Global telecom infrastructure market outlook after a dismal 2024
Despite the telecom industry’s hopes that 2025 will usher in a turnaround for the global network equipment market, there’s no hint of that happening considering how bad 2024 was.
According to Dell’Oro Group, worldwide telecom equipment market revenues in 2024 dropped 11% year-over-year – marking “the steepest annual decline in more than 20 years.”
Dell’Oro VP Stefan Pongratz wrote:
“Preliminary findings suggest that worldwide telecom equipment revenues across the six telecom programs tracked at Dell’Oro Group—Broadband Access, Microwave & Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network (MCN), Radio Access Network (RAN), and SP Router & Switch—declined 11% year-over-year (YoY) in 2024, recording the steepest annual decline in more than 20 years (decline was >20% in 2002), propelling total equipment revenue to fall by 14% over the past two years. This remarkable output deceleration was broad-based across the telecom segments and driven by multiple factors, including excess inventory, challenging macro environment, and difficult 5G comparisons.
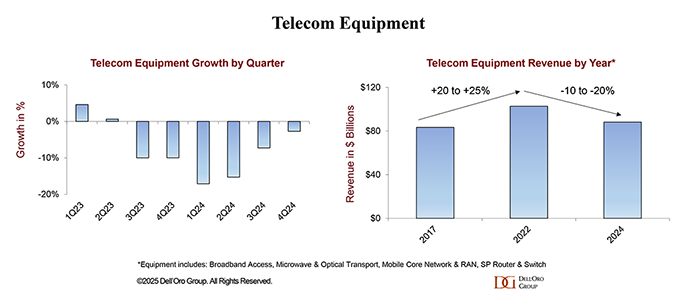
In 4Q24, stabilization was driven by growth in North America and EMEA, which nearly offset constrained demand in Asia Pacific (including China).
The full-year decline was uneven across the six telecom programs. Optical Transport, SP Routers, and RAN saw double-digit contractions, collectively shrinking by 14% in 2024. Microwave Transport and MCN experienced a more moderate combined decline in the low single digits, while Broadband Access revenues were fairly stable.
Similarly, regional developments were mixed in 2024. While the slowdown was felt across the five regions — North America, EMEA, Asia Pacific, China, and CALA — the deceleration was more pronounced in the broader Asia Pacific region, reflecting challenging conditions in China and Asia Pacific outside of China.
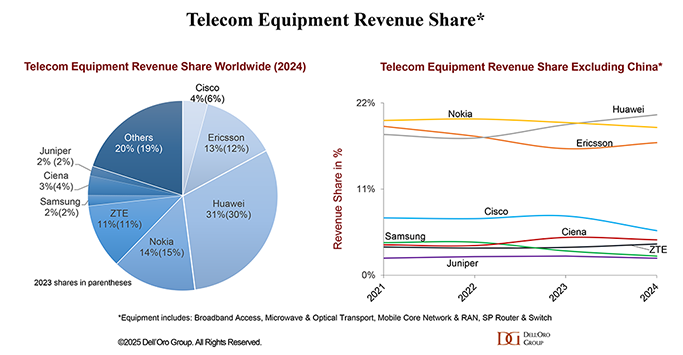
Supplier rankings were mostly unchanged globally, while revenue shares shifted slightly as both Huawei and Ericsson positions improved. Overall market concentration was stable with the 8 suppliers comprising around ~80% of the worldwide market in 2024.
Rankings changed outside of China. Initial estimates suggest Huawei passed Nokia to become the #1 supplier, followed by Nokia and Ericsson. Huawei’s revenue share outside of China was up 2 to 3 percentage points in 2024, relative to 2021, while Ericsson is down roughly two percentage points over the same period/region.
A glimmer of hope is that the Covid instigated inventory correction is over and the supply chain is starting to recover. For example, Ciena recently noted its problems with “inventory digestion” are mostly over. CEO Gary Smith said that customers are again investing in scaling their networks, specifically for the anticipated increase in cloud traffic and new AI workloads, including Managed Optical Fiber Networks opportunities with the cloud providers.
However, that might take time to play out. Vendors may have to take at least 6-12 months to retool their supply chains due to tariffs, AvidThink Principal Roy Chua has said. And given the “will-they, won’t-they” situation going on with the tariffs, their ultimate impact remains to be seen.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
It’s been six years since 5G networks have been commercially deployed. But aside from deploying fixed wireless access (FWA), telcos have struggled to “find large use cases that require 5G speeds and features,” Deloitte said in its latest telecom industry forecast.
“Not only were there seemingly few additional use cases driving 5G adoption and monetization in 2024, but there may not be many more for 2025 or even 2026 either.” The market research/accounting firm continued:
Our outlook focuses on three of those difficult choices, and we have a full chapter on each:
- In 2025, the most discussed source of growth for many industries is generative AI, and telcos are asking how they can share in that excitement. Telcos are using gen AI to reduce costs, become more efficient, and offer new services. Some are building new gen AI data centers to sell training and inference to others. A gen AI gold rush expected over the next five years. Spending estimates range from hundreds of billions to over a trillion dollars on the physical layer required for gen AI: chips, data centers, electricity. Close to another hundred billion US dollars will likely be spent on the software and services layer.
- At the same time, telcos are roughly at the midpoint between the launch of 5G and the expected launch of 6G, and they want to confirm that they can shape 6G to be more profitable than 5G has so far been.
- Finally, after years of divesting noncore assets, telcos are getting primed to deploy M&A strategies in pursuit of growth.
Globally, the telecommunications industry is expected to have revenues of about US$1.53 trillion in 2024, up about 3% over the prior year. Both in 2024 and out to 2028, growth is expected to be higher in Asia Pacific and Europe, Middle East, and Africa, with growth in the Americas being around 1% annually. All three regions are expected to surpass half a trillion dollars in revenue each by 2027. By market cap, the sector is about US$2.6 trillion globally (Figure 1, below).
Stefan summed up: “Market conditions are expected to stabilize in 2025 on an aggregated basis, though it will still be a challenging year. The analyst team is collectively forecasting global telecom equipment revenues across the six programs to stay flat.”
