Alphabet’s 2026 capex forecast soars; Gemini 3 AI model is a huge success
Google parent company Alphabet forecast 2026 capital expenditures of $175 billion to $185 billion this year, a massive jump compared with average analyst expectations that it would spend about $115.26 billion this year, according to data compiled by LSEG. The midpoint capex forecast of $180 billion was well above the $119.5 billion projected by analysts tracked by Bloomberg. Alphabet’s fourth quarter capex of $27.9 billion was slightly less than the expected $28.2 billion for the period, per Bloomberg estimates.
“We’re seeing our AI investments and infrastructure drive revenue and growth across the board,” CEO Sundar Pichai said in the company’s press release. He said the higher 2026 spending would allow the company “to meet customer demand and capitalize on the growing opportunities.”
The release of Google’s Gemini 3 AI model — which outperformed competing models on benchmark tests and prompted rival OpenAI to declare a “code red” — as well as the announcement of a landmark deal with Apple, cemented Alphabet’s position as an AI winner. Google Gemini gained significant market share against ChatGPT. This changed the AI landscape from a near-monopoly to a more competitive duopoly. Although ChatGPT still leads in total traffic, Gemini’s growth has narrowed the gap. This growth is due Gemini’s integration into Google’s ecosystem, especially Chrome, Android phones/tablets and Google Cloud.
“The launch of Gemini 3 was a major milestone and we have great momentum,” Pichai noted. He added that the Gemini app now has more than 750 million monthly active users.
In a related comment, Emarketer analyst Nate Elliott wrote:
“Gemini continues to grow quickly, from 650 million monthly active users at the end of Q3 to 750 million at the end of the year. But it’s worth noting that Gemini’s user number grew only about one-third as fast in Q4 as in Q3. That might explain why Google continues to keep its flagship AI tool advertising-free, hoping the lack of ads makes it more attractive to users than ChatGPT. It also explains why the company is now more aggressively pushing search users from AI Overviews into AI Mode: it’s looking for additional avenues to increase usage of its full-fledged AI chatbots.”
Google offices in Mountain View, Calif. (Reuters/Manuel Orbegozo) · Reuters / Reuters
Alphabet’s 4th quarter revenue climbed 18% to $113.8 billion from the year-ago period, ahead of the $111.4 billion expected by analysts. The tech giant’s earnings per share rose to $2.82 from $2.15 in the previous year, also higher than the $2.65 projected. The big increase in sales was spurred by a 48% spike in Google Cloud revenue to $17.7 billion, more than the $16.2 billion expected by analysts.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Update:
“Both Alphabet and Amazon delivered strong underlying business performance, driven by better-than-expected growth in cloud. But that hasn’t been enough to distract markets from their ballooning capital investment plans,” said Aarin Chiekrie, equity analyst, Hargreaves Lansdown.

References:
https://s206.q4cdn.com/479360582/files/doc_financials/2025/q4/2025q4-alphabet-earnings-release.pdf
Google announces Gemini: it’s most powerful AI model, powered by TPU chips
Comparing AI Native mode in 6G (IMT 2030) vs AI Overlay/Add-On status in 5G (IMT 2020)
Analysis: Edge AI and Qualcomm’s AI Program for Innovators 2026 – APAC for startups to lead in AI innovation
China’s open source AI models to capture a larger share of 2026 global AI market
China gaining on U.S. in AI technology arms race- silicon, models and research
IDC Report: Telecom Operators Turn to AI to Boost EBITDA Margins
AI spending boom accelerates: Big tech to invest an aggregate of $400 billion in 2025; much more in 2026!
Amazon’s Jeff Bezos at Italian Tech Week: “AI is a kind of industrial bubble”
OpenAI and Broadcom in $10B deal to make custom AI chips
AI Frenzy Backgrounder; Review of AI Products and Services from Nvidia, Microsoft, Amazon, Google and Meta; Conclusions
Will billions of dollars big tech is spending on Gen AI data centers produce a decent ROI?
China’s telecom industry rapid growth in 2025 eludes Nokia and Ericsson as sales collapse
According to a Chinese government update, “Telecommunications business volume and revenue grew steadily, mobile internet access traffic maintained rapid growth, and the construction of network infrastructure such as 5G, gigabit optical networks, and the Internet of Things was further promoted.”
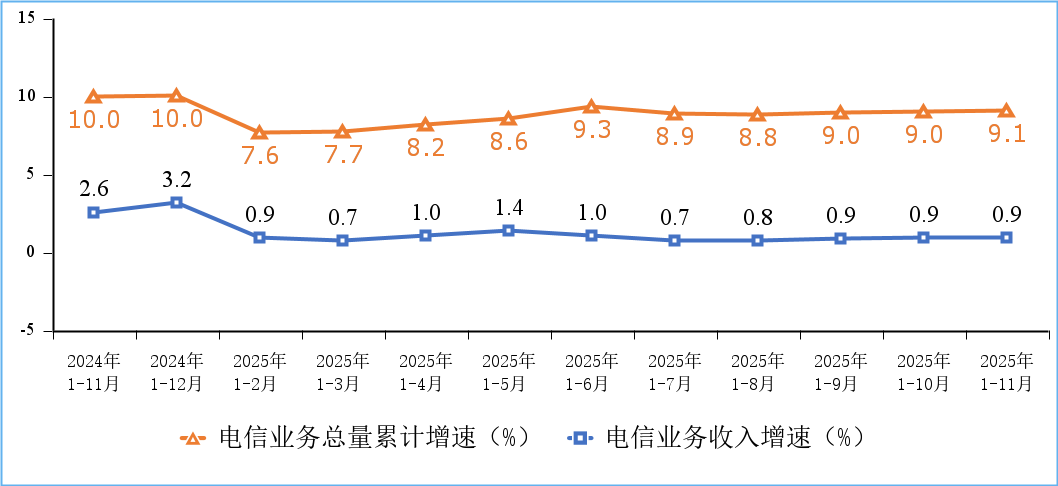
Figure 1. Cumulative growth rate of telecommunications service revenue and total telecommunications service volume
There were 4.83 million 5G base stations in service in China at the end of November 2025, an increase of 579,000 since late 2024 and 37.4% of the total number of mobile base stations in China. In one year, China claims to have added more 5G base stations than Europe has installed since the 5G technology was first put into service.
The total number of mobile phone users of the top four Chinese telcos (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom, China Broadcasting Network) reached 1.828 billion, a net increase of 38.54 million from the end of last year. Among them, 5G mobile phone users reached 1.193 billion, a net increase of 179 million from the end of last year, accounting for 65.3% of all mobile phone users.
Meanwhile, the total number of fixed broadband internet access users of the three state owned telecom operators (China Mobile, China Telecom and China Unicom) reached 697 million, a net increase of 27.12 million from the end of last year. Among them, fixed broadband internet access users with access speeds of 100Mbps and above reached 664 million, accounting for 95.2% of the total users; fixed broadband internet access users with access speeds of 1000Mbps and above reached 239 million, a net increase of 32.52 million from the end of last year, accounting for 34.3% of the total users, an increase of 3.4 percentage points from the end of last year.
The construction of gigabit fiber optic broadband networks continues to advance. As of the end of November, the number of broadband internet access ports nationwide reached 1.25 billion, a net increase of 48.11 million compared to the end of last year. Among them, fiber optic access (FTTH/O) ports reached 1.21 billion, a net increase of 49.42 million compared to the end of last year, accounting for 96.8% of all broadband internet access ports. As of the end of November, the number of 10G PON ports with gigabit network service capabilities reached 31.34 million, a net increase of 3.133 million compared to the end of last year.
The penetration rate of gigabit and 5G users continued to increase across all regions. As of the end of November, the penetration rates of fixed broadband access users with speeds of 1000Mbps and above in the eastern, central, western, and northeastern regions were 34.6%, 33.8%, 35.8%, and 28.5%, respectively, representing increases of 3.4, 2.6, 4.1, and 4.9 percentage points compared to the end of last year; the penetration rates of 5G mobile phone users were 64.9%, 65.9%, 65.1%, and 65.9%, respectively, representing increases of 8.2, 8.7, 8.8, and 9.6 percentage points compared to the end of last year.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Separately, Light Reading reports that Ericsson and Nokia sales of networking equipment to China have collapsed.
Ericsson recently published earnings release for the final quarter of 2025 puts China revenues at just 3% of total sales last year. This would equate to revenues of 7.1 billion Swedish kronor (US$798 million). Based on a rounding range of 2.5% to 3.4%, it works out to be between SEK5.92 billion ($665 million) and SEK8.05 billion ($905 million) – down sharply compared with the SEK10.2 billion ($1.15 billion) Ericsson made in 2024, according to that year’s Ericsson annual report.
Nokia does not break out details of revenues from mainland China, instead lumping them together with the sales it generates in neighboring Hong Kong and Taiwan. But this “Greater China” business is in decline. Total annual revenues – which include Nokia’s sales of fixed, Internet Protocol and optical network products, as well as 5G – slumped from almost €2.2 billion ($2.6 billion) in 2019 to around €1.5 billion ($1.8 billion) in 2020, before creeping back up to nearly €1.6 billion ($1.9 billion) by 2022. Two years later, they had fallen to about €1.1 billion ($1.3 billion).
