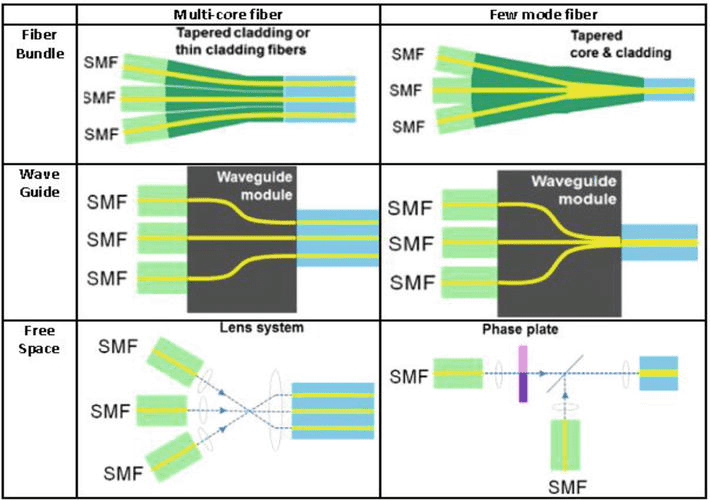
Optical network transmission
STL completes successful Multi-Core Fiber (MCF) trial with Colt in London, UK
India based STL, a global provider of optical and digital connectivity solutions for AI-era networks, has completed multi-core fiber (MCF) field trials with Colt Technology Services on Colt’s London metro optical network. The trial is a meaningful proof point for space-division multiplexing (SDM) in carrier environments, demonstrating that MCF can lift per-fiber strand capacity while staying within existing civil and duct constraints and improving overall network energy and cost metrics.
The deployment used STL’s Multiverse™ four-core MCF, designed with the same 125 µm cladding diameter as conventional single-mode fibre (SMF) and a 250/200 µm coating, enabling seamless handling with existing cable designs and installation practices. The trial route connected two Colt Points of Presence (PoPs) on the London metro network over spans of approximately 9 km and 63 km, representing both short-haul metro and longer metro-regional use cases.
From a transmission standpoint, the network achieved an 800 Gbps line rate with service validation for 100GE and 400GE, aligning with current high-capacity router and data-centre interconnect interfaces. STL and Colt validated performance across a broad set of optical and system parameters, including chromatic dispersion (CD), polarization mode dispersion (PMD), inter-core crosstalk, throughput, fault behavior, OTDR signatures, insertion loss, and optical return loss (ORL), with results within expected design envelopes. This indicates that Multiverse™ MCF can be engineered and operated to comparable performance baselines as legacy SMF while delivering higher spatial capacity.
Architecturally, STL’s MCF platform integrates four independent cores within a standard SMF cladding profile, effectively multiplying per-fibre capacity without increasing cable diameter. For operators, this directly addresses constraints in congested metro ducts, legacy civil infrastructure, and brownfield routes where augmenting capacity by pulling additional cables is either cost-prohibitive or operationally disruptive. In these scenarios, MCF creates a higher bit-per-mm² and bit-per-duct investment profile, improving both capex efficiency (less civil work, fewer ducts) and opex metrics such as energy per transported bit.
STL positions itself as one of the early movers in taking MCF from controlled lab demonstrations into operational networks, including buried and ducted plant, backed by a full ecosystem spanning fibre, cable, and connectivity hardware through its Optotec portfolio. Coupled with STL’s broader focus on AI-ready optical infrastructure and 5G-ready digital network solutions, the Colt trial underlines a practical migration path for carriers looking to future-proof metro and data-centre interconnect footprints against emerging AI, cloud, and 5G traffic patterns without wholesale rebuilds of underlying passive infrastructure.
“As network demand accelerates, customers are looking for more bandwidth without sacrificing security, performance, or sustainability,” said Buddy Bayer, Chief Operating Officer, Colt Technology Services. “At Colt, we continue to push optical networking forward, and this pilot represents an important step in Europe and the USA. It reflects our focus on building scalable networks that deliver growth in capacity without increasing environmental impact.”
Dr Badri Gomatam, CTO, STL, said the trial highlights the value of joint innovation in advancing optical infrastructure. “Collaborations like this speed up adoption of next-generation connectivity technologies. STL’s Multiverse MCF portfolio is designed for the high-density, ultra-low latency, and resilient connectivity requirements of AI, hyperscale cloud, and future digital platforms globally,” he said. STL stated that the trial results strengthen confidence in MCF as a viable technology for the growing bandwidth requirements driven by AI workloads, cloud scale-out, and new digital services.
“As network demand accelerates, customers are looking for more bandwidth without sacrificing security, performance, or sustainability,” said Buddy Bayer, Chief Operating Officer, Colt Technology Services. “At Colt, we continue to push optical networking forward, and this pilot represents an important step in Europe and the USA. It reflects our focus on building scalable networks that deliver growth in capacity without increasing environmental impact.”
Dr Badri Gomatam, CTO, STL, said the trial highlights the value of joint innovation in advancing optical infrastructure. “Collaborations like this speed up adoption of next-generation connectivity technologies. STL’s Multiverse MCF portfolio is designed for the high-density, ultra-low latency, and resilient connectivity requirements of AI, hyperscale cloud, and future digital platforms globally,” he said. STL stated that the trial results strengthen confidence in MCF as a viable technology for the growing bandwidth requirements driven by AI workloads, cloud scale-out, and new digital services.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
About STL-– Sterlite Technologies Ltd:
STL is a global provider of advanced connectivity solutions, offering end-to-end products and services for building AI-ready networks across FTTx, rural broadband, enterprise, and data centres. With manufacturing operations in North America, Europe, and Asia, STL supplies connectivity solutions in more than 100 countries and works with telecom operators, cloud and data center companies, internet service providers, and large enterprises to build future-ready AI digital infrastructure.
