IEEE SCV March 28th Event: A Conversation with IEEE President and IEEE Region 6 Director Elect
A Conversation with IEEE President and IEEE Region 6 Director Elect
Time/Date: 5pm-7:30pm March 28, 2024
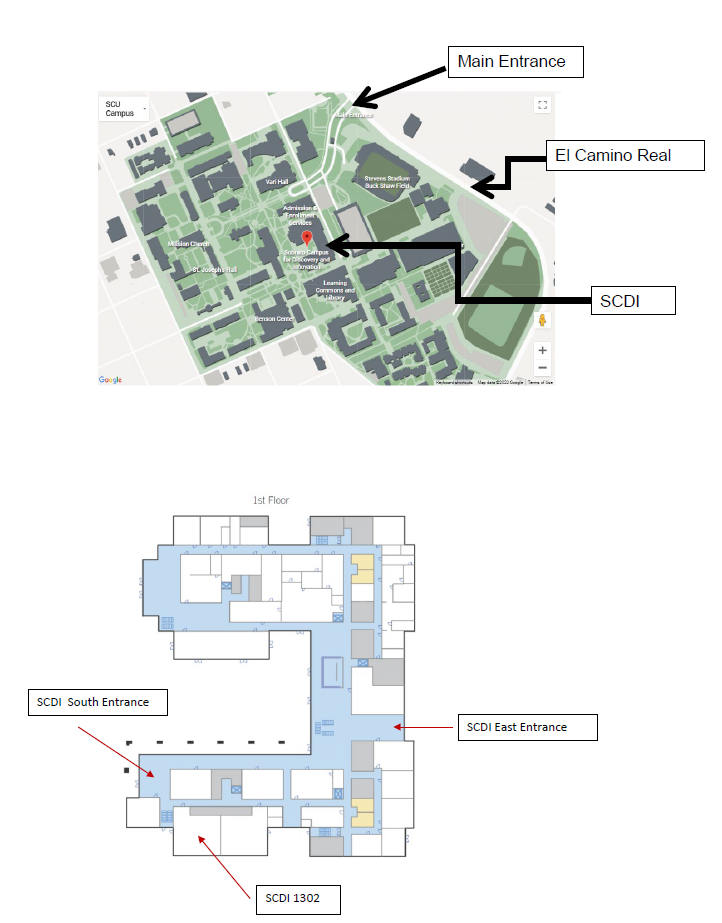
Venue: Santa Clara University Room SCDI 1302 & 1308 (see map for room location)
Register at: https://events.vtools.ieee.org/m/410534
Abstract:
Please join us for a lively and enlightening conversation with IEEE President Tom Coughlin and IEEE Region 6 Director Elect Joseph Wei, moderated by Alan J Weissberger. We will discuss and debate how to make IEEE more relevant to its members, explore volunteer opportunities, ways to elevate the awareness and perception of IEEE as the world’s largest tech non-profit organization.
In the past decade, IEEE membership has significantly declined, there are fewer volunteers, and many IEEE initiatives (e.g. 5G, cloud computing, IoT and smart grid) have fizzled. IEEE Conferences and Journals are now dominated by academia and for the most part are not of interest to industry as the content is not realizable and has little or no practical value. Many engineers, sales and marketing people think that IEEE is irrelevant and won’t help them advance their careers. Clearly, IEEE has been in a severe decline for several years.
How can we turn that around? Can IEEE provide better tools and support for the active volunteers and to grow its professional membership while encouraging student members to upgrade to full membership? How can we retain, encourage and train younger members to volunteer for officer positions and provide fresh leadership? Can we find a more equitable balance between industry and academia for IEEE conferences, publications, and local chapters? What are the important, high priority tech initiatives that IEEE should focus on to ensure success? Finally, can we orchestrate a leadership transition to ensure high priority projects are progressed?

Timeline:
5pm-5:30pm: Registration and Networking
5:30pm-7pm: Opening statements by each participant followed by a conversation/debate about IEEE key issues and initiatives.
7pm-7:25pm: Audience Q & A
7:25pm-7:30pm: Closing remarks and thanks from the participants
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Addendum:
Hope everyone was satisfied with yesterday’s stimulating panel discussion and conversation at SCU. The 3 of us went back & forth discussing critical issues and needed improvements for IEEE to regain credibility & respect. Nothing was rehearsed.
We followed the mutually agreed list of discussion topics (see Comment below) and mixed them up a bit to ensure continuity of various themes.
- Thanks to Behnam, his students, Ed and Joseph for buying the refreshments.
- Thanks to Shoba for securing the SCU room for us.
- Thanks to Kim and Glenn for their cogent comments & remarks
- And many thanks to our two outstanding panelists- Tom and Joseph!!