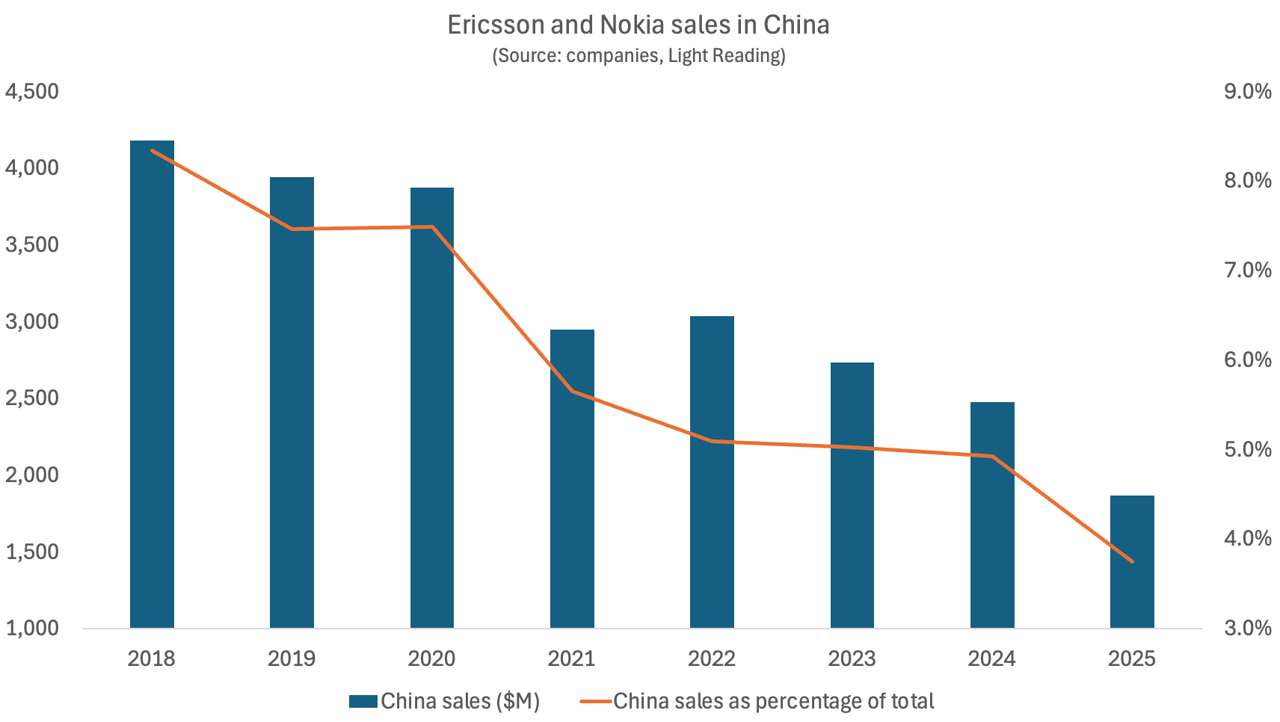
Bar Chart Credit: Light Reading
Nokia has recently indicated the complete disappearance of its China business. “Western suppliers, which is only us and Ericsson, have 3% market share now in China and it’s been coming down, and we are going to be excluded from China for national security reasons,” said Tommi Uitto, the former president of Nokia’s mobile networks business group, at a September press conference in Finland also attended by Justin Hotard, Nokia’s CEO. It implies China’s government is now treating the Nordic vendors in the same way Europe and the U.S. are banning Huawei and ZTE networking equipment.
Nokia revealed in its latest earnings update that Greater China revenues for 2025 had fallen by another 19%, to €913 million ($1.08 billion) – just 42% of what Nokia earned in the region seven years earlier. In the last few years, moreover, Nokia has cut more jobs in Greater China than in any other single region. While figures are not yet available for 2025, the Greater China headcount numbered 8,700 employees in 2024, down from 15,700 in 2019.
Ericsson has significantly reduced its China operations following greatly reduced 5G market share. In September 2021, the company consolidated three operator-specific customer units into a unified structure, impacting several hundred sales and delivery roles within its ~10,000-person local workforce. This followed the divestment of a Nanjing-based R&D center (approx. 650 employees), aligning with strategic pivots away from legacy 2G-4G technologies. The company’s total workforce in Northeast Asia plummeted from about 14,000 in mid-2021 to roughly 9,500 at the end of last year, according to Ericsson’s financial statements.
Exclusion from China would leave Ericsson and Nokia on the outside of the world’s most promising 6G market in 2030. That would intensify concern about a bifurcation of 6G into Western and Chinese variants of IMT 20230 RIT/SRIT standard and the 3GPP specified 6G core network.
References:
https://www.miit.gov.cn/gxsj/tjfx/txy/art/2025/art_7514154ec01c42ecbcb76057464652e4.html
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/ericsson-and-nokia-see-their-sales-in-china-fall-off-a-cliff
China’s open source AI models to capture a larger share of 2026 global AI market
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
China Telecom’s 2025 priorities: cloud based AI smartphones (?), 5G new calling (GSMA), and satellite-to-phone services
China ITU filing to put ~200K satellites in low earth orbit while FCC authorizes 7.5K additional Starlink LEO satellites
China gaining on U.S. in AI technology arms race- silicon, models and research
Analysis: Edge AI and Qualcomm’s AI Program for Innovators 2026 – APAC for startups to lead in AI innovation
Qualcomm is a strong believer in Edge AI as an enabler of faster, more secure, and energy-efficient processing directly on devices—rather than the cloud—unlocking real-time intelligence for industries like robotics and smart cities.
In support of that vision, the fabless SoC company announced the official launch of its Qualcomm AI Program for Innovators (QAIPI) 2026 – APAC, a regional startup incubation initiative that supports startups across Japan, Singapore, and South Korea in advancing the development and commercialization of innovative edge AI solutions.
Building on Qualcomm’s commitment to edge AI innovation, the second edition of QAIPI-APAC invites startups to develop intelligent solutions across a broad range of edge-AI applications using Qualcomm Dragonwing™ and Snapdragon® platforms, together with the new Arduino® UNO Q development board, strengthening their pathway toward global commercialization.
Startups gain comprehensive support and resources, including access to Qualcomm Dragonwing™ and Snapdragon® platforms, the Arduino® UNO Q development board, technical guidance and mentorship, a grant of up to US$10,000, and eligibility for up to US$5,000 in patent filing incentives, accelerating AI product development and deployment.
Applications are open now through April 30, 2026 and will be evaluated based on innovation, technical feasibility, potential societal impact, and commercial relevance. The program will be implemented in two phases. The application phase is open to eligible startups incorporated and registered in Japan, Singapore, or South Korea. Shortlisted startups will enter the mentorship phase, receiving one-on-one guidance, online training, technical support, and access to Qualcomm-powered hardware platforms and development kits for product development. They will also receive a shortlist grant of up to US$10,000 and may be eligible for a patent filing incentive of up to US$5,000. At the conclusion of the program, shortlisted startups may be invited to showcase their innovations at a signature Demo Day in late 2026, engaging with industry leaders, investors, and potential collaborators across the APAC innovation ecosystem.
Comment and Analysis:
Qualcomm is a strong believer in Edge AI—the practice of running AI models directly on devices (smartphones, cars, IoT, PCs) rather than in the cloud—because they view it as the next major technological paradigm shift, overcoming limitations inherent in cloud computing. Despite the challenges of power consumption and processing limitations, Qualcomm’s strategy hinges on specialized, heterogenous computing rather than relying solely on RISC-based CPU cores.
Key Issues for Qualcomm’s Edge AI solutions:
- Qualcomm® AI Engine: This combines specialized hardware, including the Hexagon NPU (Neural Processing Unit), Adreno GPU, and CPU. The NPU is specifically designed to handle high-performance, complex AI workloads (like Generative AI) far more efficiently than a generic CPU.
- Custom Oryon CPU: The latest Snapdragon X Elite platform features customized cores that provide high performance while outperforming traditional x86 solutions in power efficiency for everyday tasks.
- Specialization Saves Power: By using specialized AI engines (NPUs) rather than general-purpose CPU/GPU cores, Qualcomm can run inference tasks at a fraction of the power cost.
- Lower Overall Energy: Doing AI at the edge can save total energy by avoiding the need to send data to a power-hungry data center, which requires network infrastructure, and then sending it back.
- Intelligent Efficiency: The Snapdragon 8 Elite, for example, saw a 27% reduction in power consumption while increasing AI performance significantly.
- Instant Responsiveness (Low Latency): For autonomous vehicles or industrial robotics, a few milliseconds of latency to the cloud can be catastrophic. Edge AI provides real-time, instantaneous analysis.
- Privacy and Security: Data never leaves the device. This is crucial for privacy-conscious users (biometrics) and compliance (GDPR), which is a major advantage over cloud-based AI.
- Offline Capability: Edge devices, such as agricultural sensors or smart home devices in remote areas, continue to function without internet connectivity.
- Diversification: With the smartphone market maturing, Qualcomm sees the “Connected Intelligent Edge” as a huge growth opportunity, extending their reach into automotive, IoT, and PCs.
- “Ecosystem of You”: Qualcomm aims to connect billions of devices, making AI personal and context-aware, rather than generic.
- Qualcomm AI Hub: This makes it easier for developers to deploy optimized models on Snapdragon devices.
- Model Optimization: They specialize in making AI models smaller and more efficient (using quantization and specialized AI inference) to run on devices without requiring massive, cloud-sized computing power.
