Verizon to buy Frontier Communications
Wall Street Journal reported today that Verizon is on the verge of buying Frontier Communications for as much as $7 billion in a deal that would bolster the company’s fiber network to compete with rivals notably AT&T. With a market value of over $7 billion, Dallas, TX based Frontier provides broadband (mostly fiber optic) connections to about three million locations across 25 states. Frontier is in the midst of upgrading its legacy copper landline network to cutting-edge fiber. Rising interest rates sparked fears among investors, however, that the business would run out of cash and not be able to raise more before completing those upgrades. Frontier has a 25-state footprint and serves largely rural areas. It reported sales of $5.8 billion in 2023, with about 52% of total revenue from activities related to its fiber-optic products and bills itself as “largest pure-play fiber internet company in the US.”
An all-cash deal between the two companies could be announced as soon as Thursday, a person familiar with the negotiations told Bloomberg.
Fiber M&A has heated up as telecom companies and financial firms pour capital into neighborhoods that lack high-speed broadband or offer only one internet provider, usually from a cable-TV company. New fiber-optic construction is expensive and time-consuming, making existing broadband providers attractive takeover targets.
Verizon, with a market valuation of around $175 billion, will be under pressure from shareholders to justify any big purchase after the company paid more than $45 billion to secure C-band 5G wireless spectrum licenses and spent billions more to use them. Executives have said they are focused on trimming the telecom giant’s leverage to put it on a firmer financial footing.
Verizon, the top cellphone carrier by subscribers, has faced increased pressure from competitors and from cable-TV companies that offer discounted wireless service backed by Verizon’s own cellular network. Faced with slowing wireless revenue growth and an expensive dividend, Verizon has invested in expanding its home-internet footprint. It has both 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) and its Fios-branded fiber to the premises network.
T-Mobile is the only major U.S. cellphone carrier that lacks a large landline business. Since its 2020 takeover of rival carrier Sprint, the company has focused on 5G dominance and succeeded in growing its cellphone business faster than rivals. That network has also linked millions of customers to its fixed 5G broadband service, which offers cablelike service over the air. T-Mobile’s strategy has shifted in recent months, however, as the company dabbles in partnerships and wholesale leasing agreements with companies that build fiber lines to homes and businesses. The wireless “un-carrier” in July agreed to spend about $4.9 billion through a joint venture with private-equity giant KKR to buy Metronet, a Midwestern broadband provider.
Photo Credit: Jeenah Moon/Bloomberg News
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
A deal for Frontier would be a round trip of sorts for some of the network infrastructure that Frontier bought from Verizon in 2016 for $10.54 billion in cash. Frontier later filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in April 2020 as it burned through cash and was burdened by a heavy debt load. It emerged as a leaner business in 2021 with about $11 billion less debt and focused on building a next-generation fiber optic network.
Frontier’s biggest investors today include private-equity firms Ares Management and Cerberus Capital Management. The company drew the attention of activist Jana Partners last year, which built a stake in the business. Jana delivered a letter to Frontier’s board late last year asking the company to take steps immediately to help reverse its sinking share price, including a possible outright sale.

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
AT&T has focused on expanding its fiber network since spinning off its WarnerMedia assets in 2022 to Warner Brothers Discovery. AT&T has 27.8 million fiber homes/businesses passed, growing at ~2.4 million per year, plus more locations passed via its Gigapower joint venture. AT&T’s fiber internet business is expected to contribute to an increase in consumer broadband and wireline revenue. AT&T expects broadband revenue to increase by at least 7% in 2024, which is more than double the rate of growth for wireless service revenue. In contrast, Verizon only has about 18 million fiber locations, growing at about 500,000 per year.
Other recent deals in the fiber transport market sector include the $3.1 billion acquisition, including debt, of fiber provider Consolidated Communications in late 2023 by Searchlight Capital Partners and British Columbia Investment Management.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
It’s All About Convergence (fiber based home internet combined with mobile service):
Speaking at a Bank of America investors conference today, Verizon’s CEO for the Consumer Group Sowmyanarayan Sampath said when Verizon bundles Fios with wireless, it sees a 50% reduction in mobile churn and a 40% reduction in broadband churn. He said they don’t see the same benefits with FWA. Sampath was scheduled to speak at the Mobile Future Forward conference tomorrow, but he canceled at the last minute, which may be a sign that this deal for Frontier is imminent.
The analysts at New Street Research led by Jonathan Chaplin said Verizon’s rationale for the purchase is “convergence baby.” They wrote, wrote, “Verizon seemed complacent. No longer.” Indeed, Verizon CEO Hans Vestberg was challenged on the company’s second quarter 2024 earnings call by analysts who questioned whether Verizon had a big enough fiber footprint to compete in the future. The New Street analysts said Sampath’s comments today “marked a shift in rhetoric from: ‘convergence is important, but we can do it with FWA.”
The analysts at New Street wrote today, “We have been arguing for a couple of years that all the fiber assets would eventually be rolled up into the three big national carriers (AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile). We always knew that if one carrier started the process, others would have to follow swiftly because there are three wireless carriers and only one fiber asset in every market with a fiber asset.”
Other potential fiber companies that the big three national carriers might be eyeing include Google Fiber, Windstream, Stealth Communications and TDS Telecom.
After its annual summer conference in August in Boulder, Colorado, the analysts at TD Cowen, led by Michael Elias, said there was a lot of conversation about the wireline-wireless “convergence” frenzy. “We believe convergence is a race to the bottom, but if one player is going in with a slight advantage (AT&T), the others must reluctantly follow,” wrote TD Cowen. In the mid-term they speculated that T-Mobile might look at fiber roll-ups with Ziply or Lumen (formerly or other regional players.
