KDDI unveils AU Starlink direct-to-cell satellite service
KDDI-owned AU [1.] launched Japan’s first direct satellite service, connecting 40% of remote island and mountain populations in Japan that terrestrial networks cannot now reach. The new service, called AU Starlink Direct, is also available to subscribers of Okinawa Cellular, a KDDI-owned company serving the group of islands located in southern Japan. KDDI and Okinawa Cellular will start providing AU Starlink Direct, a direct to cell service between satellites and AU smartphones, on April 10, 2025. This is the first Direct to Cell satellite service in Japan.
Note 1. AU is a brand marketed by KDDI in the main islands of Japan and by Okinawa Cellular in Okinawa for their mobile cellular services. acquired au in 2001, initially through a merger of DDI, KDD, and IDO, and subsequently absorbing au’s parent company. KDDI continues to operate the AU brand for its mobile services.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The service is compatible with 50 smartphone models and is available free of charge to au users from today for the time being without the need to apply. Subscribers of AU and Okinawa Cellular whose iPhone and Android devices support satellite mode can try the service.

Source: Sean Prior/Alamy Stock Photo
Although AU has nearly 100% population coverage, mobile operators’ 4G and 5G networks effectively serve only about 60% of the population because mobile signal cannot reach remote islands and mountainous areas. The new AU Starlink Direct service allows the operator to bridge this digital divide by enabling customers in these dead zones to connect directly to a Starlink satellite using compatible smartphones.
The service can be used to communicate with family members and friends, in emergencies, etc., even in mountainous areas, island areas, and campgrounds and at sea where it is difficult to provide a telecommunications environment. KDDI is expanding the AU coverage area to all of Japan to bring the experience of “Connecting the Unconnected. wherever you see the sky.”
Gwynne Shotwell, President & COO of SpaceX, said: “I’m very excited to bring direct-to-cell phone connectivity to Japan through KDDI, the first in Asia and one of the first in the world. Both Starlink and direct-to-cell are game-changing technologies, making connecting the unconnected simple and bringing potentially life-saving capability to the people of Japan for disaster and other emergency responses.”
KDDI conducted a successful field test of AU Starlink Direct in Kumejima, Okinawa Prefecture, nearly six months ago.
References:
https://newsroom.kddi.com/english/news/detail/kddi_nr-533_3818.html
https://newsroom.kddi.com/english/news/detail/kddi_nr-299_3557.html
KDDI Partners With SpaceX to Bring Satellite-to-Cellular Service to Japan
SpaceX and KDDI to test Satellite Internet in Japan
KDDI Deploys DriveNets Network Cloud: The 1st Disaggregated, Cloud-Native IP Infrastructure Deployed in Japan
AWS Integrated Private Wireless with Deutsche Telekom, KDDI, Orange, T-Mobile US, and Telefónica partners
Samsung and KDDI complete SLA network slicing field trial on 5G SA network in Japan
KDDI claims world’s first 5G Standalone (SA) Open RAN site using Samsung vRAN and Fujitsu radio units
Samsung vRAN to power KDDI 5G network in Japan
T‑Mobile and EQT close JV to acquire FTTH network provider Lumos
T-Mobile and EQT (a purpose-driven global investment organization) announced the successful close of their joint venture (JV) to acquire fiber-to-the-home provider Lumos. As part of the transaction, many Lumos customers will soon become T-Mobile Fiber customers and begin enjoying new offers and benefits as they’re welcomed into the Magenta family.
This deal marks a major milestone in T-Mobile’s broadband growth and builds on the Un-carrier’s success in delivering best-in-class connectivity. By bringing more value and choice to the millions of Americans who have previously been underserved, T-Mobile continues to deliver on its mission to change broadband for good. T-Mobile will take full ownership of the customer experience, using its proven brand, nationwide retail footprint, differentiated marketing and customer-first service model to attract new subscribers.
Currently, Lumos operates a 7,500-mile fiber network, providing high-speed connectivity to 475,000 homes across the Mid-Atlantic. The joint venture combines the Un-carrier’s unique assets with EQT’s fiber infrastructure expertise, and Lumos’ scalable build capabilities to drive rapid network expansion, with the goal of reaching 3.5 million homes by the end of 2028. To fuel this growth, T-Mobile invested $950 million into the joint venture, with an additional $500 million planned between 2027 and 2028 to support further expansion. T-Mobile will provide an update to its full year 2025 guidance resulting from this transaction during its Q1 earnings call.
“T-Mobile is already the fastest-growing broadband provider in America, and expanding into fiber helps us take the next big step in delivering what customers truly want – faster, more reliable internet that simply works,” said Mike Katz, T-Mobile President of Marketing, Strategy and Products. “People deserve better when it comes to their home internet: fewer disruptions, more value, and support that actually feels supportive. We’re excited to welcome Lumos customers to the T-Mobile family and bring them the Un-carrier experience – built around their needs, fueled by innovation, and focused on making life easier.”