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/global-telecom-infra-faced-ultimate-pitfall-2024
Telco spending on RAN infrastructure continues to decline as does mobile traffic growth
Dell’Oro: Global RAN Market to Drop 21% between 2021 and 2029
Dell’Oro: Global telecom CAPEX declined 10% YoY in 1st half of 2024
Dell’Oro: Private RAN revenue declines slightly, but still doing relatively better than public RAN and WLAN markets
Dell’Oro: RAN market still declining with Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE and Samsung top vendors
Dell’Oro: 4G and 5G FWA revenue grew 7% in 2024; MRFR: FWA worth $182.27B by 2032
Highlights of Dell’Oro’s 5-year RAN forecast
Telecom sessions at Nvidia’s 2025 AI developers GTC: March 17–21 in San Jose, CA
Nvidia’s annual AI developers conference (GTC) used to be a relatively modest affair, drawing about 9,000 people in its last year before the Covid outbreak. But the event now unofficially dubbed “AI Woodstock” is expected to bring more than 25,000 in-person attendees!
Nvidia’s Blackwell AI chips, the main showcase of last year’s GTC (GPU Technology Conference), have only recently started shipping in high volume following delays related to the mass production of their complicated design. Blackwell is expected to be the main anchor of Nvidia’s AI business through next year. Analysts expect Nvidia Chief Executive Jensen Huang to showcase a revved-up version of that family called Blackwell Ultra at his keynote address on Tuesday.
March 18th Update: The next Blackwell Ultra NVL72 chips, which have one-and-a-half times more memory and two times more bandwidth, will be used to accelerate building AI agents, physical AI, and reasoning models, Huang said. Blackwell Ultra will be available in the second half of this year. The Rubin AI chip, is expected to launch in late 2026. Rubin Ultra will take the stage in 2027.
Nvidia watchers are especially eager to hear more about the next generation of AI chips called Rubin, which Nvidia has only teased at in prior events. Ross Seymore of Deutsche Bank expects the Rubin family to show “very impressive performance improvements” over Blackwell. Atif Malik of Citigroup notes that Blackwell provided 30 times faster performance than the company’s previous generation on AI inferencing, which is when trained AI models generate output. “We don’t rule out Rubin seeing similar improvement,” Malik wrote in a note to clients this month.
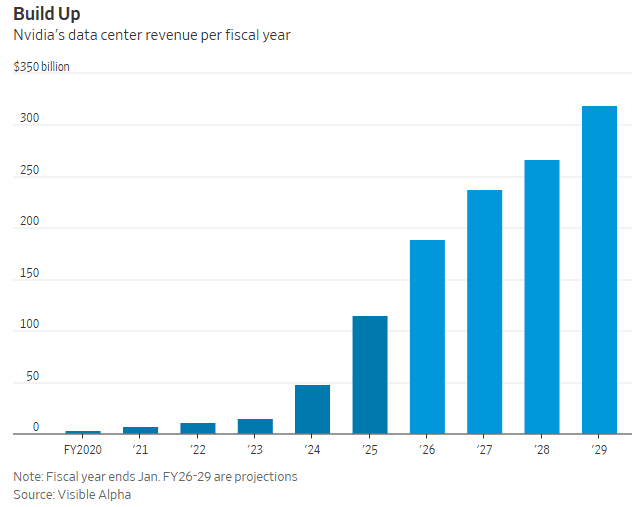
Rubin products aren’t expected to start shipping until next year. But much is already expected of the lineup; analysts forecast Nvidia’s data-center business will hit about $237 billion in revenue for the fiscal year ending in January of 2027, more than double its current size. The same segment is expected to eclipse $300 billion in annual revenue two years later, according to consensus estimates from Visible Alpha. That would imply an average annual growth rate of 30% over the next four years, for a business that has already exploded more than sevenfold over the last two.
Nvidia has also been haunted by worries about competition with in-house chips designed by its biggest customers like Amazon and Google. Another concern has been the efficiency breakthroughs claimed by Chinese AI startup DeepSeek, which would seemingly lessen the need for the types of AI chip clusters that Nvidia sells for top dollar.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Telecom Sessions of Interest:
Wednesday Mar 19 | 2:00 PM – 2:40 PM
Delivering Real Business Outcomes With AI in Telecom [S73438]
In this session, executives from three leading telcos will share their unique journeys of embedding AI into their organizations. They’ll discuss how AI is driving measurable value across critical areas such as network optimization, customer experience, operational efficiency, and revenue growth. Gain insights into the challenges and lessons learned, key strategies for successful AI implementation, and the transformative potential of AI in addressing evolving industry demands.
Thursday Mar 20 | 11:00 AM – 11:40 AM PDT
AI-RAN in Action [S72987]
Thursday Mar 20 | 9:00 AM – 9:40 AM PDTHow Indonesia Delivered a Telco-led Sovereign AI Platform for 270M Users [S73440]
Thursday Mar 20 | 3:00 PM – 3:40 PM PDT
Driving 6G Development With Advanced Simulation Tools [S72994]
Thursday Mar 20 | 2:00 PM – 2:40 PM PDT
Thursday Mar 20 | 4:00 PM – 4:40 PM PDT
Pushing Spectral Efficiency Limits on CUDA-accelerated 5G/6G RAN [S72990]
Thursday Mar 20 | 4:00 PM – 4:40 PM PDT
Enable AI-Native Networking for Telcos with Kubernetes [S72993]
Monday Mar 17 | 3:00 PM – 4:45 PM PDT
Automate 5G Network Configurations With NVIDIA AI LLM Agents and Kinetica Accelerated Database [DLIT72350]
Learn how to create AI agents using LangGraph and NVIDIA NIM to automate 5G network configurations. You’ll deploy LLM agents to monitor real-time network quality of service (QoS) and dynamically respond to congestion by creating new network slices. LLM agents will process logs to detect when QoS falls below a threshold, then automatically trigger a new slice for the affected user equipment. Using graph-based models, the agents understand the network configuration, identifying impacted elements. This ensures efficient, AI-driven adjustments that consider the overall network architecture.
We’ll use the Open Air Interface 5G lab to simulate the 5G network, demonstrating how AI can be integrated into real-world telecom environments. You’ll also gain practical knowledge on using Python with LangGraph and NVIDIA AI endpoints to develop and deploy LLM agents that automate complex network tasks.
Prerequisite: Python programming.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
Nvidia AI-RAN survey results; AI inferencing as a reinvention of edge computing?
