China to build ground stations in Antartica to support ocean monitoring satellites
China, only the third country to put a man in space after the Soviet Union and United States, is to build ground stations on Antarctica to back its network of ocean monitoring satellites, state media said on Thursday.
Renders of the 43.95 million yuan ($6.52 million) project show four radome-covered antennas at China’s Zhongshan research base in East Antarctica. It is unknown if these are new and additional to antennas already established at the base.
The antennas will assist data acquisition from Chinese satellites that orbit in polar and near-polar orbits. Satellites in these orbits are visible near the poles multiple times a day, allowing more frequent opportunities for downlink than with stations at lower latitudes.
China has already launched eight Haiyang series ocean observation satellites into sun-synchronous orbits between 2002 and 2021, and plans more in the coming years. The first new-generation Haiyang-3 satellite is scheduled for launch this year, according the China’s main space contractor, CASC.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
China Satellites and Balloons used for Espionage?
China’s global network of ground stations to support a growing number of satellites and outer space ambitions has drawn concern from some nations that it could be used for espionage, a suggestion China rejects.
In 2020, Sweden’s state-owned space company, which had provided ground stations that helped fly Chinese spacecraft and transmit data, declined to renew contracts with China or accept new Chinese business due to “changes” in geopolitics.
The United States military shot down a Chinese spy balloon on Saturday that had spent the last week traversing the country. The balloon, which spent five days traveling in a diagonal southeast route from Idaho to the Carolinas, had moved off the coast by midday Saturday and was shot down within moments of its arrival over the Atlantic Ocean.
One of two F-22 fighter jets from Langley Air Force Base fired a Sidewinder air-to-air missile, downing the balloon, which was flying at an altitude of 60,000 to 65,000 feet. The F-22s were at 58,000 feet, with other American fighters in support.
In announcing the cancellation of his trip to China, U.S. Secretary of State, Antony J. Blinken said the entry of the spy balloon was a “clear violation of U.S. sovereignty and international law.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
China Aerospace Science and Technology Group Co. is to build the stations at the Zhongshan research base, one of two permanent Chinese research stations on Antarctica, after winning the tender with its 43.95 million yuan ($6.53 million) bid, state-controlled China Space News reported.

Liftoff of a Long March 2C from Taiyuan carrying the Haiyang-1D ocean observation satellite on June 10, 2020. Image Credit: CASC
No technical details of the project were given in the report, though China Space News published two accompanying illustrations of an artist’s rendering that shows four ground stations at Zhongshan, located by Prydz Bay in East Antarctica, south of the Indian Ocean.
The project was part of broader initiatives aimed at building China’s marine economy and turning China into a marine power, according to China Space News.
References:
Ericsson, Intel and Microsoft demo 5G network slicing on a Windows laptop in Sweden
Ericsson, Intel and Microsoft successfully demonstrating end-to-end 5G standalone (SA) network slicing capabilities on a Windows laptop at Ericsson’s Lab in Sweden. This pioneering trial demonstrates the applicability of the technology on devices beyond smartphones, paving the way for new business/enterprise opportunities and for consumer use cases such as mobile gaming and collaboration applications for 5G cellular-connected laptops.
The trial used User Equipment Route Selection Policy (URSP), which enables devices to automatically select between different slices according to which application they are using. It also used Ericsson’s Dynamic Network Slicing Selection, Ericsson’s dual-mode 5G Core, and Ericsson’s RAN Slicing capabilities to ‘secure end-user service differentiation.’
Network slicing has long been seen as vital to capturing the value that a 5G network can provide for communications service providers (CSPs) and enterprises. The market for network slicing alone in the enterprise segment is projected at USD 300 billion by 2025, according to the GSMA. By demonstrating a single Windows 11 device can make use of multiple slices, which are used according to the on-device usage profiles and network policies defined at the CSP level, the partners show the flexibility and range of potential use cases available using this technology.
This trial illustrates the opportunities for 5G monetization beyond smartphone devices and opens the door to a wider 5G device ecosystem, allowing CSPs and other members of the telecoms and IT world to expand their horizons when considering opportunities to generate profitable use cases for 5G. Laptop type devices, in particular, are vital to enterprise productivity. The inclusion of Windows 11 laptops in the ranks of devices that can be used for commercializing 5G network slicing is a sign of the ecosystem maturing. Network slicing capabilities will benefit consumer and enterprise segments by defining specific Service Level Agreement per slice for existing and emerging Windows applications and use cases, such as real-time enterprise applications like Microsoft Teams and Office365, game/media streaming, and emerging AI and augmented reality/extended reality (AR/XR) applications.
Sibel Tombaz, Head of Product Line 5G RAN at Ericsson, said: “Expanding the range of devices for network slicing to include laptops will allow new business segments to create a variety of use cases for consumer and enterprises. We have shown, together with Intel and Microsoft, how ecosystem collaboration can open new possibilities. We will continue to strengthen Ericsson’s network slicing capabilities and work with industry partners to enable more applications on several devices, spreading the benefits of 5G in the consumer and enterprise segments.”
Ian LeGrow, Microsoft Corporate Vice-President of Core OS Innovation said: “We are thrilled to showcase our cutting-edge technology and its ability to deliver fast, dependable and secure 5G connectivity on Windows 11. Partnering with Intel and Ericsson only further solidifies our commitment to innovation and openness in our platform.”
This ground-breaking network slicing demo will be showcased jointly with Intel and Microsoft in the Ericsson Hall during MWC Barcelona 2023 from February 27 to March 2.
Andrew Wooden of telecoms.com wrote:
“There are so many tests and trials going on, and while technically seem to signal a bit of incremental progress each time, it can be easy to lose the context of what is supposed to be offered while digging around in the weeds of experimental telecoms architecture. That said if trials like this can keep the emphasis on how they provide some extra money-making opportunities for those in the business of flogging 5G, and some genuine benefits for the rest of us, perhaps it will gain some traction when they show it off in Barcelona.”
Source: Viavi Solutions
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/2023/2/ericsson-intel-and-microsoft-show-network-slicing-capabilities-on-a-laptop-for-consumer-and-enterprise-applications
https://www.ericsson.com/en/network-slicing#dynamicnetworksliceselection
https://www.ericsson.com/en/core-network/5g-core
https://telecoms.com/519733/ericsson-intel-and-microsoft-slice-up-a-network-and-feed-it-to-a-laptop/
Ericsson and Nokia demonstrate 5G Network Slicing on Google Pixel 6 Pro phones running Android 13 mobile OS
Samsung and KDDI complete SLA network slicing field trial on 5G SA network in Japan
5G Network Slicing Tutorial + Ericsson releases 5G RAN slicing software
https://www.viavisolutions.com/en-us/5g-network-slicing
Network Slicing and 5G: Why it’s important, ITU-T SG 13 work, related IEEE ComSoc paper abstracts/overviews
China is global IoT Superpower with 1.8 billion connections as of Dec 2022
As of December 2022, the number of connections for cellular Internet of Things (IoT) services hit 1.8 billion in China, accounting for 70 percent of the world’s total, according to the country’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT).
