Author: Alan Weissberger
Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTNs): market, specifications & standards in 3GPP and ITU-R
Introduction:
A recent survey showed that Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTNs) are viewed by the telecom industry as reinforcing service reliability and adding an extra layer of network redundancy to 5G. This view increasingly makes the convergence of satellites and 5G (and fiber) a mainstream application in telecoms. With LEO constellation service revenues forecast to reach $15 billion next year, the industry is expected to experience unprecedented growth.
However, that growth will depend on interoperability to realize economies of scale. To achieve that goal NTN standards, regulatory and policy frameworks must evolve to keep pace and ensure equitable access to space for all. As such, we examine the status and future NTN work in 3GPP and ITU-R in this article.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) has established NTNs as a key part of 5G and future 6G by defining standards in Release 17, which introduced support for satellites and High-Altitude Platforms (HAPS) for direct-to-device (D2D) communication, enabling ubiquitous connectivity. Current work in Release 18 and beyond (including ongoing Release 19 studies) focuses on enhancing performance, expanding spectrum, improving security, and integrating NTNs seamlessly with terrestrial networks for better resource management, leading towards a unified, hybrid telecom ecosystem for global coverage.
- Release 15 & 16 (Foundational): Established NTN use cases, system architectures, and channel models for satellite-based systems.
- Release 17 (First Standardized Release): Introduced the first normative specifications for 5G NR and NB-IoT NTNs, covering GEO and LEO/MEO satellites, addressing technical hurdles like propagation delay and Doppler shift for mass-market devices.
- Release 18 (Enhancements): Studied security aspects, improved 5G NR NTN for higher frequencies (above 10 GHz), and focused on resource management for efficient integration.
- Release 19 & Beyond (Ongoing): Continues to evolve NTNs, introducing features like regenerative payloads, Ku-band support, and further integration for future 5G-Advanced and 6G networks, with studies on 6G architecture.
- Hybrid Networks: Creating a unified framework for seamless terrestrial and non-terrestrial operation.
- Direct-to-Device (D2D) Evolution: Expanding services beyond basic IoT to support smartphones for voice and data in remote areas.
- Technical Refinements: Addressing RF performance, spectrum coordination, and operational complexity for LEO/MEO systems.
- 6G Foundation: Building architectural principles for ubiquitous connectivity that will underpin future 6G systems.
The International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) Working Party 4B is actively shaping NTN’s by developing reports and recommendations to integrate satellites (LEO, MEO, GEO) and High-Altitude Platforms (HAPs) with 5G and future 6G cellular networks. The aim is to enable ubiquitous coverage, Direct-to-Device (D2D) services, and seamless hybrid networks, with ongoing work focusing on radio interface specifications, spectrum harmonization, and performance enhancements for reliable connectivity.

- Standardization: ITU-R is finalizing Recommendation ITU-R M.IMT-2020-SAT.SPECS (based on 3GPP’s Release 17/18 specs) to standardize 5G satellite-to-ground communication, supporting IoT and advanced mobile services.
- Working Groups: WP 4B (Satellite services) and other groups are key to defining NTN requirements, spectrum usage, and interoperability.
- Focus Areas:
- Hybrid Networks: Creating seamless service continuity between terrestrial and space/aerial segments.
- Direct-to-Device (D2D): Enabling smartphones to connect directly to satellites.
- Spectrum: Harmonizing spectrum for NTNs, including Ku-band, for expanded services.
- Performance: Addressing challenges like Doppler shift, propagation delay, and handover management for LEO/MEO constellations.
- 3GPP is a crucial partner, introducing NTN frameworks in Release 17 (IoT) and Release 18 (enhanced 5G), with continuous updates for 6G and beyond, closely coordinating with ITU-R.
- ITU-R’s reports discuss future trends, including AI-driven interfaces, diverse terminals (wearables, implants), and the role of NTNs in achieving global, resilient connectivity, supporting Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
References:
https://www.gsma.com/solutions-and-impact/technologies/networks/gsma_resources/non-terrestrial-networks-opportunities-and-challenges/
https://www.telecoms.com/satellite/key-non-terrestrial-network-developments-in-2025
https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/ntn-overview
Telecoms.com’s survey: 5G NTNs to highlight service reliability and network redundancy
ITU-R recommendation IMT-2020-SAT.SPECS from ITU-R WP 5B to be based on 3GPP 5G NR-NTN and IoT-NTN (from Release 17 & 18)
Standards are the key requirement for telco/satellite integration: D2D and satellite-based mobile backhaul
GSMAi: key telecom developments in 2025; major trends to watch in 2026
Deutsche Telekom: successful completion of the 6G-TakeOff project with “3D networks”
AST SpaceMobile to deliver U.S. nationwide LEO satellite services in 2026
MTN Consulting: Satellite network operators to focus on Direct-to-device (D2D), Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud-based services
Samsung announces 5G NTN modem technology for Exynos chip set; Omnispace and Ligado Networks MoU
How will fiber and equipment vendors meet the increased demand for fiber optics in 2026 due to AI data center buildouts?
Fiber optic vendors are employing a mix of manufacturing expansion, technological innovation in high-density and next-generation fibers, and strategic supply chain alignment to meet the anticipated surge in demand from AI and data centers in 2026. The demand is so high that at least one major fiber manufacturer, whose name was not explicitly disclosed in news reports, has already sold all its fiber inventory through 2026. Major fiber optic vendors by category are:
- Fiber & Cable Manufacturing: Corning, Prysmian Group, Sumitomo Electric, Fujikura, CommScope, Sterlite Technologies (STL), Yangtze Optical Fibre & Cable (YOFC)
- Optical Transport/Networking: Nokia, Ciena (gaining share), Cisco, Fujitsu, Huawei, Infinera (now part of Nokia)
- Optical Components/Transceivers: Coherent Corporation, Lumentum, Broadcom, Innolight, Accelink
Major focus areas of selected vendors:
- Corning: Leading in fiber cable quality and innovation
- Nokia & Ciena: Strong in optical transport and network solutions, gaining market share
- Cisco & Huawei: Significant players in optical transceivers, catching up to leaders
- CommScope, Clearfield, STL: Preparing for huge demand surges
John McGirr, SVP and general manager for Corning Optical Fiber & Cable, said, “The surge in hyperscale and AI network loads has significantly increased our expectations for fiber demand. Enterprise sales grew 58% year-over-year in Q3 2025, driven by continued strong adoption of Corning’s Gen AI products, largely due to AI network growth demands. The 72-GPU nodes, such as (Nvidia’s) Blackwell, require 16 times more fiber than traditional cloud switch racks. We see no signs of AI network growth slowing down especially as operators scale up (increase computational power by adding more resources within the existing backend AI network node) and scale out (increase the number of nodes to accommodate increasing demand) their networks.”
