Month: June 2024
Analysys Mason’s gloomy CAPEX forecast: “there will not be a cyclical recovery”
Telco capex declined worldwide in 2023, and predictions in end-of-financial year results indicate further declines this year. Analysys Mason warns that a “long decline” in capital expenditure has now started. “There will not be a cyclical recovery,” says one subhead (see below). Analysys Mason crunched a lot of numbers to arrive at this conclusion, processing historical data for about 50 of the largest operators in the world. Importantly, it also looked at the long-term guidance issued by those companies. Capex has peaked partly because telcos in many regions have completed or are near completing a once-in-a-lifetime upgrade to full-fiber networks. Clearly, that’s bad news for companies selling the actual fiber. Operators will continue to invest in the active electronics for these lines, but that represents a “tiny fraction” of the initial cost.
This new Analysys Mason gloomy CAPEX forecast comes after Dell’Oro and Omdia (owned by Informa) previously forecast another sharp fall in telco spending on mobile network products this year after the big dip of 2023.
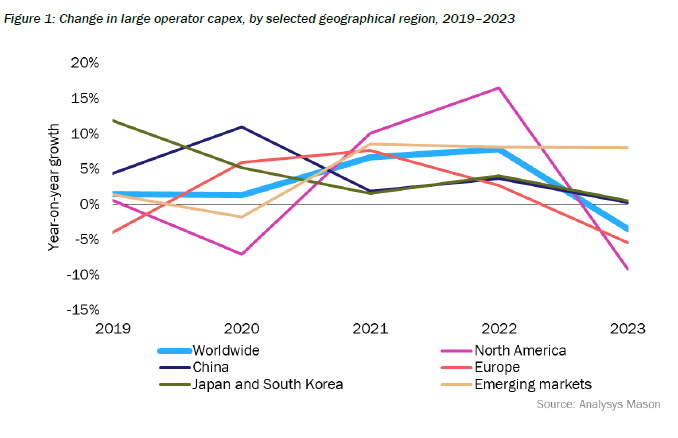
Figure 1. below aggregates change in capex, excluding spectrum, in 2023 (or FY2023/2024) for 50 of the largest operators in the world, all with annual capex of over USD1 billion in 2023. These operators account for about 78% of telecoms capex worldwide. Of the 42 operators that provided guidance on capex in 2024, 28 forecast a fall. A notable class of exceptions consisted of cable operators and latecomers to FTTP upgrade, but most of the emerging-market-focused operators indicated a decline.
The steepest decline was in North America. The decline was steeper for the three largest mobile network operator (MNO) groups (–18.1%). This was offset by rises in capex by the two large US cablecos, for which upgrades of HFC plant are now an imperative. The obvious reason for the sharp decline is the near-completion of 5G roll-out, although FTTP capex remains flat.
In China, capex was flat overall. This disguises a decline in 5G and fixed broadband capex, which, taken together with transmission, fell 7% in 2023. The delta of capex has gone on what operators call ‘computility’ (compute power in data centers and edge) and capabilities (developing the ability to serve mainly the industrial enterprise). Together these two items now account for about 35% of operator capex.
In Japan and South Korea, capex was also more or less flat (+0.5%). As in China, a high proportion of capex in Japan now goes on adjacent lines of business.
Capex declined by 5.5% in Europe. The European figure disguises the impact of the large number of smaller players in the continent. 5G spending has peaked, but so too has FTTP spending. FTTP spend represents a very high share of capex in Europe (about one half), although this is distributed differently across individual countries. Countries like France and Spain have passed that peak, but even in the UK, a relatively late starter, spend has plateaued. Among operators in emerging markets, the smallest group in absolute capex terms, there was a rise of 8%, steady now for three years running, driven almost entirely by India, and offset by declines elsewhere.
There will not be cyclical recovery of capex:
Operators’ longer-term projections of capex suggest, if anything, steepening declines in capex. Our forecasts indicate that capital intensity (capex/revenue) will fall from around 20% now to 12–14% by the end of the decade. Capex will fall basically because customers do not need more than the 1Gbit/s fibre and unlimited 5G that the current networks are easily capable of delivering, and growth in measurable demand slows every year. This will have the following effects:
•Fall in fixed access spend. Capex on FTTP is essentially a one-off investment in passive assets with very long useful lives. Future capex on upgrades (in effect replacements) of FTTP actives will come at a tiny fraction of this cost. The pipeline of plans for commercial build is running dry, although this is offset by some hefty subsidies for rural build, particularly in the USA. Those cablecos that have not already started will have to brace themselves for programs of replacement of HFC/DOCSIS by FTTP/xPON.
•We expect only limited uplift for 5G SA/5G Advanced. This is in part because some operators will not be able to justify a further upgrade after 5G NSA, in part because of slack demand, and in part because the sums involved will be lower than for the roll-out of 5G NSA.
•6G will not be capex-intensive. There is little appetite in free-market economies without centralised planning (and perhaps not so much even there) for a capex-intensive generational upgrade to 6G. There will be no cyclical uplift.
•There will be more outsourcing, i.e. replacement of capex by an opex line. This occurs mainly in infrastructure, but also in migrations of operations (IT capex) to the cloud. Yet this does not mean that capex is simply shifting from one class of business to another; infra companies exist in a world with similar constraints.
•In these circumstances there is a clear case for capex investment in anything that maximizes the efficient (and sustainable) use of the physical assets as they stand, and unlocks any opportunities that exist in new business-models. This is prominent in many operator outlooks.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
William Webb, an independent consultant and former executive at UK telecom regulator Ofcom, forecasts an S-curve flattening by 2027. In a forthcoming book called “The end of telecoms history,” Webb returns to predictions he first made in 2016 to gauge their accuracy. Using recent historical data from Barclays, he was able to show a close alignment with the S-curve he drew about eight years ago. If this behavior continues, growth rates “will fall to near zero by around 2027, with significant variations by country,” says Webb in his book, giving a sneak preview to Light Reading.