References:
https://www.wsj.com/business/deals/verizon-nearing-deal-for-frontier-communications-9e402bb4
https://www.fierce-network.com/broadband/verizon-rumored-buy-frontier-its-convergence-game
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/verizon-talks-buy-frontier-communications-180419091.html
https://videos.frontier.com/detail/videos/internet/video/6322692427112/why-fiber
Building out Frontier Communications fiber network via $1.05 B securitized debt offering
Fiber builds propels Frontier Communication’s record 4th Quarter; unveils Fiber Innovation Labs
Frontier Communications fiber build-out boom continues: record number of fiber subscribers added in the 1st quarter of 2023
Frontier’s Big Fiber Build-Out Continued in Q3-2022 with 351,000 fiber optic premises added
AT&T and BlackRock’s Gigapower fiber JV may alter the U.S. broadband landscape
AT&T Highlights: 5G mid-band spectrum, AT&T Fiber, Gigapower joint venture with BlackRock/disaggregation traffic milestone
AT&T to use Frontier’s fiber infrastructure for 4G/5G backhaul in 25 states
Frontier Communications offers first network-wide symmetrical 5 Gig fiber internet service
Frontier Communications adds record fiber broadband customers in Q4 2022
Verizon Q2-2024: strong wireless service revenue and broadband subscriber growth, but consumer FWA lags
Summary of Verizon Consumer, FWA & Business Segment 1Q-2024 results
Huawei’s First-Half Net Profit Rose on Strong Smartphone Sales, Car Business
Huawei Technologies Co.’s revenue grew for the sixth straight quarter as its smartphones gained significant market share in China. Net profit climbed 18% in the first half of the year, thanks to strong smartphone sales and robust growth in its car business. Huawei reports a handful of unaudited financial figures throughout the year and releases a more detailed audited annual report each spring. It didn’t provide data broken down by business segment for the first half.
The Chinese networking and electronics behemoth posted revenue of 239 billion yuan ($33.6 billion) in the June quarter, up 33.7% from a year earlier, according to calculations based on the company’s six-month financial figures. Implied net profit was 35.5 billion yuan, a drop of 18.6% from a year ago when Huawei recorded one-time gains from divestments. The company sold mobile maker Honor Device Co. to a consortium in 2020 and parts of its server business in 2021, with proceeds from both paid out in installments.
The Shenzhen-based company’s smartphone shipments rose by 50% last quarter as it and other local players like Vivo and Xiaomi Corp. beat out Apple, which dropped to sixth place among handset makers in China, according to market tracker IDC. Apple’s sales in China fell 6.5% in the June quarter, missing Wall Street projections, even as overall shipments in China grew.
Huawei’s next flagship Mate 70 will be closely watched for any processor upgrades when the device is introduced later this year. The Mate 60 roiled US policymakers when it debuted a China-made 7-nanometer chip a year ago, despite US-imposed sanctions and export controls geared to stem advances in China’s chip technologies.
Last year, Huawei more than doubled its net profit as it rebuilt the market share of its core businesses in consumer electronics and cloud computing, which were severely eroded by several years of U.S. sanctions that limited its access to advanced semiconductors.
In the second quarter, Huawei was the No. 2 smartphone seller in China, the world’s largest smartphone market, with an 18.1% market share, according to market-research firm International Data Corp. Counterpoint Research said Huawei’s sales jumped 44.5% in the quarter from a year earlier, the fastest growth among Chinese original equipment manufacturers, thanks to the Pura 70 and Nova 12 series. The company launched its Pura 70 series in April.
Huawei and other local smartphone makers like Vivo and Xiaomi Corp. beat out Apple, which dropped to sixth place among handset makers in China, according to market tracker IDC.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Huawei has invested in its car business as Beijing ramps up support for high-tech industries as part of efforts to reduce the economy’s reliance on the property sector for growth.
The company’s automotive unit, which offers self-driving technology to electric vehicle makers, earned a revenue of 10 billion yuan as of early July, according to a report by a Chinese media outlet, more than the combined revenue in the previous two years. Huawei didn’t provide a breakdown of its sales.
Changan Automobile-backed Avatr Technology said in an exchange filing last week that it will acquire a 10% stake in Yinwang Smart Technology, Huawei’s car unit that provides autonomous-driving technology to automakers, valuing the company at 115 billion yuan. Seres on Monday said it will acquire a 10% stake in Yinwang.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Despite U.S. sanctions, Huawei has come “roaring back,” due to massive China government support and policies
Dell’Oro: RAN market still declining with Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE and Samsung top vendors
China Unicom-Beijing and Huawei build “5.5G network” using 3 component carrier aggregation (3CC)
Will AI clusters be interconnected via Infiniband or Ethernet: NVIDIA doesn’t care, but Broadcom sure does!
InfiniBand, which has been used extensively for HPC interconnect, currently dominates AI networking accounting for about 90% of deployments. That is largely due to its very low latency and architecture that reduces packet loss, which is beneficial for AI training workloads. Packet loss slows AI training workloads, and they’re already expensive and time-consuming. This is probably why Microsoft chose to run InfiniBand when building out its data centers to support machine learning workloads. However, InfiniBand tends to lag Ethernet in terms of top speeds. Nvidia’s very latest Quantum InfiniBand switch tops out at 51.2 Tb/s with 400 Gb/s ports. By comparison, Ethernet switching hit 51.2 Tb/s nearly two years ago and can support 800 Gb/s port speeds.

While InfiniBand currently has the edge, several factors point to increased Ethernet adoption for AI clusters in the future. Recent innovations are addressing Ethernet’s shortcomings compared to InfiniBand:
- Lossless Ethernet technologies
- RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE)
- Ultra Ethernet Consortium’s AI-focused specifications
Some real-world tests have shown Ethernet offering up to 10% improvement in job completion performance across all packet sizes compared to InfiniBand in complex AI training tasks. By 2028, it’s estimated that: 1] 45% of generative AI workloads will run on Ethernet (up from <20% now) and 2] 30% will run on InfiniBand (up from <20% now).
In a lively session at VM Ware-Broadcom’s Explore event, panelists were asked how to best network together the GPUs, and other data center infrastructure, needed to deliver AI. Broadcom’s Ram Velaga, SVP and GM of the Core Switching Group, was unequivocal: “Ethernet will be the technology to make this happen.” Velaga opening remarks asked the audience, “Think about…what is machine learning and how is that different from cloud computing?” Cloud computing, he said, is about driving utilization of CPUs; with ML, it’s the opposite.