Rahul Puri, CEO of the Optical Networking Business at STL, said, “AI-focused data centers require significantly more fiber — about 36x more fiber than traditional CPU-based racks — to handle the massive data volumes and high-speed connectivity required by GPU clusters.” Puri predicts that cumulative hyperscale data capacity will increase by three times in the next few years alone. “The U.S. will need to add 213.3 million more fiber miles by 2029, more than doubling its current amount from 159.6 million fiber miles to 372.9 million miles. Our roadmap is shaped directly with the world’s leading cloud, AI and data center operators,”” Puri added.
CommScope’s VP of Technology John Chamberlain and VP of Hyperscale Cloud Erik Gronvall noted that the company has expanded its fiber manufacturing capacity in recent years to meet increased demand. “We are also innovating to reduce the amount of time it takes to deploy AI clusters,” said Chamberlain and Grovall.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Fiber Vendor Strategies:
Capacity Increase: Vendors like Corning and CommScope are investing in increasing their production capacity for fiber optic cables and the necessary preforms (raw material for fiber). This includes expanding existing facilities to help alleviate the current supply chain tightness and long lead times.
Technological Innovation in Fiber Design: To support the extreme bandwidth and low-latency needs of AI, vendors are focusing on advanced fiber technologies.
-
- Higher Fiber Counts: Companies are launching cables with extremely high fiber counts (e.g., 1,728+ strands) and higher density options to pack more capacity into existing infrastructure.
- Next-Generation Fibers: Research is ongoing in areas like hollow-core fiber (which uses air or a vacuum to transmit light faster and with less loss) and multicore fiber (multiple cores in one strand to increase capacity). These technologies, while not yet mainstream for 2026, are part of the long-term strategy.
- Bend-Insensitive Fiber: Innovations in bend-insensitive and ultra-high fiber count cables are improving durability and easing deployment in complex data center environments.
Pre-connectorized and Modular Solutions: To counter a persistent skilled labor shortage and speed up deployment, vendors are pushing factory-terminated, plug-and-play fiber systems and modular platforms (like Siemon’s LightStack). These solutions require less on-site expertise and reduce installation time.
Strategic Partnerships and Supply Chain Alignment: Vendors are forming strategic collaborations with hyperscalers and network operators (like the agreement between Corning and Lumen) to align manufacturing platforms with future demand and ensure supply. They are also working to optimize supply chains and, in some cases, regionalize manufacturing to reduce lead times.
Structured Cabling and Photonics: There is a renewed focus on structured cabling architectures, as recommended by some AI platform providers, to ensure predictable, low-latency performance and simpler long-term management. The industry is also exploring integrated photonics to address the power and thermal challenges of future systems.
Focus on AI-Specific Demands: Vendors recognize that AI data centers require up to five times more connectivity than traditional hyperscaler topologies and network architectures. Their strategies are specifically tailored to high-volume, intra-bay, inter-bay, and middle-mile fiber connections to link distributed data center clusters into a single, unified AI computing environment.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Ciena and Nokia:
- Ramping up Production: Ciena is accelerating the production of 800G ZR+ optical pluggables, with plans to ship a large volume in 2026 to major cloud providers who are currently testing the technology.
- New Architectures: The company is developing new interconnect solutions under the “Scaleacross” architecture designed to support growing AI workloads by significantly increasing capacity and density within the data center.
- Increased Forecasts: Driven by record orders from hyperscalers, Ciena has raised its revenue guidance for fiscal 2026 to a range of $5.7 billion to $6.1 billion, a significant increase that analysts tie directly to AI-driven demand.
- Strategic Positioning: Ciena emphasizes that the network will be the primary limiter of AI performance by 2026, positioning its high-speed fiber solutions as critical for moving massive amounts of data between compute nodes efficiently.
- Major U.S. Investment: Nokia announced a $4 billion investment in U.S. R&D and manufacturing capabilities for “AI-ready” network technologies, including optical and data center networking, to ensure robust domestic supply.
- Strategic Reorganization: Effective at the start of 2026, Nokia will reorganize into two primary segments, one of which is “Network Infrastructure” (including optical networks), which it sees as the center of the “AI supercycle.”
- Industry Collaboration: Nokia has deepened its commitment to the Open Compute Project (OCP) at the Platinum level, aiming to collaborate on open, interoperable AI networking innovations that optimize space, cost, and power efficiency with standards-driven technology.
- Advocacy for Network Modernization: Nokia’s research highlights that current networks are insufficient for future AI growth, advocating for substantial investment and cross-industry collaboration to modernize digital infrastructure to handle the uplink-heavy, distributed data flows generated by AI.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/major-fiber-vendors-strategize-huge-demand-ai-2026
https://www.fierce-network.com/premium/research/1410126?pk=FN-Research-Commscope-111925-listing
NTT to launch 25 Gps FTTH service in Tokyo starting March 2026
AI wireless and fiber optic network technologies; IMT 2030 “native AI” concept
AI infrastructure investments drive demand for Ciena’s products including 800G coherent optics
AT&T sets 1.6 Tbps long distance speed record on its white box based fiber optic network
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
Lumen and Ciena Transmit 1.2 Tbps Wavelength Service Across 3,050 Kilometers
Co-Packaged Optics to play an important role in data center switches
Coherent Optics: Synergistic for telecom, Data Center Interconnect (DCI) and inter-satellite Networks
Hyper Scale Mega Data Centers: Time is NOW for Fiber Optics to the Compute Server
Microsoft acquires Lumenisity – hollow core fiber high speed/low latency leader
China Mobile to deploy 400G QPSK by the end of 2023
NTT to launch 25 Gps FTTH service in Tokyo starting March 2026
NTT East plans to launch a 25 Gbps Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) service in Tokyo starting March 2026, according to Telecompaper, The service will offer significantly faster residential broadband, building on their existing fiber services and recent developments in higher-speed business options. Currently, the highest speed Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) access plan commercially available in Japan is 10 Gbps offered by multiple fiber optic network providers, including NTT East/West and Sony-backed NURO Hikari.
NTT’s forthcoming Flet Hikari 25G service will be a best-effort FTTH access product, utilizing shared subscriber fiber to connect customers to their chosen Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
The launch is part of NTT’s broader initiative to develop next-generation digital infrastructure, which also includes the development of key devices for an ultrafast optical network under its “Innovative Optical and Wireless Network” (IOWN) project in 2026.