References:
Qualcomm CEO: AI will become pervasive, at the edge, and run on Snapdragon SoC devices
Huawei, Qualcomm, Samsung, and Ericsson Leading Patent Race in $15 Billion 5G Licensing Market
Private 5G networks move to include automation, autonomous systems, edge computing & AI operations
Nvidia’s networking solutions give it an edge over competitive AI chip makers
Nvidia AI-RAN survey results; AI inferencing as a reinvention of edge computing?
CES 2025: Intel announces edge compute processors with AI inferencing capabilities
Qualcomm CEO: expect “pre-commercial” 6G devices by 2028
SoftBank and Ericsson-Japan achieve 24% 5G throughput improvement using AI-optimized Massive MIMO
SoftBank Corp. and Ericsson Japan K.K. have announced a successful demonstration and deployment of an AI-powered, externally controlled optimization system for Massive MIMO, resulting in a 24% improvement in 5G downlink throughput, increasing speeds from 76.9 Mbps to 95.5 Mbps during periods of high traffic fluctuation.
- Dynamic Beam Patterns: The system automatically adjusts horizontal and vertical beam patterns every minute based on real-time user distribution.
- Packet Stalling Mitigation: By reacting to sudden traffic surges (e.g., during fireworks or concerts), the AI helps prevent “packet stalling,” where data transmission typically freezes due to congestion.
- Commercial Deployment: Following the successful trials at Expo 2025, SoftBank and Ericsson have begun deploying this AI-based system at other large-scale event venues, including major arenas and dome-type facilities in the Tokyo metropolitan area, to manage heavily fluctuating traffic patterns.
Overview of the System:
- An external control device (server) uses user distribution data collected from base stations at one-minute intervals to automatically determine event occurrence using AI
- Dynamically and automatically optimizes the horizontal and vertical coverage patterns of Massive MIMO base stations

Overview of demonstration at Expo 2025:
An AI model was constructed using performance results obtained when multiple coverage patterns were changed in advance as training data. Based on user distribution-related data such as Massive MIMO beam estimation information*2 acquired by an external control device from base stations at one-minute intervals, the system automatically determined event occurrence status and switched base station coverage patterns to optimal configurations.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
ABOUT SOFTBANK:
Guided by the SoftBank Group’s corporate philosophy, “Information Revolution – Happiness for everyone,” SoftBank Corp. (TOKYO: 9434) operates telecommunications and IT businesses in Japan and globally. Building on its strong business foundation, SoftBank Corp. is expanding into non-telecom fields in line with its “Beyond Carrier” growth strategy while further growing its telecom business by harnessing the power of 5G/6G, IoT, Digital Twin and Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) solutions, including High Altitude Platform Station (HAPS)-based stratospheric telecommunications. While constructing AI data centers and developing homegrown LLMs specialized for the Japanese language, SoftBank is integrating AI with radio access networks (AI-RAN), with the aim of becoming a provider of next-generation social infrastructure. To learn more, please visit https://www.softbank.jp/en/corp/
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
SoftBank’s Transformer AI model boosts 5G AI-RAN uplink throughput by 30%, compared to a baseline model without AI
Softbank developing autonomous AI agents; an AI model that can predict and capture human cognition
Nokia, BT Group & Qualcomm achieve enhanced 5G SA downlink speeds using 5G Carrier Aggregation with 5 Component Carriers
T‑Mobile achieves record 5G Uplink speed with 5G NR Dual Connectivity
Huawei, Qualcomm, Samsung, and Ericsson Leading Patent Race in $15 Billion 5G Licensing Market
Ericsson announces capability for 5G Advanced location based services in Q1-2026
Highlights of Ericsson’s Mobility Report – November 2025
Ericsson integrates Agentic AI into its NetCloud platform for self healing and autonomous 5G private networks
Analysis: SpaceX FCC filing to launch up to 1M LEO satellites for solar powered AI data centers in space
SpaceX has applied to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for permission to launch up to 1 million LEO satellites for a new solar-powered AI data center system in space. The private company, 40% owned by Elon Musk, envisions an orbital data center system with “unprecedented computing capacity” needed to run large-scale AI inference and applications for billions of users, according to SpaceX’s filing entered late on Friday.
Credit: Blueee/Alamy Stock Photo
The proposed new satellites would operate in “narrow orbital shells” of up to 50 kilometers each. The satellites would operate at altitudes of between 500 kilometers and 2,000 kilometers, and 30 degrees, and “sun-synchronous orbit inclinations” to capture power from the sun. The system is designed to be interconnected via optical links with existing Starlink broadband satellites, which would transmit data traffic back to ground Earth stations.
“Fortunately, the development of fully reusable launch vehicles like Starship that can deploy millions of tons of mass per year to orbit when launching at rate, means on-orbit processing capacity can reach unprecedented scale and speed compared to terrestrial buildouts, with significantly reduced environmental impact,” SpaceX said.
- Energy Density & Sustainability: By tapping into “near-constant solar power,” SpaceX aims to utilize a fraction of the Sun’s output—noting that even a millionth of its energy exceeds current civilizational demand by four orders of magnitude.
- Thermal Management: To address the cooling requirements of high-density AI clusters, these satellites will utilize radiative heat dissipation, eliminating the water-intensive cooling loops required by terrestrial facilities.
- Opex & Scalability: The financial viability of this orbital layer is tethered to the Starship launch platform. SpaceX anticipates that the radical reduction in $/kg launch costs provided by a fully reusable heavy-lift vehicle will enable rapid scaling and ensure that, within years, the lowest LCOA (Levelized Cost of AI) will be achieved in orbit.
- Vacuum-Speed Data Transmission: In a vacuum, light propagates roughly 50% faster than through terrestrial fiber optic cables. By utilizing Starlink’s optical inter-satellite links (OISLs)—a “petabit” laser mesh—data can bypass terrestrial bottlenecks and subsea cables. This potentially reduces intercontinental latency for AI inference to under 50ms, surpassing many long-haul terrestrial routes.
- Edge-Native Processing & Data Gravity: Current workflows require downlinking massive raw datasets (e.g., Synthetic Aperture Radar imagery) for terrestrial processing, a process that can take hours. Shifting to orbital edge computing allows for “in-situ” AI inference, processing data onboard to deliver actionable insights in minutes rather than hours. This “Space Cloud” architecture eliminates the need to route raw data back to the Earth’s internet backbone, reducing data transmission volumes by up to 90%.
- LEO Proximity vs. Terrestrial Hops: While terrestrial fiber remains the “gold standard” for short-range latency (typically 1–10ms), it is often hindered by inefficient routing and multiple hops. SpaceX’s LEO constellation, operating at altitudes between 340km and 614km, currently delivers median peak-hour latencies of ~26ms in the US. Future orbital configurations may feature clusters at varying 50km intervals to optimize for specific workload and latency tiers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The SpaceX FCC filing on Friday follows an exclusive report by Reuters that Elon Musk is considering merging SpaceX with his xAI (Grok chatbot) company ahead of an IPO later this year. Under the proposed merger, shares of xAI would be exchanged for shares in SpaceX. Two entities have been set up in Nevada to facilitate the transaction, Reuters said. Musk also runs electric automaker Tesla, tunnel company The Boring Co. and neurotechnology company Neuralink.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
References:
Google’s Project Suncatcher: a moonshot project to power ML/AI compute from space
Blue Origin announces TeraWave – satellite internet rival for Starlink and Amazon Leo
China ITU filing to put ~200K satellites in low earth orbit while FCC authorizes 7.5K additional Starlink LEO satellites
Amazon Leo (formerly Project Kuiper) unveils satellite broadband for enterprises; Competitive analysis with Starlink
Telecoms.com’s survey: 5G NTNs to highlight service reliability and network redundancy
Huge significance of EchoStar’s AWS-4 spectrum sale to SpaceX
U.S. BEAD overhaul to benefit Starlink/SpaceX at the expense of fiber broadband providers
Telstra selects SpaceX’s Starlink to bring Satellite-to-Mobile text messaging to its customers in Australia
SpaceX launches first set of Starlink satellites with direct-to-cell capabilities
AST SpaceMobile to deliver U.S. nationwide LEO satellite services in 2026
GEO satellite internet from HughesNet and Viasat can’t compete with LEO Starlink in speed or latency
How will fiber and equipment vendors meet the increased demand for fiber optics in 2026 due to AI data center buildouts?
Subsea cable systems: the new high-capacity, high-resilience backbone of the AI-driven global network
Analysis: Ethernet gains on InfiniBand in data center connectivity market; White Box/ODM vendors top choice for AI hyperscalers
Disclaimer: The author used Perplexity.ai for the research in this article.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Introduction:
Ethernet is now the leader in “scale-out” AI networking. In 2023, InfiniBand held an ~80% share of the data center switch market. A little over two years later, Ethernet has overtaken it in data center switch and server port counts. Indeed, the demand for Ethernet-based interconnect technologies continues to strengthen, reflecting the market’s broader shift toward scalable, open, and cost-efficient data center fabrics. According to Dell’Oro Group research published in July 2025, Ethernet was on track to overtake InfiniBand and establish itself as the primary fabric technology for large-scale data centers. The report projects cumulative data center switch revenue approaching $80 billion over the next five years, driven largely by AI infrastructure investments. Other analysts say Ethernet now represents a majority of AI‑back‑end switch ports, likely well above 50% and trending toward 70–80% as Ultra Ethernet / RoCE‑based fabrics (Remote Direct Memory Access/RDMA over Converged Ethernet) scale.
