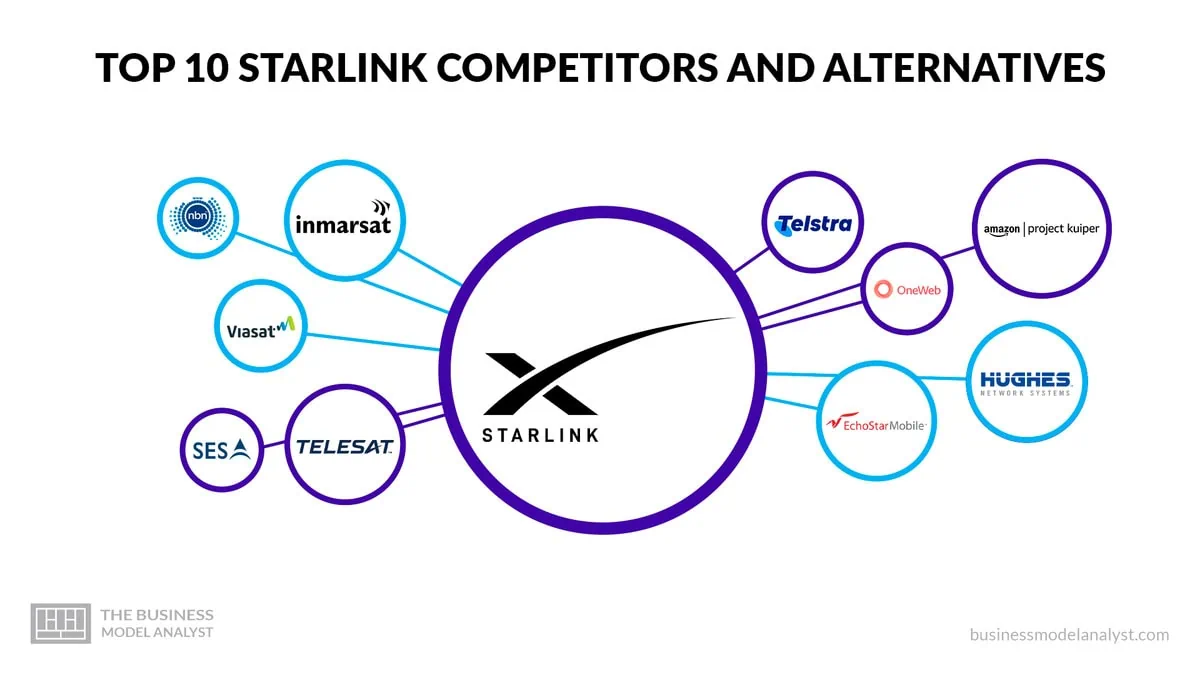
Starlink competitors include:
OneWeb is a solid alternative to Starlink’s satellite internet service by offering similar capabilities and coverage. The company plans to launch a constellation of approximately 650 satellites to provide seamless broadband connectivity to users worldwide, including remote and underserved areas. By operating in low-earth orbits (LEO), OneWeb’s satellites can offer low latency and high-speed internet access, suitable for a wide range of commercial, residential, and governmental applications. OneWeb’s satellites will be deployed in polar orbit, allowing them to cover even the Earth’s most remote regions. This global coverage makes OneWeb an attractive option for users who require internet connectivity in areas where traditional terrestrial infrastructure is limited or unavailable.
Viasat has a fleet of satellites in geostationary orbit, allowing it to provide internet services to customers in remote and rural areas. This coverage is essential for customers living in areas with limited terrestrial internet options. In addition to its satellite coverage, Viasat also offers competitive internet speeds. The company’s satellite technology allows fast and reliable internet connections, making it a viable alternative to traditional wired internet providers. This is especially beneficial for customers who require high-speed internet for activities such as streaming, online gaming, or remote work.