“No one…machine learning workload can run on a single GPU…No single GPU can run an entire machine learning workload. You have to connect many GPUs together…so machine learning is a distributed computing problem. It’s actually the opposite of a cloud computing problem,” Velaga added.
Nvidia (which acquired Israel interconnect fabless chip maker Mellanox [1.] in 2019) says, “Infiniband provides dramatic leaps in performance to achieve faster time to discovery with less cost and complexity.” Velaga disagrees saying “InfiniBand is expensive, fragile and predicated on the faulty assumption that the physical infrastructure is lossless.”
Note 1. Mellanox specialized in switched fabrics for enterprise data centers and high performance computing, when high data rates and low latency are required such as in a computer cluster.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Ethernet, on the other hand, has been the subject of ongoing innovation and advancement since, he cited the following selling points:
- Pervasive deployment
- Open and standards-based
- Highest Remote Direct Access Memory (RDMA) performance for AI fabrics
- Lowest cost compared to proprietary tech
- Consistent across front-end, back-end, storage and management networks
- High availability, reliability and ease of use
- Broad silicon, hardware, software, automation, monitoring and debugging solutions from a large ecosystem
To that last point, Velaga said, “We steadfastly have been innovating in this world of Ethernet. When there’s so much competition, you have no choice but to innovate.” InfiniBand, he said, is “a road to nowhere.” It should be noted that Broadcom (which now owns VMWare) is the largest supplier of Ethernet switching chips for every part of a service provider network (see diagram below). Broadcom’s Jericho3-AI silicon, which can connect up to 32,000 GPU chips together, competes head-on with InfiniBand!
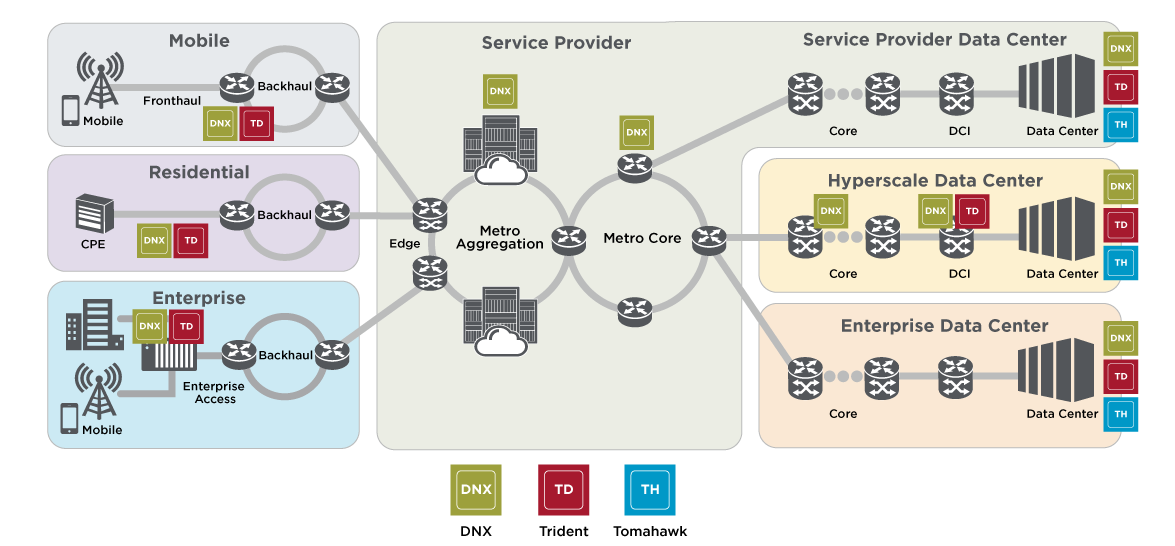
Image Courtesy of Broadcom
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Conclusions:
While InfiniBand currently dominates AI networking, Ethernet is rapidly evolving to meet AI workload demands. The future will likely see a mix of both technologies, with Ethernet gaining significant ground due to its improvements, cost-effectiveness, and widespread compatibility. Organizations will need to evaluate their specific needs, considering factors like performance requirements, existing infrastructure, and long-term scalability when choosing between InfiniBand and Ethernet for AI clusters.
–>Well, it turns out that Nvidia’s Mellanox division in Israel makes BOTH Infiniband AND Ethernet chips so they win either way!
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.perplexity.ai/search/will-ai-clusters-run-on-infini-uCYEbRjeR9iKAYH75gz8ZA
https://www.theregister.com/2024/01/24/ai_networks_infiniband_vs_ethernet/
Broadcom on AI infrastructure networking—’Ethernet will be the technology to make this happen’
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/products/infiniband/h
ttps://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/products/ethernet/
Part1: Unleashing Network Potentials: Current State and Future Possibilities with AI/ML
Using a distributed synchronized fabric for parallel computing workloads- Part II
Part-2: Unleashing Network Potentials: Current State and Future Possibilities with AI/ML
India’s TRAI releases Recommendations on use of Tera Hertz Spectrum for 6G
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) is urging the government and wireless network operators to explore the use of terahertz spectrum for new 6G technologies and services. “The government should introduce a new experimental authorization for the spectrum in the 95 GHz to 3 THz range termed as ‘Tera Hertz Experimental Authorization’ [THEA],” said a press release issued by TRAI.
THEA’s primary objective would be to promote “research and development (R&D), indoor and outdoor testing, technology trial, experimentation and demonstration in the 95 GHz to 3 TZ range,” said TRAI. Any Indian entity, including academic institutes, R&D labs, telecom service providers, central or state government bodies and original equipment makers, will be eligible for an authorization covering a maximum of five years. The scope of THEA should be to conduct R&D, indoor and outdoor testing, technology trial, experimentation, and demonstration in the 95 GHz to 3 THz range; and to market experimental devices designed to operate in the 95 GHz to 3 THz range via direct sale.