With Nvidia’s expanding influence across the data center ecosystem (via its Mellanox acquisition), Ethernet-based switching platforms are expected to maintain strong growth momentum through 2026 and the next investment cycle.
The past, present, and future of Ethernet speeds depicted in the Ethernet Alliance’s 2026 Ethernet Roadmap:
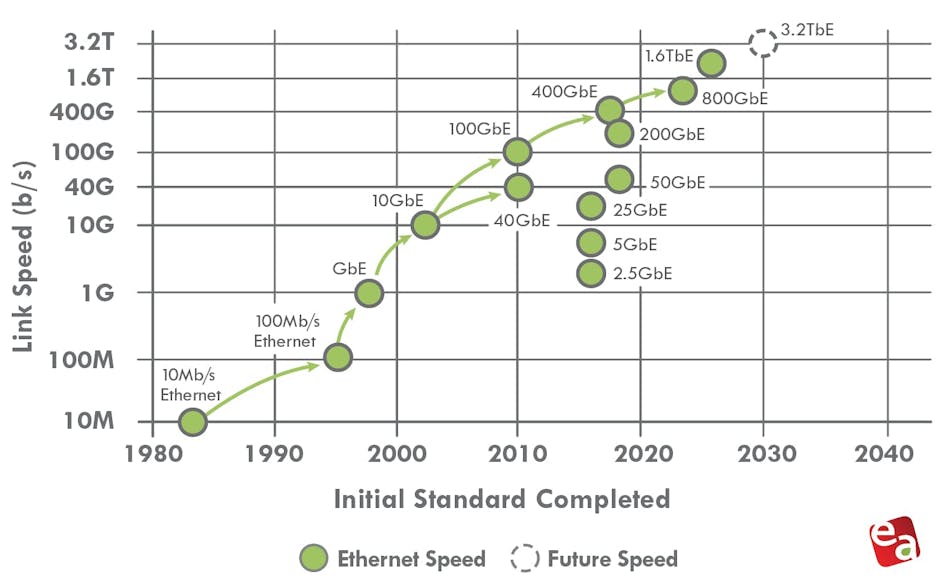
- IEEE 802.3 expects to complete IEEE 802.3dj, which supports 200 Gb/s, 400 Gb/s, 800 Gb/s, and 1.6 Tb/s, by late 2026.
- A 400-Gb/s/lane Signaling Call For Interest (CFI) is already scheduled for March.
- PAM-6 is an emerging, high-order modulation format for short-reach, high-speed optical fiber links (e.g., 100G/400G+ data center interconnects). It encodes 2.585 bits per symbol using 6 distinct amplitude levels, offering a 25% higher bitrate than PAM-4 within the same bandwidth.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Dominant Ethernet speeds and PHY/PMD trends:
In 2026, the Ethernet portfolio spans multiple tiers of performance, with 100G, 200G, 400G, and 800G serving as the dominant server‑ and fabric‑facing speeds, while 1.6T begins to appear in early AI‑scale spine and inter‑cluster links.
-
Server‑to‑leaf topology:
-
100G and 200G remain prevalent for general‑purpose and mid‑tier AI inference workloads, often implemented over 100GBASE‑CR4 / 100GBASE‑FR / 100GBASE‑LR and their 200G counterparts (e.g., 200GBASE‑CR4 / 200GBASE‑FR4 / 200GBASE‑LR4) using 4‑lane PAM4 modulation.
-
Many AI‑optimized racks are migrating to 400G server interfaces, typically using 400GBASE‑CR8 / 400GBASE‑FR8 / 400GBASE‑LR8 with 8‑lane 50 Gb/s PAM4 lanes, often via QSFP‑DD or OSFP form‑factors.
-
-
Leaf‑to‑spine and spine‑to‑spine topology:
-
400G continues as the workhorse for many brownfield and cost‑sensitive fabrics, while 800G is increasingly targeted for new AI and high‑growth pods, typically deployed as 800GBASE‑DR8 / 800GBASE‑FR8 / 800GBASE‑LR8 over 8‑lane 100 Gb/s PAM4 links.
-
IEEE 802.3dj is progressing toward completion in 2026, standardizing 200 Gb/s per lane operation a
-
For cloud‑resident (hyperscale) data centers, the Ethernet‑switch leadership is concentrated among a handful of vendors that supply high‑speed, high‑density leaf‑spine fabrics and AI‑optimized fabrics.
Core Ethernet‑switch leaders:
-
NVIDIA (Spectrum‑X / Spectrum‑4)
NVIDIA has become a dominant force in cloud‑resident Ethernet, largely by bundling its Spectrum‑4 and Spectrum‑X Ethernet switches with H100/H200/Blackwell‑class GPU clusters. Spectrum‑X is specifically tuned for AI workloads, integrating with BlueField DPUs and offering congestion‑aware transport and in‑network collectives, which has helped NVIDIA surpass both Cisco and Arista in data‑center Ethernet revenue in 2025. -
Arista Networks
Arista remains a leading supplier of cloud‑native, high‑speed Ethernet to hyperscalers, with strong positions in 100G–800G leaf‑spine fabrics and its EOS‑based software stack. Arista has overtaken Cisco in high‑speed data‑center‑switch market share and continues to grow via AI‑cluster‑oriented features such as cluster‑load‑balancing and observability suites. -
Cisco Systems
Cisco maintains broad presence in cloud‑scale environments via Nexus 9000 / 7000 platforms and Silicon One‑based designs, particularly where customers want deep integration with routing, security, and multi‑cloud tooling. While its share in pure high‑speed data‑center switching has eroded versus Arista and NVIDIA, Cisco remains a major supplier to many large cloud providers and hybrid‑cloud operators.
Other notable players:
-
HPE (including Aruba and Juniper post‑acquisition)
HPE and its Aruba‑branded switches are widely deployed in cloud‑adjacent and hybrid‑cloud environments, while the HPE‑Juniper combination (via the 2025 acquisition) strengthens its cloud‑native switching and security‑fabric portfolio. -
Huawei
Huawei supplies CloudEngine Ethernet switches into large‑scale cloud and telecom‑owned data centers, especially in regions where its end‑to‑end ecosystem (switching, optics, and management) is preferred. -
White‑box / ODM‑based vendors
Most hyperscalers also source Ethernet switches from ODMs (e.g., Quanta, Celestica, Inspur) running open‑source or custom NOS’ (SONiC, Cumulus‑style stacks), which can collectively represent a large share of cloud‑resident ports even if they are not branded like Cisco or Arista. White‑box / ODM‑based Ethernet switches hold a meaningful and growing share of the data‑center Ethernet market, though they still trail branded vendors in overall revenue. Estimates vary by source and definition. - ODM / white‑box share of the global data‑center Ethernet switch market is commonly estimated in the low‑ to mid‑20% range by revenue in 2024–2025, with some market trackers putting it around 20–25% of the data‑center Ethernet segment. Within hyperscale cloud‑provider data centers specifically, the share of white‑box / ODM‑sourced Ethernet switches is higher, often cited in the 30–40% range by port volume or deployment count, because large cloud operators heavily disaggregate hardware and run open‑source NOSes (e.g., SONiC‑style stacks).
-
ODM‑direct sales into data centers grew over 150% year‑on‑year in 3Q25, according to IDC, signaling that white‑box share is expanding faster than the overall data‑center Ethernet switch market.
-
Separate white‑box‑switch market studies project the global data‑center white‑box Ethernet switch market to reach roughly $3.2–3.5 billion in 2025, growing at a ~12–13% CAGR through 2030, which implies an increasing percentage of the broader Ethernet‑switch pie over time.
Ethernet vendor positioning table:
| Vendor | Key Ethernet positioning in cloud‑resident DCs | Typical speed range (cloud‑scale) |
|---|---|---|
| NVIDIA | AI‑optimized Spectrum‑X fabrics tightly coupled to GPU clusters | 200G/400G/800G, moving toward 1.6T |
| Arista | Cloud‑native, high‑density leaf‑spine with EOS | 100G–800G, strong 400G/800G share |
| Cisco | Broad Nexus/Silicon One portfolio, multi‑cloud integration | 100G–400G, some 800G |
| HPE / Juniper | Cloud‑native switching and security fabrics | 100G–400G, growing 800G |
| Huawei | Cost‑effective high‑throughput CloudEngine switches | 100G–400G, some 800G |
| White‑box ODMs | Disaggregated switches running SONiC‑style NOSes | 100G–400G, increasingly 800G |
Supercomputers and modern HPC clusters increasingly use high‑speed, low‑latency Ethernet as the primary interconnect, often replacing or coexisting with InfiniBand. The “type” of Ethernet used is defined by three layers: speed/lane rate, PHY/PMD/optics, and protocol enhancements tuned for HPC and AI. Slingshot, the proprietary Ethernet-based solution from HPE, commanded 48.1% of performance for the Top500 list in June 2025 and 46.3% in November 2025. On both of the lists, it provided interconnectivity for six of the top 10 – including the top three: El Capitan, Frontier, and Aurora.
HPC Speed and lane‑rate tiers:
-
Mid‑tier HPC / legacy supercomputers:
-
100G Ethernet (e.g., 100GBASE‑CR4/FR4/LR4) remains common for mid‑tier clusters and some scientific workloads, especially where cost and power are constrained.