MIIT’s figures, which are based on data from three major telecommunication companies in China, show that the total number of terminal connections for mobile network have reached 3.528 billion, among which 1.845 billion are cellular IoT end users. The biggest proportion of the IoT services in China are using NB-IoT (the most popular 3GPP and ITU-R standard for cellular IoT), rather than LTE-M or other cellular IoT variant.
The ministry says four NB-IoT use cases have scaled to more than 10 million connections: water meters, gas meters, smoke detectors and tracking. Another seven, including agriculture and streetlights, have crossed the 1 million mark. The MIIT has also issued a breakdown of end-user terminal numbers, with 496 million deployed in public services, 375 million in internet of vehicles, 350 million in smart retail and 192 million in smart home. In area without service coverage, NB-IoT is deployed to achieve connectivity, such as soil sensors for smart agriculture.
China’s cellular IoT end users, for the first time, have surpassed that of mobile phone users by 161 million, accounting for 52.3 percent of the total, MIIT said.

Cellular IoT connects a wide variety of machines and devices, allowing them to communicate with each other by piggybacking on the cellular networks often used. Simply put, it facilitates massive data streams among sensors, actuators, etc., without building additional physical infrastructure.
While the IoT services are heavily applied across a myriad of industries, such as manufacturing, logistics, agriculture and transportation, cellular IoT modules fulfill a critical role as part of IoT systems or products in serving as the gateway for data transfer through 5G, 4G and LTE.
Government think tank CAICT predicts that by 2030 China will have tens of billions mobile IoT connections. The three operators, with their monopoly over communications infrastructure, will be at the center of this growth story.
In 2021 China Mobile reported 11.4 billion Chinese yuan (US$1.57 billion) in revenue from its IoT business, a 21% year-over-year (YoY) rise, with the number of connections 20% higher. It hasn’t yet reported revenue from 2022 but says total connections rose 14% to 1.2 billion, website C114 reported.
China Telecom’s 2021 IoT revenue was 2.9 billion yuan, while in the first three quarters of 2022, China Unicom claimed 366 million connections and 6.2 billion yuan in revenue, up 26% YoY.
The revenue numbers are low and will probably remain relatively so, but with this sort of growth rate, and with no external competitors, the telcos will be expecting their IoT portfolios to become a healthy niche income stream. However, while the growth numbers are good, we have no insight into the underlying cost or profitability of these IoT services. The obvious parallel is 5G, where the telcos have built networks and user numbers at huge scale but with limited returns so far.
China also leads in IoT silicon:
China also leads the world in supply of IoT chips. Counterpoint Research data shows that three Chinese companies – Quectel, Fibocom and Sunsea – accounted for half of the global mobile IoT module market in Q3. The no. 5 supplier is China Mobile, which has developed two types of RISC-V chips, and has shipped more than 100 million IoT chips. It has also sold more than 30 million OneOS operating system terminals.
With the expansion of 5G coverage, China is set to expand its IoT industry that covers chips, modules, terminals, software, platform and service. Meanwhile, its NB-IoT has been applied for smart metering, sensing, tracking and smart agriculture.
References:
Using a distributed synchronized fabric for parallel computing workloads- Part II
by Run Almog Head of Product Strategy, Drivenets (edited by Alan J Weissberger)
Introduction:
In the previous part I article, we covered the different attributes of AI/HPC workloads and the impact this has on requirements from the network that serves these applications. This concluding part II article will focus on an open standard solution that addresses these needs and enables these mega sized applications to run larger workloads without compromising on network attributes. Various solutions are described and contrasted along with a perspective from silicon vendors.
Networking for HPC/AI:
A networking solution serving HPC/AI workloads will need to carry certain attributes. Starting with scale of the network which can reach thousands of high speed endpoints and having all these endpoints run the same application in a synchronized manner. This requires the network to run like a scheduled fabric that offers full bandwidth between any group of endpoints at any given time.
Distributed Disaggregated Chassis (DDC):
DDC is an architecture that was originally defined by AT&T and contributed to the Open Compute Project (OCP) as an open architecture in September 2019. DDC defines the components and internal connectivity of a network element that is purposed to serve as a carrier grade network router. As opposed to the monolithic chassis-based router, the DDC defines every component of the router as a standalone device.
- The line card of the chassis is defined as a distributed chassis packet-forwarder (DCP)
- The fabric card of the chassis is defined as a distributed chassis fabric (DCF)
- The routing stack of the chassis is defined as a distributed chassis controller (DCC)
- The management card of the chassis is defined as a distributed chassis manager (DCM)
- All devices are physically connected to the DCM via standard 10GbE interfaces to establish a control and a management plane.
- All DCP are connected to all DCF via 400G fabric interfaces in a Clos-3 topology to establish a scheduled and non-blocking data plane between all network ports in the DDC.
- DCP hosts both fabric ports for connecting to DCF and network ports for connecting to other network devices using standard Ethernet/IP protocols while DCF does not host any network ports.
- The DCC is in fact a server and is used to run the main base operating system (BaseOS) that defines the functionality of the DDC
Advantages of the DDC are the following:
- It’s capacity since there is no metal chassis enclosure that needs to hold all these components into a single machine. This allows building a wider Clos-3 topology that expands beyond the boundaries of a single rack making it possible for thousands of interfaces to coexist on the same network element (router).
- It is an open standard definition which makes it possible for multiple vendors to implement the components and as a result, making it easier for the operator (Telco) to establish a multi-source procurement methodology and stay in control of price and supply chain within his network as it evolves.
- It is a distributed array of components that each has an ability to exist as a standalone as well as act as part of the DDC. This gives a very high level of resiliency to services running over a DDC based router vs. services running over a chassis-based router.
AT&T announced they use DDC clusters to run their core MPLS in a DriveNets based implementation and as standalone edge and peering IP networks while other operators worldwide are also using DDC for such functionality.