As Lumos customers continue to enjoy the same high-speed fiber internet they rely on today at low monthly prices, they’ll now also enjoy the value-add benefits they get from simply being a part of the T-Mobile family. They will have access to T-Mobile’s best-in-class customer experience and nationwide retail presence. Every plan also comes with unlimited data plus Wi-Fi equipment and installation included, so customers can enjoy the freedom and flexibility of reliable internet. Additionally, new and existing customers will enjoy VIP treatment through Magenta Status, which includes exclusive benefits like discounts on food, gas, entertainment and top brands, plus freebies every Tuesday in the T-Life app. All with T-Mobile’s standard ‘no exploding bills’ pricing structure.
“We’re excited to begin this joint venture and even more energized about what’s ahead,” said Brian Stading, CEO of Lumos. “Partnering with EQT and T-Mobile, we’re ready to scale faster, deliver cutting-edge fiber technology to more people, and change even more lives. This is about more than just internet – it’s about building the infrastructure of the future and creating lasting opportunity, connection, and impact for communities.”
“We are thrilled to officially embark on this next chapter of growth with Lumos alongside our partners at T-Mobile,” said Nirav Shah, Partner within EQT’s Infrastructure Advisory team. “This joint venture represents a powerful combination of EQT’s digital infrastructure expertise, Lumos’ proven fiber deployment capabilities, and T-Mobile’s customer-first approach and national reach. Together, we are well-positioned to accelerate access to high-quality fiber broadband to millions of underserved Americans and look forward to executing on our plans to deliver the critical connectivity that empowers communities across the country.”
As the fifth-largest and fastest-growing Internet service provider in the U.S., T-Mobile offers 5G Home Internet to 70 million homes, serving more than 6.4 million customers nationwide as of the end of 2024, and has introduced T-Mobile Fiber in parts of 32 U.S. markets. Fiber-to-the-home complements T-Mobile’s successful 5G Home Internet offering, which currently has over 1 million customers on its waitlist. This expansion in fiber opens an additional avenue to meet the growing demand for T-Mobile broadband. Through its strategic fiber partnerships and joint ventures, the Un-carrier expects to reach 12 to 15 million households, or more, with fiber by the end of 2030.
References:
https://www.t-mobile.com/news/business/t-mobile-eqt-close-lumos-fiber-jv
T-Mobile & EQT Joint Venture (JV) to acquire Lumos and build out T-Mobile Fiber footprint
T-Mobile posts impressive wireless growth stats in 2Q-2024; fiber optic network acquisition binge to complement its FWA business
AT&T’s leads the pack of U.S. fiber optic network service providers
Fiber and Fixed Wireless Access are the fastest growing fixed broadband technologies in the OECD
Lumen and Ciena Transmit 1.2 Tbps Wavelength Service Across 3,050 Kilometers
Lumen and Ciena have teamed up for a significant new network trial. They have successfully demonstrated a 1.2Tbps wavelength spanning 3,050k m (more than 1,800 miles) on Lumen’s Ultra-Low-Loss (ULL) fiber network, making it the world’s longest 1.2 terabit non-regenerated signal. The trial leveraged Ciena’s WL6e technology over a 6500 photonic line system and Lumen’s fiber network between Denver and Dallas. They also used 800Gbps routing technology from Juniper’s PTX Series to establish Ethernet and IP services. Lumen’s 400G-enabled network already spans over 78,000 route miles, and the company continues to invest in next-generation fiber to enhance its Ultra-Low Loss (ULL) fiber network, the largest in North America.
Using 800G interfaces, Lumen and Ciena successfully tested and qualified the services to support wavelength, Ethernet, and IP services over the 1.2 Tbps single carrier channel. The live network trial from Denver to Dallas used Ciena’s latest WaveLogic 6 Extreme (WL6e) technology equipped in the Waveserver platform running over a 6500 photonic line system.
“1.2 terabits per second isn’t just about incredible speed and long distances, it’s about the value of enabling the next wave of digital transformation. Lumen is at the forefront of building a next-generation network designed to handle the explosive growth of AI and cloud workloads,” said Dave Ward, Lumen’s chief technology and product officer. “Our investment in increased capacity, powered by Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 technology, provides our hyperscale cloud partners and enterprises with the ultra-high-capacity connectivity needed to scale their AI and cloud applications. With 400G connectivity speeds today and a seamless upgrade path to 1.2 terabits, Lumen stands as the trusted network for AI.”
The trial also showcased the impressive performance and seamless interoperability between Ciena’s Waveserver platform and the Juniper PTX10002-36QDD Packet Transport Router at 800 Gbps over the ultra-long-haul 1.2 Tbps intercity network. By leveraging the performance, flexibility and scalability of the Juniper PTX Series Routers, Lumen successfully established Ethernet and IP services with minimal latency and zero packet loss throughout the tests.
Editor’s Note:
While the companies March 27th joint press release stated the 1.2T bps wavelength transport was a record, AT&T claimed two weeks earlier that it “achieved a long distance world record top speed of 1.6Tb/s over a single wavelength across 296 km of its long haul fiber optic network.” We reported that in this IEEE Techblog post. So yes, it’s a record considering the Lumen network wavelength distance was > 10 times that claimed by AT&T.