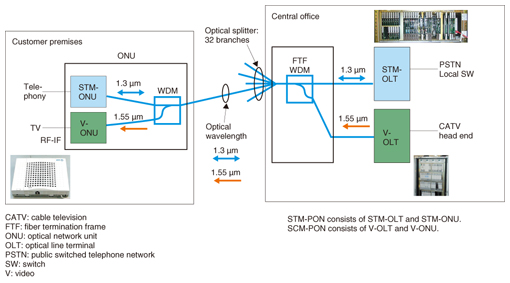
Source: NTT Access Service Systems Laboratories
Separately, researchers in Japan have set world records for internet transmission speeds using experimental fiber optic technology, reaching speeds of over 1 petabit per second (which is over a million gigabits per second) in laboratory settings. These are research achievements and not a commercially available service for everyday use.
References:
https://www.ntt-review.jp/archive/ntttechnical.php?contents=ntr201604fa6.html
https://www.telecompaper.com/news/ntt-east-and-west-launch-10-gbps-service–1538339
NTT’s IOWN provides ultra low latency and energy efficiency in Japan and Hong Kong
NTT Data and Google Cloud partner to offer industry-specific cloud and AI solutions
Sony and NTT (with IOWN) collaborate on remote broadcast production platform
NTT & Yomiuri: ‘Social Order Could Collapse’ in AI Era
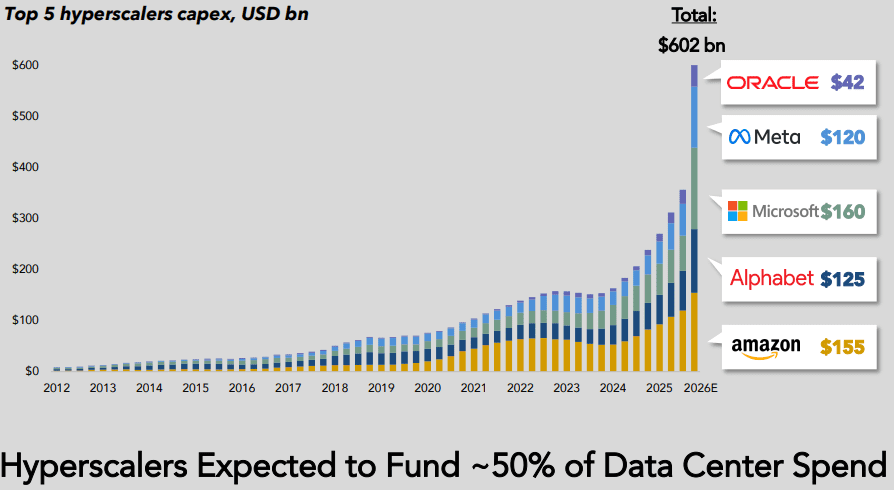
Hyperscaler capex > $600 bn in 2026 a 36% increase over 2025 while global spending on cloud infrastructure services skyrockets
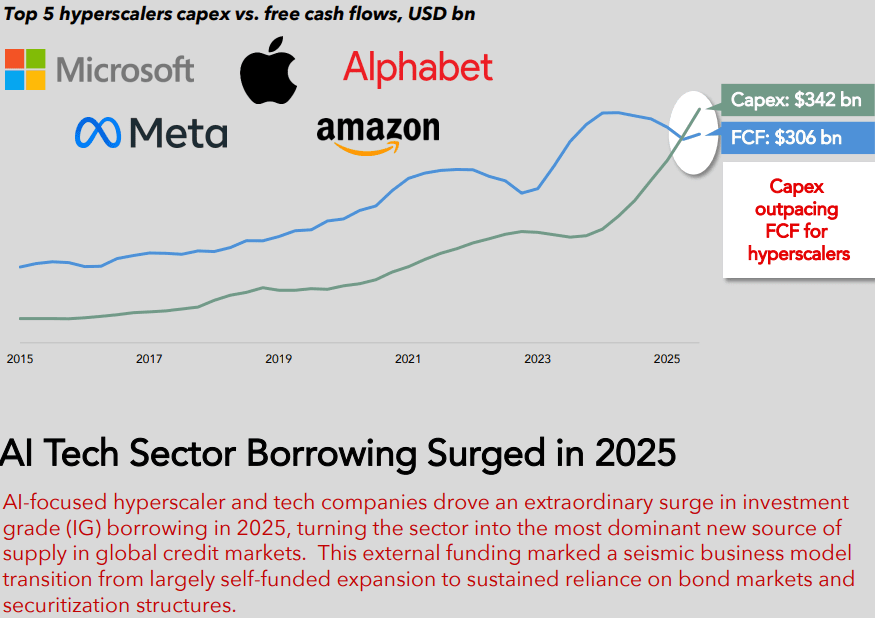
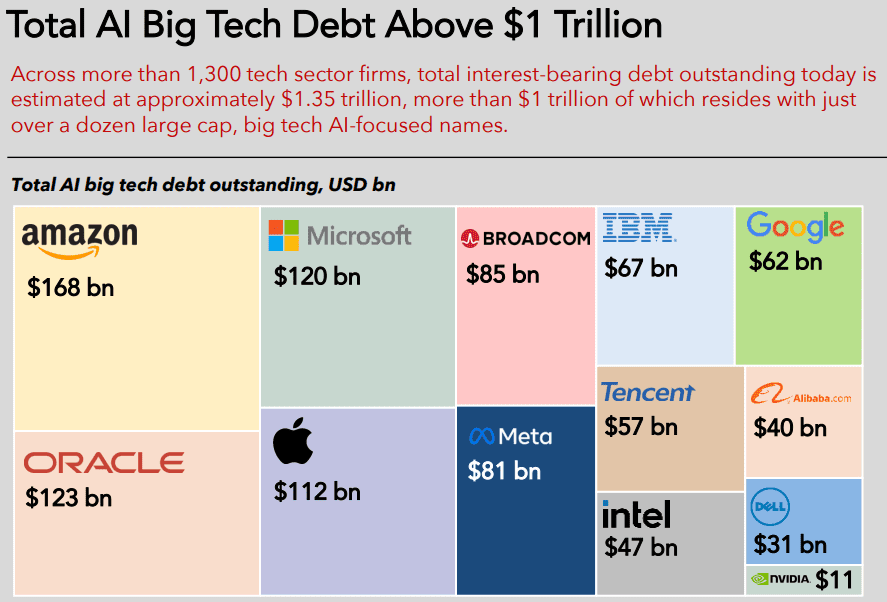
Hyperscaler capex for the “big five” (Amazon, Alphabet/Google, Microsoft, Meta/Facebook, Oracle) is now widely forecast to exceed $600 bn in 2026, a 36% increase over 2025. Roughly 75%, or $450 bn, of that spend is directly tied to AI infrastructure (i.e., servers, GPUs, datacenters, equipment), rather than traditional cloud. Hyperscalers are increasingly leaning on debt markets to bridge the gap between rapidly rising AI capex budgets and internal free cash flow, transforming historically cash-funded business models into ones utilizing leverage, albeit with still very strong balance sheets. Aggregate capex for “the big five”, after buybacks and dividends are included, are now above projected cash flows, thereby necessitating external funding needs.