Author: Alan Weissberger
Google X spin-out Taara and Digicomm International partner to offer high speed wireless communications
Taara, a Google X “Moonshot Factory” spinoff, has chosen Colorado-based Digicomm International, a leading telecommunications distributor and manufacturer, to stock and expand the deployment of Taara’s innovative wireless optical (speeds) communication technology which is generically called Free Space Optics (FSO). Taara has been successful in FSO deployments with fiber and mobile operators in more than a dozen countries (see use cases below). The company has focused on the middle-mile market and intends also to pursue the last-mile connectivity arena, hopes to scale up its reach with operators even further following a new value-added reseller deal with Digicomm which will primarily focus on the North America market.
Taara Lightbridge is a wireless terminal that’s about the size of a traffic light and weights 14 kilograms. It uses beams of light to deliver fiber optic-like speeds through the air, providing an ideal solution for middle-mile connectivity, network resilience, and rapid service restoration. Taara’s core technology traces back to Project Loon, a one-time Google X initiative that explored how to create floating cell towers via the deployment of stratospheric balloons hovering at about 66,000 feet that connected with FSO technology. Taara CEO Mahesh Krishnaswamy, who worked on Project Loon, later decided that Loon’s core connectivity technology could be applied to terrestrial use cases. That idea spawned Taara which was spun off from Google X (Alphabet’s innovation hub) on March 17, 2025.
Taara uses free space optics technology in the unlicensed infrared band (193THz) and eye-safe 1535-1565 nanometer wavelength to deliver low-latency, bidirectional speeds of up to 20 Gbit/s across distances up to 20 kilometers. “It’s almost like a fiber, but it’s in the air,” Krishnaswamy told Light Reading.

By adding Taara Lightbridge to its portfolio, Digicomm says it will strengthen its commitment to provide customers with innovative and scalable products that address today’s growing broadband demands. Digicomm and Taara first connected at last year’s Fiber Connect show, according to Digicomm CEO Rob Donziger.
“Partnering with Taara marks an exciting milestone for Digicomm and our customers,” said Jennifer Nelson, FTTx and Wireless Sales Leader at Digicomm International. “Taara’s Wireless Optical Communication technology is a perfect complement to our extensive wireless, HFC, and FTTx offerings, empowering service providers to expand faster, more efficiently, and at a lower cost.”
“We’re excited to welcome Digicomm as our Master Value-Added Reseller in the Americas region,” said Sanjay Nagpal, Senior Vice President of Global Sales and Partnerships at Taara. “Digicomm’s deep regional expertise and strong ecosystem of relationships will accelerate the deployment of Taara’s high-speed wireless optical technology where it’s needed most. This partnership marks a significant milestone in our mission to expand affordable, reliable internet access with partners seeking innovative, fiber-equivalent solutions.”
FSO has been around for decades, but its success in the market has been limited by weather issues, such as rain, fog and vibration-inducing winds, that can cause service disruptions and reduce overall reliability. Krishnaswamy said Taara isn’t immune to those conditions. However, he said that the company has developed ways to compensate for them, including a pointing-and-tracking system that keeps the beam between terminals centered despite movement and vibrations.
Taara also boosts reliability with the use of automatic repeat request (ARQ) techniques that quickly resend data when, for example, a bird flies in front of the beam or connectivity is impacted by rain droplets. Fog presents a more difficult scenario, but Taara can use a “hybrid” approach – such as creating a redundant path via a different frequency and the use of microwave technology as a failover – to compensate, Krishnaswamy said.
Taara also has developed a planning tool based on years of weather data to help partners predict when weather-related issues might surface. Weather is not the only FSO culprit. In earlier deployment days in India, for example, outages were caused by monkeys jumping on towers and making them sway. The new pointing-and-tracking system resolved that issue by compensating for that movement and keeping the connection stable, Krishnaswamy added. He likened Taara’s technical and operational approach as a “second coming” for free space optics, believing it’s now “primed and ready for the real world.”
Taara was spun out from Google X after there was a “clear signal” that the company’s technology had matured to a certain level and that there was enough traction to support a sustainable business. Taara is now “ready to scale and go to the next stage,” Krishnaswamy said.
Taara currently employs fewer than 100 people and is not yet profitable. However, it has been racking up deployments in more than a dozen countries for a wide range of use cases in both rural and urban areas. Those use cases include bringing fiber-like speeds where fiber can’t (because of factors such as cost and difficult terrain), enterprise connectivity – for portable, redundant connectivity when a service provider experiences a fiber cut – and disaster recovery.
Taara’s technology “has been very versatile and we’ve been very surprised at how customers have been teaching us on how best to use this product,” Krishnaswamy noted. Examples of Taara’s early deployment partners include Liberty Latin America (redundancy and island-to-island connectivity), Airtel (connecting multiple dwelling units and 4G/5G tower backhaul), T-Mobile (portable 5G connectivity), Liquid Telecom in Nairobi (connecting surrounding towns from existing fiber) and Digicel (service failovers).
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
With decades of experience delivering advanced broadband technologies, Digicomm’s logistical capabilities and customer reach make it an ideal partner to scale deployment quickly and effectively. Digicomm will stock and support Taara Lightbridge wireless optical solutions, offering link planning services, rapid order fulfillment, and customer service to meet the unique needs of broadband network operators.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About Digicomm International:
Founded in 1993, Digicomm is an industry-leading, value-added broadband distributor and manufacturer – and a key strategic partner to its customers helping them meet the rigorous demands of broadband network operations. Service providers around the world depend on Digicomm’s extensive inventory of Wireless, HFC, and FTTx products, representing trusted manufacturers such as AOI, PPC, Commscope, Tarana Wireless, and many others. Digicomm also designs and manufactures products including EDFAs, optical passives and more.
For further information, visit www.digicomm.com
About Taara:
Taara is a moonshot for connectivity, with a mission to extend and amplify the global communications network with beams of light. Born at X, Google’s Moonshot Factory, the team combines expertise across disciplines to tackle the world’s toughest connectivity challenges. Taara is now deploying wireless optical communications with industry partners in over a dozen countries, expanding access to fast, reliable connectivity. The company is located in Sunnyvale, CA.
Following about seven years in the incubation phase, Taara spun-out of the Google X Moonshot Factory in March 2025. It has Alphabet and Series X Capital among its financial backers.
Projects such as Wing (lightweight drones to deliver goods), Project Loon, Dandelion (the use of geothermal energy to heat and cool homes) and Waymo (the autonomous vehicle company spun out in 2016) also started at Google X.