Telesat offers a wide range of satellite services tailored to different industries and applications. Telesat’s satellite fleet includes geostationary satellites, low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites, and high-throughput satellites (HTS), allowing it to deliver high-speed internet connectivity, broadcast services, and backhaul solutions to customers in remote and underserved areas. Telesat has extensive coverage and capacity in terms of satellite internet services. They have a strong presence in North America, South America, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, making their services accessible to millions of users.
Telstra’s extensive network infrastructure and coverage make it a strong competitor to Starlink. The company operates a vast network of undersea cables, satellites, and terrestrial infrastructure, which enables it to provide reliable and high-speed connectivity across Australia and beyond. Telstra also has a solid customer base and brand recognition in the telecommunications industry, which gives it a competitive advantage. One of the critical business challenges that Telstra poses to Starlink is its established presence and dominance in the Australian market. Telstra has a significant market share and customer base in Australia, which gives it a strong foothold in the telecommunications industry. This makes it more difficult for Starlink to penetrate the market and attract customers away from Telstra. In addition, Telstra’s network coverage and infrastructure in remote and rural areas of Australia are competitive advantages.
Project Kuiper is backed by Amazon’s vast resources and infrastructure. Amazon’s deep pockets and logistics and cloud services expertise give Project Kuiper a decisive advantage in deploying and scaling its satellite network. By providing affordable and accessible broadband services, Project Kuiper intends to empower individuals, businesses, and communities with the opportunities and resources that come with internet access. With a constellation of low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites, Project Kuiper plans to deliver high-speed internet connectivity to areas with limited traditional terrestrial infrastructure.
Hughes Network System has a strong foothold in the market, particularly in rural areas with limited terrestrial broadband options. The company’s HughesNet service utilizes geostationary satellites to provide internet connectivity, offering up to 100 Mbps for downloads.
Inmarsat offers a range of satellite-based communication solutions that cater to its customers’ diverse needs. One key area where Inmarsat differentiates itself is its focus on mission-critical applications. The company’s satellite network is designed to provide uninterrupted and reliable connectivity, even in the most remote and challenging environments. Inmarsat’s portfolio includes services such as voice and data communications, machine-to-machine connectivity, and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions. The company’s satellite network covers most of the Earth’s surface, ensuring its customers can stay connected wherever they are.
Freeing Up Spectrum to Support Satellite Broadband Service:
At the FCC’s September 26th Open Commission Meeting, the Commission will consider a Report and Order that will provide 1300 megahertz of spectrum in the 17 GHz band for non-geostationary satellite orbit (NGSO) space stations in the fixed-satellite service (FSS) while also protecting incumbent operations. The Order provides a more cohesive global framework for FSS operators and maximizes the efficient use of the 17 GHz band spectrum. (IB Docket No. 22-273).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.fcc.gov/september-2024-open-commission-meeting
https://businessmodelanalyst.com/starlink-competitors/
SpaceX launches first set of Starlink satellites with direct-to-cell capabilities
Starlink Direct to Cell service (via Entel) is coming to Chile and Peru be end of 2024
SpaceX has majority of all satellites in orbit; Starlink achieves cash-flow breakeven
Starlink’s Direct to Cell service for existing LTE phones “wherever you can see the sky”
Amazon launches first Project Kuiper satellites in direct competition with SpaceX/Starlink
Rakuten Symphony exec: “5G is a failure; breaking the bank; to the extent 6G may not be affordable”
In a Linkedin post, Rakuten Symphony CMO Geoff Hollingworth says 5G has been a failure, that it will never achieve ubiquitous coverage and it’s time for the mobile industry to invest in customers rather than networks:
5G is a failure. We build technology to deliver a promise, the promise made was commercial. If that promise is not delivered then it has failed. If that promise is delivered but the cost of delivery is prohibitively expensive versus the return, then that technology is a failure. Currently the promise has not been delivered and there is no line of sight to delivery.