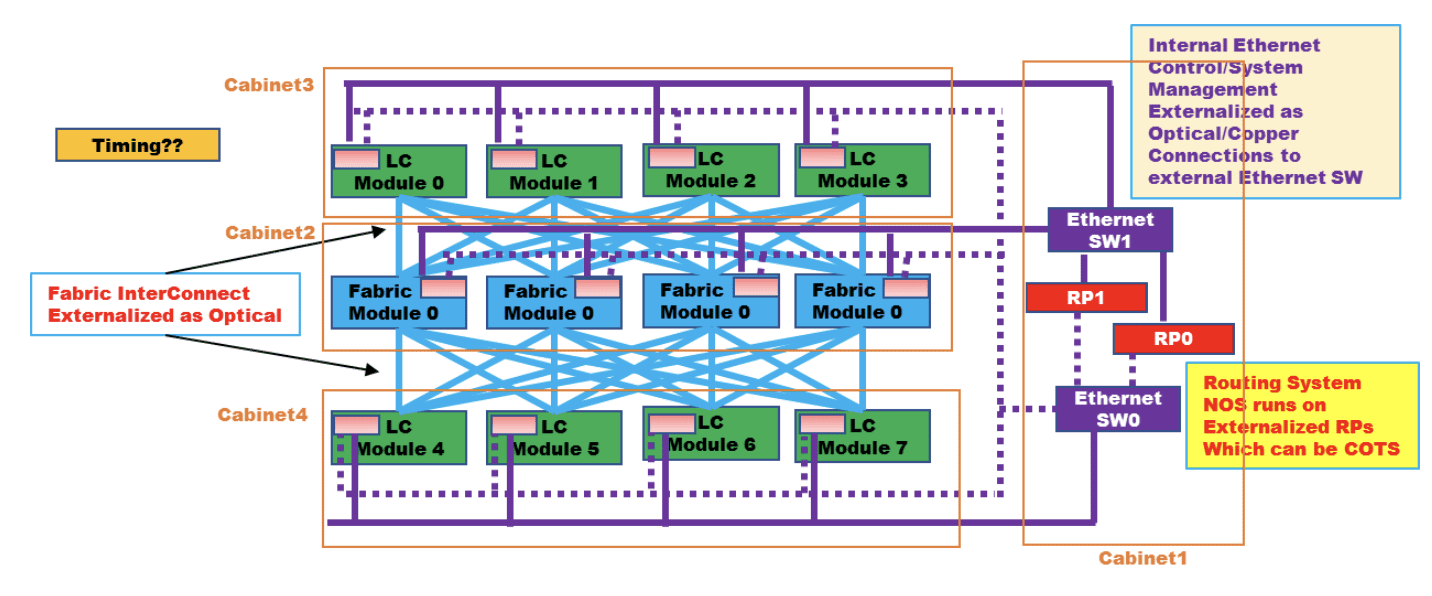
Figure 1: High level connectivity structure of a DDC
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
LC is defined as DCP above, Fabric module is defined as DCF above, RP is defined as DCC above, Ethernet SW is defined as DCM above
Source: OCP DDC specification
DDC is implementing a concept of disaggregation. The decoupling of the control plane from data plane enables the sourcing of the software and hardware from different vendors and assembling them back into a unified network element when deployed. This concept is rather new but still has had a lot of successful deployments prior to it being used as part of DDC.
Disaggregation in Data Centers:
The implementation of a detached data plane from the control plane had major adoption in data center networks in recent years. Sourcing the software (control plane) from one vendor while the hardware (data plane) is sourced from a different vendor mandate that the interfaces between the software and hardware be very precise and well defined. This has brought up a few components which were developed by certain vendors and contributed to the community to allow for the concept of disaggregation to go beyond the boundaries of implementation in specific customers networks.
Such components include open network install environment (ONIE) which enables mounting of the software image onto a platform (typically a single chip 1RU/2RU device) as well as the switch abstraction interface (SAI) which enable the software to directly access the application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) and operate directly onto the data plane at line rate speeds.
Two examples of implementing disaggregation networking in data centers are:
- Microsoft which developed their network operating system (NOS) software Sonic as one that runs on SAI and later contributed its source code to the networking community via OCP and he Linux foundation.
- Meta has defined devices called “wedge” who are purpose built to assume various NOS versions via standard interfaces.
These two examples of hyperscale companies are indicative to the required engineering effort to develop such interfaces and functions. The fact that such components have been made open is what enabled other smaller consumers to enjoy the benefits of disaggregation without the need to cater for large engineering groups.
The data center networking world today has a healthy ecosystem with hardware (ASIC and system) vendors as well as software (NOS and tools) which make a valid and widely used alternative to the traditional monolithic model of vertically integrated systems.
Reasons for deploying a disaggregated networking solution are a combination of two. First, is a clear financial advantage of buying white box equipment vs. the branded devices which carry a premium price. Second, is the flexibility which such solution enables, and this enables the customer to get better control over his network and how it’s run, as well as enable the network administrators a lot of room to innovate and adapt their network to their unique and changing needs.
The image below reflects a partial list of the potential vendors supplying components within the OCP networking community. The full OCP Membership directory is available at the OCP website.
Between DC and Telco Networking:
Data center networks are built to serve connectivity towards multiple servers which contain data or answer user queries. The size of data as well as number of queries towards it is a constantly growing function as humanity grows its consumption model of communication services. Traffic in and out of these servers is divided to north/south that indicates traffic coming in and goes out of the data center, and east/west that indicates traffic that runs inside the data center between different servers.
As a general pattern, the north/south traffic represent most of the traffic flows within the network while the east/west traffic represent the most bandwidth being consumed. This is not an accurate description of data center traffic, but it is accurate enough to explain the way data center networks are built and operated.
A data center switch connects to servers with a high-capacity link. This tier#1 switch is commonly known as a top of rack (ToR) switch and is a high capacity, non-blocking, low latency switch with some minimal routing capabilities.
- The ToR is then connected to a Tier#2 switch that enables it to connect to other ToR in the data center.
- The Tier#2 switches are connected to Tier#3 to further grow the connectivity.
- Traffic volumes are mainly east/west and best kept within the same Tier of the network to avoid scaling the routing tables.
- In theory, a Tier#4/5/6 of this network can exist, but this is not common.
- The higher Tier of the data center network is also connected to routers which interface the data center to the outside world (primarily the Internet) and these routers are a different design of a router than the tiers of switching devices mentioned earlier.
- These externally facing routers are commonly connected in a dual homed logic to create a level of redundancy for traffic to come in and out of the datacenter. Further functions on the ingress and egress of traffic towards data centers are also firewalled, load-balanced, address translated, etc. which are functions that are sometimes carried by the router and can also be carried by dedicated appliances.
As data centers density grew to allow better service level to consumers, the amount of traffic running between data center instances also grew and data center interconnect (DCI) traffic became predominant. A DCI router on the ingress/egress point of a data center instance is now a common practice and these devices typically connect over larger distance of fiber connectivity (tens to hundreds of Km) either towards other DCI routers or to Telco routers that is the infrastructure of the world wide web (AKA the Internet).
While data center network devices shine is their high capacity and low latency and are built from the ASIC level via the NOS they run to optimize on these attributes, they lack in their capacity for routing scale and distance between their neighboring routers. Telco routers however are built to host enough routes that “host” the Internet (a ballpark figure used in the industry is 1M routes according to CIDR) and a different structure of buffer (both size and allocation) to enable long haul connectivity. A telco router has a superset of capabilities vs. a data center switch and is priced differently due to the hardware it uses as well as the higher software complexity it requires which acts as a filter that narrows down the number of vendors that provide such solutions.
Attributes of an AI Cluster:
As described in a previous article HPC/AI workloads demand certain attributes from the network. Size, latency, lossless, high bandwidth and scale are all mandatory requirements and some solutions that are available are described in the next paragraphs.
Chassis Based Solutions:
This solution derives from Telco networking.
Chassis based routers are built as a black box with all its internal connectivity concealed from the user. It is often the case that the architecture used to implement the chassis is using line cards and fabric cards in a Clos-3 topology as described earlier to depict the structure of the DDC. As a result of this, the chassis behavior is predictable and reliable. It is in fact a lossless fabric wrapped in sheet metal with only its network interfaces facing the user. The caveat of a chassis in this case is its size. While a well-orchestrated fabric is a great fit for the network needs of AI workloads, it’s limited capacity of few hundred ports to connect to servers make this solution only fitting very small deployments.