March 28th video recording of our conversation:
References:
https://techblog.comsoc.org/2024/02/05/ieee-presidents-priorities-and-strategic-direction-for-2024/
https://events.vtools.ieee.org/m/410534
IEEE President Elect: IEEE Overview, 2024 Priorities and Strategic Plan
Téral Research: global wireless infrastructure market sank 9% YoY in 2023; will decline 6% in 2024
|
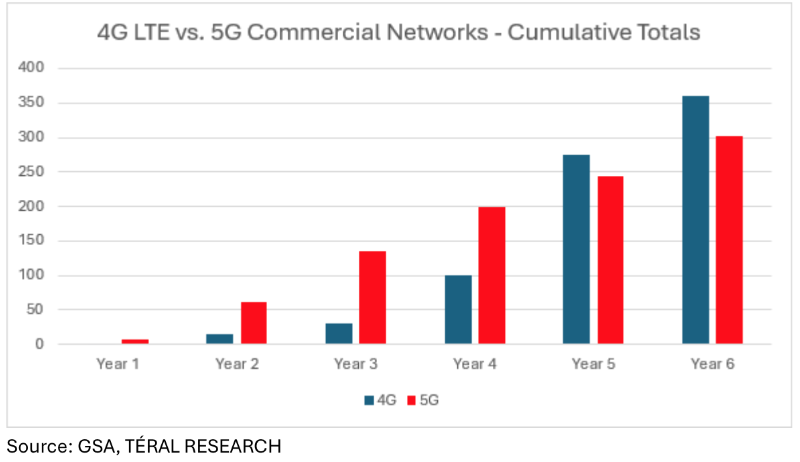
As expected, the global wireless infrastructure market comprised of all RAN and core networks sank 9% YoY despite a strong China-driven 4Q23 that was not enough to offset 3 consecutive quarters of sales declines. 2023 will be remembered by the U.S. market posting its steepest drop in history, the strong 5G rollouts in China which is way ahead of its government-set target, and India’s fast 5G rollout led by Bharti Airtel and Reliance Jio. Meanwhile, 5G core—mostly fueled by China again, and 5G RAN showed some steam in 4Q23. In this environment, for 2023, Huawei kept its lead over Ericsson in global market share, followed by Nokia and ZTE, both managed to increase their market share. Samsung remained #5 but lost shares. We are now entering the third year of this disinvestment cycle. The 5G investment cycle that started in 2019 and ended in 2021 was driven by hundreds of communications service providers (CSPs), including the ones with the world’s largest cellular footprints (i.e., China), and led to a total of 302 commercial 5G networks launched as of December 31, 2023. But the pace is quickly slowing down: by comparison, 2023 was Year 6 for 5G rollouts, at that stage, 360 4G LTE networks were live. |
 |
|
At this point, the global Wireless Infrastructure market will be characterized by much smaller footprints that have yet to be upgraded to 5G as well as 5G-Advanced upgrades for the early 5G adopters, and an open RAN ramp up driven by Tier 1 CSPs. In addition, the slow 5G monetization, the normalization after the 5G surge in China and India and the rise of the secondhand equipment market are chief inhibitors that contribute to the declining pattern. Nonetheless, there is no new wave in the horizon and as a result, this year, we expect the market to decline 6% compared to 2023, despite an AT&T-induced pickup expected in 2H24 in the U.S. market. In the long run, our CSP 20-year wireless infrastructure footprint pattern analysis points to a 2023-2029 CAGR of -3% characterized by steady declines through 2026, which appears to be the bottom leading to flatness. In fact, we expect 5G to slightly pick up in 2027, driven by 5G-Advanced and other upgrades needed to prepare networks for 6G. Given the ongoing 6G activity, we believe something labeled 6G will be deployed in 2028. |
References:
Téral Research :: February 2024 Wireless Infrastructure 4Q23 & FY23 (teralresearch.com)
Dell’Oro: RAN revenues declined sharply in 2023 and will remain challenging in 2024; top 8 RAN vendors own the market
Dell’Oro: Broadband network equipment spending to drop again in 2024 to ~$16.5 B
Global 5G Market Snapshot; Dell’Oro and GSA Updates on 5G SA networks and devices
LightCounting: Wireless infrastructure market down in 2Q-23 (no surprise)
LightCounting: Wireless infrastructure market dropped both YoY and sequentially in 1Q23
IBM: 5G use cases that are transforming the world (really ?)
For many years, this author has been very skeptical about the commercial success of highly touted 5G use cases. That’s mainly because the 3GPP 5G specs and ITU-R M.2150 5G RIT/SRIT standard did not (and still do not) meet the ITU-R M.2410 minimum performance requirements for the URLLC use case for either ultra high reliability or ultra low latency.
Another reason for our skepticism is that “real 5G,” which provides 3GPP specified 5G features (like network slicing, edge computing/MEC, and 5G Security), requires a 5G SA core network, which relatively few wireless network operators have deployed.
Nonetheless, IBM has published an article citing 5G use cases that are transforming the world. Here they are:
Autonomous vehicles
From taxi cabs to drones and beyond, 5G technology underpins most of the next-generation capabilities in autonomous vehicles. Until the 5G cellular standard came along, fully autonomous vehicles were a bit of a pipe dream due to the data transmission limitations of 3G and 4G technology. Now, 5G’s lightning-fast connection speeds have made transport systems for cars, trains and more much faster than previous generations, transforming the way systems and devices connect, communicate and collaborate.
Smart factories
5G, along with AI and ML, is poised to help factories become not only smarter but more automated, efficient and resilient. Today, many mundane but necessary tasks associated with equipment repair and optimization are being turned over to machines thanks to 5G connectivity paired with AI and ML capabilities. This is one area where 5G is expected to be highly disruptive, impacting everything from fuel economy to the design of equipment lifecycles and how goods arrive at our homes.
For example, on a busy factory floor, drones and cameras connected to smart devices utilizing the IoT can help locate and transport something more efficiently than in the past and prevent theft. Not only is this better for the environment and consumers, but it also frees up employees to dedicate their time and energy to tasks that are more suited to their skill sets.
Smart cities
The idea of a hyper-connected urban environment that uses 5G network speeds to spur innovation in areas like law enforcement, waste disposal and disaster mitigation is fast becoming a reality. Some cities already use 5G-enabled sensors to track traffic patterns in real time and adjust signals, helping guide the flow of traffic, minimize congestion and improve air quality.
In another example, 5G power grids monitor supply and demand across heavily populated areas and deploy AI and ML applications to “learn” what times energy is in high or low demand. This process has been shown to significantly impact energy conservation and waste, potentially reducing carbon emissions and helping cities reach sustainability goals.
Smart healthcare
Hospitals, doctors and the healthcare industry as a whole already benefit from the speed and reliability of 5G networks every day. One example is the area of remote surgery that uses robotics and a high-definition live stream connected to the internet via a 5G network. Another is the field of mobile health, where 5G gives medical workers in the field quick access to patient data and medical history, enabling them to make smarter decisions, faster, and potentially save lives.
Lastly, as we saw during the pandemic, contact tracing and the mapping of outbreaks are critical to keeping populations safe. 5G’s ability to deliver of volumes of data swiftly and securely allows experts to make more informed decisions that have ramifications for everyone.
Better employee experiences
5G paired with new technological capabilities won’t just result in the automation of employee tasks, it will dramatically improve them and the overall employee experience. Take virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), for example. VR (digital environments that shut out the real world) and AR (digital content that augments the real world) are already used by stockroom employees, transportation drivers and many others. These employees rely on wearables connected to a 5G network capable of high-speed data transfer rates that improve several key capabilities, including the following:
- Live views: 5G connectivity provides live, real-time views of equipment, events and even people. One way in which this feature is being used in professional sports is to allow broadcasters to remotely call a sporting event from outside the stadium where the event is taking place.