Learn more at www.taaraconnect.com
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
After 9 years Alphabet pulls the plug on Loon; Another Google X “moonshot” bites the dust!
Ultra-secure quantum messages sent a record distance over a fiber optic network
Unlike binary bit based digital communications, quantum information is transmitted in qubits, which can store multiple values at once, making quantum communications more secure. A recently published article in Nature states that scientists have sent quantum information across a record-breaking 158 miles using ordinary computers and fiber-optic cables. It’s the first time coherent quantum communication—an ultra-secure means of transmitting data—has been achieved using existing telecommunications infrastructure, without the expensive cryogenic cooling that is typically required.
“Our equipment was running alongside the fibers that we use for regular communication literally buried underneath the roads and train stations,” said Mirko Pittaluga, a physicist and lead author of the study. Pittaluga and his colleagues at Toshiba Europe sent quantum information from regular computers hooked into the telecommunications network at data centers in the German cities of Kehl and Frankfurt, relaying them through a detector at a third data center roughly midway between them in Kirchfeld. The three-location setup enabled the group to extend the distance the messages were sent more than 150 miles, an uninterrupted distance only ever achieved in a laboratory environment.
Pittaluga said that his team’s work is critical to solving the problem of keeping sensitive data out of the reach of hackers. One means of fixing this problem, Pittaluga said, is through quantum cryptography, which relies on the physics of quantum mechanics rather than mathematical algorithms to generate encryption keys. But to use quantum encryption keys, you have to successfully distribute them across meaningful distances, a task that has stymied researchers outside the lab for decades.
Quantum data was sent over an ordinary telecom network with fiber-optic cables.© julie sebadelha/Agence France-Presse/Getty Images
Integrating the technology into existing infrastructure using largely off-the-shelf equipment is a key step in expanding the accessibility of quantum communication and its use in encrypting information for more secure transmission of data, according to multiple physicists and engineers who weren’t involved in the study.
“This is about as real-world as one could imagine,” said David Awschalom, a professor of physics and molecular engineering at the University of Chicago who wasn’t a part of the new work. “It’s an impressive, quite beautiful demonstration.” Working at these types of distances, Awschalom said, means that quantum information could be sent across entire metropolitan areas or between nearby cities, making it useful for hospitals, banks and other institutions, for which secure communications are paramount.
“The likelihood of them being able to reverse engineer a quantum key, which is the number you would need to decrypt your information, is vanishingly small,” according to Awschalom.
Other groups in the U.K. and U.S., including researchers at the University of Pennsylvania, are also working on extending the distances achievable by quantum communication.
Today, bank statements, health records and other data transmitted online are protected using mathematically formulated encryption keys. These keys are the only means of unlocking the data, keeping it secure from cyber thieves. For conventional computers, breaking these keys takes an impractically long time, but quantum computers are up to the task, and as they become more powerful, encryption keys become vulnerable to attack.
“Anything meaningful that’s over the internet can be tapped, recorded and saved for the next decade, and can be decrypted years later,” according to Prem Kumar, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at Northwestern University, who wasn’t a part of the new work. “It’s what’s called harvest now and decrypt later.”
Internet and telecommunications infrastructure are based on optical fibers all over the world that carry pulses of light containing photons. Classical bits of information are sent as a single impulse of light carrying tens of millions of photons. Quantum information, stored in qubits, is sent in a package of a single photon.
Efficiently detecting single photons usually requires expensive superconducting detectors that cost on the order of hundreds of thousands of dollars. These high-efficiency sensors must be cryogenically cooled, using liquid helium, to super low temperatures below minus 454 degrees Fahrenheit, making the technology expensive and incompatible with existing infrastructure.
Pittaluga and his colleagues at Toshiba got around this by using cheaper detectors known as avalanche photodiodes, which cost just thousands of dollars and can run at or just below room temperature, like today’s traditional internet equipment.
Such detectors hadn’t been used for coherent quantum communication before, as they can be nearly an order of magnitude less efficient at detecting single photons and are affected by what is called the afterpulse effect—when the current detection is frustrated by leftover echoes from an earlier transmission. Superconducting detectors aren’t affected by afterpulsing, Pittaluga said.
To address the effect in the more practical and cost-effective photodiodes, his group employed two separate sets of the detectors, using one to read the signal and the other to remove the environmental noise from that signal. The goal of this setup is to bring us one step closer to a quantum internet, with incredibly secure information, Pittaluga added.
Yet despite this innovation, the technology remains expensive and difficult to implement compared with current encryption systems and networks—for now. “My personal view is that we’ll be seeing quantum encryption of data sets and metropolitan-scale quantum networks within a decade,” Awschalom added.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Why quantum computers are faster at solving problems:
Quantum computers are faster than traditional computers for optimization problems, such as finding the more efficient options for supply chains.
A traditional computer tries each combination individually. A quantum computer tries all combinations at once.

Source: Google Quantum AI
Peter Champelli/THE WALL STREET JOURNAL
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08801-w
Google’s new quantum computer chip Willow infinitely outpaces the world’s fastest supercomputers
Quantum Computers and Qubits: IDTechEx report; Alice & Bob whitepaper & roadmap
Bloomberg on Quantum Computing: appeal, who’s building them, how does it work?
SK Telecom and Thales Trial Post-quantum Cryptography to Enhance Users’ Protection on 5G SA Network
SK Telecom and Thales Trial Post-quantum Cryptography to Enhance Users’ Protection on 5G SA Network
Research on quantum communications using a chain of synchronously moving satellites without repeaters
Frontier Communications fiber growth accelerates in Q1 2025
Frontier Communications reported record fiber subscriber net adds in Q1-2025. However, the “fiber first” carrier had a loss of $0.26 per share, compared to break-even earnings per share a year ago. The telco posted revenues of $1.51 billion for the quarter ended March 2025, compared to year-ago revenues of $1.46 billion.
“We had the strongest start to a year yet, led by continued strength in our fiber business,” said Nick Jeffery, President and Chief Executive Officer of Frontier. “Consumers, business owners and technology companies are increasingly relying on fiber to power networks and connect to the digital economy – and that trend is shining through in our results. The team delivered 19% growth in fiber broadband customers and 24% growth in fiber broadband revenues this quarter, which taken together drove record first-quarter growth in both revenue and Adjusted EBITDA.”
