Graphiant: MPLS and SD-WAN Fail to Meet the Needs of the Modern Enterprise
Network-as-a-service startup Graphiant has released a report suggesting MPLS and SD-WAN are insufficient for meeting enterprise networking needs, and that businesses are starting to gravitate towards NaaS products.
In a survey of 200 network architects and admins across North America, Graphiant highlighted three use cases MPLS and SD-WAN are “failing” to meet. According to respondents, the most difficult task is connecting with external entities, such as customers or other companies. Other challenges include connecting to enterprise resources, which has grown more complex due to the rise of remote work, as well as connectivity with public clouds.
“This happens every 10-11 years,” says Khalid Raza, founder & CEO of Graphiant. “I saw this in 2000 while pioneering MPLS at Cisco. I saw it when I co-founded Viptela in 2012. And now It’s time again for a new approach to the network edge.”
Respondents called out three critical uses cases:
- Enterprise connectivity has changed in recent years, with a surge in remote workers, remote offices, and IoT.
- Cloud connectivity is the second use case that stretches enterprise capabilities.
- And trends such as digital transformation and the service economy are pushing enterprises to connect more often with customers and partners.
“These new use cases are tough for MPLS and SD-WAN,” says Robert Spangler, Senior Network Engineer at Ballad Health. “MPLS is too slow to deploy and change and far too expensive. And SD-WAN can’t handle that number of tunnels.”
The survey shows enterprises aren’t happy with MPLS and SD-WAN for these new use cases. Network architects gave both technologies D’s and F’s for metrics such as scalability, agility, and cost.
Graphiant Founder and CEO Khalid Raza told Fierce Telecom while MPLS has the advantage of being private and doesn’t place a heavy operational burden on the enterprise, it’s expensive, slow to provision and its scalability is tied to the service provider.
“If the Provider Edge needs to be upgraded to provide the bandwidth, routing table or site increase…it will take a while to get done,” he said. Regarding SD-WAN, Raza noted it gives enterprises last mile flexibility and the ability to add commodity bandwidth. However, SD-WAN’s need for an overlay (a virtual network created on top of a physical network) for every underlay “create[s] a huge tunnel scale problem,” which leads to challenges with hardware and software licenses and increases the operational burden for enterprises.
“SD-WAN leverages public transport so connecting to the resources the enterprise needs should be simple, but it’s not,” said Raza. “The security, privacy and compliance concerns that public networks create a huge operational burden that enterprises aren’t prepared to handle.”
Mauricio Sanchez, Dell’Oro Group’s research director of network security, SASE and SD-WAN, said larger enterprises with more sophisticated networking needs and architectures usually run into problems with MPLS and SD-WAN. For MPLS, he brought up the cost component and how “few enterprises are happy with how long it takes carriers to provision or change.”
“With regards to SD-WAN, it’s done wonders in the last mile where access routers used to rule,” Sanchez told Fierce. “However, SD-WAN hasn’t penetrated the middle-mile as much where meshed-SD-WAN stands to replace classic BGP-based [Border Gateway Protocol] networking.”
He explained meshed SD-WAN is more common in the enterprise WAN core than on the WAN edge, meaning smaller branch offices likely have their SD-WAN CPE router connect with a single-head end. Sanchez also noted it’s not easy for enterprises to set up large meshed SD-WAN deployments, “usually because the equipment starts running out of steam.” VPN capacity is one example of an issue.
“So I wouldn’t paper everything in SD-WAN and MPLS as having ‘failed,’ but more so highlight that there are areas where definite improvement opportunity exists,” he concluded.
Author’s Note: I have been blown away by SD-WANs success as there are no standards and therefore no interoperability. Especially needed is a NNI standard that would interconnect different vendor specific SD-WANs to facilitate communications between two or more enterprise networks.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Graphiant’s report indicated more enterprises are thinking about implementing network-as-a-service solutions, with 62% of respondents saying they are “somewhat likely” to move to NaaS.
Launched last September, Graphiant has pitched a combination of MPLS-like performance in speed, scale and security with as-a-service agility. Raza told Fierce enterprises can connect to Graphiant’s core from any location – the data center, branch office, at home or the edge – and build their networks “in minutes instead of months.”
Separately, Graphiant in March closed a $62 million funding round led by Two Bear Capital, Sequoia Capital as well as other VC and private equity firms. The latest round brings Graphiant’s total funding to $96 million.
References:
https://www.fiercetelecom.com/telecom/graphiant-says-sd-wan-mpls-fail-meet-enterprise-needs
South Korea has 30 million 5G users, but did not meet expectations; KT and SKT AI initiatives
South Korea is arguably one of the leading countries that has deployed 5G. According to the Ministry of Science and ICT, the country had 29.6 million users as of this March, and given that number of subscribers has increased to around 500,000 per month up to now, it is more than likely that as of early May, there are 30 million 5G users. This milestone comes four years after 5G became available in smartphones in the country in April 2019 (based on 3GPP Release 15 specs).
South Korea started 2G code division multiple access (CDMA) services in 1996 and 3G wide CDMA in 2003, starting the cell phone era. This allowed South Korean telecommunication companies to expand abroad. The launch of WCDMA also allowed Qualcomm and Samsung to become leaders in application processors and smartphones, respectively, today. Then in 2011 came 4G long-term evolution (LTE) services. This truly enabled smartphones which could now stream videos in real time. South Korean wireless network operators SK Telecom, KT and LG Uplus became board members of GSMA, the global telecommunications suppliers organization.
Expectations were high for 5G. The government and telcos claimed in marketing before launch that 5G will be, compared to 4G, 20 times faster, 100 times better simultaneous access and 10 times shorter delays. They claimed new augmented reality, virtual reality, 3D content and IoT services would be introduced. However, the reality after 5G launched was quite different and none of the promises were kept.
According to the Ministry of Science and ICT, 5G download speed on average was 896.10Mbps as of October. Upload speed was on average 93.16Mbps. This was only faster by 5.9 times and 2.8 times faster, respectively than 4G LTE in the same month.
Image Credit: TheElec (http://thelec.net)
5G coverage was also only around 33.1% of the country, which means on a national level, most people were using non-standalone 5G services (5G NR with LTE infrastructure and EPC).
Spending to obtain 28 GHz mmWave spectrum has effectively ended. KT and LG Uplus had their spectrum cancelled in December; SK Telecom is also expected to lose theirs within the year (SEE UPDATE BELOW)! Without spending on 28GHz, there will be no “20 times faster 5G.” The country’s Fair Trade Commission is expected to penalize the three South Korean telcos for violating advertisement laws.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
On the positive side, 5G is being combined with AI. KT announced the commercial launch of a new solution, which it calls its “5G Infrastructure Intelligent Control Solution”, that is based on artificial intelligence (AI) technology. The South Korean network operator noted that this solution is designed to control 5G infrastructure with the aim of making that infrastructure more efficient and stable.