On January 23, 2026, STL reported continued sequential improvement in Operational EBITDA margin for the fifth consecutive quarter, driven by a higher-margin product mix and increased contribution from the US market. With the US–India Bilateral Trade Agreement under advanced discussion, STL remains well-positioned to leverage emerging opportunities by offering reliable, high-quality solutions for building AI-ready digital infrastructure.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/78908
How will fiber and equipment vendors meet the increased demand for fiber optics in 2026 due to AI data center buildouts?
Big tech spending on AI data centers and
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport Systems market +15% year-over-year in 3Q2025 driven by Cloud Service Providers
Dell’Oro Group recently published its 3Q25 Optical Transport report, highlighting continued strength in the market as demand accelerates across customer segments and technology areas. Below is a summary of the key findings from this latest research.
The Optical Transport Systems market increased by 15% year-over-year (Y/Y) in 3Q2025, driven by robust demand across all major customer groups and technology segments. The most significant growth was seen in Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) which grew +58% Y/Y and the DWDM Long Haul segment which grew +24% Y/Y. Direct sales for data center interconnect (DCI) continued to be the driving application for optical transport equipment sales, growing 34% Y/Y. Non-DCI also performed well, rising 7% Y/Y, driven by increased spending by communication service providers (CSPs).
In the first nine months of 2025, two vendors—Ciena and Nokia—gained more than one percentage point of market share. Other vendors that gained some market share included 1Finity, Adtran, Cisco, and Smartoptics. Note that Nokia acquired Infinera -a fiber optic equipment company on February 28, 2025.
Image Source: Jimmy Yu, Dell’Oro Group
The Dell’Oro Group Optical Transport Quarterly Report offers complete, in-depth coverage of the market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, and unit shipments (by speed up to 1.6 Tbps). The report tracks DWDM long haul, WDM metro, multiservice multiplexers (SONET/SDH), data center interconnect (metro and long haul), disaggregated WDM systems, and IPoDWDM ZR/ZR+ Optics. To purchase this report, please contact us at [email protected].
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Backgrounder:
- Optical Transceivers: Convert electrical signals into optical signals for transmission over fibers, and vice versa, at the endpoints of a link.
- Wavelength Division Multiplexers (WDM/DWDM): Devices that combine multiple optical signals (each on a different wavelength) into a single fiber for transmission, and separate them at the receiving end, maximizing fiber capacity.
- Optical Add/Drop Multiplexers (OADMs): Allow specific wavelengths (channels) to be added or removed from a fiber link at intermediate points in the network without interrupting the other channels.
- Optical Cross-Connects (OXCs) / Optical Switches: Used to route optical signals from one incoming fiber to a different outgoing fiber in the optical domain, often used in core networks.
- Regenerators / Optical Amplifiers (EDFAs): Used to amplify or regenerate optical signals over long distances to maintain signal strength and quality.
- OTN Terminal Equipment / Muxponders & Transponders: These devices package client signals (like Ethernet, Fibre Channel, or even SONET/SDH signals) into the standard OTN frame format (ITU G.709) for efficient transport.
- SONET/SDH: These are legacy, connection-oriented, circuit-switched technologies originally designed for carrying voice traffic in North America (SONET) and globally (SDH). They operate at the physical layer (Layer 1) and use Time Division Multiplexing (TDM).
- Usage: They are still widely deployed in existing network infrastructure, especially where high reliability and stringent latency requirements for legacy TDM services are necessary.
- OTN: OTN (ITU-T G.709 standard) is the modern successor, designed to combine the management and protection capabilities of SONET/SDH with the bandwidth efficiency of WDM.
- Usage: OTN has largely replaced SONET/SDH in new core and metro networks due to its ability to transparently carry multiple types of traffic (Ethernet, IP, Fibre Channel, and SONET/SDH frames) over a single, high-capacity infrastructure. It offers enhanced performance monitoring, Forward Error Correction (FEC) for longer reach, and greater scalability.
- Huawei has consistently maintained a leading position in the global optical networking market.
- Ciena is a major leader, particularly in North America (holding nearly 50% share in the U.S. market) and among cloud providers, benefiting from strong demand for its WaveLogic 6e and 400ZR/ZR+ solutions.
- Nokia has significantly strengthened its position, becoming the second-largest optical networking vendor globally (with approximately 20% market share) following its acquisition of Infinera in February 2025. The combined company saw substantial growth in revenue from cloud customers.
- Cisco saw a 31% increase in revenue from cloud operators in Q2 2025, a key driver of market growth.
- ZTE and FiberHome are also among the top six, often noted for their competitive solutions in global and emerging markets.
- Excluding sales into China, the leading vendors are Ciena, Huawei, Nokia, Infinera (now part of Nokia), and Fujitsu, accounting for around 80% of that specific market segment.
References:
Optical Transport Market Surges 15% in 3Q25, According to Dell’Oro Group
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport market to hit $17B by 2027; Lumen Technologies 400G wavelength market
LightCounting: Q1 2024 Optical Network Equipment market split between telecoms (-) and hyperscalers (+)
Highlights of LightCounting’s December 2023 Quarterly Market Update on Optical Networking
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport Market Down 2% in 1st 9 Months of 2021
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport Equipment Market Stagnant in 1Q 2021; Jimmy Yu’s Take
Dell’ Oro: Huawei still top telecom equipment supplier; optical transport market +1% in 2020
NTT’s IOWN provides ultra low latency and energy efficiency in Japan and Hong Kong
The rapid uptake of generative AI in data centers and semiconductor factories is causing a surge in power consumption, which is predicted to reach 11 times the current level by 2033. To address this issue, the NTT Group has proposed the “IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network)” concept, which aims to improve energy efficiency and achieve ultra-low latency and high-capacity communications through innovative optical communications technology.