- Digital overlays: IoT applications in a warehouse or industrial setting allow workers equipped with smart glasses (or even just a smartphone) to obtain real-time insights from an application, including repair instructions or the name and location of a spare part.
- Drone inspections: Right now, one of the leading causes of employee injury is inspection of equipment or project sites in remote and potentially dangerous areas. Drones, connected via 5G networks, can safely monitor equipment and project sites and even take readings from hard-to-reach gauges.
Edge computing
Edge computing, a computing framework that allows computations to be done closer to data sources, is fast becoming the standard for enterprises. According to this Gartner white paper (link resides outside ibm.com), by 2025, 75% of enterprise data will be processed at the edge (compared to only 10% today). This shift saves businesses time and money and enables better control over large volumes of data. It would be impossible without the new speed standards generated by 5G technology.
Ultra-reliable edge computing and 5G enable the enterprise to achieve faster transmission speeds, increased control and greater security over massive volumes of data. Together, these twin technologies will help reduce latency while increasing speed, reliability and bandwidth, resulting in faster, more comprehensive data analysis and insights for businesses everywhere.
5G solutions with IBM Cloud Satellite
5G presents big opportunities for the enterprise, but first, you need a platform that can handle its speed. IBM Cloud Satellite lets you deploy and run apps consistently across on-premises, edge computing and public cloud environments on a 5G network. And it’s all enabled by secure and auditable communications within the IBM Cloud. The IBM Cloud Satellite-managed distributed cloud solution delivers cloud services, APIs, access policies, security controls and compliance.
References:
https://www.ibm.com/products/satellite
Big 5 Event: wireless connectivity use cases for healthcare, network slicing, security and private networks
Qualcomm Introduces the World’s First “5G NR-Light” Modem-RF System for new 5G use cases and apps
MoffettNathanson: 5G use cases and revenue streams have not yet materialized
CELLSMART: 5G upload speeds are insufficient for industrial/enterprise applications
BofA on 5G Use Cases and Industry Vertical Applications
Korea’s KAIST develops next-gen ultra-low power Gen AI LLM accelerator
Researchers in South Korea have developed the world’s first artificial intelligence (AI) semiconductor chip that operates at ultra-high speeds with minimal power consumption for processing large language models (LLMs), based on principles that mimic the structure and function of the human brain.
The research team was from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) PIM Semiconductor Research Center and the Graduate School of AI Semiconductor (led by Professor Yu Hoi-jun). This ultra-low power “complementary transformer” semiconductor using Samsung Electronics’ 28 nm process as announced by Korea’s Ministry of Science and ICT on Feb. 6th. The chip is 41 times smaller in area than the Nvidia AI processor, enabling it to be used on devices like mobile phones.
The new AI chip successfully ran GPT 2 using only 1/625 of the power consumption and at 1/41 the size of Nvidia’s A100 graphics processing unit (GPU). This breakthrough is considered a key development in the escalating global AI semiconductor war.
Previously, the technology was less accurate than deep neural networks (DNNs) and mainly capable of simple image classifications, but the research team succeeded in improving the accuracy of the technology to match that of DNNs to apply it to LLMs.
The team said its new AI chip optimizes computational energy consumption while maintaining accuracy by using unique neural network architecture that fuses DNNs and SNNs, and effectively compresses the large parameters of LLMs.
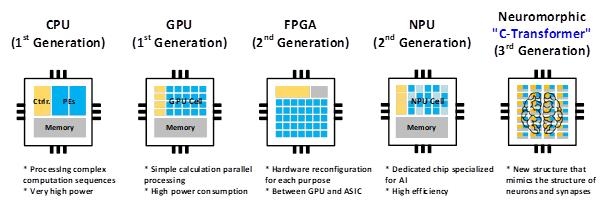
A photo describing an artificial intelligence chip which processes a large language model with neuromorphic computing technology provided by the Ministry of Science and ICT on March 6, 2024.
References:
HGC Global Communications, DE-CIX & Intelsat perspectives on damaged Red Sea internet cables
Earlier this week, four underwater data cables were damaged in the Red Sea. Hong Kong telecom HGC Global Communications said about 25% of internet traffic in Asia, Europe, and the Middle East had to be rerouted.
There are more than 15 undersea internet cables in the Red Sea. To have four damaged at a single time is ”exceptionally rare,” HGC said in a separate earlier statement.
The disruption of the cables did not disconnect any country from the internet, but the Wall Street Journal reports service in India, Pakistan, and parts of East Africa was noticeably degraded.
No services have yet offered a reason for the cuts. Yemen’s telecom ministry denied speculation it was responsible for the failures, saying it was “keen to keep all telecom submarine cables…away from any possible risks.”
Underwater cables are responsible for most of the internet’s data traffic. They’re cheaper than land-based cables, but are prone to damage from ships’ anchors.
The ongoing conflict in the Middle East has experts wondering about the timing and severity of this outage, though. Iran-based Houthi has been particularly aggressive in the Red Sea, including in mid-February when a cargo ship was abandoned by its crew following an Houthi attack. The ship, which had weighed anchor, drifted for weeks before sinking.
According to U.S. officials, the anchor of the Rubymar, a UK-owned ship, likely severed three cables in the Red Sea on February 18, 2024. The Rubymar was struck by a Houthi missile on February 18, 2024, and sank after taking on water. As it was sinking, its anchor likely cut the cables that provide global telecommunications and internet data.
Houthi control of the region and the ongoing strife in Yemen makes repairing the damaged cables more complicated. One of the four companies affected said it expects to start that process early in the second quarter, though permit issues, weather, and the civil war in that country could impact that.

Statement by Dr. Thomas King, Chief Technology Officer, DE-CIX:
“As a global Internet Exchange (IX) operator, DE-CIX rents capacity on submarine cables in the Red Sea as part of its global network, which interconnects more than 50 IXs and Cloud Exchanges around the world. One of our data pathways from Asia to Europe makes use of the Asia-Africa-Europe 1 (AAE1) cable, one of three that were damaged in a recent incident. According to the information we have, the cause of the damage was the anchor of a freighter that the Houthi rebels had attacked. At some point, the crew abandoned the ship and dropped anchor so that the unmanned ship would not drift out of control. Unfortunately, the anchor did not hold, and the drifting wreck dragged the anchor across the seabed, rupturing the three affected lines before the ship finally sank.”