I do not believe the market is going to deliver on this promise further down the road, the networks do not work this way. 5G will never have ubiquitous coverage, and this is getting worse. We can get closer to ubiquitous coverage as a network of networks but then all the complexity embedded in 5G for advanced management of the network is a cost. There is never only one “G” in a market, there tend to be at least 3 at any moment. Each G takes time to retire, from a customer, device, and ROI point of view. APIs cannot get deployed universally and by the the time networks are universal the next G is starting to be rolled out. We are still waiting for “real 5G” but even when it shows what will it translate to commercially? Will it arrive before something labeled “6G” is starting to roll out?
“The current cost for 5G is breaking the bank, to the extent where 6G might not be affordable. None of this is good for an industry that is supposedly powering the global GDP and defining the future state of all countries.”
Of course, we agree as we’ve been pounding the table since the 3GPP Release 15 pre-standard version of 5GNR was introduced in 2018. The “real 5G” must include standardized 5G SA core network, URLLC that meets ITU-R M.2410 performance requirements and harmonized frequencies.
“We are already repeating the narrative into 6G with the same concept of ubiquitous coverage mindset. We are not segmenting for actual coverage and actual market reality when comparing to cost, time, and need,” Hollingworth warns. “We must embrace that there are other better ways to solve for coverage, depending [on] the use case and the coverage type required. We have less of a coverage problem and more of a seamless access problem, as one moves from indoor to outdoor city to outdoor suburb to rural.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Future Network Trends -AI native and cloud native operations:
To see future network needs, there is a need to understand future AI software design patterns. We now see these appearing and they are different from what we have seen before.
- They depend on large data streams where the data and interpretation has time sensitivity.
- Compute is distributing to where the data is rather than bringing the data to where the compute is.
- This forces distribution of models and software to where the data and compute is, and overhead must be kept to a minimum and automation must be maximized to be cost effective.
- There is need for rapid iteration and continuous fine tuning of the models and algorithms as more data is analyzed and performance improves.
The first applications with these design requirements are the 5G++ network architected functions. The test of the industry is whether the software can be adopted with true AI native, cloud native operations or whether they will be deployed traditionally. If we succeed in deploying a true hyperscale operation for our own software we can take our tooling and knowledge, and expand it to support any application and service.
Now there are many networks that devices can connect to, and 80% of the time traffic does not travel through cellular networks at all. In markets with high fiber penetration Wi-Fi connectivity and latency has higher performance than cellular, especially indoors, where higher frequency spectrum no longer travels inside buildings, especially those with reflective sustainability materials.
We previously solved as if cellular was the only way to solve all the problems. We must embrace that there are other better ways to solve for coverage, depending the use case and the coverage type required. We have less of a coverage problem and more of a seamless access problem, as one moves from indoor to outdoor city to outdoor suburb to rural.
References:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/cost-delusion-promise-reality-geoff-hollingworth-vt4xe/
https://www.itu.int/pub/R-REP-M.2410
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/jumping-off-the-g-train
Verizon to buy Frontier Communications
Wall Street Journal reported today that Verizon is on the verge of buying Frontier Communications for as much as $7 billion in a deal that would bolster the company’s fiber network to compete with rivals notably AT&T. With a market value of over $7 billion, Dallas, TX based Frontier provides broadband (mostly fiber optic) connections to about three million locations across 25 states. Frontier is in the midst of upgrading its legacy copper landline network to cutting-edge fiber. Rising interest rates sparked fears among investors, however, that the business would run out of cash and not be able to raise more before completing those upgrades. Frontier has a 25-state footprint and serves largely rural areas. It reported sales of $5.8 billion in 2023, with about 52% of total revenue from activities related to its fiber-optic products and bills itself as “largest pure-play fiber internet company in the US.”
An all-cash deal between the two companies could be announced as soon as Thursday, a person familiar with the negotiations told Bloomberg.
Fiber M&A has heated up as telecom companies and financial firms pour capital into neighborhoods that lack high-speed broadband or offer only one internet provider, usually from a cable-TV company. New fiber-optic construction is expensive and time-consuming, making existing broadband providers attractive takeover targets.