By utilizing optical communications technology, IOWN aims to achieve dramatically low-power, high-quality, high-capacity, and low-latency communications by migrating from conventional electronics-based networks to photonics (optical)-based networks.
“Our research and development efforts are focused on achieving 1/200th the current level of latency, 125x the current level of capacity, and 100x the current level of power efficiency by 2032,” said NTT’s Tetsushi Shoji.
NTT Group is working toward “IOWN 1.0,” a goal that will see the network become all-optical. Even with current networks using optical fiber, data is repeatedly converted into electrical signals through routers and switches. However, if communication from terminal to terminal were to be entirely optical, the power consumption required for conversion would be significantly reduced.
Furthermore, communication latency is expected to be reduced. “Traditional communications involve delays because data passes through multiple nodes. However, with the IOWN APN (All Photonics Network), data reaches its destination directly, dramatically improving communication latency,” says Shoji.
On August 29, 2024, a 2,893-km IOWN APN demonstration experiment connecting Tokyo and Taiwan. The optical transport connection linked the Chunghwa Telecom Headquarter in Taipei City with the Musashino R&D Center in Musashino, Japan, achieving an ultra-low latency of approximately 17 milliseconds over an approximately 3,000 km network. Latency fluctuations were also extremely small, The innovative application was showcased publicly at the NTT R&D Forum 2024 in November 2024.

NTT Group is also considering optical fiber inside computers as part of its IOWN 2.0 and beyond concept.
Currently, the wiring inside computers uses electrical signals, and as processing speeds increase, problems with power consumption and heat generation become more serious. To solve this, the goal is to opticalize communication between boards and chips, dramatically improving data transfer efficiency.
“Ultimately, by utilizing optical fiber even inside computers, we believe it will be possible to improve power efficiency by 100 times and communication speeds by 125 times,” says Shoji.
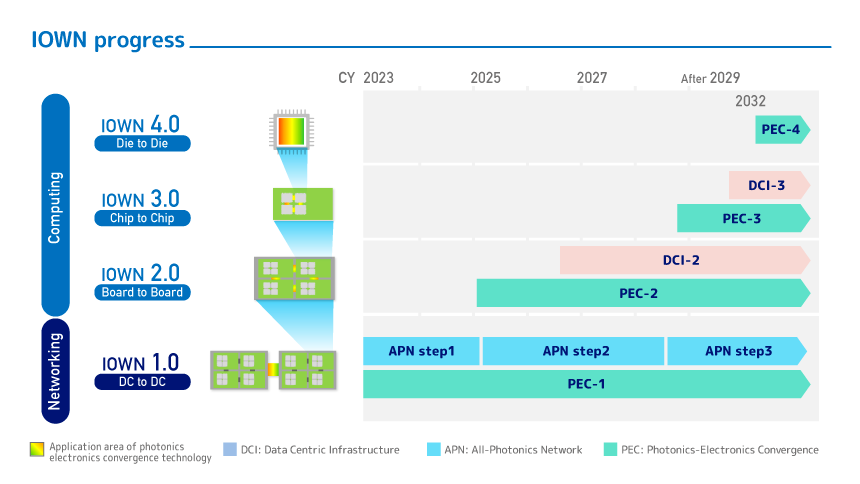
Source: NTT Group
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Nearly two weeks ago, NTT Docomo Business and NTT Com Asia launched the APN InterLink service, which is targeted at Hong Kong’s financial services sector. This all optical/photonic network, promised in the late 1990s, eliminates Optical to Electrical to Optical (OEO) repeaters, thereby greatly improving transmission performance.
“As an all-photonic solution, data is transmitted entirely at the speed of light with minimal conversion, resulting in significantly reduced latency and jitter. This capability enables mission-critical applications such as real-time trading and advanced AI workloads,” said Steven So, chief technology officer at NTT Com Asia.
So noted that recent performance tests have shown that an all-photonic network substantially improves upon a traditional setup.
In Japan, NTT Data and NTT West collaborated with MUFG Bank to conduct a successful test of APN during a live IT migration involving multiple data centers situated 50km to 100km apart. The demonstration included long-distance, synchronous database management system replication between locations up to 2,500km apart. The results showed less than one second of downtime.
“This highlights how APN addresses next-generation infrastructure requirements of the financial services sector,” So said. ” IOWN APN can deliver ultra-low latency, high-capacity, and energy-efficient network photonics-based connectivity to address their needs – where every millisecond counts in the digital world.”
References:
https://www.ntt.com/business/services/xmanaged/lp/itsmf/202511-nttcom.html
https://group.ntt/en/group/iown/function/
NTT pins growth on IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network)
Sony and NTT (with IOWN) collaborate on remote broadcast production platform
Lumen and Ciena Transmit 1.2 Tbps Wavelength Service Across 3,050 Kilometers
Lumen and Ciena have teamed up for a significant new network trial. They have successfully demonstrated a 1.2Tbps wavelength spanning 3,050k m (more than 1,800 miles) on Lumen’s Ultra-Low-Loss (ULL) fiber network, making it the world’s longest 1.2 terabit non-regenerated signal. The trial leveraged Ciena’s WL6e technology over a 6500 photonic line system and Lumen’s fiber network between Denver and Dallas. They also used 800Gbps routing technology from Juniper’s PTX Series to establish Ethernet and IP services. Lumen’s 400G-enabled network already spans over 78,000 route miles, and the company continues to invest in next-generation fiber to enhance its Ultra-Low Loss (ULL) fiber network, the largest in North America.
Using 800G interfaces, Lumen and Ciena successfully tested and qualified the services to support wavelength, Ethernet, and IP services over the 1.2 Tbps single carrier channel. The live network trial from Denver to Dallas used Ciena’s latest WaveLogic 6 Extreme (WL6e) technology equipped in the Waveserver platform running over a 6500 photonic line system.