The case for and against AI-RAN technology using Nvidia or AMD GPUs
FT: Nvidia invested $1bn in AI start-ups in 2024
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
AT&T claims it achieved a long distance world record top speed of 1.6Tb/s over a single wavelength across 296 km of its long haul fiber optic network (spanning Newark, New Jersey to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania). That is four times faster than its current top speed of 400Gb/s per wavelength!
The 1.6Tb/s wavelength carried two IEEE 802.3df-2024 standard-based 800 Gigabit Ethernet end-to-end circuits, an industry first. It is a full, uninterrupted data path utilizing a single light frequency across the entire fiber length between two endpoints. The single-carrier 1.6 Tb/s wavelength was transported alongside existing live customer traffic on 100Gb/s and 400Gb/s wavelengths.
Open-sourced white box switches were the network equipment used during the trial. The white boxes are designed using the Broadcom Jericho3 packet processor chip and can provide up to 18 x 800G network interface ports all within a 2RU platform. The (Israel based) DriveNets Network Cloud software-based solution is hardware-agnostic and runs open APIs on the white boxes to perform data and control plane functions, including routing at 800G. The use of white boxes and the disaggregation of the hardware and software control costs and facilitate faster innovation.
The two 800GbE signals from the white box were multiplexed to 1.6 Tb/s in Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 Extreme coherent optical transponder, which is the first coherent optical solution to use a 200Gbaud design and 3nm coherent DSP ASIC and to reach speeds up to 1.6 Tb/s on a single carrier. The WL6e technology reduces the space and power per transmitted bit by 50% compared to current 800G transponders. This trial is the first to demonstrate WL6e at 1.6Tb/s with standards compliant 800GbE clients.
In the Newark and Philadelphia offices, 800G DR8 pluggable transceivers from Coherent were installed in the white box router and WL6e transponder to create the cross-office connectivity between the packet and optical technologies. And 800GbE client signals, provided by Keysight’s AresOne-M 800GE testset, fed the white box through additional pairs of 800G DR8 pluggable client optics, allowing verification of end-to-end performance of the two 800GbE services from Newark to Philadelphia.
Quotes:
“Traffic on AT&T’s network continues to increase as consumers are using more connected devices,” said Mike Satterlee, vice president, Network Infrastructure and Services, AT&T. “We anticipate network traffic growth to double by 2028 and the technologies demonstrated in this trial will play a key role in AT&T’s continued efforts to keep up with increasing customer demand to send data, watch videos, and use streaming services.”
“This groundbreaking achievement with AT&T adds to a growing list of Ciena industry-firsts that push the boundaries of optical network speed and capacity,” said Dino DiPerna, senior vice president, Global Research and Development, Ciena. “Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 coherent optics will support AT&T’s next gen converged optical network and efforts to build a cloud-based and AI-ready network with greater scale, flexibility and efficiency.”

Verizon’s 1.6Tb/s on Metro Fiber Network:
AT&T’s announcement comes just a few months after arch-rival Verizon announced a 1.6 Tb/s milestone of its own. Verizon also, working with Ciena, achieved that peak speed on a single wavelength, but on its metro fiber (not long distance) network. Verizon is mainly looking to advance through M&A. Its proposed acquisition of Frontier Communications is still pending, with some Frontier shareholders insisting that the US$20 billion price tag undervalues the operator.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
AT&T has spent the past six months demonstrating that it aims to build its way to fiber domination. It rolled out fiber to around 600,000 premises in the 4th quarter of last year, taking its total fiber footprint to 28.9 million locations; it is shooting for 50 million by the end of 2029.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2025/data-transport.html
https://www.business.att.com/products/wavelength-services.html
https://www.telecoms.com/fibre/at-t-touts-1-6-tbps-fibre-speed-milestone-as-us-battle-continues
AT&T Highlights: 5G mid-band spectrum, AT&T Fiber, Gigapower joint venture with BlackRock/disaggregation traffic milestone
Nokia, Windstream Wholesale and Colt complete world’s first ultra-fast 800GbE optical and IP service trial
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
T-Mobile posts impressive wireless growth stats in 2Q-2024; fiber optic network acquisition binge to complement its FWA business
Bell Canada buying Ziply Fiber for C$7 billion; will become 3rd largest fiber ISP in U.S.
Standards are the key requirement for telco/satellite integration: D2D and satellite-based mobile backhaul
At the Satellite 2025 conference in Washington DC, Analysys Mason Research Director Lluc Palerm moderated a panel session discussing Direct to Device (D2D) and satellite mobile backhaul. Market forecasts have been impressive. Analysys Mason says investments in the satellite communications industry from AT&T, Google, Vodafone, Apple “could well surpass $20 billion in 2025.” The market research firm believes annual satellite telecoms service revenue will reach $165 billion by 2033.
Indeed, many analysts believe that the 3GPP non-terrestrial networks (NTN) specification work will facilitate new markets and opportunities, lowers costs, and provides seamless mobility sought by certain markets, such as first responders, military and aviation. Airbus is leading by example, as demonstrated in its deployment of 5G NTN over OneWeb LEO satellites and chips from MediaTek.
- Amina Boubendir, PhD, head of research and standardization for Airbus Defense and Space, shared an update on related 3GPP specification work during the session. She pointed out that in 3GPP Releases 17, 18 and (forthcoming) 19 and 20, the work has progressed from IoT to broadband to low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites. “LEO comes into the integration between terrestrial and non-terrestrial network (NTN) in Release 19, and both IoT and broadband are being covered as we move with the community into Release 20,” Boubendir said.
- Jean-Philippe Gillet, Vice President and General Manager, Networks Intelsat US, said that telcos and their suppliers are also pushing to integrate 5G NTN into future deployments, according to JP Gillet, SVP Intelsat. He said it’s not if but when. “The reality is mobile network operators are under tremendous pressure,” he said. “They need to drive innovation to stay relevant.”
- Telesat CMO Glenn Katz said the mobile backhaul market will reach $600 billion in the mid-2030s and that Telesat expects to capture its share of that total by continuing to focus on carrier applications in the enterprise, maritime, aviation and government markets. Telesat has already run Release 19 on its test LEO satellite – Katz said where these efforts lead commercially remains an open question. “We can’t close the business case on how much it’s going to cost to put those specific types of technologies on a satellite,” he added. “We’re a carrier’s carrier. I think some of us in the industry need to continue to think that way. Those telcos are giant. We’re not going to take business from them. We have to be complimentary.”
