Author: Alan Weissberger
Nokia to acquire Infinera for $2.3 billion, boosting optical network division size by 75%
Nokia has agreed to buy optical networking equipment vendor Infinera in a deal worth $2.3 billion. 70% of the sum will be paid in cash, the remaining 30% in Nokia shares. Nokia said it will accelerate its share buyback program to offset the dilution.
The acquisition will grow the size of its Optical Networks division by 75%, enabling the company to accelerate its product roadmap and increase its exposure to webscale customers, which account for around 30% of Infinera’s revenue.

Nokia and Infinera see a significant opportunity in merging to improve scale and profitability, enabling the combined business to accelerate the development of new products and solutions to benefit customers. The transaction aligns strongly with Nokia’s strategy, as it is expected to strengthen the company’s technology leadership in optical and increase exposure to webscale customers, the fastest growing segment of the market.
- Creates a highly scaled and truly global optical business with increased in-house technology capabilities and vertical integration.
- Strengthens Nokia’s optical position, specifically in North America.
- Accelerates Nokia’s customer diversification strategy, expanding webscale presence.
- Targeted net comparable operating profit synergies of EUR 200 million by 2027.
Nokia believes the transaction has compelling financial and strategic merit. The combination with Infinera is projected to accelerate Nokia’s journey to a double-digit operating margin in its Optical Networks business. Nokia targets to achieve EUR 200 million of net comparable operating profit synergies by 2027. This transaction along with the recently announced sale of Submarine Networks will create a reshaped Network Infrastructure built on three strong pillars of Fixed Networks, IP Networks and Optical Networks. Nokia targets mid-single digit organic growth for the overall Network Infrastructure business and to improve its operating margin to mid-to-high teens level.
The combined Nokia and Infinera will have a global market share of around 20%, broadly equal to Ciena (which acquired Nortel’s optical network division in November 2009 for $769 billion) but lagging behind Huawei’s 31%, according to J.P. Morgan analyst Samik Chatterjee.
“Ciena is less likely to make a competing bid given complexity in integrating competing optical portfolios as well as hurdles in regulatory approval given Ciena’s majority (51%) share of the North America market,” wrote Chatterjee in a research note.
Omdia (Informa) expects optical networking market sales to rise at a compound annual growth rate of 5% between now and 2029. A well-executed takeover may, then, give Nokia a growth story during a period of difficulty for its large mobile business group, responsible for about 44% of total sales last year.
The transaction is expected to be accretive to Nokia’s comparable EPS in the first year post close and to deliver over 10% comparable EPS accretion by 2027*, with a return on invested capital (RoIC) comfortably above Nokia’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
Pekka Lundmark, President and CEO of Nokia, said:
“In 2021 we increased our organic investment in Optical Networks with a view to improving our competitiveness. That decision has paid off and has delivered improved customer recognition, strong sales growth and increased profitability. We believe now is the right time to take a compelling inorganic step to further expand Nokia’s scale in optical networks. The combined businesses have a strong strategic fit given their highly complementary customer, geographic and technology profiles. With the opportunity to deliver over 10% comparable EPS accretion, we believe this will create significant value for shareholders.”
Federico Guillén, President of Network Infrastructure at Nokia, said: “Today, Network Infrastructure offers a unique portfolio across the fixed access, optical and IP networks domains built on leading technology innovation and a strong customer focus. This acquisition will further strengthen the optical pillar of our business, expand our growth opportunities across all our target customer segments and improve our operating margin. I am extremely pleased that we are bringing together these two talented and dedicated teams. Separately, we have long respected each other as competitors. Together, we find the logic of combination irresistible.”
David Heard, CEO of Infinera, said: “We are really excited about the value this combination will bring to our global customers. We believe Nokia is an excellent partner and together we will have greater scale and deeper resources to set the pace of innovation and address rapidly changing customer needs at a time when optics are more important than ever – across telecom networks, inter-data center applications, and now inside the data center. This combination will further leverage our vertically integrated optical semiconductor technologies. Furthermore, our stakeholders will have the opportunity to participate in the upside of a global leader in optical networking solutions.”
Compelling strategic benefits for Nokia, Infinera and customers:
- Improving global scale and product roadmap: The combination will increase the scale of Nokia’s Optical Networks business by 75%, enabling it to accelerate its product roadmap timeline and breadth; providing better products for customers and creating a business that can sustainably challenge the competition.
- The combined business will have significant in-house capabilities, including an expanded digital signal processor (DSP) development team, expertise across silicon photonics and indium phosphide-based semiconductor material sciences, and deeper competency in photonic integrated circuit (PIC) technology. The result will be a strong innovative player with a deep and diverse pool of optical networking talent and expertise.
- Gaining scale in North America optical market: The two companies have limited customer overlap, putting the combined business in a strong position in all regions (excluding China). Infinera has built a solid presence in the North America optical market, representing ~60% of its sales, which will improve Nokia’s optical scale in the region and complement Nokia’s strong positions in APAC, EMEA and Latin America.
- Building on Nokia’s commitment to investment in U.S. based manufacturing and advanced testing and packaging capabilities.
- Accelerating Nokia’s expansion into enterprise and particularly webscale: The combination of these two businesses is also expected to accelerate Nokia’s strategic goal of diversifying its customer base and growing in enterprise. Internet content providers (ICP or webscale as Nokia typically calls this segment) make up over 30% of Infinera’s sales. With recent wins in line systems and pluggables, Infinera is well established in this fast-growing market. Infinera has also recently been developing high-speed and low-power optical components for use in intra-data center (ICE-D) applications and which are particularly suited to AI workloads which can become a very attractive long-term growth opportunity. Overall, the acquisition offers an opportunity for a step change in Nokia’s penetration into webscale customers.
