Month: March 2021
LightCounting: the rise of disaggregated white box routers for wireless infrastructure
LightCounting’s new report explores the emergence of the Disaggregated Open Routers (DOR) [1.] market in wireless infrastructure. DOR are white-box cell site, aggregation and core routers based on an open and disaggregated architecture for existing 2G/3G/4G and future 5G network architectures.
Note 1. A disaggregated router is an open approach to routing where the customer can choose hardware and software from a range of vendors that best meets their needs. This open approach enables innovation, avoids vendor lock-in, and drives cost down. The hardware is provided by a whitebox vendor while the software is mostly proprietary from vendors like Israel’s Drivenets.
“Still incipient, the DOR market is just about to take off and is here to stay but requires more CSPs (Communications Service Providers) to take the plunge and drive volumes. And with China’s lack of appetite for DOR, North America is taking the lead,” said Stéphane Téral, Chief Analyst at LightCounting Market Research.
SOURCE: LightCounting
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The major findings in the report are:
- The Open RAN ascension brought router disaggregation to the spotlight and paved the way to 4 fundamental routes. This phenomenon would have never happened without TIP’s DOR initiative [2].
- Although NOS software vendors are mushrooming and by far outnumbering the white box hardware suppliers, one vendor dominates the networking silicon domain.
- Communications service providers (CSPs) remain cautiously optimistic about router disaggregation but have yet to see more maturity and the full benefits because an onslaught of software can boost OPEX.
- With all inputs from all vendors and CSPs with DOR rollout plans taken into consideration, our cell site-based model produced a forecast showing a slow start that reflects the early stage of this market and an uptick at the end of the 2021-2026 forecast period marked by a double digit CAGR.
Note 2. Telecom Infra Project (TIP)’s Disaggregated Open Routers (DOR) group is led by KDDI and Vodafone. The DOR project group is part of TIP’s Open Optical & Packet Transport (OOPT) Group. The DOR group will focus on open and disaggregated routing platforms for transport networks and will drive technological development toward white box solutions for backbone networks including aggregation routers and open BNGs.
The Telecom Infra Project (TIP) is a global community of companies and organizations working together to accelerate the development and deployment of open, disaggregated, and standards-based solutions that deliver the high-quality connectivity that the world needs – now and in the decades to come. Founded in 2016 by Deutsche Telekom, Intel, Facebook, Nokia and SK Telecom, TIP has grown into a diverse membership that includes hundreds of member companies – from service providers and technology partners, to system integrators and other connectivity stakeholders.
LightCounting’s Disaggregated Open Routers report explores the emergence of the Disaggregated Open Routers (DOR) market. Disaggregated open routers are white-box routers based on separated white box hardware and software with cloud enabled software functions for existing 2G/3G/4G and future 5G network architectures. The report analyzes the disaggregated open routers’ (aggregation and core) architectures and implementations in wireless infrastructure, including the emerging vendor ecosystem, and tracks white box hardware units and sales, and software sales, all broken down by region including North America, Europe Middle East Africa, Asia Pacific, and Caribbean Latin America. It includes the total number of cell sites worldwide and a 5-year market forecast. As this market is just emerging, it is too early to publish vendor market shares.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
More information on the report is available at: https://www.lightcounting.com/products/DOR/
Cisco Plus: Network as a Service includes computing and storage too
Cisco Systems is extending the concept of software-as-a-service (SaaS) technology with the introduction of Cisco Plus, which is a network-as-a-service (NaaS) offering focused on cybersecurity and hybrid cloud services. The new service offering can also provide computing-as-a-service and data-storage-as-a-service.
- Cisco announcing plans to lead the industry with new Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) solutions to deliver simpler IT and flexible procurement for customers looking for greater speed, agility and scale
- Cisco also reveals plans to help customers build a SASE foundation today (with Cisco SD-WAN and security) with as-a-service offer coming soon
- Cisco Plus offers include flexible consumption for data center networking, compute and storage now, and commits to delivering the majority of its portfolio as-a-service over time
“I believe every organization would benefit from simplifying powerful technology,” said Todd Nightingale, Senior Vice President and General Manager, Enterprise Networking and Cloud, Cisco. “Network-as-a-service is a great option for businesses wanting to shift to a cloud operating model without a heavy lift. Cisco is leading the industry in its approach with Cisco Plus. Together with our partners, we intend to offer the majority of our technology portfolio in the simplest, most flexible way: cloud-driven, cloud-delivered, cloud-managed and as-a-service.”
“Network-as-a-service delivery is a great option for businesses wanting to shift to a cloud operating model that makes its easy and simple to buy and consume the necessary components to improve and grow their businesses,” said James Mobley, senior vice president and general manager of Cisco’s Network Services Business Unit.
Cisco Plus NaaS solutions will provide:
- Seamless and secure onramps to applications and cloud providers
- Flexible delivery models, including pay-per-use or pay-as-you-grow options
- End-to-end visibility from the client to the application to the ISP
- Unified policy engine to ensure the right users have access
- Security across everything, not bolted on as another point solution
- Real-time analytics providing AI/ML-driven insights for cost and performance tracking
- API extensibility across the technology stack
- Partners layering additional value and delivering their services faster
The NaaS rollout will first focus on a cloud-based solution as-a-service for secure access service edge (SASE). The Cisco SASE offer currently available enables customers to easily leverage future services with investment protection. Cisco is planning limited release NaaS solutions later this calendar year that will unify networking, security and visibility services across access, WAN and cloud domains.
While Cisco plans in the next few years to introduce what will likely be many service options under Cisco Plus, for now it is introducing two flavors. The first, Cisco Plus Hybrid Cloud, includes the company’s data-center compute, networking, and storage portfolio in addition to third-party software and storage components all controlled by the company’s Intersight cloud management package. Customers can choose the level of services they want for planning, design and installation Mobley said.
Cisco Plus Hybrid Cloud, which will be available mid-year, offers pay-as-you-go with delivery of orders within 14 days, Mobley said.