KT’s new solution is equipped with AI technology to detect abnormalities in the status of networks and equipment in real-time. By comparing dozens of equipment quality data in real-time with pre-learned data, the new solution can determine whether the equipment is abnormal or not with a single indicator, KT said. Also, the solution also displays the status of access and core equipment in five stages, making it easy to “intuitively check the equipment and the degree of abnormality” that occurred, the Korean telco added.
The company highlighted that companies and institutions without expertise in network management can use KT’s 5G solution to operate 5G networks without any “burden.” KT said it has already implemented the solution in four institutions, including Bundang Seoul National University Hospital, Samsung Seoul Hospital, Korea Aerospace Industries Co., Ltd. and Navy Headquarters.
“When KT’s 5G specialized network testbed is established, it will be possible to perform a one-stop service for testing equipment for 5G specialized network, interworking with terminals, and conducting network trial operation and inspection. It is expected to greatly reduce the cost and technical burden of companies considering the introduction of a 5G specialized network,” KT said.
“SK Telecom (SKT) is stepping up efforts on all fronts to transform itself into an AI company,” CFO Kim Jin Won told a results briefing Wednesday. Its strategy is to grow through partnerships with local and global top-tier AI companies while also continuing to develop its own AI technology.
SKT has been trialing generative AI in its A. (pronounced “A-dot”) service, built on its own technology and capable of holding complex conversations and developing long-term memories. Last month the telco invested 15 billion Korean won (US$11.4 million) in local startup Scatter Lab, which has used deep learning to create a chatbot that can hold empathetic conversations. SKT wants to work with Scatter Lab to develop an AI agent that can have human-like conversations with A. customers. The two companies also aim to develop a hyperscale language model equipped with emotions and knowledge domains.
May 15 2023 Update:
On Friday, May 12th South Korea’s Ministry of Science and ICT cancelled SKT’s 28 GHz 5G license. The Korean network operator’s major rivals KT Corp and LG U+ had their 28 GHz licences cancelled last year for the same reason, but SKT held on to its concession by the skin of its teeth and escaped with a warning.
“It is regrettable that this result has finally come about despite the government’s active efforts so far,” said Choi Woo-hyuk, director of radio wave policy at the Ministry of Science and ICT, in a Korean language statement confirming the licence withdrawal.
The three South Korean mobile operators each acquired 800 MHz of 28 GHz spectrum, alongside 3.5 GHz frequencies, in 2018, with the band being available for use by the end of that year. The licence conditions required them to deploy 15,000 base stations using 28 GHz within three years. But an investigation on the part of the last year Ministry showed that the telcos had built only 10% of the number of sites they had committed to, which led to it pulling the licences of the worst offenders: KT and LG U+.
https://telecoms.com/521670/south-korea-cancels-skts-28-ghz-5g-licence/
References:
https://www.thelec.net/news/articleView.html?idxno=4524
https://irsvc.teletogether.com/skt/pdf/skt2023Q1_Subtitles_eng.pdf?2
Omdia: ARPU declining or flat for South Korean 5G network operators
3 South Korean mobile operators to share 5G networks in remote areas
Infinera trial for Telstra InfraCo’s intercity fiber project delivered 61.3 Tbps between Melbourne and Sydney, Australia
Infinera has completed a simulated intercity network trial for Telstra InfraCo’s intercity fiber project in Australia. The trial delivered 61.3 Tbps of unregenerated data transmission capacity on a fiber pair over the equivalent of 1,240 route km between Melbourne and Sydney, Australia. The network trial was implemented using Infinera’s 800G-capable ICE6 coherent solution [1.] and Corning Incorporated’s SMF-28® ULL fiber with advanced bend, demonstrating the high-performance capability of the express network, which is part of the intercity fiber network Telstra InfraCo is building across Australia.
Note 1. The sixth-generation Infinite Capacity Engine (ICE6), from Infinera’s Advanced Coherent Optical Engines and Subsystems, is a 1.6 Tb/s optical engine that delivers two independently programmable wavelengths at up to 800 Gb/s each. Utilizing a 7-nm CMOS process node DSP and advanced PIC technology, ICE6 leverages ultra-high baud rates, high modem SNR, and innovative features to break performance and spectral efficiency barriers, including 800G single-wavelength performance over 1000+ km in a commercial network. ICE6 is also beating optical transmission expectations at lower rates, including 600 Gb/s and 400 Gb/s per wavelength.

Image Credit: Infinera
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The trial was performed with real-world configurations, including 1,240 kilometers of ultra-low-loss fiber simulating one of Telstra InfraCo’s planned express Melbourne-Sydney routes. Infinera performed an in-service, non-traffic-impacting upgrade from C-band to combined C-band plus L-band as part of the capacity expansion process. With Infinera’s ICE6 and Corning’s optical fiber, Telstra InfraCo achieved 61.3 Tbps total capacity with 6.2 milliseconds latency across the combined C-band and L-band, with wavelengths up to 700 Gbps.
Telstra InfraCo’s express network is designed to be a high-performance national network for customers who need reliable, ultra-high bandwidth between capital cities and international submarine cable landing stations. For hyperscalers, global cloud providers, content companies, and governments, this means access to scalable high capacity and more direct routes, with optional route redundancy.
“Based on these results, Telstra InfraCo’s express network and overall intercity fiber build will lead the world in scale, low latency, and high data transmission performance rate,” said Kathryn Jones, Fiber Executive at Telstra InfraCo. “The simulation exceeds our expectations, offering almost seven times today’s typical capacity of 8.8 Tbps per fibre pair and validates our selection of Corning’s SMF-28 ULL fiber in the cable design. This will enable Telstra to develop market-leading solutions for our customers today and for years to come – a key element of Telstra’s ambitious T25 strategy and transformation goals.”
“To meet the rigorous demands of a vast network over Australia’s unique terrain, Telstra InfraCo needed fiber infrastructure with advanced bend capability and minimal signal loss to deliver ultra-high cable capacity. That’s why they turned to Corning,” said Sharon Bois, Division Vice President, Product Line and Marketing, Corning Optical Fiber and Cable. “Our SMF-28® ULL fiber with advanced bend is designed to meet exactly those needs.”
“Infinera’s 800G-capable ICE6 solution demonstrated industry-leading performance, maximizing fiber capacity and reach on Telstra InfraCo’s express network configuration,” said Nick Walden, Senior Vice President of Worldwide Sales at Infinera. “This achievement underscores the enhanced performance Infinera’s technology can bring to meet Telstra InfraCo’s express network requirements for bandwidth today and into the future.”
Media Contact:
Anna Vue
Tel. +1 (916) 595-8157
[email protected]
Referencs:
Fiber Build-Out Boom Update: GTT & Ziply Fiber, Infinera in Louisiana, Bluebird Network in Illinois
AWS expanding in Southeast Asia, especially Malaysia and Philippines
The adoption of cloud computing is accelerating across different customer segments in Southeast Asia, a top Malaysia-based regional executive for Amazon Web Services told Nikkei Asia, as the company competes for business with other global providers descending on the region.
AWS is investing big in the race to develop cloud data centers in Southeast Asia. It announced in March a 25.5 billion ringgit ($6 billion) investment in Malaysia after pouring money into Singapore, Indonesia and Thailand. AWS’ investment in Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries now stands at $22.5 billion.

Other big names that offer cloud data services have joined the fray, including Microsoft, Alibaba, Tencent, IBM, Oracle, and Google. Microsoft announced a five-year $1 billion investment in 2021 in Malaysia, while Google will be setting up a cloud region — the location where the public cloud data is stored — in the country, one of its 33 such systems worldwide. Malaysia topped real estate consultancy Knight Frank’s inaugural SEA-5 Data Centre Opportunity Index published last month as the most attractive destination for data center investment among five Southeast Asian countries, beating out Indonesia, Vietnam, the Philippines and Thailand.
Peter Murray, head of Malaysia and ASEAN Emerging Markets for AWS, described a noticeable pickup in the embrace of cloud technology, including by startups and enterprises in various industries as well as sectors such as financial services, natural resources and energy. “We are seeing significant growth across media and telecommunications as well and we believe that will continue to play a key role in helping Malaysia, ASEAN as well as global organizations who may have operations and be based in Malaysia to increase their productivity,” Murray said in a recent interview. AWS’ strategy amid the intensifying competition is “to build what our customers are telling us is the most important thing to them,” he said. “And 90% of what Amazon builds is driven by what customers are telling us matters the most to them.”
Murray cited two banks in Malaysia AWS has worked with, Bank Islam and Al-Rajhi Bank, that are utilizing its cloud in launching digital banking services. Bank Islam’s Be U digital bank, meanwhile, was developed with AWS’ support to create new digital financial services like mobile applications, loan facilities and services that adhere to Islamic financial regulations.
Carsome, Southeast Asia’s largest integrated car e-commerce platform, is running their services on AWS’ serverless technologies and using its machine learning technology to digitalize and improve customer experience. Carsome, Malaysia’s first unicorn, or startup valued at $1 billion or more, utilized workflow system Amazon SageMaker to streamline customer services by developing machine learning systems that incorporated 175 car inspection points.
AWS is also helping Malaysia’s state-owned oil conglomerate Petronas commercialize its cloud-based logistics services to improve efficiency via the Stear platform, which was launched in November last year and jointly developed with Petronas, professional services company Accenture and AWS. Murray said Stear supports offshore exploration, production and development and is enabling improved fuel management, intelligent routing and better vessel scheduling with near real time voyage traffic tracking.
Murray said Petronas aims to use Stear to reduce carbon emissions associated with logistics operations. “That’s a really exciting future statement and intent that we will have with many customers, the way that they are able to build and run innovative new technology workloads, which are actually able to show a dividend in terms of the reduction in carbon consumption and the increase in energy efficiency as well,” he added.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“We see continued [cloud technology] adoption [and] we see continued growth and skills within the Philippines,” Eric Conrad, company regional managing director for Southeast Asia, told a press conference on the sidelines of the AWS ASEAN Summit in Singapore on Thursday.
AWS announced late last year its plan to launch a local zone in the Philippines, which is part of a bigger undertaking to establish 10 new local zones in the region. The local zones are meant to help AWS customers reduce latency of critical workloads and drive productivity, among others. In the Philippines, AWS provides cloud services to companies like BDO Unibank, Globe, GCash and UnionBank.
The upcoming local zone in the country is a “reflection” of AWS’s optimism in the Philippines, Conrad said. The facility will complement AWS’s existing infrastructure in the Philippines, which include Amazon CloudFront and AWS Outposts.
“In the Philippines, we see continued acceleration in terms of the digitalization and the use of technology to drive sustainability, and good environmental practices,” he added.
“We’re really excited with the momentum that we’re seeing,” Conor McNamara, company managing director for Southeast Asia, said in his keynote address.
In Singapore, AWS has spent over $6.5 billion on infrastructure and jobs in the island state. One of AWS’s clients is Singapore-based superapp Grab, which has powered its mapping system with the help of AWS’s cloud technology.
“We estimate better ETAs, and all of it are powered by data,” Philipp Kandal, chief product officer at Grab, said during the opening session of the AWS Summit.
Meanwhile, AWS has also promised billions of dollars in investments in Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand. Since 2017, the Amazon unit has trained over 1 million people across the region on cloud skills.
“We offer the most complete set of relational and purpose-built databases,” Laura Grit, VP/distinguished engineer at AWS, said during the summit. “Our goal is for you to focus on innovation that matters for your business,” she added.
References:
https://aws.amazon.com/government-education/worldwide/asean/
IDC Telecom Services Tracker: Worldwide spending on Telecom and Pay TV services will increase by 2.0% in 2023
Worldwide spending on Telecom Services and Pay TV Services reached $1,478 billion in 2022, increasing by 2.2% year over year, according to the International Data Corporation (IDC) Worldwide Semiannual Telecom Services Tracker. IDC expects Worldwide spending on Telecom and Pay TV services will increase by 2.0% next year and reach a total of $1,541 billion. The latest forecast is slightly more optimistic compared to the version published in November last year as it assumes a 0.3 percentage point higher growth in 2023. IDC believes this acceleration is a consequence of the increase in tariffs of telecommunication services fueled by inflation.
This is the second time in the last six months that we have increased our forecast for the telecom services market and positive adjustments have been made for all global regions. This confirms the thesis that inflation is equally happening in all parts of the world and that operators are all behaving in similar way when their profitability is threatened by the inflationary pressures. And what is more, the effects that we observe now are the outcome of the initial tariff adjustments that were generally happening in mid-2022. According to the latest IMF forecasts, inflation is here to stay for the next three years at least which means that operators will continue to increase tariffs, clients will be paying more for telco services, and the total nominal value of the market will be growing at faster pace. This is the explanation for why we increased our forecast not only for 2023, but for the entire first half of the forecast period.
| Global Regional Services Revenue and Year-on-Year Growth (revenues in $B) | |||
| Global Region | 2021 Revenue | 2022 Revenue | 22/21
Growth |
| Americas | $572 | $580 | 1.4% |
| Asia/Pacific | $467 | $481 | 3.0% |
| EMEA | $438 | $449 | 2.4% |
| Grand Total | $1,478 | $1,510 | 2.2% |
| Source: IDC Worldwide Semiannual Services Tracker – 2H 2022 | |||
Our forecast for Asia-Pacific was boosted by 0.7 percentage points, for Americas by 0.3 percentage points, and for EMEA by 0.1 percentage points. At the first sight, the magnitude of change in EMEA, region that is witnessing a higher-than-average inflation while struggling to find a replacement for the cheap Russian energy, might seem relatively low. It can be explained by 1) the war in Ukraine and the related economic sanctions imposed to Russia, the biggest market of the CEE subregion, and 2) significant slowdown of the major WE economies driven by the drastic growth of the central banks’ interest rates. The fact that during the previous update the EMEA region witnessed the highest upward revision should also be taken into consideration. Nonetheless, the fastest growth this year, as well as in the entire forecast period, is expected in the Asia/Pacific region, fueled by the relatively lower saturation of the markets in less-developed countries.
High inflation is not good news for any market, because the positive boost it produces is only nominal. A closer look at the forecasted growth rates reveals that they are much lower than the annual inflation rates published by monetary statisticians, which means that the market is witnessing a decline in value in real terms. For that reason, the telecom operators continue to heavily invest into advanced telco technologies. They hope that the migration to all-IP and new-generation access (NGA) broadband will help offset the fixed and mobile voice decline. They also believe that 5G will unlock new opportunities by allowing massive machine-type communications and ultra-reliable low-latency communications.
The companies are also increasing the pace of digitalization and software-ization of their business processes, create new go-to-market strategies based on data and intelligence, and deploy innovative business models based on telco-as-a-platform and co-creation within ecosystems. They also look for additional revenue streams in the non-telco areas such as IoT, data center, cloud, AR/VR, IT services, VoD, enterprise vertical solutions, financial solutions, cyber security, digital media, e-commerce, etc.
“Telecom operators are completely transforming – from providers of traditional commodity-style services they are becoming modern all-round full-stack technology suppliers,” says Kresimir Alic, Research Director, Worldwide Telecom Services. “In that way they become leaders of the digital transformation revolution and rightly hope they can acquire one of the central positions in the new digitalized world.”
About IDC Trackers:
IDC Tracker products provide accurate and timely market size, vendor share, and forecasts for hundreds of technology markets from more than 100 countries around the globe. Using proprietary tools and research processes, IDC’s Trackers are updated on a semiannual, quarterly, and monthly basis. Tracker results are delivered to clients in user-friendly excel deliverables and on-line query tools.
For more information about IDC’s Worldwide Semiannual Telecom Services Tracker, please contact Kathy Nagamine at 650-350-6423 or [email protected].
References:
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS50644723
Gartner: Robust growth for telecom equipment spending, tepid growth for telco services, PC sales flat
Dell’Oro: XGS, 25G, and Early 50G PON Rollouts to Fuel Broadband Spending
Synergy Research: Growth in Hyperscale and Enterprise IT Infrastructure Spending; Telcos Remain in the Doldrums
AT&T to provide free WiFi and private 5G at DFW airport; will invest $10 million worth of network upgrades
Dallas Fort Worth International Airport (DFW) entered into a partnership with AT&T, to provide the airport with a comprehensive wireless platform (CWP) that will enhance connectivity and critical infrastructure. As part of the proposed agreement, AT&T will invest $10 million worth of network upgrades in modernizing and expanding the network covering the DFW airport, to support airport operations and advance the free public Wi-Fi in the Airport’s terminals. This includes installing 200 new access points — and updating the 800 access points DFW already provides — to enable better coverage and faster speeds for customers. AT&T will also deploy a private 5G network for the Airport’s internal use to meet the rising demand for Internet of Things (IoT) uses cases and the digitization of airport operations.
“We know that being connected to the internet is an absolute must-have service for our customers. This proposed agreement signifies our commitment to ensure our customers will always remain connected at DFW Airport, so they can reliably stay online for work or entertainment while traveling,” said Mike Youngs, Vice President of Information Technology Services at DFW Airport.
The CWP will provide enhanced connectivity throughout the airport, including indoor and outdoor spaces, parking lots and runways. This faster connectivity means that travelers will have even faster access to airport services through the DFW Airport or airline app such as automated check-in, baggage tracking and lounge access.
The private cellular 5G network will offer more reliability and security, lower latency and greater capacity, providing operations teams with optimal connectivity that can be used for future use cases such as real-time data analytics and enhanced communication with critical airport systems. With these use cases, the airport’s management team will be better able to monitor and manage passenger traffic, security systems and baggage handling – improving efficiency and safety.

Image Credit: AT&T
“Modernizing airport technology needs to focus on both improving the efficiency and convenience for airlines and airport operations and the overall travel experience for passengers, while ensuring the safety and security of all those who pass through its gates,” said Jason Inskeep, Assistant Vice President, 5G Center of Excellence at AT&T. “We’re proud to work alongside DFW Airport and look forward to continuing our collaboration to bring the best connectivity solutions for all.”
DFW and AT&T will begin upgrading the network this summer, with the enhancements coming online by the fall. The project is contingent upon a final contract between AT&T and the DFW. Dallas Fort Worth International Airport is one of the most connected airports in the world and serves as a major job generator for the North Texas region by connecting people through business and leisure travel. With 168 gates in five terminals and an area spanning 18,000 acres, DFW Airport is the third-largest airport in the world by size.
In February 2021, AT&T and Boingo Wireless said in a press release that they were “working to deploy” AT&T 5G+ in 12 airports nationwide, including John F. Kennedy International Airport and LaGuardia Airport in New York City and Chicago O’Hare International Airport and Midway International Airport. Dallas Love Field Airport in also was among the airports announced.
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2021/5g_plus_boingo.html
AT&T touts 5G advances; will deploy Standalone 5G when “the ecosystem is ready”- when will that be?
AT&T realizes huge value from AI; will use full suite of NVIDIA AI offerings
AT&T Highlights: 5G mid-band spectrum, AT&T Fiber, Gigapower joint venture with BlackRock/disaggregation traffic milestone
AT&T and BlackRock’s Gigapower fiber JV may alter the U.S. broadband landscape
MoffettNathanson: Fiber Bubble May Pop; AT&T is by far the largest (fiber) overbuilder in U.S.
A Tale of two Telcos: AT&T up (fiber & mid-band 5G); VZ down (net income falls; cost-cutting coming)
Frontier Communications fiber build-out boom continues: record number of fiber subscribers added in the 1st quarter of 2023
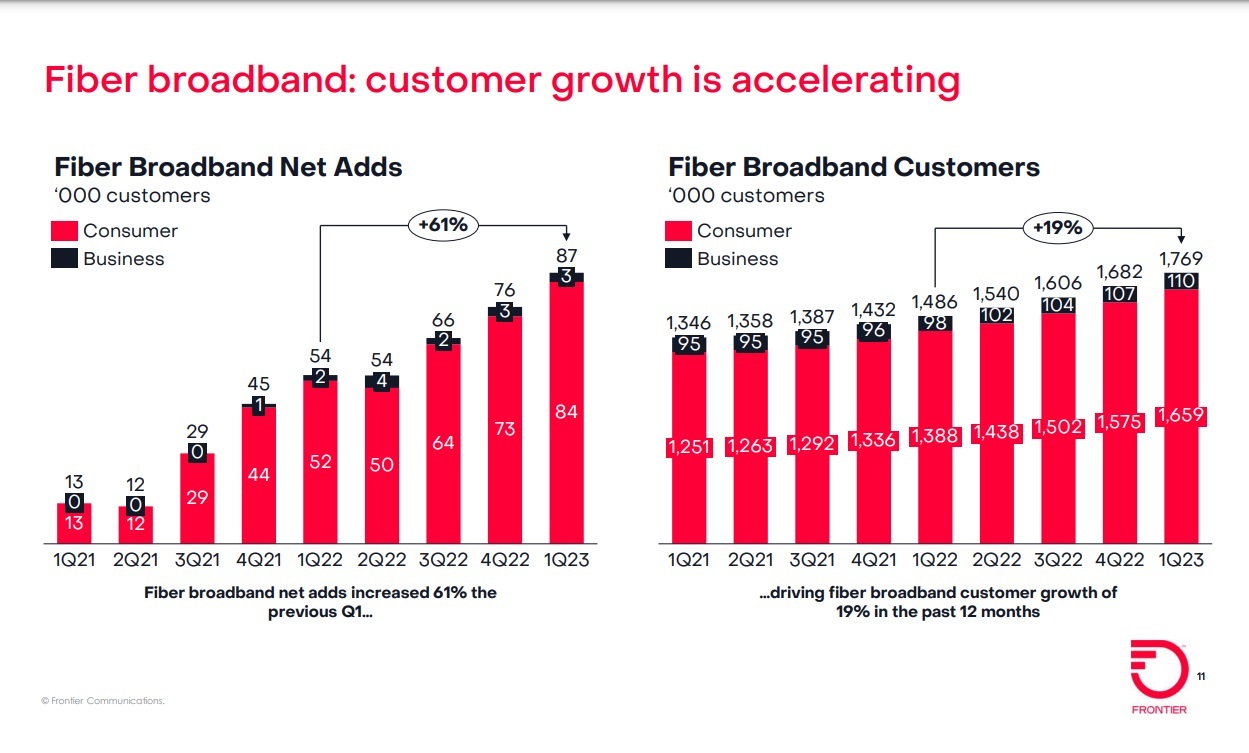
Frontier Communications added record number of fiber broadband customers in the 1st quarter of 2023. The fiber facility based network operator added 87,000 fiber subscribers (including 83,000 residential subs) in the first quarter of 2023, up from +54,000 in the year-ago quarter. Those results beat the 76,000 residential fiber subs Frontier was expected to add in the period. Frontier ended the quarter with 1.76 million fiber customers: 1.65 million residential subscribers and 110,000 business customers.
“We delivered another strong quarter and reached a critical milestone in our transformation. Thanks to our team’s consistent operational performance, we achieved EBITDA growth for the first time in five years,” said Nick Jeffery, President and Chief Executive Officer of Frontier.
“We are creating an internet company that people love. Over the last two years, we have rallied around our purpose of Building Gigabit America, invested in fiber, enhanced our product, put the customer at the center of everything we do and made it easier to do business with us. We are quickly becoming an agile, digital infrastructure company, and I’m confident we will return to growth this year.”
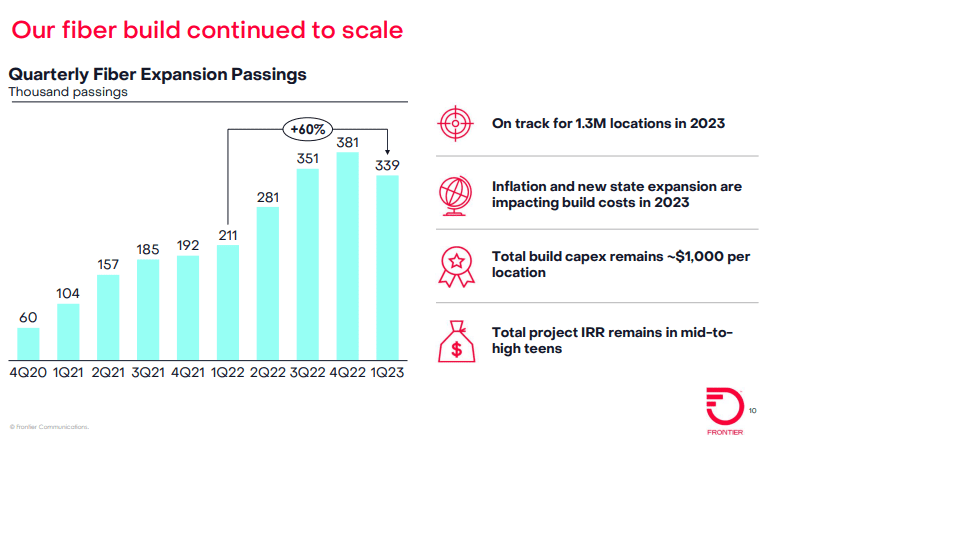
Frontier said it built fiber to an additional 339,000 locations in Q1 2023, up 60% from the 211,000 it built in the year-ago period. Frontier’s Q1 buildout was better than the 300,000 locations expected by the analysts at New Street Research. Frontier ended the quarter with 5.5 million fiber passings and 15.4 million total passings.
First-Quarter 2023 Consolidated Financial Results:
• Revenue of $1.44 billion decreased 0.5% from the first quarter of 2022 as growth in consumer, business and wholesale fiber was more than offset by declines in legacy copper
• Operating income was $143 million and net income was $3 million
• Adjusted EBITDA of $519 million increased 2.0% over the first quarter of 2022 as revenue declines were more than offset by lower content, selling, general and administrative expenses, and cost-saving initiatives
• Adjusted EBITDA margin of 36.0% increased from 35.2% in the first quarter of 2022
• Capital expenditures of $1.15 billion increased from $0.45 billion in the first quarter of 2022 as fiber expansion initiatives accelerated First-Quarter 2023
Consumer Results:
• Consumer revenue of $761 million decreased 1.9% from the first quarter of 2022 as strong growth in fiber broadband was more than offset by declines in legacy copper broadband and voice
• Consumer fiber revenue of $448 million increased 10.1% over the first quarter of 2022 as growth in consumer broadband, voice, and other more than offset declines in video
• Consumer fiber broadband revenue of $298 million increased 17.3% over the first quarter of 2022 driven by growth in fiber broadband customers
• Consumer fiber broadband customer net additions of 84,000 resulted in consumer fiber broadband customer growth of 19.5% from the first quarter of 2022
• Consumer fiber broadband customer churn of 1.20% was roughly flat with churn of 1.19% in the first quarter of 2022
• Consumer fiber broadband ARPU of $61.44 decreased 1.1% from the first quarter of 2022 driven primarily by the autopay and gift-card incentives introduced in the third quarter of 2021 First-Quarter 2023
Business and Wholesale Results:
• Business and wholesale revenue of $657 million decreased 1.4% from the first quarter of 2022 as growth in fiber was more than offset by declines in copper
• Business and wholesale fiber revenue of $281 million increased 6.0% over the first quarter of 2022 as growth in business was partly offset by modest declines in wholesale
• Business fiber broadband customer churn of 1.45% increased from 1.24% in the first quarter of 2022
• Business fiber broadband ARPU of $104.38 decreased 1.2% from the first quarter of 2022
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
While Frontier’s fiber growth engine continues to hum along, the company is dealing with higher costs related to its fiber initiative. The company raised its 2023 capex guidance to a range of $3 billion to $3.2 billion, up from an original outlook of $2.8 billion.
Frontier blamed the increase on a couple of factors – a decision to build inventory opportunistically where it saw supply chains ease a bit in the quarter and higher build costs as it scales its build into new geographies. Frontier is also seeing higher labor costs being driven by general inflation and higher rates as some of its multi-year labor contracts come up for renewal.
The anticipated increase in capex this year concerned investors. Frontier shares were down $2.33 (-10.94%) to $19.13 each in Friday morning trading.
Overall, Frontier expects fiber build costs in 2023 to be in the range of $1,000 to $1,100. But it’s confident that total project build costs will remain at about $1,000 per location as it mixes in lower-cost locations in some new-build states and benefits from aerial builds and an increased focus on multiple dwelling units (MDUs), Frontier CFO Scott Beasley said on Friday’s earnings call.
The current capex picture isn’t expected to impact Frontier’s overall fiber buildout/upgrade plan. “We’re confident that the 10 million locations is still attractive to build out,” Beasley said. Frontier is also continuing to explore an additional 1 million to 2 million additional fiber passings beyond the original 10 million target.
Frontier says it’s too early to tell how this year’s cost headwinds might impact future opportunities coming by way of the $42.5 billion Broadband Equity, Access and Deployment (BEAD) program. New Street Research estimates that there are 1.2 million BEAD-eligible locations in Frontier’s footprint. New Street Research expects ARPU pressure at Frontier to ease in the second quarter of the year and return to growth in the third quarter.
Frontier recently initiated several consumer pricing changes for value-added services that were previously free. Whole-home Wi-Fi, for example, now costs $10 per month, its Home Shield Elite product is now $6 per month extra and the company is now charging $50 for professional installs. Those actions are driving new fiber customer monthly ARPU to a range of $65 to $70, the company said.
Frontier is also speeding up its original cost savings target to $500 million by the end of 2024. Its prior target was $400 million by the end of 2024. Frontier is approaching that target through a range of streamlining and simplification initiatives, including improved field operations, self-service capabilities, the consolidation of call centers and an ongoing reduction in copper infrastructure.
Frontier’s guidance for the full year 2023:
• Adjusted EBITDA of $2.11 – $2.16 billion, unchanged from prior guidance
• Fiber build of 1.3 million new locations, unchanged from prior guidance
• Cash capital expenditures of $3.00 – $3.20 billion, an increase from prior guidance of $2.80 billion, reflecting higher inventory levels and fiber build costs
• Cash taxes of approximately $20 million, unchanged from prior guidance
• Net cash interest payments of approximately $655 million, an increase from prior guidance of $630 million, reflecting the $750 million of debt raised in March 2023
• Pension and OPEB expense of approximately $50 million (net of capitalization), unchanged from prior guidance
• Cash pension and OPEB contributions of approximately $125 million, unchanged from prior guidance
References:
Fiber builds propels Frontier Communication’s record 4th Quarter; unveils Fiber Innovation Labs
AT&T to use Frontier’s fiber infrastructure for 4G/5G backhaul in 25 states
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Frontier Communications adds record fiber broadband customers in Q4 2022
Frontier’s Big Fiber Build-Out Continued in Q3-2022 with 351,000 fiber optic premises added
Frontier Communications sets another fiber buildout record; raises FTTP buildout target for 2022
“Fiber is the future” at Frontier, which added a record 54K fiber broadband customers in 1Q-2022
Frontier’s FTTP to reach 10M locations by 2025; +192,000 FTTP passings in 4Q-2021
Frontier Communications reports added 45,000 fiber broadband subscribers in 4Q-2021 – best in 5 years!
OneWeb and NOW Corp sign MoU to boost connectivity for critical infrastructure in the Philippines
OneWeb, the low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite communications company, and NOW Corporation, a publicly listed firm in the Philippine Stock Exchange with investments in telecom, media, and technology, announce they have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to bring high-speed, low-latency broadband connectivity to the Philippines. As an archipelago of more than 7,500 islands, the Philippines lends itself well to satellite connectivity. Partnering with OneWeb will augment Now’s terrestrial coverage, and give it the ability to offer connectivity services to the aviation and maritime industries, and provide backup connectivity for mission critical communications.
Now Corp’s Now Telecom unit already offers cellular fixed-wireless access (FWA) services to enterprises and SMEs across the Philippines under the Fiber Air brand. It is also in the middle of building out a 5G standalone (SA) network in partnership with Nokia and Cisco – and with a little help in the form of a grant from the US Trade and Development Agency (USTDA) – in a bid to take on Smart, Globe and Dito in the Philippines retail mobile market.
The partnership combines the innovative satellite technology of OneWeb with NOW Corp’s existing broadband service and strong local presence especially in the enterprise market. OneWeb’s LEO satellites will provide seamless connectivity, enabling NOW to offer a wide range of enhanced broadband services to sectors including government, aviation, maritime, military, energy, healthcare and banking. With an eye toward serving such critical infrastructure, NOW will work closely with OneWeb in order to deliver stable, high-speed, low latency broadband connectivity with committed information rates (CIR).
Under this MoU, OneWeb will bring to enterprise, government, and other customers in the Philippines the connectivity solutions it offers in a swiftly growing number of markets. With its constellation of LEO satellites now fully built out, OneWeb is set to complete its rollout of global coverage this year. By tapping into the power of this global network, NOW will be able to extend services into hard-to-reach areas and enhance the speed, latency, and resiliency of its existing offerings.

Source: OneWeb
Neil Masterson, CEO of OneWeb, commented: “This is an exciting partnership that is set to bring transformational connectivity to people, businesses, and government bodies throughout the Philippines. We are thrilled to count NOW as a partner and ally in our push to bring true global connectivity. NOW has done tremendous work toward getting the people of the Philippines online, and we’re honored to have the opportunity to enhance and build upon this work with an LEO connectivity solution that is fast, secure and reliable across vast distances, seas and rugged terrain.”
Mel Velarde, Chairman of NOW Corporation, said, “The integration of multi-orbit satellites provides a surprisingly compelling customer experience in both fixed and mobile applications. Our alliance with OneWeb and with the support of the United States government to the NOW Group will provide a clean, secure, and SLA-based connectivity to critical infrastructures such as banks, hospitals, schools, mining sites, power plants, government, and all other entities under the country’s digital economy. NOW Telecom is perhaps the only franchised Philippine telecom company that includes a mandate to operate in the outer space, making us able to cover the whole archipelago.”
References:
LEO operator Sateliot joins GSMA; global roaming agreements to extend NB-IoT coverage
Sateliot, a company operating a low-Earth orbit (LEO) nanosatellite constellation under the 3GPP/ITU-R NB- IoT standard (which is part of 5G), has joined the GSMA as a network operator member. This membership allows Sateliot to sign standard roaming agreements with any mobile network operator (MNO) and mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) that is also a member of the GSMA. Sateliot launched the first-ever 5G standard LEO satellite, named Sateliot_0 The GroundBreaker, this past April.
According to Sateliot, The same unmodified NB-IoT cellular devices that are currently being used can now be deployed in remote areas as well, where there is a lack of terrestrial cellular infrastructure.
Sateliot’s LEO nanosatellite constellation is designed to provide coverage in areas where traditional terrestrial connectivity is limited or non-existent, such as remote locations, fields of crops, mountains, or oceans. The standard protocol will allow massive deployment of 5G IoT solutions without captivity risks or inflated prices.
Sateliot’s membership with GSMA demonstrates its commitment to democratizing access to NTN IoT, as the company is the first to sign standard roaming agreements with global MNOs and MVNOs. With this membership, Sateliot becomes the first LEO satellite operator to have standard roaming agreements with global MNOs and MVNOs.
Sateliot’s network is designed to provide coverage in areas where traditional terrestrial connectivity is limited or non-existent, such as remote locations, fields of crops, mountains or for instance oceans. The standard protocol will allow massive deployment of 5G IoT solutions without captivity risks or inflated prices.
“We are thrilled to have become a GSMA member,” said Jaume Sanpera, CEO of Sateliot. “This is a fantastic milestone we’ve accomplished, we are the first LEO satellite operators to have standard roaming agreements with global MNOS and MVNOS.”
Sateliot runs the constellation that will democratize access to NTN IoT, demonstrated first by being a major contributor to the 3GPP standard and now by joining GSMA as an operator.
The GSMA’s mission is to drive the growth and development of worldwide mobile communications and provide industry leadership and advocacy. With its membership, Sateliot is poised to become a leader in IoT connectivity, providing seamless global connectivity for 5G IoT devices and applications.“We are seeing significant developments in the area of satellite communications, and we warmly welcome Sateliot as a member of the GSMA. We look forward to having them join the GSMA’s Wholesale Agreements & Solutions Group to work collectively and gain from the benefits of our membership,” said Lara Dewar, Chief Marketing Officer, GSMA.
References:
Generative AI could put telecom jobs in jeopardy; compelling AI in telecom use cases
The loss of jobs due to AI forecasts are very grim. IBM’s CEO Arvind Krishna this week announced a hiring freeze while speculating that 7,800 jobs could be replaced by AI in the next few years. A new report from the World Economic Forum (WEF) states that AI will cause 14 million jobs to be lost by 2027. The organization’s Future of Jobs Report 2023 shows that 590 million jobs will not change, while 69 million will be created and 83 million positions will be lost.
Even more scary was Goldman Sachs issued a report in March predicting AI would “replace” 300 million jobs and citing the recent impact of generative AI. Generative AI, able to create content indistinguishable from human work, is “a major advancement”, the report says. However, those predictions don’t usually forecast let alone mention the new jobs that will be created in an AI prevalent world.
According to Light Reading’s Iain Morris, new types of AI like Hawk-Eye, ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot and other permutations threaten a jobs apocalypse. The telecom sector looks extraordinarily exposed. For one thing, it’s stocked with people in sales, marketing and customer services, including high-street stores increasingly denuded of workers, like those coffee chains where you select your beverage on a giant touchscreen instead of telling somebody what you want. Chatbots have already replaced some roles. One very big (unnamed) network operator is known to be exploring the use of ChatGPT in customer services for added efficiency – a move that could turn thinned ranks anorexic.
The schema is that telco networks could feasibly be a self-operating, self-healing entity, stripped clean of people, run by an AI that’s probably been developed by Google or Microsoft even though it lives in facilities owned by the telco to keep GDPR watchdogs and other regulatory authorities on side. All those fault-monitoring, trouble-ticketing and other routine technical jobs have gone. If staff have been “freed up,” it’s not to do other jobs at the telco.
Opinion: This author strongly disagrees as these new versions of AI have not proven themselves to be that effective in doing telecom network tasks. Meanwhile, chat bots are somewhere between ineffective and totally dysfunctional so won’t replace live/real person chat or call centers till they improve.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
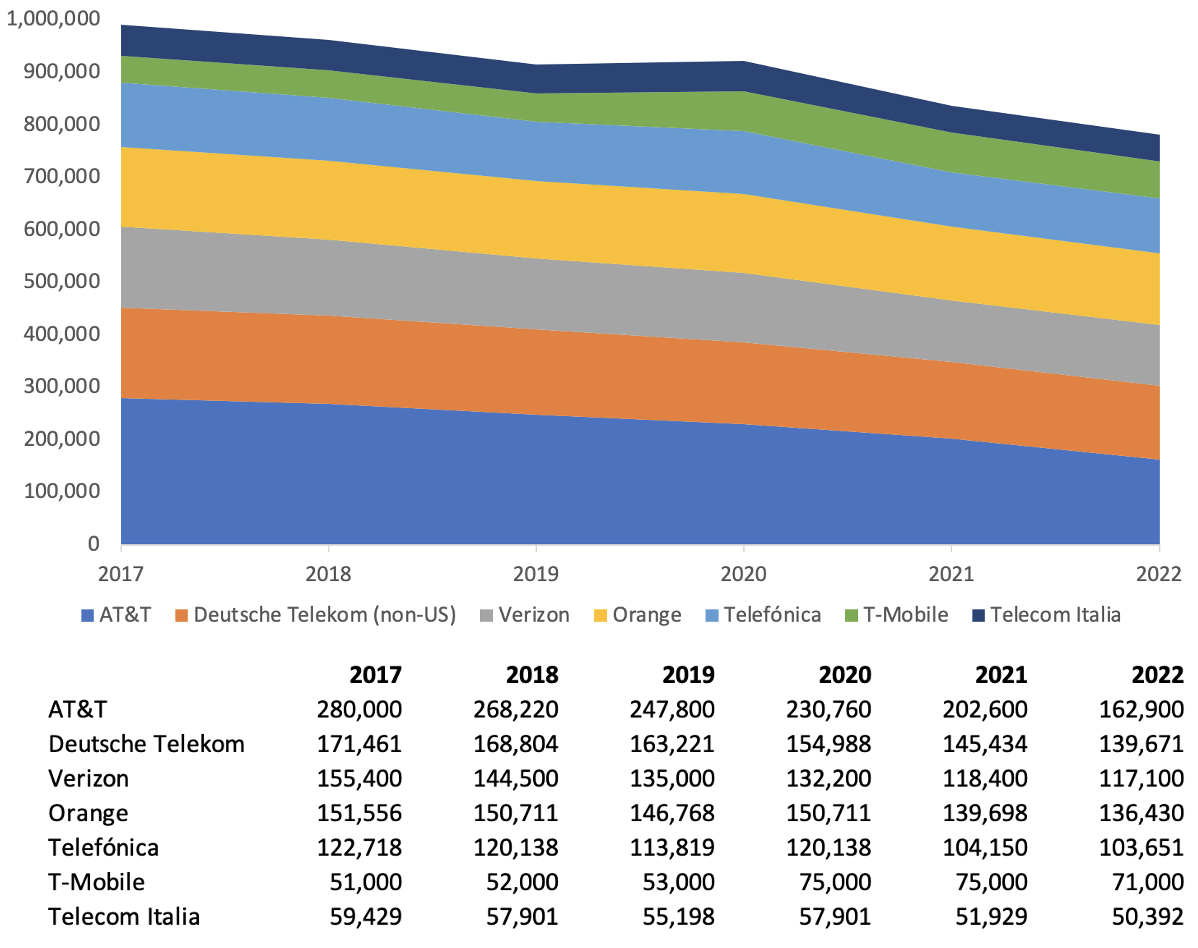
At big telcos tracked by Light Reading, collective headcount fell nearly 58,000 last year. Across AT&T, T-Mobile and Verizon, the big three of the U.S. mobile telecom market, around 45,000 jobs disappeared in 2022, more than 11% of the end-2021 total.
Source: Companies tracked by Light Reading
Outside the U.S., around 11,000 jobs were cut at Deutsche Telekom, Orange, Telecom Italia and Telefónica. That was a much smaller 2.5% of the earlier total, and yet more than 67,000 non-US jobs have been cut from the payrolls of these companies since 2018, a figure equal to 13.5% of headcount at the end of the previous year.
Much of this attrition has very little if anything to do with technology. Instead, it’s the result of more routine efficiency measures and the disposal of assets, including geographical units, infrastructure (such as towers) once but no longer deemed strategically important, and IT resources farmed out to the public cloud. This is a frightening thought for employees.
Morris asks, “If jobs were disappearing this fast before the arrival of ChatGPT, what does the future hold?”
AI Can Improve Telecom Industry without causing major job losses:
We think AI has the potential to improve various aspects of the telecommunication industry without causing major job losses. For example, Ericsson has reported that the implementation of AI-powered solutions in networks can lead to a 35 percent decrease in critical incidents and a 60 percent decrease in network performance problems. Additionally, energy costs can be reduced by 15 percent through the automation, making the network more environmentally sustainable.
AI can help telcos optimize their networks by automatically adjusting network settings and configurations to improve performance and reduce costs. AI algorithms can further be used to analyze vast amounts of data generated by telecommunication networks, providing valuable insights into network performance, and helping to identify and resolve issues in real-time. This can significantly improve network reliability and reduce downtime, ultimately leading to enhanced customer satisfaction.
Some of the other compelling AI use cases in telecom are:
- Fraud detection and prevention: AI algorithms can play a crucial role by analyzing massive amounts of data to detect and prevent various forms of fraudulent activities in real time, such as SIM-swapping, unauthorized network access, fake profiles, and bill fraud.
- Predictive maintenance: AI can analyze data from telecom equipment to predict when it will require maintenance—reducing downtime and costs associated with maintenance.
- Personalized marketing: AI can analyze customer data to create targeted marketing campaigns—improving customer engagement and reducing the costs associated with marketing efforts. Using machine learning models to recommend products or services to customers based on their usage patterns and preferences.
- Automated decision making: Using deep learning models to automate decisions such as network routing, dynamic pricing, and more.
References:
Allied Market Research: Global AI in telecom market forecast to reach $38.8 by 2031 with CAGR of 41.4% (from 2022 to 2031)
The case for and against AI in telecommunications; record quarter for AI venture funding and M&A deals
Global AI in Telecommunication Market at CAGR ~ 40% through 2026 – 2027
SK Telecom inspects cell towers for safety using drones and AI
Cybersecurity threats in telecoms require protection of network infrastructure and availability