Verizon, with a market valuation of around $175 billion, will be under pressure from shareholders to justify any big purchase after the company paid more than $45 billion to secure C-band 5G wireless spectrum licenses and spent billions more to use them. Executives have said they are focused on trimming the telecom giant’s leverage to put it on a firmer financial footing.
Verizon, the top cellphone carrier by subscribers, has faced increased pressure from competitors and from cable-TV companies that offer discounted wireless service backed by Verizon’s own cellular network. Faced with slowing wireless revenue growth and an expensive dividend, Verizon has invested in expanding its home-internet footprint. It has both 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) and its Fios-branded fiber to the premises network.
T-Mobile is the only major U.S. cellphone carrier that lacks a large landline business. Since its 2020 takeover of rival carrier Sprint, the company has focused on 5G dominance and succeeded in growing its cellphone business faster than rivals. That network has also linked millions of customers to its fixed 5G broadband service, which offers cablelike service over the air. T-Mobile’s strategy has shifted in recent months, however, as the company dabbles in partnerships and wholesale leasing agreements with companies that build fiber lines to homes and businesses. The wireless “un-carrier” in July agreed to spend about $4.9 billion through a joint venture with private-equity giant KKR to buy Metronet, a Midwestern broadband provider.
Photo Credit: Jeenah Moon/Bloomberg News
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
A deal for Frontier would be a round trip of sorts for some of the network infrastructure that Frontier bought from Verizon in 2016 for $10.54 billion in cash. Frontier later filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in April 2020 as it burned through cash and was burdened by a heavy debt load. It emerged as a leaner business in 2021 with about $11 billion less debt and focused on building a next-generation fiber optic network.
Frontier’s biggest investors today include private-equity firms Ares Management and Cerberus Capital Management. The company drew the attention of activist Jana Partners last year, which built a stake in the business. Jana delivered a letter to Frontier’s board late last year asking the company to take steps immediately to help reverse its sinking share price, including a possible outright sale.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
AT&T has focused on expanding its fiber network since spinning off its WarnerMedia assets in 2022 to Warner Brothers Discovery. AT&T has 27.8 million fiber homes/businesses passed, growing at ~2.4 million per year, plus more locations passed via its Gigapower joint venture. AT&T’s fiber internet business is expected to contribute to an increase in consumer broadband and wireline revenue. AT&T expects broadband revenue to increase by at least 7% in 2024, which is more than double the rate of growth for wireless service revenue. In contrast, Verizon only has about 18 million fiber locations, growing at about 500,000 per year.
Other recent deals in the fiber transport market sector include the $3.1 billion acquisition, including debt, of fiber provider Consolidated Communications in late 2023 by Searchlight Capital Partners and British Columbia Investment Management.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
It’s All About Convergence (fiber based home internet combined with mobile service):
Speaking at a Bank of America investors conference today, Verizon’s CEO for the Consumer Group Sowmyanarayan Sampath said when Verizon bundles Fios with wireless, it sees a 50% reduction in mobile churn and a 40% reduction in broadband churn. He said they don’t see the same benefits with FWA. Sampath was scheduled to speak at the Mobile Future Forward conference tomorrow, but he canceled at the last minute, which may be a sign that this deal for Frontier is imminent.
The analysts at New Street Research led by Jonathan Chaplin said Verizon’s rationale for the purchase is “convergence baby.” They wrote, wrote, “Verizon seemed complacent. No longer.” Indeed, Verizon CEO Hans Vestberg was challenged on the company’s second quarter 2024 earnings call by analysts who questioned whether Verizon had a big enough fiber footprint to compete in the future. The New Street analysts said Sampath’s comments today “marked a shift in rhetoric from: ‘convergence is important, but we can do it with FWA.”
The analysts at New Street wrote today, “We have been arguing for a couple of years that all the fiber assets would eventually be rolled up into the three big national carriers (AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile). We always knew that if one carrier started the process, others would have to follow swiftly because there are three wireless carriers and only one fiber asset in every market with a fiber asset.”