-
-
AI‑scale and next‑gen HPC:
-
400G and 800G Ethernet (400GBASE‑DR4/FR4/LR4, 800GBASE‑DR8/FR8/LR8) are now the workhorses for GPU‑based supercomputers and large‑scale HPC fabrics.
-
1.6T Ethernet (IEEE 802.3dj, 200 Gb/s per lane) is entering early deployment for spine‑to‑spine and inter‑cluster links in the largest AI‑scale “super‑factories.”
-
In summary, NVIDIA and Arista are the most prominent Ethernet‑switch leaders specifically for AI‑driven, cloud‑resident data centers, with Cisco, HPE/Juniper, Huawei, and white‑box ODMs rounding out the ecosystem depending on region, workload, and procurement model. In hyperscale cloud‑provider data centers, ODMs hold a 30%-to-40% market share.
References:
Will AI clusters be interconnected via Infiniband or Ethernet: NVIDIA doesn’t care, but Broadcom sure does!
Big tech spending on AI data centers and infrastructure vs the fiber optic buildout during the dot-com boom (& bust)
Fiber Optic Boost: Corning and Meta in multiyear $6 billion deal to accelerate U.S data center buildout
AI Data Center Boom Carries Huge Default and Demand Risks
Markets and Markets: Global AI in Networks market worth $10.9 billion in 2024; projected to reach $46.8 billion by 2029
Using a distributed synchronized fabric for parallel computing workloads- Part I
Using a distributed synchronized fabric for parallel computing workloads- Part II
Huawei, Qualcomm, Samsung, and Ericsson Leading Patent Race in $15 Billion 5G Licensing Market
According to a new LexisNexis report, the 5G patent licensing market is now worth ~$15 billion a year. The report underscores that high-fidelity patent data has become a core business variable, with millions of dollars in annual licensing value potentially reallocated as courts, licensors, and implementers increasingly anchor negotiations, litigation strategy, and Fair, Reasonable, and Non-Discriminatory (FRAND) rate-setting on standards-essential patents (SEP) and portfolio analytics. As the 5G end point market scales out from smartphones into industrial IoT, automotive, healthcare, and other mission- and safety-critical infrastructure domains, SEPs are now a primary lever shaping competitive dynamics and value capture in global technology markets.
Lately, Ericsson CEO Börje Ekholm has been talking about humanoid robots and “physical AI” as future cellular connected objects. Others are forecasting the transformation of passive, data-collecting Internet of Things (IoT) devices into autonomous, intelligent agents that leverage 5G/6G networks, edge computing, and on-device neural processing.
The LexisNexis report extends their patent analysis to leadership across granted and in-force 5G SEP family declarations, value-adjusted portfolio strength indicators, and the depth and quality of technical contributions into the 3GPP work program.
Key findings from the 2026 analysis include:
- Huawei, Qualcomm, Samsung, and Ericsson continued to lead the global ranking of 5G patent powerhouses as assessed by granted and active 5G patent family volume, portfolio impact, and standards contributions.
- Patent data accuracy has a significant financial impact, as even small discrepancies in perceived portfolio share can translate into hundreds of millions of dollars in annual licensing value in a $15 billion global market.
- New entrants to the Top 50 list in 2026 include research-focused organizations, licensing and investment-led IP holders, and automotive and IoT connectivity specialists, which replaced several operator-centric and diversified industrial portfolios that fell below the Top 50 threshold.
- Top 50 5G patent owners reflected broad geographic diversity, with companies headquartered in China (14), Japan (9), the United States (9), Europe (7), Taiwan (5), South Korea (5), and Canada (1).
- Patent data is increasingly relied upon in FRAND determinations, making the quality, consistency, and verification of declaration data a critical factor for both licensors and implementers.
Top 10 5G Patent Leaders 2026:
The Top 10 ultimate patent owners based on granted and active 5G patent families, value-adjusted portfolio indicators, and sustained participation in 3GPP standards development.
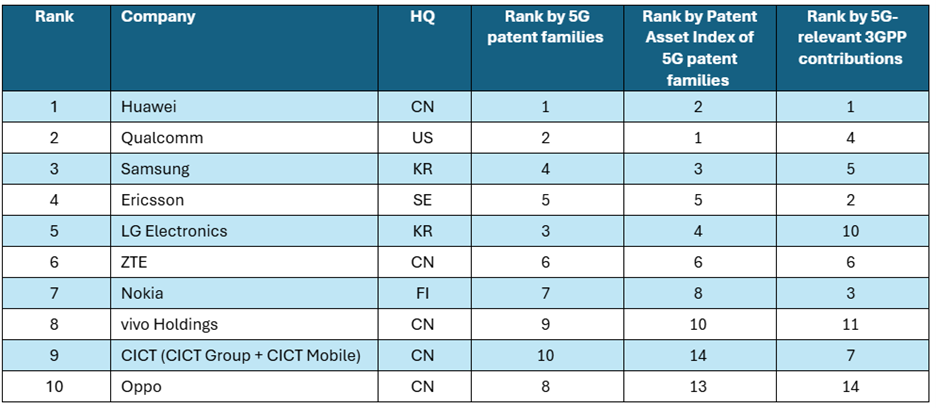
“As 5G licensing moves deeper into industrial, automotive, and infrastructure markets, the financial stakes tied to patent data accuracy continue to rise,” said Tim Pohlmann, Director of SEP Analytics for LexisNexis Intellectual Property Solutions. “In a licensing environment of this scale, even small differences in how 5G patent portfolios are measured can materially influence negotiations. That is why verified, unbiased data has become essential, not only for understanding who leads the 5G patent race, but for supporting defensible, data-driven FRAND discussions.”
The 2026 analysis is grounded in the Cellular Verified initiative led by LexisNexis Intellectual Property Solutions. Through this initiative, LexisNexis compared public ETSI declaration data with internal records from 35 ETSI-declaring companies, applying rigorous matching, normalization, patent family expansion, and corporate-tree ownership analysis.
This validation process is designed to reduce bias introduced by differing declaration practices and to provide a more accurate and impartial representation of declared 5G patent portfolios, an increasingly critical requirement as rankings and portfolio assessments are used as economic and legal reference points in licensing and litigation contexts.
About LexisNexis® Legal & Professional
LexisNexis® Legal & Professional provides AI-powered legal, regulatory, business information, analytics, and workflows that help customers increase their productivity, improve decision-making, achieve better outcomes, and advance the rule of law around the world. As a digital pioneer, the company was the first to bring legal and business information online with its Lexis® and Nexis® services. LexisNexis Legal & Professional, which serves customers in more than 150 countries with 11,800 employees worldwide, is part of RELX, a global provider of information-based analytics and decision tools for professional and business customers.
About LexisNexis® Intellectual Property Solutions
LexisNexis® Intellectual Property Solutions brings clarity to innovation for businesses worldwide. We enable innovators to accomplish more by helping them make informed decisions, be more productive, comply with regulations, and ultimately achieve a competitive advantage for their business. Our broad suite of workflow and analytics solutions (LexisNexis® PatentSight+™, LexisNexis® Classification, LexisNexis® TechDiscovery, LexisNexis® IPlytics™, LexisNexis PatentOptimizer®, LexisNexis PatentAdvisor®, and LexisNexis TotalPatent One®, LexisNexis® IP DataDirect), enables companies to be more efficient and effective at bringing meaningful innovations to our world. We are proud to directly support and serve these innovators in their endeavors to better humankind.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Comment and Analysis:
Huawei’s #1 5G patent position, while significant on headline indicators, does not fully capture the nuances of 5G SEP strength and monetization potential. Portfolio experts consistently stress that patent quality and essentiality vary widely; not every declared SEP underpins a core feature, just as a car seat does not have the same system-critical role as the motor in the overall vehicle architecture.
Beyond raw declaration counts and 3GPP contribution volume, LexisNexis applies its Patent Asset Index methodology to weight portfolio value using factors such as citation impact and international coverage, a framework under which Qualcomm currently ranks first and Huawei second. This aligns with the industry view that some of the most fundamental 5G capabilities extend directly from 4G-era OFDM-based air-interface work, an area where Qualcomm consolidated a strong position with its roughly 600 million dollar acquisition of OFDM specialist Flarion in 2006.
On the licensing side, Qualcomm remains the most financially leveraged SEP holder in the current ranking peer group: its Qualcomm Technology Licensing (QTL) unit generated about 5.6 billion dollars in fiscal 2024 revenue, or roughly 14% of total sales, and delivered around 4 billion dollars in pre-tax earnings, close to 30% of company-wide profit. Huawei, by contrast, reported approximately 630 million dollars in patent licensing revenue for 2024, equivalent to around 0.5% of its overall turnover, and notes that its cumulative royalty outpayments are nearly triple the royalties it has collected to date. While Huawei’s licensing income has roughly doubled compared with its pre‑2020 baseline, the company still spends several times more on patents and R&D than it earns from licensing, reflecting its dual role as both major licensor and large-scale implementer across devices and networks.