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
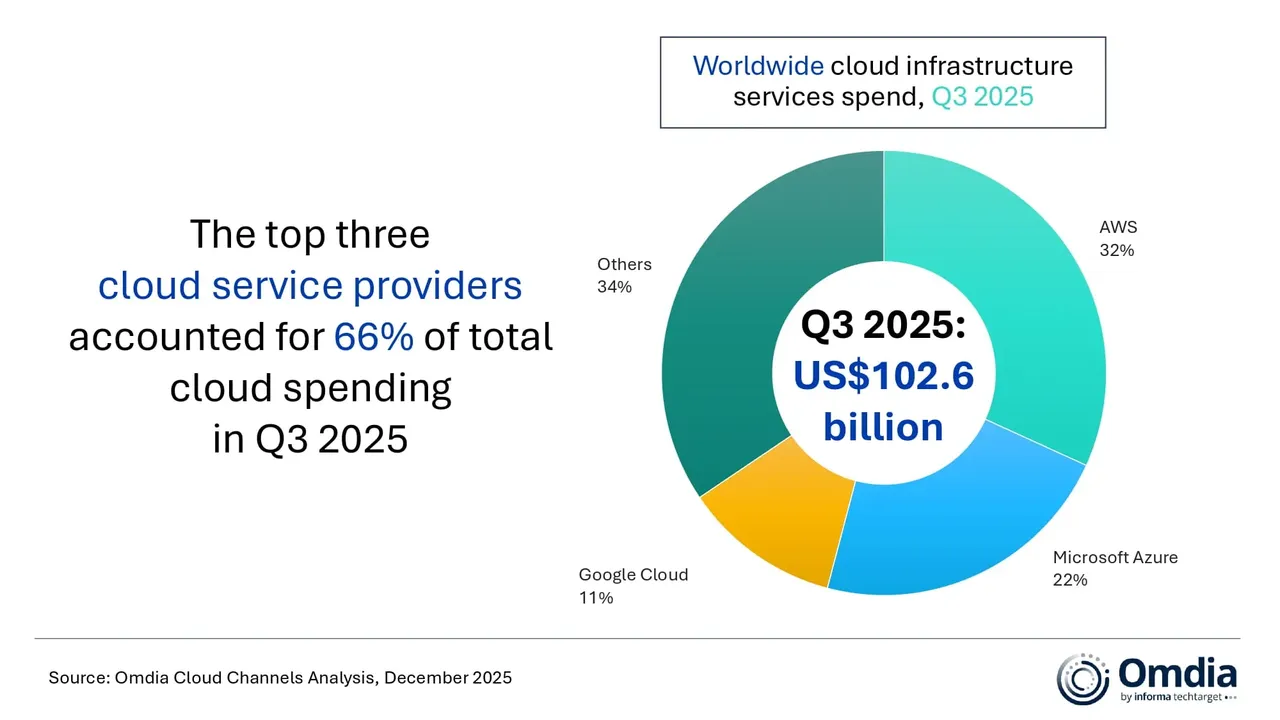
According to market research from Omdia (owned by Informa) global spending on cloud infrastructure services reached $102.6 billion in Q3 2025 — a 25% year-on-year increase. It was the fifth consecutive quarter in which cloud spending growth remained above 20%. Omdia says it “reflects a significant shift in the technology landscape as enterprise demand for AI moves beyond early experimentation toward scaled production deployment.” AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud – maintained their market rankings from the previous quarter, and collectively accounted for 66% of global cloud infrastructure spending. Together, the three firms had 29% year-on-year growth in their cloud spending.
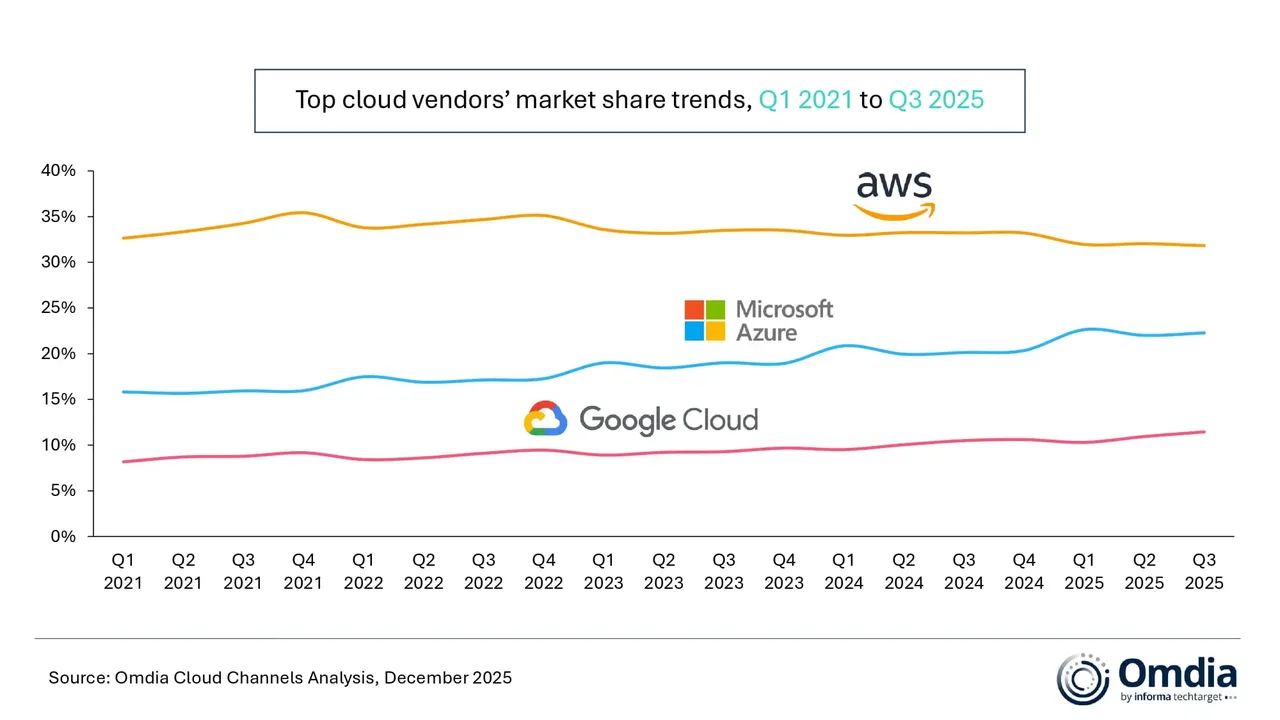
Hyperscaler AI strategies are shifting from a focus on incremental model performance to platform-driven, production-ready approaches. Enterprises are now evaluating AI platforms based not solely on model capabilities, but also on their support for multi-model strategies and agent-based applications. This evolution is accelerating hyperscalers’ move toward platform-level AI capabilities. According to the report, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are integrating proprietary foundation models with a growing range of third-party and open-weight models to meet these new demands.