Other potential fiber companies that the big three national carriers might be eyeing include Google Fiber, Windstream, Stealth Communications and TDS Telecom.
After its annual summer conference in August in Boulder, Colorado, the analysts at TD Cowen, led by Michael Elias, said there was a lot of conversation about the wireline-wireless “convergence” frenzy. “We believe convergence is a race to the bottom, but if one player is going in with a slight advantage (AT&T), the others must reluctantly follow,” wrote TD Cowen. In the mid-term they speculated that T-Mobile might look at fiber roll-ups with Ziply or Lumen (formerly or other regional players.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/business/deals/verizon-nearing-deal-for-frontier-communications-9e402bb4
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/verizon-rumored-buy-frontier-its-convergence-game
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/verizon-talks-buy-frontier-communications-180419091.html
https://videos.frontier.com/detail/videos/internet/video/6322692427112/why-fiber
Building out Frontier Communications fiber network via $1.05 B securitized debt offering
Fiber builds propels Frontier Communication’s record 4th Quarter; unveils Fiber Innovation Labs
Frontier Communications fiber build-out boom continues: record number of fiber subscribers added in the 1st quarter of 2023
Frontier’s Big Fiber Build-Out Continued in Q3-2022 with 351,000 fiber optic premises added
AT&T and BlackRock’s Gigapower fiber JV may alter the U.S. broadband landscape
AT&T Highlights: 5G mid-band spectrum, AT&T Fiber, Gigapower joint venture with BlackRock/disaggregation traffic milestone
AT&T to use Frontier’s fiber infrastructure for 4G/5G backhaul in 25 states
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Frontier Communications adds record fiber broadband customers in Q4 2022
Verizon Q2-2024: strong wireless service revenue and broadband subscriber growth, but consumer FWA lags
Summary of Verizon Consumer, FWA & Business Segment 1Q-2024 results
Huawei’s First-Half Net Profit Rose on Strong Smartphone Sales, Car Business
Huawei Technologies Co.’s revenue grew for the sixth straight quarter as its smartphones gained significant market share in China. Net profit climbed 18% in the first half of the year, thanks to strong smartphone sales and robust growth in its car business. Huawei reports a handful of unaudited financial figures throughout the year and releases a more detailed audited annual report each spring. It didn’t provide data broken down by business segment for the first half.
The Chinese networking and electronics behemoth posted revenue of 239 billion yuan ($33.6 billion) in the June quarter, up 33.7% from a year earlier, according to calculations based on the company’s six-month financial figures. Implied net profit was 35.5 billion yuan, a drop of 18.6% from a year ago when Huawei recorded one-time gains from divestments. The company sold mobile maker Honor Device Co. to a consortium in 2020 and parts of its server business in 2021, with proceeds from both paid out in installments.
The Shenzhen-based company’s smartphone shipments rose by 50% last quarter as it and other local players like Vivo and Xiaomi Corp. beat out Apple, which dropped to sixth place among handset makers in China, according to market tracker IDC. Apple’s sales in China fell 6.5% in the June quarter, missing Wall Street projections, even as overall shipments in China grew.
Huawei’s next flagship Mate 70 will be closely watched for any processor upgrades when the device is introduced later this year. The Mate 60 roiled US policymakers when it debuted a China-made 7-nanometer chip a year ago, despite US-imposed sanctions and export controls geared to stem advances in China’s chip technologies.
Last year, Huawei more than doubled its net profit as it rebuilt the market share of its core businesses in consumer electronics and cloud computing, which were severely eroded by several years of U.S. sanctions that limited its access to advanced semiconductors.
In the second quarter, Huawei was the No. 2 smartphone seller in China, the world’s largest smartphone market, with an 18.1% market share, according to market-research firm International Data Corp. Counterpoint Research said Huawei’s sales jumped 44.5% in the quarter from a year earlier, the fastest growth among Chinese original equipment manufacturers, thanks to the Pura 70 and Nova 12 series. The company launched its Pura 70 series in April.