Webb’s broad rationale is that there is an upper limit on daily gigabyte consumption, just as there is only so much the average person can eat or drink. All Webb had to do was assume there will be some future gorging by customers on high-quality video, the most calorific meal for any smartphone. “Once they are watching video for all their free moments while downloading updates and attachments there is little more that they could usefully download,” he writes.
What of future services people do not currently enjoy? Outside virtual reality – which, for safety reasons, will probably always happen in a fixed-line environment – no app seems likely to chew through gigabytes as hungrily as moving images do in high definition. Webb clearly doubts the sort of artificial intelligence (AI) services being advertised by Apple will have much impact whatsoever.
“There may be substantially more traffic between data centers as models are trained but this will flow across high-capacity fiber connections which can be expanded easily if needed,” he told Light Reading by email. “At present AI interactions are generally in the form of text, which amounts to miniscule amounts of traffic.”
“Indeed, if time is diverted from consuming video to AI interactions, then AI may reduce the amount of network traffic,” he continued. Even if AI is used in future to create images and videos, rather than words, it will probably make no difference given the amount of video already consumed, merely substituting for more traditional forms of content, said Webb.
For those confident that data traffic growth stimulates investment, the other problem is the lack of any correlation between volumes and costs. Advanced networks are designed to cope with usage up to a certain high threshold before an upgrade is needed. Headline expenses have not risen in lockstep with gigabytes.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/ericsson-and-nokia-may-be-stuck-with-skinflint-customers-for-years
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
U.S. Network Operators and Equipment Companies Agree: 5G CAPEX slowing more than expected
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network & Cable CPE shipments all declined in 1Q-2024
Dell’Oro: 2023 global telecom equipment revenues declined 5% YoY; Huawei increases its #1 position
Where Have You Gone 5G? Midband spectrum, FWA, 2024 decline in CAPEX and RAN revenue
“The “5G Train Wreck” we predicted five years ago has come to pass. With the possible exception of China and South Korea, 5G has been an unmitigated failure- for carriers, network equipment companies, and subscribers/customers. And there haven’t been any significant performance advantages over 4G.”
Infinera, DZS, and Calnex Successfully Demonstrate 5G Mobile xHaul with Open XR
Infinera announced today a successful multi-vendor demonstration of 5G mobile broadband xHaul using coherent open XR optics point-to-multipoint optical transmission. The multi-vendor interoperability testing, conducted with DZS and Calnex, represents a key step toward enabling mobile operators to greatly simplify and cost-reduce 5G and next-generation mobile transport network rollouts through the reduction of the number of optical transceivers, resulting in significant total cost of ownership savings.
Hosted in the European Open Test & Integration Center in Torino by TIM, the high-capacity xHaul application testing included fronthaul, midhaul, and backhaul transport scenarios with XR-based coherent pluggable optics deployed in third-party hosts supporting point-to-point and point-to-multipoint optical transmission. Results of the performance testing included successful demonstration of xHaul synchronization and timing distribution in a point-to-multipoint optical transport architecture.
“It is not only the significant bandwidth demands of 5G that create challenges for mobile operators, but also the fundamental misalignment between actual 5G network traffic patterns and the underlying transport technology,” said Ron Johnson, SVP and General Manager, Optical Subsystems and Global Engineering Group, Infinera. “Working in close collaboration with industry-leading mobile operators such as TIM, this testing validates the critical role that XR optics innovation can play in transforming the economics of 5G transport and paving the way for efficient 6G networks.”
Equipment used in the interoperable xHaul testing included Infinera ICE-X intelligent coherent pluggables, the DZS Saber 2200, and Calnex Paragon-NEO. Part of the work carried out by TIM and Infinera was supported by the EU project ALLEGRO, GA No. 101092766.
About DZS:
DZS (Nasdaq: DZSI) is a developer of Network Edge, Connectivity and Cloud Software solutions enabling broadband everywhere.
About Infinera:
Infinera is a global supplier of innovative open optical networking solutions and advanced optical semiconductors that enable carriers, cloud operators, governments, and enterprises to scale network bandwidth, accelerate service innovation, and automate network operations. Infinera solutions deliver industry-leading economics and performance in long-haul, submarine, data center interconnect, and metro transport applications. To learn more about Infinera, visit www.infinera.com, follow us on X and LinkedIn, and subscribe for updates.
References:
Telenor Deploys 5G xHaul Transport Network from Cisco and NEC; xHaul & ITU-T G.8300 Explained
Orange Deploys Infinera’s GX Series to Power AMITIE Subsea Cable
Infinera trial for Telstra InfraCo’s intercity fiber project delivered 61.3 Tbps between Melbourne and Sydney, Australia
Fiber Build-Out Boom Update: GTT & Ziply Fiber, Infinera in Louisiana, Bluebird Network in Illinois
LightCounting: Q1 2024 Optical Network Equipment market split between telecoms (-) and hyperscalers (+)
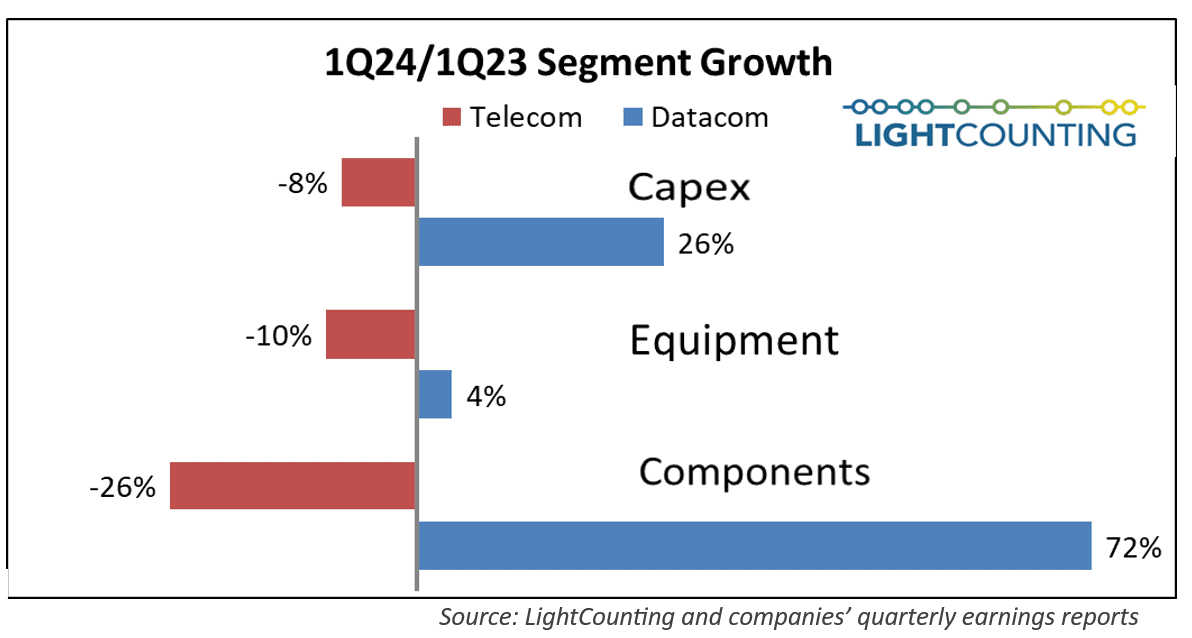
As has been the trend for the past several quarters, Q1 2024 results for the optical communications market were sharply split between very weak sales in the telecom segment (Communications Service Providers or CSPs) and continued strong demand by the hyperscalers (cloud giants). The combined capex of the Top 15 CSPs declined year-over-year for the sixth quarter in a row, while the Top 15 ICPs spending grew for the second quarter in a row, paced by Alphabet (+91%) and Microsoft (+66%). Chinese ICPs spending also increased dramatically, suggesting the AI boom is hitting China too.