- Nikola Kromer, VP Product Marketing, ST Engineering iDirect said there are other requirements. “So, it’s not just the 5G NTN standard that we need,” she said. In particular, she mentioned the Digital Intermediate Frequency Interoperability (DIFI) Consortium and the Waveform Architecture for Virtualized Ecosystems (WAVE) Consortium. ST Engineering iDirect announced a subscription-based model, Intuition Unbound, offering operations as a service (OaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS). According to ST Engineering, the selling point is that satellite providers and telcos can subscribe to a ground network service and turn a massive capital spending outlay into smaller, more digestible monthly payments.
Standardization efforts such as DIFI are important to accelerate innovation, Boubendir said. “Telcos have already gone through this digitalization process. The space industry, I would say, has to catch up.” Building out new systems in cloud-native environments is a challenge, especially if you want to be efficient and fast.

Illustration of the classes of orbits of satellites [source: 3GPP TR 22.822]
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
5G NTN and Status in ITU-R WP 4B:
ITU-R Working Party 4B (WP 4B) is responsible for recommendations related to: systems, air interfaces, performance and availability objectives for FSS, BSS and MSS, including IP-based applications and satellite news gathering. Many analysts believe NTNs will be an essential component of 6G/IMT-2030. ITU-R, the official standards body for IMT (all the Gs) envisions 6G networks to deliver intelligent, seamless connectivity that supports reliable, sustainable, and resilient communications. To achieve this vision, NTNs represent a significant advancement by extending connectivity beyond the Earth’s surface. These networks integrate advanced communication technologies that go beyond conventional terrestrial infrastructure, enabling comprehensive global connectivity across domains such as the Internet, Internet of Things (IoT), navigation, disaster recovery, remote access, Earth observation, and even scientific initiatives like interplanetary communication.
An October 28, 2024 4B Working document is a related preliminary draft new Report ITU-R M.[SAT IOT] – Technical and operational aspects of satellite Internet of Things (IoT) applications. This document is intended as a snapshot of evolving satellite IoT technologies and practices. Satellite IoT encompasses a variety of technologies that have been in use for decades, yet continue to evolve rapidly. The information presented reflects the state of the industry as of the date of this Report and is subject to change. The purpose of this report is to provide an overview of the current and emerging satellite IoT applications and their technical and operational aspects. It is also noted that the implementation of [current and emerging] satellite IoT does not require specific regulatory provisions in the Radio Regulations, and this Report does not address any spectrum requirements and technical requirements for satellite IoT applications, and does not preclude future technologies.
At it’s October 2024 meeting, Sub-Working Group (SWG) 4B1 dealt with satellites in Next Generation Access Technologies. 4B1 started work on a preliminary draft new Recommendation ITU-R M.[IMT 2020-SAT.SPECS]. That proposed ITU-R Recommendation will identify satellite radio interface technologies of International Mobile Telecommunications-2020 (IMT-2020) and provides the detailed radio interface specifications. SWG 4B1 first focused on reviewing the Final Evaluation Reports on the proposed candidate IMT-2020 satellite radio interface technologies and preparing responses back to 3GPP and feedback to the Independent Expert Groups as well as other IMT-2020 matters.
At 4B’s Shanghai, China 30 April – 6 May, 2025 meeting, received contributions will be considered in an attempt to finalize the working document, elevate it to Draft New Recommendation and send it to SG 4 plenary for approval. It is highly unlikely all that can be done in a single ITU-R WP meeting so that objective is unrealistic in this author’s opinion!
Separately, a proposed work plan for the future development of satellite IMT-2030 – Work plan, timeline, process and deliverables for the future development of satellite IMT-2030 was started. These are necessary to provide the expected ITU-R outcomes of evolved satellite IMT in support of the next generation of mobile communications systems beyond IMT-2020, around the 2030 timeframe. Circular Letter(s) are expected to be issued at the appropriate time(s) to announce the invitation for submitting formal proposals and other relevant information. The deliverable backgrounds and processes together with the Circular Letter(s) will describe the comprehensive methodology for developing technology proposals for satellite IMT-2030. WP 4B plans to hold a workshop on IMT‑2030, focusing on satellite radio interfaces.
In summary, it appears the NTN specification work is ONLY being done in 3GPP which will liase relevant documents to 4B in preparation for their ITU-R NTN 5G and 6G Recommendations.
References:
https://www.analysysmason.com/events-and-webinars/events/satellite-2025/
https://www.analysysmason.com/about-us/news/predictions-2025/telco-investment-space/
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/ntn-overview
Momentum builds for wireless telco- satellite operator engagements
5G connectivity from space: Exolaunch contract with Sateliot for launch and deployment of LEO satellites
Satellite 2024 conference: Are Satellite and Cellular Worlds Converging or Colliding?
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
5G connectivity from space: Exolaunch contract with Sateliot for launch and deployment of LEO satellites
SatCom market services, ITU-R WP 4G, 3GPP Release 18 and ABI Research Market Forecasts
U.S. BEAD overhaul to benefit Starlink/SpaceX at the expense of fiber broadband providers
The U.S. The Commerce Department is examining changes to the NTIA’s $42.5 billion broadband funding bill (Broadband Equity Access and Deployment- BEAD), which endeavors to expand internet access in underserved/unserved areas. [BEAD was part of the 2021 Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) during the Biden administration] The proposed new rules will make it much easier for Elon Musk owned Starlink satellite-internet service, to tap in to rural broadband funding, according to the Wall Street Journal. [Starlink is owned by SpaceX which is majority owned by Elon Musk).
Commerce Department Secretary Howard Lutnick said that BEAD will be revamped “to take a tech-neutral approach that is rigorously driven by outcomes, so states can provide internet access for the lowest cost.” The department is also “exploring ways to cut government red tape that slows down infrastructure construction. We will work with states and territories to quickly get rid of the delays and the waste. Thereafter, we will move quickly to implementation in order to get households connected. All Americans will receive the benefit of the bargain that Congress intended for BEAD. We’re going to deliver high-speed internet access, and we will do it efficiently and effectively at the lowest cost to taxpayers.”