Jeffery continued, “We also hit a milestone in the first quarter, growing our fiber network to reach more than 8 million passings. We started this turnaround journey with a goal of 10 million fiber passings and four years later, I’m proud to say that we’re nearly there. As we scale our network, we’re expanding access for millions of Americans and building a legacy that will continue to endure long after our planned combination with Verizon.”
First-Quarter 2025 Highlights
- Added 321,000 fiber passings to reach 8.1 million total locations passed with fiber
- Added 107,000 fiber broadband customers, resulting in fiber broadband customer growth of 19.3% year-over-year
- Consumer fiber broadband ARPU of $68.21 increased 4.7% year-over-year
- Revenue of $1.51 billion increased 3.4% year-over-year as growth in fiber-based products was partly offset by declines in copper-based products
- Operating income of $76 million and net loss of $64 million
- Adjusted EBITDA of $583 million increased 6.6% year-over-year driven by revenue growth and lower content expense, partially offset by higher customer acquisition costs1
- Cash capital expenditures of $757 million plus $16 million of vendor financing payments resulted in total cash capital investment of $773 million2
- Generated net cash from operations of $519 million
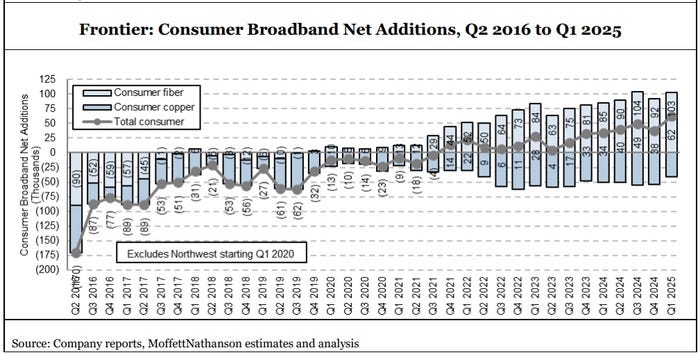
Frontier added 103,000 residential fiber broadband customers in Q1 2025, beating the 95,000 expected by MoffettNathanson (see graph below). Frontier’s residential fiber additions in the quarter were just shy of the record 104,000 it added in Q3-2024. The fiber facilities based carrier gained a record 59,000 net broadband customers in the period, which included losses of legacy copper subscribers.
Frontier built another 321,000 fiber passings in Q1-2025, pushing its total past the 8 million mark. Alongside subscriber growth, Frontier’s consumer fiber broadband average revenue per unit (ARPU) also climbed – to $68.21, up 4.7% versus the year-ago period.
Frontier said the “vast majority” of new fiber subs are now taking multi-gigabit speeds. A specific number wasn’t shared, but back in Q2 2024 more than 60% of new Frontier fiber customers took speeds of 1 Gbit/s or more.
CEO Jeffery said Frontier is sticking with its plan to build fiber to 1.3 million locations in 2025. The current pace puts Frontier on a path to reach its 10 million fiber passing goal around the third quarter of 2026, New Street Research analyst Jonathan Chaplin said in a research note.
Jeffery said Frontier’s “fiber build machine” is capable of going faster, but he stressed that the current pace gives the company the time it needs to also sell, service and support fiber broadband as it builds. “The whole company needs to be in balance. We want more customers and higher ARPU, and we’ve demonstrated that it’s doable,” Jeffery said.
He attributed ARPU growth to multiple factors, including customers taking higher-level speed tiers and subscribing to additional, premium services. Frontier estimates that more than 50% of new customers take some type of add-on, including whole-home Wi-Fi and YouTube TV.
Jeffery said Frontier is seeing good adoption of “Unbreakable Wi-Fi,” a $25 per month add-on that flips to 4G cellular backup (with 130 gigabytes of data per billing cycle) when the primary fiber connection is down. Those customers can also opt for a battery backup that provides up to four hours of backup power.
Frontier’s Q1 results come as it moves ahead with its proposed acquisition by Verizon which is currently expected to close by the first quarter of 2026. Jeffery would only say that the deal process is going smoothly at the state and federal levels.
“My job is now very much to deliver this asset in the best possible shape it can be to its future owner, Verizon,” he said. “I’m delighted to say that that’s really been evident in our first quarter results.”
References:
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20250429128668/en/Frontier-Reports-First-Quarter-2025-Results
Verizon to buy Frontier Communications
Frontier Communications recovering from unknown cyberattack!
Building out Frontier Communications fiber network via $1.05 B securitized debt offering
Frontier Communications fiber build-out boom continues: record number of fiber subscribers added in the 1st quarter of 2023
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Fiber builds propels Frontier Communication’s record 4th Quarter; unveils Fiber Innovation Labs
AT&T to use Frontier’s fiber infrastructure for 4G/5G backhaul in 25 states
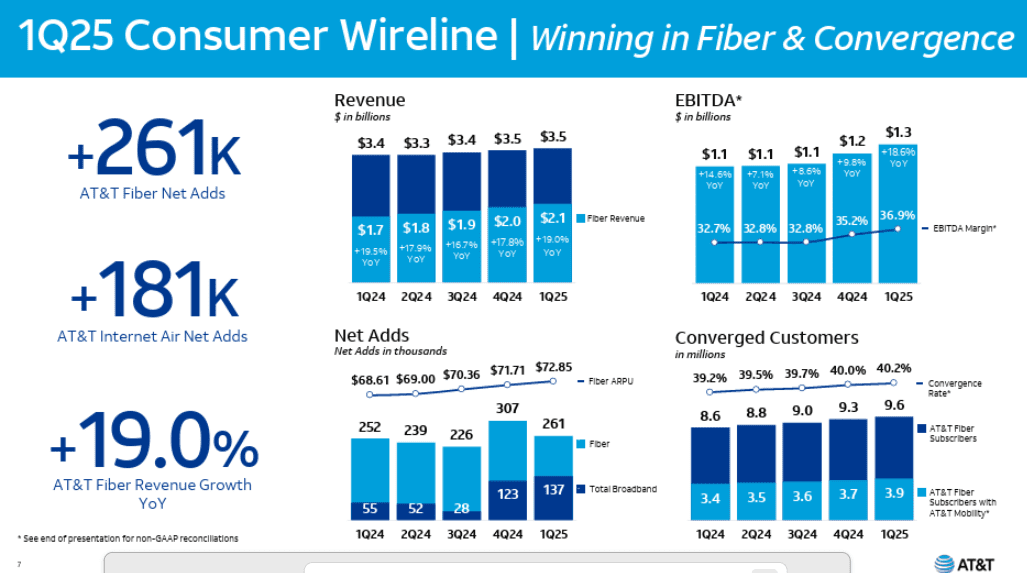
AT&T grows fiber revenue 19%, 261K net fiber adds and 29.5M locations passed by its fiber optic network
In the 1st quarter of 2025, AT&T’s fiber business showed strong performance, with fiber revenue growing by 19% year-over-year and 261,000 net fiber subscribers added. This growth helped drive overall wireline revenue and operating income, with fiber revenue contributing significantly to the 9.6% broadband revenue increase. AT&T’s fiber strategy is a key part of its broader plan for growth, including 5G wireless, and is expected to continue contributing to strong financial results. At the end of the 1Q2025, AT&T said that 29.5 million locations were passed with its fiber network. The company expects to surpass 30 million by midyear, months ahead of its original target. Consumer fiber broadband revenue was $2.1 billion in the quarter, up 19% year-over-year, as more customers upgraded to faster service tiers. Executives noted that more than 40% of AT&T Fiber households now also subscribe to AT&T wireless, part of a deliberate strategy to drive “converged” customer relationships.