Ericsson and Nokia sit between the two on monetization intensity: in 2024, Ericsson’s IPR licensing revenue was about 14 billion Swedish kronor (roughly 1.57 billion dollars), or around 6% of group sales, while Nokia’s licensing business generated approximately 1.9 billion euros (about 2.3 billion dollars), roughly 10% of its total revenue, with both vendors showing solid double‑digit percentage growth in licensing since 2019. The updated LexisNexis study also segments 5G SEP leadership by 3GPP release based on active and granted declared 5G patent families: for Release 15, characterized as the foundational 5G baseline, the top six are Huawei, Qualcomm, Samsung, Ericsson, ZTE, and Nokia, while for Release 18—framing the first wave of 5G‑Advanced—the leaders shift toward LG Electronics, ETRI Korea, Samsung, Oppo, Foxconn, and Huawei, with Nokia the highest-ranked European or US player at eighth.
Assuming the ecosystem avoids major standards fragmentation, current trajectories suggest that Huawei and Qualcomm are well placed to carry substantial 5G-era influence into 6G, which is increasingly positioned as an evolutionary extension of 5G that pushes OFDM-based radio technologies into higher frequency bands and more advanced use cases. Barring disruptive structural changes, future 3GPP plenary and working group meetings are therefore likely to remain populated by the same core SEP powerhouses that dominate today’s 5G landscape.
References:
https://www.lexisnexisip.com/resources/5g-patent-race-2026/
The full “Who Is Leading the 5G Patent Race 2026” analysis, including the Top 50 5G Patent Rankings 2026 and detailed information on the underlying data methodology and validation process, is available at www.LexisNexisIP.com/5G-Report-2026
https://www.lightreading.com/5g/huawei-and-qualcomm-tussle-for-5g-patents-lead-as-6g-draws-closer
Huawei’s Electric Vehicle Charging Technology & Top 10 Charging Trends
ABI Research: Telco transformation measured via patents and 3GPP contributions; 5G accelerating in China
Huawei or Samsung: Leader in 5G declared Standard Essential Patents (SEPs)?
5G Specifications (3GPP), 5G Radio Standard (IMT 2020) and Standard Essential Patents
GreyB study: Huawei undisputed leader in 5G Standard Essential Patents (SEPs)
Chinese companies’ patents awarded in the U.S. increased ~10% while U.S. patent grants declined ~7% in 2021
Samsung Partners with NEC and Qualcomm for 5G, Licenses Nokia Patents
Fiber Optic Boost: Corning and Meta in multiyear $6 billion deal to accelerate U.S data center buildout
Corning Incorporated and Meta Platforms, Inc. (previously known as Facebook) have entered a multiyear agreement valued at up to $6 billion. This strategic collaboration aims to accelerate the deployment of cutting-edge data center infrastructure within the U.S. to bolster Meta’s advanced applications, technologies, and ambitious artificial intelligence initiatives. The agreement specifies that Corning will furnish Meta with its latest advancements in optical fiber, cable, and comprehensive connectivity solutions. As part of this commitment, Corning plans to significantly scale its manufacturing capabilities across its North Carolina facilities.
A key element of this expansion is a substantial capacity increase at its fiber optic cable manufacturing plant in Hickory NC, for which Meta will serve as the foundational anchor customer. The construction and operation of these data centers — critical infrastructure that supports our technologies and moves us toward personalized superintelligence — necessitate robust server and hardware systems designed to facilitate information transfer and connectivity with minimal latency. Fiber optic cabling is a cornerstone component for enabling this high-speed, near real-time connectivity, powering applications from sophisticated wearable technology like the Ray-Ban Meta AI glasses to the global connectivity services utilized by billions of individuals and enterprises.
“This long-term partnership with Meta reflects Corning’s commitment to develop, innovate, and manufacture the critical technologies that power next-generation data centers here in the U.S.,” said Wendell P. Weeks, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Corning Incorporated. “The investment will expand our manufacturing footprint in North Carolina, support an increase in Corning’s employment levels in the state by 15 to 20 percent, and help sustain a highly skilled workforce of more than 5,000 — including the scientists, engineers, and production teams at two of the world’s largest optical fiber and cable manufacturing facilities. Together with Meta, we’re strengthening domestic supply chains and helping ensure that advanced data centers are built using U.S. innovation and advanced manufacturing.”
Meta is expanding its commitment to build industry-leading data centers in the U.S. and to source advanced technology made domestically. Here are two quotes from them:
- “Building the most advanced data centers in the U.S. requires world-class partners and American manufacturing,” said Joel Kaplan, Chief Global Affairs Officer at Meta. “We’re proud to partner with Corning – a company with deep expertise in optical connectivity and commitment to domestic manufacturing – for the high-performance fiber optic cables our AI infrastructure needs. This collaboration will help create good-paying, skilled U.S. jobs, strengthen local economies, and help secure the U.S. lead in the global AI race.”
- “As digital tools and generative AI continue to transform our economy — in fields like healthcare, finance, agriculture, and more — the demand for fiber connectivity will continue to grow. By supporting American companies like Corning and building and operating data centers in America, we’re helping ensure that our nation maintains its competitive edge in the digital economy and the global race for AI leadership.”
Key elements of the agreement:
- Multiyear, up to $6 billion commitment.
- Corning to supply latest generation optical fiber, cable and connectivity products designed to meet the density and scale demands of advanced AI data centers.
- New optical cable manufacturing facility in Hickory, North Carolina, in addition to expanded production capacity across Corning’s North Carolina operations.
- Agreement supports Corning’s projected employment growth in North Carolina by 15 to 20 percent, sustaining a skilled workforce of more than 5,000 employees in the state, including thousands of jobs tied to two of the world’s largest optical fiber and cable manufacturing facilities.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Comment and Analysis:
Corning’s “up to $6 billion” Meta agreement is essentially a long‑term, anchor‑tenant bet that AI‑era data centers will be fundamentally more fiber‑intensive than legacy cloud resident data centers, with Corning positioning itself as the default U.S. optical plant for Meta’s buildout through ~2030. In practice, this deal is a long‑term take‑or‑pay style capacity lock that de‑risks Corning’s capex while giving Meta priority access to scarce, high‑performance data‑center‑grade fiber and cabling.
AI data centers are becoming the new FTTH in the sense that hyperscale AI buildouts are now the primary structural driver of incremental fiber demand, design innovation, and capex prioritization—but with far higher fiber intensity per site and far tighter performance constraints than residential access ever imposed.
Why “AI Data Centers are the new FTTH” for fiber optic vendors:
For fiber‑optic vendors, AI data centers now play the role that FTTH did in the 2005–2015 cycle: the anchor use case that justifies new glass, cable, and connectivity capacity.
-
AI‑optimized data centers need 2–4× more fiber cabling than traditional hyperscalers, and in some designs more than 10×, driven by massively parallel GPU fabrics and east–west traffic.
-
U.S. hyperscale capacity is expected to triple by 2029, forcing roughly a 2× increase in fiber route miles and a 2.3× increase in total fiber miles, a demand shock comparable to or larger than the early FTTH boom but concentrated in fewer, much larger customers.
-
This is already reshaping product roadmaps toward ultra‑high‑fiber‑count (UHFC) cable, bend‑insensitive fiber, and very‑small‑form‑factor connectors to handle hundreds to thousands of fibers per rack and per duct.
In other words, where FTTH once dictated volume and economies of scale, AI data centers now dictate density, performance, and margin mix.
Carrier‑infrastructure: from access to fabric:
From a carrier perspective, the “new FTTH” analogy is about what drives long‑haul and metro planning: instead of last‑mile penetration, it’s AI fabric connectivity and east–west inter‑DC routes.
-
Each new hyperscale/AI data center is modeled to require on the order of 135 new fiber route miles just to reach three core network interconnection points, plus additional miles for new long‑haul routes and capacity upgrades.
-
An FBA‑commissioned study projects U.S. data centers alone will need on the order of 214 million additional fiber miles by 2029, nearly doubling the installed base from ~160M to ~373M fiber miles; that is the new “build everywhere” narrative operators once used for FTTH.
-
Carriers now plan backbone routes, ILAs, and regional rings around dense clusters of AI campuses, treating them as primary traffic gravity wells rather than as just a handful of peering sites at the edge of a consumer broadband network.
The strategic shift: FTTH made the access network fiber‑rich; AI makes the entire cloud and transport fabric fiber‑hungry.
Strategic implications:
-
AI is now the dominant incremental fiber use case: residential fiber adds subscribers; AI adds orders of magnitude more fibers per site and per route.
-
Network economics are moving from passing more homes to feeding more GPUs: route miles, fiber counts, and connector density are being dimensioned to training clusters and inference fabrics, not household penetration curves.
-
Policy and investment narratives should treat AI inter‑DC and campus fiber as “national infrastructure” on par with last‑mile FTTH, given the scale of projected doubling in route miles and more than doubling in fiber miles by 2029.
In summary, the next decade of fiber innovation and capex will be written less in curb‑side PON and more in ultra‑dense, AI‑centric data centers with internal fiber optical fabrics and interconnects.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
References:
Meta Announces Up to $6 Billion Agreement With Corning to Support US Manufacturing
Big tech spending on AI data centers and infrastructure vs the fiber optic buildout during the dot-com boom (& bust)
Analysis: Cisco, HPE/Juniper, and Nvidia network equipment for AI data centers
Networking chips and modules for AI data centers: Infiniband, Ultra Ethernet, Optical Connections
Will billions of dollars big tech is spending on Gen AI data centers produce a decent ROI?