“Collaboration across the ecosystem remains critical,” said Rachel Brindley, Senior Director at Omdia. “Multi-model support is increasingly viewed as a production requirement rather than a feature, as enterprises seek resilience, cost control, and deployment flexibility across generative AI workloads.”
Facing challenges with practical application, major cloud providers are boosting resources for AI agent lifecycle management, including creation and operationalization, as enterprise-level deployment proves more intricate than anticipated.
Yi Zhang, Senior Analyst at Omdia, said, “Many enterprises still lack standardized building blocks that can support business continuity, customer experience, and compliance at the same time, which is slowing the real-world deployment of AI agents. This is where hyperscalers are increasingly stepping in, using platform-led approaches to make it easier for enterprises to build and run agents in production environments.”
This past October, Omdia released a report forecasting that growth of cloud adoption among communications service providers (CSPs) will double this year. It also forecasted a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% to 2030, resulting in the telco cloud market being worth $24.8 billion.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Editor’s Note: Does anyone remember the stupendous increase in fiber optic spending from 1998-2001 till that bubble burst? Caveat Emptor!
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/public-cloud/global-cloud-infrastructure-spend-up-25-in-q3
https://www.telecoms.com/public-cloud/telco-investment-in-cloud-infrastructure-is-accelerating-omdia
AI infrastructure spending boom: a path towards AGI or speculative bubble?
Expose: AI is more than a bubble; it’s a data center debt bomb
Can the debt fueling the new wave of AI infrastructure buildouts ever be repaid?
AI spending boom accelerates: Big tech to invest an aggregate of $400 billion in 2025; much more in 2026!
Gartner: AI spending >$2 trillion in 2026 driven by hyperscalers data center investments
AI spending is surging; companies accelerate AI adoption, but job cuts loom large
Will billions of dollars big tech is spending on Gen AI data centers produce a decent ROI?
Big tech spending on AI data centers and infrastructure vs the fiber optic buildout during the dot-com boom (& bust)
Canalys & Gartner: AI investments drive growth in cloud infrastructure spending
Sovereign AI infrastructure for telecom companies: implementation and challenges
AI Echo Chamber: “Upstream AI” companies huge spending fuels profit growth for “Downstream AI” firms
Custom AI Chips: Powering the next wave of Intelligent Computing
Palo Alto Networks and Google Cloud expand partnership with advanced AI infrastructure and cloud security
- End-to-End AI Security from Code to Cloud: Customers can protect live AI workloads and data on Google Cloud, including instances on Vertex AI and Agent Engine, using Palo Alto Networks Prisma AIRS. Securing key developer tools like the Agent Development Kit (ADK) with Prisma AIRS provides a secure foundation for developing next-generation AI applications on Google Cloud. This includes capabilities such as AI Posture Management, AI Runtime Security™, AI Agent Security for autonomous systems, AI Red Teaming, and AI Model Security.
- AI-Driven, Next-Generation Software Firewall (SWFW): Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewalls, designed for securing cloud and virtualized environments via deep packet inspection and Threat Prevention, will feature deep integrations with Google Cloud to help customers maintain robust security policies and accelerate cloud adoption.
- AI-Driven Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) Platform: Palo Alto Networks Prisma SASE platform secures access and networking for remote users and branch offices. Deeper integration with Google Cloud’s native AI services will improve the user experience by leveraging Google’s network for Prisma Access execution and utilizing Google Cloud Interconnect for consistent security policies across multi-cloud WAN infrastructure.
- Simplified and Unified Security Experience: The deep engineering alignment ensures that joint solutions are pre-vetted and optimized for seamless interoperability, reducing integration complexity and operational overhead for security teams. This enables faster deployment of protective measures, simplified compliance, and a unified security posture across the entire hybrid multicloud ecosystem.
- BJ Jenkins, President, Palo Alto Networks: “The critical question for modern governance boards is how to leverage AI without introducing undue risk. This partnership provides the definitive answer. We are eliminating the operational friction between security and development, delivering a unified platform where cutting-edge security is an inherent component of innovation. By embedding our AI-powered security deeply into the Google Cloud infrastructure, we are transforming the platform into a proactive defense system.”
- Matt Renner, President and Chief Revenue Officer, Google Cloud: “Enterprises increasingly rely on the combined capabilities of Google Cloud and Palo Alto Networks for seamless application and data security. This partnership expansion guarantees our joint clientele access to the necessary solutions for securing their most critical AI infrastructure and developing secure-by-design AI agents from inception.”

About Palo Alto Networks:
As the global AI and cybersecurity leader, Palo Alto Networks (NASDAQ: PANW) is dedicated to protecting our digital way of life via continuous innovation. Trusted by more than 70,000 organizations worldwide, we provide comprehensive AI-powered security solutions across network, cloud, security operations and AI, enhanced by the expertise and threat intelligence of Unit 42®. Our focus on platformization allows enterprises to streamline security at scale, ensuring protection fuels innovation. Explore more at www.paloaltonetworks.com.
Palo Alto Networks, Prisma, Prisma AIRS, and the Palo Alto Networks logo are trademarks of Palo Alto Networks, Inc. in the United States and in jurisdictions throughout the world. All other trademarks, trade names, or service marks used or mentioned herein belong to their respective owners.
About Google Cloud:
Google Cloud is the new way to the cloud, providing AI, infrastructure, developer, data, security, and collaboration tools built for today and tomorrow. Google Cloud offers a powerful, fully integrated and optimized AI stack with its own planet-scale infrastructure, custom-built chips, generative AI models and development platform, as well as AI-powered applications, to help organizations transform. Customers in more than 200 countries and territories turn to Google Cloud as their trusted technology partner.
- Learn more about Palo Alto Networks and the Google Cloud partnership here.