“1.2 terabits per second isn’t just about incredible speed and long distances, it’s about the value of enabling the next wave of digital transformation. Lumen is at the forefront of building a next-generation network designed to handle the explosive growth of AI and cloud workloads,” said Dave Ward, Lumen’s chief technology and product officer. “Our investment in increased capacity, powered by Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 technology, provides our hyperscale cloud partners and enterprises with the ultra-high-capacity connectivity needed to scale their AI and cloud applications. With 400G connectivity speeds today and a seamless upgrade path to 1.2 terabits, Lumen stands as the trusted network for AI.”
The trial also showcased the impressive performance and seamless interoperability between Ciena’s Waveserver platform and the Juniper PTX10002-36QDD Packet Transport Router at 800 Gbps over the ultra-long-haul 1.2 Tbps intercity network. By leveraging the performance, flexibility and scalability of the Juniper PTX Series Routers, Lumen successfully established Ethernet and IP services with minimal latency and zero packet loss throughout the tests.
Editor’s Note:
While the companies March 27th joint press release stated the 1.2T bps wavelength transport was a record, AT&T claimed two weeks earlier that it “achieved a long distance world record top speed of 1.6Tb/s over a single wavelength across 296 km of its long haul fiber optic network.” We reported that in this IEEE Techblog post. So yes, it’s a record considering the Lumen network wavelength distance was > 10 times that claimed by AT&T.

Faster connections up to 1.2 Tbps wavelengths means less lag, more capacity and the flexibility to handle the most data-hungry applications across multiple industries:
- AI & Machine Learning
- Hyperscale Cloud & Data Center Interconnects
- Financial Trading and Market Data Transport
- Cybersecurity & AI-powered Threat Intelligence
- Media & Streaming
“At Microsoft, the demand for ultra-high-speed, low-latency connectivity is growing exponentially as AI workloads, cloud applications, and real-time analytics scale,” Lumen said. “Lumen and Ciena’s successful wavelength trial showcases a forward-thinking approach to meeting these growing demands. By enabling more efficient data movement over vast distances, this solution helps us optimize cloud performance, enhance customer experiences, and support the rapid expansion of AI training and inferencing models across our global infrastructure.”
Ciena’s WL6e is the industry’s first high-bandwidth coherent transceiver using state-of-the-art 3nm silicon, capable of carrying capacity up to 1.6 terabits per second per wavelength.
“As the pioneer in high-speed optical innovation, we are dedicated to helping our customers set new benchmarks in network performance and efficiency,” said Brodie Gage, Ciena senior vice president, global products and supply chain. “This industry-first trial with Lumen marks a pivotal step in our efforts to prepare networks for the AI era. Lumen’s network does not stand still. Continuous investment in the latest network technology is essential for keeping up with bandwidth demands today and into the future.”
Additional Resources:
About Lumen Technologies:
Lumen is unleashing the world’s digital potential. We ignite business growth by connecting people, data, and applications – quickly, securely, and effortlessly. As the trusted network for AI, Lumen uses the scale of our network to help companies realize AI’s full potential. From metro connectivity to long-haul data transport to our edge cloud, security, managed service, and digital platform capabilities, we meet our customers’ needs today and as they build for tomorrow.
SOURCE: Lumen Technologies
References:
Analysts weigh in: AT&T in talks to buy Lumen’s consumer fiber unit – Bloomberg
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
AT&T claims it achieved a long distance world record top speed of 1.6Tb/s over a single wavelength across 296 km of its long haul fiber optic network (spanning Newark, New Jersey to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania). That is four times faster than its current top speed of 400Gb/s per wavelength!
The 1.6Tb/s wavelength carried two IEEE 802.3df-2024 standard-based 800 Gigabit Ethernet end-to-end circuits, an industry first. It is a full, uninterrupted data path utilizing a single light frequency across the entire fiber length between two endpoints. The single-carrier 1.6 Tb/s wavelength was transported alongside existing live customer traffic on 100Gb/s and 400Gb/s wavelengths.
Open-sourced white box switches were the network equipment used during the trial. The white boxes are designed using the Broadcom Jericho3 packet processor chip and can provide up to 18 x 800G network interface ports all within a 2RU platform. The (Israel based) DriveNets Network Cloud software-based solution is hardware-agnostic and runs open APIs on the white boxes to perform data and control plane functions, including routing at 800G. The use of white boxes and the disaggregation of the hardware and software control costs and facilitate faster innovation.
The two 800GbE signals from the white box were multiplexed to 1.6 Tb/s in Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 Extreme coherent optical transponder, which is the first coherent optical solution to use a 200Gbaud design and 3nm coherent DSP ASIC and to reach speeds up to 1.6 Tb/s on a single carrier. The WL6e technology reduces the space and power per transmitted bit by 50% compared to current 800G transponders. This trial is the first to demonstrate WL6e at 1.6Tb/s with standards compliant 800GbE clients.
In the Newark and Philadelphia offices, 800G DR8 pluggable transceivers from Coherent were installed in the white box router and WL6e transponder to create the cross-office connectivity between the packet and optical technologies. And 800GbE client signals, provided by Keysight’s AresOne-M 800GE testset, fed the white box through additional pairs of 800G DR8 pluggable client optics, allowing verification of end-to-end performance of the two 800GbE services from Newark to Philadelphia.
Quotes:
“Traffic on AT&T’s network continues to increase as consumers are using more connected devices,” said Mike Satterlee, vice president, Network Infrastructure and Services, AT&T. “We anticipate network traffic growth to double by 2028 and the technologies demonstrated in this trial will play a key role in AT&T’s continued efforts to keep up with increasing customer demand to send data, watch videos, and use streaming services.”
