Author: Alan Weissberger
ITU World Radiocommunication Conference 2023 opens in Dubai, UAE
The World Radiocommunication Conference 2023 (WRC-23) opened today in Dubai, United Arab Emirates (UAE), bringing governments together for negotiations on the allocation of radio-frequency spectrum. Overall, 4,000 participants are expected for WRC-23, including delegates from ITU Member States and ITU Radiocommunication Sector Members representing international organizations, equipment manufacturers, network operators and industry forums attending as observers.
The conference, organized every three to four years by the ITU, will review and update the Radio Regulations, the international treaty governing the use of spectrum and geostationary and non-geostationary satellite orbits.
Much of the technology in everyday life uses radio-frequency spectrum allocated by ITU’s world radiocommunication conferences. Ensuring that the Radio Regulations reflect the changing demand for spectrum use is critical for the efficient operation of existing and future radiocommunication services and equipment.
“We are at an inflection point in tech history, and radiocommunications are at the top of the global agenda,” said Doreen Bogdan-Martin, ITU Secretary-General. “Equitably managed spectrum and the associated satellite orbits are among the best tools in our toolbox to make good on our commitment to build a digital future that works for everyone and for our planet.”
“While today’s world is full of challenges, this conference comes to set the course and direct the compass toward sustainable human development by updating the Radio Regulations and establishing international consensus on the frequencies necessary for the coming era,” said H.E. Eng. Majed Sultan Al Mesmar, Director General of the UAE Telecommunications and Digital Government Regulatory Authority (TDRA). “With the broad horizons it brings in the fields of smart cities, digital economy, knowledge society, space and others, we are confident that this conference will achieve the results that meet the expectations and aspirations of our peoples.”
“This conference will revise and update the Radio Regulations to support the introduction of new radio-based technologies, systems, technologies and services and their growing spectrum requirements while continuing to protect the vital radio services we rely on today,” said Mario Maniewicz, Director of ITU’s Radiocommunication Bureau. “Newer innovative technologies will allow us to better monitor our changing planet, and better connect communities and people everywhere: on land, at sea, in the air, and in space. I count on the spirit of cooperation of the ITU Membership and your technical expertise to make WRC-23 a resounding success and leave a legacy of prosperity for billions of people across the globe.”
The WRC-23 agenda items include:
- Identifying additional frequency bands for the continued development of International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT), including the use of high-altitude platform stations as IMT base stations for the universal deployment of wireless networks. This work will include the integration of satellites into 5G and 6G services. As noted by Via Satellite, there’s a WRC-23 agenda item to consider adding spectrum bands for phone-to-satellite communications.
- Improvements to the international regulatory framework for geostationary orbit (GSO) and non-geostationary orbit (NGSO) satellites while promoting equitable access for all countries.
- Use of satellite technologies for broadband services to improve connectivity, particularly in remote areas.
- New spectrum to enhance radiocommunications in the aeronautical mobile service, including by satellite, and to facilitate the use of the space research and Earth exploration-satellite services for climate monitoring, weather prediction and other scientific missions.
- The modernization of the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS).
- The regulatory framework for the use of earth stations in motion on board aircraft and ships for communication with GSO and NGSO satellites.
- The future of the ultra-high frequency (UHF) broadcasting band which has implications for television broadcast, programme-making and special events, as well as public protection and disaster relief.
- ITU-R Resolution 65 paves the way for “studies on the compatibility of current regulations with potential 6th generation IMT radio interface technologies for 2030 and beyond.”
A complete list of matters to be considered at WRC 23 is available here.
The Radio Regulations ensure that the use of the radio-frequency spectrum is rational, equitable, efficient, and economical – all while aiming to prevent harmful interference between different radiocommunication services.
The international treaty on radiocommunications dates back to 1906, when the International Radiotelegraph Convention was signed. In the 117 years since, the Radio Regulations have undergone 38 revisions and expanded to a four-volume agreement of more than 2,000 pages.
WRC-23 was preceded by the ITU Radiocommunication Assembly (RA-23) which met in Dubai from 13-17 November to establish the structure, working methods and program of the ITU Radiocommunication Sector.
Discussion highlights during RA-23:
- Agreement on “IMT-2030″ as the technical reference for the 6th generation of International Mobile Telecommunications;
- Revision of ITU-R Resolution 65, paving the way for studies on the compatibility of current regulations with potential 6th generation IMT radio interface technologies for 2030 and beyond;
- Adoption of the new Recommendation ITU-R M. 2160 on the “IMT-2030 Framework,” setting the basis for the development of IMT-2030. The next phase will be the definition of relevant requirements and evaluation criteria for potential radio interface technologies (RIT);
- Adoption of a new resolution on the use of IMT technologies for fixed wireless broadband;
- In accordance with Resolution 219 (Bucharest, 2022), adoption of a new resolution on space sustainability to facilitate the long-term sustainable use of radio-frequency spectrum and associated satellite orbit resources used by space services. This will be supportive of further cooperation with other United Nations organisations and beneficial to the satellite industry;
- Conclusion of a new ITU-R Recommendation on the protection of the radio navigation-satellite service and amateur satellite services;
- Revision of Resolution ITU-R 8-3 to promote the participation of engineers and scientists from developing countries in propagation campaigns in tropical and subtropical regions of the world for which there is limited data monitoring.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
About ITU:
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICTs), driving innovation in ICTs together with 193 Member States and a membership of over 900 companies, universities, and international and regional organizations. Established over 150 years ago, ITU is the intergovernmental body responsible for coordinating the shared global use of the radio spectrum, promoting international cooperation in assigning frequencies and, if necessary, associated satellite orbits, improving communication infrastructure in the developing world, and establishing the worldwide standards that foster seamless interconnection of a vast range of communications systems. From broadband networks to cutting-edge wireless technologies, aeronautical and maritime navigation, radio astronomy, oceanographic and satellite-based earth and oceanographic monitoring as well as converging fixed and mobile phone, Internet and broadcasting technologies, ITU is committed to connecting the world.
For more information, visit: www.itu.int
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.itu.int/en/mediacentre/Pages/PR-2023-11-20-WRC23-opening-ceremony.aspx
https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-r/opb/act/R-ACT-CPM-2023-PDF-E.pdf
https://techchannel.news/itu-sets-the-stage-for-the-development-of-6g/
Bell and FirstLight: 3 new wavelength routes with triple redundancy and speeds up to 400G b/sec
In partnership with FirstLight Fiber, Bell Canada announced new, unique wavelength data routes this week with speeds up to 400G b/sec with triple redundancy between Secaucus, NJ, Toronto, and Montreal, Canada. These data routes, enabling triversity, are expected to be available in Q1 of 2024.