In case chassis is used at a scale larger than the sum number of ports per single chassis, a Clos (this is in fact a non-balanced Clos-8 topology) of chassis is required and this breaks the fabric behavior of this model.
Standalone Ethernet Solutions:
This solution derives from data center networking.
As described previously in this paper, data center solutions are fast and can carry high bandwidth of traffic. They are however based on standalone single chip devices connected in a multi-tiered topology, typically a Clos-5 or Clos-7. as long as traffic is only running within the same device in this topology, behavior of traffic flows will be close to uniform. With the average number of interfaces per such device limited to the number of servers physically located in one rack, this single ToR device cannot satisfy the requirements of a large infrastructure. Expanding the network to higher tiers of the network also means that traffic patterns begin to alter, and application run-to-completion time is impacted. Furthermore, add-on mechanisms are mounted onto the network to turn the lossy network into a lossless one. Another attribute of the traffic pattern of AI workloads is the uniformity of the traffic flows from the perspective of the packet header. This means that the different packets of the same flow, will be identified by the data plane as the same traffic and be carried in the exact same path regardless of the network’s congestion situation, leaving parts of the Clos topology poorly utilized while other parts can be overloaded to a level of traffic loss.
Proprietary Locked Solutions:
Additional solutions in this field are implemented as a dedicated interconnect for a specific array of servers. This is more common in the scientific domain of heavy compute workloads, such as research labs, national institutes, and universities. As proprietary solutions, they force
the customer into one interconnect provider that serves the entire server array starting from the server itself and ending on all other servers in the array.
The nature of this industry is such where a one-time budget is allocated to build a “super-computer” which means that the resulting compute array is not expected to further grow but only be replaced or surmounted by a newer model. This makes the vendor-lock of choosing a proprietary interconnect solution more tolerable.
On the plus side of such solutions, they perform very well, and you can find examples on the top of the world’s strongest supercomputers list which use solutions from HPE (Slingshot), Intel (Omni-Path), Nvidia (InfiniBand) and more.
Perspective from Silicon Vendors:
DSF like solutions have been presented in the last OCP global summit back in October-2022 as part of the networking project discussions. Both Broadcom and Cisco (separately) have made claims of superior silicon implementation with improved power consumption or a superior implementation of a Virtual Output Queueing (VOQ) mechanism.
Conclusions:
There are differences between AI and HPC workloads and the required network for each.
While the HPC market finds proprietary implementations of interconnect solutions acceptable for building secluded supercomputers for specific uses, the AI market requires solutions that allow more flexibility in their deployment and vendor selection. This boils down to Ethernet based solutions of various types.
Chassis and standalone Ethernet based solutions provide reasonable solutions up to the scale of a single machine but fail to efficiently scale beyond a single interconnect machine and keep the required performance to satisfy the running workloads.
A distributed fabric solution presents a standard solution that matches the forecasted industry need both in terms of scale and in terms of performance. Different silicon implementations that can construct a DSF are available. They differ slightly but all show substantial benefits vs. chassis or standard ethernet solutions.
This paper does not cover the different silicon types implementing the DSF architecture but only the alignment of DSF attributes to the requirements from interconnect solutions built to run AI workloads and the advantages of DSF vs. other solutions which are predominant in this space.
–>Please post a comment in the box below this article if you have any questions or requests for clarification for what we’ve presented here and in part I.
References:
Using a distributed synchronized fabric for parallel computing workloads- Part I
Using a distributed synchronized fabric for parallel computing workloads- Part I
by Run Almog Head of Product Strategy, Drivenets (edited by Alan J Weissberger)
Introduction:
Different networking attributes are needed for different use cases. Endpoints can be the source of a service provided via the internet or can also be a handheld device streaming a live video from anywhere on the planet. In between endpoints we have network vertices that handle this continuous and ever-growing traffic flow onto its destination as well as handle the knowhow of the network’s whereabouts, apply service level assurance, handle interruptions and failures and a wide range of additional attributes that eventually enable network service to operate.
This two part article will focus on a use case of running artificial intelligence (AI) and/or high-performance computing (HPC) applications with the resulting networking aspects described. The HPC industry is now integrating AI and HPC, improving support for AI use cases. HPC has been successfully used to run large-scale AI models in fields like cosmic theory, astrophysics, high-energy physics, and data management for unstructured data sets.
In this Part I article, we examine: HPC/AI workloads, disaggregation in data centers, role of the Open Compute Project, telco data center networking, AI clusters and AI networking.
HPC/AI Workloads, High Performance Compute Servers, Networking:
HPC/AI workloads are applications that run over an array of high performance compute servers. Those servers typically host a dedicated computation engine like GPU/FPGA/accelerator in addition to a high performance CPU, which by itself can act as a compute engine, and some storage capacity, typically a high-speed SSD. The HPC/AI application running on such servers is not running on a specific server but on multiple servers simultaneously. This can range from a few servers or even a single machine to thousands of machines all operating in synch and running the same application which is distributed amongst them.
The interconnect (networking) between these computation machines need to allow any to any connectivity between all machines running the same application as well as cater for different traffic patterns which are associated with the type of application running as well as stages of the application’s run. An interconnect solution for HPC/AI would resultingly be different than a network built to serve connectivity to residential households or a mobile network as well as be different than a network built to serve an array of servers purposed to answers queries from multiple users as a typical data center structure would be used for.
Disaggregation in Data Centers (DCs):
Disaggregation has been successfully used as a solution for solving challenges in cloud resident data centers. The Open Compute Project (OCP) has generated open source hardware and software for this purpose. The OCP community includes hyperscale data center operators and industry players, telcos, colocation providers and enterprise IT users, working with vendors to develop and commercialize open innovations that, when embedded in product are deployed from the cloud to the edge.
High-performance computing (HPC) is a term used to describe computer systems capable of performing complex calculations at exceptionally high speeds. HPC systems are often used for scientific research, engineering simulations and modeling, and data analytics. The term high performance refers to both speed and efficiency. HPC systems are designed for tasks that require large amounts of computational power so that they can perform these tasks more quickly than other types of computers. They also consume less energy than traditional computers, making them better suited for use in remote locations or environments with limited access to electricity.
HPC clusters commonly run batch calculations. At the heart of an HPC cluster is a scheduler used to keep track of available resources. This allows for efficient allocation of job requests across different compute resources (CPUs and GPUs) over high-speed networks. Several HPC clusters have integrated Artificial Intelligence (AI).
While hyperscale, cloud resident data centers and HPC/AI clusters have a lot of similarities between them, the solution used in hyperscale data centers is falling short when trying to address the additional complexity imposed by the HPC/AI workloads.
Large data center implementations may scale to thousands of connected compute servers. Those servers are used for an array of different application and traffic patterns shift between east/west (inside the data center) and north/south (in and out of the data center). This variety boils down to the fact that every such application handles itself so the network does not need to cover guarantee delivery of packets to and from application endpoints, these issues are solved with standard based retransmission or buffering of traffic to prevent traffic loss.