TRAI believes the terahertz frequency band is likely to play a crucial role in upcoming 6G technology. “The high-speed point-to-point wireless data link is an emerging usage of Terahertz radiation,” said TRAI in its recommendations. “For this reason, communications in the Terahertz band are expected to play a pivotal role in the upcoming 6th generation (6G) of wireless mobile communications, enabling ultra-high bandwidth communication paradigms.”
“The large Terahertz bandwidths and massive antenna arrays, combined with the inherent densification caused by machine-type communications, will result in an enhanced communication system performance,” added TRAI.
“TRAI is laying the groundwork for India to become a global powerhouse in testing as well as in research and development so that we are fully geared to produce cutting-edge technologies and services in the near future,” said TV Ramachandran, the president of the Broadband India Forum (BIF), in his response to the announcement.
The recommendations are a further sign of India’s interest in shaping the 6G standard, likely to appear around 2030. Vocal about its ambitions, India has already set up the Bharat 6G Alliance to actively contribute to 6G activities. It has also collaborated with several organizations, including the US-based Next G Alliance, Europe’s 6G Smart Networks and Services Industry Association (6G IA) and the 6G Flagship of Oulu University as it tries to position itself as a “global leader” in digital infrastructure and innovation.
The terahertz band has been attracting attention as an option for 6G deployment, with the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) recently releasing two reports on the band and the use cases it could support.
“Due to their shorter wavelengths, Terahertz communication systems can support higher link directionality, are less susceptible to free-space diffraction and inter-antenna interference, can be realized in much smaller footprints, and possess a higher resilience to eavesdropping,” said the TRAI report. Even so, there are several challenges that would need to be addressed before terahertz could be feasible for widespread usage. Above all, signal propagation is generally weak in higher frequency bands and power limitations can also result in poor coverage, said TRAI.
The Recommendations have been placed on the TRAI’s website (www.trai.gov.in). For any clarification! information Shri Akhilesh Kumar Trivedi, Advisor (Networks, Spectrum and Licensing), TRAI may be contacted at Telephone Number +91-11-20907758.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/6g/india-gets-behind-terahertz-push-for-6g
https://www.trai.gov.in/sites/default/files/PR_No.56of2024.pdf
www.trai.gov.in
China adds 20M “5G package” subscribers in July; 1H-2024 earnings gains outpace revenues for all 3 major China telcos
The number of 5G subscribers in China increased by a sizeable 20 million last month, according to new data from the country’s big three state owned network providers (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom). Of the three, China Mobile is still the only one to report actual customers using its 5G network; China Telecom and China Unicom are sticking to their 5G package subscribers metric, which essentially means customers signed up to a 5G plan, regardless of whether they use 5G network services (most continue to use 4G).
- China Mobile’s July net adds came in at 13.7 million, pushing its 5G customer base up to a colossal 528 million. China Mobile disclosed that it has 129 million customers using its 5G New Calling over high-definition video service reached 129 million, of which, smart application subscribers numbered 11.82 million.
- China Telecom added 3.1 million 5G package customers for a total of 340 million. They did not talk about 5G in their earnings report (more below).
- China Unicom added 2.9 million 5G package customers for a total of 279 million. China Unicom shared details of its 5G network build-out, pointing out that its 5G mid-band base stations numbered in excess of 1.31 million as of mid-year, while low-band sites reached 780,000.
For each of them, cloud and digital transformation (rather than 5G subs) drove topline growth, profit rose more than revenue and shareholder returns increased.
- China Mobile said net profit had improved 5.3% to RMB80.2 billion ($11.2 billion), outpacing revenue, which rose 3% to RMB546.7 billion ($76.6 billion).
- China Telecom, reported net earnings of 21.8 billion Chinese yuan (US3.1 billion), an 8.2% gain over last year, with revenue up 2.8% and service revenue 4.3% higher.
- China Unicom reported 11.3% higher net income of 13.8 billion ($1.93) on the back of a 2.9% lift in sales to RMB197.3 billion ($27.6 billion).
China Mobile says its digital transformation business grew 11% to RMB147.1 billion ($20.6 billion), accounting for 26% of all revenue. China Telecom reported digital industry sales of RMB73.7 billion ($10.3 billion), a 7% increase, and China Unicom said revenue grew 7% to RMB43.5 billion ($6.1 billion).

Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo)
All three state owned telcos experienced double-digit growth in cloud services. China Telecom’s Tianyi Cloud grew revenue by 20% to RMB55 billion ($7.7 billion), while China Mobile Cloud hiked sales by 19% to RMB50 billion ($7 billion) and China Unicom grew 24% to RMB32 billion ($4.5 billion).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Silence is Golden?
There was a distinct lack of 5G commentary in China Telecom’s half year report; it is the last of the three to post numbers and did so alongside the publication of the market’s operational statistics for July. The telco shared its 5G package figures – it added almost 18 million in the first six months of 2024, incidentally – but made no other reference to the technology in a fairly wordy statement about its year-to-date performance. Instead, the operator focused on the progress of its digital transformation strategy, leaning heavily on the promise of artificial intelligence. Specifically, China Telecom is talking up what it terms AI+ – there’s always one – and the Xingchen large language model it launched at the back end of last year.
“The Company strengthened the integration and mutual promotion of capabilities in various fields, continuously enriched the Xingchen large model series product portfolio, empowered the intelligent transformation for thousands of industries, and supported enterprises to achieve costs reduction and efficiency enhancement,” it said.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.telecoms.com/5g-6g/china-added-20-million-5g-subs-last-month
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/cloud-digital-transformation-drive-chinese-telcos-h1-growth
GSMA: China’s 5G market set to top 1 billion this year
MIIT: China’s Big 3 telcos add 24.82M 5G “package subscribers” in December 2023
China Telecom and China Mobile invest in LEO satellite companies
WSJ: China’s Telecom Carriers to Phase Out Foreign Chips; Intel & AMD will lose out
China’s telecom industry business revenue at $218B or +6.9% YoY
Dell’Oro: RAN market still declining with Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE and Samsung top vendors
RAN market conditions continued to remained challenging in the second quarter despite some faint signs of improvements. Dell’Oro estimates that the overall 2G–5G Radio Access Network (RAN) market—including baseband plus radio hardware and software, excluding services—declined at a double-digit rate for a fourth consecutive quarter in 2Q24. The results in the second quarter were mostly an extension of what we have seen over the past year, characterized by cautious capex spending and challenging comparisons.