AT&T continues to lead the Fiber-to-the-Home market, and has reportedly been in talks to acquire Lumen Technologies’ consumer fiber business in a deal valued at more than $5.5 billion, according to Bloomberg and Reuters
CFO Pascal Duroche on the 1Q2025 earnings call:
“We delivered 261,000 AT&T Fiber net adds, up from 252,000 in the first quarter of last year. This was driven by growth in our consumer locations served with fiber, which reached 23,800,000 at the end of 1Q and growing contribution of net adds in regions served with Giga Power Fiber. We love the return profile of fiber and the lift it provides our mobility business only makes investing in fiber more attractive. AT and T Internet Air net adds were 181,000 in the quarter, which is a significant improvement from a year ago, driven by broader availability across our distribution channels. Our combined success with these two services helped us deliver 137,000 total broadband net adds in the quarter.
This marks our seventh straight quarter of overall broadband subscriber growth and second consecutive quarter with more than 100,000 broadband net adds. We grew Consumer Wireline revenue by 5.1% versus the prior year. This was driven by fiber revenue growth of 19%, reflecting subscriber gains and solid fiber ARPU growth of 6.2%. Consumer wireline EBITDA grew 18.6% for the quarter. Our first quarter results benefited from vendor settlements that positively impacted our total wireline operating expenses by approximately $100,000,000 Roughly $55,000,000 of the impact was in Consumer Wireline with the rest in Business Wireline.”
AT&T is investing heavily in its fiber network which is reflected in the increase in its capital expenditures (CAPEX) which are expected to remain in the $22 billion range annually from 2025 through 2027.

AT&T logo on a building in Pasadena, California, U.S., January 24, 2018. REUTERS/Mario Anzuoni/File Photo Purchase Licensing Rights
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“Where we have fiber, we win,” said CEO John Stankey. “This dynamic continues to drive growth, shown by our increasing rate of convergence, customer penetration and significant wireless share gains within our fiber footprint.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2025/1q-earnings.html
Analysts weigh in: AT&T in talks to buy Lumen’s consumer fiber unit – Bloomberg
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
AT&T Highlights: 5G mid-band spectrum, AT&T Fiber, Gigapower joint venture with BlackRock/disaggregation traffic milestone
Corning to Build New Fiber Optic Plant in Phoenix, AZ for AT&T Fiber Network Expansion
AT&T CEO John Stankey: 30M or more locations could be passed by AT&T fiber (he said that in Sept. 2021)
AT&T and Verizon cut jobs another 6% last year; AI investments continue to increase
U.S. export controls on Nvidia H20 AI chips enables Huawei’s 910C GPU to be favored by AI tech giants in China
Damage of U.S. Export Controls and Trade War with China:
The U.S. big tech sector, especially needs to know what the rules of the trade game will be looking ahead instead of the on-again/off-again Trump tariffs and trade war with China which includes 145% tariffs and export controls on AI chips from Nvidia, AMD, and other U.S. semiconductor companies.
The latest export restriction on Nvidia’s H20 AI chips are a case in point. Nvidia said it would record a $5.5 billion charge on its quarterly earnings after it disclosed that the U.S. will now require a license for exporting the company’s H20 processors to China and other countries. The U.S. government told the chip maker on April 14th that the new license requirement would be in place “indefinitely.”
Nvidia designed the H20 chip to comply with existing U.S. export controls that limit sales of advanced AI processors to Chinese customers. That meant the chip’s capabilities were significantly degraded; Morgan Stanley analyst Joe Moore estimates the H20’s performance is about 75% below that of Nvidia’s H100 family. The Commerce Department said it was issuing new export-licensing requirements covering H20 chips and AMD’s MI308 AI processors.
Big Chinese cloud companies like Tencent, ByteDance (TikTok’s parent), Alibaba, Baidu, and iFlytek have been left scrambling for domestic alternatives to the H20, the primary AI chip that Nvidia had until recently been allowed to sell freely into the Chinese market. Some analysts suggest that H20 bulk orders to build a stockpile were a response to concerns about future U.S. export restrictions and a race to secure limited supplies of Nvidia chips. The estimate is that there’s a 90 days supply of H20 chips, but it’s uncertain what China big tech companies will use when that runs out.
The inability to sell even a low-performance chip into the Chinese market shows how the trade war will hurt Nvidia’s business. The AI chip king is now caught between the world’s two superpowers as they jockey to take the lead in AI development.
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang “flew to China to do damage control and make sure China/Xi knows Nvidia wants/needs China to maintain its global ironclad grip on the AI Revolution,” the analysts note. The markets and tech world are tired of “deal progress” talks from the White House and want deals starting to be inked so they can plan their future strategy. The analysts think this is a critical week ahead to get some trade deals on the board, because Wall Street has stopped caring about words and comments around “deal progress.”

- Baidu is developing its own AI chips called Kunlun. It recently placed an order for 1,600 of Huawei’s Ascend 910B AI chips for 200 servers. This order was made in anticipation of further U.S. export restrictions on AI chips.
- Alibaba (T-Head) has developed AI chips like the Hanguang 800 inference chip, used to accelerate its e-commerce platform and other services.
- Cambricon Technologies: Designs various types of semiconductors, including those for training AI models and running AI applications on devices.
- Biren Technology: Designs general-purpose GPUs and software development platforms for AI training and inference, with products like the BR100 series.