Faster connections up to 1.2 Tbps wavelengths means less lag, more capacity and the flexibility to handle the most data-hungry applications across multiple industries:
- AI & Machine Learning
- Hyperscale Cloud & Data Center Interconnects
- Financial Trading and Market Data Transport
- Cybersecurity & AI-powered Threat Intelligence
- Media & Streaming
“At Microsoft, the demand for ultra-high-speed, low-latency connectivity is growing exponentially as AI workloads, cloud applications, and real-time analytics scale,” Lumen said. “Lumen and Ciena’s successful wavelength trial showcases a forward-thinking approach to meeting these growing demands. By enabling more efficient data movement over vast distances, this solution helps us optimize cloud performance, enhance customer experiences, and support the rapid expansion of AI training and inferencing models across our global infrastructure.”
Ciena’s WL6e is the industry’s first high-bandwidth coherent transceiver using state-of-the-art 3nm silicon, capable of carrying capacity up to 1.6 terabits per second per wavelength.
“As the pioneer in high-speed optical innovation, we are dedicated to helping our customers set new benchmarks in network performance and efficiency,” said Brodie Gage, Ciena senior vice president, global products and supply chain. “This industry-first trial with Lumen marks a pivotal step in our efforts to prepare networks for the AI era. Lumen’s network does not stand still. Continuous investment in the latest network technology is essential for keeping up with bandwidth demands today and into the future.”
Additional Resources:
About Lumen Technologies:
Lumen is unleashing the world’s digital potential. We ignite business growth by connecting people, data, and applications – quickly, securely, and effortlessly. As the trusted network for AI, Lumen uses the scale of our network to help companies realize AI’s full potential. From metro connectivity to long-haul data transport to our edge cloud, security, managed service, and digital platform capabilities, we meet our customers’ needs today and as they build for tomorrow.
SOURCE: Lumen Technologies
References:
Analysts weigh in: AT&T in talks to buy Lumen’s consumer fiber unit – Bloomberg
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
ITU-R recommendation IMT-2020-SAT.SPECS from ITU-R WP 5B to be based on 3GPP 5G NR-NTN and IoT-NTN (from Release 17 & 18)
Backgrounder:
Non-terrestrial networks (NTN) are networks or segments of networks that use either Uncrewed Aircraft Systems (UAS) operating typically between 8 and 50km altitudes, including High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) or satellites in different constellations to carry a transmission equipment relay node or a base station:
- LEO (Low Earth Orbit): Circular orbit in altitudes of typ. 500-2.000km (lower delay and better link budget but larger number of satellites needed for coverage)
- MEO (Medium Earth Orbit): Circular orbit in altitudes of typ. 8.000-20.000km
- GEO (Geostationary Earth Orbit): Circular orbit 35.786 km above the Earth’s equator (Note: Due to gravitational forces a GEO satellite is still moving within a range of a few km around its nominal orbital position).
- HEO (Highly Elliptical Orbiting): Elliptical orbit around the earth.

Figure 1: Illustration of the classes of orbits of satellites [source: TR 22.822]
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Future ITU-R NTN standard – Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT-2020-SAT.SPECS]:
ITU-R SG04 Circular 134 invited proposal submissions for candidate radio interface technologies for the satellite component of the radio interface(s) for IMT-2020 (ITU-R M.2150 recommendation) and invitation to participate in their subsequent evaluation. Acting on behalf of 3GPP (which it is a member of), ATIS recently submitted three 3GPP documents to ITU-R WP’s 5B and 5D for consideration. The submitted material consists of 3GPP Releases 17 and 18 and it is provided in the following documents:
1. 3GPP 5G-NTN: RIT
o NR-NTN
2. 3GPP 5G-NTN: SRIT
o Component RIT: NR-NTN
o Component RIT: IoT-NTN
Legend:
NTN=Non Terrestrial Network
RIT: Radio Interface Technology
SRIT: Set of Radio Interface Technologies
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
3GPP looks forward to the continuous collaboration with ITU-R WP 4B for the finalization of Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT-2020-SAT.SPECS], which will be the official standard for 5G satellite to ground communications.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
-
Release 17:
- Foundation for 5G NTN: Established the foundation for integrating 5G with non-terrestrial networks (NTNs), enabling satellite connectivity for 5G services.
- Focus on Transparent Architecture: Rel-17 NTN was based on a transparent (bent-pipe) architecture, where the satellite acts as a radio repeater, limiting payload complexity and enabling early deployment.
- Initial Standardization: 3GPP pursued a range of solutions for 5G non-terrestrial networking (NTN) based on options for the type of non-terrestrial platform and the use cases supported.
- IoT-NTN: Introduced IoT-NTN, enabling satellite connectivity for Internet of Things devices.
- Frequency Bands: Focused on L-band and S-band in FR1 for NTN.
- Foundation for 5G NTN: Established the foundation for integrating 5G with non-terrestrial networks (NTNs), enabling satellite connectivity for 5G services.
-
Release 18 (5G-Advanced):
- NTN-IoT Enhancements: Further optimized NTN for IoT, including enhancements for Machine-Type Communication (MTC).
- New Service and Traffic Models: Introduced new service and traffic models to better support NTN applications.
- New Frequency Bands: Expanded frequency support to include Frequency Range 2 (FR2), spanning 17,300 MHz to 30,000 MHz.
- Focus on Ka-band: Prioritized the use of Ka-band for NR NTN deployment.
- Uplink Coverage and Mobility Enhancements: Improved uplink coverage and mobility/service continuity between NTN and terrestrial networks (NTN-TN) and between NTN networks (NTN-NTN).