“This groundbreaking achievement with AT&T adds to a growing list of Ciena industry-firsts that push the boundaries of optical network speed and capacity,” said Dino DiPerna, senior vice president, Global Research and Development, Ciena. “Ciena’s WaveLogic 6 coherent optics will support AT&T’s next gen converged optical network and efforts to build a cloud-based and AI-ready network with greater scale, flexibility and efficiency.”

Verizon’s 1.6Tb/s on Metro Fiber Network:
AT&T’s announcement comes just a few months after arch-rival Verizon announced a 1.6 Tb/s milestone of its own. Verizon also, working with Ciena, achieved that peak speed on a single wavelength, but on its metro fiber (not long distance) network. Verizon is mainly looking to advance through M&A. Its proposed acquisition of Frontier Communications is still pending, with some Frontier shareholders insisting that the US$20 billion price tag undervalues the operator.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
AT&T has spent the past six months demonstrating that it aims to build its way to fiber domination. It rolled out fiber to around 600,000 premises in the 4th quarter of last year, taking its total fiber footprint to 28.9 million locations; it is shooting for 50 million by the end of 2029.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2025/data-transport.html
https://www.business.att.com/products/wavelength-services.html
https://www.telecoms.com/fibre/at-t-touts-1-6-tbps-fibre-speed-milestone-as-us-battle-continues
AT&T Highlights: 5G mid-band spectrum, AT&T Fiber, Gigapower joint venture with BlackRock/disaggregation traffic milestone
Nokia, Windstream Wholesale and Colt complete world’s first ultra-fast 800GbE optical and IP service trial
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
T-Mobile posts impressive wireless growth stats in 2Q-2024; fiber optic network acquisition binge to complement its FWA business
Bell Canada buying Ziply Fiber for C$7 billion; will become 3rd largest fiber ISP in U.S.
Nokia, Windstream Wholesale and Colt complete world’s first ultra-fast 800GbE optical and IP service trial
Nokia, Windstream, and Colt Technology Services have completed an 800 Gigabit Ethernet (800 GbE) trial spanning 8,500km between London and Chicago over a subsea and terrestrial route. The trial showcased innovative power-saving networking technologies from the three global tech businesses to test the boundaries of next-generation wavelength, capacity, speed and latency between two of the world’s largest financial trading hubs.
Colt’s five transatlantic subsea cables and part of its extensive terrestrial fiber optic network were connected with Windstream Wholesale’s domestic U.S. low latency, optical fiber Intelligent Converged Optical Network (ICON) monitoring speed and performance. Colt and Windstream Wholesale have partnered to demonstrate the world’s first transoceanic 800 gigabit ethernet (GbE) end-to-end service transport from router to router over 1Tbps optical transport. The trial was successfully delivered using Nokia’s sixth-generation Photonic Service Engine (PSE-6s) coherent optics and 7750 Service Router (SR) high-performance routing platforms boosting internet service speeds and supporting ultra-high wavelength capacity, while maintaining power efficiency.
The companies say that 800G marks a breakthrough in service bandwidth, doubling capacity to support advanced network applications like AI data center networking, content delivery networks, and financial data hub connections.
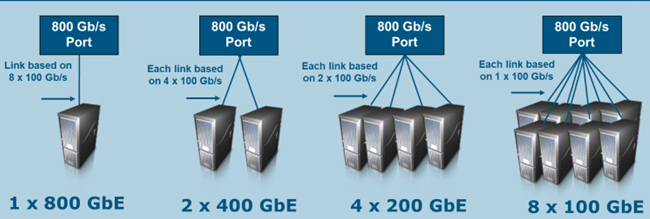
| Ethernet Rate | AUI | BP | Cu Cable | MMF 50m | MMF 100m | SMF 500m | SMF 2km |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 Gb/s | — | — | — | — | — | — | 4 pairs |
| 800 Gb/s | 8 lanes | 8 lanes | 8 pairs | 8 pairs | 8 pairs | 8 pairs | 8 pairs |
Quotes:
Buddy Bayer, Chief Operating Officer of Colt Technology Services, said: “Pushing the boundaries of technology innovation is a fundamental part of our customer commitment: it means we stay a step ahead of the market, so we’re ready when our customers ask, “What’s next for us?” This trial has seen us build a powerful industry collaboration to explore the ‘what’s next?’. It’s tested the limits of infrastructure performance and capability across thousands of miles of land and sea with incredible networking technologies, and it’s demonstrated the power and potential of what can be achieved, without skipping a beat.”
Joe Scattareggia, President of Windstream Wholesale, said: “Our latest innovation represents a true game-changer for global connectivity. By partnering with two extraordinary leaders in the industry, we’re enabling unprecedented bandwidth capabilities that are essential for driving AI-powered applications worldwide for our customers. As an optical technology leader, Windstream Wholesale and our partners are establishing 800GbE as the next evolutionary advancement increase for wave services. This collaboration has pushed the boundaries of what’s possible, creating a network solution like no other. Together, we’re not just meeting the demands of the future—we’re shaping it.”
Federico Guillén, President of Network Infrastructure at Nokia, said: “Such an ambitious project — to link two of the world’s most important financial hubs — sets the bar very high for network capacity, speed, security and reliability. This demonstration would simply not have been possible without the commitment of Nokia and our partners to the highest standards of innovation in networking technology. Together, we are redefining the art of the possible for IP and optical networks enabling cross-continental subsea and terrestrial communications.”
Following the successful completion of the trial, the organizations are currently exploring options to bring 800GbE connectivity services to market for global business customers.
Resources and additional information:
Webpage: Nokia PSE-6s
Webpage: Nokia Optical Networks
About Nokia:
As a B2B technology innovation leader, we are pioneering networks that sense, think and act by leveraging our work across mobile, fixed and cloud networks. In addition, we create value with intellectual property and long-term research, led by the award-winning Nokia Bell Labs.