“Even if the RAN market is still down at a double-digit rate in the first half, the second quarter offered some glimmer of hope that the nadir of this cycle with double-digit declines might now be in the past for the time being,” said Stefan Pongratz, Vice President and analyst at the Dell’Oro Group. “This does not change the fact that the RAN market is expected to decline at a 2 percent CAGR over the next five years. But the pace of the decline should moderate somewhat going forward,” continued Pongratz.
Additional highlights from the 2Q 2024 RAN report:
- Total RAN revenues were mostly in line with expectations.
- Strong growth in North America and stable trends in China were not enough to offset steep declines in the Asia Pacific region, partly driven by sharp drops in India.
- Vendor rankings are mostly unchanged. The top 5 RAN suppliers based on worldwide revenues are Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, and Samsung.
- Relative to 2023, Huawei’s 1H 2024 revenue share is up, ZTE is stable, and Nokia/Ericsson are together down 3 to 4 percentage points.
- Short-term RAN projections are mostly unchanged since the 5-year forecast update. Global RAN is expected to decline 8 percent to 12 percent outside of China.
On the bright side, the overall results were fairly aligned with expectations, and more regions are now growing. Our initial analysis shows that three out of the six tracked regions advanced on a year-over-year basis in the quarter, up from just one region in the first quarter (North America, MEA, and CALA increased while Europe, China, and Asia Pacific Excl. China declined).
Strong growth in North America and stable trends in China were not enough to offset steep declines in the Asia Pacific region, partly driven by sharp drops in India.
The supplier landscape is mostly unchanged with Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE Corporation, and Samsung Networks still leading the way, while many of the non-top 5 suppliers are declining.
Relative to 2023, Huawei’s 1H 2024 revenue share is up, ZTE is stable, and Nokia/Ericsson are together down 3 to 4 percentage points.
Short-term RAN projections have remained mostly unchanged since the 5-year forecast update. Global RAN is expected to decline 8% to 12% outside of China. This implies a stronger-than-typical 2024 second half, comprising more than 53% of full-year revenues.
References:
RAN Market Still Down with Some Glimmer of Hope, According to Dell’Oro Group
Analysts: Telco CAPEX crash looks to continue: mobile core network, RAN, and optical all expected to decline
Where Have You Gone 5G? Midband spectrum, FWA, 2024 decline in CAPEX and RAN revenue
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
Dell’Oro: RAN market declines at very fast pace while Mobile Core Network returns to growth in Q2-2023
Dell’Oro: RAN Market to Decline 1% CAGR; Mobile Core Network growth reduced to 1% CAGR
ZTE reports H1-2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion (+2.9% YoY) and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion (+4.8% YoY)
China’s ZTE reported a 2.9% rise in total revenue to RMB62.5 billion ($8.76 billion), with net profit attributable to holders of ordinary shares of the Hong Kong listed company at RMB 5.73 billion, up 4.8% year-over-year (YoY). The biggest growth surge was in the corporate and government unit, which boosted revenue by 56% to RMB9.2 billion yuan ($1.29 billion), mainly through stronger server and storage sales. However, that was offset by a 68% hike in costs, depressing the gross margin by 5.7 points – a result of “changes in revenue mix,” the company said.
The company’s core carrier network equipment business declined 8.6% in the first half of 2024, holding back underlying earnings to 4.96 billion Chinese yuan (US$700 million) – a gain of just 1.1% over last year. The carrier unit, which accounted for 60% of the company’s total revenue, brought in RMB37 billion ($5.18 billion) in sales in H1, the company revealed in its stock exchange filing.
ZTE said demand from Chinese telecom operators had been constrained by “overall investment sentiments,” but it pointed to improved sales of indoor distribution, high-speed rail and metro networking equipment. ZTE’s consumer business, which includes mostly handsets and home routers, grew 14% to RMB16 billion ($2.24 billion). R&D spending remained flat at RMB12.7 billion ($1.78 billion).
_International_Software_Products.jpeg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
Source: Cynthia Lee/Alamy Stock Photo
China’s domestic market accounted for 69% of total sales, roughly the same as last year. The biggest offshore growth region was Asia (excluding China), which grew 23%. ZTE said it is positioning itself as a “path-builder for the digital economy” and aimed to further expand its legacy connectivity business while growing its computing business. Its AI portfolio includes full-stack intelligent solutions, backed by key technologies such as high-speed networking, network computing and data processing.
ZTE is developing their own custom silicon. In the first half of 2024, the company continued to increase investment in advanced semiconductor process technologies, advanced architecture and seal packaging design, core intellectual properties and digitalized efficient development platform on the back of close to 30 years’ R&D build-up. We are an industry leader in terms of the ability to design the whole process of chip. On top of a solid foundation in the R&D of base-level technology for DICT chip, the Group has also constructed an ultra-efficient, green and intelligent full-stack computing network base pivoting on “data, computing and network” in line with developments in computing-network integration. The creation of a product regime meeting the core requirements of the diversified scenarios of “cloud, edge, terminal” has supported our ongoing leading position in terms of competitiveness.
ZTE has used its expertise in communication software and hardware development, engineering capabilities and industrialization to intensify its investment in computing power products and solutions. The company has launched a comprehensive suite of full-stack, full-scenario intelligent computing solutions, covering computing, networks, capabilities, intelligence and applications. These solutions include a full range of general computing servers, high-performance AI training servers, inference servers, liquid-cooled servers, distributed storage systems, high-end multi-control magnetic arrays, integrated training-inference machines and high-speed lossless switches.