- Network Verified UE Location: Enabled the network to verify UE location as per regulatory requirements.
- RedCap Enhancements: RedCap solutions were further optimized to reduce device cost and power consumption.
- Support for Store & Forward (S&F) operation based on regenerative payload: Release 18 and beyond will support Store & Forward operation based on regenerative payload, including the support of feeder link switchover.
- NTN-IoT Enhancements: Further optimized NTN for IoT, including enhancements for Machine-Type Communication (MTC).
References:
2 ATIS contributions to ITU-R WP 5D and 5B (only available to ITU TIES account members)
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/ntn-overview
Standards are the key requirement for telco/satellite integration: D2D and satellite-based mobile backhaul
SatCom market services, ITU-R WP 4B, 3GPP Release 18 and ABI Research Market Forecasts
Momentum builds for wireless telco- satellite operator engagements
Juniper Research: 5G Satellite Networks are a $17B Operator Opportunity
Samsung announces 5G NTN modem technology for Exynos chip set; Omnispace and Ligado Networks MoU
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
5G connectivity from space: Exolaunch contract with Sateliot for launch and deployment of LEO satellites
China’s state owned telcos slash CAPEX to the lowest in decades!
China’s big three state-owned telecom operators are drastically slashing capital expenditures (CAPEX) before the next wave of heavy spending on 6G mobile network infrastructure beginning in 2030. Over a year ago, the IEEE Techblog reported the planned CAPEX reductions in this post.
- China Telecom expects its capital expenditure to decline by 11% to 83.6 billion yuan in 2025, returning to pre-5G expansion levels.
- China Mobile also plans to cut its capital expenditure by 8% in 2025, bringing spending close to 2012 levels.
- China Unicom, the smallest of the three, recorded the sharpest drop in spending.
Reasons for the Cuts:
- The 5G network infrastructure buildout has largely reached its peak, with China already having 3.5 million 5G base stations.
- The companies are preparing for the next major investment cycle, which is expected to focus on 6G and AI infrastructure.
- The CAPEX cuts are also being driven by government directives to improve market value and increase shareholder dividends.
- The companies are prioritizing investments in AI infrastructure and computational infrastructure.
- China Mobile’s Chairman Yang Jie stated that the next major investment cycle is expected to focus on 6G and is unlikely to begin before 2028.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
1. China Mobile, the largest wireless carrier in China with over 1 billion subscribers, slashed its annual capital expenditure by over 9% to 164 billion yuan in 2024. The company plans to cut another 8% this year to 151.2 billion yuan. That amount is approaching the 2012 level of 127.4 billion yuan, and is set to decline further in the years to come.
“The overall investment size in the next two to three years will continue to steadily fall,” Yang Jie, China Mobile’s chairman, told reporters in Hong Kong last Thursday. Asked what would trigger the next capital spending spree, Yang said: “From what I see now, the next investment peak will be on 6G” — but he expects that to kick off around 2028. Until then, the industry veteran expects “the proportion of investment to expand in the areas of computation and AI.”

China Mobile Chairman Yang Jie told reporters in Hong Kong on March 20 that the next telecom investment peak would be for 6G mobile network building. (Photo by Kenji Kawase)
Jefferies telecom analyst Edison Lee, said China Mobile’s capex figures were “lower than expected.” The ratio versus its revenue was 18% last year, marking the first dip below 20%, and he expects this proportion to further sink to 16% this year. “This is negative for equipment vendors such as ZTE,” Lee said, although it provides more room for returns to shareholders.
2. China Telecom (#2 in China) announced on Tuesday that its CAPEX for 2024 came to 93.51 billion yuan ($12.9 billion), 5% lower than the previous year. The forecast for this year is even lower, at 83.6 billion yuan, down 11% and lowering the amount to the level before the peak 5G network investment years of around 2020 to 2023. However, with soaring demand for AI computing, it plans a further hike in digital infrastructure spending. It will boost investment in cloud computing and data centers by 22% to RMB45.5 billion ($6.3 billion), making it the biggest single capex item, accounting for 38% of the total.
The company said it’s focused on four technology directions: network, cloud and cloud-network integration, AI and quantum security. It revealed it had deployed 70,000 5G-A base stations in 121 cities, with 5G RedCap coverage in more than 200 cities, and said it had signed up 2.4 million subs to its pioneering D2D mobile satellite service.
Chairman Ke Ruiwen told Nikkei Asia that “the general trend is heading downward.” He added that “before building the new large-scale network (apparently referring to 6G), the investment trend is going continue falling.” He said the company would continue to pursue its strategy focused on cloud and digital transformation.

Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo
3. China Unicom, the smallest of the three state owned telcos, also slashed its capital spending by 17% to 61.37 billion yuan in 2024, while planning a further reduction to 55 billion yuan this year. “Our investment emphasis has already shifted away from mobile broadband to computing network capabilities for internet data centers and cloud,” said Tang Yongbo, Unicom’s vice president. He also mentioned the impending heavy investment period when the 6G era arrives.