By making the broadband the grant program “technology-neutral,” it will free up states to award more funds to satellite-internet providers such as Starlink, rather than mainly to companies that lay fiber-optic cables which connect the millions of U.S. households that lack high-speed internet service.
The potential new rules could greatly increase the share of funding available to Starlink. Under the BEAD program’s original rules, Starlink was expected to get up to $4.1 billion, said people familiar with the matter. With Commerce’s overhaul, Starlink, a unit of Musk’s SpaceX, could receive $10 billion to $20 billion.
“The Trump administration is committed to slashing government bureaucracy and harnessing cutting-edge technology to deliver real results for the American people, especially rural Americans who were left behind” under the Biden administration, White House spokesman Kush Desai said.
“Leave it alone; let the states do what they’ve done,” Missouri State Rep. Louis Riggs, a Republican, said in a recent interview. “The feds could not do what the states have done. In 10 or 15 years, all they basically did, they walked in and screwed everything up. God love them, they just keep throwing money at the problem, which is okay when you give it to the states and let us do our jobs, but trying to claw that funding back and stand up a new grant round is the worst idea I’ve heard in a very long time, and that’s saying a lot coming out of D.C.”
The overhaul could be announced as soon as this week, possibly without some details in place, the people said. Following any changes, states might have to rewrite their plans for how to spend their funding from the program, which could delay the implementation.
Lutnick told Commerce staff he plans to do away with other BEAD program rules, including some related to climate impact and sustainability, as well as provisions that encouraged states to fund companies with a racially diverse workforce or union participation, the people said. The program requires internet-service providers that receive funding to offer affordable plans for lower-income customers. Lutnick saids he is considering reducing those obligations.
Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick at the White House last month. Photo: Francis Chung/Pool/Cnp/ZUMA Press
Many broadband providers worried the Musk-led Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) would eliminate or reduce the program’s funding. Is that not a conflict of interest considering that Musk owns Starlink/SpaceX?
Given the overhaul, fiber broadband providers may not benefit from it as much as they expected because non-fiber technologies are poised to receive more funding than before.
Fiber Broadband Association CEO Gary Bolton said in a statement that all “Americans deserve fiber for their critical broadband infrastructure. Fiber provides significantly better performance on every metric, such as broadband speeds, capacity, lowest latency and jitter, highest resiliency, sustainability and provides the maximum benefit for economic development and is required for AI, Quantum Networking, smart grid modernization, public safety, 5G and the future of mobile wireless communications. We urge our policymakers to do what’s right for people and to not penalize Americans for where they live or their current income levels.”
Telecommunications and broadband consultant John Greene wrote that states that have started the sub-grantee selection process, such as Louisiana, “might be forced to rethink their process in light of potential new rules.” Other “states, like Texas, might be better served to pause their process until after Commerce has completed their review and made any necessary changes,” he said.
References:
Nokia will manufacture broadband network electronics in U.S. for BEAD program
New FCC Chairman Carr Seen Clarifying Space Rules and Streamlining Approvals Process
Highlights of FiberConnect 2024: PON-related products dominate
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
According to a new research report from Goldman Sachs-China, the three major, state owned telecom operators (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom) are quietly becoming the core beneficiaries of China’s AI boom. One reason is that, thanks to their deployment of China’s most extensive cloud infrastructure, they can serve other cloud companies as well as provide their own cloud services to their end user customers. They also enjoy the cost and scale advantages of owning their own data centers and bandwidth. For some IaaS companies, data center and connectivity together account for as much as 60% of total expense, according to Goldman-China.
Goldman analysts believe that telecom operators’ cloud businesses have obvious cost advantages compared to other cloud companies. Those are the following:
- The big 3 Chinese network operators have built their own Data Centers (DCs) and so do not rely on external DC service providers. They even provide DC services to other cloud companies such as Alibaba, which makes the IDC expenses of their cloud business lower.
- The bandwidth cost of operator cloud business is significantly lower than that of other cloud companies because operators use their own network infrastructure, while other cloud companies need to pay operators for bandwidth and private network fees connecting different data centers.
- For the IaaS cloud business, if external DC and bandwidth are used, data center costs (DC services and bandwidth) will account for a considerable proportion of the total cost of the cloud company. Goldman cites QingCloud Technology as an example, its data center costs (including cabinets, bandwidth, etc.) account for 50%-60% of its total costs.
Looking ahead, the telcos are strongly placed to take advantage of the DeepSeek AI boom, thanks to their early embrace of DeepSeek and the government’s push to promote AI among the state-owned enterprises that account for about 30% of operator revenue, Goldman argues. The report states, “the state-owned enterprise background makes the deployment of AI/Deepseek by government agencies and state-owned enterprises more beneficial to telecom operators.”
In the past two weeks, China’s three major operators have begun to help important customers deploy DeepSeek models. China Mobile supports PetroChina in deploying a full-stack Deepseek model; China Telecom provides the same service to Sinopec; and China Unicom cooperates with the Foshan Municipal Bureau of Industry and Information Technology. More importantly, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council (SASAC) launched the “AI+” action plan on February 21 to encourage Chinese state-owned enterprises to accelerate the development and commercial application of AI. According to Goldman Sachs research, government-related customers account for about 30% of telecom operators’ cloud revenue. Therefore, the deployment of AI/DeepSeek by government agencies and state-owned enterprises will clearly benefit telecom operators.
Separately, China Mobile announced at Mobile World Congress 2025 in Barcelona that it is leveraging artificial intelligence to transform telecommunications networks and drive unprecedented data growth while positioning itself at the forefront of AI-Native network innovation. China Mobile Executive Vice President Li Huidi outlined the company’s ambitious “AI+NETWORK” strategy in a keynote address titled “AI+NETWORK, Pioneering the Digital-Intelligent Future” during the Global MBB Forum Top Talk Summit on Sunday.
.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
Li Huidi, executive vice president of China Mobile, speaks at the Global MBB Forum Top Talk Summit at Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, Spain, March 2, 2025. (Photo/China Mobile)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://wallstreetcn.com/articles/3741901 (Chinese)
https://www.telecoms.com/partner-content/china-mobile-unveils-ai-network-strategy-at-mwc
https://www.lightreading.com/ai-machine-learning/china-telcos-rush-to-embrace-deepseek
China Telecom’s 2025 priorities: cloud based AI smartphones (?), 5G new calling (GSMA), and satellite-to-phone services
Quartet launches “Open Telecom AI Platform” with multiple AI layers and domains
At Mobile World Congress 2025, Jio Platforms (JPL), AMD, Cisco, and Nokia announced the Open Telecom AI Platform, a new project designed to pioneer the use of AI across all network domains. It aims to provide a centralized intelligence layer that can integrate AI and automation into every layer of network operations.