Superclusters of Nvidia GPU/AI chips combined with end-to-end network platforms to create next generation data centers
Lumen Technologies to connect Prometheus Hyperscale’s energy efficient AI data centers
Proposed solutions to high energy consumption of Generative AI LLMs: optimized hardware, new algorithms, green data centers
Hyper Scale Mega Data Centers: Time is NOW for Fiber Optics to the Compute Server
China’s open source AI models to capture a larger share of 2026 global AI market
Overview of AI Models – China vs U.S. :
Chinese AI language models (LMs) have advanced rapidly and are now contesting with the U.S. for global market leadership. Alibaba’s Qwen-Image-2512 is emerging as a top-performing, free, open-source model capable of high-fidelity human, landscape, and text rendering. Other key, competitive models include Zhipu AI’s GLM-Image (trained on domestic chips), ByteDance’s Seedream 4.0, and UNIMO-G.
Today, Alibaba-backed Moonshot AI released an upgrade of its flagship AI model, heating up a domestic arms race ahead of an expected rollout by Chinese AI hotshot DeepSeek. The latest iteration of Moonshot’s Kimi can process text, images, and videos simultaneously from a single prompt, the company said in a statement, aligning with a trend toward so-called omni models pioneered by industry leaders like OpenAI and Alphabet Inc.’s Google.
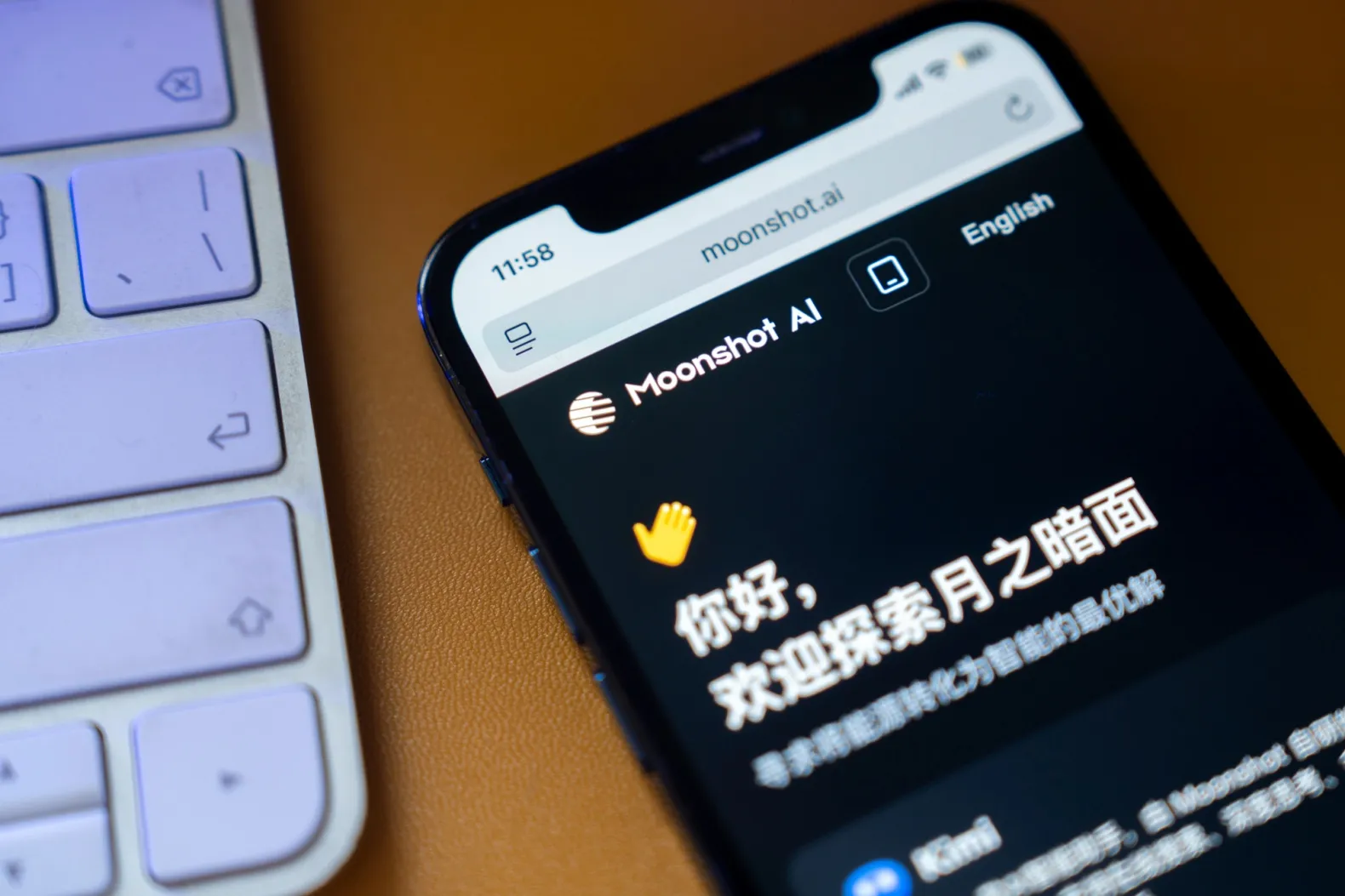
Moonshot AI Kimi website. Photographer: Raul Ariano/Bloomberg
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Chinese AI models are rapidly narrowing the gap with Western counterparts in quality and accessibility. That shift is forcing U.S. AI leaders like Alphabet’s Google, Microsoft’s Copilot, OpenAI, and Anthropic to fight harder to maintain their technological lead in AI. That’s despite their humongous spending on AI data centers, related AI models and infrastructure.
In early 2025, investors seized on DeepSeek’s purportedly lean $5.6 million LM training bill as a sign that Nvidia’s high-end GPUs were already a relic and that U.S. hyperscalers had overspent on AI infrastructure. Instead, the opposite dynamic played out: as models became more capable and more efficient, usage exploded, proving out a classic Jevons’ Paradox and validating the massive data-center build-outs by Microsoft, Amazon, and Google.
The real competitive threat from DeepSeek and its peers is now coming from a different direction. Many Chinese foundation models are released as “open source” or “open weight” AI models which makes them effectively free to download, easy to modify, and cheap to run at scale. By contrast, most leading U.S. players keep tight control over their systems, restricting access to paid APIs and higher-priced subscriptions that protect margins but limit diffusion.
That strategic divergence is visible in how these systems are actually used. U.S. models such as Google’s Gemini, Anthropic’s Claude, and OpenAI’s GPT series still dominate frontier benchmarks [1′] and high‑stakes reasoning tasks. According to a recently published report by OpenRouter, a third-party AI model aggregator, and venture capital firm Andreessen Horowitz. Chinese open-source models have captured roughly 30% of the “working” AI market. They are especially strong in coding support and roleplay-style assistants—where developers and enterprises optimize for cost efficiency, local customization, and deployment freedom rather than raw leaderboard scores.
Note 1. A frontier benchmark for AI models is a high-difficulty evaluation designed to test the absolute limits of artificial intelligence in complex,, often unsolved, reasoning tasks. FrontierMath, for example, is a prominent benchmark focusing on expert-level mathematics, requiring AI to solve hundreds of unpublished problems that challenge, rather than merely measure, current capabilities.
China’s open playbook:
China’s more permissive stance on model weights is not just a pricing strategy — it’s an acceleration strategy. Opening weights turns the broader developer community into an extension of the R&D pipeline, allowing users to inspect internals, pressure‑test safety, and push incremental improvements upstream.
As Kyle Miller at Georgetown’s Center for Security and Emerging Technology argues, China is effectively trading away some proprietary control to gain speed and breadth: by letting capability diffuse across the ecosystem, it can partially offset the difficulty of going head‑to‑head with tightly controlled U.S. champions like OpenAI and Anthropic. That diffusion logic is particularly potent in a system where state planners, big tech platforms, and startups are all incentivized to show visible progress in AI.
Even so, the performance gap has not vanished. Estimates compiled by Epoch AI suggest that Chinese models, on average, trail leading U.S. releases by about seven months. The window briefly narrowed during DeepSeek’s R1 launch in early 2025, when it looked like Chinese labs might have structurally compressed the lag; since then, the gap has widened again as U.S. firms have pushed ahead at the frontier.
Capital, chips, and the power problem:
The reason the U.S. lead has held is massive AI infrastructure spending. Consensus forecasts put capital expenditure by largely American hyperscalers at roughly $400 billion in 2025 and more than $520 billion in 2026, according to Goldman Sachs Research. By comparison, UBS analysts estimate that China’s major internet platforms collectively spent only about $57 billion last year—a fraction of U.S. outlays, even if headline Chinese policy rhetoric around AI is more aggressive.
But sustaining that level of investment runs into a physical constraint that can’t be hand‑waved away: electricity. The newest data-center designs draw more than a gigawatt of power each—about the output of a nuclear reactor—turning grid capacity into a strategic bottleneck. China now generates more than twice as much power as the U.S., and its centralized planning system can more readily steer incremental capacity toward AI clusters than America’s fragmented, heavily regulated electricity market.
That asymmetry is already shaping how some on Wall Street frame the race. Christopher Woods, global head of equity strategy at Jefferies, recently reiterated that China’s combination of open‑source models and abundant cheap power makes it a structurally formidable AI competitor. In his view, the “DeepSeek moment” of early last year remains a warning that markets have largely chosen to ignore as they rotate back into U.S. AI mega‑caps.