China Telecom and China Unicom have a “co-build, co-share” partnership for 5G investment.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
All three Chinese network operators’ actual capital expenditure in 2024 were lower than the previous guidance they had provided, by an average of 5%. The sum of annual capital expenditure for the three Chinese telcos was 319 billion yuan for 2024, and the combined estimate for 2025 is 289.8 billion yuan. Including China Tower — a tower builder established in 2014 through a merger of the three telecom companies’ related businesses, and publicly listed in 2018 — the total capex last year was 351 billion yuan. This year’s projected amount of 322 billion yuan would be one of the lowest in decades.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/china-telecom-boosts-profit-cuts-capex
China Mobile & China Unicom increase revenues and profits in 2023, but will slash CAPEX in 2024
Dell’Oro: Global telecom CAPEX declined 10% YoY in 1st half of 2024
Omdia: Huawei increases global RAN market share due to China hegemony
Analysts weigh in: AT&T in talks to buy Lumen’s consumer fiber unit – Bloomberg
Update:
AT&T will acquire substantially all of Lumen’s Mass Markets fiber business for $5.75 billion, subject to purchase price adjustments, in an all-cash transaction that is expected to close in early 2026. Lumen’s fiber business has approximately 1 million fiber customers and reaches more than 4 million fiber locations across 11 U.S. states.
“We’re leading the race to connect more Americans with fiber, the best broadband connectivity technology available,” said John Stankey, Chairman and CEO, AT&T. “This deal with Lumen represents a significant investment in U.S. connectivity infrastructure that will create jobs and spur economic activity in numerous regions and major metro areas across 11 states. As we advance our fiber build, we’ll serve more communities with world-class connectivity and expect to roughly double where AT&T Fiber is available by the end of 2030.”
https://about.att.com/story/2025/lumen-mass-markets-fiber-business.html
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Bloomberg News reports that AT&T is in talks to acquire Lumen Technologies’ consumer fiber operations, in a deal that could value the unit at more than $5.5 billion, citing people with knowledge of the matter. The companies are in exclusive discussions about a transaction valuing the unit at more than $5.5 billion, said one of the people, who requested to not be identified discussing confidential information. The terms of the unfinalized deal could change or the talks might still collapse, according to the report.
“If the rumored price is correct, it is a great deal for AT&T,” wrote the financial analysts at New Street Research in a note to investors. “The value per [fiber] location at $5.5 billion would be about $1,300 which compares to Frontier at $2,400, Ziply at $3,800, and Metronet at $4,700,” the analysts continued.

https://www.lightreading.com/fttx/is-at-t-getting-a-screaming-deal-on-lumen-s-fiber-
Lumen Technologies to connect Prometheus Hyperscale’s energy efficient AI data centers
Microsoft choses Lumen’s fiber based Private Connectivity Fabric℠ to expand Microsoft Cloud network capacity in the AI era
Lumen, Google and Microsoft create ExaSwitch™ – a new on-demand, optical networking ecosystem
ACSI report: AT&T, Lumen and Google Fiber top ranked in fiber network customer satisfaction
Lumen to provide mission-critical communications services to the U.S. Department of Defense
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
Bloomberg: BT in talks with AT&T and Orange as its international unit struggles
BT Group has approached major telecommunications companies about partnerships to help turn around its struggling international business, according to a Bloomberg article. The UK-based network operator approached potential partners including AT&T and Orange to explore arrangements that could involve selling a stake in its global segment, according to people familiar with the matter. Deliberations are preliminary, talks are private, and there’s no guarantee of a transaction, said the referenced people.
BT’s global unit, which was recently folded into a larger business segment, has dragged down growth metrics for years, with steadily declining earnings and revenue. The unit accounted for about 11% of BT’s revenue in the first half of the 2025 fiscal year. It allows the British network operator to serve customers around the world, but many of the contracts generate little profit and are costly to maintain. Meanwhile, BT is the UK leading network operator in both fixed line and mobile customers.
Revenue at BT’s global unit declined 9.9% in the six months ended in September from a year earlier to about £1.1 billion ($1.4 billion).
“We’re keeping everything open and this means we’ve been speaking to third parties about a range of possibilities,” a BT spokesperson said by email to Bloomberg.

In the release of its financial results for the quarter ending 31 December 2024, CEO Allison Kirkby confirmed that “In (BT) Business, our core UK channels were stable. Cost transformation remains firmly on track, with excellent progress on both energy costs and productivity in the quarter.”
“We continue to make progress towards becoming fully focused on the UK, with the sale of our data centre business in Ireland,” she added.
References:
https://totaltele.com/bt-in-partnership-talks-with-att-and-orange-as-international-unit-struggles/
Nokia, BT Group & Qualcomm achieve enhanced 5G SA downlink speeds using 5G Carrier Aggregation with 5 Component Carriers
BT Group, Ericsson and Qualcomm demo network slicing on 5G SA core network in UK
Qualcomm and BT open 5G Lab in Farnborough, UK
Global telecom infrastructure market outlook after a dismal 2024
Despite the telecom industry’s hopes that 2025 will usher in a turnaround for the global network equipment market, there’s no hint of that happening considering how bad 2024 was.
According to Dell’Oro Group, worldwide telecom equipment market revenues in 2024 dropped 11% year-over-year – marking “the steepest annual decline in more than 20 years.”