The AI platform will be large language model (LLM) agnostic and use open APIs to optimize functionality and capabilities. By collectively harnessing agentic AI and using LLMs, domain-specific SLMs and machine learning techniques, the Telecom AI Platform is intended to enable end-to-end intelligence for network management and operations. The founding quartet of companies said that by combining shared elements, the platform provides improvements across network security and efficiency alongside a reduction in total cost of ownership. The companies each bring their specific expertise to the consortium across domains including RAN, routing, AI compute and security.
Jio Platforms will be the initial customer. The Indian telco says it will be AI-agnostic and use open APIs to optimize functionality and capabilities. It will be able to make use of agentic AI, as well as large language models (LLMs), domain-specific small language models (SLMs), and machine learning techniques.
“Think about this platform as multi-layer, multi-domain. Each of these domains, or each of these layers, will have their own agentic AI capability. By harnessing agentic AI across all telco layers, we are building a multimodal, multidomain orchestrated workflow platform that redefines efficiency, intelligence, and security for the telecom industry,” said Mathew Oommen, group CEO, Reliance Jio.
“In collaboration with AMD, Cisco, and Nokia, Jio is advancing the Open Telecom AI Platform to transform networks into self-optimising, customer-aware ecosystems. This initiative goes beyond automation – it’s about enabling AI-driven, autonomous networks that adapt in real time, enhance user experiences, and create new service and revenue opportunities across the digital ecosystem,” he added.
On top of Jio Platforms’ agentic AI workflow manager is an AI orchestrator which will work with what is deemed the best LLM. “Whichever LLM is the right LLM, this orchestrator will leverage it through an API framework,” Oomen explained. He said that Jio Platforms could have its first product set sometime this year.
Under the terms of the agreement, AMD will provide high-performance computing solutions, including EPYC CPUs, Instinct GPUs, DPUs, and adaptive computing technologies. Cisco will contribute networking, security, and AI analytics solutions, including Cisco Agile Services Networking, AI Defense, Splunk Analytics, and Data Center Networking. Nokia will bring expertise in wireless and fixed broadband, core networks, IP, and optical transport. Finally, Jio Platforms Limited (JPL) will be the platform’s lead organizer and first adopter. It will also provide global telecom operators’ initial deployment and reference model. 
The Telecom AI Platform intends to share the results with other network operators (besides Jio).
“We don’t want to take a few years to create something. I will tell you a little secret, and the secret is Reliance Jio has decided to look at markets outside of India. As part of this, we will not only leverage it for Jio, we will figure out how to democratize this platform for the rest of the world. Because unlike a physical box, this is going to be a lot of virtual functions and capabilities.”
AMD represents a lower-cost alternative to Intel and Nvidia when it comes to central processing units (CPUs) and graphics processing units (GPUs), respectively. For AMD, getting into a potentially successful telco platform is a huge success. Intel, its arch-rival in CPUs, has a major lead with telecom projects (e.g. cloud RAN and OpenRAN), having invested massive amounts of money in 5G and other telecom technologies.
AMD’s participation suggests that this JPL-led group is looking for hardware that can handle AI workloads at a much lower cost then using NVIDIA GPUs.
“AMD is proud to collaborate with Jio Platforms Limited, Cisco, and Nokia to power the next generation of AI-driven telecom infrastructure,” said Lisa Su, chair and CEO, AMD. “By leveraging our broad portfolio of high-performance CPUs, GPUs, and adaptive computing solutions, service providers will be able to create more secure, efficient, and scalable networks. Together we can bring the transformational benefits of AI to both operators and users and enable innovative services that will shape the future of communications and connectivity.”
Jio will surely be keeping a close eye on the cost of rolling out this reference architecture when the time comes, and optimizing it to ensure the telco AI platform is financially viable.
“Nokia possesses trusted technology leadership in multiple domains, including RAN, core, fixed broadband, IP and optical transport. We are delighted to bring this broad expertise to the table in service of today’s important announcement,” said Pekka Lundmark, President and CEO at Nokia. “The Telecom AI Platform will help Jio to optimise and monetise their network investments through enhanced performance, security, operational efficiency, automation and greatly improved customer experience, all via the immense power of artificial intelligence. I am proud that Nokia is contributing to this work.”
Cisco chairman and CEO Chuck Robbins said: “This collaboration with Jio Platforms Limited, AMD and Nokia harnesses the expertise of industry leaders to revolutionise networks with AI.
“Cisco is proud of the role we play here with integrated solutions from across our stack including Cisco Agile Services Networking, Data Center Networking, Compute, AI Defence, and Splunk Analytics. We look forward to seeing how the Telecom AI Platform will boost efficiency, enhance security, and unlock new revenue streams for service provider customers.”
If all goes well, the Open Telecom AI Platform could offer an alternative to Nvidia’s AI infrastructure, and give telcos in lower-ARPU markets a more cost-effective means of imbuing their network operations with the power of AI.
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/ai/jio-s-new-ai-club-could-offer-a-cheaper-route-into-telco-ai
Does AI change the business case for cloud networking?
For several years now, the big cloud service providers – Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud – have tried to get wireless network operators to run their 5G SA core network, edge computing and various distributed applications on their cloud platforms. For example, Amazon’s AWS public cloud, Microsoft’s Azure for Operators, and Google’s Anthos for Telecom were intended to get network operators to run their core network functions into a hyperscaler cloud.
AWS had early success with Dish Network’s 5G SA core network which has all its functions running in Amazon’s cloud with fully automated network deployment and operations.
Conversely, AT&T has yet to commercially deploy its 5G SA Core network on the Microsoft Azure public cloud. Also, users on AT&T’s network have experienced difficulties accessing Microsoft 365 and Azure services. Those incidents were often traced to changes within the network’s managed environment. As a result, Microsoft has drastically reduced its early telecom ambitions.