Huawei and other local smartphone makers like Vivo and Xiaomi Corp. beat out Apple, which dropped to sixth place among handset makers in China, according to market tracker IDC.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Huawei has invested in its car business as Beijing ramps up support for high-tech industries as part of efforts to reduce the economy’s reliance on the property sector for growth.
The company’s automotive unit, which offers self-driving technology to electric vehicle makers, earned a revenue of 10 billion yuan as of early July, according to a report by a Chinese media outlet, more than the combined revenue in the previous two years. Huawei didn’t provide a breakdown of its sales.
Changan Automobile-backed Avatr Technology said in an exchange filing last week that it will acquire a 10% stake in Yinwang Smart Technology, Huawei’s car unit that provides autonomous-driving technology to automakers, valuing the company at 115 billion yuan. Seres on Monday said it will acquire a 10% stake in Yinwang.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Despite U.S. sanctions, Huawei has come “roaring back,” due to massive China government support and policies
Dell’Oro: RAN market still declining with Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE and Samsung top vendors
China Unicom-Beijing and Huawei build “5.5G network” using 3 component carrier aggregation (3CC)
Will AI clusters be interconnected via Infiniband or Ethernet: NVIDIA doesn’t care, but Broadcom sure does!
InfiniBand, which has been used extensively for HPC interconnect, currently dominates AI networking accounting for about 90% of deployments. That is largely due to its very low latency and architecture that reduces packet loss, which is beneficial for AI training workloads. Packet loss slows AI training workloads, and they’re already expensive and time-consuming. This is probably why Microsoft chose to run InfiniBand when building out its data centers to support machine learning workloads. However, InfiniBand tends to lag Ethernet in terms of top speeds. Nvidia’s very latest Quantum InfiniBand switch tops out at 51.2 Tb/s with 400 Gb/s ports. By comparison, Ethernet switching hit 51.2 Tb/s nearly two years ago and can support 800 Gb/s port speeds.

While InfiniBand currently has the edge, several factors point to increased Ethernet adoption for AI clusters in the future. Recent innovations are addressing Ethernet’s shortcomings compared to InfiniBand:
- Lossless Ethernet technologies
- RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE)
- Ultra Ethernet Consortium’s AI-focused specifications
Some real-world tests have shown Ethernet offering up to 10% improvement in job completion performance across all packet sizes compared to InfiniBand in complex AI training tasks. By 2028, it’s estimated that: 1] 45% of generative AI workloads will run on Ethernet (up from <20% now) and 2] 30% will run on InfiniBand (up from <20% now).
In a lively session at VM Ware-Broadcom’s Explore event, panelists were asked how to best network together the GPUs, and other data center infrastructure, needed to deliver AI. Broadcom’s Ram Velaga, SVP and GM of the Core Switching Group, was unequivocal: “Ethernet will be the technology to make this happen.” Velaga opening remarks asked the audience, “Think about…what is machine learning and how is that different from cloud computing?” Cloud computing, he said, is about driving utilization of CPUs; with ML, it’s the opposite.
“No one…machine learning workload can run on a single GPU…No single GPU can run an entire machine learning workload. You have to connect many GPUs together…so machine learning is a distributed computing problem. It’s actually the opposite of a cloud computing problem,” Velaga added.
Nvidia (which acquired Israel interconnect fabless chip maker Mellanox [1.] in 2019) says, “Infiniband provides dramatic leaps in performance to achieve faster time to discovery with less cost and complexity.” Velaga disagrees saying “InfiniBand is expensive, fragile and predicated on the faulty assumption that the physical infrastructure is lossless.”