- Moore Threads: Develops GPUs designed for training large AI models, with data center products like the MTT KUAE.
- Horizon Robotics: Focuses on AI chips for smart driving, including the Sunrise and Journey series, collaborating with automotive companies.
- Enflame Technology: Designs chips for data centers, specializing in AI training and inference.
“With Nvidia’s H20 and other advanced GPUs restricted, domestic alternatives like Huawei’s Ascend series are gaining traction,” said Doug O’Laughlin, an industry analyst at independent semiconductor research company SemiAnalysis. “While there are still gaps in software maturity and overall ecosystem readiness, hardware performance is closing in fast,” O’Laughlin added. According to the SemiAnalysis report, Huawei’s Ascend chip shows how China’s export controls have failed to stop firms like Huawei from accessing critical foreign tools and sub-components needed for advanced GPUs. “While Huawei’s Ascend chip can be fabricated at SMIC, this is a global chip that has HBM from Korea, primary wafer production from TSMC, and is fabricated by 10s of billions of wafer fabrication equipment from the US, Netherlands, and Japan,” the report stated.
Huawei’s New AI Chip May Dominate in China:
Huawei Technologies plans to begin mass shipments of its advanced 910C artificial intelligence chip to Chinese customers as early as next month, according to Reuters. Some shipments have already been made, people familiar with the matter said. Huawei’s 910C, a graphics processing unit (GPU), represents an architectural evolution rather than a technological breakthrough, according to one of the two people and a third source familiar with its design. It achieves performance comparable to Nvidia’s H100 chip by combining two 910B processors into a single package through advanced integration techniques, they said. That means it has double the computing power and memory capacity of the 910B and it also has incremental improvements, including enhanced support for diverse AI workload data.
Conclusions:
The U.S. Commerce Department’s latest export curbs on Nvidia’s H20 “will mean that Huawei’s Ascend 910C GPU will now become the hardware of choice for (Chinese) AI model developers and for deploying inference capacity,” said Paul Triolo, a partner at consulting firm Albright Stonebridge Group.
The markets, tech world and the global economy urgently need U.S. – China trade negotiations in some form to start as soon as possible, Wedbush analysts say in a research note today. The analysts expect minimal or no guidance from tech companies during this earnings season as they are “playing darts blindfolded.”
References:
https://qz.com/china-six-tigers-ai-startup-zhipu-moonshot-minimax-01ai-1851768509#
https://www.huaweicloud.com/intl/en-us/
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
Telecom sessions at Nvidia’s 2025 AI developers GTC: March 17–21 in San Jose, CA
Nvidia AI-RAN survey results; AI inferencing as a reinvention of edge computing?
FT: Nvidia invested $1bn in AI start-ups in 2024
Omdia: Huawei increases global RAN market share due to China hegemony
Huawei’s “FOUR NEW strategy” for carriers to be successful in AI era
Evercore: T-Mobile’s fiber business to boost revenue and achieve 40% penetration rate after 2 years
NOTE: COMMENTS ARE CLOSED FOR THIS POST:
T-Mobile first entered into the fiber optic Internet access market in 2021. What started as a pilot program four years ago has officially launched as T‑Mobile Fiber Home Internet, offering new plans and expanding availability to over 500,000 U.S. households as of June 2025.
T-Mobile’s fiber business could serve about 5 million U.S. customers and generate up to $5 billion in revenue during the next five years, according to financial analysts at Evercore. That call is the investment advisor firm’s first take at evaluating the maturation of T-Mobile’s fiber plans. It’s based on the assumption that T-Mobile will close its deal to acquire fiber operator Metronet, following the recent closure of another deal with EQT for fiber operator Lumos. Evercore’s projections do not assume that T-Mobile will make a play for another fiber operator like Lumen Technologies.
“Looking to 2030, we expect 14 million [fiber] passings … and 4.8 million subscribers,” the analysts wrote in a note to investors this week. “Assuming a $75 ARPU [average revenue per user] growing 4% year over year implies ~$5 billion of revenue in 2030. “While it hasn’t shared subscriber targets, [T-Mobile] management has expressed confidence that it would see higher long-term market penetration than typical [fiber] overbuilders (e.g., ~35%) benefitting from its national brand and advertising, digital and retail distribution, ability to take advantage of the waiting list it has for FWA [fixed wireless access] in markets where demand outstrips supply,” the Evercore analysts added.
Evercore assumes that T-Mobile Fiber (see plans below) will be able to capture 10% market share within six months of launch and 20% within a year. After two years, the analysts predict T-Mobile Fiber will command 40% penetration (meaning, 40% of the customers reached by its fiber connections will subscribe to those connections).
T-Mobile Fiber Plans:
- Fiber 500 (500 Mbps): Superfast performance for gaming, streaming, and more.
- Fiber 1 Gig (1000 Mbps): Blistering speeds for every device and user in your home.
- Fiber 2 Gig (2000 Mbps): Our fastest speeds and largest capacity for more devices and users.
 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….“For now, until there’s greater color from management, we’ve assumed T-Mobile will see 25% EBITDA [earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization] margins on its Fiber revenue. This could be conservative over time,” the Evercore analysts wrote. They predicted overall EBITDA from T-Mobile Fiber of around $340 million in 2026, growing to $1.24 billion in 2030. And that, they said, would equate to free cash flow of $270 million in 2026, growing to $1 billion by 2030.
“Pricing will evolve as T-Mobile acquires and operates Metronet and Lumos’ subscribers along with the competitive dynamics across the broadband market. T-Mobile has a clear history of being a disruptor, so it could be more aggressive on pricing than we expect, resulting in downside to our ARPU and revenue estimates,” the Evercore analysts warned. They noted that T-Mobile Fiber in some Colorado markets today costs $55 per month for 500 Mbit/s connections. That’s similar to local incumbents Lumen Technologies ($50 for 500 Mbit/s) and Comcast ($55 per month for 600 Mbit/s).

Convergence of mobile and fiber access will provide a tailwind for T-Mobile, potentially driving increased postpaid phone share and revenue. “Despite management’s tone around the benefits of convergence, we believe there will clearly be an opportunity to drive higher postpaid phone share across the growing number of households that ultimately end up taking T-Mobile fiber,” according to the Evercore analysts. They predicted that T-Mobile’s fiber operations would eventually help improve the operator’s postpaid smartphone net customer additions by up to 650,000 per year, and that it will drive the operator’s annual wireless service revenues up by $200 million to $350 million.