Several pundits now say that AI will significantly strengthen the business case for cloud networking by enabling more efficient resource management, advanced predictive analytics, improved security, and automation, ultimately leading to cost savings, better performance, and faster innovation for businesses utilizing cloud infrastructure.
“AI is already a significant traffic driver, and AI traffic growth is accelerating,” wrote analyst Brian Washburn in a market research report for Omdia (owned by Informa). “As AI traffic adds to and substitutes conventional applications, conventional traffic year-over-year growth slows. Omdia forecasts that in 2026–30, global conventional (non-AI) traffic will be about 18% CAGR [compound annual growth rate].”
Omdia forecasts 2031 as “the crossover point where global AI network traffic exceeds conventional traffic.”
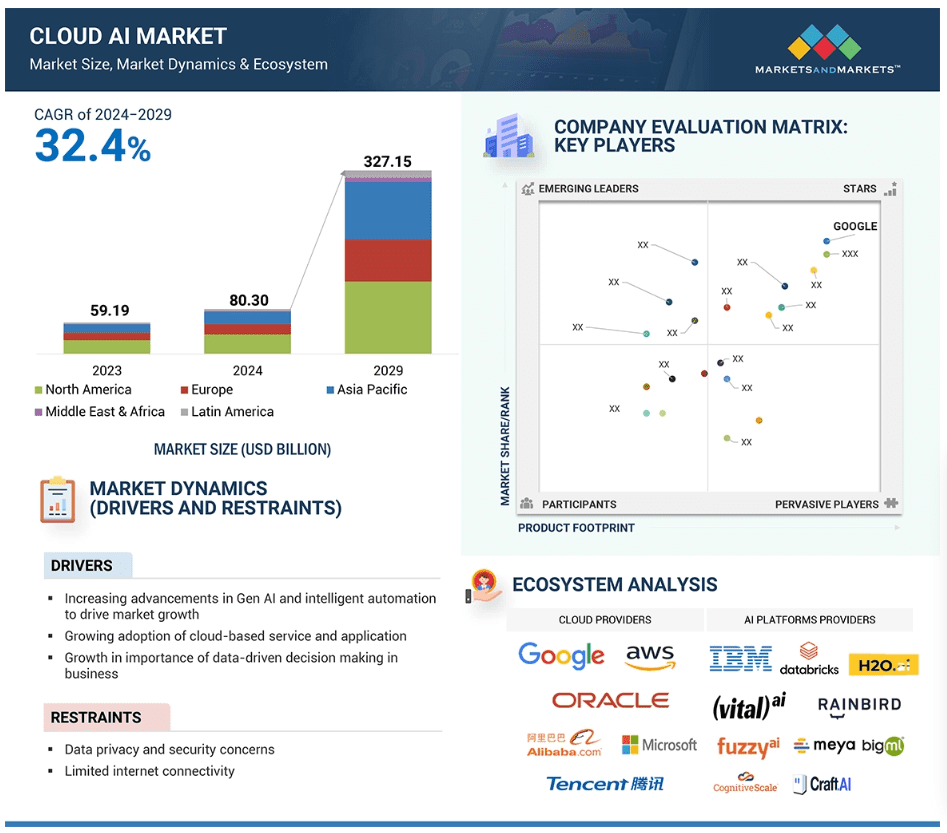
Markets & Markets forecasts the global cloud AI market (which includes cloud AI networking) will grow at a CAGR of 32.4% from 2024 to 2029.
AI is said to enhance cloud networking in these ways:
- Optimized resource allocation:
AI algorithms can analyze real-time data to dynamically adjust cloud resources like compute power and storage based on demand, minimizing unnecessary costs. - Predictive maintenance:
By analyzing network patterns, AI can identify potential issues before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing downtime. - Enhanced security:
AI can detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time through anomaly detection and behavioral analysis, improving overall network security. - Intelligent routing:
AI can optimize network traffic flow by dynamically routing data packets to the most efficient paths, improving network performance. - Automated network management:
AI can automate routine network management tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
The pitch is that AI will enable businesses to leverage the full potential of cloud networking by providing a more intelligent, adaptable, and cost-effective solution. Well, that remains to be seen. Google’s new global industry lead for telecom, Angelo Libertucci, told Light Reading:
“Now enter AI,” he continued. “With AI … I really have a power to do some amazing things, like enrich customer experiences, automate my network, feed the network data into my customer experience virtual agents. There’s a lot I can do with AI. It changes the business case that we’ve been running.”
“Before AI, the business case was maybe based on certain criteria. With AI, it changes the criteria. And it helps accelerate that move [to the cloud and to the edge],” he explained. “So, I think that work is ongoing, and with AI it’ll actually be accelerated. But we still have work to do with both the carriers and, especially, the network equipment manufacturers.”
Google Cloud last week announced several new AI-focused agreements with companies such as Amdocs, Bell Canada, Deutsche Telekom, Telus and Vodafone Italy.
As IEEE Techblog reported here last week, Deutsche Telekom is using Google Cloud’s Gemini 2.0 in Vertex AI to develop a network AI agent called RAN Guardian. That AI agent can “analyze network behavior, detect performance issues, and implement corrective actions to improve network reliability and customer experience,” according to the companies.
And, of course, there’s all the buzz over AI RAN and we plan to cover expected MWC 2025 announcements in that space next week.
https://www.lightreading.com/cloud/google-cloud-doubles-down-on-mwc
Nvidia AI-RAN survey results; AI inferencing as a reinvention of edge computing?
The case for and against AI-RAN technology using Nvidia or AMD GPUs
Generative AI in telecom; ChatGPT as a manager? ChatGPT vs Google Search
Deutsche Telekom and Google Cloud partner on “RAN Guardian” AI agent
Deutsche Telekom and Google Cloud today announced a new partnership to improve Radio Access Network (RAN) operations through the development of a network AI agent. Built using Gemini 2.0 in Vertex AI from Google Cloud, the agent can analyze network behavior, detect performance issues, and implement corrective actions to improve network reliability, reduce operational costs, and enhance customer experiences.
Deutsche Telekom says that as telecom networks become increasingly complex, traditional rule-based automation falls short in addressing real-time challenges. The solution is to use Agentic AI which leverages large language models (LLMs) and advanced reasoning frameworks to create intelligent agents that can think, reason, act, and learn independently.