- Net comparable operating profit synergies of EUR 200 million: The combination is expected to deliver EUR 200 million of net comparable operating profit synergies by 2027*. Approximately one third of the synergies are expected to come from cost of sales due to supply chain efficiencies and the remainder from operating expenses due to portfolio optimization and integration along with reduced product engineering costs and standalone entity costs. Nokia expects one-time integration costs of approximately EUR 200 million related to the transaction.
- Creating value for shareholders: The transaction is expected to be accretive to Nokia’s comparable operating profit and EPS in year 1 and to deliver more than 10% comparable EPS accretion in 2027*. Nokia also expects the deal to deliver a return on invested capital (RoIC) comfortably above Nokia’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC). In addition, Infinera’s investors will have the opportunity to participate in the exciting upside of investing in a global leader in optical networking solutions.
Transaction details:
Under the terms of the definitive agreement, Nokia is acquiring Infinera for $6.65 per share, which equates to an enterprise value of $2.3 billion. For each Infinera share, Infinera shareholders will be able to elect to receive either: 1) $6.65 cash, 2) 1.7896 Nokia shares, or 3) a combination of $4.66 in cash and 0.5355 Nokia shares for each Infinera share. All Nokia shares will be issued in the form of American Depositary Shares. The definitive agreement includes a proration mechanism so that the Nokia shares issued in the transaction do not exceed an amount equal to approximately 30% of the aggregate consideration that may be paid to Infinera shareholders.
References:
https://www.barrons.com/articles/infinera-stock-price-buy-sell-nokia-ciena-658c7898
https://www.infinera.com/press-release/nokia-to-acquire-infinera/
LightCounting: Q1 2024 Optical Network Equipment market split between telecoms (-) and hyperscalers (+)
Infinera, DZS, and Calnex Successfully Demonstrate 5G Mobile xHaul with Open XR
Orange Deploys Infinera’s GX Series to Power AMITIE Subsea Cable
Infinera trial for Telstra InfraCo’s intercity fiber project delivered 61.3 Tbps between Melbourne and Sydney, Australia
Dell’Oro: Campus Ethernet Switch Revenues dropped 23% YoY in 1Q-2024
Worldwide Campus Ethernet Switch [1.] revenues plummeted by 23% YoY in the 1st quarter of 2024 to a 2-year low, according to the Dell’Oro Group.
- The only two vendors that grew campus switch revenues year over year were Santa Clara, CA based Arista Networks and Ubiquiti [2.].
- Cisco’s campus switch revenues fell more than the worldwide average.
Note 1. With higher demand from new use cases for wired connectivity such as automation, analytics, and network visibility, and the need for new access switches to aggregate Wireless LAN access points, Dell’Oro Group is offering in-depth analysis specifically on Ethernet Switches built and optimized for deployment outside the data center, for the purpose of connecting users and things to the corporate Local Area Network (LAN).
“Basically, campus switches are really the networking gear to connect users and devices and laptops,” said Sameh Boujelbene, VP with Dell’Oro Group. “Access points are probably the number one application.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Note 2. Although headquartered in New York, NY, Ubiquiti wrote in a 2019 SEC filing:
“We use contract manufacturers, primarily located in China, Vietnam and Taiwan, to manufacture our products. Our relationships with contract manufacturers allow us to conserve working capital, reduce manufacturing costs and minimize delivery lead times while maintaining high product quality and the ability to scale quickly to handle increased order volume. Over the long term, our contract manufacturers are not required to manufacture our products for any specific period or in any specific quantity. If necessary, we expect that it would take approximately 3 to 6 months to transition manufacturing, quality assurance and shipping services to new providers.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“Vendor backlogs of campus switch orders have now been completely run down, and the market is in a multi-quarter digestion cycle,” said Siân Morgan, Research Director at Dell’Oro Group. “The shipments of most port speeds declined, and the Average Sales Price (ASP) also dropped on a YoY basis.
“However, in 1Q 2024, Arista had its third sequential quarter of (market) share gain, growing Campus Switch sales to large enterprises.
On the downside, Cisco’s Campus Switch shipments contracted sharply. This reduction contrasts with their shipments in 2023, when Cisco opened the “floodgate” for Catalyst and Meraki port shipments which had been on backorder,” added Morgan.

Additional highlights from the 1Q 2024 Ethernet Switch – Campus Report:
- The contraction in campus switch sales was broad-based across all regions, with the exception of Central America-Latin America (CALA).
- Some vendors bucked the price trend and were able to grow port ASPs thanks to richer product mixes.
- 5/5.0 Gbps switch ports are expected to return to growth as shipments of Wi-Fi 7 Access Points accelerate.
The Dell’Oro Group Ethernet Switch – Campus Quarterly Report offers a detailed view of Ethernet switches built and optimized for deployment outside the data center, to connect users and things to the Local Area Networks. The report contains in-depth market and vendor-level information on manufacturers’ revenue, ports shipped and average selling prices for both Modular and Fixed, and Fixed Managed and Unmanaged Ethernet Switches (100 Mbps, 1/2.5/5/10/25/40/50/100/400 Gbps), Power-over-Ethernet, plus regional breakouts as well as split by customer size (Enterprise vs. SMB) and vertical segments.
To purchase these reports, email [email protected]
References:
Campus Ethernet Switch Revenues Crash to a Two-Year Low in 1Q 2024, According to Dell’Oro Group
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network & Cable CPE shipments all declined in 1Q-2024
Dell’Oro: Broadband network equipment spending to drop again in 2024 to ~$16.5 B
Telefónica and Nokia partner to boost use of 5G SA network APIs
Telefónica and Nokia today announced an agreement to jointly explore new opportunities leveraging 5G Standalone (SA) capabilities for network APIs to support developers in creating new use cases for consumer, enterprise, and industrial customers.
Through this agreement, Telefónica will harness Nokia’s Network Exposure Function (NEF) for various purposes that enable developers to access the operator’s 5G network capabilities, like precise device location, enhanced notifications based on connectivity status, edge discovery, and more.
Having access to these capabilities will enhance developers’ capacity to build new applications and drive new service APIs for the industry.
Nokia’s NEF solution, based on 3GPP specifications, provides a process for interfacing with well-defined functions in the core network. It also enables API mashups so developers can combine multiple APIs from different core functions into a new customized API, which is easier for developers to use to create new applications. NEF is said to be “a robust platform for creating new services by consolidating APIs and presenting unified access to the API framework for in-house or 3rd party app developers.”
- Secure exposure of network services (voice, data connectivity, charging, subscriber data, etc.) towards 3rd party application over APIs
- Developer environment and SDK for operator and community
- Service mashup for creating end-to-end offering by combining any of the network assets into your application
- Integration layer that connects your application to operator’s network.
Last week, it was announced that Nokia Network as Code platform with developer portal will run on Google Cloud. The purpose is to promote specific use cases to the Google Cloud developer community, starting with healthcare. Google Cloud stresses it developers cover “all major industries and geographies”.
Nokia’s Network as Code platform brings together networks, systems integrators, and software developers, into a unified ecosystem that provides developers a simple way for integrating advanced 5G capabilities into their applications; without having to navigate the complexity of the underlying network technologies.
Nokia has signed collaboration agreements with 14 network operators and ecosystem partners, in Europe, North America, and South America, to use the platform since its launch in September 2023.
Quotes:
Cayetano Carbajo Martin, Core & Transport Director, Global CTIO at Telefónica said: “We are pleased to take this step with Nokia in recognition of the tremendous opportunity we have to further empower developers with the tools they require to deliver new use cases and experiences for their customers and beyond. This partnering agreement is about steering the industry in building new APIs and more use cases over 5G SA capabilities that have been launched across Telefonica’s main operations.”
Shkumbin Hamiti, Head of Network Monetization Platform, Cloud and Network Services at Nokia said: “There continues to be a rising recognition that sustaining closed networks is a thing of the past and that embracing ecosystems is the way forward for deepening collaboration and creating new use cases; delivering better customer experiences; and generating new revenue opportunities. Our agreement with Telefónica is added proof of the much greater telco ecosystem openness that we are now seeing today and we look forward to jointly working to support developers in harnessing a broader array of network capabilities.”
References:
https://www.nokia.com/networks/core-networks/network-exposure-function/
https://www.nokia.com/networks/programmable-networks/network-as-code/
https://www.mobileeurope.co.uk/telefonica-nokia-aim-to-boost-use-of-5g-sa-network-apis/
Nokia, Google Cloud to help developers create 5G apps with telco APIs
Telefónica launches 5G SA in >700 towns and cities in Spain
Telefónica launches 5G SA in >700 towns and cities in Spain
TÉRAL Research: Sharp declines in Wireless Infrastructure Market 1Q-2024
The global wireless infrastructure market, including 2G/3G/4G/5G RAN and core networks, experienced significant declines both sequentially (-31%) and YoY (-26%) in 1Q-2024. However, these declines are not unprecedented.
“Such decline has happened before in 2002 and 2003 due to a sharp decrease in TDMA and PDC systems shipments, as well as in the post-LTE peak era from 2016 to 2019, when each year’s first quarter posted a 20%+ YoY decline. And that’s not all, looking at bellwether Ericsson’s networks sales historical data, 1Q was also down 20%+ sequentially during the 5G boom,” said Stéphane Téral, Founder and Chief Analyst at TÉRAL RESEARCH.
Huawei continues to be the largest wireless network infrastructure vendor, Nokia and ZTE Corporation’s lost market share, while Samsung Networks position was steady.
Téral states that 2024 marks the third consecutive year of a wireless disinvestment cycle yet the market is poised for a slight rebound in 2H2024 driven by open RAN and 5G upgrades.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Stéphane attended Oracle’s Applications & Industries Analyst Summit at the Oracle Conference Center in Redwood Shores, California. This two-day event showcased how Oracle is integrating Generative AI into its Fusion Data Intelligence Platform, enhancing ERP, EPM, SCM, HCM, and CX applications with AI-powered updates. Oracle’s industry verticals, particularly their 5G CSP monetization and digital experience strategies, promise to end the 5G monetization drought. With Oracle migrating databases to its cloud and leveraging AI, CSPs can expect increased efficiency and growth.
References:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/whats-new-t%C3%A9ral-research-t-ral-research-qsmec/
https://www.teralresearch.com/resources
Dell’Oro: RAN revenues declined sharply in 2023 and will remain challenging in 2024; top 8 RAN vendors own the market
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network & Cable CPE shipments all declined in 1Q-2024
Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices
Dell’Oro: Mobile Core Network market has lowest growth rate since 4Q 2017
What is 5G Advanced and is it ready for deployment any time soon?
Data infrastructure software: picks and shovels for AI; Hyperscaler CAPEX
For many years, data volumes have been accelerating. By 2025, global data volumes are expected to reach 180 zettabytes (1 zettabyte=1 sextillion bytes), up from 120 zettabytes in 2023.
In the age of AI, data is viewed as the currency for large language models (LLMs) and AI–enabled offerings. Therefore, demand for tools to integrate, store and process data is a growing priority amongst enterprises.
The median size of datasets required to train AI models increased from 5.9 million data points in 2010 to 750 billion in 2023, according to BofA Global Research. As demand rises for AI-enabled offerings, companies are prioritizing tools to integrate, store, and process data.
In BofA’s survey, data streaming/stream processing and data science/ML were selected as key use cases in regard to AI, with 44% and 37% of respondents citing usage, respectively. Further, AI enablement is accelerating data to the cloud. Gartner estimates that 74% of the data management market will be deployed in the cloud by 2027, up from 60% in 2023.
Data infrastructure software [1.] represents a top spending priority for the IT department. Survey respondents cite that data infrastructure represents 35% of total IT spending, with budgets expected to grow 9% for the next 12 months. No surprise that the public cloud hyper-scaler platforms were cited as top three vendors. Amazon AWS data warehouse/data lake offerings, Microsoft Azure database offerings, and Google BigQuery are chosen by 45%, 39% and 35% of respondents, respectively.
Note 1. Data infrastructure software refers to databases, data warehouses/lakes, data pipelines, data analytics and other software that facilitate data management, processing and analysis.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The top three factors for evaluating data infrastructure software vendors are security, enterprise capabilities (e.g., architecture scalability and reliability) and depth of technology.
BofA’s Software team estimates that the data infrastructure industry (e.g., data warehouses, data lakes, unstructured databases, etc.) is currently a $96bn market that could reach $153bn in 2028. The team’s proprietary survey revealed that data infrastructure is 35% of total IT spending with budgets expected to grow 9% over the next 12 months. Hyperscalers including Amazon and Google are among the top recipients of dollars and in-turn, those companies spend big on hardware.
Key takeaways:
- Data infrastructure is the largest and fastest growing segment of software ($96bn per our bottom-up analysis, 17% CAGR).
- AI/cloud represent enduring growth drivers. Data is the currency for LLMs, positioning data vendors well in this new cycle
- BofA survey (150 IT professionals) suggests best of breeds (MDB, SNOW and Databricks) seeing highest expected growth in spend
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
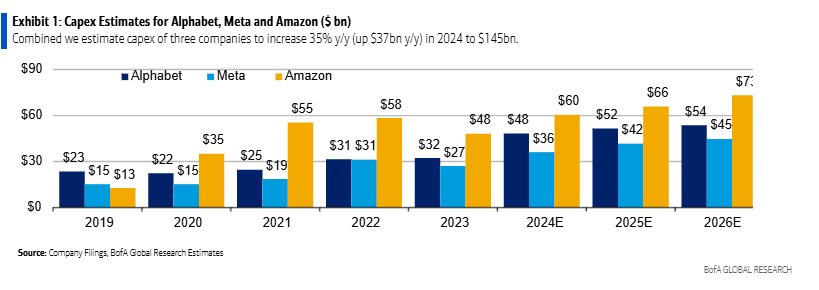
BofA analyst Justin Post expects server and equipment capex for mega-cap internet companies (Amazon, Alphabet/Google, Meta/Facebook) to rise 43% y/y in 2024 to $145bn, which represents $27bn of the $37bn y/y total capex growth. Despite the spending surge, Mr. Post thinks these companies will keep free cash flow margins stable at 22% y/y before increasing in 2025. The technical infrastructure related capex spend at these three companies is expected to see steep rise in 2024, with the majority of the increase for servers and equipment.
Notes:
- Alphabet categorizes its technical infrastructure assets under the line item ‘Information Technology Assets‘
- Amazon take a much a broader categorization and includes Servers, networking equipment, retail related heavy equipment & fulfillment equipment under ‘Equipment‘.
- Meta gives more details and separately reports Server & Networking, and Equipment assets.
In 2024, BofA estimates CAPEX for the three hyperscalers as follows:
- Alphabet‘s capex for IT assets will increase by $12bn y/y to $28bn.
- Meta, following a big ramp in 2023, server, network and equipment asset spend is expected to increase $7bn y/y to $22bn.
- Amazon, equipment spend is expected to increase $8bn y/y to $41bn (driven by AWS, retail flattish). Amazon will see less relative growth due to retail equipment capex leverage in this line.
On a relative scale, Meta capex spend (% of revenue) remains highest in the group and the company has materially stepped up its AI related capex investments since 2022 (in–house supercomputer, LLM, leading computing power, etc.). We think it‘s interesting that Meta is spending almost as much as the hyperscalers on capex, which should likely lead to some interesting internal AI capabilities, and potential to build a “marketing cloud“ for its advertisers.
From 2016-22, the sector headcount grew 26% on average. In 2023, headcount decreased by 9%. BofA expects just 3% average. annual job growth from 2022-2026. Moreover, AI tools will likely drive higher employee efficiency, helping offset higher depreciation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Source for all of the above information: BofA Global Research
Analysys Mason Open Network Index: survey of 50 tier 1 network operators
Open networks apply proven cloud concepts to the networking domain while enabling components to be sourced from a broad ecosystem of vendors. Open networks boast high levels of automation and programmability and are built around the concept of utilizing a common, horizontal cloud platform that supports cloud-native network functions from multiple vendors and from multiple network domains. Network operators can enhance the flexibility, agility, composability, innovation and operational efficiency of their networks by implementing open architectures and open operating models.
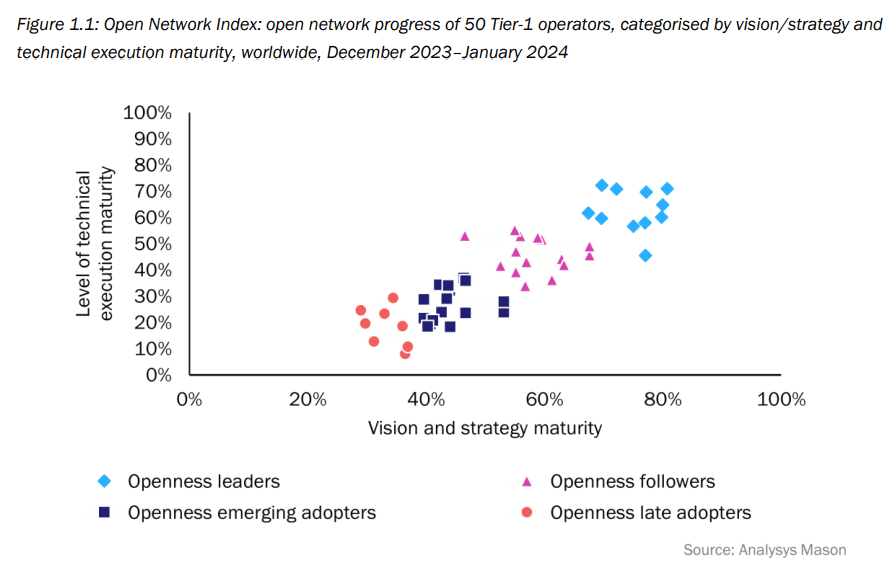
According to a survey conducted by Analysys Mason, ninety percent of global telecom service providers believe open networks are critical to their survival. However, only 20% have an open network strategy in place. Analysys Mason surveyed 50 leading Tier-1 operators worldwide between December 2023 and January 2024.
The analysts then benchmarked operator progress from a vision/strategy perspective and a technical perspective to form the first iteration of Analysys Mason’s Open Network Index (ONI). The survey and report were commissioned by Dell Technologies, but Analysys Mason says it does not endorse any of the vendor’s products or services.
The market research firm defines open networks as those based on non-proprietary technologies and standards, including open hardware and software developed by open communities, as well as software technologies that individual vendors are exposing, typically through open application programming interfaces (APIs), to anyone who wants to use them.
“Operators need to urgently develop an openness strategy and ensure that they approach openness in the right way,” the report authors said.
The analysts said that overall, survey respondents displayed a strong willingness to align themselves with open networking principles. But the technical implementation of open network architectures remains challenging.

The survey results partitioned the 50 network operators into four distinct categories:
- Openness leaders have a deep commitment to open networks and are supported at the highest levels of the organization. This category includes a higher proportion of operators from developed Asia–Pacific (APAC) than in any of the following categories.
- Openness followers are implementing aspects of open networks, but they take a more tactical approach because they lack the strong level of senior executive support that the openness leaders enjoy.
- Openness emerging adopters are operators that are just starting their journey. The category includes operators from developing markets that have a vision but have not yet started to deploy the architectures. The category also includes cautious adopters with lower ambitions for open networks.
- Openness late adopters do not have a clear concept of what an open network is, and they have not yet started to formulate a strategy for achieving openness or to win senior executive support. They have a low appetite for risk and perceive significant risks associated with moving away from incumbent vendors.
Many operators have strong engagements with well-established telecoms industry bodies such as the GSMA and the TM Forum. These bodies have traditionally aimed to improve standardisation and foster multi-vendor interoperability, but their activities in the areas of open cloud platforms and open operating models have been somewhat peripheral. Operators should deepen their involvement with initiatives such as the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), Nephio and Sylva, which champion open infrastructure and open operations, and support the fundamentals of horizontal cloud platforms.
In addition, operators should engage with the O-RAN Alliance (which is NOT a standards body/SDO), which is leading multi-vendor Open RAN interface and interoperability standards, with these standards leveraging distributed, cloud-native-based architectures. Participation in these initiatives facilitates knowledge sharing, enables operators to shape future standardization efforts and empowers operators to exert greater influence over their vendors.
References:
https://www.analysysmason.com/operator-network-index-rma16-rma18
Analysys Mason’s gloomy CAPEX forecast: “there will not be a cyclical recovery”
IEEE/SCU SoE May 1st Virtual Panel Session: Open Source vs Proprietary Software Running on Disaggregated Hardware
Analysys Mason: 40 operational 5G SA networks worldwide; Sub-Sahara Africa dominates new launches
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
Two of China’s state-owned telcos have taken stakes in new LEO satellite companies.
- China Telecom has set up a new fully owned subsidiary, Tiantong Satellite Technology Co., registered in Shenzhen with 1 billion Chinese yuan (US$138 million) paid-in capital. China Telecom, which is currently the only operator with a mobile satellite license, operates three Tiantong Geo orbit satellites, launched between 2016 and 2021, covering China, the western Pacific and its neighbors.
- In April China Mobile took a 20% stake in a new RMB4 billion ($551 million) state-owned company, China Shikong Xinxi Co., registered in Xiongan. China Satellite Network Group, the company behind Starnet, China’s biggest LEOsat project, will own 55%, and aerospace contractor Norinco, a 25% shareholder.
China Telecom will shutter its legacy satellite subsidiary, established in 2009, and transfer the assets into the new company.
The other new business, China Shikong, lists its scope as satellite communication, satellite navigation and remote sensing services.
The two investments come as China Starnet is readying to launch its first satellites in the second half of the year. It is aiming to build a constellation of 13,000, with the first 1,300 going into operation over the next five years, local media has reported.

In addition to Starnet, two other mass constellations are planned – the state-owned G60 and a private operator, Shanghai Hongqing. Neither has set a timetable. They will be playing catch up with western operators like Starlink and OneWeb, which are already operating thousands of commercial satellites.
Since foreign operators are forbidden from selling into China, it is not yet clear how China is going to structure its LEO satellite industry and what role precisely the new operators are going to play.
References:
Chinese telcos tip cash into satellite (lightreading.com)
China Mobile launches LEO satellites to test 5G and 6G – Developing Telecoms
Very low-earth orbit satellite market set to reach new heights | TelecomTV
5G connectivity from space: Exolaunch contract with Sateliot for launch and deployment of LEO satellites
LEO operator Sateliot joins GSMA; global roaming agreements to extend NB-IoT coverage
Momentum builds for wireless telco- satellite operator engagements
Satellite 2024 conference: Are Satellite and Cellular Worlds Converging or Colliding?
5G connectivity from space: Exolaunch contract with Sateliot for launch and deployment of LEO satellites
Overview and Backgrounder:
Exolaunch, a global leader in launch mission management, integration, and satellite deployment services, today announced a new launch and deployment services agreement with Sateliot [1.], which claims to be the first company to operate a low Earth orbit (LEO) 5G NB-IoT satellite constellation. It’s the first collaboration between the two companies.
Note 1. Sateliot is based in Barcelona, Spain and San Diego, CA. The start-up company is backed by strong investors such as Evonexus (investment arm of Qualcomm and Verizon among others), Banco Santander, CELLNEX and INDRA, and partners of the GSMA and the ESA (European Space Agency).
Sateliot claims to be a “trailblazer in facilitating connectivity for all current narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) devices via satellite through its constellation.”
Sateliot is building a constellation of 250 unique satellites enabling 5G NB-IoT connectivity from space, revolutionizing connectivity solutions globally. Under the terms of this agreement, Sateliot is set to deploy four additional satellites to join its growing 5G IoT constellation, utilizing Exolaunch’s industry-leading services and hardware.
The constellation of LEO satellites will enable Sateliot to offer services at comparable costs to those of terrestrial cellular networks, a significant stride towards widespread adoption of IoT in previously inaccessible regions.
Sateliot’s four 6U satellites, named Sateliot_1, Sateliot_2, Sateliot_3, and Sateliot_4, are manifested via Exolaunch on the Transporter-11 Rideshare mission with SpaceX, which is slated to launch in mid-2024. Sateliot will benefit from Exolaunch’s renowned mission management services and integration support, and will leverage Exolaunch’s innovative and flight-proven containerized satellite separation system, the EXOpod Nova, for the deployment of its satellites.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
About Sateliot’s Technology:
Sateliot’s solution is based on 5G NB-IoT in 3GPP Rel 17 NTN (Non Terrestrial Network). The company says that is “a clear minimum workable solution under 5G ecosystem.” The claim “5G from space,” is based on the use of LEO satellites for connectivity- not HAPS or other NTN types.
While 3GPP Rel 19 (to be completed December 2025) will provide a complete solution, Sateliot says that is not needed now to offer a minimum workable solution, via 3GPP Rel 17 NTN. This minimum workable Rel 17 NTN solution is related to NB-IoT only, so, there is no need to wait for Rel 18 or Rel 19. Sateliot has already found a commercially available chipset and RF module from its main vendor.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) for Internet of Things (IoT) Phase 3:
With IoT-NTN specified in 3GPP RAN Rel-17, with optimizations following in Rel-18, commercial deployments are now ongoing. Now, further evolution of IoT-NTN is underway with a dedicated Rel-19 work item, focusing in on three areas:
- Support of Store & Forward (S&F) operation based on regenerative payload, including the support of feeder link switchover.
- Uplink capacity enhancements.
3GPP R19 is part of the 3GPP’s “5G Advanced” releases, which are intended to improve network performance and support new applications and use cases.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Quotes:
“Partnering with Exolaunch marks a significant milestone for Sateliot as we continue our mission to revolutionize 5G IoT connectivity from space. With Exolaunch’s expertise and industry-leading services, we are confident in the successful launch and deployment of our next four satellites, further advancing our vision of ubiquitous IoT connectivity,” remarked Jaume Sanpera, chief executive officer at Sateliot.
“We are delighted to welcome Sateliot as our newest customer and partner,” said Pablo Lobo, mission manager at Exolaunch. “This agreement highlights Exolaunch’s dedication to facilitating the growth and success of innovative European companies like Sateliot. Exolaunch is proud to provide our industry-leading services and technology to support Sateliot’s vision of advancing 5G IoT connectivity from space. With the launch campaign underway, our team’s excitement for this mission is palpable and we look forward to a smooth and successful deployment of these satellites later this year.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.3gpp.org/news-events/3gpp-news/5g-ntn
LEO operator Sateliot joins GSMA; global roaming agreements to extend NB-IoT coverage
Momentum builds for wireless telco- satellite operator engagements
Satellite 2024 conference: Are Satellite and Cellular Worlds Converging or Colliding?
Space X “direct-to-cell” service to start in the U.S. this fall, but with what wireless carrier?
Samsung announces 5G NTN modem technology for Exynos chip set; Omnispace and Ligado Networks MoU
Point Topic: FTTP broadband subs to reach 1.12bn by 2030 in 29 largest markets
Point Topic forecasts 1.39 billion fixed broadband connections by the end of the decade in the 29 largest broadband markets in the world. Fiber to the Premises (FTTP) is already dominating most of the markets and it will be the preferred option for most consumers, where it is available.
Between 2023 and 2030 Point Topic projects a 15% growth in total fixed broadband subscribers in the top 29 markets. The growth will come mainly from FTTP – although the increase in the total fiber lines will be lower than that in Fixed Wireless Access lines – 25% and 61% respectively, the sheer number of already existing and new FTTP connections will drive the total growth.

Figure 1. Fixed broadband lines by technology (Top 29 markets)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Split by technology we estimate that by 2030 there will be 1.12 billion FTTP, 149 million cable, 79 million FTTX, 16 million FWA[1] and only 28 million DSL lines in these markets.
 Figure 2. Change in fixed broadband lines, 2023-2030 (Top 29 markets)
Figure 2. Change in fixed broadband lines, 2023-2030 (Top 29 markets)Cable is a term used as a proxy for those legacy MSOs/cablecos (e.g. Charter, VMO2, Comcast, etc.) that still have significant networks based on coaxial cable, mainly DOCSIS 3.0 and 3.1. We forecast some decline (-6%) in cable broadband lines by the end of the decade as these networks are being replaced with full fibre. The new generation DOCSIS4, which is in development, will match the capabilities of FTTH with XGPON, so markets with established cable networks will see a slight growth or stable take-up figures for ‘cable’ broadband lines.
FTTX (where fibre is present in the local loop with copper, mainly fiber to the cabinet) will decline over the next seven years (-19%). Some modest growth from new subscribers will remain in a few markets where legacy infrastructure is still widespread. Also, it will remain a cheaper option even where other technologies are available as it still offers enough bandwidth for some users.
DSL will see the largest decline at -44%. However, while being a slower and less reliable solution, it can provide enough bandwidth at a low price to some single or older households that are reluctant to upgrade. Besides, some of them will not have a choice of other technologies, especially in certain regions and markets.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………

Figure 3. Fixed broadband penetration, 2023 and 2030 (top 29 markets)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Point Topic only included FWA in its data in significant markets and where it was able to source reliable figures, such at the U.S., Canada, and Italy. Therefore, the total number of FWA subscribers could end up higher if FWA takes off in other markets.
In the U.S., T-Mobile US and Verizon are the FWA leaders with 8.6 million connections between them as of March 2024. T-Mobile recently added a new FWA service offer to its portfolio aimed at customers who might need a back-up for unreliable fiber or cable connections.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
China will be among the 16 markets with 90%-plus broadband penetration in seven years time. The potential for signing up new customers in those markets will shrink, leaving broadband providers with the task of converting existing customers to higher bandwidths and more advanced technologies for growth.
At the other end of the scale, there is still lots of room for broadband growth. India will have the lowest percentage of premises with a fixed broadband connection by 2030 at 33%, up from just 11% last year.
“There is significant growth to come in the ‘youthful’ markets with low fixed broadband penetration, with plenty of consumers in India, Indonesia and other fast-growing economies hungry for the advantages offered by fixed broadband and full fibre in particular,” Point Topic said.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.point-topic.com/post/fttp-broadband-subscriber-forecasts-q4-2023
https://www.telecoms.com/fibre/fibre-to-drive-15-broadband-growth-by-2030
U.S. broadband subscriber growth slowed in 1Q-2024 after net adds in 2023
Dell’Oro: Broadband access equipment sales to increase in 2025 led by XGS-PON deployments
Altice USA transition to fiber access; MoffettNathanson analysis of low population growth on cablecos broadband growth
Analysys Mason’s gloomy CAPEX forecast: “there will not be a cyclical recovery”
Telco capex declined worldwide in 2023, and predictions in end-of-financial year results indicate further declines this year. Analysys Mason warns that a “long decline” in capital expenditure has now started. “There will not be a cyclical recovery,” says one subhead (see below). Analysys Mason crunched a lot of numbers to arrive at this conclusion, processing historical data for about 50 of the largest operators in the world. Importantly, it also looked at the long-term guidance issued by those companies. Capex has peaked partly because telcos in many regions have completed or are near completing a once-in-a-lifetime upgrade to full-fiber networks. Clearly, that’s bad news for companies selling the actual fiber. Operators will continue to invest in the active electronics for these lines, but that represents a “tiny fraction” of the initial cost.
This new Analysys Mason gloomy CAPEX forecast comes after Dell’Oro and Omdia (owned by Informa) previously forecast another sharp fall in telco spending on mobile network products this year after the big dip of 2023.
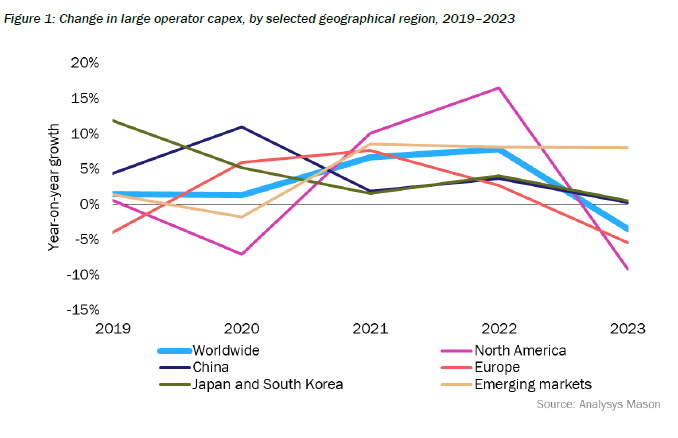
Figure 1. below aggregates change in capex, excluding spectrum, in 2023 (or FY2023/2024) for 50 of the largest operators in the world, all with annual capex of over USD1 billion in 2023. These operators account for about 78% of telecoms capex worldwide. Of the 42 operators that provided guidance on capex in 2024, 28 forecast a fall. A notable class of exceptions consisted of cable operators and latecomers to FTTP upgrade, but most of the emerging-market-focused operators indicated a decline.
The steepest decline was in North America. The decline was steeper for the three largest mobile network operator (MNO) groups (–18.1%). This was offset by rises in capex by the two large US cablecos, for which upgrades of HFC plant are now an imperative. The obvious reason for the sharp decline is the near-completion of 5G roll-out, although FTTP capex remains flat.
In China, capex was flat overall. This disguises a decline in 5G and fixed broadband capex, which, taken together with transmission, fell 7% in 2023. The delta of capex has gone on what operators call ‘computility’ (compute power in data centers and edge) and capabilities (developing the ability to serve mainly the industrial enterprise). Together these two items now account for about 35% of operator capex.
In Japan and South Korea, capex was also more or less flat (+0.5%). As in China, a high proportion of capex in Japan now goes on adjacent lines of business.
Capex declined by 5.5% in Europe. The European figure disguises the impact of the large number of smaller players in the continent. 5G spending has peaked, but so too has FTTP spending. FTTP spend represents a very high share of capex in Europe (about one half), although this is distributed differently across individual countries. Countries like France and Spain have passed that peak, but even in the UK, a relatively late starter, spend has plateaued. Among operators in emerging markets, the smallest group in absolute capex terms, there was a rise of 8%, steady now for three years running, driven almost entirely by India, and offset by declines elsewhere.
There will not be cyclical recovery of capex:
Operators’ longer-term projections of capex suggest, if anything, steepening declines in capex. Our forecasts indicate that capital intensity (capex/revenue) will fall from around 20% now to 12–14% by the end of the decade. Capex will fall basically because customers do not need more than the 1Gbit/s fibre and unlimited 5G that the current networks are easily capable of delivering, and growth in measurable demand slows every year. This will have the following effects:
•Fall in fixed access spend. Capex on FTTP is essentially a one-off investment in passive assets with very long useful lives. Future capex on upgrades (in effect replacements) of FTTP actives will come at a tiny fraction of this cost. The pipeline of plans for commercial build is running dry, although this is offset by some hefty subsidies for rural build, particularly in the USA. Those cablecos that have not already started will have to brace themselves for programs of replacement of HFC/DOCSIS by FTTP/xPON.
•We expect only limited uplift for 5G SA/5G Advanced. This is in part because some operators will not be able to justify a further upgrade after 5G NSA, in part because of slack demand, and in part because the sums involved will be lower than for the roll-out of 5G NSA.
•6G will not be capex-intensive. There is little appetite in free-market economies without centralised planning (and perhaps not so much even there) for a capex-intensive generational upgrade to 6G. There will be no cyclical uplift.
•There will be more outsourcing, i.e. replacement of capex by an opex line. This occurs mainly in infrastructure, but also in migrations of operations (IT capex) to the cloud. Yet this does not mean that capex is simply shifting from one class of business to another; infra companies exist in a world with similar constraints.
•In these circumstances there is a clear case for capex investment in anything that maximizes the efficient (and sustainable) use of the physical assets as they stand, and unlocks any opportunities that exist in new business-models. This is prominent in many operator outlooks.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
William Webb, an independent consultant and former executive at UK telecom regulator Ofcom, forecasts an S-curve flattening by 2027. In a forthcoming book called “The end of telecoms history,” Webb returns to predictions he first made in 2016 to gauge their accuracy. Using recent historical data from Barclays, he was able to show a close alignment with the S-curve he drew about eight years ago. If this behavior continues, growth rates “will fall to near zero by around 2027, with significant variations by country,” says Webb in his book, giving a sneak preview to Light Reading.
Webb’s broad rationale is that there is an upper limit on daily gigabyte consumption, just as there is only so much the average person can eat or drink. All Webb had to do was assume there will be some future gorging by customers on high-quality video, the most calorific meal for any smartphone. “Once they are watching video for all their free moments while downloading updates and attachments there is little more that they could usefully download,” he writes.
What of future services people do not currently enjoy? Outside virtual reality – which, for safety reasons, will probably always happen in a fixed-line environment – no app seems likely to chew through gigabytes as hungrily as moving images do in high definition. Webb clearly doubts the sort of artificial intelligence (AI) services being advertised by Apple will have much impact whatsoever.
“There may be substantially more traffic between data centers as models are trained but this will flow across high-capacity fiber connections which can be expanded easily if needed,” he told Light Reading by email. “At present AI interactions are generally in the form of text, which amounts to miniscule amounts of traffic.”
“Indeed, if time is diverted from consuming video to AI interactions, then AI may reduce the amount of network traffic,” he continued. Even if AI is used in future to create images and videos, rather than words, it will probably make no difference given the amount of video already consumed, merely substituting for more traditional forms of content, said Webb.
For those confident that data traffic growth stimulates investment, the other problem is the lack of any correlation between volumes and costs. Advanced networks are designed to cope with usage up to a certain high threshold before an upgrade is needed. Headline expenses have not risen in lockstep with gigabytes.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/ericsson-and-nokia-may-be-stuck-with-skinflint-customers-for-years
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
U.S. Network Operators and Equipment Companies Agree: 5G CAPEX slowing more than expected
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network & Cable CPE shipments all declined in 1Q-2024
Dell’Oro: 2023 global telecom equipment revenues declined 5% YoY; Huawei increases its #1 position
Where Have You Gone 5G? Midband spectrum, FWA, 2024 decline in CAPEX and RAN revenue
“The “5G Train Wreck” we predicted five years ago has come to pass. With the possible exception of China and South Korea, 5G has been an unmitigated failure- for carriers, network equipment companies, and subscribers/customers. And there haven’t been any significant performance advantages over 4G.”