Dell’Oro VP Stefan Pongratz wrote:
“Preliminary findings suggest that worldwide telecom equipment revenues across the six telecom programs tracked at Dell’Oro Group—Broadband Access, Microwave & Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network (MCN), Radio Access Network (RAN), and SP Router & Switch—declined 11% year-over-year (YoY) in 2024, recording the steepest annual decline in more than 20 years (decline was >20% in 2002), propelling total equipment revenue to fall by 14% over the past two years. This remarkable output deceleration was broad-based across the telecom segments and driven by multiple factors, including excess inventory, challenging macro environment, and difficult 5G comparisons.
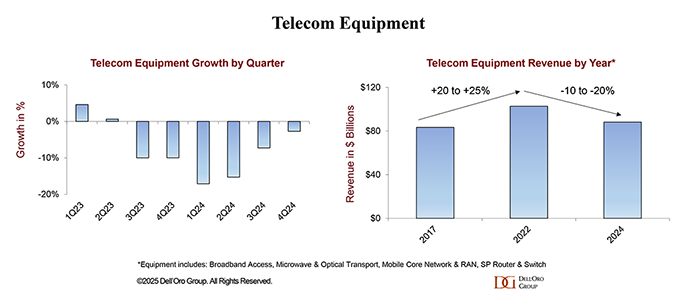
In 4Q24, stabilization was driven by growth in North America and EMEA, which nearly offset constrained demand in Asia Pacific (including China).
The full-year decline was uneven across the six telecom programs. Optical Transport, SP Routers, and RAN saw double-digit contractions, collectively shrinking by 14% in 2024. Microwave Transport and MCN experienced a more moderate combined decline in the low single digits, while Broadband Access revenues were fairly stable.
Similarly, regional developments were mixed in 2024. While the slowdown was felt across the five regions — North America, EMEA, Asia Pacific, China, and CALA — the deceleration was more pronounced in the broader Asia Pacific region, reflecting challenging conditions in China and Asia Pacific outside of China.
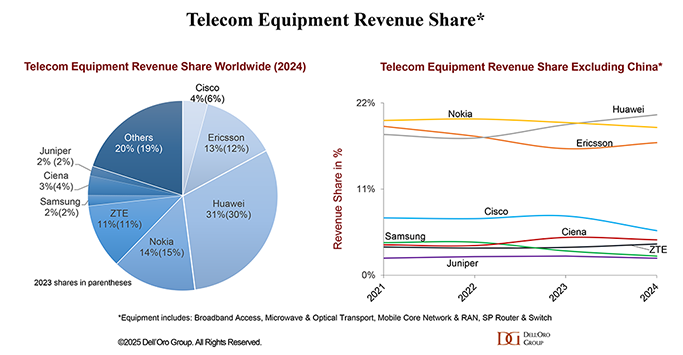
Supplier rankings were mostly unchanged globally, while revenue shares shifted slightly as both Huawei and Ericsson positions improved. Overall market concentration was stable with the 8 suppliers comprising around ~80% of the worldwide market in 2024.
Rankings changed outside of China. Initial estimates suggest Huawei passed Nokia to become the #1 supplier, followed by Nokia and Ericsson. Huawei’s revenue share outside of China was up 2 to 3 percentage points in 2024, relative to 2021, while Ericsson is down roughly two percentage points over the same period/region.
A glimmer of hope is that the Covid instigated inventory correction is over and the supply chain is starting to recover. For example, Ciena recently noted its problems with “inventory digestion” are mostly over. CEO Gary Smith said that customers are again investing in scaling their networks, specifically for the anticipated increase in cloud traffic and new AI workloads, including Managed Optical Fiber Networks opportunities with the cloud providers.
However, that might take time to play out. Vendors may have to take at least 6-12 months to retool their supply chains due to tariffs, AvidThink Principal Roy Chua has said. And given the “will-they, won’t-they” situation going on with the tariffs, their ultimate impact remains to be seen.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
It’s been six years since 5G networks have been commercially deployed. But aside from deploying fixed wireless access (FWA), telcos have struggled to “find large use cases that require 5G speeds and features,” Deloitte said in its latest telecom industry forecast.
“Not only were there seemingly few additional use cases driving 5G adoption and monetization in 2024, but there may not be many more for 2025 or even 2026 either.” The market research/accounting firm continued:
Our outlook focuses on three of those difficult choices, and we have a full chapter on each:
- In 2025, the most discussed source of growth for many industries is generative AI, and telcos are asking how they can share in that excitement. Telcos are using gen AI to reduce costs, become more efficient, and offer new services. Some are building new gen AI data centers to sell training and inference to others. A gen AI gold rush expected over the next five years. Spending estimates range from hundreds of billions to over a trillion dollars on the physical layer required for gen AI: chips, data centers, electricity. Close to another hundred billion US dollars will likely be spent on the software and services layer.
- At the same time, telcos are roughly at the midpoint between the launch of 5G and the expected launch of 6G, and they want to confirm that they can shape 6G to be more profitable than 5G has so far been.
- Finally, after years of divesting noncore assets, telcos are getting primed to deploy M&A strategies in pursuit of growth.
Globally, the telecommunications industry is expected to have revenues of about US$1.53 trillion in 2024, up about 3% over the prior year. Both in 2024 and out to 2028, growth is expected to be higher in Asia Pacific and Europe, Middle East, and Africa, with growth in the Americas being around 1% annually. All three regions are expected to surpass half a trillion dollars in revenue each by 2027. By market cap, the sector is about US$2.6 trillion globally (Figure 1, below).