FWA a bright spot in otherwise gloomy Internet access market
Parks Associates’ newly launched Broadband Market Tracker, states that U.S. Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) adoption from a mobile network operator hit 7.8 million U.S. residential home internet connections in Q1-2024. That’s in comparison to 106.3 million U.S. households that had home internet service at the end of 2023.
Kristen Hanich, director of research at Parks Associates, told Fierce Network FWA and satellite internet are the “fastest growing” segments of the broadband market, “attracting consumers who were previously unserved or underserved by traditional providers.” She noted for the past several years, the FWA base has grown by 700,000 to 900,000 subscribers per quarter while cable connections have declined.
T-Mobile in Q1-2024 passed the 5 million mark for FWA subscribers and Verizon reported a total FWA tally of 3.4 million subscribers. These figures include both residential and business FWA customers.
Key FWA Findings from OpenSignal:
- 5G FWA has reshaped the U.S. broadband market. It has allowed U.S. mobile operators to rapidly expand their broadband footprints for minimal incremental network investment. This has seen 5G FWA absorb all broadband subscriber growth in the market since mid-2022.
- FWA is the secret sauce for 5G monetization. FWA benefits from lower prices compared to wireline competition, access to existing mobile retail channels and subscribers, and the ability to deliver a “good enough” broadband service.
- U.S. mobile networks have proven to be resilient. Despite adding millions of 5G FWA subs since 2021, 5G speeds on T-Mobile and Verizon’s mobile networks have continued to improve. Their success in managing FWA traffic is due to a variety of factors, including plentiful access to mid-band spectrum, localized load management, and differences in peak usage time of day patterns between mobile and FBB usage.
- Elsewhere, there are mixed results. In India, Jio is seeing no discernible impact from FWA on the mobile experience of its users, while in Saudi Arabia Zain is seeing the additional load on its network from FWA having a greater influence on mobile users’ experience, depending on the time of day or the level of FWA penetration.
“Despite adding more than eight million 5G FWA subs using 400+ GB per month of data since Q1 2021, the overall mobile network experience on T-Mobile and Verizon’s mobile networks has not been compromised,” Opensignal analyst Robert Wyrzykowski wrote in the firm’s new assessment of FWA technology.

In its new report, Opensignal found that areas in the U.S. with a larger number of FWA customers actually showed better networking performance than areas with fewer FWA customers. Meaning, Verizon and T-Mobile offered increasingly speedy connections even in geographic locations with higher concentrations of FWA users.
“We would expect low-FWA penetration areas to see better mobile and FWA performance because of less load on the network. However, our data demonstrates the opposite trend,” Wyrzykowski explained.

Other Opensignal findings:
- Around 6% of urban Internet customers subscribe to FWA; in rural areas that figure is 7%.
- Some 74% of FWA customers pay less than $75 per month for their services.
- 35% of FWA customers are between 18-34 years old, whereas that age range is 25% for cable.
Opensignal’s findings provide an important view into the FWA industry in the US as its subscriber growth begins to slow. For example, T-Mobile added 405,000 FWA customers during the first quarter, far less than the 541,000 FWA customers it added during the fourth quarter of 2023.
“5G FWA services have been on a dramatic growth trajectory in the U.S., absorbing all broadband subscriber growth in the market since mid-2022 and amassing more than 600-700 thousand net adds per quarter,” wrote Opensignal’s Wyrzykowski. “This is despite the USA being a mature broadband market with nearly 97% broadband adoption and modest household growth.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
U.S. cable companies have recorded historic declines in their core Internet businesses amid the growth of FWA in the U.S. Financial analysts at TD Cowen predict the U.S. cable industry will collectively lose more than half a million customers in the second quarter of this year. They attribute that decline to FWA competition as well as other factors including the end of the U.S. government’s Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP).
The situation for cable might get even worse if FWA providers like T-Mobile and Verizon decide to invest further into their fixed wireless businesses.
“The pain for cable may continue for longer than expected as the ability for cable to return to broadband subscriber growth may take longer (if ever),” wrote the TD Cowen analysts in a recent note to investors.
Others agree. For example, the analysts at S&P Global wrote that cable service providers in general have been losing value to wireless network operators despite cable’s efforts to bundle mobile services into cable offerings.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Parks’ Hanich said fiber optic access technology is on an upswing and Parks is seeing “excellent growth in the markets where it is available and high customer satisfaction with the customers who have it.”