A fragile U.S. AI advantage:
For now, U.S. companies still control the most important chokepoint in the stack: advanced AI accelerators. Access to Nvidia’s cutting‑edge GPUs remains a decisive advantage. Yesterday, Microsoft announced the Maia 200 chip – their first silicon and system platform optimized specifically for AI inference. The chip was was designed for efficiency, both in terms of its ability to deliver tokens per dollar and performance per watt of power used.
“Maia 200 can deliver 30% better performance per dollar than the latest generation hardware in our fleet today,” Microsoft EVP for Cloud and AI Scott Guthrie wrote in a blog post.

Image Credit: Microsoft
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Leading Chinese AI research labs have struggled to match training results using only domestic designed silicon. DeepSeek, which is developing the successor to its flagship model and is widely expected to release it around Lunar New Year, reportedly experimented with chips from Huawei and other local vendors before concluding that performance was inadequate and turning to Nvidia GPUs for at least part of the training run.
That reliance underscores the limits of China’s current self‑reliance push—but it also shouldn’t be comforting to U.S. strategists. Chinese firms are actively working around the hardware gap, not waiting for it to close. DeepSeek’s latest research focuses on training larger models with fewer chips through more efficient memory design, an incremental but important reminder that architectural innovation can partially offset disadvantages in raw compute.
From a technology‑editorial perspective, the underlying story is not simply “China versus the U.S.” at the model frontier. It is a clash between two AI industrial strategies: an American approach that concentrates capital, compute, and control in a handful of tightly integrated platforms, and a Chinese approach that leans on open weights, diffusion, and state‑backed infrastructure to pull the broader ecosystem forward.
The question for 2026 is whether U.S. AI firms’ lead in capability and chips can keep outrunning China’s advantages in openness and power—or whether the market will again wait for a shock like DeepSeek to re‑price that risk.
Deepseek and Other Chinese AI Models:
DeepSeek published research this month outlining a method of training larger models using fewer chips through a more efficient memory design. “We view DeepSeek’s architecture as a new, promising engineering solution that could enable continued model scaling without a proportional increase in GPU capacity,” wrote UBS analyst Timothy Arcuri.
Export controls haven’t prevented Chinese companies from training advanced models, but challenges emerge when the models are deployed at scale. Zhipu AI, which released its open-weight GLM 4.7 model in December, said this month it was rationing sales of its coding product to 20% of previous capacity after demand from users overwhelmed its servers.
Moonshot, Zhipu AI and MiniMax Group Inc are among a handful of AI LM front-runners in a hotly contested battle among Chinese large language model makers, which at one point was dubbed the “War of One Hundred Models.”
“I don’t see compute constraints limiting [Chinese companies’] ability to make models that are better and compete near the U.S. frontier,” Georgetown’s Miller says. “I would say compute constraints hit on the wider ecosystem level when it comes to deployment.”
Gaining access to Nvidia AI chips:
U.S. President Donald Trump’s plan to allow Nvidia to sell its H200 chips to China could be pivotal. Alibaba Group and ByteDance, TikTok’s parent company, have privately indicated interest in ordering more than 200,000 units each, Bloomberg reported. The H200 outperforms any Chinese-produced AI chip, with a roughly 32% processing-power advantage over Huawei’s Ascend 910C.
With access to Nvidia AI chips, Chinese labs could build AI-training supercomputers as capable as American ones at 50% extra cost compared with U.S.-made ones, according to the Institute for Progress. Subsidies by the Chinese government could cover that differential, leveling the playing field, the institute says.
Conclusions:
A combination of open-source innovation and loosened chip controls could create a cheaper, more capable Chinese AI ecosystem. The possibility is emerging just as OpenAI and Anthropic consider public stock listings (IPOs) and U.S. hyperscalers such as Microsoft and Meta Platforms face pressure to justify heavy spending.
The risk for U.S. AI leaders is no longer theoretical; China’s open‑weight, low‑cost model ecosystem is already eroding the moat that Google, OpenAI, and Anthropic thought they were building. By prioritizing diffusion over tight control, Chinese firms are seeding a broad developer base, compressing iteration cycles, and normalizing expectations that powerful models should be cheap—or effectively free—to adapt and deploy.
U.S. AI leaders could face pressure on pricing and profit margins from China AI competitors while having to deal with AI infrastructure costs and power constraints. Their AI advantage remains real, but fragile—highly exposed to regulatory shifts, export controls, and any breakthrough in China’s workarounds on hardware and training efficiency. The uncomfortable prospect for U.S. AI incumbents is that they could win the race for the best models and still lose ground in the market if China’s diffusion‑driven strategy defines how AI is actually consumed at scale.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
References:
https://www.barrons.com/articles/deepseek-ai-gemini-chatgpt-stocks-ccde892c
https://blogs.microsoft.com/blog/2026/01/26/maia-200-the-ai-accelerator-built-for-inference/
China gaining on U.S. in AI technology arms race- silicon, models and research
U.S. export controls on Nvidia H20 AI chips enables Huawei’s 910C GPU to be favored by AI tech giants in China
Goldman Sachs: Big 3 China telecom operators are the biggest beneficiaries of China’s AI boom via DeepSeek models; China Mobile’s ‘AI+NETWORK’ strategy
Bloomberg: China Lures Billionaires Into Race to Catch U.S. in AI
Comparing AI Native mode in 6G (IMT 2030) vs AI Overlay/Add-On status in 5G (IMT 2020)
Fierce Network Research report examines telcos role in the AI economy and profiles early AI adopters
The telecommunications industry is at a critical crossroads. As AI reshapes global value chains, communications service providers (CSPs) must determine their strategic position: will they remain infrastructure enablers or evolve into full-scale participants in the AI economy?
A new Fierce Network Research report — “Risk, Reward and Revenue: Defining Telcos’ Role in the AI Economy” — examines this identity challenge — and how network operators are recalibrating for the next generation of network-driven intelligence. Based on a global survey of 500 technology decision-makers across 40 countries, the findings reveal a pronounced industry divide. A majority (57%) of operators see their core opportunity in infrastructure — networks, data centers, and secure connectivity — while 43% advocate for a more integrated position, aspiring to orchestrate AI ecosystems (19%) or participate fully in the AI value chain (24%).
Some of the industry’s early adopters are already showing what that future might look like.
- AT&T reports a twofold increase in cash flow for every dollar it invests in AI, emphasizing measurable outcomes over vague productivity gains. An AT&T executive said that success in the AI era depends on “Goldilocks governance” — a balance not too rigid to stifle innovation, and not too loose to compromise compliance and trust.
- Bell Canada is moving in a similar direction, targeting a doubling of enterprise AI revenue by 2028 and positioning its Ateko subsidiary and AI Fabric platform as the backbone of a “sovereign digital spine” for Canada.
- “We’re using AI to enhance our products and services and make them better,” Ed Fox, MetTel CTO. The company provides a private network to deliver integrated communications and IT services to U.S. businesses and government agencies, including voice, data, network, cloud, mobility, IoT and security solutions. MetTel also provides managed network services such as SD-WAN and secure access service edge (SASE).
- Rick Lievano, Microsoft CTO for the worldwide telecommunications industry, sees operators expanding their use of AI beyond efficiency. “Initially, the first place where telcos began to experiment with AI is around efficiency gains — how can I save money, and how can I do more with fewer people? That’s been the target of the first couple of waves of AI,” Lievano said. “However, their eyes light up when we talk with them about new revenue opportunities,” Lievano said.
The research highlights that telcos possess critical assets few other industries can match: globally distributed data center capacity, secure and resilient networks, and deep, long-standing relationships with enterprise and government customers. But the barriers are equally significant — from proving the business case for AI infrastructure to navigating a shortage of data science and AI talent. Legacy technology debt continues to drag, with one executive lamenting that 145 years of accumulated systems make modern data integration “extraordinarily complex.”

A new Fierce Network Research report reveals how communication service providers are navigating the AI economy amid uncertainty about their role and strategy. (Google Gemini)
The bottom line is clear: to remain relevant in the AI-driven economy, telcos must modernize both infrastructure and business models — transforming from connectivity providers into intelligent digital enablers. However, we’ve heard that cry for telco transformation from dumb pipes to intelligent and autonomous network and IT providers, but it has yet to be realized. Will this time be any different?
References:
https://www.fierce-network.com/cloud/dumb-pipes-or-ai-powerhouses-telcos-face-identity-crisis
Full REPORT: “Risk, Reward and Revenue: Defining telcos’ role in the AI economy.”
Private 5G networks move to include automation, autonomous systems, edge computing & AI operations
Palo Alto Networks and Google Cloud expand partnership with advanced AI infrastructure and cloud security
Generative AI could put telecom jobs in jeopardy; compelling AI in telecom use cases
Generative AI in telecom; ChatGPT as a manager? ChatGPT vs Google Search
Allied Market Research: Global AI in telecom market forecast to reach $38.8 by 2031 with CAGR of 41.4% (from 2022 to 2031)
Markets and Markets: Global AI in Networks market worth $10.9 billion in 2024; projected to reach $46.8 billion by 2029
Ericsson integrates Agentic AI into its NetCloud platform for self healing and autonomous 5G private networks
Ericsson CEO’s strong statements on 5G SA, WRC 27, and AI in networks
New Linux Foundation white paper: How to integrate AI applications with telecom networks using standardized CAMARA APIs and the Model Context Protocol (MCP)