An HPC/AI workload on the other hand, is measured by how fast a job is completed and is interfacing to machines so latency and accuracy are becoming more of a critical factor. A delayed packet or a packet being lost, with or without the resulting retransmission of that packet, drags a huge impact on the application’s measured performance. In HPC/AI world, this is the responsibility of the interconnect to make sure this mishaps do not happen while the application simply “assumes” that it is getting all the information “on-time” and “in-synch” with all the other endpoints it shares the workload with.
–>More about how Data centers use disaggregation and how it benefits HPC/AI in the second part of this article (Part II).
Telco Data Center Networking:
Telco data centers/central offices are traditionally less supportive of deploying disaggregated solutions than hyper scale, cloud resident data centers. They are characterized by large monolithic, chassis based and vertically integrated routers. Every such router is well-structured and in fact a scheduled machine built to carry packets between every group of ports is a constant latency and without losing any packet. A chassis based router would potentially pose a valid solution for HPC/AI workloads if it could be built with scale of thousands of ports and be distributed throughout a warehouse with ~100 racks filled with servers.
However, some tier 1 telcos, like AT&T, use disaggregated core routing via white box switch/routers and DriveNets Network Cloud (DNOS) software. AT&T’s open disaggregated core routing platform was carrying 52% of the network operators traffic at the end of 2022, according to Mike Satterlee, VP of AT&T’s Network Core Infrastructure Services. The company says it is now exploring a path to scale the system to 500Tbps and then expand to 900Tbps.
“Being entrusted with AT&T’s core network traffic – and delivering on our performance, reliability and service availability commitments to AT&T– demonstrates our solution’s strengths in meeting the needs of the most demanding service providers in the world,” said Ido Susan, DriveNets founder and CEO. “We look forward to continuing our work with AT&T as they continue to scale their next-gen networks.”
Satterlee said AT&T is running a nearly identical architecture in its core and edge environments, though the edge system runs Cisco’s disaggregates software. Cisco and DriveNets have been active parts of AT&T’s disaggregation process, though DriveNets’ earlier push provided it with more maturity compared to Cisco.
“DriveNets really came in as a disruptor in the space,” Satterlee said. “They don’t sell hardware platforms. They are a software-based company and they were really the first to do this right.”
AT&T began running some of its network backbone on DriveNets core routing software beginning in September 2020. The vendor at that time said it expected to be supporting all of AT&T’s traffic through its system by the end of 2022.
Attributes of an AI Cluster:
Artificial intelligence is a general term that indicates the ability of computers to run logic which assimilates the thinking patterns of a biological brain. The fact is that humanity has yet to understand “how” a biological brain behaves, how are memories stored and accessed, how come different people have different capacities and/or memory malfunction, how are conclusions being deduced and how come they are different between individuals and how are actions decided in split second decisions. All this and more are being observed by science but not really understood to a level where it can be related to an explicit cause.
With evolution of compute capacity, the ability to create a computing function that can factor in large data sets was created and the field of AI focuses on identifying such data sets and their resulting outcome to educate the compute function with as many conclusion points as possible. The compute function is then required to identify patterns within these data sets to predict the outcome of new data sets which it did not encounter before. Not the most accurate description of what AI is (it is a lot more than this) but it is sufficient to explain why are networks built to run AI workloads different than regular data center networks as mentioned earlier.
Some example attributes of AI networking are listed here:
- Parallel computing – AI workloads are a unified infrastructure of multiple machines running the same application and same computation task
- Size – size of such task can reach thousands of compute engines (e.g., GPU, CPU, FPGA, Etc.)
- Job types – different tasks vary in their size, duration of the run, the size and number of data sets it needs to consider, type of answer it needs to generate, etc. this as well as the different language used to code the application and the type of hardware it runs on contributes to a growing variance of traffic patterns within a network built for running AI workloads
- Latency & Jitter – some AI workloads are resulting a response which is anticipated by a user. The job completion time is a key factor for user experience in such cases which makes latency an important factor. However, since such parallel workloads run over multiple machines, the latency is dictated by the slowest machine to respond. This means that while latency is important, jitter (or latency variation) is in fact as much a contributor to achieve the required job completion time
- Lossless – following on the previous point, a response arriving late is delaying the entire application. Whereas in a traditional data center, a message dropped will result in retransmission (which is often not even noticed), in an AI workload, a dropped message means that the entire computation is either wrong or stuck. It is for this reason that AI running networks requires lossless behavior of the network. IP networks are lossy by nature so for an IP network to behave as lossless, certain additions need to be applied. This will be discussed in. follow up to this paper.
- Bandwidth – large data sets are large. High bandwidth of traffic needs to run in and out of servers for the application to feed on. AI or other high performance computing functions are reaching interface speeds of 400Gbps per every compute engine in modern deployments.
The narrowed down conclusion from these attributes is that a network purposed to run AI workloads differs from a traditional data center network in that it needs to operate “in-synch.
There are several such “in-synch” solutions available. The main options are: Chassis based solutions, Standalone Ethernet solutions, and proprietary locked solutions.–>These will be briefly described to their key advantages and deficiencies in our part II article.
Conclusions:
There are a few differences between AI and HPC workloads and how this translates to the interconnect used to build such massive computation machines.
While the HPC market finds proprietary implementations of interconnect solutions acceptable for building secluded supercomputers for specific uses, the AI market requires solutions that allow more flexibility in their deployment and vendor selection.
AI workloads have greater variance of consumers of outputs from the compute cluster which puts job completion time as the primary metric for measuring the efficiency of the interconnect. However, unlike HPC where faster is always better, some AI consumers will only detect improvements up to a certain level which gives interconnect jitter a higher impact than latency.
Traditional solutions provide reasonable solutions up to the scale of a single machine (either standalone or chassis) but fail to scale beyond a single interconnect machine and keep the required performance to satisfy the running workloads. Further conclusions and merits of the possible solutions will be discussed in a follow up article.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About DriveNets:
DriveNets is a fast-growing software company that builds networks like clouds. It offers communications service providers and cloud providers a radical new way to build networks, detaching network growth from network cost and increasing network profitability.
DriveNets Network Cloud uniquely supports the complete virtualization of network and compute resources, enabling communication service providers and cloud providers to meet increasing service demands much more efficiently than with today’s monolithic routers. DriveNets’ software runs over standard white-box hardware and can easily scale network capacity by adding additional white boxes into physical network clusters. This unique disaggregated network model enables the physical infrastructure to operate as a shared resource that supports multiple networks and services. This network design also allows faster service innovation at the network edge, supporting multiple service payloads, including latency-sensitive ones, over a single physical network edge.