With truly open architectures that seamlessly integrate into any ecosystem, our high-performance networks create new opportunities for monetization and scale. Service providers, enterprises and partners worldwide trust Nokia to deliver secure, reliable and sustainable networks today – and work with us to create the digital services and applications of the future.
About Colt Technology Services:
Colt Technology Services (Colt) is a global digital infrastructure company which creates extraordinary connections to help businesses succeed. Powered by amazing people and like-minded partners, Colt is driven by its purpose: to put the power of the digital universe in the hands of its customers, wherever, whenever and however they choose.
Since 1992, Colt has set itself apart through its deep commitment to its customers, growing from its heritage in the City of London to a global business spanning 40+ countries, with over 6,000 employees and more than 80 offices around the world. Colt’s customers benefit from expansive digital infrastructure connecting 32,000 buildings across 230 cities, more than 50 Metropolitan Area Networks and 250+ Points of Presence across Europe, Asia, the Middle East, Africa and North America’s largest business hubs.
Privately owned, Colt is one of the most financially sound companies in the sector. Obsessed with delivering industry-leading customer experience, Colt is guided by its dedication to customer innovation, by its values and its responsibility to its customers, partners, people and the planet.
For more information, please visit www.colt.net
About Windstream Wholesale:
Windstream Wholesale is an innovative optical technology leader that delivers fast, flexible, and customized wavelength and dark fiber solutions to carriers, content providers, and hyperscalers in the U.S. and Canada. Windstream Wholesale is one of three brands managed by Windstream. The company’s quality-first approach connects customers to new opportunities and possibilities by delivering a full suite of advanced communications services. Windstream also offers fiber-based broadband to residential and small business customers in 18 states as well as managed cloud communications and security services to mid-to-large enterprises and government entities across the U.S. Windstream is a privately held company headquartered in Little Rock, Ark. Additional information about Windstream Wholesale is available at windstreamwholesale.com. Follow us on X (Twitter) @Windstream and LinkedIn at @Windstream.
To view the Windstream Wholesale network map, visit https://www.windstreamwholesale.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Windstream-Wholesale-National-Network.pdf
References:
https://standards.ieee.org/beyond-standards/ethernets-next-bar/
AI adoption to accelerate growth in the $215 billion Data Center market
Ethernet Alliance multi-vendor interoperability demo (10GbE to 800GbE) at OFC 2023
Cisco 800G line card for Cisco 8000 Series Routers powered by Silicon One ASIC
Infinera, DZS, and Calnex Successfully Demonstrate 5G Mobile xHaul with Open XR
Infinera announced today a successful multi-vendor demonstration of 5G mobile broadband xHaul using coherent open XR optics point-to-multipoint optical transmission. The multi-vendor interoperability testing, conducted with DZS and Calnex, represents a key step toward enabling mobile operators to greatly simplify and cost-reduce 5G and next-generation mobile transport network rollouts through the reduction of the number of optical transceivers, resulting in significant total cost of ownership savings.
Hosted in the European Open Test & Integration Center in Torino by TIM, the high-capacity xHaul application testing included fronthaul, midhaul, and backhaul transport scenarios with XR-based coherent pluggable optics deployed in third-party hosts supporting point-to-point and point-to-multipoint optical transmission. Results of the performance testing included successful demonstration of xHaul synchronization and timing distribution in a point-to-multipoint optical transport architecture.
“It is not only the significant bandwidth demands of 5G that create challenges for mobile operators, but also the fundamental misalignment between actual 5G network traffic patterns and the underlying transport technology,” said Ron Johnson, SVP and General Manager, Optical Subsystems and Global Engineering Group, Infinera. “Working in close collaboration with industry-leading mobile operators such as TIM, this testing validates the critical role that XR optics innovation can play in transforming the economics of 5G transport and paving the way for efficient 6G networks.”
Equipment used in the interoperable xHaul testing included Infinera ICE-X intelligent coherent pluggables, the DZS Saber 2200, and Calnex Paragon-NEO. Part of the work carried out by TIM and Infinera was supported by the EU project ALLEGRO, GA No. 101092766.
About DZS:
DZS (Nasdaq: DZSI) is a developer of Network Edge, Connectivity and Cloud Software solutions enabling broadband everywhere.
About Infinera:
Infinera is a global supplier of innovative open optical networking solutions and advanced optical semiconductors that enable carriers, cloud operators, governments, and enterprises to scale network bandwidth, accelerate service innovation, and automate network operations. Infinera solutions deliver industry-leading economics and performance in long-haul, submarine, data center interconnect, and metro transport applications. To learn more about Infinera, visit www.infinera.com, follow us on X and LinkedIn, and subscribe for updates.