“From a telecommunications perspective, the Red Sea is a neuralgic point connecting Europe and Asia. DE-CIX has leased capacity on two separate submarine cables in the Red Sea, located several kilometers apart. We operate them in active-active mode, which means that the second cable is fully available if one should fail. The data is rerouted fully automatically, without manual intervention. As we monitor all of our systems automatically 24/7, we were alerted immediately to the failure of the connection. At the same time, the carrier that we rent our capacity from also informed us of the incident.”
“Given that we always work with redundant connections, the impact of the incident is not critical for DE-CIX customers. We share our capacities across multiple submarine cable routes worldwide and check the exact routes, including GPS coordinates, to ensure that these routes do not overlap at any point. We plan in such a way that we can fully compensate for the failure of at least one submarine cable, and we can always use different data pathways. We generally expect damage to submarine cables to take two to three months to repair because special ships are needed for this. In the meantime, we are also working to establish alternative redundancy channels.”
“In terms of the impact on Internet users in Europe and Asia, if Internet service providers and carriers have built their networks redundantly and therefore resiliently, Internet users should not experience any disruption. If Internet service providers choose a different risk scenario for cost reasons, for example, then even the failure of a single cable can lead to disruption for users/customers. Such a disruption is noticeable in the latency, i.e. the time it takes for the data to reach its destination. This could, for example, lead to the participants in a video conference interrupting each other because it takes too long for the spoken word to reach the other person.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Rhys Morgan, general manager and VP, media and networks, EMEA at Intelsat is seeing demand for satellite capacity as well.
“We’ve had reports from customers that they’re seeing a slowdown in some of their Internet connectivity,” he tells Capacity Media.
Morgan notes that disruption to data traffic passing through the Red Sea has been a concern for sometime due to the Houthi militants potential to target the infrastructure.
“It’s something we’ve been keeping an eye on more broadly over a long period of time,” he says. “We’ve been working with large customers to make sure that they’ve got a hybrid approach to networking.”
Morgan is keen to emphasise that a hybrid approach to networking is crucial in times of disruption, as seen this week.
Intelsat have implemented short-term services for customers that have suffered disruption in light of the cuts.
“As part of a hybrid network approach, customers will look for mission critical or highly sensitive communications to be passed through different means,” he explains. “Fibre may be their primary method, but satellite connectivity could be on standby as a backup”.
Satellite connectivity in its current form is not well enough equipped to completely replace the vast quantities of data that travel through subsea cables every day. But for certain types of data, the technology can offer a suitable alternative.
References:
https://fortune.com/2024/03/04/internet-cables-cut-red-sea/
https://www.networkcomputing.com/author/dr-thomas-king-cto-de-cix
Ericsson and ACES partner to revolutionize indoor 5G connectivity in Saudi Arabia
Ericsson and Advanced Communications and Electronics Systems (ACES) [1.] have signed a strategic three-year Neutral Host Provider (NHP) agreement, to address the surging demand for indoor 5G connectivity and 5G technology. This agreement aims to create a neutral host ecosystem, allowing service providers to share infrastructure and deliver high-performance 5G connectivity in high-traffic indoor locations in Saudi Arabia.
Note 1. Advanced Communications & Electronic Systems Company (ACES) is a leading international neutral host operator and a digital infrastructure company based in Saudi Arabia. Established in early 1990s, ACES is specialized in implementing total solutions and turn-key projects in wireless communication, network monitoring & testing and information technology systems.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Using multi-operator infrastructure sharing to address rising demand for indoor connectivity will significantly improve user experience. With the rise of high-attraction landmarks and the need for network densification, it has become crucial to provide reliable and high-performing indoor solutions for portability, agility and flexibility.
The NHP agreement allows ACES to provide Ericsson indoor 5G products to service providers, enabling them to share the same infrastructure, and ensure cost-effective coverage expansion and efficient utilization of resources.
This agreement will establish a neutral host ecosystem, supporting CSPs in enhancing their indoor 5G coverage with flexibility and ease of operation and maintenance. It will contribute to the footprint expansion of indoor 5G networks across the Kingdom.

Image Credit: Ericsson
By deploying Ericsson’s Radio Dot System, CSPs can deliver high-performing 5G connectivity to users in large locations such as airports, hotels, hospitals, stadiums, and shopping malls.
One of the key activations as a result of this agreement is enhancing the 5G indoor connectivity at an international airport in the Kingdom that welcomes millions of visitors regularly. The agreement paves the way for a resilient infrastructure in high-density locations.
Akram Aburas, Chief Executive Officer of ACES, says: “At ACES, we seek to empower businesses and individuals with a transformative digital experience, and our agreement with Ericsson is a momentous step towards that. With Ericsson’s cutting-edge indoor 5G solutions, we aim to create a neutral host ecosystem that offers seamless and high-performance connectivity in high-traffic indoor locations across the Kingdom. Our agreement with Ericsson will support and meet the surging demand for indoor connectivity across Saudi Arabia and unlock unparalleled opportunities for telecom operators to enrich their offerings and deliver exceptional user experiences.”
Ericsson’s indoor 5G solutions, powered by the Radio Dot System, will enable faster and more reliable network performance in indoor environments and will cater to the increasing need for seamless connectivity.
Håkan Cervell, Vice President and Head of Ericsson Saudi Arabia and Egypt at Ericsson Middle East and Africa, says: “By fostering a neutral host ecosystem, we are enabling communications service providers to embrace unprecedented flexibility and cost efficiency in their network expansion. Our indoor 5G solutions, powered by the Radio Dot System, will enhance how businesses and individuals experience seamless connectivity within indoor environments. We look forward to this agreement with ACES, which will ensure robust indoor 5G connectivity across the Kingdom, in line with Saudi Vision 2030, while setting new benchmarks for network performance that propel Saudi Arabia to the forefront of the global 5G revolution.”
To date, the Ericsson Radio Dot System has been deployed in more than 115 countries around the world in high-traffic indoor venues.
References:
Telstra achieves 340 Mbps uplink over 5G SA; Deploys dynamic network slicing from Ericsson
BT Group, Ericsson and Qualcomm demo network slicing on 5G SA core network in UK
Finland’s Elisa, Ericsson and Qualcomm test uplink carrier aggregation on 5G SA network
Ericsson and IIT Kharagpur partner for joint research in AI and 6G
Ericsson expects continuing network equipment sales challenges in 2024
Recon Analytics (x-China) survey reveals that Ericsson, Nokia and Samsung are the top RAN vendors
T-Mobile US, Ericsson, and Qualcomm test 5G carrier aggregation with 6 component carriers
NTT advert in WSJ: Why O-RAN Will Change Everything; AT&T selects Ericsson for its O-RAN
Telco and IT vendors pursue AI integrated cloud native solutions, while Nokia sells point products
The move to AI and cloud native is accelerating amongst network equipment and IT vendors which have announced highly integrated smart cloud solutions designed to migrate their telco customers into a new and profitable cloud future. The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), as the name suggests, is a vendor-neutral consortium dedicated to making cloud native ubiquitous. The group defines cloud native as a collection of “technologies [that] empower organizations to build and run scalable applications in modern, dynamic environments such as public, private and hybrid clouds. Containers, service meshes, microservices, immutable infrastructure and declarative APIs exemplify this approach.”
CNCF writes that the cloud native approach “enable[s] loosely coupled systems that are resilient, manageable and observable. Combined with robust automation, they allow engineers to make high-impact changes frequently and predictably with minimal toll.”

In particular, Ericsson, HPE/Juniper, Cisco, Huawei, ZTE, IBM, and Dell have all announced telco end to end solutions that provide a platform for new services and applications by integrating AI, automation, orchestration and APIs over cloud-native based infrastructure. Let’s look at each of those capabilities:
- AI (Artificial Intelligence): Leveraging AI capabilities allows telcos to automate processes, optimize network performance, and enhance customer experiences. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI-driven insights enable better decision-making and predictive maintenance.
- Automation: Automation streamlines operations, reduces manual intervention, and accelerates service delivery. Whether it’s provisioning new network resources, managing security protocols, or handling routine tasks, automation plays a pivotal role in modern telco infrastructure.
- Orchestration: Orchestration refers to coordinating and managing various network functions and services. It ensures seamless interactions between different components, such as virtualized network functions (VNFs) and physical infrastructure. By orchestrating these elements, telcos achieve agility and flexibility.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): APIs facilitate communication between different software components. In the telco context, APIs enable interoperability, allowing third-party applications to interact with telco services. This openness encourages innovation and the development of new applications.
- Cloud-Native Infrastructure: Moving away from traditional monolithic architectures, cloud-native infrastructure embraces microservices, containerization, and scalability. Telcos are adopting cloud-native principles to build resilient, efficient, and adaptable networks.
While each company has its unique approach, the overarching goal is to empower telcos to deliver cutting-edge services, enhance network performance, and stay competitive in an ever-evolving industry. These advancements pave the way for exciting possibilities in the telecommunications landscape. When fully integrated, these technologies will enable the creation of smart cloud networks that can run themselves without human involvement and do so less expensively — but also more efficiently, responsively and securely than anything that exists today.
Our esteemed UK colleague Stephen M Saunders, MBE (Member of the Order of the British Empire– more below) notes that Nokia is not embracing smart cloud telco solutions, but is instead focusing on individual products. Last October, the company announced strategic and operational changes to its business model and divided the company into four business units. At that time, Nokia’s President and CEO Pekka Lundmark said:
“We continue to believe in the mid to long term attractiveness of our markets. Cloud Computing and AI revolutions will not materialize without significant investments in networks that have vastly improved capabilities. However, while the timing of the market recovery is uncertain, we are not standing still but taking decisive action on three levels: strategic, operational and cost. First, we are accelerating our strategy execution by giving business groups more operational autonomy. Second, we are streamlining our operating model by embedding sales teams into the business groups and third, we are resetting our cost-base to protect profitability. I believe these actions will make us stronger and deliver significant value for our shareholders.”
Steve says Nokia’s new divide-and-conquer strategy is being reinforced at its sales meetings, according to an attendee at one such gathering this year, with sales reps being urged to laser-focus on selling point products.
“The telco capex situation at the moment means Nokia — and others — have no choice but to examine every aspect of their business to work out how to adjust for a future CSP market that is itself going through dramatic change,” said Jeremiah Caron, global head of research and analysis at market research firm GlobalData Technology.
Most telcos are increasingly adopting cloud-native technologies to meet the demands of 5G SA core networks and to better automate their services.. However, some telcos are hesitant to fully embrace cloud-native due to concerns about complexity, cost, and reliability. Other challenges of cloud native are: changing the software development life cycle, privacy and security, guaranteeing end to end latency, and cloud vendor lock-in due to a lack of standards (every cloud vendor has their own proprietary APIs and network access configurations.
References:
https://www.silverliningsinfo.com/multi-cloud/report-smart-cloud-and-coming-paradigm-shift
https://www.fiercewireless.com/5g/op-ed-whither-nokia
Building and Operating a Cloud Native 5G SA Core Network
Omdia and Ericsson on telco transitioning to cloud native network functions (CNFs) and 5G SA core networks
https://www.ericsson.com/en/ran/intelligent-ran-automation/intelligent-automation-platform
https://www.huaweicloud.com/intl/en-us/solution/telecom/cloud-native-development-platform.html
https://sdnfv.zte.com.cn/en/solutions/VNF/5G-core-network/cloud-native
https://www.ibm.com/products/cloud-pak-for-network-automation
https://www.dell.com/en-us/dt/industry/telecom/index.htm#tab0=0

Steve Saunders (a.k.a. Silverlinings‘ Sky Captain), is a British-born communications analyst, investor, and digital media entrepreneur. In 2018 he was awarded an MBE in the Queen’s Birthday Honours List for services to the telecommunications industry and business.
Kuwait stc/Huawei deploy 5G Redcap FWA in Kuwait; Huawei’s 5G core wins
Kuwait Telecommunications Company – stc [1.], which provides innovative services and platforms to customers that enable digital transformation in Kuwait, announced the Middle East’s first commercial deployment of 5G RedCap Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) using Huawei network equipment. The announcement was made at the second forum of the ELITE FWA Club, held on the sidelines of MWC 2024.
Note 1. stc is Saudi Telecom Group, Kuwait Telecoms parent organization.
The service represents a transformative advancement in high-speed, reliable internet access for both residential and commercial clientele. The forum attracted founding members alongside an array of global telecom leaders and ecosystem stakeholders.
5G RedCap FWA heralds a new era in broadband services, offering users unparalleled, seamless connectivity. It stands out for its ability to provide stable, reliable speeds while ensuring cost-effectiveness. This innovation is achieved through optimized hardware design, which includes extended battery life, reduced power consumption, and improved spectrum efficiency on 5G CPE routers, making high-quality 5G technology accessible at significantly lower costs. Consequently, it not only enhances customer experience but also lowers the barriers to 5G adoption, encouraging the transition from 4G to 5G.
Key features of 5G RedCap FWA service include:
- High-Speed Connectivity: Delivers robust and consistent internet speeds, catering to the digital needs of today’s lifestyle.
- Unmatched Reliability: Ensures a stable and dependable home broadband connection, providing uninterrupted access to online services.
- Innovation Leadership: Demonstrates stc’s dedication to leading innovation in the region, introducing the latest technological breakthroughs to its customers.
Eng. Amer Atoui, Chief Consumer Officer of stc Kuwait, stated, “Launching 5G RedCap FWA ushers in a groundbreaking chapter for internet connectivity in the Middle East. We take pride in being the region’s pioneer, reaffirming our commitment to delivering innovative solutions that enrich our customers’ lives.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, GlobalData’s “5G Mobile Core: Competitive Landscape Assessment report” rated Huawei 5G Core as a “Leader” in the 5G mobile core network field for the sixth consecutive year. Huawei’s 5G Core was also awarded full scores in all dimensions for the first time. Since the inception of this report in 2018, Huawei is the only vendor to ever get perfect scores in all dimensions.
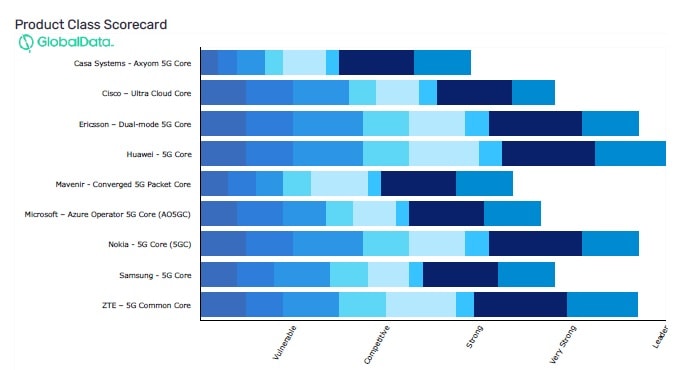
Source: 5G Mobile Core: Competitive Landscape Assessment, by GlobalData
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The GlobalData report highlights the competitive advantages of Huawei 5G Core products. By leveraging Cloud Native architecture, Huawei 5G Core converges full-range services across the 2G to 5G spectrum, marking an industry first. The solution also stands out with an innovative disaster recovery (DR) architecture for high reliability. And on top of this, Huawei provides professional integration and O&M services with extensive experience. All of the above capabilities have made Huawei 5G Core a market leader in terms of the in-depth and broad commercial use.
References:
Nokia and du (UAE) complete 5G-Advanced RedCap trial; future or RedCap?
Ericsson, Vodafone and Qualcomm: 1st Reduced Capability (RedCap) 5G data call in Europe
https://www.huawei.com/en/news/2024/3/leader-5g-core
GlobalData: MWC 2024 roundup + More balanced IT workforces
MWC 2024 Roundup:
Huawei, Qualcomm, and Ericsson, were singled out for praise, recognized for their groundbreaking work in advancing 5G technology. Their contributions were seen as pivotal in propelling the widespread adoption and ongoing development of 5G, setting new benchmarks for the future of tech innovation.
Huawei Technologies
Huawei took center stage at MWC 2024 with its pioneering 5.5G products, including the Telecom Foundation Model and the industry’s first 5.5G intelligent core network. Influencers applauded the innovative all-optical products like the OptiX OSN 9800 K36, OptiXaccess MA5800T, and iFTTR OptiXstar F50, highlighting Huawei’s foresight in enhancing network capabilities and digital transformation. The reception was largely positive, underscoring Huawei’s role in the next generation of connectivity.
Qualcomm
Qualcomm unveiled its latest Snapdragon processors, which powered the highly discussed OnePlus Watch 2, at MWC 2024. Influencers praised the new chipset for its efficiency and performance, emphasizing Qualcomm’s pivotal role in advancing the wearable tech space. The buzz reflects Qualcomm’s successful push towards more powerful and energy-efficient chip designs, which are set to redefine user experiences across devices.
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
Ericsson showcased its commitment to advancing 5G infrastructure and network capabilities, earning positive reactions for its efforts to enhance global connectivity. Ericsson’s innovations in network evolution and digital transformation were recognized as key to the future of telecommunications, with influencers noting the company’s significant contributions to a more connected world.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
A More Balanced IT Workforce:
With a focus on creating more inclusive work environments, telecommunications firms are not only fostering a culture of acceptance but also reaping significant financial rewards in the process, says GlobalData, a leading data and analysis company.
Robert Pritchard, Principal Analyst, Enterprise Technology and Services at GlobalData: “With the tech sector being driven at high pace by change and innovation, recruiting teams that more closely resemble the world at large has become more of a priority amongst leading companies. It is telling that 60% of Fortune 500 companies were founded by immigrants.”
GlobalData analysis reveals that more balanced (by gender, race, and disability) workforces are emerging over time, often led by the C-Suite and the Board, but also in the wider employee base.
“With Indian-born CEOs at Google and Microsoft, ever more women CEOs across telecoms and tech companies, and a gay man in charge at Apple, the sector is again leading the way.
“DEI has largely moved from a tick-box exercise to a key strategic management consideration. The companies that are more advanced have been proven to be more successful, with their customers preferring brands and organizations that align with their values and identities.”
Studies by Boston Consulting Group and Harvard Business Review have found that companies with more diverse management teams have 19% higher revenues and 9 percentage points higher EBIT margin. In addition, in the battle for scarce talent in tech, DEI is seen as a key deciding factor for potential recruits – especially amongst Generation Z.
Pritchard concludes: “In terms of rebalancing the overall workforce, it is a long journey as most employees stay in post for over four years. Nevertheless, demonstration of a cultural shift and a more inclusive approach is vital. This can be helped in the short-term through training, mentoring, cross-team building, volunteering, and commitment to employee wellbeing. Success in DEI is reflected in commercial success in the long-run.”
EdgeQ’s breakthrough demos and partnerships showcased at MWC 2024 & MWC 2023
EdgeQ Inc, an innovative 4G/5G System on a Chip (SoC) semiconductor startup, had several defining showcases at MWC 2024 as well partnership announcements which included:
1. A partnership with DenseAir and Radisys to deliver industry’s first cloud-native, neutral host solution for mobile networks. It’s the world’s first O-RAN split 6 solution where multiple operators and multiple data streams are all supported off a common platform – single box, single silicon.
- EdgeQ fundamentally enabled DenseAir to deliver a solution that converged 4G+5G on a single silicon, while providing elastic scaling up to 4 component carriers and 256 users, with software-defined O-RAN split 6.
2. EdgeQ and BlinQ showcased a single integrated 5G+WiFi platform (PCW-400i), running simultaneously 5G at 3.3-4.2GHz frequency band spectrum and Wi-Fi 2.4GHz and 6GHz spectrum. This fully integrated small cell solution by BlinQ operates in bands n48, n77 and n78 along with the three bands from the Wi-Fi 7 standard. Using EdgeQ’s SoC, BlinQ enables novel deployment schemes like completely 5G cable-less backhaul, while enabling PoE++ (IEEE 802.3bt is the latest and most powerful Power over Ethernet standard. It provides up to 100 watts of power per port. at affordable unit economics).
- “Not only does the PCW-400i provide incredible capacity, it also incorporates BLiNQ’s enterprise-level management suite and zero-touch provisioning, making it easy to install and operate in any size organization,” says Pete Vavra, VP of Sales at BLiNQ. “The product was designed with scalability and ease of deployment in mind without taking the focus away from performance,” Vara added.
- “Our collaboration with BLiNQ is about massively converging two major wireless protocols into a single platform that give customers flexibility and freedom of choice. This is a phenomenal achievement delivering state-of-the art 5GNR and Wi-Fi 7 in a sleek, compact form factor that can elastically scale with connection density and capacity demands while maintaining breakthrough unit economics at unprecedented low power,” says Ziyao Xu, Director of Product Management at EdgeQ. “This will compel the market with novel use cases for enterprise, private networks, and home,” Xu added.
3. EdgeQ’s silicon was featured by both ARM and Analog Devices. Two landmark capabilities were revealed:
- Multi-Operator, Multi-Carrier 4cc Aggregation Running on a Single SoC Converging 4G+5G+AI.
- Industry First 5G PHY + 5G L2/L3 + Embedded User Plane Function (UPF) running on EdgeQ’s SoC:
-
Local Processing of UPF reduces the WAN tax, allowing for a lighter, less burdened core network. Having an embedded UPF can save cost, reduce latency, and maintains the pilot data from needing to leave the premise.
-
At the same time, there is enough headroom in EdgeQ’s processor architecture to run other edge applications (DPDK, virtualization, containers, etc…etc…).
-
4. Actiontec and EdgeQ announced the commercial release of ASC-308: Revolutionizing Network Flexibility, Performance and Future-Proofing 4G & 5G Small Cell.
- Enabled by EdgeQ SoC, Actiontec’s ASC-508 offers a programmable architecture, 4G & 5G multi-technology support, and ease of deployment to empower operators to build future-proof networks. The ASC-508 boasts a programmable and modular architecture, allowing operators to adapt easily the platform to their band support, specific use cases, and evolving network requirements.
- Support for various O-RAN compliant Split options, including All-in-One Split 0, Split 2, and Split 6, ensures future-proof adaptability. This is all due to the programmable nature of EdgeQ’s “Base Station-on-a-Chip.”
–>Significantly, EdgeQ’s SoC product entered production last year and has generated meaningful revenue with customers worldwide.
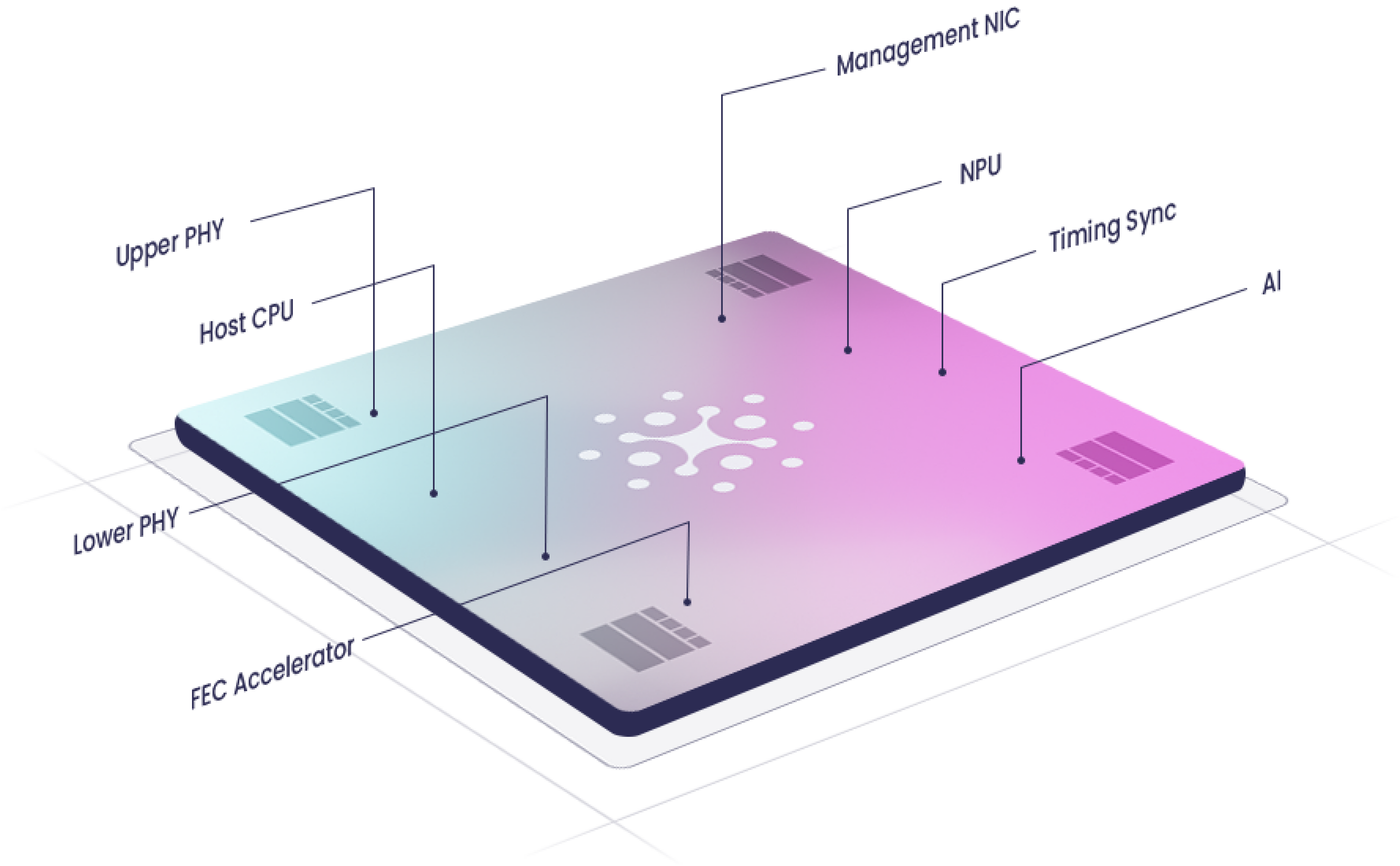
Image Credit: EdgeQ Inc.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
At MWC 2023, EdgeQ collaborated with Vodafone, a leading telecommunications mobile operator in Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN), and Dell Technologies to debut a state-of-the-art O-RAN-based, massive MIMO solution at last year’s Mobile World Congress (MWC 2023) in Barcelona, Spain. As a result, the company received the prestigious “CTO Choice Award for Outstanding Mobile Technology” and “Best Digital Technology Breakthrough.”
The collaboration and design between the three companies is a massive MIMO 5G network that leverages in line acceleration technologies to deliver high user capacity, high network bandwidth at relatively low power for the new O-RAN based deployments.
Hosted at the Vodafone stand, the live system comprised of a Dell PowerEdge XR11 server and an EdgeQ M-Series L1 accelerator will demonstrate impressive throughput of 5Gbps, with the accelerator drawing less than 50 watts. The collaboration and design between the three companies demonstrate the principles of a 5G O-RAN infrastructure solution on a standard server, an inline acceleration, a Radio Unit (RU) system, and third party L2/L3 software stack from collaborating companies.
“Vodafone is committed to driving 5G O-RAN deployments at scale. Our showcase with EdgeQ and Dell Technologies validates how open innovation can drive better performance and cost efficiencies. Technologies such as EdgeQ’s high capacity in-line L1 acceleration should enable Vodafone to scale our macro cell infrastructure to new levels of performance and efficiency without compromise,” said Paco Martin, Head of OpenRAN Product Team, Network Architecture, Vodafone.
EdgeQ’s multi-node 4G/5G Base Station-on-a-Chip solution [1.] converges connectivity, compute, and networking in a disruptively innovative software-defined platform. The highly scalable, flexibly adaptive EdgeQ platform solution uniquely features a production-grade L1 stack that is open and customizable. The scalable architecture maximizes throughput performance, compute processing, across a large range of concurrent users and multiple carriers, all within a compact power and cost envelope.
“EdgeQ was founded on the belief of reconstituting the network in simple and intuitive terms. Together with Vodafone and Dell Technologies, we have shown the first instantiation of a new market paradigm that scales openly and flexibly, without the cost burden and power penalties of traditional platform approaches,” said Vinay Ravuri, CEO and Founder at EdgeQ.
Note 1. In December 2023, EdgeQ announced a converged 4G, 5G, and AI base station SoC at 1/2 cost, 1/3 the power, and 1/10 the space of previous designs. EdgeQ’s 4G/5G base station SoC features:
- 3 to 4 Multi-carrier operation on a 4T4R small cells for enterprise private networks.
- Asymmetric carrier aggregation across multiple bandwidths – ex: 100+20, 20+10, …….
- Asymmetric carrier aggregation between licensed bands and PAL/GAA spectrum assets.
EdgeQ is the only company providing an integrated 4G+5G solution, complete with a multi-mode L1 (Physical Layer), an interoperable L2/L3 software stack, all on a single chip. Telcos and private network customers can leverage a single converged solution, upgrade over-the-air at compelling unit economics of 1/2 the cost and 1/3 the power of previous base station designs.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
On March 22, 2022, EdgeQ’s Product Development Manager Adil Kidwai participated in an IEEE ComSocSCV virtual panel session, organized by this author, where he discussed the benefits of his company’s 4G/5G SoC solution for O-RAN and private 5G networks. That virtual panel session was summarized in the November 2022 IEEE Global Communications Newsletter which was published in the November 2022 IEEE Communications magazine. You can watch a video of that very informative session here.
About EdgeQ:
EdgeQ is a leading innovator in 5G systems-on-a-chip. The company is headquartered in Santa Clara, CA, with offices in San Diego, CA and Bangalore, India. Led by executives from Qualcomm, Intel, and Broadcom, EdgeQ is pioneering converged connectivity and AI that is fully software-customizable and programmable.
The company is backed by world-renowned investors. To learn more about EdgeQ, visit www.edgeq.io. Media Contact: [email protected] 804-612-5393
References:
https://www.edgeq.io/edgeq-wins-multiple
https://www.edgeq.io/edgeq-debuts-worlds-first
EdgeQ Samples World’s 1st Software-Defined 5G Base Station-on-a-Chip
Intel FlexRAN™ gets boost from AT&T; faces competition from Marvel, Qualcomm, and EdgeQ for Open RAN silicon
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=9946966
SoC start-up EdgeQ comes out of stealth mode with 5G/AI silicon for 5G private networks/IIoT
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6736761