In the terminal sector, ZTE has introduced the concept of “AI for All”, focusing on five core consumer scenarios: sports and health, audio and video entertainment, business and travel, home and education, and smart driving. The company has launched a full range of AI-driven terminal products, including smartphones, tablets, laptops and mobile internet devices, as part of its Full-Scenario Intelligent Ecosystem 3.0. This ecosystem promotes the integration of AI technology across mobile terminal devices, smart home devices, cloud computing and automotive electronics.
Moving forward, ZTE is dedicated to advancing its core technological innovations and accelerating its expansion into the “connectivity + computing + capability + intelligence” domain. The company will focus on strengthening its digital and intelligent infrastructure. By fostering open collaboration and pursuing diverse, mutually beneficial partnerships, ZTE aims to build a highly efficient and intelligent digital future with industry partners. The company said it expects: gradual adoption of 5G-Advanced, further rollout of 400G optical and construction of intelligent computing centers to drive the China’s telecom carrier market in the second half. Offshore, it will continue to focus on large national markets and big telcos for its wirelines and wireless product lines.
References:
https://www.lightreading.com/finance/zte-s-carrier-sales-slump-9-in-h1
https://www1.hkexnews.hk/listedco/listconews/sehk/2024/0816/2024081601602.pdf
ZTE reports H1 2024 revenue of RMB 62.49 billion and net profit of RMB 5.73 billion
ZTE reports higher earnings & revenue in 1Q-2024; wins 2023 climate leadership award
China Telecom with ZTE demo single-wavelength 1.2T bps hollow-core fiber transmission system over 100T bps
China Mobile & ZTE use digital twin technology with 5G-Advanced on high-speed railway in China
Türk Telekom and ZTE trial 50G PON, but commercial deployment is not imminent
ZTE sees demand for fixed broadband and smart home solutions while 5G lags
AI RAN Alliance selects Alex Choi as Chairman
Backgrounder:
The AI RAN Alliance, formed earlier this year, is a groundbreaking collaboration aimed at revolutionizing the RAN industry. Partnering with tech giants, the goal is to transform traditional Radio Access Networks (RANs) into intelligent, self-optimizing systems using advanced AI technologies. Their website states:
Bringing together the technology industry leaders and academic institutions, the AI-RAN Alliance is dedicated to driving the enhancement of RAN performance and capability with AI. Moreover, we aim to optimize RAN asset utilization, and unlock new revenue streams. By pioneering AI-based innovations in RAN, we aspire to profitably propel the telecom industry towards 6G.
The alliance’s founding members include Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS), Arm, DeepSig Inc. (DeepSig), Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson (Ericsson), Microsoft Corporation (Microsoft), Nokia, Northeastern University, NVIDIA, Samsung Electronics, SoftBank Corp. (SoftBank) and T-Mobile USA, Inc. (T-Mobile).
The group’s mission is to enhance mobile network efficiency, reduce power consumption, and retrofit existing infrastructure, setting the stage for unlocking new economic opportunities for telecom companies with AI, facilitated by 5G and 6G.

Image Courtesy of the AI RAN Alliance.
Purpose:
The AI RAN Alliance is dedicated to eliminating the inefficiencies of traditional RAN systems by embedding AI directly into network infrastructures. This shift will enable, for example, dynamic resource allocation, predictive maintenance, and proactive network management.
Industry Benefits:
Enhanced Network Efficiency: Real-time optimized bandwidth allocation and improved user experiences.
Economic Advantages: Cost savings from AI-driven automation and reduced energy consumption.
Innovative Revenue Opportunities: New services such as real-time AI Assistants on your mobile devices.
Key Focus Areas:
- AI for RAN
- AI on RAN (RAN for AI)
- AI and RAN
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
New AI RAN Alliance Chairman:
On August 15, 2024, the AI RAN Alliance appointed Dr. Alex Jinsung Choi, Principal Fellow of SoftBank Corp.’s Research Institute of Advanced Technology as Chairman.
“The AI-RAN Alliance is set to transform telecommunications through AI-RAN advancements, increased efficiency, and new economic opportunities,” said Choi. “As Chair, I’m excited to lead this AI-RAN initiative, working with industry leaders to enhance mobile networks, reduce power consumption, and modernize infrastructure with 5G and 6G with AI/ML. Our goal is to drive societal progress through AI-RAN, transitioning from traditional to next-generation communications infrastructure.”
Satadal Bhattacharjee, Sr. Director of Marketing, Infrastructure BU, ARM, said, “We’re excited to collaborate with Choi, the Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance. Like Choi, we believe that AI will fundamentally change the way wireless services are deployed, fostering broad innovation and enhancing operational efficiency. We look forward to working with key industry leaders from silicon to software to fulfill the promise of ubiquitous AI and 6G.”
Jim Shea, Co-founder and CEO of DeepSig, said, “As a pioneer in AI-native communications together with his prior experience growing the O-RAN ALLIANCE, Choi will lead this important initiative that is shaping the future of intelligent radio access networks. DeepSig’s extensive AI/ML wireless expertise will play a key role in this exciting collaboration to leverage advanced technologies to help the industry unlock unprecedented network efficiency and accelerate innovation.”
Mathias Riback, VP & Head of Advanced Technology U.S., Ericsson, said, “I’m thrilled to welcome Dr. Choi as Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance. As a non-standardization organization, the Alliance can uniquely complement the work of existing SDOs by focusing on shaping innovative use cases that integrate AI with RAN. In addition to realizing benefits from AI in RAN implementations, it will be important to advance ‘AI on RAN’ use cases, where mobile networks play a critical role in enabling AI applications. Ericsson is fully committed to fostering a collaborative environment that unites all players in the evolving AI ecosystem to shape the future of telecom together.”
Shawn Hakl, VP of 5G Strategy, Microsoft, said, “At Microsoft, we recognize artificial intelligence (AI) as a pivotal technology of our era. We are excited to be a part of the AI-RAN Alliance and are particularly pleased to see Choi step into the role of Chair. Choi’s leadership will be key as we collaborate to leverage AI in optimizing RAN infrastructure investments and expanding the capabilities of RAN to introduce new AI-driven services for modern mobile applications.”