Stefan summed up: “Market conditions are expected to stabilize in 2025 on an aggregated basis, though it will still be a challenging year. The analyst team is collectively forecasting global telecom equipment revenues across the six programs to stay flat.”
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/global-telecom-infra-faced-ultimate-pitfall-2024
Telco spending on RAN infrastructure continues to decline as does mobile traffic growth
Dell’Oro: Global RAN Market to Drop 21% between 2021 and 2029
Dell’Oro: Global telecom CAPEX declined 10% YoY in 1st half of 2024
Dell’Oro: Private RAN revenue declines slightly, but still doing relatively better than public RAN and WLAN markets
Dell’Oro: RAN market still declining with Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE and Samsung top vendors
Dell’Oro: 4G and 5G FWA revenue grew 7% in 2024; MRFR: FWA worth $182.27B by 2032
Highlights of Dell’Oro’s 5-year RAN forecast
Telecom sessions at Nvidia’s 2025 AI developers GTC: March 17–21 in San Jose, CA
Nvidia’s annual AI developers conference (GTC) used to be a relatively modest affair, drawing about 9,000 people in its last year before the Covid outbreak. But the event now unofficially dubbed “AI Woodstock” is expected to bring more than 25,000 in-person attendees!
Nvidia’s Blackwell AI chips, the main showcase of last year’s GTC (GPU Technology Conference), have only recently started shipping in high volume following delays related to the mass production of their complicated design. Blackwell is expected to be the main anchor of Nvidia’s AI business through next year. Analysts expect Nvidia Chief Executive Jensen Huang to showcase a revved-up version of that family called Blackwell Ultra at his keynote address on Tuesday.
March 18th Update: The next Blackwell Ultra NVL72 chips, which have one-and-a-half times more memory and two times more bandwidth, will be used to accelerate building AI agents, physical AI, and reasoning models, Huang said. Blackwell Ultra will be available in the second half of this year. The Rubin AI chip, is expected to launch in late 2026. Rubin Ultra will take the stage in 2027.
Nvidia watchers are especially eager to hear more about the next generation of AI chips called Rubin, which Nvidia has only teased at in prior events. Ross Seymore of Deutsche Bank expects the Rubin family to show “very impressive performance improvements” over Blackwell. Atif Malik of Citigroup notes that Blackwell provided 30 times faster performance than the company’s previous generation on AI inferencing, which is when trained AI models generate output. “We don’t rule out Rubin seeing similar improvement,” Malik wrote in a note to clients this month.
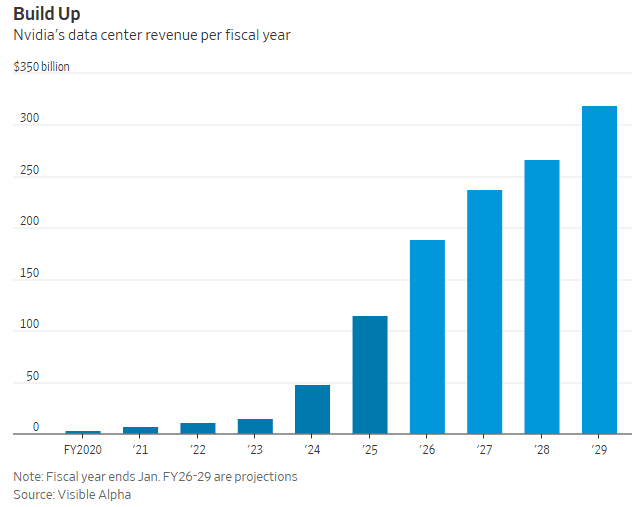
Rubin products aren’t expected to start shipping until next year. But much is already expected of the lineup; analysts forecast Nvidia’s data-center business will hit about $237 billion in revenue for the fiscal year ending in January of 2027, more than double its current size. The same segment is expected to eclipse $300 billion in annual revenue two years later, according to consensus estimates from Visible Alpha. That would imply an average annual growth rate of 30% over the next four years, for a business that has already exploded more than sevenfold over the last two.
Nvidia has also been haunted by worries about competition with in-house chips designed by its biggest customers like Amazon and Google. Another concern has been the efficiency breakthroughs claimed by Chinese AI startup DeepSeek, which would seemingly lessen the need for the types of AI chip clusters that Nvidia sells for top dollar.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Telecom Sessions of Interest:
Wednesday Mar 19 | 2:00 PM – 2:40 PM
Delivering Real Business Outcomes With AI in Telecom [S73438]
In this session, executives from three leading telcos will share their unique journeys of embedding AI into their organizations. They’ll discuss how AI is driving measurable value across critical areas such as network optimization, customer experience, operational efficiency, and revenue growth. Gain insights into the challenges and lessons learned, key strategies for successful AI implementation, and the transformative potential of AI in addressing evolving industry demands.