References:
https://drivenets.com/resources/events/nfdsp1-drivenets-network-cloud-and-serviceagility/
https://www.run.ai/guides/hpc-clusters/hpc-and-ai
https://drivenets.com/news-and-events/press-release/drivenets-network-cloud-now-carries-more-than-52-of-atts-core-production-traffic/
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2023/01/27/att-highlights-5g-mid-band-spectrum-att-fiber-gigapower-joint-venture-with-blackrock-disaggregation-traffic-milestone/
AT&T Deploys Dis-Aggregated Core Router White Box with DriveNets Network Cloud software
DriveNets Network Cloud: Fully disaggregated software solution that runs on white boxes
Lumen to provide mission-critical communications services to the U.S. Department of Defense
Lumen Technologies recently won a $223 million contract from the U.S. Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) to provide secure, mission-critical communications services to the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD).
“The U.S. Department of Defense has a far-reaching mission to provide military forces to deter war and ensure our nation’s security. DoD selected Lumen to deliver voice communications services that will help it carry out its important mission using today’s technologies,” said Zain Ahmed, senior vice president, Lumen public sector. “DoD is modernizing its network and leveraging cloud-based technologies like the new voice system enabled by Lumen that securely connects our troops with modern communications tools wherever they are.”
- Lumen will supply DISA with modern hybrid-cloud voice and audio-conferencing services that support the Department of Defense (DoD)’s mission both inside and outside the U.S.
- The new Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) system saves the government money by eliminating the need for desk phones and supporting remote users as DoD transitions to a hybrid workforce.
- Lumen is serving as a trusted provider of secure, resilient communications services that enable more than 250,000 concurrent connections to DISA’s voice cloud system.
- Lumen is supplying unified communications services via an integrated phone system that runs over the company’s fiber network.
- Delivering voice and conferencing services from cloud data centers that meet DoD Impact Level 5 security standards provides modern capabilities with scalable infrastructure ready to meet warfighters’ needs on demand.
The new voice services will support DoD’s transition to a next generation 911 (NG911) system at military bases that can better pinpoint and route first responders to a caller’s location. The Lumen NG911 platform improves the delivery of emergency calls and enables residents to contact 911 not only by making a voice call—it also lays the foundation for the delivery of pictures and videos in the future.
- The $223 million task order has a base performance period of one year, with three additional one-year options and a potential six-month extension.
- It was awarded to Lumen under the General Services Administration’s 15-year, $50 billion Enterprise Infrastructure Solutions (EIS) program.
- Tyto Government Solutions, Inc. is a strategic subcontractor to Lumen. The two companies are working to fulfill the order’s technical requirements by delivering phone and conferencing services from highly available, resilient cloud data centers that meet DoD Impact Level 5 (IL5) security standards.
- Lumen is honored to support military and government agencies with innovative adaptive networking, edge cloud, connected security and collaboration services using the company’s platform for advanced application delivery solutions.
- The company provides a platform for IT modernization that delivers the security and reliability military and civilian agencies need to carry out their important missions.

- Learn more about our Defense Information Systems Agency $1.5 billion award to provide network transport to the U.S. Indo-Pacific Command Area of Responsibility: http://news.lumen.com/2022-11-01-Lumen-wins-1-5-billion-Defense-Information-Systems-Network-contract
- Learn more about our U.S. Department of Agriculture $1.2 billion network services award: https://news.lumen.com/2022-01-20-U-S-Department-of-Agriculture-awards-Lumen-1-2-billion-network-services-contract
- Learn more about our U.S. Department of the Interior $1.6 billion network services award: https://news.lumen.com/2020-01-16-U-S-Dept-of-the-Interior-Awards-CenturyLink-1-6-Billion-EIS-Network-Services-Win
- Learn more about how Lumen is supporting the public sector here:
https://www.lumen.com/public-sector.html
Lumen is guided by our belief that humanity is at its best when technology advances the way we live and work. With approximately 400,000 route fiber miles and serving customers in more than 60 countries, we deliver the fastest, most secure platform for applications and data to help businesses, government and communities deliver amazing experiences. Learn more about the Lumen network, edge cloud, security, communication and collaboration solutions and our purpose to further human progress through technology at news.lumen.com, LinkedIn: /lumentechnologies, Twitter: @lumentechco, Facebook: /lumentechnologies, Instagram: @lumentechnologies and YouTube: /lumentechnologies. Learn more about Lumen’s public sector capabilities on Twitter at @lumengov and on LinkedIn at @lumenpublicsector. Lumen and Lumen Technologies are registered trademarks in the United States.
India to set up 100 labs for developing 5G apps, business models and use-cases
Even as India’s long delayed 5G network roll-out continues at a rapid pace, the government has outlined plans for expanding 5G’s use beyond consumers and enterprises. In her Budget speech, Union Finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman called for the development of new applications and business models, which will also create more jobs. There are plans to set up 100 labs in engineering institutions to develop applications and use-cases for 5G services. It should be noted that GE setup India’s first 5G innovation lab in July 2022.
“The labs will cover, among others, applications such as smart classrooms, precision farming, intelligent transport systems, and health care applications,” Sitharaman said in her speech.
“The proposed outlay for 5G labs will further push the development of use-cases and the set-up of private networks in India. The research across universities will push innovations and job opportunities,” said Peeyush Vaish, partner and telecom sector leader, Deloitte India.
The speed at which commercial 5G networks have rolled out, since the official launch in October, has been impressive. India’s 5G auctions, which culminated in the second half of 2022, saw Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio and Vi acquire 5G spectrum for commercial networks, while Adani Data Networks is expected to launch enterprise 5G services with the spectrum it bought. In particular, Reliance Jio confirms it has enabled 5G networks (SA) in 225 cities across India. Airtel doesn’t give a confirmed count of its 5G NSA network service coverage, but continues to add cities every day. Vi is yet to launch 5G services.
“We believe 5G will have country-specific use-cases and India is no different. In fact, India can set an example for the rest of the world,” said Tarun Pathak, research director at Counterpoint Research.
“5G networks and devices without use-cases is akin to highways without places to travel to,” said Muralikrishnan B, president, Xiaomi India.
Test labs for 5G applications provide a sandboxed environment for testing use-case prototypes. Indian telecom equipment company Himachal Futuristic Communications Limited (HFCL) is working closely with tech giant Qualcomm and has a 5G lab which focuses on rural mobile broadband.
GE’s 5G Innovation Lab in India. Top: Jan Makela, president and CEO of imaging at GE Healthcare (center), cuts the ribbon to open the 5G Innovation Lab. Second from left: Girish Raghavan, vice president of engineering for GE Healthcare.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Bipin Sapra, Tax & Regulatory Services, Partner, EY India said that the government had taken a big leap to embrace 5G much more swiftly by setting up these labs. He agreed that they would indeed further boost employment and business opportunities in the country. “Amrit Kaal focuses on being a technology-driven and knowledge-based economy with one of the primary visions of growth and job creation. India has made remarkable advancements in the digital realm and various new initiatives have been adopted to improve the lives of people, accelerating the societal benefits of these technologies,’‘ added Mr. Sapra.
“The setting up of 100 labs to develop 5G will better network connectivity in every nook and corner of the country and further help more sectors and communities to access the benefits of 5G networks,” said Sanmeet Singh Kochhar, vice-president – India and MENA at HMD Global.
Piyush N. Singh, Senior Managing Director, Accenture, said setting up new centers of excellence for AI and 5G labs for developing apps would help democratize AI and push for wider adoption of 5G services. “It will be important for the private sector ecosystem to work closely with the government to realize the digital future of India,’‘ Mr. Singh said.
References:
https://www.gehealthcare.com/insights/article/new-5g-innovation-lab-in-india-poised-to-unlock-the-future-of-healthcare
Dell’Oro: XGS, 25G, and Early 50G PON Rollouts to Fuel Broadband Spending
A newly published report by Dell’Oro Group predicts that sales of PON (Passive Optical Network) equipment for fiber-to-the-home deployments, cable broadband access equipment, and fixed wireless CPE will all increase from 2022 to 2027, as service providers continue to expand their fiber and DOCSIS 4.0 networks, while expanding the types of services they deliver to residential subscribers.
“Service providers around the world continue to transition their broadband networks to fiber and retire their existing copper and DSL networks,” said Jeff Heynen, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “With markets expected to become more competitive, broadband providers will have to continue spending in order to differentiate their services not only by increasing advertised speeds, but also improving latency and expanding managed Wi-Fi services,” added Heynen.
Additional highlights from the Broadband Access & Home Networking 5-Year January 2023 Forecast Report:
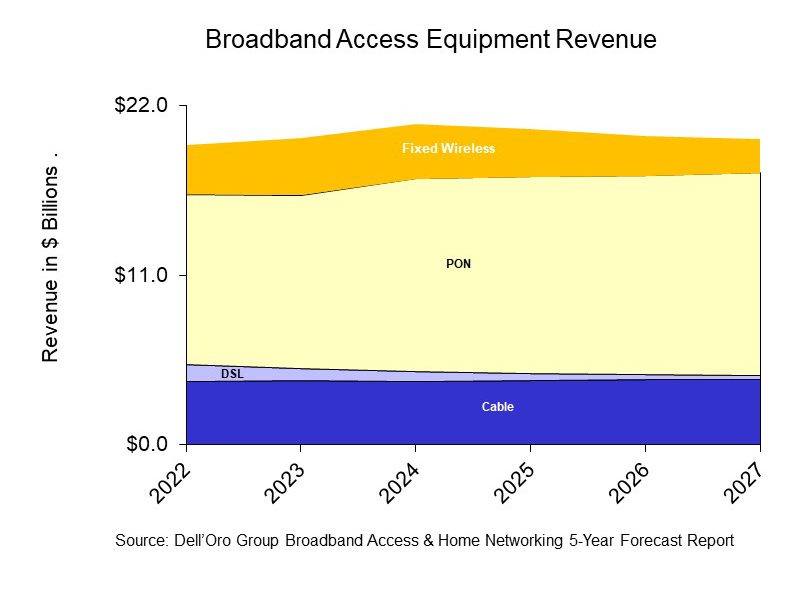
- PON equipment revenue is expected to grow from $11.0 B in 2022 to $13.2 B in 2027, driven largely by XGS-PON deployments in North America, EMEA, and CALA.
- Revenue for Cable Distributed Access Equipment (Virtual CCAP, Remote PHY Devices, Remote MACPHY Devices, and Remote OLTs [1.]) is expected to reach $1.5 B by 2027, as operators ramp their DOCSIS 4.0 and fiber deployments.
- Revenue for Fixed Wireless CPE [2.] is expected to reach $2.2 B by 2027, led by shipments of 5G sub-6GHz and 5G Millimeter Wave units.
Note 1. Remote OLTs (Optical Line Terminals) can be deployed in distributed access nodes to support targeted deployments of FTTP. Comcast is already doing that for its next-gen HFC network. But others, such as Charter Communications, are also ramping up their respective efforts and pursuing similar deployment models.
“You’re now talking about a whole new architecture with remote OLTs, virtual CMTSs and remote PHY. It will take longer to operationalize. It’s a slower burn than it used to be in the past,” Heynan said. He expects cable access network spending to continue climbing past 2027 as other cablecos join the mix.
Note 2. Heynen expects FWA CPE spending to stay steady through 2024, but notes that some providers might run into capacity issues that curtail growth and will also be faced with fiercer competition from fiber and newly upgraded HFC networks. “That puts a ceiling on how much growth can happen for fixed wireless,” he said. While T-Mobile and Verizon are now driving FWA growth in the U.S., we wonder how the future will shake out for the WISP (wireless ISP) sector, which is also seeing steady growth at the moment. As WISPs (Wireless Internet Service Providers) seek out government subsidy opportunities, some may need to consider licensed spectrum or transition to fiber across their footprint.
The Dell’Oro Group Broadband Access & Home Networking 5-Year Forecast Report provides a complete overview of the Broadband Access market with tables covering manufacturers’ revenue, average selling prices, and port/unit shipments for PON, Cable, Fixed Wireless, and DSL equipment. Covered equipment includes Converged Cable Access Platforms (CCAP), Distributed Access Architectures (DAA), DSL Access Multiplexers (DSLAMs), PON Optical Line Terminals (OLTs), Customer Premises Equipment ([CPE] for Cable, DSL, PON, Fixed Wireless), along with Residential WLAN Equipment, including Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 Gateways and Routers. For more information about the report, please contact [email protected].
Dell’Oro Group is a market research firm that specializes in strategic competitive analysis in the telecommunications, security, enterprise networks, data center infrastructure markets. Our firm provides in-depth quantitative data and qualitative analysis to facilitate critical, fact-based business decisions. For more information, contact Dell’Oro Group at +1.650.622.9400 or visit www.delloro.com.
References:
Broadband network spending set to climb as cable gets its groove back | Light Reading
Dell’Oro: FWA revenues on track to advance 35% in 2022 led by North America
Dell’Oro: PONs boost Broadband Access; Total Telecom & Enterprise Network Equipment Markets
Dell’Oro: PON ONT spending +15% Year over Year
Dell’Oro: 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) deployments to be driven by lower cost CPE
Passive Optical Network (PON) technologies moving to 10G and 25G
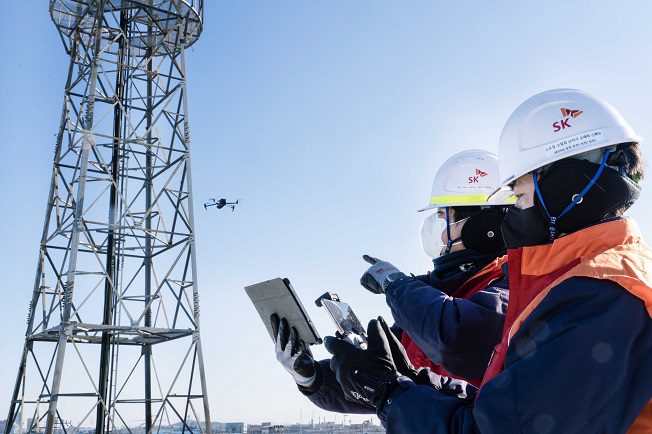
SK Telecom inspects cell towers for safety using drones and AI
SK Telecom, South Korea’s largest wireless carrier, announced on Tuesday that it’s developed a new cell tower safety inspection system using drones and image analysis artificial intelligence (AI). The newly-developed image analysis AI model checks the status of nuts and bolts by analyzing images taken by drones.
Cell towers with antennas for sending and receiving telecommunications signals are installed across the country, with their maximum height estimated at 75 meters. Since cell towers require regular maintenance to prevent accidents that can be caused by deterioration such as corrosion or loosening of nuts and bolts, specialized personnel had to climb them to inspect their condition with their bare eyes.
Engineers from a subsidiary of SK Telecom Co. inspect a cell tower in this photo provided by the wireless carrier on Jan. 31, 2023.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Now with an intelligent safety inspection system in place, not only can SK Telecom prevent accidents due to aging cell towers, but it can also ensure the safety of workers by minimizing the need to go up the cell towers. Moreover, the company can drive up work productivity through the application of an AI model that automatically identifies defects by analyzing images taken by drones.
Previously, safety inspectors had to study around 100 images to complete the inspection of one cell tower by inspecting multiple images taken by drones. With the adoption of the new AI analysis model, SK Telecom has been able to reduce the time required for the process by 95%, while increasing the reliability and consistency of the analysis results.
The company says, going forward, it will enhance the system even further by adding inspection items such as wind pressure safety/inclination. It will also look to improve the AI model and link the application with the safety management system.
In addition to drone-based cell tower inspections, the telecom company is actively applying AI to other areas of its network, including equipment error/anomaly detection, power cost reduction, and work completion inspection.
Park Myung-soon, SKT’s vice president and head of Infra DT Office, said: “By building an intelligent safety inspection system that can complement the existing visual inspection, we have secured greater safety for workers. We will continue to make efforts to achieve AI transformation of our telecommunication networks, while focusing on developing our field workers into experts who can develop and operate AI.”
References:
http://koreabizwire.com/sk-telecom-inspects-cell-towers-using-drones-and-ai/239441
South Korean telecom giant innovates safety inspection with drones
Nordic Semiconductor announces ICs & development kits for low power Wi-Fi 6 IoT applications
Nordic Semiconductor today announced the availability of the nRF7002™ Wi-Fi 6 companion IC and its associated nRF7002 Development Kit (DK). The IC is the first in Nordic’s Wi-Fi product family and is a low power Wi-Fi 6 companion IC providing seamless dual band (2.4 and 5 GHz) connectivity. The nRF7002 IC can be used together with Nordic’s award-winning nRF52® and nRF53® Series multiprotocol Systems-on-Chip (SoCs) and the nRF9160™ cellular IoT (LTE-M/NB-IoT) System-in-Package (SiP), but can equally be used in conjunction with non-Nordic host devices. The DK makes it easy for developers to get started on nRF7002-based IoT projects.
The nRF7002 complements Nordic’s cellular IoT and multiprotocol wireless solutions. By using the new IC, developers can leverage Wi-Fi 6’s higher throughput and ubiquitous domestic and industrial infrastructure when developing IoT applications. Design support through Nordic’s unified software development kit, nRF Connect SDK, and the nRF7002 DK make it easier and quicker to launch new products.
Wi-Fi 6 brings significant benefits to IoT applications—such as smart-home products, industrial sensors, asset trackers, and wearables—including power efficiency gains for battery powered Wi-Fi operation, and management of large IoT networks comprising hundreds of devices.
“The nRF7002 Wi-Fi 6 companion IC is a testament to Nordic Semiconductor’s leadership in low-power wireless technology,” says Svein-Egil Nielsen, CTO/EVP of R&D and Strategy at Nordic. “This highly integrated and flexible solution will empower developers to create new, innovative Wi-Fi 6-enabled products. Supported with the nRF7002 DK and the award-winning nRF Connect SDK, combined with Nordic’s best in class technical support, I believe it has never been easier to develop great Wi-Fi products.”
“The nRF7002 is designed to work alongside Nordic’s nRF52 and nRF53 Series making it a perfect fit for Matter, a smart-home standard backed by Amazon, Apple, Google, Nordic, Samsung, and hundreds of other companies,” says Finn Boetius, Product Marketing Engineer with Nordic. “The introduction of the IC and the nRF7002 DK now makes it easy for developers to get started on Matter and any other Wi-Fi based applications.” Matter uses Thread and Wi-Fi for data transport, and Bluetooth LE for commissioning.
The nRF7002 brings low power and secure Wi-Fi to the IoT. The dual-band IC complies with Station (STA), Soft Access Point (AP), and Wi-Fi Direct operation, and meets the IEEE 802.11b, a, g, n (“Wi-Fi 4”), ac (“5”), and ax (“6”) Wi-Fi standards. The product also offers excellent coexistence with Bluetooth LE, Thread, and Zigbee. The nRF7002 supports Target Wake Time (TWT) a key Wi-Fi 6 power saving feature. Interfacing with a host processor is done via Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) or Quad SPI (QSPI). The IC offers a single spatial stream, 20 MHz channel bandwidth, 64 QAM (MCS7), OFDMA, up to 86 Mbps PHY throughput, and BSS coloring.
In addition to its suitability for general IoT applications and Matter, the nRF7002 is the ideal choice for implementing low power SSID-based Wi-Fi locationing when used together with Nordic’s nRF9160 SiP and the company’s nRF Cloud Location Services. SSID-based Wi-Fi locationing supplements GNSS- or cell-based locationing by providing accurate positioning indoors and in places with a high density of Wi-Fi access points.
nRF7002 DK supports development of low power Wi-Fi applications:
The introduction of the nRF7002 is accompanied by the launch of the nRF7002 DK, a development kit for the Wi-Fi 6 companion IC. The DK includes an nRF7002 IC and features an nRF5340 multiprotocol SoC as a host processor for the nRF7002. The nRF5340 embeds a 128 MHz Arm Cortex-M33 application processor and a 64 MHz high efficiency network processor. The DK supports the development of low-power Wi-Fi applications and enables Wi-Fi 6 features like OFDMA, Beamforming, and TWT. The DK includes: Arduino connectors; two programmable buttons; a Wi-Fi dual-band antenna and a Bluetooth LE antenna, and current measurement pins.
nRF7002 DK – Development Kit for nRF7002 Wi-Fi 6 IC:
.png?h=754&iar=0&mw=350&w=350&hash=1DF0EC6A97E1329DCCD435B7FDBF0B90)
Source Nordic Semiconductor
Together with the DK, developing nRF7002-based designs is made simpler by the support for the IC in the nRF Connect SDK, Nordic’s scalable and unified software development kit for building products based on the company’s wireless devices. With the nRF7002 IC, nRF7002 DK, and nRF Connect SDK, developers can quickly and easily add Wi-Fi connectivity to their products, allowing them to connect to the Internet and communicate with other devices over a Wi-Fi network. Example applications for the nRF7002 DK are included with nRF Connect SDK.
The nRF7002 companion IC and nRF7002 DK are available now from Nordic’s distribution partners.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/nRF7002
https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/Development-hardware/nRF7002-DK