Ari Kynäslahti, Head of Strategy and Technology, Mobile Networks at Nokia commented, “Nokia is proud to be part of the AI-RAN Alliance and contribute towards integrating AI into radio access networks. The potential of AI to optimize networks, predict and resolve issues, and enhance performance and service quality is significant. As we embark on this transformative journey, collaboration is essential to harness our collective expertise. We are pleased to see Dr. Alex Choi appointed to this role, and look forward to him guiding our efforts to achieve these goals.”
Tommaso Melodia, William L. Smith Professor, Northeastern University, said, “We are pleased to have Choi as the Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance, leading our efforts to transform the industry. Choi has been a strong advocate for the evolution towards a more open, software-driven, and AI-integrated future. Under Choi’s leadership, the AI-RAN Alliance is set to fast-track the development of new services and use cases by leveraging openness, softwarization, and AI integration to enhance network performance, energy efficiency, spectrum sharing, and security, ultimately redefining the landscape of global communications.”
Soma Velayutham, GM, AI and Telecoms, NVIDIA, said, “The AI-RAN Alliance is a critical initiative for advancing the convergence of AI and 5G/6G technologies to drive innovation in mobile networks. The consortium’s new leadership will bring a fresh perspective and focus on delivering the next generation of connectivity.”
Dr. Ardavan Tehrani, Samsung Research, AI-RAN Alliance Board of Directors Vice Chair, said, “We are excited to have Dr. Alex Choi leading the AI-RAN Alliance as the Chair of the Board. The Alliance will play a pivotal role in fostering collaboration, driving innovation, and transforming future 6G networks utilizing AI. Under Dr. Choi’s leadership, the Alliance will strive to deliver substantial value to end users and operators through pioneering AI-based use cases and innovations.”
Ryuji Wakikawa, VP and Head of Research Institute of Advanced Technology, SoftBank Corp., said, “SoftBank is committed to realizing an AI-powered network infrastructure, and we strongly believe that Choi’s extensive background and expertise will be a great force in advancing AI-RAN technology and driving significant progress for the mobile industry in this AI era with lightning speed.”
John Saw, EVP and CTO, T-Mobile, said, “We are thrilled to have Alex Choi as Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance. AI is advancing at an unprecedented rate and with our 5G network advantage we have a unique opportunity to harness this momentum. By developing solutions that make the most of both RAN and AI on GPUs — and working alongside Choi and the top industry leaders within the Alliance — we believe there is potential for change that will revolutionize the industry.”
Dr. Akihiro Nakao, Professor, The University of Tokyo, said, “Dr. Alex Jinsung Choi’s appointment as Chair of the AI-RAN Alliance represents a pivotal step in advancing AI within the telecommunications sector. His leadership is expected to unite academic and industry efforts, nurturing the next wave of innovators who will drive the future of AI and telecommunications. This initiative will not only fast-track the adoption of AI across diverse applications but also foster international collaboration and set new standards for efficiency, energy management, resilience, and the development of AI-driven services that will reshape the telecommunications industry and benefit society worldwide.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
https://ai-ran.org/news/industry-leaders-in-ai-and-wireless-form-ai-ran-alliance/
AI sparks huge increase in U.S. energy consumption and is straining the power grid; transmission/distribution as a major problem
Dell’Oro & Omdia: Global RAN market declined in 2023 and again in 2024
Tech layoffs continue unabated: pink slip season in hard-hit SF Bay Area
A combination of strategic pivots toward the red-hot AI sector and corrections after pandemic-era over hiring have pushed companies across the tech sector to lay off massive number of employees, according to outplacement firm Challenger, Grey & Christmas. Tech companies including Cisco Systems, Intel and Dell have cut tens of thousands of jobs in August, the latest in a year that began with layoffs at companies such as Amazon and Google.
On Wednesday, Cisco announced in a notice posted with the Securities and Exchange Commission that it was laying off 5,500 workers (7% of its employees) as part of an effort to invest more in AI. In a short statement, CEO Chuck Robbins used the term “AI” five times, highlighting the company’s efforts to keep up in the ongoing AI race. Earlier this year, Cisco also laid off 4,000 or 5% of its workforce, saying that the company wanted to “realign the organization and enable further investment in key priority areas.” Cisco joins a litany of other companies like Microsoft and Intuit that have used AI as the justification for mass layoffs.
- As of August 17, 2024, 404 tech companies have laid off 132,498 workers this year, according to layoffs.fyi, a website that tracks tech industry job cuts. This includes major tech companies like Amazon, Google, Microsoft, Tesla, TikTok, and Snap, as well as smaller startups and apps.
- Crunchbase says that in 2023, more than 191,000 workers in U.S.-based tech companies (or tech companies with a large U.S. workforce) were laid off in mass job cuts. In 2022, more than 93,000 jobs were slashed from public and private tech companies in the U.S.
The SF Bay Area has been particularly hard-hit, with companies such as Twitter, Meta, and Salesforce announcing significant job cuts. The layoffs are sending shockwaves through the region’s economy. The tech industry has long been a major driver of growth and employment in the Bay Area, accounting for a significant portion of tax revenue and supporting numerous ancillary businesses. The sudden loss of jobs has raised concerns about a potential economic downturn. Many of the affected workers are highly skilled in areas such as software engineering, product development, and data science.
Here are the largest Bay Area tech company layoffs in 2024 and 2023:
| March 14, 2023 | Meta/FB |
21,000
|
13% | Menlo Park |
| August 1, 2024 | Intel |
18,720
|
15% | Santa Clara |
| January 20, 2023 | Alphabet |
12,000
|
6% | Mountain View |
| Feb 14 & Aug14, 2024 | Cisco Systems | 9,500 | 13% | San Jose |
The tech layoffs have created a fiercely competitive job market, with many qualified individuals seeking new employment. This has put pressure on salaries and benefits, further exacerbating the economic impact. The tech layoffs have also had a psychological toll on the Bay Area community. Many workers have lost their sense of stability and are worried about their financial future. The uncertainty has created a climate of anxiety and stress, particularly among those who are still employed.