Thursday Mar 20 | 11:00 AM – 11:40 AM PDT
AI-RAN in Action [S72987]
Thursday Mar 20 | 9:00 AM – 9:40 AM PDTHow Indonesia Delivered a Telco-led Sovereign AI Platform for 270M Users [S73440]
Thursday Mar 20 | 3:00 PM – 3:40 PM PDT
Driving 6G Development With Advanced Simulation Tools [S72994]
Thursday Mar 20 | 2:00 PM – 2:40 PM PDT
Thursday Mar 20 | 4:00 PM – 4:40 PM PDT
Pushing Spectral Efficiency Limits on CUDA-accelerated 5G/6G RAN [S72990]
Thursday Mar 20 | 4:00 PM – 4:40 PM PDT
Enable AI-Native Networking for Telcos with Kubernetes [S72993]
Monday Mar 17 | 3:00 PM – 4:45 PM PDT
Automate 5G Network Configurations With NVIDIA AI LLM Agents and Kinetica Accelerated Database [DLIT72350]
Learn how to create AI agents using LangGraph and NVIDIA NIM to automate 5G network configurations. You’ll deploy LLM agents to monitor real-time network quality of service (QoS) and dynamically respond to congestion by creating new network slices. LLM agents will process logs to detect when QoS falls below a threshold, then automatically trigger a new slice for the affected user equipment. Using graph-based models, the agents understand the network configuration, identifying impacted elements. This ensures efficient, AI-driven adjustments that consider the overall network architecture.
We’ll use the Open Air Interface 5G lab to simulate the 5G network, demonstrating how AI can be integrated into real-world telecom environments. You’ll also gain practical knowledge on using Python with LangGraph and NVIDIA AI endpoints to develop and deploy LLM agents that automate complex network tasks.
Prerequisite: Python programming.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Nvidia AI-RAN survey results; AI inferencing as a reinvention of edge computing?
The case for and against AI-RAN technology using Nvidia or AMD GPUs
FT: Nvidia invested $1bn in AI start-ups in 2024
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
AT&T claims it achieved a long distance world record top speed of 1.6Tb/s over a single wavelength across 296 km of its long haul fiber optic network (spanning Newark, New Jersey to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania). That is four times faster than its current top speed of 400Gb/s per wavelength!
The 1.6Tb/s wavelength carried two IEEE 802.3df-2024 standard-based 800 Gigabit Ethernet end-to-end circuits, an industry first. It is a full, uninterrupted data path utilizing a single light frequency across the entire fiber length between two endpoints. The single-carrier 1.6 Tb/s wavelength was transported alongside existing live customer traffic on 100Gb/s and 400Gb/s wavelengths.
Open-sourced white box switches were the network equipment used during the trial. The white boxes are designed using the Broadcom Jericho3 packet processor chip and can provide up to 18 x 800G network interface ports all within a 2RU platform. The (Israel based) DriveNets Network Cloud software-based solution is hardware-agnostic and runs open APIs on the white boxes to perform data and control plane functions, including routing at 800G. The use of white boxes and the disaggregation of the hardware and software control costs and facilitate faster innovation.
The two 800GbE signals from the white box were multiplexed to 1.6 Tb/s in Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 Extreme coherent optical transponder, which is the first coherent optical solution to use a 200Gbaud design and 3nm coherent DSP ASIC and to reach speeds up to 1.6 Tb/s on a single carrier. The WL6e technology reduces the space and power per transmitted bit by 50% compared to current 800G transponders. This trial is the first to demonstrate WL6e at 1.6Tb/s with standards compliant 800GbE clients.
In the Newark and Philadelphia offices, 800G DR8 pluggable transceivers from Coherent were installed in the white box router and WL6e transponder to create the cross-office connectivity between the packet and optical technologies. And 800GbE client signals, provided by Keysight’s AresOne-M 800GE testset, fed the white box through additional pairs of 800G DR8 pluggable client optics, allowing verification of end-to-end performance of the two 800GbE services from Newark to Philadelphia.
Quotes:
“Traffic on AT&T’s network continues to increase as consumers are using more connected devices,” said Mike Satterlee, vice president, Network Infrastructure and Services, AT&T. “We anticipate network traffic growth to double by 2028 and the technologies demonstrated in this trial will play a key role in AT&T’s continued efforts to keep up with increasing customer demand to send data, watch videos, and use streaming services.”
“This groundbreaking achievement with AT&T adds to a growing list of Ciena industry-firsts that push the boundaries of optical network speed and capacity,” said Dino DiPerna, senior vice president, Global Research and Development, Ciena. “Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 coherent optics will support AT&T’s next gen converged optical network and efforts to build a cloud-based and AI-ready network with greater scale, flexibility and efficiency.”

Verizon’s 1.6Tb/s on Metro Fiber Network:
AT&T’s announcement comes just a few months after arch-rival Verizon announced a 1.6 Tb/s milestone of its own. Verizon also, working with Ciena, achieved that peak speed on a single wavelength, but on its metro fiber (not long distance) network. Verizon is mainly looking to advance through M&A. Its proposed acquisition of Frontier Communications is still pending, with some Frontier shareholders insisting that the US$20 billion price tag undervalues the operator.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
AT&T has spent the past six months demonstrating that it aims to build its way to fiber domination. It rolled out fiber to around 600,000 premises in the 4th quarter of last year, taking its total fiber footprint to 28.9 million locations; it is shooting for 50 million by the end of 2029.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2025/data-transport.html
https://www.business.att.com/products/wavelength-services.html
https://www.telecoms.com/fibre/at-t-touts-1-6-tbps-fibre-speed-milestone-as-us-battle-continues