- Please see References below for Google Cloud initiatives
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/engage/global-multi-platform-security/palo-alto-devops-in
NTT Data and Google Cloud partner to offer industry-specific cloud and AI solutions
Google Cloud targets telco network functions, while AWS and Azure are in holding patterns
Deutsche Telekom and Google Cloud partner on “RAN Guardian” AI agent
Google Cloud announces TalayLink subsea cable and new connectivity hubs in Thailand and Australia
Ericsson and Google Cloud expand partnership with Cloud RAN solution
Google Cloud infrastructure enhancements: AI accelerator, cross-cloud network and distributed cloud
T-Mobile and Google Cloud collaborate on 5G and edge compute
Cloud RAN with Google Distributed Cloud Edge; Strategy: host network functions of other vendors on Google Cloud
Casa Systems and Google Cloud strengthen partnership to progress cloud-native 5G SA core, MEC, and mobile private networks
Google Cloud expands footprint with 34 global regions
GSMAi: key telecom developments in 2025; major trends to watch in 2026
Introduction:
During a recent GSMA Intelligence (GSMAi) webinar, key developments in the 2025 telecom sector were identified. They include satellite communications expansion/partnerships, eSIM proliferation, and industry consolidation.
Projections for 2026 suggest that 6G evolution (in 3GPP and ITU-R WP 5D) and artificial intelligence (AI) will have the greatest impact within the telecom space.
Mergers & Acquisitions:
Radhika Gupta, GSMAi’s Head of Data Acquisition, asserted that 2025 marked a pivotal shift, signaling that “ice finally broke on consolidation” within the telecommunications sector. The completion of the Vodafone UK and Three UK merger is cited as primary evidence, reducing the UK market from four major competitors to three.
“This particular event is important because Europe historically had been very particular about not approving such mergers that shrink a market from four players to three players for competition reasons. Even in the UK, back in 2016, Three and O2 [now Virgin Media O2] attempted to merge, which was not approved by the European Commission on competition reasons only.”
- A mandatory £11bn joint network investment plan over eight years for infrastructure upgrades.
- Capped consumer tariffs for three years to mitigate price escalation.
- Pre-set wholesale prices for three years, ensuring fair access for Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs).
“While I don’t think we will see satellite providers overtaking terrestrial services, as some have speculated, it shows that direct-to-device is a formidable trend right now… operators representing almost 70% of [the global mobile] market share has at least one satellite partnership with companies like Starlink,” Hatt added.
Editor’s Note: AST SpaceMobile, Iridium and Skylo and other satellite network operators are also making similar partnerships with cellular network operators to offer direct-to-device (D2D) satellite connectivity. The use cases are emergency texting and future voice/data, aiming to eliminate mobile dead zones by connecting standard smartphones to LEO satellites. These collaborations leverage existing mobile networks and spectrum to provide ubiquitous coverage, with AT&T and Verizon focusing on AST SpaceMobile and T-Mobile partnering with Starlink for expanded services.
 Image Credit: European Space Agency
Image Credit: European Space Agency
Accelerating eSIM Adoption and OEM Strategy:
GSMA, ETSI, IEEE, ITU & TM Forum: AI Telco Troubleshooting Challenge + TelecomGPT: a dedicated LLM for telecom applications
GSMA Vision 2040 study identifies spectrum needs during the peak 6G era of 2035–2040
Gartner: Gen AI nearing trough of disillusionment; GSMA survey of network operator use of AI
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
Highlights of GSMA study: Mobile Net Zero 2024, State of the Industry on Climate Action
Sovereign AI infrastructure for telecom companies: implementation and challenges
Sovereign AI infrastructure refers to the domestic capability of a nation or an organization to own and control the entire technology stack for artificial intelligence (AI) systems within its own borders, subject to local laws and governance. This includes the physical data centers, specialized hardware (like GPUs), software, data, and skilled workforce. Sovereign AI infrastructure involves a full “stack” designed to ensure national control and reduce reliance on foreign providers. A few key features:
- Policies and technical controls (e.g., data localization, encryption) to ensure that sensitive data used for training and inference remains within the jurisdiction.
- Development and hosting of proprietary or locally tailored AI models and software frameworks that align with national values, languages, and ethical standards.
- Workforce Development: Investing in domestic talent, including data scientists, engineers, and legal experts, to build and maintain the local AI ecosystem.
- Regulatory Framework: A comprehensive legal and ethical framework for AI development and deployment that ensures compliance with national laws and standards.
Why It’s Important – The pursuit of sovereign AI infrastructure is driven by several strategic considerations for both governments and private enterprises:
- National Security: To ensure that critical systems in defense, intelligence, and public infrastructure are not dependent on potentially adversarial foreign technologies or subject to extraterritorial access laws (like the U.S. CLOUD Act).
- Economic Competitiveness: To foster a domestic tech industry, create high-skilled jobs, protect intellectual property, and capture the significant economic benefits of AI-driven growth.
- Data Privacy and Compliance: To comply with stringent local data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR in the EU) and build public trust by ensuring citizen data is handled securely and according to local laws. Cultural Preservation: To train AI models on local datasets and languages, preserving cultural nuances and avoiding bias found in generalized, globally trained models.

Image Credit: Nvidia
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Governments around the world are starting to build sovereign AI infrastructure, and according to a new report from Morningstar DBRS, which opines that major telecommunications companies are uniquely positioned to benefit from that shift. Here are a few take-aways from the report:
- Sovereign AI funding opens a new growth path for telcos – Governments investing in domestic AI infrastructure are increasingly turning to operators, whose network and regulatory strengths position them to capture a large share of this emerging market.
- Telcos’ capabilities align with sovereignty needs – Their expertise in large-scale networks, local presence, and established government relationships give them an edge over hyperscalers for sensitive, sovereignty-focused AI projects.
- Early adopters gain advantage – Operators in Canada and Europe are already moving into sovereign AI, positioning themselves to secure higher-margin enterprise and government workloads as national AI buildouts accelerate.
- Infrastructure Demands: Building robust domestic AI ecosystems requires specialized expertise spanning hardware, software, data governance, and policy.
- Resource Constraints: Dr. Matt Hasan, CEO at aiRESULTS and a former AT&T executive, highlights specific bottlenecks:
- Compute Density at Scale.
- Spectrum Allocation amidst political pressures.
- Energy Demand exceeding existing grid capacity.
- Intensified Reliability Requirements: Sovereign AI implementation places heightened demands on telecom providers for system uptime, reliability, quality, and data privacy. This necessitates a focus on efficient power consumption, resilient routing and backups, robust encryption, and comprehensive cybersecurity measures.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Geopolitical tensions introduce risks to the supply of critical components such as GPUs and specialized chips, underscoring the interconnected nature of global hardware supply chains.