The RAN Guardian agent, which has been tested and verified at Deutsche Telekom, collaborates in a human-like manner, detecting network anomalies and executing self-healing actions to optimize RAN performance. It will be exhibited at next week’s Mobile World Congress (MWC) in Barcelona, Spain.
–>This cooperative initiative appears to be a first step towards building autonomous and self-healing networks.
In addition to Gemini 2.0 in Vertex AI, the RAN Guardian also uses CloudRun, BigQuery, and Firestore to help deliver:
- Autonomous RAN performance monitoring: The RAN Guardian will continuously analyze key network parameters in real time to predict and detect anomalies.
- AI-driven issue classification and routing: The agent will identify and prioritize network degradations based on multiple data sources, including network monitoring data, inventory data, performance data, and coverage data.
- Proactive network optimization: The agent will also recommend or autonomously implement corrective actions, including resource reallocation and configuration adjustments.

“By combining Deutsche Telekom’s deep telecom expertise with Google Cloud’s cutting-edge AI capabilities, we’re building the next generation of intelligent networks,” said Angelo Libertucci, Global Industry Lead, Telecommunications, Google Cloud. “This means fewer disruptions, faster speeds, and an overall enhanced mobile experience for Deutsche Telekom’s customers.”
“Traditional network management approaches are no longer sufficient to meet the demands of 5G and beyond. We are pioneering AI agents for networks, working with key partners like Google Cloud to unlock a new level of intelligence and automation in RAN operations as a step towards autonomous, self-healing networks” said Abdu Mudesir, Group CTO, Deutsche Telekom.
Mr. Mudesir and Google Cloud’s Muninder Sambi will discuss the role of AI agents in the future of network operations at MWC next week.
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/ai/deutsche-telekom-and-google-cloud-team-up-on-ai-agent-for-ran-operations
Nvidia AI-RAN survey results; AI inferencing as a reinvention of edge computing?
The case for and against AI-RAN technology using Nvidia or AMD GPUs
AI RAN Alliance selects Alex Choi as Chairman
AI sparks huge increase in U.S. energy consumption and is straining the power grid; transmission/distribution as a major problem
Ookla: Europe severely lagging in 5G SA deployments and performance
According to a new joint study from Omdia and Ookla, Europe has had the poorest 5G SA availability and performance among major regions. In Q4 2024, China (80%), India (52%), and the United States (24%) led the world in 5G SA availability based on Speedtest® sample share, markedly ahead of Europe (2%).
The European region also lagged behind its peers in performance, with the median European consumer experiencing 5G SA download speeds of 221.17 Mbps—lower than those in the Americas (384.42 Mbps) and both Developed (237.04 Mbps) and Emerging (259.73 Mbps) Asia Pacific. The interplay of earlier deployments, a more diversified multi-band spectrum strategy, and greater operator willingness to invest in the 5G core to monetize new use cases have driven rollouts at a faster pace in regions outside Europe.
The European Commission has championed measures to accelerate private investment in 5G SA, highlighting network slicing—a flagship capability of cloud-native core networks—as a key potential driver of its broader industrial strategy in sectors such as precision manufacturing, defense and clean energy. Up until this point, high-quality public data examining Europe’s progress in 5G SA—and benchmarking its competitive position relative to other global regions—has been scarce. In its latest annual report, Connect Europe, the trade body representing Europe’s telecoms operators, noted that “there is limited information available about the extent of operators’ rollout of 5G SA.”
Advanced network capabilities enabled by the technology remain stubbornly limited to just a few operators in leading markets such as the U.S., according to the study, while Europe lags behind its peers on several 5G SA performance indicators, “raising concerns about the bloc’s competitiveness in the technology.”
Network operator investment per capita also lags in Europe as per the below chart:
When faced with choices among investments in fiber, 5G RAN, and 5G SA core, the latter frequently loses out, since operators can still launch a “5G” network by leveraging alternative technologies. There is also a lack of 5G SA-compatible devices, especially devices with User Equipment Routing Selection Policy (URSP) technology, which allows a device to dynamically select a slice (or multiple slices) provisioned by an operator. However, only Android 12/iOS 17 mobile devices support that largely unknown technology.
While capital spending on the 5G core transition is now increasing rapidly, European network operators will remain committed to strict cost discipline Based on Omdia’s Q3 2024 quarterly core software market share and forecast, the research firm believes that the global core market revenue from both 4G and 5G network functions will grow with a five-year CAGR of 3.2% between 2023 and 2028. When considering the spending in 5G core software, the forecasted growth with a five-year CAGR during the same period is of 17.0%.
Omdia now forecasts that 5G SA core spending in EMEA will grow with a five-year CAGR of 26.2% between 2023 and 2028. Nonetheless, as a prerequisite, deploying the 5G core also requires a good 5G radio coverage, to avoid a degraded experience where the 5G coverage is limited or nonexistent, and where the user falls back on 4G-LTE or 2G/3G. This means operators must invest in 5G RAN, which is usually considered the highest capex draining activity for an operator. While 5G is known for very high throughput speeds using mid-band (and particularly C-band) spectrum, these bands need to be complemented by sub-GHz spectrum deployment, in order to offer improved in-building and wide area coverage. This rollout has been slow in many European markets, with 5G availability in all countries outside the Nordics remaining significantly lower than that in the United States and China, according to Ookla’s Q4 2024 Speedtest Intelligence® data.
One bright spot is that Europe has made progress on achieving low latency on its 5G networks. In Q4 2024, the average country-wide median latency in Europe was 32 milliseconds (ms) compared to 35 ms in the Americas and 36 ms in Emerging Asia Pacific region.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/eurobites-europe-behind-on-5g-sa-study
https://www.ookla.com/s/media/2025/02/ookla_omdia-5GSA_0225.pdf
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
Latest Ericsson Mobility Report talks up 5G SA networks and FWA
GSA 5G SA Core Network Update Report
ABI Research: Expansion of 5G SA Core Networks key to 5G subscription growth
Vision of 5G SA core on public cloud fails; replaced by private or hybrid cloud?
Nokia and Eolo deploy 5G SA mmWave “Cloud RAN” network
Nokia, BT Group & Qualcomm achieve enhanced 5G SA downlink speeds using 5G Carrier Aggregation with 5 Component Carriers