References:
Telenor Deploys 5G xHaul Transport Network from Cisco and NEC; xHaul & ITU-T G.8300 Explained
Orange Deploys Infinera’s GX Series to Power AMITIE Subsea Cable
Infinera trial for Telstra InfraCo’s intercity fiber project delivered 61.3 Tbps between Melbourne and Sydney, Australia
Fiber Build-Out Boom Update: GTT & Ziply Fiber, Infinera in Louisiana, Bluebird Network in Illinois
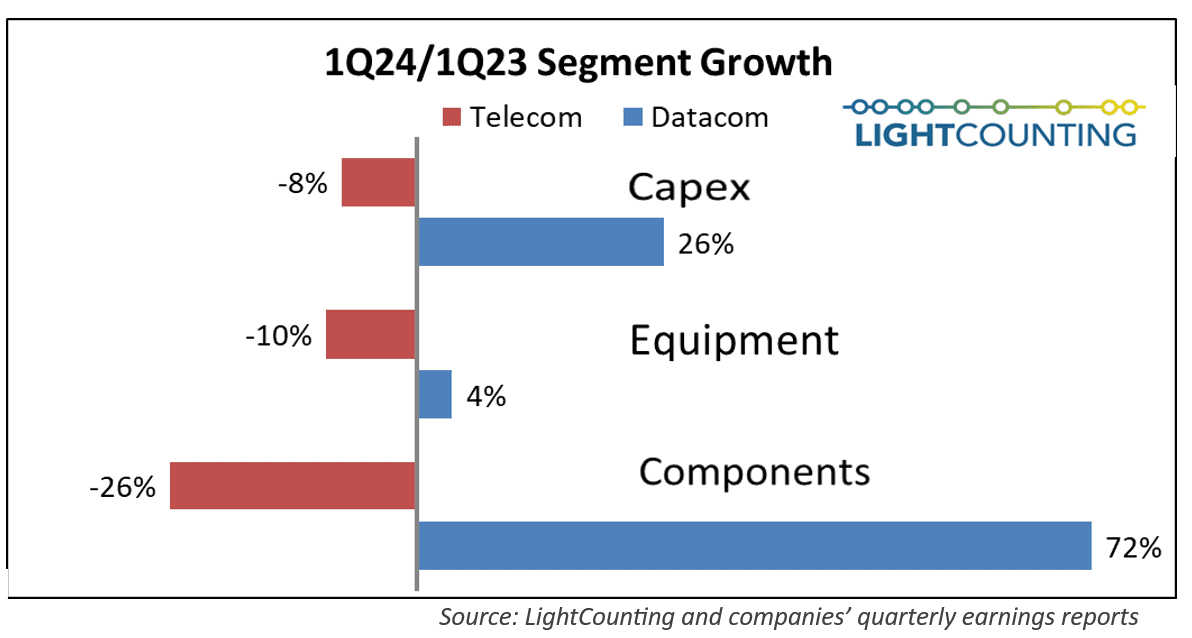
LightCounting: Q1 2024 Optical Network Equipment market split between telecoms (-) and hyperscalers (+)
As has been the trend for the past several quarters, Q1 2024 results for the optical communications market were sharply split between very weak sales in the telecom segment (Communications Service Providers or CSPs) and continued strong demand by the hyperscalers (cloud giants). The combined capex of the Top 15 CSPs declined year-over-year for the sixth quarter in a row, while the Top 15 ICPs spending grew for the second quarter in a row, paced by Alphabet (+91%) and Microsoft (+66%). Chinese ICPs spending also increased dramatically, suggesting the AI boom is hitting China too.
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network & Cable CPE shipments all declined in 1Q-2024
Apparently, there’s no place to hide in any telecom or datacom market? We all know the RAN market has been in a severe decline, but recent Dell’Oro Group reports indicate that Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network and Cable CPE shipments have also declined sharply in the 1st Quarter of 2024.
Here are a few selected quotes from Dell’Oro analysts:
“The North American broadband market is in the midst of a fundamental shift in the competitive landscape, which is having a significant impact on broadband equipment purchases,” said Jeff Heynen, Vice President with Dell’Oro Group. “In particular, cable operators are trying to navigate mounting, but predictable, broadband subscriber losses with the need to invest in their networks to keep pace with further encroachment by fiber and fixed wireless providers,” explained Heynen.
Omdia, owned by the ADVA, expects cable access equipment spending to grow later in 2024 and peak in 2026 at just over $1 billion, then drop off to $700 million in 2029.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“Customer’s excess inventory of DWDM systems continued to be at the center stage of the Optical Transport market decline in the first quarter of 2024,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “However, we think the steeper-than-expected drop in optical transport revenue in 1Q 2024 may have been driven by communication service providers becoming increasingly cautious about the macroeconomic conditions, causing them to delay projects into future quarters,” added Yu.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“Inflation has impacted the ability of some Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) to raise capital, and it has also impacted subscribers when it comes to upgrading their phones to 5G. Many MNOs have lowered their CAPEX plans and announced that they have fewer than expected 5G subscribers on their networks; which limits MNOs’ growth plans. As a result, we are lowering our expectations for 2024 from a positive growth rate to a negative one,” by Research Director Dave Bolan.
- As of 1Q 2024, 51 MNOs have commercially deployed 5G SA (Stand Alone) eMBB networks with two additional MNOS launching in 1Q 2024.
References:
Optical Transport Equipment Market Forecast to Decline in 2024, According to Dell’Oro Group
Optical Transport Equipment Market Forecast to Decline in 2024, According to Dell’Oro Group
Quintessent: Supporting “newer AI workloads” with lasers and DWDM
Integrated-photonics companies have increasingly seized on the opportunities in advanced AI. Many are building high-speed optical interconnects for data centers, with the electrical–optical conversion as close as possible to the number-crunching GPU or application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC).
However, Goleta, CA based startup Quintessent, is focusing on solving what it says is a major bottleneck hindering commercial deployment of such high-speed optical interconnects for AI – the light source or laser, which is currently the “weakest link” in system reliability and scalability, according to co-founder and CEO, Alan Liu.
Quintessent’s answer lies in part in its laser technology, incorporating quantum dots (QDs)—the semiconductor nanocrystals celebrated in the 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry—and multiwavelength comb lasers. The firm believes that combination can boost bandwidth, improve efficiency and cut latency by enabling highly parallel dense wavelength-division multiplexed (DWDM) optical links for computing clusters and data centers. And in late March, the company announced that it had secured US$11.5 million in new seed funding to push its vision closer to commercialization.
Quintessent was co-founded in 2019 by Optica Fellow John Bowers of the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB), USA, who serves as the company’s board chairman, and Liu, formerly a student in Bowers’ lab. In a conversation with OPN in November 2023, Liu noted that his Ph.D. work in the lab, which spanned the years from 2011 to 2017, focused on what he called “one of the glaring holes in silicon photonics”: how to integrate the light source. His work specifically involved integration of QD lasers with silicon photonics, which subsequently became “one of the core technologies for Quintessent.”