According to the statement, Bell launched 400G wavelength technology in April 2021, delivering increased speeds and the capacity required for large cloud and data centre providers. The technology is said to offer reliable, secure fibre-optic networks for the transport of voice, data, and video.
Additionally, Bell noted that, as Secaucus, NJ is a major data centre hub experiencing growth and increased customer demand, this development will support the company in enhancing network resilience. This improvement addresses the needs of customers requiring connectivity between Canada and the US.
The new routes will terminate at Equinix’s data centre campus in Secaucus, facilitating traffic flow into the U.S. and strengthening the networks for Bell customers.
The introduction of new routes brings triversity to Secaucus, offering alternative connections without the need to pass through New York City for two key routes.
The first route originates in Toronto, directly connecting to Secaucus. The second route from Montreal to Secaucus travels via Albany, creating a diverse pathway. The third route, also from Montreal to Secaucus through the Maritimes, passes through Manhattan.
These routes not only enhance accessibility to Secaucus but also contribute to triversity in New York City. Alongside the existing routes to New York City, these new connections with diverse paths include Toronto to Secaucus to NYC, Montreal to NYC via Albany, and Montreal to NYC via the Maritimes.
Bell Canada said these new routes will fortify its extensive footprint, enabling faster and more reliable data transport between major hubs in Secaucus, Toronto, and Montreal.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“With continued growth in data demand, – particularly because of cloud technology and AI delivered by leading telecom networks like Bell Canada – we are excited to fortify Bell’s extensive footprint further with these new routes, which will enable faster and more reliable data transport between the major hubs in Secaucus, Toronto, and Montréal.”
– Ivan Mihaljevic, SVP, Bell Wholesale
“Given the vast amount of bandwidth we expect AI will require, coupled with the criticality of network resilience, we are delighted to work with Bell Canada to offer these unique routes that provide bandwidth up to 400G, diversely routed between Canada and the United States.”
– Patrick Coughlin, Chief Development Officer for FirstLight.
Bell is Canada’s largest communications company,1 providing advanced broadband wireless, TV, Internet, media, and business communication services throughout the country. Founded in Montréal in 1880, Bell is wholly owned by BCE Inc. To learn more, please visit Bell.ca or BCE.ca.
Through Bell for Better, we are investing to create a better today and a better tomorrow by supporting the social and economic prosperity of our communities. This includes the Bell Let’s Talk initiative, which promotes Canadian mental health with national awareness and anti-stigma campaigns like Bell Let’s Talk Day and significant Bell funding of community care and access, research, and workplace leadership initiatives throughout the country. To learn more, please visit Bell.ca/LetsTalk.
|
1 Based on total revenue and total combined customer connections. |
FirstLight, headquartered in Albany, New York, provides fibre-optic data, Internet, data center, cloud, unified communications, and managed services to enterprise and carrier customers throughout the Northeast and mid-Atlantic connecting more than 15,000 locations in service with more than 125,000 locations serviceable by our more than 25,000-route mile network. FirstLight offers a robust suite of advanced telecommunications products featuring a comprehensive portfolio of high bandwidth connectivity solutions including Ethernet, wavelength and dark fibre services as well as dedicated Internet access solutions, data center, cloud and voice services. FirstLight’s clientele includes national cellular providers and wireline carriers and many leading enterprises, spanning high tech manufacturing and research, hospitals and healthcare, banking and financial, secondary education, colleges and universities, and local and state governments FirstLight was named a Top Workplace USA in 2022 and 2023.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Bell Canada Announces New High-Speed Data Routes With FirstLight
Bell MTS Launches 3 Gbps Symmetrical Internet Service in Manitoba, Canada
Bell Canada deploys the first AWS Wavelength Zone at the edge of its 5G network
Bell Canada Partners selects Google Cloud to Deliver Next-Generation Network Experiences
AWS deployed in Digital Realty Data Centers at 100Gbps & for Bell Canada’s 5G Edge Computing
Bell Canada Announces Largest 5G Network in Canada
Orange France satellite Internet based on Eutelsat Konnect VHTS satellite
Orange France has expanded its range of connectivity offerings to include satellite Internet in its technology mix, alongside fiber, ADSL, 4G and 5G Home FWA. This new Satellite offering from Orange is aimed at customers who are not eligible for fiber and those with ADSL speeds of less than 8 Mbps. It is marketed through Orange’s distribution channels and operated by Nordnet, an Orange subsidiary company that has been specializing in satellite Internet for 15 years.
This offer is part of the French government’s Cohésion Numérique des Territoires (Digital Cohesion of Regions) program, and meets the government’s objective of guaranteeing access to superfast broadband (greater than 30 Mbps) for all by 2025.
Homes without good wired broadband can benefit from a subsidy to access a better connection via wireless technology.
An offer based on the expertise of the French and European space industry:
This offer is based on the Eutelsat Konnect VHTS satellite, designed by Thalès Alenia Space in Cannes and launched by on Ariane 5 in September 2022. Weighing 6.5 tons and measuring 9 meters in height, Eutelsat Konnect VHTS is the largest European satellite ever designed. It is part of the new generation of electric propulsion satellites [3] launched from the all-electric platform built by Spacebus NEO, with the financial support of the European Space Agency and the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (French Space Agency).
Konnect VHTS | Broadband Satellites | Eutelsat
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
For €49.99 per month (with the first month free), customers of this satellite offer can enjoy unlimited superfast broadband with a connection speed of up to 200 Mbps downstream and 15 Mbps upstream [1]. This offer requires no change of phone number and includes unlimited calls to landlines in mainland France and 50 other destinations [2] as well as calls to mobiles in mainland France and eight other destinations.
After subscribing, customers will receive a Satellite Kit, which they can install by themselves or with the help of Nordnet and its network of specialist installation partners. The Satellite Kit can be purchased for €299 or rented for €8/month. Nordnet’s installation kit option costs €299, with a one-year warranty.
Jean-François Fallacher, Executive Vice President, CEO Orange France: “The launch of Orange Satellite with Nordnet is another step towards the deployment of superfast broadband for everyone, everywhere in mainland France. At Orange, we’re proud to be able to offer all our customers a superfast broadband access solution thanks to our technology mix. Our range of connectivity offers now includes satellite, in addition to 4G and 5G Home, fiber and ADSL. This new offer responds to the needs of the French population, whatever their connectivity requirements, even in the most remote areas.”