- The rapid evolution of AI technology mandates continuous investment and technical agility to ensure sovereign deployments remain current.
- The interplay between global hyperscalers and regional telecom operators is expected to shift.
- Hasan predicts a collaborative model, with regional telcos leveraging their position as sovereign partners through joint ventures, rather than an outright displacement of hyperscalers.
References:
Telcos Across Five Continents Are Building NVIDIA-Powered Sovereign AI Infrastructure
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20251202/ai/sovereign-ai-telcos
Subsea cable systems: the new high-capacity, high-resilience backbone of the AI-driven global network
Analysis: OpenAI and Deutsche Telekom launch multi-year AI collaboration
AI infrastructure spending boom: a path towards AGI or speculative bubble?
Market research firms Omdia and Dell’Oro: impact of 6G and AI investments on telcos
Omdia: How telcos will evolve in the AI era
OpenAI announces new open weight, open source GPT models which Orange will deploy
Expose: AI is more than a bubble; it’s a data center debt bomb
Can the debt fueling the new wave of AI infrastructure buildouts ever be repaid?
Custom AI Chips: Powering the next wave of Intelligent Computing
AI spending boom accelerates: Big tech to invest an aggregate of $400 billion in 2025; much more in 2026!
IBM and Groq Partner to Accelerate Enterprise AI Inference Capabilities
Dell’Oro: Analysis of the Nokia-NVIDIA-partnership on AI RAN
Ookla: FWA Speed Test Results for big 3 U.S. Carriers & Wireless Connectivity Performance at Busy Airports
Ookla just released two new reports based on Speedtest Intelligence data, revealing critical shifts in how Americans connect to the Internet- from their homes and from the country’s 50 busiest airports.
Key findings from the first report:
- T-Mobile, AT&T and Verizon — adding 1.04 million new subscribers in Q3 2025 bringing the total number of FWA customers to 14.7 million, which is slightly more than 12.5% of the 117.4 million U.S. households with broadband, according to the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2024 American Community Survey.
- T-Mobile, Verizon and AT&T all experienced declines in both their median download and upload speeds during Q2 2025 and Q3 2025.
- T-Mobile is the FWA speed leader with median download speed of 209.06 Mbps for Q3 2025, which is approximately double that of AT&T’s median download speed of 104.63 Mbps in the same quarter.
- AT&T and T-Mobile customers in the 10th percentile of users are experiencing speed declines during peak hours in the late afternoon and evening. Verizon subscribers in the 10th percentile don’t have the same sorts of declines, indicating the operator’s enforcement of speed caps may be helping it deliver a more consistent experience to those customers.
- AT&T Internet Air’s latency is higher than its peers but it’s improving. AT&T’s median multi-server latency is ~ 67 milliseconds, “consistently higher” than Verizon (54 ms) and T-Mobile (50 ms) but a notable improvement from 78 ms in Q3 2024.
Separately, the analysts at New Street Research estimated AT&T, T-Mobile and Verizon can currently support up to 32 million FWA customers and they have already added nearly 50% of that number. Operators could potentially increase that load to 36 million following the Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC) upper C-Band auction.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Ookla’s second report analyzes cellular and Wi-Fi performance across the top 50 U.S. airports by passengers. Key findings:
- Cellular network providers had a faster median download speed than Wi-Fi in most airports and more than twice as fast on average. The overall median download speed for cellular was 219.24 Mbps. Note that 5G/4G splits were not explicitly examined.
- Verizon was fastest in the most airports comparing among all mobile providers and airport Wi-Fi including ties.
- Airport Wi-Fi was faster than mobile networks in just over one-third of head-to-head comparisons (including ties), and faster than all mobile providers in five airports.
- Older Wi-Fi technologies may be holding back internet speed in airports with 72.9% of Speedtest samples on Wi-Fi 5 and older generation versus 46.0% in the U.S. overall.

Wi-Fi was faster than any mobile provider in these five airports:
- Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International
- San Francisco International
- Orlando International
- Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International
- Baltimore/Washington International (tie)
Wi-Fi is better by the Bay:
As shown in Wi-Fi’s fastest five airports, Oakland International and Norman Y. Mineta San José International made that list. Rounding out the Bay Area airportstrio, the Wi-Fi speed in San Francisco International comfortably topped the mobile providers.
| Airport | AT&T | T-Mobile | Verizon | Airport Wi-Fi |
| Oakland International | 229.70 | 28.58 | 103.90 | 194.23 |
| Norman Y. Mineta San José International | 103.83 | 211.40 | 251.06 | 176.59 |
| San Francisco International (SFO) | 67.07 | 92.91 | 100.56 | 169.51 |
SFO was the only airport in Ookla’s analysis with Speedtest samples using the 6 GHz band. This was on Wi-Fi 6E – too soon to expect Wi-Fi 7 in airports – with a median download speed of 364.74 Mbps (also remarkable were the median upload speed of 426.04 Mbps and an 8 ms multi-server latency).
References:
https://www.ookla.com/articles/u-s-fwa-report-december-2025
https://www.ookla.com/articles/cellular-faster-than-wi-fi-in-us-airports
Ookla: Global performance of Apple’s in-house designed C1 modem in iPhone 16e
Ookla: Uneven 5G deployment in Europe, 5G SA remains sluggish; Ofcom: 28% of UK connections on 5G with only 2% 5G SA
Ookla: Europe severely lagging in 5G SA deployments and performance
Highlights of Ookla’s 1st Half 2024 U.S. Connectivity Report
Ookla: T-Mobile and Verizon lead in U.S. 5G FWA
Ookla Q2-2023 Mobile Network Operator Speed Tests: T-Mobile is #1 in U.S. in all categories!
Hellas Sat and Space Compass sign MoU for optical inter-satellite connectivity for cross-operator interoperability
Hellas Sat (Greece) and Space Compass (Japan) have executed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to establish a strategic technical and commercial framework for optical inter-satellite connectivity. The collaboration focuses on integrating the forthcoming Hellas Sat 5 geostationary (GEO) satellite with Space Compass’s planned GEO optical data-relay system to enable seamless, cross-operator interoperability.
Strategic Objectives and Infrastructure Integration Inter-Satellite Interoperability:
The partners identify cross-operator optical compatibility as a critical prerequisite for deploying next-generation, high-capacity space communications.
Hellas Sat 5 (HS5) Architecture:
The HS5 satellite is expected to play an important role in advancing space-based optical communications. Currently in the design phase, HS5 will be positioned at 39° East. It is engineered to host the European Space Agency (ESA) HydRON (High Throughput Optical Network) payload. Data Relay Capabilities: The partnership aims to validate ultra-fast laser links and ground connectivity, bridging GEO and Low Earth Orbit (LEO) systems to provide near-real-time data delivery for Earth observation missions. By integrating the optical payload, HS5 will bridge geostationary and low earth orbit systems, enable seamless optical data relay.