An important insight into T-Mobile’s convergence strategy emerged in the wake of its acquisition of Lumos. “New and existing customers will enjoy VIP treatment through Magenta Status, which includes exclusive benefits like discounts on food, gas, entertainment and top brands, plus freebies every Tuesday in the T-Life app. All with T-Mobile’s standard ‘no exploding bills’ pricing structure,” T-Mobile said of its new Lumos customers.
“One app. All the things,” T-Mobile proclaims of the T-Life app it launched roughly a year ago. The app is available to all T-Mobile smartphone customers – and now its new fiber customers.
“Get the latest exclusive perks from T-Mobile Tuesdays, and take advantage of all your Magenta Status benefits,” T-Mobile said of its T-Life app. “You can also pay your bill, add a line to your account, and track orders straight from the app. And you can manage your account, configure your T-Mobile Home Internet gateway, and more. If you need help with anything, customer care is available at the tap of a button.”
The analysts expect T-Mobile’s fixed wireless access business to continue gaining traction, potentially reaching 7% of the total broadband subscriber base by 2025.
Separately, Verizon is now Evercore’s top pick among wireless network operators and is its top value idea.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/fttx/t-mobile-fiber-could-see-5m-customers-and-5b-in-revenue-by-2030
Malaysia’s U Mobile signs MoU’s with Huawei and ZTE for 5G network rollout
Malaysia’s second 5G network operator, U Mobile Sdn Bhd has signed separate memorandum of understandings (MoU’s) with Chinese technology leaders Huawei Technologies Co Ltd and ZTE Corporation to facilitate the implementation of Malaysia’s second 5G network. U Mobile has invested over RM8 billion in its network and technological infrastructure, with over 10,000 network sites. DNB, the country’s first wholesale 5G network, selected Ericsson as its network equipment provider.
U Mobile chairman Tan Sri Vincent Tan said Huawei will be responsible for deploying the 5G network in Peninsular Malaysia, while ZTE will manage the rollout in Sabah and Sarawak. “We are pleased to formalize our vendor agreements with Huawei and ZTE, two of the world’s leading 5G technology providers. The vendor selection process was conducted in a transparent manner to ensure we chose the most suitable technology partners to support our ambitious goals,” Tan said in his speech at the signing ceremony in Putrajaya. “Huawei and ZTE are no strangers to U Mobile. Having been our long-term infrastructure partners, they have a proven global deployment track record, hence, we are looking forward to pivoting our business together,” Tan added.
U Mobile chief technology officer Woon Ooi Yuen said the selection process began last year with invitations to tender issued to network equipment and software providers from various regions. “Ultimately, only two Chinese companies responded to our 5G tender and we are delighted to work with Huawei and ZTE on this significant endeavor. Apart from their global technology track record, they have also shared vision for an efficient and rapid rollout,” Woon said.
_theedgemalaysia.jpg&w=1080&q=75https://assets.nst.com.my/images/articles/HQ2411038834.jpg_1744701671.jpg)
From left: Huawei M’sia CEO Simon Sun, Huawei president of Apac Terry He, U Mobile CEO Wong Heang Tuck and chairman Tan Sri Vincent Tan, Communications Ministry Deputy SecGen (Telecommunications Infrastructure) Mano Verabathran, Communications Minister Datuk Fahmi Fadzil, China’s Industry & IT Ministry Party Secretary Li Lecheng, Chinese Ambassador to M’sia Ouyang Yujing, U Mobile deputy CEO Kenneth Chang, ZTE vice president of marketing & solutions for Asia & CIS region Bai Yang, and ZTE Malaysia Managing Director Steven Ge.

NSTP/ASWADI ALIAS
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
U Mobile chief executive officer Wong Heang Tuck said the company is targeting to achieve 80% 5G network penetration within 12 months of its rollout, which is scheduled to begin in the second half of this year (2H25). He said the goal is expected to be achievable through the appointment of Huawei and ZTE as strategic technology partners for the implementation of next-generation 5G networks in the country.
“Huawei and ZTE will play a key role in helping U Mobile meet its network expansion targets. We aim to achieve 80% coverage in populated areas within the first 12 months of rollout and subsequently reach 90% coverage in the following 12 months,” he said during the press conference.
Wong said this move aligns with U Mobile’s overall strategy to accelerate the adoption of 5G and 5G-A technologies in Malaysia, with a strong emphasis on supporting the enterprise sector. The signing with Huawei today was witnessed by Communications Minister Datuk Fahmi Fadzil, Tan, party secretary of China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology Li Lecheng and Huawei Asia Pacific president Terry He. U Mobile reaffirmed that it remains committed to going for a public listing, though it cautioned that timing would depend on global market conditions which are in an “upheaval state today,” Wong said.
The separate MOU with ZTE was approved by U Mobile’s Fahmi, Li Lecheng, Tan and Bai Yang, ZTE’s vice president of marketing and solutions for the Asia and CIS Region. Separately, the ZTE Privacy Protection White Paper (2025) was released today. The White Paper offers a systematic and comprehensive overview of the company’s achievements in privacy compliance, spanning privacy protection policy, framework, co-building, and practical implementation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Backgrounder:
The Malaysian government announced its dual 5G network model in May 2023 to ensure competition, better quality of service and wider coverage, especially in underserved and remote areas. It committed to allowing the construction of a second wholesale network once the DNB network reached 80% coverage. U Mobile was appointed by the government to deploy the second 5G network in November 2024, winning out over larger and more established telco rivals such as CelcomDigi and Maxis. Industry observers considered this a controversial choice. U Mobile is the smallest operator in Malaysia, raising questions about its ability to build a 5G network to rival DNB’s.
The Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission (MCMC) issued the official letter of award to U Mobile more than two weeks ago, paving the way for the construction of the country’s second 5G network.