Note 1. Mellanox specialized in switched fabrics for enterprise data centers and high performance computing, when high data rates and low latency are required such as in a computer cluster.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ethernet, on the other hand, has been the subject of ongoing innovation and advancement since, he cited the following selling points:
- Pervasive deployment
- Open and standards-based
- Highest Remote Direct Access Memory (RDMA) performance for AI fabrics
- Lowest cost compared to proprietary tech
- Consistent across front-end, back-end, storage and management networks
- High availability, reliability and ease of use
- Broad silicon, hardware, software, automation, monitoring and debugging solutions from a large ecosystem
To that last point, Velaga said, “We steadfastly have been innovating in this world of Ethernet. When there’s so much competition, you have no choice but to innovate.” InfiniBand, he said, is “a road to nowhere.” It should be noted that Broadcom (which now owns VMWare) is the largest supplier of Ethernet switching chips for every part of a service provider network (see diagram below). Broadcom’s Jericho3-AI silicon, which can connect up to 32,000 GPU chips together, competes head-on with InfiniBand!
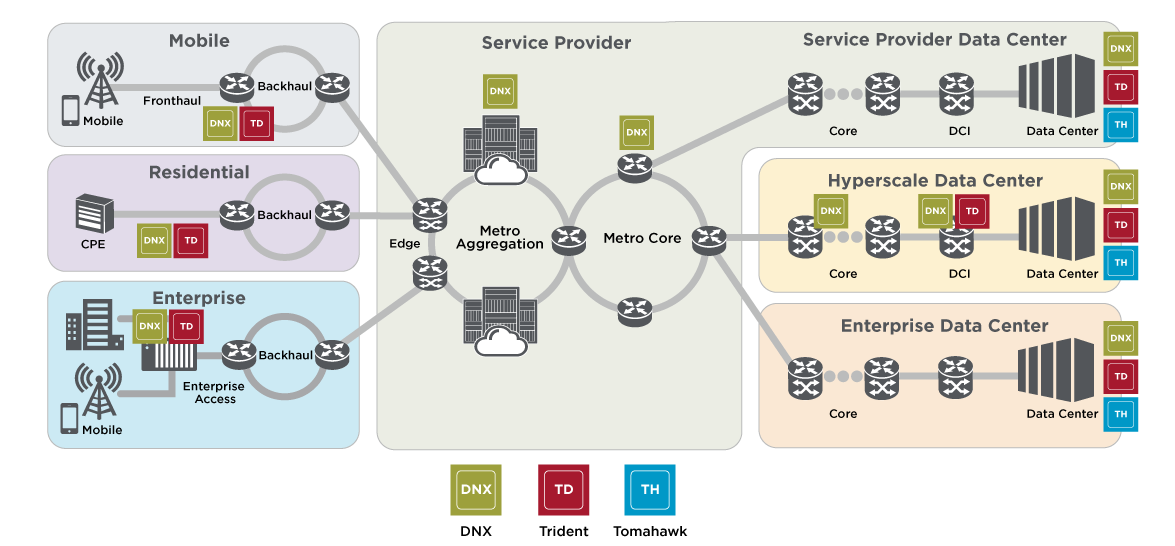
Image Courtesy of Broadcom
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Conclusions:
While InfiniBand currently dominates AI networking, Ethernet is rapidly evolving to meet AI workload demands. The future will likely see a mix of both technologies, with Ethernet gaining significant ground due to its improvements, cost-effectiveness, and widespread compatibility. Organizations will need to evaluate their specific needs, considering factors like performance requirements, existing infrastructure, and long-term scalability when choosing between InfiniBand and Ethernet for AI clusters.
–>Well, it turns out that Nvidia’s Mellanox division in Israel makes BOTH Infiniband AND Ethernet chips so they win either way!
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.perplexity.ai/search/will-ai-clusters-run-on-infini-uCYEbRjeR9iKAYH75gz8ZA
https://www.theregister.com/2024/01/24/ai_networks_infiniband_vs_ethernet/
Broadcom on AI infrastructure networking—’Ethernet will be the technology to make this happen’
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/products/infiniband/h
ttps://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/products/ethernet/
Part1: Unleashing Network Potentials: Current State and Future Possibilities with AI/ML
Using a distributed synchronized fabric for parallel computing workloads- Part II
Part-2: Unleashing Network Potentials: Current State and Future Possibilities with AI/ML