“But the numbers are not quite as dramatic as what’s been going on with T-Mobile, Verizon and Starlink,” she said, noting the “growing convergence” of satellite and mobile networks is something else to keep an eye on.
Asked whether the demise of the Affordable Connectivity Program has had any impact on Parks’ findings, Hanich said, “we are concerned that the end of the program will result in households and families needing to disconnect from the internet for financial reasons.”
“For a good percentage of Americans, household budgets have been hit by rising inflation and lower-income families especially are having to cut back,” she said. “Thankfully we are seeing ISPs step up, try and transition people onto other plans and initiatives.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Separately, Parks found adoption of mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) services reached over 15 million residential customer mobile lines in the quarter. In an MVNO model, broadband operators lease spectrum capacity from a wireless network to stand up their own mobile offering.
NTIA published some findings from its latest Internet Use Survey. Unsurprisingly, internet usage in the U.S. has gone up, with 13 million more people using the internet in 2023 compared to 2021. However, a lot of that usage is coming from lower-income households. Specifically, internet adoption among households making less than $25,000 per year increased from 69% in 2021 to 73% in 2023.
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/fixed-wireless-continues-its-climb-among-us-homes-parks
https://www.lightreading.com/fixed-wireless-access/fwa-in-the-usa-getting-ready-for-phase-2
Fiber and Fixed Wireless Access are the fastest growing fixed broadband technologies in the OECD
Summary of Verizon Consumer, FWA & Business Segment 1Q-2024 results
Verizon’s 2023 broadband net additions led by FWA at 375K
AT&T’s fiber business grows along with FWA “Internet Air” in Q4-2023
Ericsson: Over 300 million Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) connections by 2028
Deutsche Telekom offers 5G mmWave for industrial customers in Germany on 5G SA network
Deutsche Telekom (DT) has successfully trialed 5G millimeter wave (mmWave) frequencies at 26 gigahertz (GHz) with industrial use cases and is now offering them commercially to industrial customers. For the customer Ger4tech Mechatronik Center, autonomous industrial machines and robots were networked with a router in the 5G campus environment of the Werner-von-Siemens Centre for Industry and Science in Berlin. In addition to the 5G standalone (SA) network in the industrial spectrum at 3.7 GHz, this router also supports mmWave spectrum for the first time. With low latency times of three to four milliseconds RTT (round trip time) and a data rate of over 4 gigabits per second in download and 2 gigabits in upload, mmWave has huge potential in data-intensive applications in the manufacturing industry. The 5G mmWave communications are enabled by Telit Cinterion, a global end-to-end IoT solutions provider.
5G mmWave is playing an increasingly important role in wireless communication technology and imaging, among others. It is characterized by short coverage range and high bandwidth and speeds. It has enormous potential for development within 5G campus networks and for applications in the field of autonomous vehicles and the manufacturing industry. The special ability of mmWave lies in its ability to transmit large amounts of data in real time. The frequency spectrum around 26 GHz is allocated exclusively to interested parties in Germany by the Federal Network Agency. It can currently only be used for local applications.
“It is important for our industrial customers in the age of artificial intelligence to be able to upload data from machines and thus make it available and analyzable in real time,” explains Klaus Werner, Managing Director Business Customers at Telekom Deutschland GmbH. “This is the only way for companies to introduce AI applications sensibly and efficiently and derive great benefits for their business,” he added.
“We’re enabling customers to access unparalleled levels of efficiency, productivity and innovation. Through the seamless integration of 5G mmWave into their operations, every device and process can achieve connectivity at an unprecedented scale,” said Marco Contento, VP of Product Management, Mobile Broadband at Telit Cinterion. “Collaboratively, we’re helping to pave the way for industries to streamline operations, anticipate maintenance needs, and a multitude of future possibilities.”

The 5G standalone campus network at the Werner-von-Siemens Centre operates separately from Telekom’s public mobile network. The entire infrastructure, from the antennas and active system technology to the core network, comes from Ericsson. Based on this network, a fleet of autonomously driving and operating robots works on various use cases at the center. The 5G standalone network is often sufficient to control the robots. The 5G millimeter waves come into play when the requirements for communication and data transmission increase, and therefore also when solving more complex tasks. For example, in a computer vision application: the robot picks up an order and checks whether the ordered goods are complete on the way to the next destination. If there is a discrepancy, it immediately reorders the goods.
In addition to these, many other scenarios are mapped in the Werner-von-Siemens Centre. Here, industry, research institutions (including TU Berlin and Fraunhofer), small and medium-sized enterprises and start-ups work on practical solutions for companies – including for autonomous production logistics and other challenges in industrial manufacturing.
In the UK, regulator Ofcom launched a new consultation in April and the sector is awaiting the details of when and in what form an auction will take place.
Additional Resources:
About Ger4Tech Mechatronik Center
About Telit Cinterion
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/deutsche-telekom-looking-to-flog-5g-mmwave-to-industrial-sector
Daryl Schoolar: 5G mmWave still in the doldrums!
Momentum builds for wireless telco- satellite operator engagements
Over the past two years, the wireless telco-satellite market has seen significant industry-wide growth, driven by the integration of Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) in 5G New Radio as part of 3GPP Release 17. GSMA Intelligence reports that 91 network operators, representing about 5 billion global connections (60% of the total mobile market), have partnered with satellite operators. Although the regulatory landscape and policy will influence the commercial launch of these services in various regions, the primary objective is to achieve ubiquitous connectivity through a blend of terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks.
Recent developments include:
- AT&T and AST SpaceMobile have signed a definitive agreement extending until 2030 to create the first fully space-based broadband network for mobile phones. This summer, AST SpaceMobile plans to deliver its first commercial satellites to Cape Canaveral for launch into low Earth orbit. These initial five satellites will help enable commercial service that was previously demonstrated with several key milestones. These industry first moments during 2023 include the first voice call, text and video call via space between everyday smartphones. The two companies have been on this path together since 2018. AT&T will continue to be a critical collaborator in this innovative connectivity solution. Chris Sambar, Head of Network for AT&T, will soon be appointed to AST SpaceMobile’s board of directors. AT&T will continue to work directly with AST SpaceMobile on developing, testing, and troubleshooting this technology to help make continental U.S. satellite coverage possible.

- SpaceX owned Starlink has officially launched its commercial satellite-based internet service in Indonesia and received approvals to offer the service in Malaysia and the Philippines. Starlink is already available in Southeast Asia in Malaysia and the Philippines. Indonesia, the world’s largest archipelago with more than 17,000 islands, faces an urban-rural connectivity divide where millions of people living in rural areas have limited or no access to internet services. Starlink secured VSAT and ISP business permits earlier in May, first targeting underdeveloped regions in remote locations.Jakarta Globe reported the service costs IDR750,000 ($46.95) per month, twice the average spent in the country on internet service. Customers need a VSAT (very small aperture terminal) device or signal receiver station to use the solution.Internet penetration in Indonesia neared 80% at the end of 2023, data from Indonesian Internet Service Providers Association showed. With about 277 million people, Indonesia has the fourth largest population in the world. The nation is made up of 17,000 islands, which creates challenges in deploying mobile and fixed-line internet nationwide.Starlink also in received approvals to offer the service in Malaysia and the Philippines. The company aims to enable SMS messaging directly from a network of low Earth orbit satellites this year followed by voice and data starting in 2025. In early January, parent SpaceX launched the first of six satellites to deliver mobile coverage.
- Space X filed a petition with the FCC stating that it “looks forward to launching commercial direct-to-cellular service in the United States this fall.” That will presumably be only for text messages, because the company has stated that ONLY text will available in 2024 via Starlink. Voice and data won’t be operational until 2025. Importantly, SpaceX did not identify the telco who would provide Direct-to Cell satellite service this fall.
In August 2022, T-Mobile and SpaceX announced their plans to expand cellular service in the US using low-orbit satellites. The service aims to provide direct-to-cell services in hard-to-reach and underserved areas such as national parks, uninhabited areas such as deserts and mountain ranges, and even territorial waters. Traditional land-based cell towers cannot cover most of these regions.
- SpaceX said that “supplemental coverage from space (“SCS”) will enable ubiquitous mobile coverage for consumers and first responders and will set a strong example for other countries to follow.” Furthermore, SpaceX said the “FCC should reconsider a single number in the SCS Order—namely, the one-size-fits-all aggregate out-of-band power flux-density (“PFD”) limit of -120 dBW/m2 /MHz that it adopted in the new Section 25.202(k) for all supplemental coverage operations regardless of frequency band.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://about.att.com/story/2024/ast-spacemobile-commercial-agreement.html
AT&T, AST SpaceMobile draw closer to sat-to-phone launch
Starlink sat-service launches in Indonesia
Space X “direct-to-cell” service to start in the U.S. this fall, but with what wireless carrier?
Harnessing the Power of 5G
Revolutionizing Telecom with Programmable Networks and APIs
By Ameer Shohail L with Ajay Lotan Thakur
Ameer Shohail is an experienced ICT Solutions Design Specialist and IEEE Senior Member at a Tier 1 telecom operator in the Middle East, specializing in advanced wireless technologies.
Ajay Lotan Thakur is a Senior IEEE Member, IEEE Techblog Editorial Board Member (who edits/adds to blog posts), BCS Fellow, TST Member of ONF’s open source Aether (Private 5G) Project, Cloud Software Architect at Intel Canada.
Abstract
The telecom industry is on the verge of a significant transformation driven by the convergence of 5G/Beyond 5G and programmable networks. This article explores the immense potential of these advancements, emphasizing the shift from rigid infrastructures to dynamic platforms that offer their capabilities as services. We delve into the importance of programmable networks, the Network as a Service (NaaS) model, and the critical role of APIs. The article highlights the Network Exposure Function (5G CORE – NEF) and its role in creating new revenue streams for CSPs and fostering a thriving digital ecosystem. The TM (TeleManagement) Forum’s emphasis on service lifecycle management and the collective effort towards a digitally interconnected future are key themes, inviting all stakeholders to embrace this transformative journey.
Introduction: The Paradigm Shift in Telecom
The telecom industry is undergoing a profound transformation from traditional infrastructures to more dynamic and flexible systems. This shift is essential to meet the increasing demands for faster, more reliable, and scalable network services. Innovation and collaboration are now crucial drivers of industry growth, enabling communication service providers (CSPs) to leverage cutting-edge technologies to enhance their offerings and stay competitive.
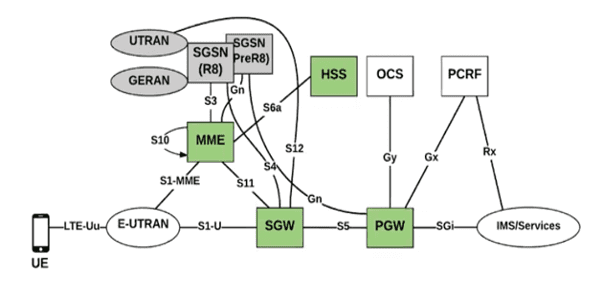
Figure1: EPS Architecture
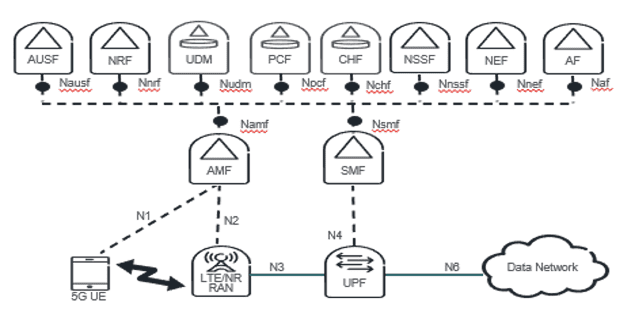
Figure2: 5GS Architecture
Programmable Networks and NaaS: The New Frontier
Programmable networks and Network as a Service (NaaS) represent the next frontier in telecom innovation. These technologies allow CSPs to offer network capabilities as customizable services, enhancing flexibility and efficiency. The TM Forum’s Open Digital Architecture (ODA) is central to this transformation, providing a standardized framework for the seamless integration of network services. By adopting ODA, CSPs can decouple network functions from the underlying hardware, enabling greater agility and innovation
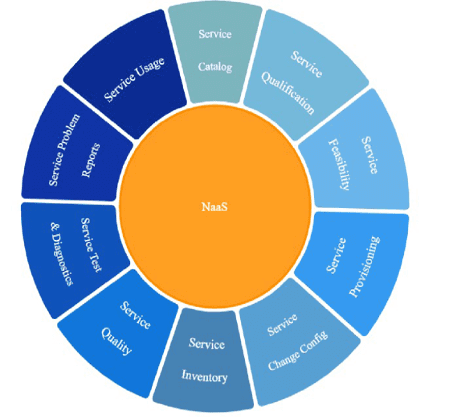
Figure3: NaaS function wheel, depicting various NaaS functions offered to consumers, REF[1]
APIs: The Engine of Innovation
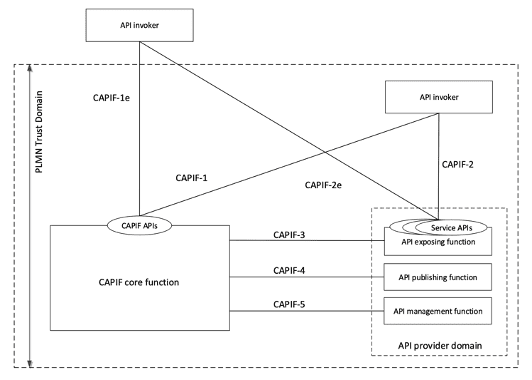
APIs are fundamental to the telecom industry’s transformation, empowering developers to create innovative services that leverage network capabilities. The Common API Framework (CAPIF) by 3GPP standardizes API usage across various network functions, ensuring smooth and secure communication. This framework acts as a universal language, facilitating collaboration and enhancing security across diverse applications and industries.
Figure4: Functional model for the CAPIF
Network Exposure Function (NEF): Unlocking New Potential
3GPP 5G Core architecture
5GC (Figure2) is the new 3GPP standard for core networks defining how the core network should evolve to support the needs of 5G New Radio (NR) and the advanced use cases enabled by it. The figure below depicts NEF representation in the non-roaming architecture, using 5G reference point representation.
Figure5: Network Exposure Function in reference point representation REF[4]
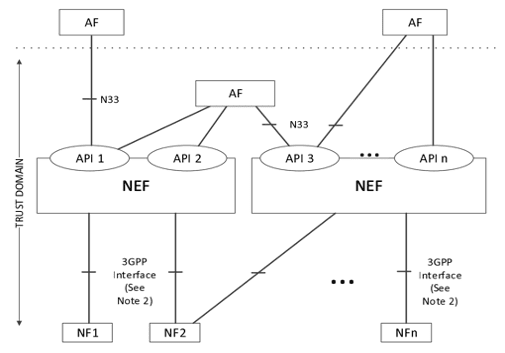
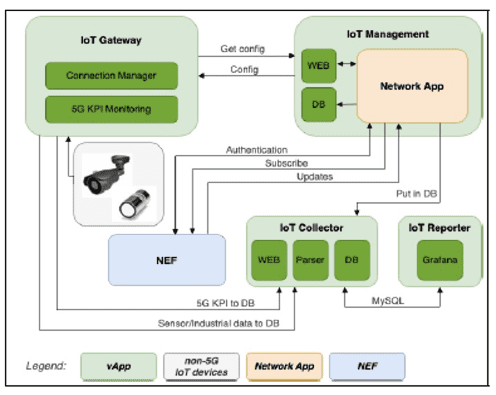
The Network Exposure Function (NEF) provides a secure, standardized method for exposing APIs, enabling CSPs to broaden their service offerings and explore new revenue streams. NEF is essential for fostering a thriving digital ecosystem, driving innovation, and economic growth in the telecom sector. Figure below depicts how NEF plays a role with the IoT ecosystem in enabling the communication exchange through API.
Figure6: Illustrates NEF and its role in enabling the network and external applications to exchange information, REF[5]
CAMARA Project: Accelerating Innovation through Standardized APIs
The CAMARA project, an open-source initiative hosted by the Linux Foundation, is pivotal in advancing the telecom industry’s move towards programmable networks and Network as a Service (NaaS). CAMARA aims to develop standardized APIs for network services, enabling seamless integration and interoperability across diverse network functions and applications.
This initiative promotes community-driven development and open-source principles, fostering collaboration among CSPs, technology vendors, and developers. Supported by leading industry players, CAMARA drives the adoption of robust, secure, and widely accepted APIs, facilitating new business models and revenue streams. By focusing on the needs of future technologies, CAMARA ensures that the telecom sector is well-equipped to leverage the unique capabilities of 5G, B5G, and beyond. REF[8]
Transition to a Service-Centric Model
The TM Forum’s focus on NaaS and service lifecycle management underscores the industry’s shift towards a service-centric model. This approach emphasizes managing the entire lifecycle of network services, from design and deployment to operation and optimization. By adopting a service-centric mindset, CSPs can deliver more personalized and efficient services, improving customer satisfaction and driving business growth. This approach also helps CSPs optimize operations and reduce costs by streamlining processes and improving resource utilization.
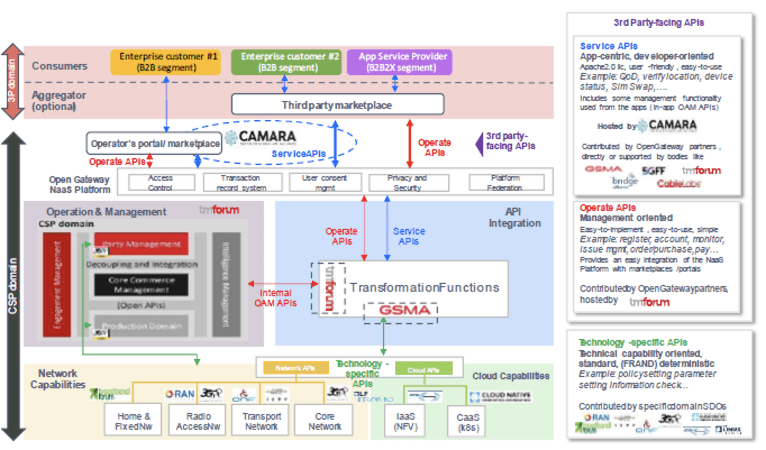
Figure7: Open Gateway NaaS Architecture and contributing stakeholders REF[7]
Conclusion
The telecom industry’s shift to programmable networks and NaaS marks a pivotal moment in its evolution. By embracing APIs, NEF, and service lifecycle management, CSPs can unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth. The collective efforts of industry stakeholders, supported by initiatives from TM Forum, GSMA, and CAMARA, will pave the way for a digitally interconnected future where collaboration and innovation are the norms. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing these advancements will be crucial for CSPs to stay competitive and meet the ever-growing demands of the digital age.
This journey is not just about technological advancement; it’s a collective endeavor towards a digitally interconnected future. It’s an invitation for all stakeholders, from telecom operators and technology providers to developers, to contribute to and reap the benefits of the expanding digital economy. Let’s embrace this transformative time, shaping the way we connect and interact in the digital world.
References
- IG1224 NaaS Transformation v12.0.0″: https://www.tmforum.org/resources/reference/ig1224-naas-transformation-v12-0-0/
- “Northbound exposure – how NEF and CAMARA can enable telecom’s platform play” by James Crawshaw, Practice Leader: https://omdia.tech.informa.com/om028769/northbound-exposure–how-nef-and-camara-can-enable-telecoms-platform-play
- ETSI TS 129 522 V16.4.0 (2020-08) – 5G; 5G System; Network Exposure Function Northbound APIs; Stage 3.
- 3GPP TS 23.501 version 15.3.0 Release 15; System Architecture for the 5G System
- “Common Framework for 5G Northbound APIs”: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/123200_123299/123222/15.03.00_60/ts_123222v150300p.pdf
- “5G and B5G NEF exposure capabilities towards an Industrial IoT use case” : https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=5G+and+B5G+NEF+exposure+capabilities+towards+an+Industrial+IoT+use+case&hl=en&as_sdt=0&as_vis=1&oi=scholart
- “The-Ecosystem-for-Open-Gateway-NaaS-API-development”: https://www.gsma.com/solutions-and-impact/gsma-open-gateway/gsma_resources/naas-ecosystem-whitepaper/
- https://camaraproject.org/; APIs enabling seamless access to Telco network capabilities
Ameer Shohail, Experienced ICT Solutions Design Specialist and IEEE Senior Member at a Tier 1 telecom operator in the Middle East, specializing in advanced wireless technologies
Nokia and Hong Kong Broadband Network Ltd deploy 25G PON
Nokia today announced that Hong Kong Broadband Network Ltd (HKBN), a leading telecom and technology solutions provider in Hong Kong, will deploy its 25G PON to provide customers with some of the fastest, most reliable broadband access speeds in the region. The 25G PON deployment will deliver 20Gb/s symmetrical broadband speeds essential for new applications and business services powering today’s digital economy.
Based on the Quillion chipset, Nokia’s 25G PON fiber broadband solution (more below) allows HKBN to reuse its existing fiber broadband equipment to immediately address demand for more capacity and enhanced broadband services.
William Yeung, HKBN Co-Owner, Executive Vice-chairman and Group CEO: “Since 2004, HKBN has been the market leader in introducing Hong Kong’s first fiber-to-the-home broadband service. With an unwavering commitment to innovation, we have joined forces with Nokia to achieve a groundbreaking upgrade, proudly providing customers with a revolutionary 25Gbps broadband speed that meets their ever-increasing demands for network connectivity. Looking ahead, we will continue to stay at the forefront of technological advancements, investing resources to expand network coverage and upgrade infrastructure. This will enable more households and businesses to benefit from our exceptional and high-quality services.”
Geert Heyninck, Vice President of Broadband Networks at Nokia: “Nokia’s technology enables HKBN to upgrade its existing fiber network quickly and efficiently, leveraging both passive and active assets. With Nokia’s technology and HKBN ‘s citywide network, we’re leading customers into a new era of seamless connectivity.”
Roland Montagne, Director and Principal Analyst for FTTH at IDATE: “The momentum behind 25G PON continues to build with the number of deployments growing substantially over the past year. Clearly the ability to quickly upgrade GPON and XGS-PON to deliver true 25Gbs without having to deploy additional network elements is attractive for large operators like HKBN that want to deliver 25G PON services to its customers.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Nokia recently deployed XGS-PON services with Baktelcom in Azerbaijan. That network can be upgraded in the future to 25G PON which would increase capacity and stay ahead of demand for higher bandwidth.
Nokia has also deployed with Global Fiber Peru a new subaquatic and future-proof Optical, IP and XGS-PON fiber broadband network in the Amazon rainforest, helping to reduce the digital divide. The extensive network connects over 400 communities to multi-gigabit broadband access that is critical in today’s digital economy.
About Nokia’s 25G PON Solution:
• Nokia’s 25G PON increases service agility with operational efficiency.
• The fiber access node supports multiple fiber technologies including GPON, XGS-PON, 25GS-PON and Point-to-Point Ethernet to deliver a wide range of services.
Resources and additional information:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://x.com/nokia/status/1181473779320594433
Nokia’s launches symmetrical 25G PON modem
U.S. fiber rollouts now pass ~52% of homes and businesses but are still far behind HFC
Google Fiber planning 20 Gig symmetrical service via Nokia’s 25G-PON system
HPE Aruba Launches “Cloud Native” Private 5G Network with 4G/5G Small Cell Radios
HPE Aruba has launched an end-to-end private 5G network platform which is designed to help customers accelerate and simplify the deployment and management of private 5G networks, provide high levels of reliable wireless coverage across large campus and industrial environments, and open new, untapped use cases for private cellular. This integration follows HPE’s 2023 acquisition of private cellular technology provider Athonet.
Highlights:
- HPE Aruba Networking provides a comprehensive solution that removes the complexity of managing, deploying and purchasing enterprise private cellular networks.
- With this expansion of its secure edge-to-cloud portfolio, HPE Aruba Networking becomes the only global enterprise infrastructure vendor to provide comprehensive Wi-Fi and private 5G solutions.
- HPE Aruba Networking Enterprise Private 5G provides high levels of reliable wireless coverage across large campus and industrial environments, opening up new, untapped use cases for private cellular.
“Enterprise and industrial customers are increasingly seeking to deliver wireless coverage in demanding environments, including large outdoor areas, serving fast-moving clients, and providing deterministic access in dedicated spectrum,” said Stuart Strickland, wireless chief technology officer, HPE Aruba Networking.
“The complexity of conventional approaches to private cellular networks has held them back. Building on HPE Aruba’s networking history of wireless innovation and leadership, we have uniquely positioned ourselves to enable new applications for private cellular by integrating Athonet core cellular solutions with our traditional strengths in enterprise networking.”
With the debut of HPE Aruba Networking Enterprise Private 5G, enterprises can increase reliable, secure, high-performance connectivity with a fully integrated private 5G network that features:
- An end-to-end offering that includes a 4G/5G core, HPE ProLiant Gen11 servers, SIM/eSIM cards, 4G/5G small cells, and dashboard.
- New 4G/5G small cell radios from HPE that provide indoor/outdoor coverage, eliminating the need to integrate and use a separate management tool from a 3rd party vendor.
- Simplified cloud-native management and automation for subscriber management, deployment management, core monitoring and radio monitoring, with future plans for integration with HPE Aruba Networking Central.
- Expanded AI data capture and delivery for building AI data lakes and activating inference solutions.
- Interoperability with shared spectrum for private enterprise use: Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) spectrum in the US, and globally, where regulatory frameworks allow, beginning in 2025.
- Simplified configuration with pre-integrated, tested solution including everything needed to deploy an enterprise private 4G/5G network.
- Ability to deploy solutions in under 30 minutes with zero touch provisioning and configuration wizards that mask the 3GPP cellular complexity.
“HPE Aruba Networking Enterprise Private 5G is a significant step forward to solve for the complexity, cost, control, and management challenges associated with many private network deployments today,” said Patrick Filkins, Senior Research Manager, IoT and Telecommunications, IDC. “HPE Aruba Networking takes a grounded approach focusing on how to most efficiently integrate a private cellular network within an enterprise’s existing IT framework, streamlining network and device management through the use of familiar tools, as well as dynamically assigning and preserving device policy across 4G/5G, Wi-Fi, and wired LAN networks.”
“‘Many private network solutions are too complex, even for large enterprises with internal network expertise,” said Tom Rebbeck, Partner, Analysys Mason. “We expect customers to embrace solutions that can make private networks easier to deploy and manage.”
“For IronYun’s Vaidio Platform to be able to provide AI inferencing at the edge and drive accurate AI video search results, we needed an infrastructure that provided fast, available and reliable bandwidth without any complexity,” said Paul Sun, IronYun CEO. “We found it with HPE Aruba Networking, which provides us with all the components needed to deliver an end-to-end private 5G network for AI. HPE Aruba Networking’s private 5G network is the technical foundation for all Vaidio functions for real-time video analysis and AI inferencing that deliver AI insights to help improve security outcomes.”
“Private cellular, with its wide area, deterministic coverage, is the ideal fit for Disc Golf Network’s global live competition coverage of the Disc Golf Pro Tour,” said Baker Helton, DGPT Vice President of Business Administration. “The new HPE Aruba Networking Enterprise Private 5G offering will make it that much easier for companies to do what we’ve done and meet their requirements for pervasive coverage with an integrated offering using CBRS.”
5 Reasons to adopt HPE Aruba Networking Enterprise Private 5G
HPE completes acquisition of private 5G leader Athonet
HPE acquires private cellular network provider Athonet (Italy) to strengthen HPE Aruba’s networking portfolio
SNS Telecom & IT: Private 5G Network market annual spending will be $3.5 Billion by 2027
Dell’Oro: Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network & Cable CPE shipments all declined in 1Q-2024
Apparently, there’s no place to hide in any telecom or datacom market? We all know the RAN market has been in a severe decline, but recent Dell’Oro Group reports indicate that Optical Transport, Mobile Core Network and Cable CPE shipments have also declined sharply in the 1st Quarter of 2024.
Here are a few selected quotes from Dell’Oro analysts:
“The North American broadband market is in the midst of a fundamental shift in the competitive landscape, which is having a significant impact on broadband equipment purchases,” said Jeff Heynen, Vice President with Dell’Oro Group. “In particular, cable operators are trying to navigate mounting, but predictable, broadband subscriber losses with the need to invest in their networks to keep pace with further encroachment by fiber and fixed wireless providers,” explained Heynen.
Omdia, owned by the ADVA, expects cable access equipment spending to grow later in 2024 and peak in 2026 at just over $1 billion, then drop off to $700 million in 2029.

………………………………………………………………………………………………………
“Customer’s excess inventory of DWDM systems continued to be at the center stage of the Optical Transport market decline in the first quarter of 2024,” said Jimmy Yu, Vice President at Dell’Oro Group. “However, we think the steeper-than-expected drop in optical transport revenue in 1Q 2024 may have been driven by communication service providers becoming increasingly cautious about the macroeconomic conditions, causing them to delay projects into future quarters,” added Yu.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“Inflation has impacted the ability of some Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) to raise capital, and it has also impacted subscribers when it comes to upgrading their phones to 5G. Many MNOs have lowered their CAPEX plans and announced that they have fewer than expected 5G subscribers on their networks; which limits MNOs’ growth plans. As a result, we are lowering our expectations for 2024 from a positive growth rate to a negative one,” by Research Director Dave Bolan.
- As of 1Q 2024, 51 MNOs have commercially deployed 5G SA (Stand Alone) eMBB networks with two additional MNOS launching in 1Q 2024.
References:
Optical Transport Equipment Market Forecast to Decline in 2024, According to Dell’Oro Group
Optical Transport Equipment Market Forecast to Decline in 2024, According to Dell’Oro Group