The choice of the Chinese vendors was somewhat controversial in light of Western sanctions against them. In September 2023, Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim sparked controversy when he said that the decision to allow a second wholesale 5G network would allow for “more effective participation by Huawei.” Ibrahim argued the construction of a second 5G network was made so that Malaysia could benefit from different technologies. “We in Malaysia, and I believe rightly, decided that while we get the best from the West, we also should benefit the best from the East,” he said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
U Mobile’s other MoU:
Last week, U Mobile announced that it has signed a memorandum of understanding with EdgePoint Infrastructure to become one of its preferred partners for 5G in-building communications (IBC) infrastructure. U Mobile will leverage EdgePoint’s expertise for its 5G IBC infrastructure rollout, with plans to collaborate on 5G IBC innovations Both parties will also seek to achieve the most cost-effective rapid rollout through a competitive commercial offer.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
U Mobile picks Chinese giants Huawei, ZTE for 5G network rollout
U Mobile to roll out 5G network with Huawei, ZTE; sees ‘similar’ rates to DNB
U Mobile collaborates with Huawei, ZTE for 5G infrastructure rollout
U Mobile picks Huawei and ZTE to deploy Malaysia’s second 5G network
U Mobile Names EdgePoint as a Preferred 5G IBC Infrastructure Partner for Its Upcoming 5G Rollout
Malaysia’s Maxis agreement with DNB to provide nationwide 5G services
TM and ZTE Malaysia to develop next-gen hybrid cloud 5G core network
Malaysia’s DNB to offer free 5G services to telcos during initial rollout
TM and ZTE Malaysia to develop next-gen hybrid cloud 5G core network
Momentum builds for wireless telco- satellite operator engagements
KDDI unveils AU Starlink direct-to-cell satellite service
KDDI-owned AU [1.] launched Japan’s first direct satellite service, connecting 40% of remote island and mountain populations in Japan that terrestrial networks cannot now reach. The new service, called AU Starlink Direct, is also available to subscribers of Okinawa Cellular, a KDDI-owned company serving the group of islands located in southern Japan. KDDI and Okinawa Cellular will start providing AU Starlink Direct, a direct to cell service between satellites and AU smartphones, on April 10, 2025. This is the first Direct to Cell satellite service in Japan.
Note 1. AU is a brand marketed by KDDI in the main islands of Japan and by Okinawa Cellular in Okinawa for their mobile cellular services. acquired au in 2001, initially through a merger of DDI, KDD, and IDO, and subsequently absorbing au’s parent company. KDDI continues to operate the AU brand for its mobile services.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The service is compatible with 50 smartphone models and is available free of charge to au users from today for the time being without the need to apply. Subscribers of AU and Okinawa Cellular whose iPhone and Android devices support satellite mode can try the service.

Source: Sean Prior/Alamy Stock Photo
Although AU has nearly 100% population coverage, mobile operators’ 4G and 5G networks effectively serve only about 60% of the population because mobile signal cannot reach remote islands and mountainous areas. The new AU Starlink Direct service allows the operator to bridge this digital divide by enabling customers in these dead zones to connect directly to a Starlink satellite using compatible smartphones.
The service can be used to communicate with family members and friends, in emergencies, etc., even in mountainous areas, island areas, and campgrounds and at sea where it is difficult to provide a telecommunications environment. KDDI is expanding the AU coverage area to all of Japan to bring the experience of “Connecting the Unconnected. wherever you see the sky.”
Gwynne Shotwell, President & COO of SpaceX, said: “I’m very excited to bring direct-to-cell phone connectivity to Japan through KDDI, the first in Asia and one of the first in the world. Both Starlink and direct-to-cell are game-changing technologies, making connecting the unconnected simple and bringing potentially life-saving capability to the people of Japan for disaster and other emergency responses.”
KDDI conducted a successful field test of AU Starlink Direct in Kumejima, Okinawa Prefecture, nearly six months ago.
References:
https://newsroom.kddi.com/english/news/detail/kddi_nr-533_3818.html
https://newsroom.kddi.com/english/news/detail/kddi_nr-299_3557.html
KDDI Partners With SpaceX to Bring Satellite-to-Cellular Service to Japan
SpaceX and KDDI to test Satellite Internet in Japan
KDDI Deploys DriveNets Network Cloud: The 1st Disaggregated, Cloud-Native IP Infrastructure Deployed in Japan
AWS Integrated Private Wireless with Deutsche Telekom, KDDI, Orange, T-Mobile US, and Telefónica partners
Samsung and KDDI complete SLA network slicing field trial on 5G SA network in Japan
KDDI claims world’s first 5G Standalone (SA) Open RAN site using Samsung vRAN and Fujitsu radio units
Samsung vRAN to power KDDI 5G network in Japan
T‑Mobile and EQT close JV to acquire FTTH network provider Lumos
T-Mobile and EQT (a purpose-driven global investment organization) announced the successful close of their joint venture (JV) to acquire fiber-to-the-home provider Lumos. As part of the transaction, many Lumos customers will soon become T-Mobile Fiber customers and begin enjoying new offers and benefits as they’re welcomed into the Magenta family.
This deal marks a major milestone in T-Mobile’s broadband growth and builds on the Un-carrier’s success in delivering best-in-class connectivity. By bringing more value and choice to the millions of Americans who have previously been underserved, T-Mobile continues to deliver on its mission to change broadband for good. T-Mobile will take full ownership of the customer experience, using its proven brand, nationwide retail footprint, differentiated marketing and customer-first service model to attract new subscribers.
Currently, Lumos operates a 7,500-mile fiber network, providing high-speed connectivity to 475,000 homes across the Mid-Atlantic. The joint venture combines the Un-carrier’s unique assets with EQT’s fiber infrastructure expertise, and Lumos’ scalable build capabilities to drive rapid network expansion, with the goal of reaching 3.5 million homes by the end of 2028. To fuel this growth, T-Mobile invested $950 million into the joint venture, with an additional $500 million planned between 2027 and 2028 to support further expansion. T-Mobile will provide an update to its full year 2025 guidance resulting from this transaction during its Q1 earnings call.
“T-Mobile is already the fastest-growing broadband provider in America, and expanding into fiber helps us take the next big step in delivering what customers truly want – faster, more reliable internet that simply works,” said Mike Katz, T-Mobile President of Marketing, Strategy and Products. “People deserve better when it comes to their home internet: fewer disruptions, more value, and support that actually feels supportive. We’re excited to welcome Lumos customers to the T-Mobile family and bring them the Un-carrier experience – built around their needs, fueled by innovation, and focused on making life easier.”
As Lumos customers continue to enjoy the same high-speed fiber internet they rely on today at low monthly prices, they’ll now also enjoy the value-add benefits they get from simply being a part of the T-Mobile family. They will have access to T-Mobile’s best-in-class customer experience and nationwide retail presence. Every plan also comes with unlimited data plus Wi-Fi equipment and installation included, so customers can enjoy the freedom and flexibility of reliable internet. Additionally, new and existing customers will enjoy VIP treatment through Magenta Status, which includes exclusive benefits like discounts on food, gas, entertainment and top brands, plus freebies every Tuesday in the T-Life app. All with T-Mobile’s standard ‘no exploding bills’ pricing structure.