“As enterprises recommit to their digital transformation strategies, they are increasingly looking for more cloud-like, flexible consumption models for procuring and managing their IT, cloud and network infrastructure. These “as-a-service” deployment options provide much needed flexibility and scalability, along with a simplification of network deployments and ongoing operations. Cisco’s transition to as-a-service via Cisco Plus shows the company is committed to meeting customer needs for predictable costs, cloud-like agility, first-class security, and more.
“With Cisco Plus, it’s taking NaaS and its hybrid cloud offerings to the next level by including hardware and the full portfolio into this as-a-service offer, that provides cloud-like simplicity and flexibility of consumption on one end, and on the other, it provides a rich set of intelligent operational enhancements that go a long way to deliver enhanced IT experiences and outcomes. This has also been made possible by increased embedded intelligence now available in network and IT hardware and software, coupled with advanced telemetry options in many of these platforms.”
— Rohit Mehra, Vice President of Network Infrastructure, IDC.
“With Cisco Plus, we couldn’t be more excited that Cisco is diving deeper into the as-a-service era, helping us in our transformation to deliver IT as a service to our customers. In this way, we are better equipped to help our customers simplify their IT operations, and free up resources to invest in innovation of their core business.” — Jeffrey den Oudsten, CTO Office Solutions Director, Conscia Nederland
“There’s always been a push and pull in how to operationalize and finance IT infrastructure. Cisco Plus is the matching pair to a cloud operating model. Delivering Cisco Plus across the majority of Cisco’s portfolio helps us at Insight to further deliver the transformation to a cloud operating model our clients want. With Cisco Plus, organizations can not only operate their infrastructure as a cloud, but also consume it in a similar fashion, enabling a true hybrid, multi-cloud.” — Juan Orlandini, Chief Architect Cloud + Data Center Transformation, Insight
“At Presidio, we have seen this shift coming for a long time. Our customers are very clear: They want to consume reliable, best of breed infrastructure with consumption-based financial models. And with the launch of Cisco Plus, Presidio and Cisco in partnership are doing just that.” — Raphael Meyerowitz, Engineering VP, Office of the CTO, Data Center, Presidio
The second Cisco Plus service, which did not have an availability timeframe, will feature the company’s secure access services edge (SASE) components, such as Cisco’s SD-WAN and cloud-based Umbrella security software.
Security-as-a-service models offer many advantages for organizations including offloading the maintenance of hundreds or thousands of firewalls and other security appliances, said Neil Anderson, senior director of network solutions at World Wide Technology, a technology and supply-chain services provider.
“With SASE, enterprises can consume that from the cloud and let someone else take care of the toil, which frees up their security team to focus on threat vectors and prevention,” he said.
While the strategy behind delivering network components as a cloud-based service has been around for a few years, it is not a widely used enterprise-customer strategy. Cisco’s entry into NaaS is likely to change that notion significantly.
“Cisco has been on this journey for a few years now—starting with providing subscription-based offers for many of its software solutions—while working on simplifying and enriching the licensing and consumption experience,” Mehra said. “Customers understand and have embraced cloud-like IT-consumption models that are typically subscription-based and provide scalability and other on-demand capabilities,” Mehra said.
Terms such as NaaS are still largely new in an enterprise context to most IT practitioners, although they do understand that operational simplicity and flexibility will be crucial to their success in digital transformation, Mehra said.
While NaaS might be relatively new to some customers, others are already utilizing it, other experts said. For remote-access, customers are more than ready, and it’s starting to go mainstream, Anderson said.
“For connectivity to the cloud edge, it’s coming very soon, and the adoption of SASE models for security will accelerate the demand for NaaS services,” he said. “NaaS in the campus will probably take a bit longer, but we see that coming. Some customer segments, like retail, are probably ready today, while others like global financials will take longer to adopt.”
Networking is no longer just about connecting things within private networks because there is a world of networking to and between clouds to account for, Anderson said. “For example, with private WANs, I typically networked my sites to my other sites like a private data center. Now, I need to network my sites to cloud services, and I may be doing so with public-internet services,” Anderson said.
NaaS for the campus network is another use case on the horizon, he said. “To build campus networks in the past, we had access, distribution, and core layers, and the core spanned my campus and sometimes private data center. It was designed to aggregate traffic from users into my private data center,” Anderson said. “Today, much of the traffic is heading to the cloud—Office 365 is the tipping point for many organizations—so building a core network may not be necessary. I see a new architecture emerging where the goal is to tie each site, including each building of a campus, to the internet directly to connect users to cloud and enable traffic to [reach] the cloud sooner, ultimately improving the user experience.”
Naas is by no means a slam dunk, and there will be challenges for enterprises that use it. “For medium to large organizations with significant investments in existing remote, branch, campus and data-center networking network-security infrastructure, migrating to NaaS will be difficult and time consuming. Multi-vendor environments will further complicate the matter,” stated principal analyst at Doyle Research, Lee Doyle.
Widespread adoption of enterprise NaaS will occur slowly over the next five to 10 years Doyle stated. The best fits for adoption now are greenfield sites, temporary locations, and small branch offices. NaaS offerings will also be attractive to network remote, home and mobile workers who need secure, reliable application performance. Enterprise networks with the requirement to move traffic at high speeds on-site would be more difficult to deliver as a service, Doyle stated.
Key challenges, besides understanding of what NaaS will help deliver, face IT practitioners who are the potential customers as well as vendors and service providers, Mehra said.
“On the customer aspects, what we’ll need to watch will be the changing role of IT and how it can optimally consume these technologies as a service while retaining overall control of its IT environment,” Mehra said. “On the provider side, visibility across issues such as operational flexibility and simplicity will be one area to consider, while another will be the direction the industry takes on what metered-service options it makes available for its clients.”
The challenges depend on the industry and security requirements, WWT’s Anderson said. “If the organization is in a heavily regulated industry like financial, healthcare, or federal [government], one challenge will be trusting the integrated security needed,” Anderson said. “For example, there would be fewer challenges to enable everyone to connect to the internet, akin to a giant hotspot, but to adopt more of a zero-trust model, where you may need to securely isolate sessions and devices from one another, will require building trust in some integrated security technologies.”
“What Cisco is doing is very interesting because what NaaS is out there has been limited to mostly the WAN world but once you start targeting the enterprise that’s where the challenges are because customers still have to move bits and everything can’t be in the cloud,” Doyle said. “Instead of being in the first inning of a game we are really just now defining the rules of the game, so there’s a long way to go.”
References:
https://www.zdnet.com/article/cisco-launches-cisco-plus-a-step-toward-network-as-a-service/
Echo and Bifrost: Facebook’s new subsea cables between Asia-Pacific and North America
Facebook has revealed plans to build two new subsea cables between the Asia-Pacific region and North America, called Echo and Bifrost. The social media giant also revealed partnerships with Google as well as Asian telecoms operators for the project.
Although these projects are still subject to regulatory approvals, when completed, these cables will deliver much-needed internet capacity, redundancy, and reliability. The transpacific cables will follow a “new diverse route crossing the Java Sea, connecting Singapore, Indonesia, and North America,” and are expected to increase overall transpacific capacity by 70%.
Facebook says Echo and Bifrost will support further growth for hundreds of millions of people and millions of businesses. Facebook said that economies flourish when there is widely accessible internet for people and businesses.
Echo and Bifrost be the first transpacific cables through a new diverse route crossing the Java Sea. Connecting Singapore, Indonesia, and North America, these cable investments reflect Facebook’s commitment to openness and our innovative partnership model. The social media company works with a variety of leading Indonesian and global partners to ensure that everyone benefits from developing scale infrastructure and shared technology expertise.
Facebook will work with partners such as Indonesian companies Telin and XL Axiata and Singapore-based Keppel on these projects.
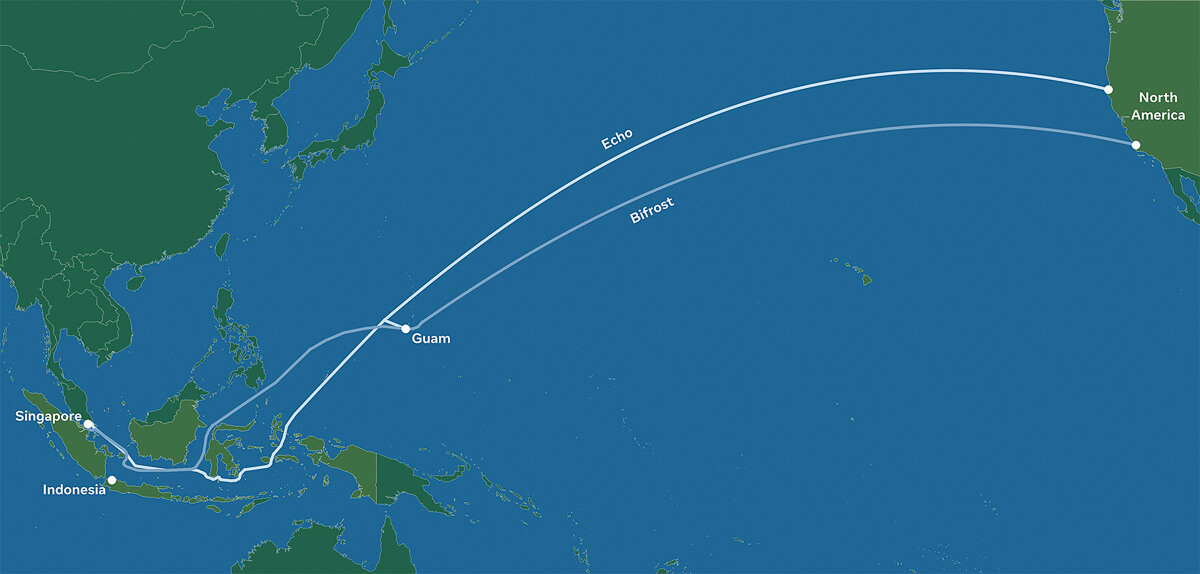
Image Credit: Facebook
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Kevin Salvadori, VP of network investments at Facebook, provided further details in an interview with Reuters. He said Echo is being built in partnership with Alphabet’s Google and XL Axiata. It should be completed by 2023. Bifrost partners include Telin, a subsidiary of Indonesia’s Telkom, and Keppel. It is due to be completed by 2024.
Aside from the Southeast Asian cables, Facebook was continuing with its broader subsea plans in Asia and globally, including with the Pacific Light Cable Network (PLCN), Salvadori said.
“We are working with partners and regulators to meet all of the concerns that people have, and we look forward to that cable being a valuable, productive transpacific cable going forward in the near future,” he said.
Indonesia
Facebook noted that Echo and Bifrost will complement the subsea cables serving Indonesia today. These investments present an opportunity to enhance connectivity in the Central and Eastern Indonesian provinces, providing greater capacity and improved reliability for Indonesia’s international data information infrastructure. Echo and Bifrost complement the subsea cables serving Indonesia today, increasing service quality and supporting the country’s connectivity demands.
This is all part of Facebook’s continued effort to collaborate with partners in Indonesia to expand access to broadband internet and lower the cost of connectivity. Facebook has partnered with Alita, an Indonesian telecom network provider, to deploy 3,000 kilometers (1,8641 miles) of metro fiber in 20 cities in Bali, Java, Kalimantan, and Sulawesi. In addition, we are improving connectivity by expanding Wi-Fi with Express Wi-Fi.
While 73% of Indonesia’s population of 270 million are online, the majority access the web through mobile data, with less than 10 percent using a broadband connection, according to a 2020 survey by the Indonesian Internet Providers Association. Swathes of the country, remain without any internet access.
Singapore
In Singapore, Echo and Bifrost are expected to provide extra subsea capacity to complement the APG and SJC-2 subsea cables. Building on Facebook’s previously announced Singapore data center investments, Echo and Bifrost will provide important diverse subsea capacity to power Singapore’s digital growth and connectivity hub. Singapore is also home to many of Facebook’s regional teams.
The Asia-Pacific region is very important to Facebook. In order to bring more people online to a faster internet, these new projects add to Facebook’s foundational regional investments in infrastructure and partnerships to improve connectivity to help close the digital divide and strengthen economies.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Advancing connectivity between the Asia-Pacific region and North America
https://www.reuters.com/article/us-facebook-internet-southeastasia-idUSKBN2BL0CH
Samsung and Marvell develop SoC for Massive MIMO and Advanced Radios
Korean electronics giant Samsung Electronics said it has developed a new System-on-Chip (SoC) for its Massive MIMO and other advanced radios in partnership with U.S. chipmaker Marvell. It is expected to be available in Q2 2021 for use in equipment sold to Tier-One network operators.
The SoC is designed to help implement new technologies, which improve cellular radios by increasing their capacity and coverage, while decreasing power consumption and size. The new SoC is equipped to support both 4G and 5G networks simultaneously and aims to improve the capacity and coverage of cellular radios. It is claimed to save up to 70 percent in chipset power consumption compared to previous solutions.
“We are excited to extend our collaboration with Marvell to unveil a new SoC that will combine both companies’ strengths in innovation to advance 5G network solutions,” said Junehee Lee, Executive Vice President and Head of R&D, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics. “Samsung prioritizes the development of high-impact 5G solutions that offer a competitive edge to our operators. We look forward to introducing this latest solution to the market shortly.”
Samsung and Marvell have been working closely to deliver multiple generations of leading network solutions. Last year, the companies announced a collaboration to develop new 5G products, including innovative radio architectures to address the compute power required for Massive MIMO deployments.
“Our collaboration with Samsung spans multiple generations of radio network products and demonstrates Samsung’s strong technology leadership. The joint effort includes 4G and 5G basebands and radios,” said Raj Singh, Executive Vice President of Marvell’s Processors Business Group. “We are again honored to work with Samsung for the next generation Massive MIMO radios which significantly raise the bar in terms of capacity, performance and power efficiency.”
“Marvell and Samsung are leading the way in helping mobile operators deploy 5G with greater speed and efficiency,” said Daniel Newman, Founding Partner at Futurum Research. “This latest collaboration advances what’s possible through SoC technology, giving operators and enterprises a distinct 5G advantage through optimized performance and power savings in network deployments.”
Samsung has pioneered the successful delivery of 5G end-to-end solutions including chipsets, radios, and core. Through ongoing research and development, Samsung drives the industry to advance 5G networks with its market-leading product portfolio from fully virtualized RAN and Core to private network solutions and AI-powered automation tools. The company is currently providing connectivity to hundreds of millions of users around the world.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
On the network equipment side, Samsung Electronics recently won a 5G contract with Japanese telco NTT DOCOMO, as it seeks to challenge incumbents like Huawei, Ericsson, and Nokia in the telecom equipment business, according to media reports.
In India, Samsung Electronics is likely to apply for a production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for telecom equipment manufacturing, benefiting from India’s program to locally make 4G and 5G gear and other equipment – for sales both in India and overseas, ET recently reported.
Samsung would then join other global manufacturers such as Cisco, Jabil, Flex and Foxconn, besides European telecom equipment vendors Nokia and Ericsson in applying for the PLI scheme that seeks to boost local production of telecom equipment and reduce imports.
References:
https://telecom.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/samsung-marvell-develop-soc-for-5g-radios/81720284
Samsung Boosts the Performance of Massive MIMO
Samsung Collaborates With NTT DOCOMO on 5G
MIIT: China has 260M 5G subs; Telecom business revenue significantly increased
China telecom regulator MIIT (Ministry of Industry and Information Technology) revealed this week that China has 260 million 5G subscribers at the end of February 2021. That is a huge number and more than the rest of the world combined [1.], but still a long way short of the 361 million claimed by the three operators. in February.
- China Mobile reported 173.2 million 5G package customers compared to 15.4 million 5G customers in February 2020. China Mobile’s overall mobile subscriber base was said to be 937.16 million at the end of February, down from 940.86 million in January.
- China Telecom added a total of 6.2 million 5G subscribers in February 2021 for a total of 103.4 million.
- China Unicom had 84.5 million 5G subscribers at the end of February 2021.
Note 1. GSA says that global 5G subscriptions grew by 57% in the fourth quarter of 2020 to reach nearly 401 million globally (representing 4.19% of the entire global mobile market). By the end of 2025, 5G will account for 31% of the global market (at 3.39 billion subscriptions), although LTE will still be dominant at 53.3% of all global mobile subscriptions.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
China’s vice-minister of industry and information technology Liu Liehong recently said that a total of 718,000 5G base stations have been built in China, accounting for nearly 70% of the world’s total 5G cell sites.
During Mobile World Congress Shanghai 2021, government officials said that Chinese carriers have invested more than CNY260 billion ($40.2 billion) to build the world’s largest 5G network.
MIIT further stated:
The growth rate of telecom business revenue has increased significantly. From January to February, the total revenue of telecommunications services reached 237.3 billion yuan, an increase of 5.8% year-on-year, and the growth rate increased by 4.3 percentage points year-on-year. The total telecommunications business calculated at the constant price of the previous year was 249.1 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 25.9%.
The scale of mobile phone users is basically stable, and 5G users are developing rapidly. As of the end of February, the total number of mobile phone users of the three basic telecommunications companies reached 1.592 billion, a year-on-year increase of 0.8%. As of the end of February, the number of 5G mobile terminal connections of the three basic telecommunications companies reached 260 million, a net increase of 61.3 million from the end of the previous year, accounting for 16.3% of mobile phone users.
Light Reading’s Robert Clark wrote: “The three (China) telcos’ annual filings over the past two weeks indicate that between them they spent a hefty 173 billion yuan ($26.5 billion) on 5G and they’re not slowing down; they’ve set aside another 185 billion yuan for 2021.”
“Their pricing, with plenty of encouragement from government officials, is also aggressive, with China Mobile’s 5G entry package costing just 128 yuan ($19.56). The heavy investment and the moderate pricing in pursuit of national objectives is why their results indicate little reward for the effort so far.”
MIIT also commented on other telecom services (besides 5G):
Data and Internet business revenue accounted for 60%, supporting the steady growth of overall telecom business revenue. From January to February, the three basic telecommunications companies completed fixed data and Internet business revenues of 41.5 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 10.2%, accounting for 17.5% of telecommunications business revenues, accounting for a year-on-year increase of 0.8 percentage points, driving a 1.7 percentage point increase in telecommunications business revenue . The revenue from mobile data and Internet services showed a decline for the first time. The completed business revenue was 106.2 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 1.2%, and its share of telecom business revenue fell to 44.7%.
Fixed and mobile voice services declined steadily, and their share of telecom business revenue continued to decline. From January to February, the three basic telecommunications companies completed fixed voice and mobile voice business revenues of 3.82 billion yuan and 18.64 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 1.1% and an increase of 5.0%, respectively, accounting for 9.5% of the total revenue of telecommunications services, and a decrease of 0.1%. Percentage points. The rapid growth of income from emerging businesses has strongly promoted the growth of telecom business income. The three basic telecommunications companies are actively transforming and upgrading, promoting IPTV, Internet data centers, big data, cloud computing, artificial intelligence and other emerging businesses. From January to February, they completed a total of 36.2 billion yuan in related business income, a year-on-year increase of 28.9%. The proportion increased sharply by 2.8 percentage points year-on-year to 15.3%, driving the growth of telecom business revenue by 3.6 percentage points.
The proportion of fixed broadband access users with speeds above 100M has exceeded 90%, and the number of gigabit users has continued to increase. The total number of fixed Internet broadband access users reached 492 million, a year-on-year increase of 8.9% and a net increase of 8.67 million from the end of the previous year. Among them, there are 463 million FTTH/O users, accounting for 94% of the total number of fixed Internet broadband users. The number of fixed Internet broadband access users with an access rate of 100Mbp and above reached 450 million, accounting for 90.4% of the total number of users, an increase of 0.5% from the end of the previous year; the promotion of gigabit broadband services was accelerated, and the access rate of 1000Mbps and above was fixed. The number of Internet broadband access users reached 8.03 million, a net increase of 1.63 million over the end of the previous year.
Mobile Internet traffic increased significantly, and DOU remained at a relatively high level in February. From January to February, the cumulative mobile Internet traffic reached 30.9 billion GB, a year-on-year increase of 31.8%. Among them, the Internet traffic through mobile phones reached 29.7 billion GB, a year-on-year increase of 31.2%, accounting for 96% of the total mobile Internet traffic. In February, the average mobile Internet access traffic (DOU) per household was 10.85GB/household, which was 1.97GB/household higher than the same period last year.
The penetration rate of fixed broadband access users of 100M and above tends to be even in all regions. As of the end of February, fixed broadband access users of 100Mbps and above in the eastern, central, western and northeastern regions reached 189.68 million, 11.17 million, 116.57 million and 26.74 million, respectively, accounting for 89.3. %, 91.7%, 90.8% and 91.8%. The difference between the highest proportion of fixed broadband access users above 100M and the lowest proportion in each province was 15.3 percentage points.
China Unicom and China Telecom say nearly a quarter of their mobile customers are on 5G plans. Chna Unicom boosted ARPU 4%, while China Telecom reported 5G ARPU nearly 50% above its blended ARPU.
China Mobile reported a 1% rise in profit but, despite the huge 5G subscriber base, recorded another decline in mobile ARPU.One winner for China Mobile was broadband access, which grew 17%, while China Telecom and China Unicom both experienced large increases in their smart home services.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Editorial Comment:
Many experts don’t trust economic numbers released by China’s government. Questions over the accuracy of China’s economic data, including industry groups like telecom, persist due to the lack of transparency used in the collection process. Critics say the government does not state how the data is collected or the different components that form the final numbers that are released to the public.
The methodology China uses to calculate its economic and industry data is opaque, and some knowledgeable people even accuse the government of abruptly changing methods without announcement to distort figures and hide declines.
The motivation seems to be to make China’s economy and industry groups look much stronger than they really are.
Most analysts treat any official Chinese data with caution and skepticism. Yet they have few, if any ways to establish an alternative, more accurate assessment of the world’s second-largest economy.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.miit.gov.cn/gxsj/tjfx/txy/art/2021/art_82f101e1d078447fac75443a50348b7c.html
https://www.lightreading.com/asia/china-5g-race-taking-its-toll-on-operators/d/d-id/768369?
https://gsacom.com/paper/lte-and-5g-subscribers-march-2021-q4/
ATIS: Next G Alliance leadership and 6G Roadmap – Is it premature?
The Alliance for Telecom Industry Solutions (ATIS) has announced election results for the Next G Alliance and its Steering Group as well as the launch of work on a 6G Roadmap.
Andre Fuetsch, Executive Vice President & Chief Technology Officer, AT&T, has been named chair of the Next G Alliance executive governing body, the Full Member Group (FMG). Jan Söderström, Ericsson’s Head of Technology Office Silicon Valley, has been named FMG vice chair. Among its many roles, the FMG sets the overall strategy and direction for the Next G Alliance as well as its organizational policies. Both the chair and vice chair serve a two-year term.
Three co-chairs have also been named for the Next G Alliance Steering Group (SG). The SG is composed of technology leaders and experts who will identify key North American R&D needs, standards strategies and market readiness policies to achieve the goals established by the Next G Alliance. The SG co-chairs are: AT&T Assistant Vice President – Standards & Industry Alliances Brian Daly; Head of North American Standardization at Nokia, Devaki Chandramouli; and VMware Director, Edge & AI Ecosystems, Telco Cloud Business Unit, Benoit Pelletier.
Setting the stage for the eventual commercialization of 6G, the work of the Next G Alliance will influence and encompass the full lifecycle of research and development, manufacturing, standardization and market readiness. As an initial priority, a 6G Roadmap Working Group has been launched. The National 6G Roadmap being developed will act as a foundation for future outputs, delivering a common vision and destination point for achieving North American 6G wireless leadership. It will define what is needed in terms of research needs, technology developments, service and application enablers, policies and government actions and market priorities.
In addition to the 6G Roadmap Working Group, the Next G Alliance will simultaneously launch a “Green G” Working Group focused on achieving energy efficiency by reducing power consumption and assessing how to achieve a sustainable ecosystem with emerging technologies. The Working Group will evaluate the environmental impact of a broad range of sources including water and materials consumption as well as the use of renewable or ambient energy.
“While innovation frequently occurs in response to market needs, long-term technology leadership takes strategic foresight and critical stakeholders committed to reaching the desired future state,” said Susan M. Miller, President and CEO, ATIS. “With its leadership set and work on both sustainability and the 6G Roadmap launched, the Next G Alliance is well positioned to create a national vision for the next decade.”
Thus far, the Next G Alliance has united 45 of the leading information and communications companies in a shared commitment to advance the evolution of 5G, chart the future of 6G technology and put North America at the forefront of wireless technology leadership for the next decade and beyond. The membership spans infrastructure, semiconductors and device vendors; operators; hyper-scalers and other organizations, including those in the area of research.

If your company is interested in joining, contact ATIS Membership Director Rich Moran.
Learn more about the Next G Alliance at: https://nextgalliance.org/
About ATIS:
As a leading technology and solutions development organization, the Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions (ATIS) brings together the top global ICT companies to advance the industry’s business priorities. ATIS’ 150 member companies are currently working to address 6G, 5G, robocall mitigation, IoT, Smart Cities, artificial intelligence-enabled networks, distributed ledger/blockchain technology, cybersecurity, emergency services, quality of service, billing support, operations, and much more. These priorities follow a fast-track development lifecycle – from design and innovation through standards, specifications, requirements, business use cases, software toolkits, open source solutions, and interoperability testing.
ATIS is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). ATIS is the North American Organizational Partner for the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), a founding Partner of the oneM2M global initiative, a member of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), as well as a member of the Inter-American Telecommunication Commission (CITEL). For more information, visit www.atis.org. Follow ATIS on Twitter and on LinkedIn.
Editorial Comment:
We think it’s very premature to start an INDEPENDENT group to plan the future of 6G networks for North America. That’s because 5G standards and specs are not even close to be finished. The standardization work on 6G hasn’t started in earnest yet. There’s only an ITU-R draft report on “Technology Trends of terrestrial IMT systems towards 2030 and beyond,” which is scheduled to be completed in July 2022.
Regarding 5G standards and specs being incomplete, revision 6 of ITU-R M.1036 recommendation specifying Frequency Arrangements for the terrestrial component of IMT (including 5G/IMT 2020) has not yet been agreed upon yet in ITU-R WP5D. It should include all the WRC 19 recommended frequencies for 5G/IMT 2020, especially mmWave.
Another example is that 3GPP Release 16 URLLC in the RAN [Physical Layer Enhancements for NR Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communication (URLLC)] has not been completed, despite that release being frozen last July.
3GPP Release 16 5G NR-URLLC in the RAN spec status as of as of March 25, 2021:
- RP-191584 5G NR Physical Layer Enhancements for Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communication (URLLC) [UID=830074 and CODE=NR_L1enh_URLLC] was 37% complete. It is scheduled for completion June 12, 2022).
- RP-190726 Performance part: Physical Layer Enhancements for NR Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communication (URLLC) spec was 0% complete and hasn’t been updated since 2019.
- RP-200472 revised NR performance requirement enhancement [UID=840094 CODE=NR_perf_enh] was 0% complete.
URLLC Enhancement of URLLC support in the 5G Core network (UID=830098) is stated to be 90% complete.
Note also that there are no ITU-T recommendations/standards that specify implementation for IMT 2020/5G non radio aspects. All the work is being done in 3GPP and at a reference architecture level that does NOT specify detailed implementation. That applies to 3GPP specs on 5G core network, network slicing, and other highly touted 5G features.
Hence, there will surely be many implementations of 5G “cloud native” core networks, network slicing, virtualization, security, etc
We think any 6G technology aspects and specification work should be done in ITU-R WP5D for the RAN and 3GPP for the RAN and Core network.
References:
https://www.3gpp.org/DynaReport/GanttChart-Level-2.htm#bm830074
ETNO Report: €300bn still missing for networks
European telecom operators have released a new report on how the sector can contribute to digital transformation and economic recovery. The “Connectivity and Beyond: How Telcos Can Accelerate a Digital Future For All” report from industry group ETNO (European Telecoms Network Operator’s association) and consulting firm BCG comes ahead of a summit of EU leaders to discuss industrial and digital policy, among other topics. The European network operators expressed the need for significant investments to realize the economic benefits of digital infrastructure.

The report sees the potential to create 2.4 million new jobs in the next four years through investment in digital transformation. This will require the telecom operators to invest EUR 300 billion in networks, along with additional action to stimulate demand and improve digital skills.
In order to achieve the opportunity, Europe must dramatically ramp up its network investment capacity to achieve gigabit speeds across territories and ensure full digital inclusion. BCG estimates €150bn is still needed to achieve a full-5G scenario in Europe, while an additional €150bn is required to finish upgrading fixed infrastructure to gigabit speeds.
However, increased investment is also much needed on the demand side, with 83% of EU SMEs still not using advanced cloud and 60% of 9 year-olds currently educated in schools that are not digitally equipped. BCG estimates that upgrading the digital infrastructure of all European schools would require €14bn/year, which corresponds to 1.8% of the Next Generation EU fund. Similarly, digitalizing all European SMEs would require €26bn/year, or 3.5% of the Next Generation EU fund.
BCG analysis finds that 5G alone can generate an annual increase of EUR 113 billion in GDP and 2.4 million new jobs in Europe by 2025. A widespread uptake of digital solutions can also help reduce carbon emissions, by up to 15 percent, the report said. This is based on rolling out smart city services and digital transformation in the transport sector.
The report highlighted the significant investment needed to realize these gains, saying Europe will need to ramp up network spending quickly to achieve its goals. BCG estimates it will cost EUR 150 billion to bring 5G to all of Europe and another EUR 150 billion to upgrade fixed infrastructure to gigabit speeds. More can be done also to stimulate demand, such as supporting digital transformation among small businesses and bringing internet infrastructure and digital skills training to schools, the report said.
The EU members agreed last year that 20 percent of the EUR 750 billion economic recovery fund should go to digital investment. ETNO members are hoping part of this funding can go towards supporting investment in the next generation of telecom networks.
The report details a series of “urgent” policy actions to support these aims, including increasing the attractiveness of investment in roll-out, allowing for more industry collaboration and scale in the sector, stimulating demand and digital transformation across industrial sectors, prioritizing leadership in European digital services and investment in digital skills.
References:
https://etno.eu/news/all-news/704-etno-bcg.html
https://etno.eu/library/reports/96-connectivity-and-beyond.html
Altiostar and Rakuten Mobile Demonstrate Success for Open RAN Network in Japan
Rakuten Mobile and Altiostar have announced a number of performance and scalability achievements for the Rakuten Mobile 4G and 5G Open RAN deployments in Japan. That network, built on Altiostar’s cloud-native Open vRAN software, was said to achieve superior levels of automation and performance.
Rakuten Mobile launched its 4G network in April 2020. The wireless network operator ended January 2021 with more than 11,000 base stations that cover 74.9 percent of the population. Rakuten Mobile plans to expand its network coverage to 96 percent of Japan’s population coverage by summer this year. That’s about five years ahead of its own schedule! The network has achieved both high performance (number one in upload speed in market at 16.8Mbps, per OpenSignal), despite having only 1/6th of the spectrum holdings of competing operators in market.
In September 2020, five months after the initial launch, Rakuten Mobile launched a commercial-scale, cloud-native 5G network, using Altiostar’s Open vRAN service. As baseband functions are deployed as VNFs (virtual network functions), Rakuten Mobile automated various operational tasks such as new cell site integration (auto-commissioning), as well as fault detection and automated recovery from failures (self-healing). Due to the automation of its network, Rakuten Mobile reports it can provide a new 5G cell site in four minutes and a 4G site in eight minutes.
The 5G network, using advanced massive MIMO and millimeter wave (mmWave) radios, covers both sub-6 GHz and mmWave frequency bands. Altiostar worked with Qualcomm Technologies, Airspan, and Rakuten Mobile on innovation in mmWave radios based on Qualcomm 5G RAN platforms. Altiostar partnered with NEC and Rakuten Mobile to introduce to the 5G network the sub-6 GHz massive MIMO radios, which were validated as compliant with O-RAN specifications during an O-RAN Alliance Plugfest held this past September in India.
The 5G network has demonstrated impressive performance for end users, with throughput of 1.77 Gbps. This compares favorably to data from a Ookla, which detailed speed test results for Japan in Q3 2020, where the fastest 10% of users realized an average download speed of 719.42 Mbps.

Image Credit: Altiostar
“Rakuten has been a disruptor in the mobile space and our 4G and 5G Open vRAN deployments reflect this strategy,” said Tareq Amin, Representative Director, Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer at Rakuten Mobile. “The performance and stability of the 5G network shows that a cloud-native framework and web-scale architecture can compete with a traditional RAN approach and provide new levels of automation to the network. We will continue to drive the transformation of the mobile industry with a rich and diverse ecosystem with companies including Altiostar, Qualcomm Technologies and NEC.”
“Rakuten has been at the forefront of the Open vRAN movement since it began. The industry is closely watching its every step, and it has been able to demonstrate a high-quality experience for their customers,” said Stéphane Teral, Chief Analyst, LightCounting. “This is validated by the performance metrics of their 5G network and I am excited to see the next steps they take as the network goes national.”
“This is a significant milestone for the Rakuten Mobile and Altiostar partnership towards commercial realization of a high performing, cloud-native 5G RAN architecture,” said Ashraf Dahod, CEO of Altiostar. “The Altiostar container-based solution allows Rakuten Mobile to quickly provision new sites and turn up service for a customer in record time. By leveraging the power of an Open virtualized RAN, Rakuten can transform its network and its business to provide a robust service for the consumer that exceeds that of a traditional operator.”
Altiostar has partnered with Rakuten Mobile to design and deploy its Open vRAN. Rakuten Mobile has standardized on the Altiostar Open vRAN software for all types of deployment models from small cells to macro to massive MIMO, across 4G and 5G radio access technologies.
About Altiostar
Altiostar provides 4G and 5G open virtualized RAN (Open vRAN) software that supports open interfaces and virtualizes the radio access baseband functions to build a disaggregated multi-vendor, web-scale, cloud-based mobile network. Operators can add intelligence, quickly adapt the network for different services and automate operations to rapidly scale the network and reduce Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). Altiostar collaborates with a growing ecosystem of partners to support a diverse Open RAN supply chain.
The company was selected by Dish last June to deliver its cloud-native O-RAN compliant solution for DISH’s nationwide 5G network buildout, the first of its kind in the U.S. The Altiostar solution will provide openness, modularity, agility and scalability to DISH, enabling faster deployment of new 5G services for consumers and businesses.
The Altiostar Open vRAN solution has been deployed globally, including the world’s first cloud-native commercial-scale mobile network with Rakuten Mobile in Japan. For more information, visit www.altiostar.com
About Rakuten Mobile
Rakuten Mobile, Inc. is a Rakuten Group company responsible for mobile communications, including mobile network operator (MNO) and mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) businesses, as well as ICT and energy. Through continuous innovation and the deployment of advanced technology, Rakuten Mobile aims to redefine expectations in the mobile communications industry in order to provide appealing and convenient services that respond to diverse customer needs.
Qualcomm 5G RAN Platform is a product of Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries.
Qualcomm is a trademark or registered trademark of Qualcomm Incorporated.
SOURCE: Altiostar
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
 References:
References:
NTT DOCOMO selects Samsung for 5G and O-RAN network solutions
Samsung Electronics announced on Monday that it has been selected as a 5G network solutions provider for NTT DOCOMO, the leading mobile operator in Japan with 82 million customers. Samsung will support DOCOMO (now wholly owned by NTT Corp.) with its innovative 5G technology, including O-RAN-compliant solutions, to bring enriched 5G services to users, advance digital transformation for businesses, and improve society at large.
As part of its ongoing strategy to deliver an advanced network and provide customers an array of enhanced mobile services, DOCOMO leverages leading edge-technologies in its 5G network.
“As a leading mobile operator, our goal is to provide our customers the best possible services for creating innovative, fun and exciting experiences and finding solutions to social issues,” said Sadayuki Abeta, General Manager of the Radio Access Network Development Department at NTT DOCOMO. “We are excited to collaborate with Samsung for the next phase of 5G Open RAN and accelerate the expansion of our ‘Lightning Speed 5G’ coverage in the nation.”
“We are pleased to be part of DOCOMO’s 5G networks and look forward to continued collaboration in advancing 5G innovation for their customers,” said Satoshi Iwao, Vice President and Head of Network Division at Samsung Electronics Japan. “Our goal is to leverage Samsung’s technical leadership to bring the best network solutions to mobile operators around the world, so they can deliver the next generation of transformative 5G services and electrifying user experiences.”
“The agreement between NTT DOCOMO and Samsung is significant,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President at Dell’Oro. “NTT DOCOMO has a history of being at the forefront with new and innovative technologies and this announcement cements Samsung’s position as a major 5G RAN supplier.”
Samsung says they have pioneered the successful delivery of 5G end-to-end solutions including chipsets, radios, and core. Through ongoing research and development, Samsung drives the industry to advance 5G networks with its market-leading product portfolio from fully virtualized RAN and Core to private network solutions and AI-powered automation tools. The company is currently providing connectivity to hundreds of millions of users around the world.
This is the latest in a series of recent contract awarded to Samsung. The company scored its biggest win when it received a $6.6 billion 5G contract from Verizon, replacing Nokia. It got a contract from Canada’s SaskTel earlier this month and is also in talks with European telecom operators to gain a foothold on the continent.
It is supplying 5G RAN to New Zealand’s Spark and last week announced it will be the sole 4G/5G core and RAN supplier to Sasktel. Samsung also supplies 5G RAN and core equipment to SK Telecom and KT in its home market.
NTT DoCoMo already has a broad slate of 5G vendors. Fujitsu supplies RAN equipment, NEC core and edge, Nokia baseband and Ericsson (a major supplier to rival KDDI) supplies RAN optimization. Six weeks after DoCoMo, a founding member of the O-RAN Alliance, unveiled its “5G Open RAN Ecosystem” aimed at “accelerating open RAN introduction to operators” worldwide. Members include NEC, Fujitsu, Mavenir, Intel and Qualcomm which are DoCoMo’s own team of preferred open RAN solution vendors.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://news.samsung.com/global/samsung-collaborates-with-ntt-docomo-on-5g
https://www.lightreading.com/asia/samsung-networks-lands-docomo-for-5g-open-ran/d/d-id/768255?
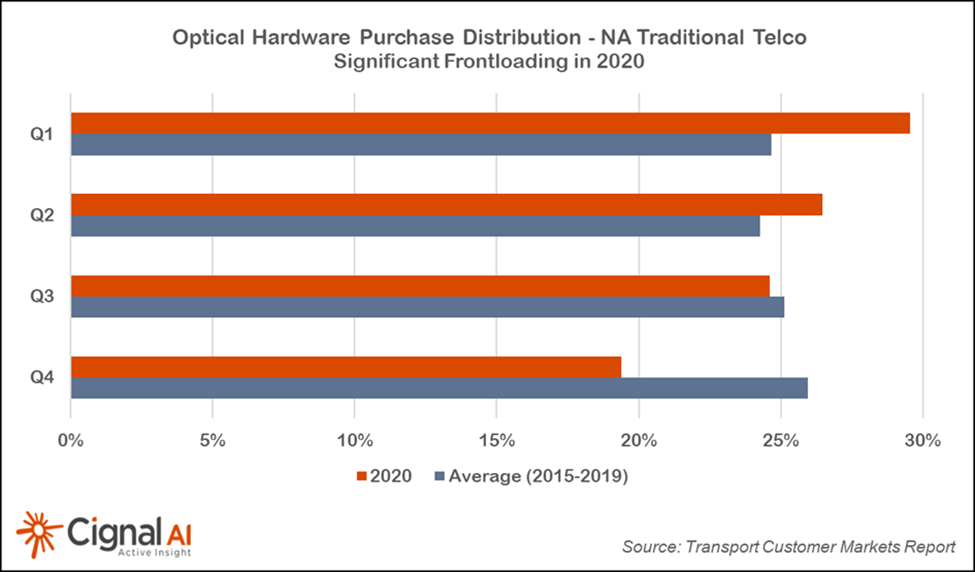
North American Cloud and Traditional Telco CapEx Drops in 4th Quarter 2020
Subhead: Exceptional 4Q Cloud & Colo Operator Spending in APAC
|
||||
 |
||||
More Key Findings from the 4Q20 Transport Customer Markets Report:
Separately, Cignal AI said on March 16th that Ciena’s revenue decline this quarter was steeper than forecast, but the company is poised to grow revenues based on the success of its WaveLogic 5e fifth generation coherent technology. On March 2nd, Cignal AI said that Infinera originally expected its ICE6 technology to enter the market in the second half of 2020. The company’s current guidance now indicates a 2H21 arrival. Infinera reports a strong order pipeline, but has not specified exactly when the first ICE6 will ship for revenue. About the Transport Customer Markets Report:
About Cignal AI:
References:https://cignal.ai/opteq-hw-dashboard/https://cignal.ai/free-articles/
|