NOTES:
[1] Offer in mainland France subject to eligibility. 12-month commitment. Maximum theoretical speeds. Details on orange.fr. €35 set-up fee & €15 equipment delivery fee
[2] List of destinations on nordnet.com
[3] The satellite’s environmental footprint is reduced thanks to its 100% electric propulsion, which is less polluting than previous propulsion systems using chemicals.
References:
https://newsroom.orange.com/orange-launches-its-satellite-offer/?lang=fr
https://www.eutelsat.com/en/satellites/2-7-east.html
Orange Business tests new 5G hybrid network service in France
AWS Integrated Private Wireless with Deutsche Telekom, KDDI, Orange, T-Mobile US, and Telefónica partners
Sony and NTT (with IOWN) collaborate on remote broadcast production platform
Sony and NTT are teaming up to develop a remote broadcast production platform that combines Sony’s video production products with NTT’s large-capacity, low-latency, wide-area network. The partnership aims to improve the customer experience by providing more content, such as content distribution at local stadiums and live music venues, which we have not been able to deliver due to cost.
The goal of this collaboration is to create a remote production platform that will:
- Reduce the costs associated with owning, operating and maintaining broadcasting equipment
- Expand video services
- Improve the customer experience
Playing a central role is NTT’s All-Photonics Network, a component of IOWN that incorporates new optical technologies at every level, from networks to devices, and even inside chips, to enable ultra-low power consumption, ultra-high-speed processing.
NTT’s IOWN—which is backed by companies including Sony, Intel, Microsoft, Cisco and others is being designed to enable ultra-high capacity (data processing of 125 times greater than networks today by volume), ultra-low latency (end-to-end latency reduced by over 200 times) and ultra-low power consumption (100 times more efficiency than transmissions today).
NTT released a new white paper highlighting the development of “Inclusive Core” architecture for the 6G/IOWN era. This architecture incorporates concepts such as In-Network Computing and Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) into the core network, reducing terminal processing load and protecting privacy for services used over the network. [Read the Full Release]
1. Background and purpose of the agreement
To achieve digital transformation of content production, broadcasters are gradually introducing IP compatible devices in order to develop flexible production and distribution environments for broadcasting facilities. In particular, when IP-enabled equipment is installed in a wide area, it is necessary to maintain a network that does not fluctuate in delays between sites to support efficient facility operation.
Considering this background, we will accelerate our research into technologies that combine Sony’s video production products and solutions with NTT’s large-capacity, low-latency, wide-area network. By forming a remote production platform, we aim to reduce the cost of owning, operating, and maintaining broadcasting equipment and improve the customer experience by expanding video services.
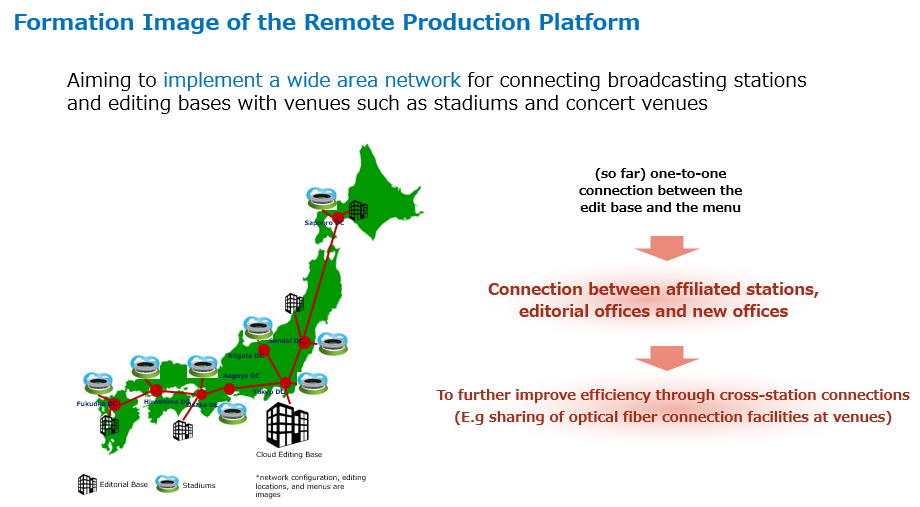
Figure 1 Formation image of the remote production platform
2. Technical elements of each company
Sony
Sony has set forth the concept of the next generation of broadcasting stations, in which the broadcasting facilities of each station are converted to IP and the cloud. Toward this realization, we will provide the next generation live production solutions, Networked Live [1]. Networked Live leverages resources on-premises, in the cloud, and in multiple locations to streamline workflows, provide agility and flexibility, and deliver high-quality live production. Mainly for broadcasters, we offer a range of products, including solutions for managing network resources en masse, switchers using on-premises cloud systems, codecs for efficient network bandwidth for media transmission, and support for remote production.
NTT
The technology development of the IOWN APN [2] enables the transparent transmission of IP capable devices over optical layer path connections via multi-device/multi-protocol. In addition, the ultra-high-capacity and end to end optical path connection enables 4K/8K class video communications to be communicated with low delay using uncompressed and lightly compressed transmission technology. Furthermore, communication without delay fluctuation enables high-quality synchronization between IP compatible devices using PTP [3]. In addition, we are aiming for an architecture that realizes strict availability requirements for video editing through high-speed line switching with optical path redundancy.

Figure 2. Research directions toward large-capacity wireless transmission
Source: NTT Technical Review (May 2019), “Toward Terabit-class Wireless Transmission: OAM Multiplexing Technology” https://www.ntt-review.jp/archive/ntttechnical.php?contents=ntr201905fa5.pdf&mode=show_pdf
3. Main areas of cooperation and collaboration
- Study on establishment and management of network environment using IOWN and Networked Live
- Study on technology and environment construction for IOWN and Networked Live
- Study on IOWN and Networked Live compared to existing networked systems
- Study on extending environments based on future IOWN and Networked Live capabilities
4. Outlook
Under this agreement, the two sides will cooperate to discuss the formation of a wide-area remote production platform while exchanging information and opinions on matters to be promoted together with the parties concerned in the cooperative agreement.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1]For details on “Networked Live,” visit: https://www.sony.jp/nxl/about/
[2]IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network) is a network and information processing infrastructure including terminals that can provide high-speed, large-capacity communications and vast computational resources utilizing innovative technologies, including light. The IOWN consists of three main components: the APN (All Photonics Network), which enables not only networks but also terminal processing; the DTC (Digital Twin Computing), which enables advanced and real-time interaction between objects and humans in cyberspace; and the Cognitive Foundation, which efficiently deploys various ICT resources including these. IOWN will contribute to the realization of a prosperous society by creating a variety of services and new value in a wide range of fields, not only in the telecommunications field. For details, visit: https://www.rd.ntt/e/iown/
[3]PTP (Precision Time Protocol) is a technology that achieves time synchronization with high precision. A time stamp is embedded in a dedicated time synchronization packet, and this packet is exchanged between systems to synchronize both times.