Expanded Ecosystem Collaboration Regulatory & Research Alignment: Space Compass is concurrently working with ESA under a separate Memorandum of Intent to conduct feasibility studies on optical communication interoperability between their respective in-orbit demonstration programs.
Advanced Optical Payload:
In partnership with Thales Alenia Space, Hellas Sat 5 is designed to support capacities reaching the Terabit-per-second scale, a significant leap over current gigabit-scale radio frequency systems. This collaboration reinforces the transition toward a standardized, high-speed optical space network, essential for securing global digital infrastructure throughout the 2030s.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
This project is one of the initiatives of space business brand under NTT Group’s “NTT C89” and SKY Perfect JSAT.


About Space Compass:
Space Compass is a joint venture between NTT, a global Information and Communications Technology (ICT) company, and SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation, Asia’s largest satellite operator. The company was established to develop the Space Integrated Computing Network, a new multi-orbital, optical communication-based independent space infrastructure designed to address social challenges. For more information, please visit: https://space-compass.com/en/
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- SDA’s Role: The Space Development Agency is a major driver, releasing Optical Communication Terminal (OCT) Standards (covering physical & data link layers) to ensure different systems can connect.
- Kepler Network: Demonstrated Optical ISLs between its satellites using SDA-compatible terminals, forming mesh networks for data relay.
- SpaceX Starlink: Added optical links for global coverage and resiliency, testing crosslinks with other partners like York.
- Project Kuiper: Amazon’s project also successfully tested end-to-end optical links for its constellation.
- Collaborative Efforts: Companies like Space Compass, Axelspace, NEC, and ESA are working on R&D for interoperable optical networks.
- Seamless Networks: Enables complex multi-platform, multi-orbit networks.
- Data Relay: Allows satellites to relay data for others, reducing ground station reliance.
- Standardization: Essential for different companies’ satellites to talk to each other.
References:
https://www.skyperfectjsat.space/en/news/20251211
https://space-compass.com/en/news/000080.html
Coherent Optics: Synergistic for telecom, Data Center Interconnect (DCI) and inter-satellite Networks
Important satellite network services to be discussed at WRC 23
SatCom market services, ITU-R WP 4B, 3GPP Release 18 and ABI Research Market Forecasts
Muon Space in deal with Hubble Network to deploy world’s first satellite-powered Bluetooth network
SNS Telecom & IT: Private LTE & 5G Network Ecosystem – CAGR 22% from 2025-2030
SNS Telecom & IT’s latest research report, “Private LTE & 5G Network Ecosystem: 2025 – 2030” indicates that the private LTE and 5G network market is estimated to be worth $7.2 billion by the end of 2028 and continues to grow as private 5G deployments overtake LTE across many vertical industries. This steady, strong growth stands in contrast to the tepid pace of infrastructure spending in the much larger but relatively stagnant public mobile network market, where standalone 5G core investments are growing but RAN (Radio Access Network) sales remain flat following a sharp decline last year.
Against this backdrop, the real-world impact of private networks – spanning both facility/campus-based and wide area deployments – is clearly visible across a diverse range of customers, from manufacturers, port operators, and airlines to sports clubs and public sector organizations.
Among many other impactful examples, Tesla, LG Electronics, and Hyundai have eliminated connection-related AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) stoppages at their production facilities; Peel Ports Group has experienced a tenfold increase in network performance at the Port of Liverpool’s metal-heavy environment, which previously hindered Wi-Fi connectivity; Lufthansa has achieved a 75% improvement in operational process speed at its LAX cargo facility; partially sighted fans are able to experience football matches in exceptional detail using private 5G-connected headsets at Crystal Palace Football Club’s Selhurst Park stadium; and police forces in Ontario’s Peel-Halton Region have had uninterrupted in-vehicle data access – especially during outages affecting public mobile operator services – since adopting their independent public safety broadband network, which has recently undergone a 5G core upgrade.
While these practical and tangible benefits are already compelling, another sign of the market’s positive momentum is how customers are increasingly incorporating private 5G networks as a key component of their new facilities. A recent case in point is GDC’s (Georgia Department of Corrections) new state prison project, which also involves the implementation of a secure and physically isolated private 5G network using Band n48 (3.5 GHz) CBRS spectrum to provide indoor and outdoor coverage at a greenfield prison campus with 13 buildings covering 800,000 square feet across 200 acres. Examples of other facilities where private 5G networks have been or are being deployed from the outset include Hitachi Rail’s Hagerstown factory, Hyundai Motor’s HMGMA electrified vehicle plant, Los Angeles Chargers’ El Segundo training facility, Formula 1’s Las Vegas complex, Cleveland Clinic’s Mentor Hospital, CHI’s (Children’s Health Ireland) New Children’s Hospital, Port of Aberdeen’s South Harbour, NEC’s Kakegawa plant; Pegatron’s Batam smart factory, PATTA’s low-carbon Renwu factory, and Jacto’s Paulópolis production facility.
SNS Telecom & IT’s “Private LTE & 5G Network Ecosystem: 2025 – 2030” report projects that global spending on private LTE and 5G network infrastructure for vertical industries will grow at a CAGR of approximately 22% between 2025 and 2028, eventually exceeding $7.2 billion by the end of 2028. More than 70% of these investments – an estimated $5.1 billion – will be directed towards the buildout of standalone private 5G networks, which are well-positioned to become the predominant wireless connectivity medium for Industry 4.0 applications in manufacturing and process industries, as well as critical communications over mission-critical broadband networks for sectors such as public safety, defense, utilities, and transportation. This unprecedented level of growth is likely to transform the private RAN, mobile core, and transport network segments into an almost parallel equipment ecosystem to public mobile operator infrastructure in terms of market size by the late 2020s. By 2030, private networks could account for as much as a fourth of all mobile network infrastructure spending.
About SNS Telecom & IT:
SNS Telecom & IT is a global market intelligence and consulting firm with a primary focus on the telecommunications and information technology industries. Developed by in-house subject matter experts, our market intelligence and research reports provide unique insights on both established and emerging technologies. Our areas of coverage include but are not limited to 6G, 5G, LTE, Open RAN, vRAN, small cells, mobile core, xHaul transport, network automation, mobile operator services, FWA, neutral host networks, private 4G/5G cellular networks, public safety broadband, critical communications, MCX, IIoT, V2X communications, and vertical applications.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.snstelecom.com/private-lte
Private 5G networks move to include automation, autonomous systems, edge computing & AI operations