“We’re excited to begin this joint venture and even more energized about what’s ahead,” said Brian Stading, CEO of Lumos. “Partnering with EQT and T-Mobile, we’re ready to scale faster, deliver cutting-edge fiber technology to more people, and change even more lives. This is about more than just internet – it’s about building the infrastructure of the future and creating lasting opportunity, connection, and impact for communities.”
“We are thrilled to officially embark on this next chapter of growth with Lumos alongside our partners at T-Mobile,” said Nirav Shah, Partner within EQT’s Infrastructure Advisory team. “This joint venture represents a powerful combination of EQT’s digital infrastructure expertise, Lumos’ proven fiber deployment capabilities, and T-Mobile’s customer-first approach and national reach. Together, we are well-positioned to accelerate access to high-quality fiber broadband to millions of underserved Americans and look forward to executing on our plans to deliver the critical connectivity that empowers communities across the country.”
As the fifth-largest and fastest-growing Internet service provider in the U.S., T-Mobile offers 5G Home Internet to 70 million homes, serving more than 6.4 million customers nationwide as of the end of 2024, and has introduced T-Mobile Fiber in parts of 32 U.S. markets. Fiber-to-the-home complements T-Mobile’s successful 5G Home Internet offering, which currently has over 1 million customers on its waitlist. This expansion in fiber opens an additional avenue to meet the growing demand for T-Mobile broadband. Through its strategic fiber partnerships and joint ventures, the Un-carrier expects to reach 12 to 15 million households, or more, with fiber by the end of 2030.
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/business/t-mobile-eqt-close-lumos-fiber-jv
T-Mobile & EQT Joint Venture (JV) to acquire Lumos and build out T-Mobile Fiber footprint
T-Mobile posts impressive wireless growth stats in 2Q-2024; fiber optic network acquisition binge to complement its FWA business
AT&T’s leads the pack of U.S. fiber optic network service providers
Fiber and Fixed Wireless Access are the fastest growing fixed broadband technologies in the OECD
Lumen and Ciena Transmit 1.2 Tbps Wavelength Service Across 3,050 Kilometers
Lumen and Ciena have teamed up for a significant new network trial. They have successfully demonstrated a 1.2Tbps wavelength spanning 3,050k m (more than 1,800 miles) on Lumen’s Ultra-Low-Loss (ULL) fiber network, making it the world’s longest 1.2 terabit non-regenerated signal. The trial leveraged Ciena’s WL6e technology over a 6500 photonic line system and Lumen’s fiber network between Denver and Dallas. They also used 800Gbps routing technology from Juniper’s PTX Series to establish Ethernet and IP services. Lumen’s 400G-enabled network already spans over 78,000 route miles, and the company continues to invest in next-generation fiber to enhance its Ultra-Low Loss (ULL) fiber network, the largest in North America.
Using 800G interfaces, Lumen and Ciena successfully tested and qualified the services to support wavelength, Ethernet, and IP services over the 1.2 Tbps single carrier channel. The live network trial from Denver to Dallas used Ciena’s latest WaveLogic 6 Extreme (WL6e) technology equipped in the Waveserver platform running over a 6500 photonic line system.
“1.2 terabits per second isn’t just about incredible speed and long distances, it’s about the value of enabling the next wave of digital transformation. Lumen is at the forefront of building a next-generation network designed to handle the explosive growth of AI and cloud workloads,” said Dave Ward, Lumen’s chief technology and product officer. “Our investment in increased capacity, powered by Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 technology, provides our hyperscale cloud partners and enterprises with the ultra-high-capacity connectivity needed to scale their AI and cloud applications. With 400G connectivity speeds today and a seamless upgrade path to 1.2 terabits, Lumen stands as the trusted network for AI.”
The trial also showcased the impressive performance and seamless interoperability between Ciena’s Waveserver platform and the Juniper PTX10002-36QDD Packet Transport Router at 800 Gbps over the ultra-long-haul 1.2 Tbps intercity network. By leveraging the performance, flexibility and scalability of the Juniper PTX Series Routers, Lumen successfully established Ethernet and IP services with minimal latency and zero packet loss throughout the tests.
Editor’s Note:
While the companies March 27th joint press release stated the 1.2T bps wavelength transport was a record, AT&T claimed two weeks earlier that it “achieved a long distance world record top speed of 1.6Tb/s over a single wavelength across 296 km of its long haul fiber optic network.” We reported that in this IEEE Techblog post. So yes, it’s a record considering the Lumen network wavelength distance was > 10 times that claimed by AT&T.

Faster connections up to 1.2 Tbps wavelengths means less lag, more capacity and the flexibility to handle the most data-hungry applications across multiple industries:
- AI & Machine Learning
- Hyperscale Cloud & Data Center Interconnects
- Financial Trading and Market Data Transport
- Cybersecurity & AI-powered Threat Intelligence
- Media & Streaming
“At Microsoft, the demand for ultra-high-speed, low-latency connectivity is growing exponentially as AI workloads, cloud applications, and real-time analytics scale,” Lumen said. “Lumen and Ciena’s successful wavelength trial showcases a forward-thinking approach to meeting these growing demands. By enabling more efficient data movement over vast distances, this solution helps us optimize cloud performance, enhance customer experiences, and support the rapid expansion of AI training and inferencing models across our global infrastructure.”
Ciena’s WL6e is the industry’s first high-bandwidth coherent transceiver using state-of-the-art 3nm silicon, capable of carrying capacity up to 1.6 terabits per second per wavelength.
“As the pioneer in high-speed optical innovation, we are dedicated to helping our customers set new benchmarks in network performance and efficiency,” said Brodie Gage, Ciena senior vice president, global products and supply chain. “This industry-first trial with Lumen marks a pivotal step in our efforts to prepare networks for the AI era. Lumen’s network does not stand still. Continuous investment in the latest network technology is essential for keeping up with bandwidth demands today and into the future.”
Additional Resources:
About Lumen Technologies:
Lumen is unleashing the world’s digital potential. We ignite business growth by connecting people, data, and applications – quickly, securely, and effortlessly. As the trusted network for AI, Lumen uses the scale of our network to help companies realize AI’s full potential. From metro connectivity to long-haul data transport to our edge cloud, security, managed service, and digital platform capabilities, we meet our customers’ needs today and as they build for tomorrow.
SOURCE: Lumen Technologies
References:
Analysts weigh in: AT&T in talks to buy Lumen’s consumer fiber unit – Bloomberg
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps