Author: Alan Weissberger
FCC legal advisor: Potential End of ACP Is the ‘Biggest Challenge’ Facing the Broadband Marketplace
On Wednesday April 17th, broadband officials and experts called for continued pressure to replenish the FCC’s Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) [1.]. Some panelists during Next Century Cities’ bipartisan tech policy conference also urged community leaders to engage with their state broadband offices as NTIA approves states’ plans for the broadband, equity, access and deployment program.
Note 1. The Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) is a benefit program from the FCC that helps households pay for broadband for work, school, and healthcare. The program is separate from the FCC’s Lifeline Program. The ACP is targeted at low-income families and individuals, and may include a one-time benefit of up to $100 for a phone or internet-capable device like a tablet, laptop, or desktop computer. The program also offers a monthly service discount and one device discount per household. The FCC said that unless lawmakers act to give the program additional funding, the full $30 discount will end at the end of April. The loss of ACP will hit poor people very hard and significantly widen the digital divide.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The biggest challenge facing the broadband marketplace right now is “the potential end of ACP next month,” said Hayley Steffen, legal adviser to Commissioner Anna Gomez. Ensuring the program is funded and continues is Gomez’s “highest priority right now,” Steffen said. FCC Consumer and Governmental Affairs Bureau Chief Alejandro Roark agreed, noting the program has “accomplished more over the past two years to bridge our country’s digital opportunity divide than any other standalone effort in our nation’s history.”
On Monday, a coalition of 271 civil-society groups and local, state and Tribal governments sent a letter to the U.S. House of Representatives that urges all members to sign a discharge petition to support the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) Extension Act. The legislation would provide an additional $7 billion to save a successful broadband-subsidy initiative.
Rep. Yvette Clarke, D-N.Y., is circulating a discharge petition (House Resolution 1119) in a bid to force a floor vote on her Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) Extension Act (HR-6929/S-3565), which would appropriate $7 billion to keep the ailing FCC broadband fund running through the end of FY 2024. ACP “has been a transformative force, empowering nearly 23 million American households in rural and urban communities with reliable, high-speed, and affordable broadband access,” Clarke said Wednesday in a statement.
“To continue this progress, I implore my colleagues to join me by signing the discharge petition. This will ensure [HR-6929] receives the vote it deserves” on the House floor. “We cannot turn our back on the progress made in closing the digital divide,” she said.
“Advocating in numbers is powerful,” said TDI CEO AnnMarie Killian. ACP “really requires that we take a stance and bring forth the importance of digital inclusion for all,” Killian said. DigitalC CEO Joshua Edmonds agreed, but “at the same time, we should walk and chew gum here and look at the value and potential of community-based networks, too.”
Affordability is “a key factor” for individuals with disabilities who rely on broadband for telecom relay services, Killian said, and the end of ACP could have a “significant impact on our economically disadvantaged consumers.” Fort Collins, Colorado, Broadband Executive Director Chad Crager encouraged local officials to start considering “another solution” to addressing affordability in their communities if ACP ends. “We hope it’s renewed” and extended, Crager said, but “the reality will not be forever.”
“This really is the moment for us to not give up” on advocating for ACP’s future, Roark said. ACP has been the FCC’s “best and most successful” effort at broadband affordability, Steffen said. Many households enrolled in the program will be eligible for the Lifeline benefit should ACP end, she said, but Lifeline is “definitely no replacement for ACP.” Roark also encouraged discussions on “how potentially ACP could be integrated into the USF framework.”
NTIA is “actively reviewing” states’ BEAD applications, Senior Policy Adviser Lukas Pietrzak said, noting that 48 states’ volume I proposals have already been approved (see 2403060046). “I have great expectations” for the states’ plans because “at the bare minimum, they did include Black community anchor institutions,” said Fallon Wilson, Multicultural Media, Telecom and Internet Council vice president-policy, citing states with several historically Black colleges and universities. The challenge now is ensuring the states’ plans are executed so that those institutions actually receive funding, Wilson said.
NTIA is also preparing to announce “in the next few weeks” how many applications it received for the second round of tribal broadband connectivity program funding, said Pietrzak. Projects funded by the middle-mile infrastructure grant program are “also starting to break ground in the spring and summer,” Pietrzak said, “which is exciting to see here.” He also noted that 20,000 devices have been distributed through the connecting minority communities program.
References:
https://communicationsdaily.com/article/view?search_id=853996&id=1940601
https://communicationsdaily.com/reference/2404100075?BC=bc_66205df7037e5
https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=aabc18cb-3e53-4085-bda8-42a894e71a08
WSJ: China’s Telecom Carriers to Phase Out Foreign Chips; Intel & AMD will lose out
China’s largest telecom firms were ordered earlier this year to phase out foreign computer chips from their networks by 2027. That news confirms and expands on reports from recent months. It was reported in the Saturday print edition of the Wall Street Journal (WSJ). The move will hit U.S. semiconductor processor companies Intel and Advanced Micro Devices. Asia Financial reported in late March that these retaliatory bans would cost the U.S. chip firms billions.
The deadline given by China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) aims to accelerate efforts by Beijing to halt the use of such core chips in its telecom infrastructure. The regulator ordered state-owned mobile operators to inspect their networks for the prevalence of non-Chinese semiconductors and draft timelines to replace them, the people said.
In the past, efforts to get the industry to wean itself off foreign semiconductors have been hindered by the lack of good domestically made chips. Chinese telecom carriers’ procurements show they are switching more to domestic alternatives, a move made possible in part because local chips’ quality has improved and their performance has become more stable, the people said.
Such an effort will hit Intel and AMD the hardest, they said. The two chip makers have in recent years provided the bulk of the core processors used in networking equipment in China and the world.
China’s MIIT, which oversees the regulation of the wireless, broadcasting and communication industries, didn’t respond to WSJ’s request for comment. China Mobile and China Telecom , the nation’s two biggest telecom carriers by revenue, also didn’t respond.
In March 2023, the Financial Times reported China is seeking to forbid the use of Intel and AMD chips, as well as Microsoft’s operating system, from government computers and servers in favor of local hardware and software. The latest purchasing rules represent China’s most significant step yet to build up domestic substitutes for foreign technology and echo moves in the US as tensions increase between the two countries. Among the 18 approved processors were chips from Huawei and state-backed group Phytium. Both are on Washington’s export blacklist. Chinese processor makers are using a mixture of chip architectures including Intel’s x86, Arm and homegrown ones, while operating systems are derived from open-source Linux software.
Beijing’s desire to wean China off American chips where there are homemade alternatives is the latest installment of a U.S.-China technology war that is splintering the global landscape for network equipment, semiconductors and the internet. American lawmakers have banned Chinese telecom equipment over national-security concerns and have restricted U.S. chip companies including AMD and Nvidia from selling their high-end artificial-intelligence chips to China.
China has also published procurement guidelines discouraging government agencies and state-owned companies from purchasing laptops and desktop computers containing Intel and AMD chips. Requirements released in March give the Chinese entities eight options for central processing units, or CPUs, they can choose from. AMD and Intel were listed as the last two options, behind six homegrown CPUs.
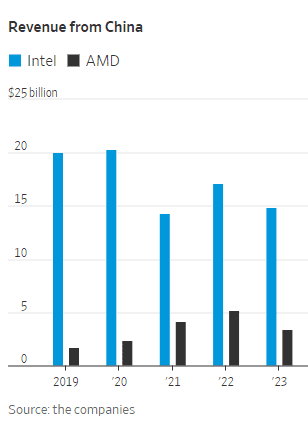
Computers with the Chinese chips installed are preapproved for state buyers. Those powered by Intel and AMD chips require a security evaluation with a government agency, which hasn’t certified any foreign CPUs to date. Making chips for PCs is a significant source of sales for the two companies.
China Mobile and China Telecom are also key customers of both chip makers in China, buying thousands of servers for their data centers in the country’s mushrooming cloud-computing market. These servers are also critical to telecommunications equipment working with base stations and storing mobile subscribers’ data, often viewed as the “brains” of the network. Intel and AMD have the lion’s share of the overall global market for CPUs used in servers, according to data from industry researcher TrendForce. In 2024, Intel will likely hold 71% of the market, while AMD will have 23%, TrendForce estimates. The researcher doesn’t break out China data.
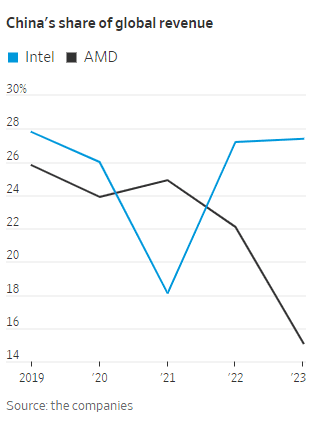
China’s localization policies could diminish Intel and AMD’s sales in the country, one of the most important markets for semiconductor firms. China is Intel’s largest market, accounting for 27% of the company’s revenue last year, Intel said in its latest annual report in January. The U.S. is its second-largest market. Its customers also include global electronics makers that manufacture in China.
In the report, Intel highlighted the geopolitical risk it faced from elevated U.S.-China tensions and China’s localization push. “We could face increased competition as a result of China’s programs to promote a domestic semiconductor industry and supply chains,” the report said.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/tech/china-telecom-intel-amd-chips-99ae99a9 (paywall)
https://www.ft.com/content/7bf0f79b-dea7-49fa-8253-f678d5acd64a
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY
IDC: Worldwide Smartphone Shipment +7.8% YoY; Samsung regains #1 position
According to preliminary data from the International Data Corporation (IDC) Worldwide Quarterly Mobile Phone Tracker, global smartphone shipments increased 7.8% year over year to 289.4 million units in the first quarter of 2024 (1Q24). This marks the third consecutive quarter of smartphone shipment growth, a strong indicator that a recovery is well underway.
“As expected, smartphone recovery continues to move forward with market optimism slowly building among the top brands,” said Ryan Reith, group vice president with IDC’s Worldwide Mobility and Consumer Device Trackers. “While Apple managed to capture the top spot at the end of 2023, Samsung successfully reasserted itself as the leading smartphone provider in the first quarter. While IDC expects these two companies to maintain their hold on the high end of the market, the resurgence of Huawei in China, as well as notable gains from Xiaomi, Transsion, OPPO/OnePlus, and vivo will likely have both OEMs looking for areas to expand and diversify. As the recovery progresses, we’re likely to see the top companies gain share as the smaller brands struggle for positioning.”
“The smartphone market is emerging from the turbulence of the last two years both stronger and changed,” said Nabila Popal, research director with IDC’s Worldwide Tracker team. “Firstly, we continue to see growth in value and average selling prices (ASPs) as consumers opt for more expensive devices knowing they will hold onto their devices longer. Secondly, there is a shift in power among the Top 5 companies, which will likely continue as market players adjust their strategies in a post-recovery world. Xiaomi is coming back strong from the large declines experienced over the past two years and Transsion is becoming a stable presence in the Top 5 with aggressive growth in international markets. In contrast, while the Top 2 players both saw negative growth in the first quarter, it seems Samsung is in a stronger position overall than they were in recent quarters.”
| Top 5 Companies, Worldwide Smartphone Shipments, Market Share, and Year-Over-Year Growth, Q1 2024 (Preliminary results, shipments in millions of units) | |||||
| Company | 1Q24 Shipments | 1Q24 Market Share | 1Q23 Shipments | 1Q23 Market Share | Year-Over-Year Change |
| 1. Samsung | 60.1 | 20.8% | 60.5 | 22.5% | -0.7% |
| 2. Apple | 50.1 | 17.3% | 55.4 | 20.7% | -9.6% |
| 3. Xiaomi | 40.8 | 14.1% | 30.5 | 11.4% | 33.8% |
| 4.Transsion | 28.5 | 9.9% | 15.4 | 5.7% | 84.9% |
| 5. OPPO | 25.2 | 8.7% | 27.6 | 10.3% | -8.5% |
| Others | 84.7 | 29.3% | 79.0 | 29.4% | 7.2% |
| Total | 289.4 | 100.0% | 268.5 | 100.0% | 7.8% |
| Source: IDC Quarterly Mobile Phone Tracker, April 15, 2024 | |||||

Notes:
• Data are preliminary and subject to change.
- Company shipments are branded device shipments and exclude OEM sales for all vendors.
- The “Company” represents the current parent company (or holding company) for all brands owned and operated as a subsidiary.
- Figures represent new shipments only and exclude refurbished units.
References:
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS52032524
AST SpaceMobile: “5G” Connectivity from Space to Everyday Smartphones
Huawei reports 1% YoY revenue growth in 3Q-2023; smartphone sales increase in China
Swisscom (with Ericsson) to offer the world’s best and most sustainable mobile network
Swisscom, the leading network operator in Switzerland, is planning to transform its wireless 3G/4G/5G network into a “smart network” by extending its partnership with Ericsson for another three years. Under the partnership, Ericsson will continue to supply the hardware and software for Swisscom, enabling it to enhance its customer experience and further develop the mobile network with a focus on sustainability.
The strategic partnership between Swisscom and Ericsson dates back to 2015 and has been underscored by a series of wins in mobile network tests from key trade magazines.
Swisscom is extending its strategic partnership with Ericsson for another three years, aiming to transform its network into a smart network. Through automation, the use of artificial intelligence (AI), and increased innovation, the network will be modernized to continue providing the best customer experience now and in the future.
Another important development stream is marked by continuous spectrum refarming to New Radio (NR), with which the service provider prepares its network for 5G Standalone deployment with the possibility of launching new services.
Ericsson has long provided Swisscom with its cloud based Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI) solution to support its telecom applications. With this new deal the service provider will now take on Ericsson’s Cloud Native Infrastructure solution (CNIS). For Swisscom, this means further enhancing the network’s well-established reliability and expanding the ability to host cloud-native telecom applications from Ericsson as well as from third-party providers. It will also help reduce overheads needed to manage the cloud platform and infrastructure, introduce further energy efficiencies, and optimize the total cost of ownership (TCO) overall. The deployment will bring together a close collection of telecom partner companies such as Extreme Networks and Dell Technologies, which contribute components, infrastructure and capabilities to the solution, all collaboratively engaged to ensure Swisscom and its subscribers enjoy the best possible network performance.

Image Credit: Ericsson
Gerd Niehage, CTIO Swisscom, explains, ” We’ve been working closely with Ericsson for over 10 years with a great amount of trust and success. We are now taking the next step in this long-standing strategic partnership as we endeavour to turn Switzerland’s best network into its smartest one. This will enable us to not only offer our customers the best customer experience, but also to place an even greater focus on sustainability and innovation.”
Daniel Leimbach, Head of Customer Unit Western Europe at Ericsson, adds, “In this innovative partnership, Swisscom’s characteristically Swiss pursuit of perfection meets the global technology leadership from Sweden’s Ericsson. Our common goal is to raise the bar even higher and continue to develop Switzerland’s best network into its smartest one. We have already set important benchmarks for the global development of the telecommunications market from within Switzerland in recent years.”
The far-reaching agreement, with a special focus on innovation, performance, and energy efficiency will see the introduction of Ericsson’s lightweight dual-band Radio 4490 as well as the company’s next-generation RAN processor from Ericsson’s RAN Compute portfolio, designed to serve all technologies from a single box and supporting real-time AI processing.
The agreement also includes deployment of Ericsson’s Massive MIMO portfolio across multiple sites as a part of the continued effort to expand coverage. It also will bring network improvements from the introduction of Ericsson’s Cloud Native Infrastructure Solution (CNIS) to support telecom applications across the business, and which enables software upgrades during operation and is also highly energy-efficient. Ericsson’s Intelligent Automation Platform (EIAP) and it’s open rApp (automation applications) ecosystem will also be introduced, offering the Swisscom network access to a wide range of new and innovative applications from Ericsson and other ecosystem members which will bring access to a host of new capabilities to create and maintain world-beating services. Here too, the focus is on performance and efficiency.
Swisscom aims to offer its customers the best and most sustainable network, so the new focus of the strategic partnership is to make the Swisscom network one of the most efficient mobile networks in the world.
Swisscom’s network is already fully powered by renewable energy, and the partners have taken a step further with the launch of an Energy Sustainability Programme (UK spelling) to intelligently reduce the energy consumption of mobile communications systems.
To maximize the partnership, Ericsson and Swisscom employees collaborate in mixed teams to drive innovations and projects forward for the continuous development of the mobile network. This close cooperation offers both companies opportunities to expand their competitive position and customer centricity. With the best network in Switzerland, Swisscom aims to strengthen the competitiveness of the Swiss economy and drive the country’s digital transformation.
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/2024/4/swisscom-selects-ericsson-to-future-proof-mobile-network
Swisscom, Ericsson and AWS collaborate on 5G SA Core for hybrid clouds
Ericsson and ACES partner to revolutionize indoor 5G connectivity in Saudi Arabia
Telstra achieves 340 Mbps uplink over 5G SA; Deploys dynamic network slicing from Ericsson
BT Group, Ericsson and Qualcomm demo network slicing on 5G SA core network in UK
Finland’s Elisa, Ericsson and Qualcomm test uplink carrier aggregation on 5G SA network
Analysis: FCC attempt to restore Net Neutrality & U.S. standards for broadband reliability, security, and consumer protection
FCC Chairwoman Rosenworcel announced the tentative agenda for the April 2024 Open Meeting scheduled for 10:30 am EDT on Thursday, April 25, 2024. As part of the agenda, the Commission will consider a draft Declaratory Ruling, Order, Report and Order, and Order on Reconsideration (Order) that would restore Net Neutrality [1.] and bring back a national standard for broadband reliability, security, and consumer protection.
Note 1. Net neutrality is a concept that internet service providers (ISPs) should treat all data on the internet equally. This means that ISPs should not block, slow down, or charge more money for access to certain websites or services. Net neutrality is important because it helps to ensure that everyone has equal access to the internet.
If the FCC order is approved, the Chairwoman’s proposal would ensure that broadband services are treated as an essential resource deserving of FCC oversight under Title II authority [2].
Note 2. U.S. carriers providing “telecommunications services,” are regulated under Title II. of the 1934 U.S. Communications Act.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
What the Declaratory Ruling and Order Would Do:
Classify broadband Internet access service as a telecommunications service and classify mobile broadband Internet access service as a commercial mobile service.
Find that reclassification would provide the Commission with additional authority to safeguard national security, advance public safety, protect consumers, and facilitate broadband deployment.
Find that classification of broadband Internet access service as a telecommunications service represents the best reading of the text of the Act, and that such reclassification accords with Commission and court precedent and is fully justified under the Commission’s long standing authority to classify services subject to its jurisdiction.
Establish broad, tailored forbearance—including no rate regulation, no tariffing, no unbundling of last-mile facilities, and no cost accounting rules—in the FCC’s application of Title II to broadband Internet access service providers (ISPs).
What the Report and Order Would Do:
Reinstate straightforward, clear rules that prohibit blocking, throttling, or engaging in paid or affiliated prioritization arrangements, and adopt certain enhancements to the transparency rule.
Reinstate a general conduct standard that prohibits unreasonable interference or unreasonable disadvantage to consumers or edge providers.
Make clear that the Commission will employ a case-by-case review under sections 201 and 202 to ensure that Internet traffic exchange practices do not harm the open Internet.
Establish a multi-faceted enforcement framework comprised of advisory opinions, enforcement advisories, Commission-initiated investigations, and informal and formal complaints.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Legal Opinions on FCC net neutrality draft order:
Legal experts and FCC watchers say the net neutrality draft order on the FCC’s April 25th open meeting agenda will face legal arguments similar to what the 2015 net neutrality order did, with many of the same parties involved.
Starting with a briefing for reporters the day before the draft order was released, the FCC argued the proposed rules would survive legal challenge. Net neutrality rules are “wildly popular,” Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel said in California last week, adding the draft rules are “court approved.” Rosenworcel said, “I want to make sure that they are again the law of the land.”
Major Questions:
The proposed order is “legally vulnerable,” Free State Foundation President Randolph May told Commissioner Brendan Carr, according to a filing Friday in docket 23-320. May said it was “extraordinary … for an agency to propose burdensome restrictive major regulatory mandates without any meaningful evidence of any present harm to consumers or competition.”
Daniel Deacon, assistant professor at the University of Michigan Law School, pointed to Justice Brett Kavanaugh’s dissent as a D.C. circuit judge in the 2017 en banc affirmation of the 2015 net neutrality rules. Kavanaugh argued that imposing net neutrality rules via Title II represents a “major” policy that requires clear congressional authorization under the major questions doctrine, and that such authorization was lacking, Deacon said: SCOTUS “could reach that conclusion regardless of what they end up doing in Loper Bright and Relentless.”
The commission tries to head off major questions arguments in the draft order. “We do not think the major-questions doctrine properly comes into play in this context at all,” it said. “We are simply following the best reading of the Communications Act, as demonstrated by the statute’s plain text, structure, and historical context: there is no call for deference to an interpretation that is not the statute’s most natural reading.”
The rules won’t “have the extraordinary economic and political effect required to implicate the major-questions doctrine,” according to the draft order.
While the rules “will have substantial benefits for the American public … not every regulatory action that has substantial effects is so momentous as to trigger the major-questions doctrine. The Internet will continue to sustain its enormous economic and social value under our actions today, just as it did under the 2015 Order.”
The pending net neutrality order “is the antithesis of the Supreme Court’s major-questions cases,” the FCC said. “There is nothing novel about the Commission’s exercise of its classification power here,” as the agency has exercised it numerous times, it said. “Regulating communications services and determining the proper regulatory classification of broadband falls squarely within the Federal Communications Commission’s wheelhouse,” the commission said.
Cato’s Skorup disagreed. The agency sees national security implications in net neutrality and finds that it’s important for free speech, “telegraphing they believe” it’s a major question, he said.
It’s unclear how the Supreme Court seemingly heading toward some change to its Chevron doctrine would play out in the inevitable appeal of the FCC’s order. The net neutrality issue isn’t about the FCC having superior insight into the nature of broadband but is a political question about oversight, said Douglas Holtz-Eakin, American Action Forum president. By the time a net neutrality case comes before the D.C. Circuit, there would likely be a SCOTUS ruling affecting Chevron, and the appellate court would have to be guided by it, he said.
CCIA’s Joyce said that even if SCOTUS rejects Chevron, that doesn’t apply to net neutrality, since it doesn’t involve a brand new and novel FCC action. “How can you possibly say that about whether broadband is a Title II service?” she asked. “This stuff is old.”
Some see a net neutrality legal fight charting new territory. The draft order is broader than 2015’s, with issues of national security and broadband contributing to Universal Service Fund (USF), so there are several different issues than were involved in the past, said Holtz-Eakin.
While it seems likely that SCOTUS will curtail or reject the Chevron doctrine sometime this summer, that isn’t going to deter the FCC, Skorup said. But it could change how the D.C. Circuit — which upheld the 2015 net neutrality order — approaches things, he said. Given SCOTUS reversals of the D.C. Circuit on federal agency deference issues, such as 2021’s Alabama Association of Realtors decision, “I would hope the D.C. Circuit would get the message … that it needs to apply more scrutiny than it is giving agencies currently,” he said.
“The net neutrality rule will undoubtedly be characterized by the reviewing court as a major question because it is an issue of ‘vast economic and political significance,’” emailed Thomas McGarity, University of Texas’ Lozano Long Professor in Administrative Law. “That being the case, Chevron will be inapplicable,” he said: “The court will only ask whether Congress has clearly authorized the agency to promulgate the rule. The clarity of the authorization will be the primary issue on appeal.”
Other lawyers said it’s not preordained that the order will be overturned.
“It’s important to remember that the only reason why broadband is an ‘information service’ is because of Chevron deference,” said Public Knowledge Senior Vice President Harold Feld. The 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals in 2003 ruled that cable modem service was a telecom service, he said. SCOTUS’ 2005 Brand X decision, then “reversed the 9th Circuit on the grounds of Chevron deference. In 2019, the 2017 order rolling back the 2015 net neutrality rules survived a challenge at the D.C. circuit only because of precedent,” Feld said.
Two of the judges, Patricia Millett and Robert Wilkins, indicated they would have found the rollback order “arbitrary … but for Chevron and Brand X. One cannot help what activist judges will do,” but if the pending order is returned to the D.C. Circuit, “I would expect it to be affirmed,” Feld added.
The Supreme Court held in Brand X that the FCC has the discretion to decide how to classify broadband, emailed Benton Institute for Broadband & Society Senior Counselor Andrew Schwartzman.
“If, as is likely, the Chevron, and Brand X precedents will be modified to some degree this spring, and depending on what the Court says, the matter might then have to be resolved by analysis of the text,” he said.
Perkins Coie’s Martin said it’s likely the D.C. Circuit could affirm the FCC’s action again, as there’s consistent precedent that agency action on the matter is OK. However, if SCOTUS overturns Chevron, the appellate court may feel compelled to come out differently, he said. And if the D.C. Circuit overturns the FCC, SCOTUS could very well deny any subsequent cert petition by the agency, he said. Schwartzman questioned whether SCOTUS will ultimately hear the case. The court is “loath to overrule precedent unless absolutely necessary,” he said.
CTIA discussed concerns about how non-broadband internet access services are treated under the draft net neutrality order circulated by Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel. In meetings with staff for all five commissioners, CTIA asked the FCC to remove warnings not present in the 2015 order. Non-BIAS services, and network slicing, have emerged as major issues. The draft “favorably references non-BIAS use cases that ‘cannot be met over the Open Internet,’ but any suggestion that an offering that can function to some extent over BIAS must be offered over BIAS would be a dramatic shift from the 2015 framework,” said a filing posted Wednesday in docket 23-320. The draft also says the commission “will closely monitor any services that have a negative effect on the performance of BIAS in any given moment or the capacity available for BIAS over time” and that the commission “will be watchful of services that do not require isolated capacity.
CTIA said, “The 2015 Order did not set forth any of these rigid warnings, and for good reason. The net effect of such guidance could restrict the offering of non-BIAS services. Customers would lose out on choice and innovation, and networks would operate less efficiently.”
References:
Link to the Draft Declaratory Ruling, Order, Report and Order, and Order on Reconsideration: https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-401676A1.pdf
Link to the April 25, 2024 Meeting webpage: https://www.fcc.gov/april-2024-open-commission-meeting
https://www.fcc.gov/document/promoting-fast-open-and-fair-internet
https://www.reuters.com/technology/fcc-vote-restore-net-neutrality-rules-reversing-trump-2024-04-02/
FCC Draft Net Neutrality Order reclassifies broadband access; leaves 5G network slicing unresolved
FCC Votes to Reverse Net Neutrality & No Longer Regulate Broadband Internet Services
Internet Association to Join Law Suits to Restore Net Neutrality
Is FCC Net Neutrality Rollback Coming? Will that spark cablcos investment in rural/ suburban areas?
https://communicationsdaily.com/article/view?search_id=851581&id=1935719
Quintessent: Supporting “newer AI workloads” with lasers and DWDM
Integrated-photonics companies have increasingly seized on the opportunities in advanced AI. Many are building high-speed optical interconnects for data centers, with the electrical–optical conversion as close as possible to the number-crunching GPU or application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC).
However, Goleta, CA based startup Quintessent, is focusing on solving what it says is a major bottleneck hindering commercial deployment of such high-speed optical interconnects for AI – the light source or laser, which is currently the “weakest link” in system reliability and scalability, according to co-founder and CEO, Alan Liu.
Quintessent’s answer lies in part in its laser technology, incorporating quantum dots (QDs)—the semiconductor nanocrystals celebrated in the 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry—and multiwavelength comb lasers. The firm believes that combination can boost bandwidth, improve efficiency and cut latency by enabling highly parallel dense wavelength-division multiplexed (DWDM) optical links for computing clusters and data centers. And in late March, the company announced that it had secured US$11.5 million in new seed funding to push its vision closer to commercialization.
Quintessent was co-founded in 2019 by Optica Fellow John Bowers of the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB), USA, who serves as the company’s board chairman, and Liu, formerly a student in Bowers’ lab. In a conversation with OPN in November 2023, Liu noted that his Ph.D. work in the lab, which spanned the years from 2011 to 2017, focused on what he called “one of the glaring holes in silicon photonics”: how to integrate the light source. His work specifically involved integration of QD lasers with silicon photonics, which subsequently became “one of the core technologies for Quintessent.”
Quintessent co-founders Alan Liu (left) and John Bowers. Image: Courtesy of A. Liu.
Even at that time, Liu had some stirrings in the direction of commercializing the technology. Ultimately, though, after earning his Ph.D. in 2017, he left Santa Barbara for a two-year stint at a consulting firm in the Washington, DC, area. There, he worked as a subject-matter expert in photonics on projects for the US Department of Defense’s advanced-research arm, DARPA, and the US Department of Energy’s counterpart, ARPA-E.
Still, the entrepreneurial itch never quite left Liu. Nor did his fascination with the promise of QD laser technology, as he saw subsequent work done in Bowers’ lab to further advance the performance of those lasers and demonstrate new functions with them, including multiwavelength comb sources.
In 2019, Liu says, he got a call from Bowers, who noted that he was seeing “a lot of interest” from industry in the technology the lab was developing, but that there was “no company to sell it.” When Bowers asked if he wanted to help start one up, Liu recalls, “it didn’t take me long to sign on and say yes.” In the course of the next few years, they built Quintessent’s core team, drawing on numerous other contacts both within and outside of Bowers’ UCSB lab, and pulled in a mix of government R&D and venture funding, including the $11.5 million seed round announced in March 2024. The business case for Quintessent, Liu says, rests largely on “some of the newer AI workloads that were coming into the fray” beginning in the late 2010s, and their immense appetite for computing resources and power.
“If you’re going to be optimizing for power efficiency and bandwidth and latency, the required architecture is one that’s wide and parallel,” he explains. And for optics, at some point, trying to achieve that level of parallelism by adding more and more spatial or fiber channels becomes unwieldy.
The alternative solution, Liu says, is a highly parallel DWDM architecture—using not lots of fibers but “lots of lambdas.” For the crushing workloads of advanced AI, DWDM is optimal, as it “allows you to both simultaneously optimize bandwidth and minimize power and latency,” without relying on digital signal processing or a potential rat’s nest of individual fiber interconnects to boost overall bandwidth.
One key for achieving that vision was “enabling a new kind of laser, and using that laser to enable new communication and transceiver architectures,” according to Liu. “That was a common gap I saw across the industry.” Particularly in the context of AI, Liu observes, a big argument for better lasers has to do with reliability.
Particularly in the context of AI, Liu observes, a big argument for better lasers—and especially for Quintessent’s concept of simplifying wavelength scaling using multiwavelength comb sources fabricated from InAs/GaAs QD material—has to do with reliability. “Optical solutions for AI are going to have to be at least an order of magnitude more reliable than what we see today in existing transceivers,” he maintains. “If you imagine a scenario where there’s 10 times more optics deployed, and your failure rates stay the same, then you’ve got 10 times more failures you’re asking the customer to deal with. That gets a little dicey.”
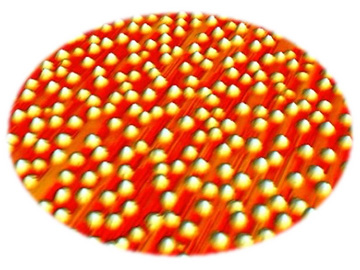
An atomic force microscopy (AFM) image of InAs/GaAs quantum dots. Image: Courtesy of A. Liu
Getting to better overall reliability will require much more reliable lasers, Liu believes, as lasers are “kind of the weakest link at the moment.” And he and the Quintessent team think that QD lasers offer a way forward, as they are “intrinsically more reliable than quantum well materials today.”
Tobias Egle, a materials scientist who works with M Ventures, one of the partners in the most recent Quintessent funding round, explained the difference further in a separate call with OPN. “These QD lasers are not as affected by material defects, dislocations and so on,” Egle says. “Simply put, a single dislocation through the facet or active region of a traditional laser can lead to complete failure. In contrast, when you have billions of QDs which are independent of one another, the presence of a single dislocation has a negligible impact on your overall performance.”
Quintessent experienced a milestone a year ago, when the company and Tower Semiconductor—the Israel-based global foundry firm with which Quintessent had partnered since 2021—announced that they had achieved what they called the world’s first heterogenous integration of GaAs quantum dot lasers in a commercial foundry silicon photonics process. The pair also unveiled a foundry silicon platform, PH18DB, targeted for the telecom and datacom optical transceiver market, and an accompanying process development kit (PDK).
Meanwhile, on the funding side, Quintessent announced an oversubscribed US$11.5 million seed round in March 2024, with an investment group led by Osage University Partners (OUP) and including, in addition to M Ventures, participation by previous Quintessent funders Sierra Ventures, Foothill Ventures and Entrada Ventures. In a press release accompanying the recent funding announcement, Liu said the new money would let the company “grow our team and accelerate the development of highly scalable and highly reliable optical interconnects that transcend the scaling limitations of incumbent solutions,” based on the firm’s core technology of QD-enabled multiwavelength comb lasers.
Operationally, Liu told OPN that—having “checked off all of the fundamental technology questions” regarding the laser technology’s feasibility—Quintessent is now focused on optimizing the laser design, which he calls “a key Lego block,” and of other pieces of the overall architecture to validate system-level functionality. Then, an important next step will be getting chips into customers’ hands for ground-truthing and feedback, and using that feedback to “drive forward the commercialization roadmap.”
“So samples, then low-volume pilots, then high-volume manufacturing—simple, right?” he laughs. Liu seems exhilarated by the challenge. “I’m one of those people that liked to play video games in the hard, hard mode,” he says. “If it’s too easy, you don’t get much enjoyment out of it.”
References:
https://www.optica-opn.org/Home/Industry/2024/April/Quintessent_Targets_Lasers_for_AI
Co-Packaged Optics to play an important role in data center switches
Ranovus Monolithic 100G Optical I/O Cores for Next-Generation Data Centers
Dell’Oro: DWDM equipment market to exceed $17 billion by 2026
Sharing of lower 3 GHz band in U.S. is unclear after DoD redacted report
The U.S. wireless industry would like to use the lower 3 GHz band, but it’s currently occupied by the military. The DoD says sharing between federal and commercial systems is not feasible unless certain conditions are met. Sharing between federal radar and mobile systems presents unique challenges, especially for airborne operations.
The DoD acknowledges the potential of freeing up some of the spectrum for 5G use, emphasizing that in order to make the lower 3 GHz band available for commercial use a “coordination framework must facilitate spectrum sharing in the time, frequency, and geography domains,” notes Broadband Breakfast.

5G already coexists with U.S. military systems in the lower 3 GHz band in more than 30 countries, said Umair Javed, CTIA senior vice president-spectrum. However, the future of the lower 3 GHz band in the U.S. is unsettled following DoD’s public release last week of a redacted version of its Emerging Mid-Band Radar Spectrum Sharing Feasibility Assessment [1.].
Note 1. Emerging Mid-Band Radar Spectrum Sharing Feasibility Assessment report
This redacted DoD report examines military systems located in lower 3 GHz spectrum, with an eye on potential sharing but not on clearing as sought by CTIA and carriers. It concludes that sharing the 3.1-3.45 GHz band between federal and commercial systems is not currently feasible “unless certain regulatory, technological, and resourcing conditions are proven and implemented.” The report originally came out in September 2023.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..

DoD Chief Information Officer John Sherman said in February the department is willing to consider clearing part of the band “perhaps for future airborne radars,” which wasn’t part of EMBRSS. The spectrum is home to the Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS), which DOD is upgrading. Airborne radars are considered the most difficult to address in a sharing regime because they are so mobile.
The lower 3 GHz is one of a few bands allowing for military radars “with small enough antenna apertures” to be mobile, with “sufficient range capabilities to serve as medium and long-range radars,” the study says. It notes the propagation characteristics of mid-band spectrum, which also make it a top target of carriers. “A complicating factor … has been the increased packing of federal systems relocated from other bands, including those as a result of repurposing from previous auctions,” the study says.
DoD found that more than 120 different ground-based, ship-borne and airborne radars use the band. While details are redacted, the report offers basic information on how the bands are used, for everything from land-based radar for tracking threats to Coast Guard and Navy search and rescue missions to air-traffic control to tracking bird migrations with an eye toward avoiding collisions. It also discusses the Department of Homeland Security’s uses.
But EMBRSS says sharing is possible using a dynamic spectrum management system (DSMS). It cites sharing in the citizens broadband radio service band. A DSMS, which “evolves the CBRS framework … with advanced interference mitigation features” addressing the unique needs of airborne systems, “provides a feasible path forward for spectrum sharing between the Federal and commercial systems,” EMBRSS said.
Blair Levin wrote Wednesday in a note to New Street clients.:
“The report’s most significant implications for investors involve what the DOD report did not do. It did not resolve any issues or provide a timetable for doing so. Thus, we remain far from resolving the question of where the spectrum that the wireless carriers argue they will need by 2027 will come from. While some advocate exclusive licensing of the band, and others sharing, DOD “almost certainly retains a veto power over any potential outcome,” he said.
DoD leaders, including John Sherman, the Pentagon’s top IT official, met Monday with the National Spectrum Consortium, a group of more than 350 members of academia and industry who work with the electromagnetic spectrum, to take the first steps to outline a framework to share the bandwidth with industry and to kickstart a discussion on a spectrum management program.
“No surprise. We know that spectrum will be challenging,” said Kevin Mulvihill, the Pentagon’s deputy chief information officer for command, control and communications. “But we need to work together across industry, government and academia to explore potential ways to achieve spectrum coexistence for the benefit of the entire nation while ensuring that the spectrum sharing that we choose does not negatively affect the primary mission of the Department of Defense.”
References:
https://dodcio.defense.gov/Portals/0/Documents/Library/DoD-EMBRSS-FeasabilityAssessmentRedacted.pdf
https://www.fierce-network.com/5g/dod-releases-long-awaited-report-lower-3-ghz
If the Pentagon has to share 5G spectrum, it wants some new ground rules – Breaking Defense
NTT & Yomiuri: ‘Social Order Could Collapse’ in AI Era
From the Wall Street Journal:
Japan’s largest telecommunications company and the country’s biggest newspaper called for speedy legislation to restrain generative artificial intelligence, saying democracy and social order could collapse if AI is left unchecked.
Nippon Telegraph and Telephone, or NTT, and Yomiuri Shimbun Group Holdings made the proposal in an AI manifesto to be released Monday. Combined with a law passed in March by the European Parliament restricting some uses of AI, the manifesto points to rising concern among American allies about the AI programs U.S.-based companies have been at the forefront of developing.
The Japanese companies’ manifesto, while pointing to the potential benefits of generative AI in improving productivity, took a generally skeptical view of the technology. Without giving specifics, it said AI tools have already begun to damage human dignity because the tools are sometimes designed to seize users’ attention without regard to morals or accuracy.
Unless AI is restrained, “in the worst-case scenario, democracy and social order could collapse, resulting in wars,” the manifesto said.
It said Japan should take measures immediately in response, including laws to protect elections and national security from abuse of generative AI.
A global push is under way to regulate AI, with the European Union at the forefront. The EU’s new law calls on makers of the most powerful AI models to put them through safety evaluations and notify regulators of serious incidents. It also is set to ban the use of emotion-recognition AI in schools and workplaces.
The Biden administration is also stepping up oversight, invoking emergency federal powers last October to compel major AI companies to notify the government when developing systems that pose a serious risk to national security. The U.S., U.K. and Japan have each set up government-led AI safety institutes to help develop AI guidelines.
Still, governments of democratic nations are struggling to figure out how to regulate AI-powered speech, such as social-media activity, given constitutional and other protections for free speech.
NTT and Yomiuri said their manifesto was motivated by concern over public discourse. The two companies are among Japan’s most influential in policy. The government still owns about one-third of NTT, formerly the state-controlled phone monopoly.
Yomiuri Shimbun, which has a morning circulation of about six million copies according to industry figures, is Japan’s most widely-read newspaper. Under the late Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and his successors, the newspaper’s conservative editorial line has been influential in pushing the ruling Liberal Democratic Party to expand military spending and deepen the nation’s alliance with the U.S.
The two companies said their executives have been examining the impact of generative AI since last year in a study group guided by Keio University researchers.
The Yomiuri’s news pages and editorials frequently highlight concerns about artificial intelligence. An editorial in December, noting the rush of new AI products coming from U.S. tech companies, said “AI models could teach people how to make weapons or spread discriminatory ideas.” It cited risks from sophisticated fake videos purporting to show politicians speaking.
NTT is active in AI research, and its units offer generative AI products to business customers. In March, it started offering these customers a large-language model it calls “tsuzumi” which is akin to OpenAI’s ChatGPT but is designed to use less computing power and work better in Japanese-language contexts.
An NTT spokesman said the company works with U.S. tech giants and believes generative AI has valuable uses, but he said the company believes the technology has particular risks if it is used maliciously to manipulate public opinion.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
From the Japan News (Yomiuri Shimbun):
Challenges: Humans cannot fully control Generative AI technology
・ While the accuracy of results cannot be fully guaranteed, it is easy for people to use the technology and understand its output. This often leads to situations in which generative AI “lies with confidence” and people are “easily fooled.”
・ Challenges include hallucinations, bias and toxicity, retraining through input data, infringement of rights through data scraping and the difficulty of judging created products.
・ Journalism, research in academia and other sources have provided accurate and valuable information by thoroughly examining what information is correct, allowing them to receive some form of compensation or reward. Such incentives for providing and distributing information have ensured authenticity and trustworthiness may collapse.
A need to respond: Generative AI must be controlled both technologically and legally
・ If generative AI is allowed to go unchecked, trust in society as a whole may be damaged as people grow distrustful of one another and incentives are lost for guaranteeing authenticity and trustworthiness. There is a concern that, in the worst-case scenario, democracy and social order could collapse, resulting in wars.
・ Meanwhile, AI technology itself is already indispensable to society. If AI technology is dismissed as a whole as untrustworthy due to out-of-control generative AI, humanity’s productivity may decline.
・ Based on the points laid out in the following sections, measures must be realized to balance the control and use of generative AI from both technological and institutional perspectives, and to make the technology a suitable tool for society.
Point 1: Confronting the out-of-control relationship between AI and the attention economy
・ Any computer’s basic structure, or architecture, including that of generative AI, positions the individual as the basic unit of user. However, due to computers’ tendency to be overly conscious of individuals, there are such problems as unsound information spaces and damage to individual dignity due to the rise of the attention economy.
・ There are concerns that the unstable nature of generative AI is likely to amplify the above-mentioned problems further. In other words, it cannot be denied that there is a risk of worsening social unrest due to a combination of AI and the attention economy, with the attention economy accelerated by generative AI. To understand such issues properly, it is important to review our views on humanity and society and critically consider what form desirable technology should take.
・ Meanwhile, the out-of-control relationship between AI and the attention economy has already damaged autonomy and dignity, which are essential values that allow individuals in our society to be free. These values must be restored quickly. In doing so, autonomous liberty should not be abandoned, but rather an optimal solution should be sought based on human liberty and dignity, verifying their rationality. In the process, concepts such as information health are expected to be established.
Point 2: Legal restraints to ensure discussion spaces to protect liberty and dignity, the introduction of technology to cope with related issues
・ Ensuring spaces for discussion in which human liberty and dignity are maintained has not only superficial economic value, but also a special value in terms of supporting social stability. The out-of-control relationship between AI and the attention economy is a threat to these values. If generative AI develops further and is left unchecked like it is currently, there is no denying that the distribution of malicious information could drive out good things and cause social unrest.
・ If we continue to be unable to sufficiently regulate generative AI — or if we at least allow the unconditional application of such technology to elections and security — it could cause enormous and irreversible damage as the effects of the technology will not be controllable in society. This implies a need for rigid restrictions by law (hard laws that are enforceable) on the usage of generative AI in these areas.
・ In the area of education, especially compulsory education for those age groups in which students’ ability to make appropriate decisions has not fully matured, careful measures should be taken after considering both the advantages and disadvantages of AI usage.
・ The protection of intellectual property rights — especially copyrights — should be adapted to the times in both institutional and technological aspects to maintain incentives for providing and distributing sound information. In doing so, the protections should be made enforceable in practice, without excessive restrictions to developing and using generative AI.
・ These solutions cannot be maintained by laws alone, but rather, they also require measures such as Originator Profile (OP), which is secured by technology.
Point 2: Legal restraints to ensure discussion spaces to protect liberty and dignity, and the introduction of technology to cope with related issues
・ Ensuring spaces for discussion in which human liberty and dignity are maintained has not only superficial economic value, but also a special value in terms of supporting social stability. The out-of-control relationship between AI and the attention economy is a threat to these values. If generative AI develops further and is left unchecked like it is currently, there is no denying that the distribution of malicious information could drive out good things and cause social unrest.
・ If we continue to be unable to sufficiently regulate generative AI — or if we at least allow the unconditional application of such technology to elections and security — it could cause enormous and irreversible damage as the effects of the technology will not be controllable in society. This implies a need for rigid restrictions by law (hard laws that are enforceable) on the usage of generative AI in these areas.
・ In the area of education, especially compulsory education for those age groups in which students’ ability to make appropriate decisions has not fully matured, careful measures should be taken after considering both the advantages and disadvantages of AI usage.
・ The protection of intellectual property rights — especially copyrights — should be adapted to the times in both institutional and technological aspects to maintain incentives for providing and distributing sound information. In doing so, the protections should be made enforceable in practice, without excessive restrictions to developing and using generative AI.
・ These solutions cannot be maintained by laws alone, but rather, they also require measures such as Originator Profile (OP), which is secured by technology.
Point 3: Establishment of effective governance, including legislation
・ The European Union has been developing data-related laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation, the Digital Services Act and the Digital Markets Act. It has been developing regulations through strategic laws with awareness of the need to both control and promote AI, positioning the Artificial Intelligence Act as part of such efforts.
・ Japan does not have such a strategic and systematic data policy. It is expected to require a long time and involve many obstacles to develop such a policy. Therefore, in the long term, it is necessary to develop a robust, strategic and systematic data policy and, in the short term, individual regulations and effective measures aimed at dealing with AI and attention economy-related problems in the era of generative AI.
・However, it would be difficult to immediately introduce legislation, including individual regulations, for such issues. Without excluding consideration of future legislation, the handling of AI must be strengthened by soft laws — both for data (basic) and generative AI (applied) — that offer a co-regulatory approach that identifies stakeholders. Given the speed of technological innovation and the complexity of value chains, it is expected that an agile framework such as agile governance, rather than governance based on static structures, will be introduced.
・ In risk areas that require special caution (see Point 2), hard laws should be introduced without hesitation.
・ In designing a system, attention should be paid to how effectively it protects the people’s liberty and dignity, as well as to national interests such as industry, based on the impact on Japan of extraterritorial enforcement to the required extent and other countries’ systems.
・ As a possible measure to balance AI use and regulation, a framework should be considered in which the businesses that interact directly with users in the value chain, the middle B in “B2B2X,” where X is the user, reduce and absorb risks when generative AI is used.
・ To create an environment that ensures discussion spaces in which human liberty and dignity are maintained, it is necessary to ensure that there are multiple AIs of various kinds and of equal rank, that they keep each other in check, and that users can refer to them autonomously, so that users do not have to depend on a specific AI. Such moves should be promoted from both institutional and technological perspectives.
Outlook for the Future:
・ Generative AI is a technology that cannot be fully controlled by humanity. However, it is set to enter an innovation phase (changes accompanying social diffusion).
・ In particular, measures to ensure a healthy space for discussion, which constitutes the basis of human and social security (democratic order), must be taken immediately. Legislation (hard laws) are needed, mainly for creating zones of generative AI use (strong restrictions for elections and security).
・ In addition, from the viewpoint of ecosystem maintenance (including the dissemination of personal information), it is necessary to consider optimizing copyright law in line with the times, in a manner compatible with using generative AI itself, from both institutional and technological perspectives.
・ However, as it takes time to revise the law, the following steps must be taken: the introduction of rules and joint regulations mainly by the media and various industries, the establishment and dissemination of effective technologies, and making efforts to revise the law.
・ In this process, the most important thing is to protect the dignity and liberty of individuals in order to achieve individual autonomy. Those involved will study the situation, taking into account critical assessments based on the value of community.
References:
‘Joint Proposal on Shaping Generative AI’ by The Yomiuri Shimbun Holdings and NTT Corp.
Major technology companies form AI-Enabled Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Workforce Consortium
MTN Consulting: Generative AI hype grips telecom industry; telco CAPEX decreases while vendor revenue plummets
Cloud Service Providers struggle with Generative AI; Users face vendor lock-in; “The hype is here, the revenue is not”
Amdocs and NVIDIA to Accelerate Adoption of Generative AI for $1.7 Trillion Telecom Industry
Major technology companies form AI-Enabled Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Workforce Consortium
A consortium of major tech companies, including Cisco, Accenture, Eightfold, Google, IBM, Indeed, Intel, Microsoft and SAP have formed the AI-Enabled Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Workforce Consortium with the aim of assessing “AI’s impact on technology jobs” and identifying “skills development pathways for the roles most likely to be affected by artificial intelligence.”
Francine Katsoudas, executive VP and chief people, policy and purpose officer at Cisco, stated:
“AI is accelerating the pace of change for the global workforce, presenting a powerful opportunity for the private sector to help upskill and re-skill workers for the future. The mission of our newly unveiled AI-Enabled Workforce Consortium is to provide organisations with knowledge about the impact of AI on the workforce and equip workers with relevant skills. We look forward to engaging other stakeholders – including governments, NGOs, and the academic community – as we take this important first step toward ensuring that the AI revolution leaves no one behind.”
The formation of the Consortium is catalyzed by the work of the U.S.-EU Trade and Technology Council Talent for Growth Task Force, Cisco Chair and CEO Chuck Robbins’ participation in the Task Force, and input from the U.S. Department of Commerce.
Advisors include the American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations, CHAIN5, Communications Workers of America, DIGITALEUROPE, the European Vocational Training Association, Khan Academy, and SMEUnited.
Working as a private sector collaborative, the Consortium is evaluating how AI is changing the jobs and skills workers need to be successful. The first phase of work will culminate in a report with actionable insights for business leaders and workers. Further details will be shared in the coming months. Findings will be intended to offer practical insights and recommendations to employers that seek ways to reskill and upskill their workers in preparation for AI-enabled environments.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Author’s Note: The consortium was likely formed to retrain workers to use AI technology, else they would be laid off or fired. In a recent survey from McKinsey, 25% of business professionals said that they expect their employer to lay off staff as a result of AI adoption. Their pessimism isn’t misplaced. According to one estimate, around 4,000 workers have lost their jobs to AI since May. And in a poll from Beautiful.ai, which makes AI-powered presentation software, nearly half of managers said that they’re hoping to replace workers with AI.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Consortium members represent a cross section of companies innovating on the cutting edge of AI that also understand the current and impending impact of AI on the workforce. Individually, Consortium members have documented opportunities and challenges presented by AI. The collaborative effort enables their organizations to coalesce insights, recommend action plans, and activate findings within their respective broad spheres of influence.
The Consortium’s work is inspired by the TTC’s Talent for Growth Task Force and Cisco Chair and CEO Chuck Robbins’ leadership of its skills training workstream, and input from the U.S. Department of Commerce. The TTC was established in June 2021 by U.S. President Biden, European Commission President von der Leyen, and European Council President Michel to promote U.S. and EU competitiveness and prosperity through cooperation and democratic approaches to trade, technology, and security.
“At the U.S. Department of Commerce, we’re focused on fueling advanced technology and deepening trade and investment relationships with partners and allies around the world. This work is helping us build a strong and competitive economy, propelled by a talented workforce that’s enabling workers to get into the good quality, high-paying, family-sustaining jobs of the future. We recognize that economic security and national security are inextricably linked. That’s why I’m proud to see the efforts of the Talent for Growth Task Force continue with the creation of the AI-Enabled ICT Workforce Consortium,” said U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo.
“I am grateful to the consortium members for joining in this effort to confront the new workforce needs that are arising in the wake of AI’s rapid development. This work will help provide unprecedented insight on the specific skill needs for these jobs. I hope that this Consortium is just the beginning, and that the private sector sees this as a call to action to ensure our workforces can reap the benefits of AI.”
The AI-Enabled ICT Workforce Consortium’s efforts address a business critical and growing need for a proficient workforce that is trained in various aspects of AI, including the skills to implement AI applications across business processes. The Consortium will leverage its members and advisors to recommend and amplify reskilling and upskilling training programs that are inclusive and can benefit multiple stakeholders – students, career changers, current IT workers, employers, and educators – in order to skill workers at scale to engage in the AI era.
In its first phase of work, the Consortium will evaluate the impact of AI on 56 ICT job roles and provide training recommendations for impacted jobs. These job roles include 80% of the top 45 ICT job titles garnering the highest volume of job postings for the period February 2023-2024 in the United States and five of the largest European countries by ICT workforce numbers (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands) according to Indeed Hiring Lab. Collectively, these countries account for a significant segment of the ICT sector, with a combined total of 10 million ICT workers.
Consortium members universally recognize the urgency and importance of their combined efforts with the acceleration of AI in all facets of business and the need to build an inclusive workforce with family-sustaining opportunities. Consortium members commit to developing worker pathways particularly in job sectors that will increasingly integrate artificial intelligence technology. To that end, Consortium members have established forward thinking goals with skills development and training programs to positively impact over 95 million individuals around the world over the next 10 years.
Consortium member goals include:
- Cisco to train 25 million people with cybersecurity and digital skills by 2032.
- IBM to skill 30 million individuals by 2030 in digital skills, including 2 million in AI.
- Intel to empower more than 30 million people with AI skills for current and future jobs by 2030.
- Microsoft to train and certify 10 million people from underserved communities with in-demand digital skills for jobs and livelihood opportunities in the digital economy by 2025.
- SAP to upskill two million people worldwide by 2025.
- Google has recently announced EUR 25 million in funding to support AI training and skills for people across Europe.
Accenture
“Helping organizations identify skills gaps and train people at speed and scale is a major priority for Accenture, and this consortium brings together an impressive ecosystem of industry partners committed to growing leading-edge technology, data and AI skills within our communities. Reskilling people to work with AI is paramount in every industry. Organizations that invest as much in learning as they do in the technology not only create career pathways, they are well positioned to lead in the market.” – Ellyn Shook, Chief Leadership & Human Resources Officer, Accenture
Eightfold
“The dynamics of work and the very essence of work are evolving at an unprecedented pace. Eightfold examines the most sought-after job roles, delving into the needs for reskilling and upskilling. Through its Talent Intelligence Platform, it empowers business leaders to adapt swiftly to the changing business environment. We take pride in contributing to the creation of a knowledgeable and responsible resource that assists organizations in preparing for the future of work.” – Ashutosh Garg, CEO and Co-Founder, Eightfold AI
“Google believes the opportunities created by technology should truly be available to everyone. We’re proud to join the AI-Enabled Workforce Consortium, which will advance our work to make AI skills training universally accessible. We’re committed to collaborating across sectors to ensure workers of all backgrounds can use AI effectively and develop the skills needed to prepare for future-focused jobs, qualify for new opportunities, and thrive in the economy.” – Lisa Gevelber, Founder, Grow with Google
IBM
“IBM is proud to join this timely business-led initiative, which brings together our shared expertise and resources to prepare the workforce for the AI era. Our collective responsibility as industry leaders is to develop trustworthy technologies and help provide workers—from all backgrounds and experience levels—access to opportunities to reskill and upskill as AI adoption changes ways of working and creates new jobs.” – Gian Luigi Cattaneo, Vice President, Human Resources, IBM EMEA
Indeed
“Indeed’s mission is to help people get jobs. Our research shows that virtually every job posted on Indeed today, from truck driver to physician to software engineer, will face some level of exposure to GenAI-driven change. We look forward to contributing to the Workforce Consortium’s important work. The companies who empower their employees to learn new skills and gain on-the-job experience with evolving AI tools will deepen their bench of experts, boost retention and expand their pool of qualified candidates.” – Hannah Calhoon, Head of AI Innovation at Indeed
Intel
“At Intel, our purpose is to create world-changing technology that improves the lives of every person on the planet, and we believe bringing AI everywhere is key for businesses and society to flourish. To do so, we must provide access to AI skills for everyone. Intel is committed to expanding digital readiness by collaborating with 30 countries, empowering 30,000 institutions, and training 30 million people for current and future jobs by 2030. Working alongside industry leaders as part of this AI-enabled ICT workforce consortium will help upskill and reskill the workforce for the digital economy ahead.” – Christy Pambianchi, Executive Vice President and Chief People Officer at Intel Corporation
Microsoft
“As a global leader in AI innovation, Microsoft is proud to join the ICT Workforce Consortium and continue our efforts to shape an inclusive and equitable technology future for all. As a member of the consortium, we will work with industry leaders to share best practices, create accessible learning opportunities, and collaborate with stakeholders to ensure that workers are equipped with the technology skills of tomorrow,” – Amy Pannoni, Vice President and Deputy General Counsel, HR Legal at Microsoft
SAP
“SAP is proud to join this effort to help prepare our workforce for the jobs of the future and ensure AI is relevant, reliable, and responsible across businesses and roles. As we navigate the complexities of our ever-evolving world, AI has the potential to reshape industries, revolutionize problem-solving, and unlock unprecedented levels of human potential, enabling us to create a more intelligent, efficient, and inclusive workforce. Over the years, SAP has supported many skills building programs, and we look forward to driving additional learning opportunities, innovation, and positive change as part of the consortium.” – Nicole Helmer, Vice President & Global Head of Development Learning at SAP
About Cisco
Cisco (NASDAQ: CSCO) is the worldwide technology leader that securely connects everything to make anything possible. Our purpose is to power an inclusive future for all by helping our customers reimagine their applications, power hybrid work, secure their enterprise, transform their infrastructure, and meet their sustainability goals. Discover more on The Newsroom and follow us on X at @Cisco.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco’s trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company.
Big tech companies form new consortium to allay fears of AI job takeovers
New ETSI Reports: 1.] Use cases for THz communications & 2.] Frequency bands of interest in the sub-THz and THz range
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) released a pair of reports from its relatively new Terahertz Industry Specification Group (ISG THz), created in December 2022. The reports envision how 6G technology might develop and what it will do. Importantly, the reports dive into more than a dozen 6G use cases – from remote surgery to real-time industrial control – as well as the terahertz spectrum bands where that might happen.
“The role of ETSI ISG THz is to develop an environment where various actors from the academia, research centres, industry can share, in a consensus-driven way, their pre-standardization efforts on THz technology resulting from various collaborative research projects and global initiatives, paving the way towards future standardization,” the organization wrote in a press release.
The first Report ETSI GR THz 001 identifies and describes use cases either enabled by or highly benefiting from the use of THz communications. Aspects addressed in the document include deployment scenarios, potential requirements, relevant operational environments and their associated propagation characteristics and/or measurements.
With the large amount of bandwidth available in THz bands, it is possible to achieve extremely high data rates and ease spectrum scarcity problems. Moreover, specific propagation properties of THz signals unlock new features such as accurate sensing and imaging capabilities. The above properties of THz communications open the way to enabling new use cases and could provide an answer to new societal challenges that need to be addressed by the future 6G communications systems. Some of these challenges relate to new functionalities that are not currently supported by cellular systems (e.g. accurate sensing, mapping, and localization), while others relate to new use cases that were not supported by previous communications systems.
The report defines the new use cases that the THz communications and sensing systems can support, along with summarizing the requirements of those use cases. For each identified use case, the report provides description of the deployment scenario, pre‑conditions required for the use case deployment, an example of service flows through a communication system supporting the use case, post-conditions enabled by the use case, identified potential requirements, and description of the physical environment, including propagation aspects, range, and mobility.
“The concept of remote surgery with support of THz communications comes with the promise of allowing people to be treated at anytime and anywhere, so that medical interventions could be done through the use of medical robots remotely controlled by a surgeon (away from the physical location where the actual surgery is performed),” according to the ETSI report.
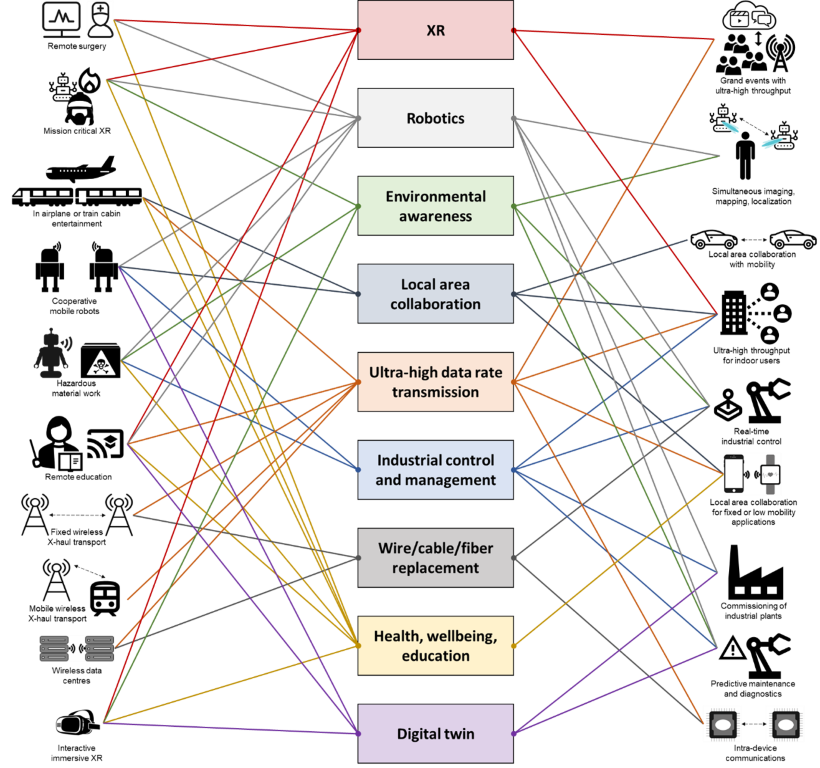
Figure 1: Use case mapping to application areas
Here’s the full list of 6G use cases in the ETSI report:
-
remote surgery
-
in-airplane or train cabin entertainment
-
cooperative mobile robots
-
hazardous material work
-
remote education
-
fixed point to point wireless applications
-
mobile wireless X-haul transport
-
wireless data centres
-
interactive immersive XR
-
mission critical XR
-
real-time industrial control
-
simultaneous imaging, mapping, and localization
-
commissioning of industrial plants
-
grand events with ultra-high throughput
-
ultra-high throughput for indoor users
-
intra-device communications
-
local area collaboration for fixed or low mobility applications
-
local area collaboration for vehicular applications
-
predictive maintenance and diagnostics
The 75-page report also offers a lengthy look at the kinds of technologies that might be involved in operating 6G networks, including AI, advanced MIMO, Reflective Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) and edge computing.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The second Report ETSI GR THz 002 identifies frequency bands of interest in the sub-THz and THz range, describes the current regulatory situation and identifies the incumbent services to be considered for coexistence studies.

Figure 2: Frequency ranges within the THz band with different regulatory status
The frequency range 100 GHz – 10 THz is referred to as the ‘THz range’. The corresponding wavelengths are from 0,03 mm to 3 mm. Below this range, the mm-wave and microwave frequency ranges are found, already heavily utilized for communications and non-communications applications. Above 10 THz the near- and mid-infrared spectrum starts.
The interest for higher frequency bands increases with the increasing demand for higher bandwidths and lower latencies to serve critical applications. This is most pronounced in the research towards 6G technologies, which are expected to be ready for early deployments around 2030. The frequency ranges from 100 GHz and upwards is already utilized for non‑communications purposes, and therefore there is a need to understand the regulatory landscape and identify the most interesting frequency bands for THz communications.
“Between 100 GHz and 275 GHz, 8 bands with sufficient contiguous bandwidths are allocated to fixed and mobile services on a co-primary basis,” according to the report. “Above 275 GHz, interesting bands have been identified for THz communications purposes based on a combination of regulatory status and favourable propagation conditions.”
To be clear, most 5G vendors don’t expect 6G to run primarily in those terahertz spectrum bands. Companies like Ericsson and Nokia have said 6G will mainly run in the so-called “centimetric” spectrum bands that sit between 7GHz and 20GHz
Webinar:
Another way of discovering more about those two deliverables will be webinar scheduled for 11 April 2024, 15h CEST:
https://www.etsi.org/events/upcoming-events/2338-webinar-use-cases-and-spectrum-key-starting-points-for-terahertz-standards.
About ETSI:
ETSI provides members with an open and inclusive environment to support the development, ratification and testing of globally applicable standards for ICT systems and services across all sectors of industry and society. We are a non-profit body, with more than 900 member organizations worldwide, drawn from 64 countries and five continents. The members comprise a diversified pool of large and small private companies, research entities, academia, government, and public organizations. ETSI is officially recognized by the EU as a European Standards Organization (ESO). For more information, please visit https://www.etsi.org/
References:
https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gr/THz/001_099/001/01.01.01_60/gr_THz001v010101p.pdf
https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gr/THz/001_099/002/01.01.01_60/gr_THz002v010101p.pdf
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/etsi-s-new-6g-report-dives-into-thz-use-cases
mmWave Coalition on the need for very high frequency spectrum; DSA on dynamic spectrum sharing in response to NSF RFI
New ITU report in progress: Technical feasibility of IMT in bands above 100 GHz (92 GHz and 400 GHz)
ITU-R Report in Progress: Use of IMT (likely 5G and 6G) above 100 GHz (even >800 GHz)
Keysight and partners make UK’s first 100 Gbps “6G” Sub-THz connection
ETSI Integrated Sensing and Communications ISG targets 6G
ETSI NFV evolution, containers, kubernetes, and cloud-native virtualization initiatives
ETSI Experiential Networked Intelligence – Release 2 Explained
Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) Market, Applications and ETSI MEC Standard-Part I
ETSI MEC Standard Explained – Part II