Quintessent co-founders Alan Liu (left) and John Bowers. Image: Courtesy of A. Liu.
Even at that time, Liu had some stirrings in the direction of commercializing the technology. Ultimately, though, after earning his Ph.D. in 2017, he left Santa Barbara for a two-year stint at a consulting firm in the Washington, DC, area. There, he worked as a subject-matter expert in photonics on projects for the US Department of Defense’s advanced-research arm, DARPA, and the US Department of Energy’s counterpart, ARPA-E.
Still, the entrepreneurial itch never quite left Liu. Nor did his fascination with the promise of QD laser technology, as he saw subsequent work done in Bowers’ lab to further advance the performance of those lasers and demonstrate new functions with them, including multiwavelength comb sources.
In 2019, Liu says, he got a call from Bowers, who noted that he was seeing “a lot of interest” from industry in the technology the lab was developing, but that there was “no company to sell it.” When Bowers asked if he wanted to help start one up, Liu recalls, “it didn’t take me long to sign on and say yes.” In the course of the next few years, they built Quintessent’s core team, drawing on numerous other contacts both within and outside of Bowers’ UCSB lab, and pulled in a mix of government R&D and venture funding, including the $11.5 million seed round announced in March 2024. The business case for Quintessent, Liu says, rests largely on “some of the newer AI workloads that were coming into the fray” beginning in the late 2010s, and their immense appetite for computing resources and power.
“If you’re going to be optimizing for power efficiency and bandwidth and latency, the required architecture is one that’s wide and parallel,” he explains. And for optics, at some point, trying to achieve that level of parallelism by adding more and more spatial or fiber channels becomes unwieldy.
The alternative solution, Liu says, is a highly parallel DWDM architecture—using not lots of fibers but “lots of lambdas.” For the crushing workloads of advanced AI, DWDM is optimal, as it “allows you to both simultaneously optimize bandwidth and minimize power and latency,” without relying on digital signal processing or a potential rat’s nest of individual fiber interconnects to boost overall bandwidth.
One key for achieving that vision was “enabling a new kind of laser, and using that laser to enable new communication and transceiver architectures,” according to Liu. “That was a common gap I saw across the industry.” Particularly in the context of AI, Liu observes, a big argument for better lasers has to do with reliability.
Particularly in the context of AI, Liu observes, a big argument for better lasers—and especially for Quintessent’s concept of simplifying wavelength scaling using multiwavelength comb sources fabricated from InAs/GaAs QD material—has to do with reliability. “Optical solutions for AI are going to have to be at least an order of magnitude more reliable than what we see today in existing transceivers,” he maintains. “If you imagine a scenario where there’s 10 times more optics deployed, and your failure rates stay the same, then you’ve got 10 times more failures you’re asking the customer to deal with. That gets a little dicey.”
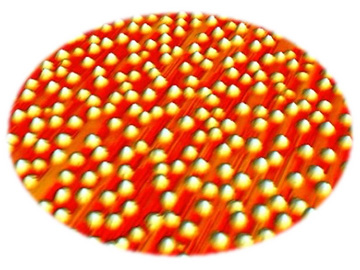
An atomic force microscopy (AFM) image of InAs/GaAs quantum dots. Image: Courtesy of A. Liu
Getting to better overall reliability will require much more reliable lasers, Liu believes, as lasers are “kind of the weakest link at the moment.” And he and the Quintessent team think that QD lasers offer a way forward, as they are “intrinsically more reliable than quantum well materials today.”
Tobias Egle, a materials scientist who works with M Ventures, one of the partners in the most recent Quintessent funding round, explained the difference further in a separate call with OPN. “These QD lasers are not as affected by material defects, dislocations and so on,” Egle says. “Simply put, a single dislocation through the facet or active region of a traditional laser can lead to complete failure. In contrast, when you have billions of QDs which are independent of one another, the presence of a single dislocation has a negligible impact on your overall performance.”
Quintessent experienced a milestone a year ago, when the company and Tower Semiconductor—the Israel-based global foundry firm with which Quintessent had partnered since 2021—announced that they had achieved what they called the world’s first heterogenous integration of GaAs quantum dot lasers in a commercial foundry silicon photonics process. The pair also unveiled a foundry silicon platform, PH18DB, targeted for the telecom and datacom optical transceiver market, and an accompanying process development kit (PDK).
Meanwhile, on the funding side, Quintessent announced an oversubscribed US$11.5 million seed round in March 2024, with an investment group led by Osage University Partners (OUP) and including, in addition to M Ventures, participation by previous Quintessent funders Sierra Ventures, Foothill Ventures and Entrada Ventures. In a press release accompanying the recent funding announcement, Liu said the new money would let the company “grow our team and accelerate the development of highly scalable and highly reliable optical interconnects that transcend the scaling limitations of incumbent solutions,” based on the firm’s core technology of QD-enabled multiwavelength comb lasers.
Operationally, Liu told OPN that—having “checked off all of the fundamental technology questions” regarding the laser technology’s feasibility—Quintessent is now focused on optimizing the laser design, which he calls “a key Lego block,” and of other pieces of the overall architecture to validate system-level functionality. Then, an important next step will be getting chips into customers’ hands for ground-truthing and feedback, and using that feedback to “drive forward the commercialization roadmap.”
“So samples, then low-volume pilots, then high-volume manufacturing—simple, right?” he laughs. Liu seems exhilarated by the challenge. “I’m one of those people that liked to play video games in the hard, hard mode,” he says. “If it’s too easy, you don’t get much enjoyment out of it.”
References:
https://www.optica-opn.org/Home/Industry/2024/April/Quintessent_Targets_Lasers_for_AI