About NTT:
NTT contributes to a sustainable society through the power of innovation. We are a leading global technology company providing services to consumers and business as a mobile operator, infrastructure, networks, applications, and consulting provider. Our offerings include digital business consulting, managed application services, workplace and cloud solutions, data center and edge computing, all supported by our deep global industry expertise. We are over $95B in revenue and 330,000 employees, with $3.6B in annual R&D investments. Our operations span across 80+ countries and regions, allowing us to serve clients in over 190 of them. We serve over 75% of Fortune Global 100 companies, thousands of other enterprise and government clients and millions of consumers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://group.ntt/en/newsrelease/2023/11/13/231113a.html
https://group.ntt/en/newsrelease/2023/10/25/pdf/231025aa.pdf
https://www.rd.ntt/e/ns/inclusivecore/whitepaper_ver1.html
NTT pins growth on IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network)
NTT to offer optical technology-based next-generation network services under IOWN initiative; 6G to follow
U.S. Launches National Spectrum Strategy and Industry Reacts
The U.S. Dept of Commerce has finally published a National Spectrum Strategy that could pave the way for 2,786MHz of frequencies to be repurposed for new use. That is nearly double NTIA’s initial target of 1,500 megahertz.
The frequencies in question, across five bands, will be studied for potential new uses, and the study could go either way. The next step will see the Biden-Harris administration develop and publish an Implementation Plan.
The spectrum target includes more than 1,600 megahertz of midband spectrum – a frequency range in high demand by the wireless industry for next-generation services.
As required by the Presidential Memorandum titled Modernizing United States Spectrum Policy and Establishing a National Spectrum Strategy, the Secretary of Commerce, through the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA), prepared this National Spectrum Strategy to both promote private-sector innovation and further the missions of federal departments and agencies, submitting it to the President through the Assistant to the President for National Security Affairs, the Assistant to the President for Economic Policy, and the Director of the Office of Science and Technology Policy.
The Strategy reflects collaboration with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), recognizing the FCC’s unique responsibilities with respect to non-Federal uses of spectrum, and coordination with other Federal departments and agencies (referred to collectively here as “agencies”).
The NTIA will study the following bands in the next two years, noting that the spectrum could support a range of uses, including mobile broadband (IMT), drones and satellite operations:
- 3.1 GHz-3.45 GHz
- 5.03 GHz-5.091 GHz
- 7.125 GHz-8.4 GHz
- 18.1 GHz-18.6 GHz
- 37.0 GHz-37.6 GHz
Note that for terrestrial IMT (3G, 4G, 5G), the only one of the above frequencies approved by ITU-R Radio Regulations in ITU-R M.1036 is 3.3 GHz-to-3.7 GHz frequency range. Please refer to my Comment in the box below this post.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The goals of the Spectrum Strategy are to: drive technological innovation (including innovative spectrum sharing technologies); boost U.S. industrial competitiveness; protect the security of the American people; foster scientific advancements; promote digital equity and inclusion; and maintain U.S. leadership in global markets for wireless equipment and services, as well as innovative spectrum-sharing technologies. Dynamic spectrum sharing will be part of the plan.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Industry Reactions to the Strategy:
“It is a critical first step, and we fully support their goal of making the 7/8 GHz band available for 5G wireless broadband and their decision to re-study all options for future full-power commercial access to the lower 3 GHz band,” said Meredith Attwell Baker, president and CEO of industry body the CTIA. “In order to meet growing consumer demand for 5G, close America’s widening 5G spectrum deficit and counter China’s global ambitions, America’s wireless networks need 1500 MHz of additional full power, licensed spectrum within the next ten years. Failure to make this spectrum available risks America’s economic competitiveness and national security,” Attwell Baker added.
“The plan released today will secure our digital future by eliminating the structural problems that hold back U.S. wireless innovation,” added Harold Feld, senior vice president of consumer advocacy group Public Knowledge.
“For six years, the United States has lacked a comprehensive spectrum strategy,” he said. “This lack of a national plan has created increasing tensions between the FCC’s efforts to meet our ever-expanding need for wireless capacity and federal agencies trying to carry out vital missions from weather forecasting to national security. These tensions, in turn, have compromised our ability to develop new wireless technologies and undermined our ability to maintain global leadership.”
“We hope this reallocation will help correct the midband spectrum imbalance that currently prioritizes unlicensed and federal uses – a disparity that fails to meet Americans’ ever-accelerating demand for mobile connectivity and neglects licensed spectrum’s place as the foundation of our wireless ecosystem,” AT&T’s Rhonda Johnson, EVP of federal regulatory relations, said.
“We don’t think the events of today should be thought of as anyone scoring a touchdown, but rather, moving the ball from one’s own 20-yard line to the opponents’ 40,” summarized the financial analysts at New Street Research in a note to investors Monday.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Light Reading’s Mike Dano had 5 takeaways from NTIA’s Spectrum plan:
1. It’s evolutionary, not revolutionary.
2. It’s pretty boring.
3. It makes no clear decision on the lower 3GHz band.
4. Sharing, and other spectrum management technologies, are encouraged.
5. 6G is mentioned, but only obliquely.
References:
https://www.ntia.gov/issues/national-spectrum-strategy
https://telecoms.com/524821/us-spectrum-plan-eases-frequency-frustrations-to-an-extent/
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/five-takeaways-from-biden-s-new-national-spectrum-strategy
https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/information/Pages/emergency-bands.aspx
Gartner Forecast: Worldwide Public Cloud End-User Spending ~$679 Billion in 2024; GenAI to Support Industry Cloud Platforms
Worldwide end-user spending on public cloud services is forecast to grow 20.4% to total $678.8 billion in 2024, up from $563.6 billion in 2023, according to the latest forecast from Gartner, Inc.
“Cloud has become essentially indispensable,” said Sid Nag, Vice President Analyst at Gartner. “However, that doesn’t mean cloud innovation can stop or even slow. The tables are turning for cloud providers as cloud models no longer drive business outcomes, but rather, business outcomes shape cloud models.”
“For example, organizations deploying generative AI (GenAI) services will look to the public cloud, given the scale of the infrastructure required. However, to deploy GenAI effectively, these organizations will require cloud providers to address nontechnical issues related to cost, economics, sovereignty, privacy and sustainability.
Hyperscalers that support these needs will be able to capture a brand-new revenue opportunity as GenAI adoption grows.” All segments of the cloud market are expected see growth in 2024. Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) is forecast to experience the highest end-user spending growth in 2024 at 26.6%, followed by platform-as-a-service (PaaS) at 21.5% (see Table 1).
Table 1. Worldwide Public Cloud Services End-User Spending Forecast (Millions of U.S. Dollars)
| 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| Cloud Application Infrastructure Services (PaaS) | 119,579 | 145,320 | 176,493 |
| Cloud Application Services (SaaS) | 174,416 | 205,221 | 243,991 |
| Cloud Business Process Services (BPaaS) | 61,557 | 66,339 | 72,923 |
| Cloud Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS) | 2,430 | 2,784 | 3,161 |
| Cloud System Infrastructure Services (IaaS) | 120,333 | 143,927 | 182,222 |
| Total Market | 478,315 | 563,592 | 678,790 |
BPaaS = business process as a service; IaaS = infrastructure as a service; PaaS = platform as a service; SaaS = software as a service
Note: Totals may not add up due to rounding.
Source: Gartner (November 2023)

……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Another key trend driving cloud spending is the continued rise of industry cloud platforms. Industry cloud platforms address industry-relevant business outcomes by combining underlying software-as-a-service (SaaS), PaaS and IaaS services into a whole-product offering with composable capabilities. Gartner predicts that by 2027, more than 70% of enterprises will use industry cloud platforms to accelerate their business initiatives, up from less than 15% in 2023.
“GenAI adoption will also support the growth in industry cloud platforms,” said Nag. “GenAI models that are applicable across diverse industry verticals might require significant customization, affecting scalability and cost-effectiveness. Public cloud providers can position themselves as partners in the responsible and tailored adoption of GenAI by building on the same approaches applied to industry clouds, sovereign clouds and distributed clouds.”
Gartner previously forecast that Public Cloud services spending to hit $1.35 trillion in 2027. The U.S. will be the largest geographic public cloud market and will reach $697 billion in 2027. Western Europe is predicted to be in second place with $273 billion, followed by China at $117 billion in 2027. IDC forecasts that software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications to be the largest cloud computing category, garnering about 40% of all public cloud spending. Next largest is infrastructure as a service (IaaS) with a CAGR of 23.5%, followed by platform as a service (PaaS) with a five-year CAGR of 27.2%.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS51179523
IDC: Public Cloud services spending to hit $1.35 trillion in 2027
Gartner: Public Cloud End-User Spending to approach $500B in 2022; $600B in 2023
Gartner: Global public cloud spending to reach $332.3 billion in 2021; 23.1% YoY increase
Gartner clients can learn more in “Forecast: Public Cloud Services, Worldwide, 2021-2027, 3Q23 Update.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Gartner IT Infrastructure, Operations & Cloud Strategies Conference:
Gartner analysts will provide additional analysis on cloud strategies and infrastructure and operations trends at the Gartner IT Infrastructure, Operations & Cloud Strategies Conferences taking place November 20-21 in London, December 6-8 in Las Vegas and December 12-13 in Tokyo. Follow news and updates from these conferences on X using #GartnerIO.
About Gartner for High Tech:
Gartner for High Tech equips tech leaders and their teams with role-based best practices, industry insights and strategic views into emerging trends and market changes to achieve their mission-critical priorities and build the successful organizations of tomorrow. Additional information is available at www.gartner.com/en/industries/high-tech.
Co-Packaged Optics to play an important role in data center switches
The commercialization of co-packaged optics (CPO) has been long anticipated but is becoming increasingly desirable as data needs accelerate. Co-Packaged Optics are an advanced heterogeneous integration of optics and silicon on a single packaged substrate aimed at addressing next generation bandwidth and power challenges.
As the bandwidth of data center switches increases, a disproportionate amount of power is becoming dedicated to the switch – optics interface. Reducing the physical separation between these two components by co-packaging enables system power savings which is essential to continued bandwidth scaling.
CPO brings together a wide range of expertise in fiber optics, digital signal processing (DSP), switch ASICs, and state-of-the-art packaging and test to provide disruptive system value for the data center and cloud infrastructure.
The companies and institutions working on CPO have made great strides in developing suitable electronic components. But hundreds of meters of fiber will be packed into the switch box for the first time, and faceplate connections will have unprecedented densities. As a result, the design and development of optical system solutions will also be critical elements in the success of CPO. Optical components with performance tailored to the CPO application and effective solutions for managing the fiber in the switch box are vital in optimizing the complete optical system. Three aspects of CPO deployment, in particular, hinge on the properties of the fiber and the optical interfaces: optical power loss, the trade-off between minimizing bend loss and controlling for MPI and maintaining the polarization state if external lasers are used.
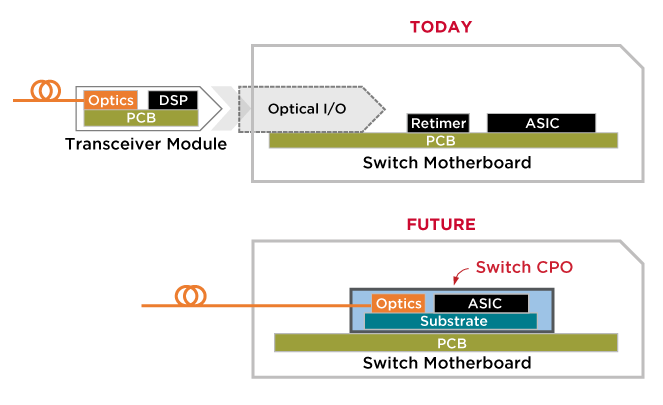
Image Courtesy of Broadcom
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Data centers face substantial challenges as they scale, particularly in reducing power dissipation and cost per bit. CPO will play a significant role in helping to meet those challenges. In today’s data center switches, external fiber optic connections that carry data terminate on pluggable transceivers on the housing faceplate. The optical data stream is coupled to the electrical signals at that interface.

With a CPO realization of a 51.2 Tbps switch, the substrate connects a central regulator ASIC to 16 optoelectronic (O/E) tiles on the substrate perimeter. These tiles are connected to optical fiber signal cables that run to the switch box faceplate and receive power from external lasers that they modulate to produce the outgoing optical signal stream.
They communicate between the transceiver and the switch application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) via copper traces on printed circuit boards. Under the CPO paradigm, as the optoelectronic conversion is pushed back from the faceplate to the switch substrate, long electrical traces are replaced with virtually loss-free optical fiber.
With CPO, the fiber path continues past a connector at the faceplate and into the switch box, ending at photonic integrated circuits (PICs) on optical tiles attached to the switch substrate. This shift presents the novel challenge of routing and connecting hundreds of optical fibers within a compact and crowded space, creating a need to minimize the footprint of the optics while still achieving performance and reliability targets.
CPO will soon be a reality that relies on a system of complex, interconnected components working well together. For optimum overall performance, these components must be designed with the specific requirements of CPO in mind, which for the optical subsystem include efficient and unobtrusive deployment within a crowded switch box, low power losses, absence of MPI impairments, and good reliability. Some CPO realizations also need optical polarization state control.
The familiar fiber and connectivity products, while having impressive attributes, are not optimum for the CPO application, and there is great scope for enhancing the performance of the optics by moving beyond default solutions to those specifically designed for the role.
References:
https://www.broadcom.com/info/optics/cpo
Coherent Optics: Synergistic for telecom, Data Center Interconnect (DCI) and inter-satellite Networks
Heavy Reading: Coherent Optics for 400G transport and 100G metro edge
ABI Research: Telco transformation measured via patents and 3GPP contributions; 5G accelerating in China
Every single telecom operator in the world is now attempting to transform from telco to techco, to break free from their antiquated, legacy, and stale connectivity business and evolve to sell technology platforms, a considerably more lucrative and promising business. Their success is not guaranteed, and many find it difficult – if not impossible – to unshackle themselves from their history and comfort zone.
ABI Research now says it’s measuring the progress of telco transformation by quantifying the number of patents that telcos hold and also measuring their involvement in standards-setting initiatives like 3GPP (whose specs are standardized by ETSI and ITU-R).
Telecom operators from China and Japan are currently at the forefront of technology transformation, which shows in their involvement in 3GPP and patent holdings,” says Dimitris Mavrakis, Senior Research Director at ABI Research. “China Mobile, NTT Docomo, and China Telecom have invested time, effort, and capital in both domains, which now translates to significant expertise, knowledge, and recognition in the industry. Although this is not the only metric for innovation, these leading network operators are well suited to transforming their business, technology, and strategic platforms to look to the future.”
The findings of the latest ABI Research report on telecom operator innovation indicate that they consistently contribute to 3GPP work, approximately 8% of the total contribution. Of these telecom operator contributions to 3GPP, 43% originate from China, 29% from Japan, 14% from Europe, and 12% from the United States. Leading operators are China Mobile, NTT Docomo, China Telecom, Orange, Vodafone, and Deutsche Telekom. Their Standards Essential Patent (SEP) holdings are similar, with China Mobile and NTT Docomo leading the market.
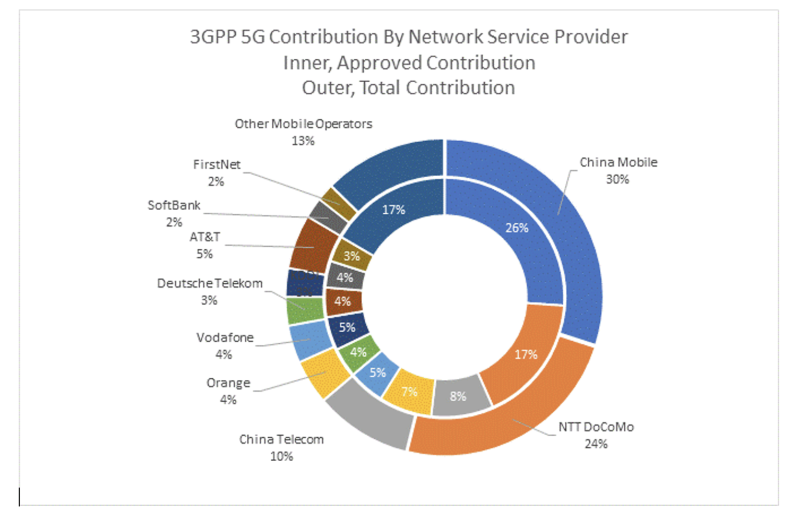
Standards contributions and patent holdings are good measures of willingness to innovate and get involved in leading the market. “Telecom operators must get involved and not let other companies lead the direction of the market – especially when geopolitics and semiconductor supply constraints are affecting the market. With 5G Advanced and upcoming 6G, they have the technology to innovate, but they must now take more risks and lead the market,” Mavrakis concludes.
Fierce Wireless asked why T-Mobile didn’t rank, given the good progress that it’s made with its 5G SA network and network slicing trials. Mavrakis said, “T-Mobile US is part of Deutsche Telekom, which is represented in the chart above. They are indeed making progress toward network slicing, but our report measures 3GPP standards activities and patents, which is a different area of innovation.”
These findings are from ABI Research’s Telco versus Techco: Operators’ Role in Shaping Cellular Innovation and 3GPP Standards application analysis report. This report is part of the company’s Cellular Standards & IPR research service, which includes research, data, and ABI Insights. Based on extensive primary interviews, Application Analysis reports present in-depth analysis on key market trends and factors for a specific application, which could focus on an individual market or geography.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, ABI Research says 5G end-user services deployment continue to accelerate in China, which is very much leaving other markets in its wake. Not only does it have 3.2 million 5G base stations up and running, but also a wide range of 5G-to-Business (5GtoB) applications.
According to China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), the country has built or upgraded more than 3.2 million 5G base stations—accounting for 30% of the overall mobile base stations nationwide—which has already exceeded the initial target of deploying 2.9 million 5G base stations by the end of 2023. A fourth mobile operator, China Broadnet, has also been issued a 5G mobile cellular license to help stimulate consumer and enterprise competition.
5G subscriber adoption has been robust. At the end of 1Q 2023, the number of 5G subscriptions in the country had increased to around 1.3 billion, which is an increase of more than 53% from approximately 850 million 5G subscribers as of March 2022. The China Telecom Research Institute reported that the average download speed for 5G is a very robust 340 Megabits per Second (Mbps).
China’s mobile operators have seen an overall increase in service revenue. China Mobile reported an 8.1% Year-over-Year (YoY) increase in telecommunication service revenue, with mobile Average Revenue per User (ARPU) up 0.4% to CNY49 (US$6.9). China Telecom also reported a 3.7% YoY increase in mobile communications service revenue with mobile ARPU up 0.4% to CNY45.2 (US$6.3), whereas China Unicom saw a 3-year consecutive growth in mobile ARPU to CNY44.3 (US$6.2).
Growth in revenue has been primed by an expansion in revenue models the telcos can offer. Revenue for China Mobile’s 5G private networks also saw an increase of 107.4% YoY growth, reaching RMB2.55 billion (US$365.5 million) by December 2022. Meanwhile, China Unicom experienced a spike in 5G industry virtual private network customers from 491 to 5,816 between June 2022 and June 2023. Across the board, the three operators have collectively reached a cumulative total of more than 49,000 5G commercial enterprise projects, with China’s MIIT reporting that the operators have built more than 6,000 5G private networks, to date.
China’s mobile cellular ecosystem is not resting on its laurels. Urged on by China’s government, the sector has been embracing 5G-Advanced, as underpinned by The 3rd Generation Partnership Project’s (3GPP) Release 18. Included in Release 18 are greater support for Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration, 10 Gigabits per Second (Gbps) for peak downlink and 1 Gbps for peak uplink experience, supporting a wider range of Internet of Things (IoT) scenarios, and integrated sensing & communication. Information gathered through sensors can enable communication to be more deterministic, which improves the accuracy of channel conditions assessment. Another example is dynamic beam alignment for vehicle communications using Millimeter Wave (mmWave). China’s mobile operators and vendors are keen to adopt 5G-Advanced due to its ability to support a 10X densification of IoT devices compared to 5G. There is also support for passive 5G IoT devices that can be queried by campus and/or indoor small cells to provide telemetry-related data. Instead of a field or warehouse worker, or even an Autonomous Guided Vehicle (AGV) with a portable Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) reader, the campus cellular network can track asset tags in real time and remotely—eliminating the need to check up and down warehouse aisles individually.
5G-Advanced (not yet standardized) deployments are materializing in China. China Mobile Hangzhou launched its Dual 10 Gigabit City project in early 2023. This project focuses on using 5G-Advanced technologies to support applications such as glasses-free Three-Dimensional (3D) experiences on different devices during the Asian Games. Such early experimental projects are not limited to only one city in China. To the northeast of Hangzhou, China Mobile Shanghai has also started its own project to build the first 5G-Advanced intelligent 10 Gigabit Everywhere City (10 GbE City). The network is built using the 2.6 Gigahertz (GHz) network initially for the main urban areas before expanding the coverage to the entirety of Shanghai.
5G deployment, integration, and usage is accelerating. The China Academy of Information and Communications Technology anticipates that US$232 billion will have been invested in 5G by 2025. An additional US$37.9 billion (RMB3.5 trillion) of investment will also take place in the upstream and downstream segments of the industrial chain. During a 2023 Science and Technology Week and Strategic Emerging Industries Co-creation and Development Conference, MIIT stated that 5G connectivity has been integrated into “60 out of 97 national economic categories, covering over 12,000 application themes.” ABI Research has not verified all the use cases reported by MIIT, but ABI Research’s ongoing research into the 5G-to-Business (5GtoB) market in Asia has validated that there are a wide range of 5GtoB trials, pilots, and commercial rollouts taking place in China.
A further ABI Insight that you may find interesting is “China Telecom Is the First Operator Worldwide to Launch a “Device-to-Device” Service on a Smartphone to Improve Coverage.”
About ABI Research:
ABI Research is a global technology intelligence firm delivering actionable research and strategic guidance to technology leaders, innovators, and decision makers around the world. Our research focuses on the transformative technologies that are dramatically reshaping industries, economies, and workforces today.
References:
https://www.fiercewireless.com/5g/abi-research-praises-china-mobile-ntt-docomo-5g-innovation
6th Digital China Summit: China to expand its 5G network; 6G R&D via the IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group
ABI Research: 5G Network Slicing Market Slows; T-Mobile says “it’s time to unleash Network Slicing”
ABI Research: Expansion of 5G SA Core Networks key to 5G subscription growth
ABI Research: Major contributors to 3GPP; How 3GPP specs become standards
ABI Research: 5G-Advanced (not yet defined by ITU-R) will include AI/ML and network energy savings
Proposed solutions to high energy consumption of Generative AI LLMs: optimized hardware, new algorithms, green data centers
Introduction:
Many generative AI tools rely on a type of natural-language processing called large language models (LLMs) to first learn and then make inferences about languages and linguistic structures (like code or legal-case prediction) used throughout the world. Some companies that use LLMs include: Anthropic (now collaborating with Amazon), Microsoft, OpenAI, Google, Amazon/AWS, Meta (FB), SAP, IQVIA. Here are some examples of LLMs: Google’s BERT, Amazon’s Bedrock, Falcon 40B, Meta’s Galactica, Open AI’s GPT-3 and GPT-4, Google’s LaMDA Hugging Face’s BLOOM Nvidia’s NeMO LLM.
The training process of the Large Language Models (LLMs) used in generative artificial intelligence (AI) is a cause for concern. LLMs can consume many terabytes of data and use over 1,000 megawatt-hours of electricity.
Alex de Vries is a Ph.D. candidate at VU Amsterdam and founder of the digital-sustainability blog Digiconomist published a report in Joule which predicts that current AI technology could be on track to annually consume as much electricity as the entire country of Ireland (29.3 terawatt-hours per year).
“As an already massive cloud market keeps on growing, the year-on-year growth rate almost inevitably declines,” John Dinsdale, chief analyst and managing director at Synergy, told CRN via email. “But we are now starting to see a stabilization of growth rates, as cloud provider investments in generative AI technology help to further boost enterprise spending on cloud services.”
Hardware vs Algorithmic Solutions to Reduce Energy Consumption:
Roberto Verdecchia is an assistant professor at the University of Florence and the first author of a paper published on developing green AI solutions. He says that de Vries’s predictions may even be conservative when it comes to the true cost of AI, especially when considering the non-standardized regulation surrounding this technology. AI’s energy problem has historically been approached through optimizing hardware, says Verdecchia. However, continuing to make microelectronics smaller and more efficient is becoming “physically impossible,” he added.
In his paper, published in the journal WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, Verdecchia and colleagues highlight several algorithmic approaches that experts are taking instead. These include improving data-collection and processing techniques, choosing more-efficient libraries, and improving the efficiency of training algorithms. “The solutions report impressive energy savings, often at a negligible or even null deterioration of the AI algorithms’ precision,” Verdecchia says.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Another Solution – Data Centers Powered by Alternative Energy Sources:
The immense amount of energy needed to power these LLMs, like the one behind ChatGPT, is creating a new market for data centers that run on alternative energy sources like geothermal, nuclear and flared gas, a byproduct of oil production. Supply of electricity, which currently powers the vast majority of data centers, is already strained from existing demands on the country’s electric grids. AI could consume up to 3.5% of the world’s electricity by 2030, according to an estimate from IT research and consulting firm Gartner.
Amazon, Microsoft, and Google were among the first to explore wind and solar-powered data centers for their cloud businesses, and are now among the companies exploring new ways to power the next wave of AI-related computing. But experts warn that given their high risk, cost, and difficulty scaling, many nontraditional sources aren’t capable of solving near-term power shortages.
Exafunction, maker of the Codeium generative AI-based coding assistant, sought out energy startup Crusoe Energy Systems for training its large-language models because it offered better prices and availability of graphics processing units, the advanced AI chips primarily produced by Nvidia, said the startup’s chief executive, Varun Mohan.
AI startups are typically looking for five to 25 megawatts of data center power, or as much as they can get in the near term, according to Pat Lynch, executive managing director for commercial real-estate services firm CBRE’s data center business. Crusoe will have about 200 megawatts by year’s end, Lochmiller said. Training one AI model like OpenAI’s GPT-3 can use up to 10 gigawatt-hours, roughly equivalent to the amount of electricity 1,000 U.S. homes use in a year, University of Washington research estimates.
Major cloud providers capable of providing multiple gigawatts of power are also continuing to invest in renewable and alternative energy sources to power their data centers, and use less water to cool them down. By some estimates, data centers account for 1% to 3% of global electricity use.
An Amazon Web Services spokesperson said the scale of its massive data centers means it can make better use of resources and be more efficient than smaller, privately operated data centers. Amazon says it has been the world’s largest corporate buyer of renewable energy for the past three years.
Jen Bennett, a Google Cloud leader in technology strategy for sustainability, said the cloud giant is exploring “advanced nuclear” energy and has partnered with Fervo Energy, a startup beginning to offer geothermal power for Google’s Nevada data center. Geothermal, which taps heat under the earth’s surface, is available around the clock and not dependent on weather, but comes with high risk and cost.
“Similar to what we did in the early days of wind and solar, where we did these large power purchase agreements to guarantee the tenure and to drive costs down, we think we can do the same with some of the newer energy sources,” Bennett said.
References:
https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/large-language-model/
https://spectrum.ieee.org/ai-energy-consumption
https://www.crn.com/news/cloud/microsoft-aws-google-cloud-market-share-q3-2023-results/6
Amdocs and NVIDIA to Accelerate Adoption of Generative AI for $1.7 Trillion Telecom Industry
SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom to Jointly Develop Telco-specific Large Language Models (LLMs)
AI Frenzy Backgrounder; Review of AI Products and Services from Nvidia, Microsoft, Amazon, Google and Meta; Conclusions
Amdocs and NVIDIA to Accelerate Adoption of Generative AI for $1.7 Trillion Telecom Industry
Amdocs and NVIDIA today announced they are collaborating to optimize large language models (LLMs) to speed adoption of generative AI applications and services across the $1.7 trillion telecommunications and media industries.(1)
Amdocs and NVIDIA will customize enterprise-grade LLMs running on NVIDIA accelerated computing as part of the Amdocs amAIz framework. The collaboration will empower communications service providers to efficiently deploy generative AI use cases across their businesses, from customer experiences to network provisioning.
Amdocs will use NVIDIA DGX Cloud AI supercomputing and NVIDIA AI Enterprise software to support flexible adoption strategies and help ensure service providers can simply and safely use generative AI applications.
Aligned with the Amdocs strategy of advancing generative AI use cases across the industry, the collaboration with NVIDIA builds on the previously announced Amdocs-Microsoft partnership. Service providers and media companies can adopt these applications in secure and trusted environments, including on premises and in the cloud.
With these new capabilities — including the NVIDIA NeMo framework for custom LLM development and guardrail features — service providers can benefit from enhanced performance, optimized resource utilization and flexible scalability to support emerging and future needs.
“NVIDIA and Amdocs are partnering to bring a unique platform and unmatched value proposition to customers,” said Shuky Sheffer, Amdocs Management Limited president and CEO. “By combining NVIDIA’s cutting-edge AI infrastructure, software and ecosystem and Amdocs’ industry-first amAlz AI framework, we believe that we have an unmatched offering that is both future-ready and value-additive for our customers.”
“Across a broad range of industries, enterprises are looking for the fastest, safest path to apply generative AI to boost productivity,” said Jensen Huang, founder and CEO of NVIDIA. “Our collaboration with Amdocs will help telco service providers automate personalized assistants, service ticket routing and other use cases for their billions of customers, and help the telcos analyze and optimize their operations.”
Amdocs counts more than 350 of the world’s leading telecom and media companies as customers, including 27 of the world’s top 30 service providers.(2) With more than 1.7 billion daily digital journeys, Amdocs platforms impact more than 3 billion people around the world.
NVIDIA and Amdocs are exploring a number of generative AI use cases to simplify and improve operations by providing secure, cost-effective and high-performance generative AI capabilities.
Initial use cases span customer care, including accelerating customer inquiry resolution by drawing information from across company data. On the network operations side, the companies are exploring how to proactively generate solutions that aid configuration, coverage or performance issues as they arise.
(1) Source: IDC, OMDIA, Factset analyses of Telecom 2022-2023 revenue.
(2) Source: OMDIA 2022 revenue estimates, excludes China.
Editor’s Note:
- Language models: These models, like OpenAI’s GPT-3, generate human-like text. One of the most popular examples of language-based generative models are called large language models (LLMs).
- Large language models are being leveraged for a wide variety of tasks, including essay generation, code development, translation, and even understanding genetic sequences.
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs): These models use two neural networks, a generator, and a discriminator.
- Unimodal models: These models only accept one data input format.
- Multimodal models: These models accept multiple types of inputs and prompts. For example, GPT-4 can accept both text and images as inputs.
- Variational autoencoders (VAEs): These deep learning architectures are frequently used to build generative AI models.
- Foundation models: These models generate output from one or more inputs (prompts) in the form of human language instructions.
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/glossary/data-science/generative-ai/
https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2023/01/26/what-are-large-language-models-used-for/
Cloud Service Providers struggle with Generative AI; Users face vendor lock-in; “The hype is here, the revenue is not”
Global Telco AI Alliance to progress generative AI for telcos
Bain & Co, McKinsey & Co, AWS suggest how telcos can use and adapt Generative AI
Generative AI Unicorns Rule the Startup Roost; OpenAI in the Spotlight
Generative AI in telecom; ChatGPT as a manager? ChatGPT vs Google Search
Generative AI could put telecom jobs in jeopardy; compelling AI in telecom use cases