Government officials and economic development agencies are working to mitigate the effects of the layoffs. They are providing support services to displaced workers, such as job retraining and placement assistance. However, the full extent of the economic impact remains to be seen. The surge in tech layoffs underscores the cyclical nature of the industry. While the Bay Area has weathered economic downturns in the past, the unprecedented scale of the current tech job cuts raises questions about the long-term health of the tech sector. As companies adapt to a changing economic landscape, the region’s economy is struggling to evolve to meet the challenges and perceived opportunities (e.g. AI).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
https://www.wsj.com/finance/investing/tech-media-telecom-roundup-market-talk-12947dd6
https://futurism.com/the-byte/cisco-layoff-ai-profit
https://news.crunchbase.com/startups/tech-layoffs/
https://www.challengergray.com/tags/job-cut-report/
Massive layoffs and cost cutting will decimate Intel’s already tiny 5G network business
Cisco to lay off more than 4,000 as it shifts focus to AI and Cybersecurity
Cisco restructuring plan will result in ~4100 layoffs; focus on security and cloud based products
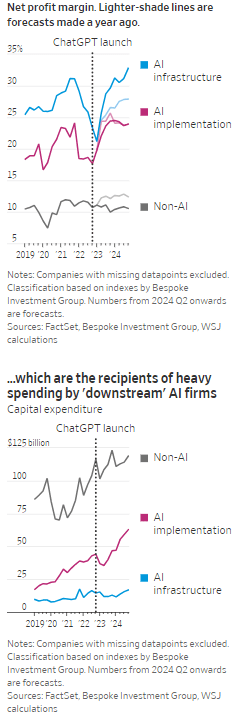
AI Echo Chamber: “Upstream AI” companies huge spending fuels profit growth for “Downstream AI” firms
According to the Wall Street Journal, the AI industry has become an “Echo Chamber,” where huge capital spending by the AI infrastructure and application providers have fueled revenue and profit growth for everyone else. Market research firm Bespoke Investment Group has recently created baskets for “downstream” and “upstream” AI companies.
- The Downstream group involves “AI implementation,” which consist of firms that sell AI development tools, such as the large language models (LLMs) popularized by OpenAI’s ChatGPT since the end of 2022, or run products that can incorporate them. This includes Google/Alphabet, Microsoft, Amazon, Meta Platforms (FB), along with IBM, Adobe and Salesforce.
- Higher up the supply chain (Upstream group), are the “AI infrastructure” providers, which sell AI chips, applications, data centers and training software. The undisputed leader is Nvidia, which has seen its sales triple in a year, but it also includes other semiconductor companies, database developer Oracle and owners of data centers Equinix and Digital Realty.
The Upstream group of companies have posted profit margins that are far above what analysts expected a year ago. In the second quarter, and pending Nvidia’s results on Aug. 28th , Upstream AI members of the S&P 500 are set to have delivered a 50% annual increase in earnings. For the remainder of 2024, they will be increasingly responsible for the profit growth that Wall Street expects from the stock market—even accounting for Intel’s huge problems and restructuring.
It should be noted that the lines between the two groups can be blurry, particularly when it comes to giants such as Amazon, Microsoft and Alphabet, which provide both AI implementation (e.g. LLMs) and infrastructure: Their cloud-computing businesses are responsible for turning these companies into the early winners of the AI craze last year and reported breakneck growth during this latest earnings season. A crucial point is that it is their role as ultimate developers of AI applications that have led them to make super huge capital expenditures, which are responsible for the profit surge in the rest of the ecosystem. So there is a definite trickle down effect where the big tech players AI directed CAPEX is boosting revenue and profits for the companies down the supply chain.
As the path for monetizing this technology gets longer and harder, the benefits seem to be increasingly accruing to companies higher up in the supply chain. Meta Platforms Chief Executive Mark Zuckerberg recently said the company’s coming Llama 4 language model will require 10 times as much computing power to train as its predecessor. Were it not for AI, revenues for semiconductor firms would probably have fallen during the second quarter, rather than rise 18%, according to S&P Global.
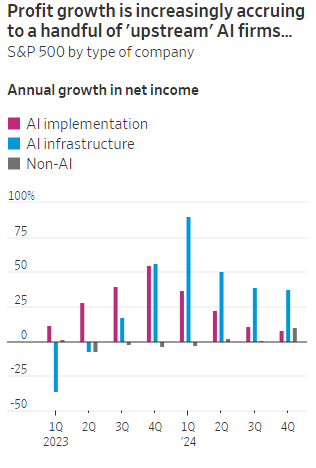 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
A paper written by researchers from the likes of Cambridge and Oxford uncovered that the large language models (LLMs) behind some of today’s most exciting AI apps may have been trained on “synthetic data” or data generated by other AI. This revelation raises ethical and quality concerns. If an AI model is trained primarily or even partially on synthetic data, it might produce outputs lacking human-generated content’s richness and reliability. It could be a case of the blind leading the blind, with AI models reinforcing the limitations or biases inherent in the synthetic data they were trained on.
In this paper, the team coined the phrase “model collapse,” claiming that training models this way will answer user prompts with low-quality outputs. The idea of “model collapse” suggests a sort of unraveling of the machine’s learning capabilities, where it fails to produce outputs with the informative or nuanced characteristics we expect. This poses a serious question for the future of AI development. If AI is increasingly trained on synthetic data, we risk creating echo chambers of misinformation or low-quality responses, leading to less helpful and potentially even misleading systems.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
In a recent working paper, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) economist Daron Acemoglu argued that AI’s knack for easy tasks has led to exaggerated predictions of its power to enhance productivity in hard jobs. Also, some of the new tasks created by AI may have negative social value (such as design of algorithms for online manipulation). Indeed, data from the Census Bureau show that only a small percentage of U.S. companies outside of the information and knowledge sectors are looking to make use of AI.
References:
https://deepgram.com/learn/the-ai-echo-chamber-model-collapse-synthetic-data-risks
https://economics.mit.edu/sites/default/files/2024-04/The%20Simple%20Macroeconomics%20of%20AI.pdf